2. OCT System Coherence, Interference and Noises
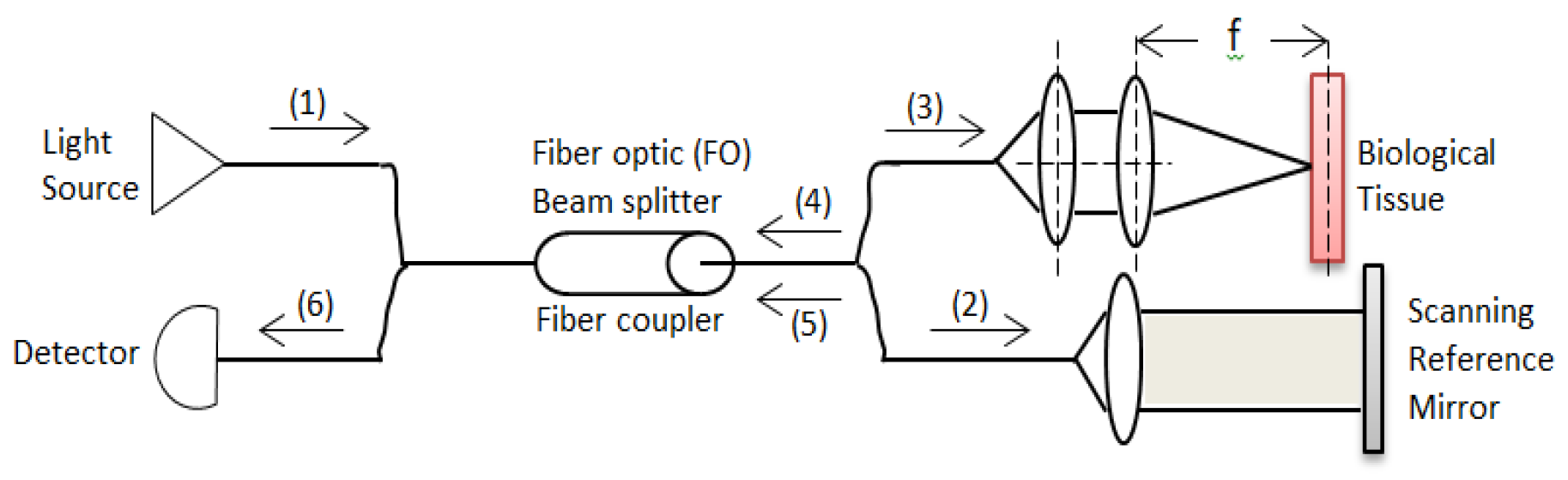
A basic OCT system consists of a simple Michelson interferometer in both a bulk optic or fiber optic version. There is source light (1) which is split in a fiber coupler. One part of the light is directed at a reference mirror (2) and the other part at the sample (3) being measured. The light reflected back from the sample (4) and reference arm (5) then pass through the beam splitter again (6) and is collected by the detector (
Figure 1).
Signals are detected when the optical path length in the sample and reference arm are within the coherence length of the source. A difference in the refractive index in the sample causes light to be reflected and the detector to detect the interference signal. Moving the fiber over the sample in two transverse directions produces a 3D image. The detector detects interference signals if the difference in the refractive index in the sample causes light to be reflected. In any OCT system noise is a crucial parameter when designing the system to achieve high resolution and large penetration depths. There are two types of OCT systems, unbalanced and balanced systems. An unbalanced OCT system contains a Michelson interferometer and the coherent part of the power backscattered from the sample is impinging on the detector. The balanced OCT system can be seen as an extension of the unbalanced system. There is double detection due to two more beam splitters. Balanced systems can have an additional beam splitter for power [
3,
4]. In our OCT we are dealing with the coherence properties of light. We consider light as electromagnetic radiation
. It is wave trains with different lifetime, where the average lifetime is
(coherence time). The wave trains are characterized by light production as random processes with different phases. The source of light produces light with frequencies
within a specific frequency spectrum. Fourier domain gives
, where,
is the spectral line width. If our source is broadband then
value big and the coherence time
is short. The coherence length (
) for the wave train is defined as
where
is the speed of the wave. Inserting the expression for coherence time
for the coherence length gives
where
is the optical frequency and
. By using differential approximation
we get
, where
represents the linewidth and
is the center wavelength (
). OCT systems include an interferometer which merges, in our case, two sources of light to create an interference signal. We know that a difference in refractive index in the sample causes the light to reflect and the detector detects an interference signal. We consider two sources of light
and
which are from the same source and travel different paths. The beams meet at point P which represents the detector. One beam travels an extra time
and the field at point P (detector) is
.
For
and
we get
for
. The Poynting vector (electric and magnetic fields at point P) is
. The power unit area (irradiance)
is measured by a detector at P and it is a time average of
equals to
. If fields
and
are orthogonal then
. This gives
The irradiances of the beams are
and
then
If the two beams have the same polarization the dot product maximizes
. We define correlation function
and a normalized correlation function
.
We define as a normalized power spectral density of the light source and define the normalized correlation function as. The complex degree of the normalized correlation functionis a Fourier transform of the power spectrum. For power spectral densities (PSD) even function of, we have complex coherence real valued factor.
The power unit area (irradiance)
can be expressed as
The intensity
varies sinusoidal with
(beam extra time parameter) and is modulated by the envelope function
, a normalized correlation function. The envelope function
is determined by the Fourier transform of the spectrum. If we define
as a constant coherence time then for a harmonic wave with frequency
we get
for
and the power unit area (irradiance)
is
We define
as the difference in optical path lengths for the two beams,
is the wavelength of the waves, then the wave number is
and
,
is the coherence length (
). The power unit area (irradiance)
is
For
the interference term vanishes (random phase variations cancel out) and the power unit area (irradiance)
is
. For
exists
. It is the condition for observing interference fringes in the OCT system detector unit (
). We define
for constant coherence time
. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is susceptible to coherent noise. The speckle noise deteriorates the contrast and fine structure of OCT images. It imposes significant limitations on the diagnostic capability of OCT. The SNR in OCT systems is defined as the ratio of the average signal intensity to the standard deviation of the noise intensity. In our OCT system, the measured signal contains noise (
). If we define the signal as current (
) then
,
is the true signal and
is defined the noise signal as current. We know that any constant property of noise in OCT systems does not affect the qualitative property of the image. If we assume the noise is random then the time average of the noise must be zero (
). We measure the noise in root mean square standard deviation (
) or mean square variance (
). For OCT systems the noise current signal is
. We measure the noise
times in our OCT system,
is the n
th noise measurement then
. To obtain a good image of the object using our OCT system, high contrast is needed to distinguish different features. If the optical path difference (OPD) between the mirror and the object of interest is zero then the OCT detection system generates a signal current
[
5,
6]. If the optical path difference (OPD) increases above the coherent length (
) then the detector no longer measures the true signal (
) but the noise
inherent in the system. We can achieve high contrast in our OCT system if the signal current is dominant compared to the noise. The definition of SNR in OCT systems is
. The maximum interference signal (
) indicates the location of the change in the refractive index in the medium,
. The SNR expression in dB is
. The total OCT system detector photocurrent variance is a summation of three independent terms
,
, and
,
where
is the receiver noise,
is the photon shot noise, and
is the excess intensity noise. The detector signal photocurrent (
) is the coherent part of the signal backscattered from the sample and it is given by
, where is the detector responsivity, is the power impinging on the photodetector reflected from the mirror andis the coherent portion of the power incident on the photodetector backscattered from the sample. The maximum function value () is for then the maximum squared signal photocurrent in a OCT system single detector is defined as. If we use an OCT balanced system, for the balanced receiver the total photocurrent is the sum of the photocurrent in each detector and the maximum squared signal photocurrent is . We define the OCT system receiver noise as the noise in the detector. The receiver noise consists of shot noise, thermal noise, amplifier noise and temperature noise. The shot noise is caused by the background light and the dark current in the OCT system detector. It is a small noise compared to other noises and can be neglected. The thermal noise terms () come from the random thermal motion of electrons in a conductor and it is expressed aswhere is Boltzmann’s constant, is the temperature in Kelvin, is the detection bandwidth, andis the effective load resistance. The temperature noise () is produced by the random fluctuations in temperature due to the statistical nature of heat transfer between the OCT detector and its environment. The temperature noise is expressed as the mean square radiant power fluctuations; , whereis the permeability, is the Stefan – Boltzmann’s constant, andis the OCT detector area. The amplifier noise is given by, where is the gain of the amplifier, is the amplifier noise temperature, is the noise temperature of the detector load resistance. Photon shot noise is arising from the signal caused by quantization of the light. The random arrival photons are detected as noise () and is expressed as, whereis the electron charge ( coulombs), is the mean detector photocurrent and it is given by, is the detector responsivity, is the power impinging on the photodetector reflected from the mirror, is the power of the incoherent light backscattered from the sample and arriving the OCT detector. The excess intensity noise caused from the time fluctuations of the intensity and is expressed by, whereis the source degree of polarization, is the effective linewidth of the source, , whereis the FWHM (Full Width at Half Maximum) wavelength bandwidth of the spectrum. In the case we don’t neglect the shot noise then we get the total photocurrent variance which constructed from three elements:
Receiver noise (), photon shot noise (), and excess noise (). The outcome is the OCT detector total photocurrent variance. It is also the OCT balanced system total photocurrent variance ().
4. OCT Balanced System
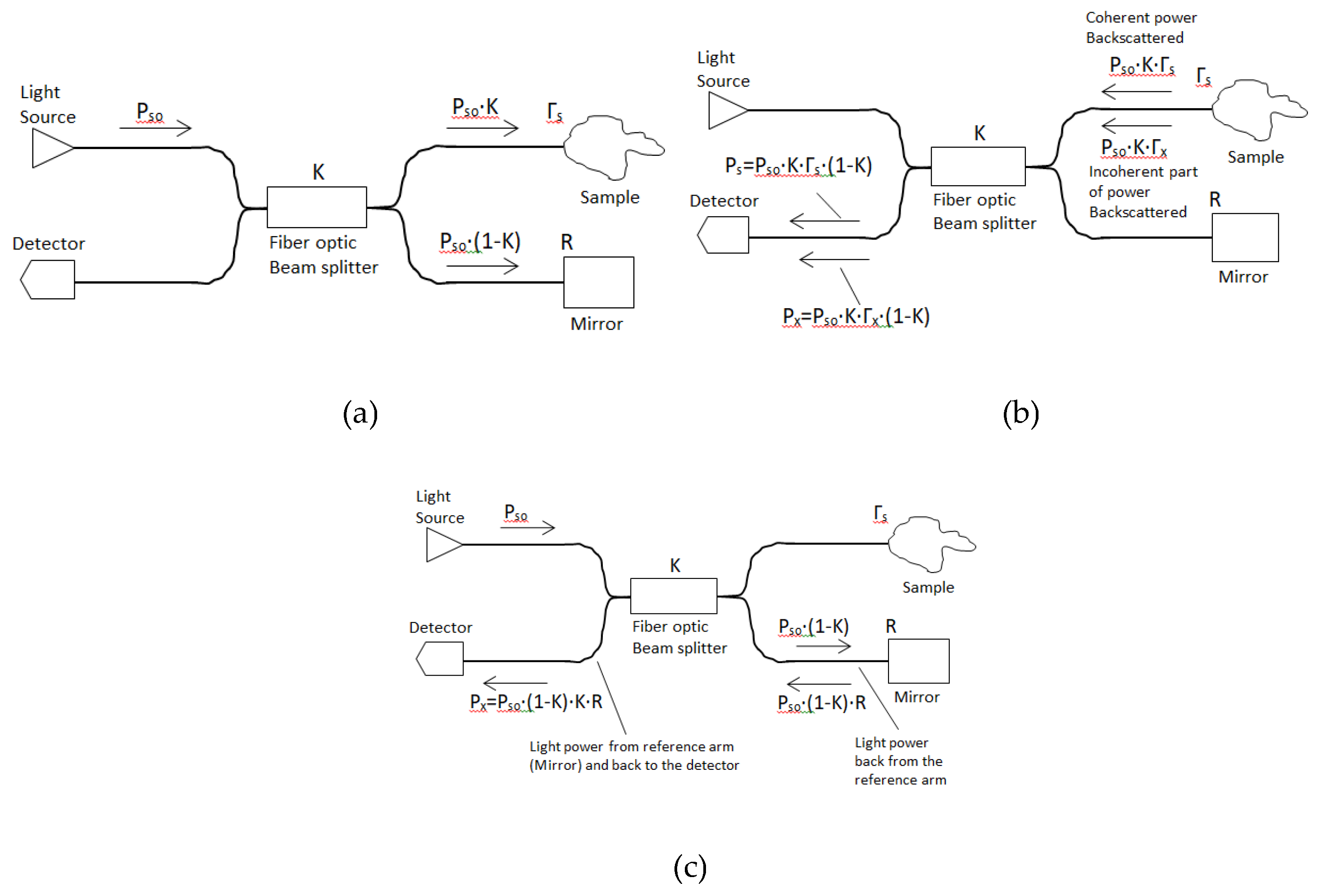
The improved OCT systems are balanced systems which contain additional elements. Namely, two more beam splitters for double detection. The OCT system SNR value can be improved by implementing a balanced detection scheme. It reduces any common mode noise which originated from the reference and sample arms. All OCT balanced systems beam splitters split beams (laser beams) into two beams. They typically come in the form of a reflective device which split beams into exactly 50/50, with half of the beam being transmitted through the splitter and the other half reflected. The OCT balanced system includes three beam splitters (
,
, and
), optical isolator (device that allows light to propagate through it in one direction only), end mirror (R), sample, and two detectors (one with attenuator in front).
is the coherent part of the optical power backscattered from the tissue sample and detected by the detector. The expression for
is
where
is the power of light from the source light and
is the reflection coefficient of the sample (coherent with the reference light). The
number comes from the fact that the beam splitter
transfers only half of the optical power to optical detector No.1 (
Figure 3a).
is the incoherent light part of the power backscattered from the sample and arriving at the detector. The expression for
is
Where,
is the power of light from the source light and
is the reflection coefficient of the tissue sample, incoherent with the reference light (
Figure 3b).
is the power from the reference arm (mirror) and it passes through beam splitters
and
, back to the detector through beam splitter
,
is the mirror reflectivity. The expression for
is
(
Figure 3c).
We use an optical isolator between beam splitters
and
to avoid power back from the mirror arriving at beam splitter
which would cause additional shot and beat noises. The pre factor 50% is the splitting ratio
and is chosen to assure that the noise intensity is suppressed. The shot noise in our system is
The beat noise in our system is
Beat noise is a spontaneous signal emission and it is generated by mixing between the optical signal and ASE noise. Amplified Spontaneous Emission (ASE) produced by spontaneous emission that has been optically amplified by the process of stimulated emission in a gain medium. It is inherent in the field of random processes. There is attenuation in OCT systems, which is related to the absorption by the tissue. Attenuation decreases the signal intensity when passing through the tissue due to absorption by the tissue [
9,
10]. The attenuation determines the penetration depth of the optical signal into the tissue. High attenuation tissues have very low penetration depth and poor visibility of deeper structures.
The optical signal passes the attenuator before arriving at optical detector No.2. It can improve the detection efficiency; the common-mode rejection is maximized when the power in the reference input of the detector is two times that in the signal input.
is the input optical power to the attenuator and
is the output optical power of the attenuator. The ratio
,
is defined as the ratio of the power of two signals
and
. The attenuation in dB is
. The Attenuation factor (AF) is defined as
and
. By adding an attenuator to our system the photo current (
) is replaced by
Whereis the attenuation factor, the maximum squared value for photocurrent is . We know that the condition for observing interference fringes in the OCT system detector unit (), where and the maximum squared value for photocurrent is accepter for then. The shot noise is
, the beat noise is
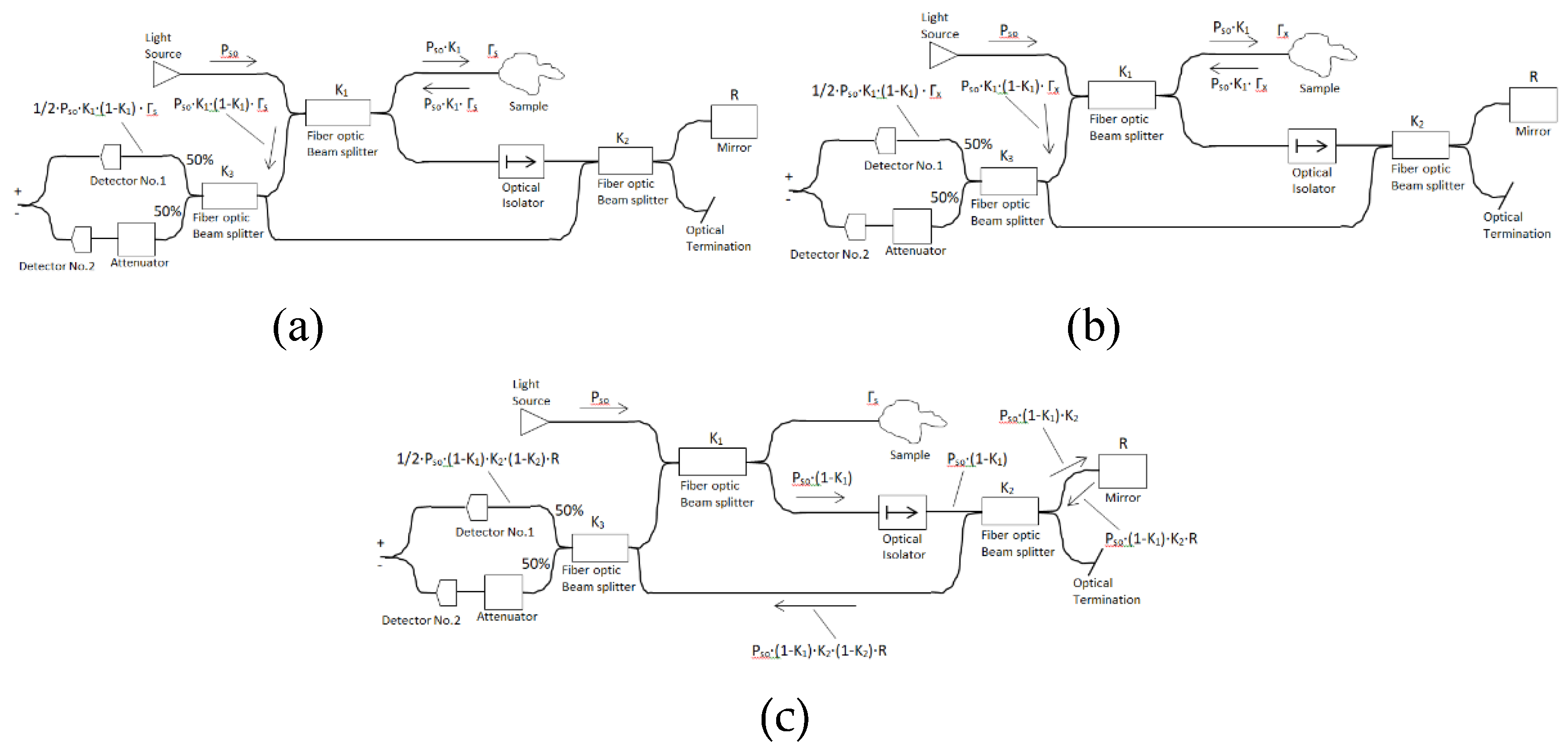
. Another type of balanced system has four beam splitters which entails an additional loss of power. We have the benefit that the length of the reference and sample arms is the same. The sample arm focuses into the tissue being observed, and the reference arm reflects back from a flat optical mirror. We take the beam splitter coefficient
as 50% in our four beam splitters architecture. The coherent part of optical power backscattered from the tissue sample and detected by the detector is
and equal to
(
Figure 4a).
The incoherent part of optical power backscattered from the tissue sample and detected by the detector is
and equal to
(
Figure 4b).
The back power light from the reference arm (mirror) is first transmitted from the source (
), passing the first beam splitter (
), then the third beam splitter (
), and back to fourth beam splitter (
) before detection by the photodetector. The power from the reference arm (mirror) which heats the detector is
,
(
Figure 4c)
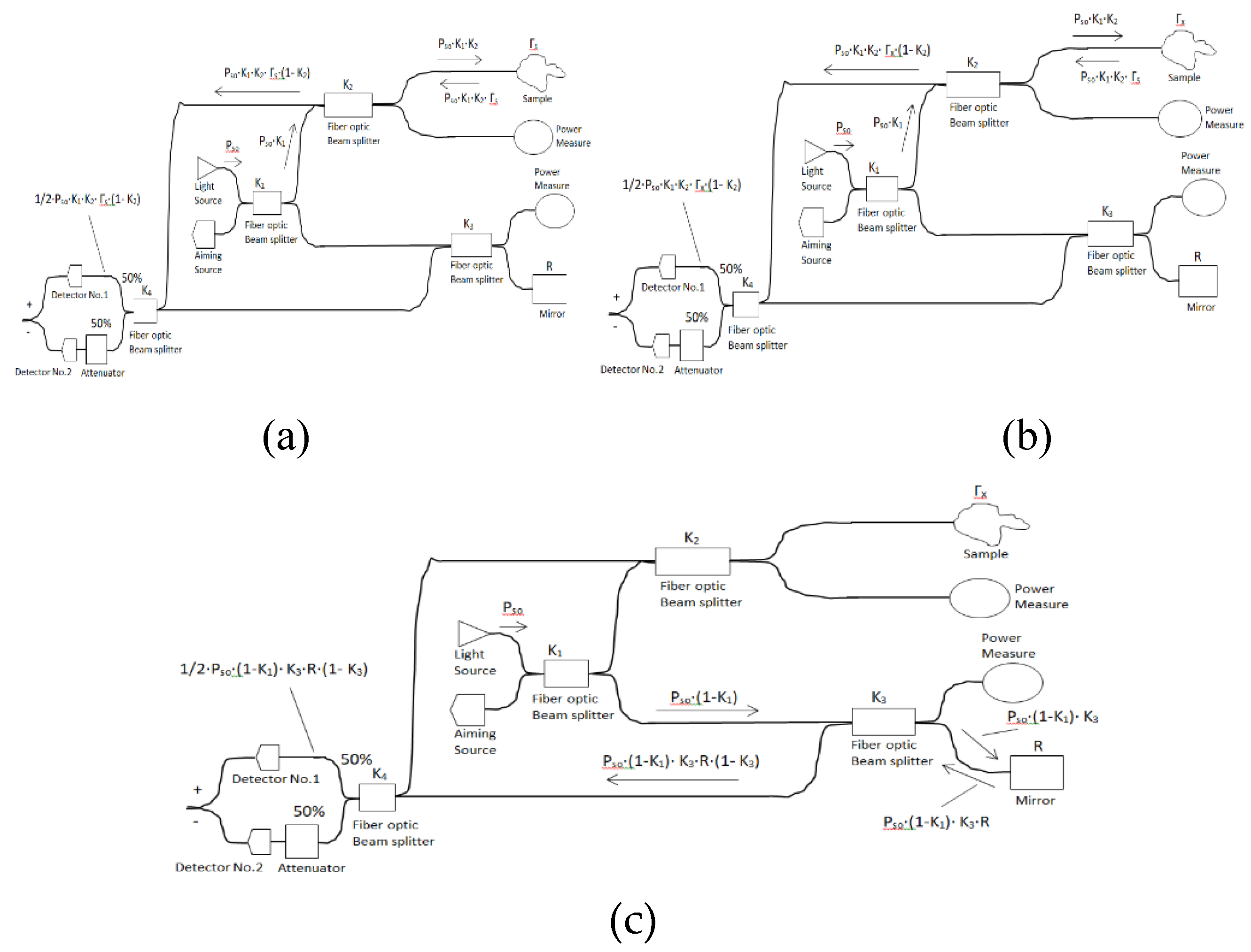
5. OCT Balanced System Four Beam Splitters and attenuator Numerical simulation
The OCT balanced system is constructed from light source power (
), sample tissue, four beam splitters (
,
,
, and
), attenuator, aiming source unit, mirror (
), two power measure units, and two detectors. The light source is SuperLum with optical bandwidth equal to 60 nm (
). SuperLum is a powerful light source based on a super luminescent diode (SLD). SLD is a semiconductor emitter combining the high brightness of laser diodes with a broad spectrum of LEDs. SLD light sources can fit many applications based on low coherence measurements, spectroscopy, low speckle illumination, and others [
11,
12]. The optical detector electrical detection bandwidth is equal to 10 kHz (
). The optical detector electrical detection bandwidth (
) is a measure of how fast the photodetector can respond to a series of incident light pulses. The enhanced intensity noise spectrum from the receiver electrical bandwidth is the cause of system performance degradation. We analyzed our system for different degree of polarization of the source. The noise is measured for
varying from 0 to 100 uA in steps of 0.5uA. The
define the type of couplers/splitter where used m/(100-m) couplers/splitter, and in our case is equal to 50%. For a 50/50 coupler we get
. The attenuator before the optical detector has attenuation of 6 dB, the optical power attenuation
is equal to
, where
,
is attenuator unit input power and
is attenuator unit output power
. The attenuator factor (AF) is defined as
, equal for 6dB attenuation to 0.2512 (d=0.2512). The detector responsivity (
) is taken as one (
). The detector responsivity is a measure of input/output gain of the detector in a Fiber optic (FO) system, and is a measure of photocurrent responsivity per incident unit of optical power [A/watt]. Commercial manufactures of optical detectors give plots of detector responsivity as a function of wavelength. The estimated impedance factor (converting system current to voltage) is taken as 0.035 V/A. The noise of
(mean detector photocurrent) is calculated and equal to 6 dB (0.2512) attenuation in our OCT balanced system and is equal to
which is a summation of three terms
(receiver noise),
(photon shot noise) and
(beat noise). The related equations are
where
,
is electrical detection bandwidth (
),
A/watt,
coulomb ,
,
. The amplification of our system affects the final noise, for amplification of 0dB, 5dB, 10dB, 15dB, 20dB, and 25dB, the calculated noise is multiplied by the appropriate amplification factor
. The calculated noise is also multiplied by the impedance factor (0.035 V/A) [
13,
14]. For our OCT balanced system four beam splitter and attenuator, plots of noise as a function of I
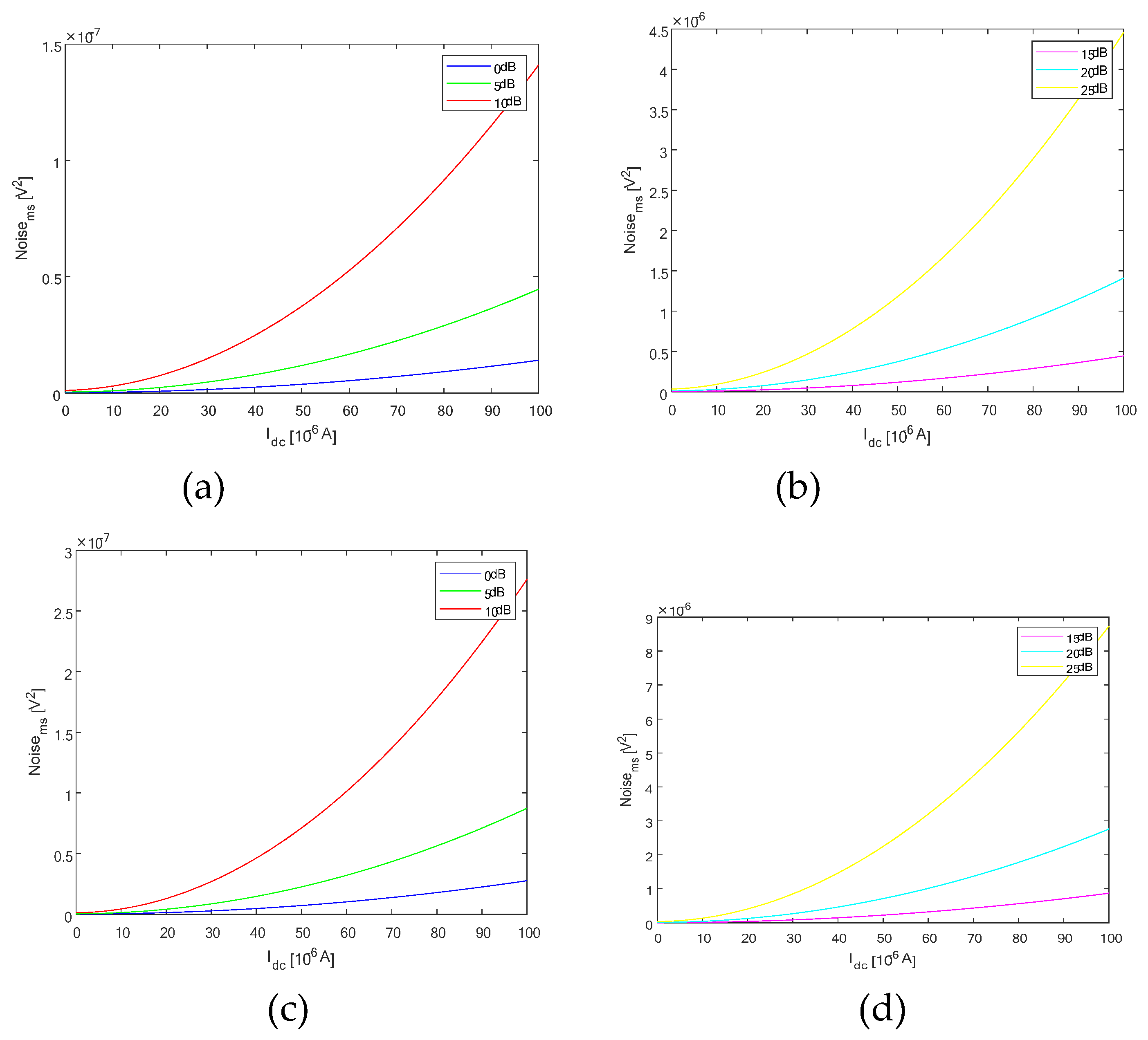
dc (unpolarized), at amplifications of 0dB, 5dB, and 10dB are presented (
Figure 5a).
For our OCT balanced system four beam splitter and attenuator, plots of noise as a function of Idc (unpolarized), at amplifications of 15dB, 20dB, and 25dB are presented (5b).
The OCT balanced system four beam splitter and attenuator Noise vs I
dc (polarized), amplification 0dB, 5dB, and 10dB is presented (
Figure 5c).
For our OCT balanced system four beam splitter and attenuator, plots of noise as a function of I
dc (polarized), at amplifications of 15dB, 20dB, and 25dB are presented (
Figure 5d).
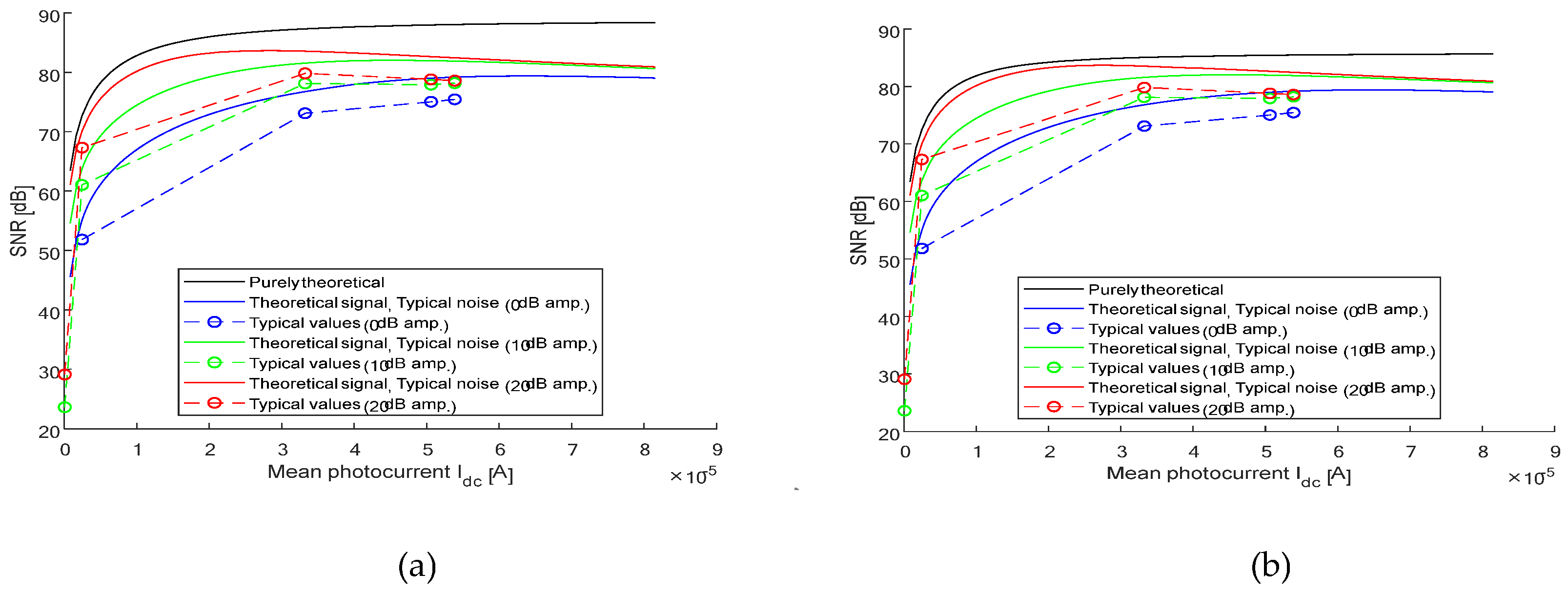
We plot the function (SNR vs
) for our four splitter OCT system, with 6dB attenuation, amplification values are 0 dB, 10 dB, and 20 dB. It is achieved by using (1) pure theoretical formulas, (2) theoretical calculated
with typical noise values, and (3) by using only typical noise values. It is performed for an unpolarized light source
and polarized light source
. First we choose the attenuation of our system as 6 dB (0.02512) and then set the parameters to fit a 3
rd order polynomial (three amplifications, 0 dB, 10 dB, and 20 dB). The SNR as a function of
is plotted where the light source power (
) is set from the initial value
to a final value of
. The initial value of the light source power is 9.4 x 10
-6 watt (
). The receiver responsivity is equal to one (
), the beam splitters parameters have lower value (
,
,
, and
). The estimated sample reflection coefficients are and [
15,
16]. The mirror reflectivity is 0.6 (
). The FWHM wavelength bandwidth of the source is
(
). The optical bandwidth of the source is calculated by using the formula
, where
is the light source wavelength and it equals 1545 nm (
),is
the speed of light in a vacuum, and
is the optical bandwidth of the light source. The electrical detection bandwidth is equal to 30 kHz (
). The receiver noise is set to the level of noise equivalent power (NEP) and is equal to
. The calculated system parameters for different values of light source power
are
,
, and
. The estimated impedance for converting current to voltage (
) in the optical detector is 0.0467 x 10
6 V/A. The detector responsivity (
) is equal to one. In our theoretical calculations of
, we define the level of
as there is no typical data above that value, then turn the domain light source power (
) down. The OCT balanced system four beam splitter and attenuator, plot of SNR as a function of
for unpolarized light source
is presented (
Figure 6a).
The OCT balanced system, four beam splitter and attenuator SNR as a function
for a polarized light source
is also presented (
Figure 6b).
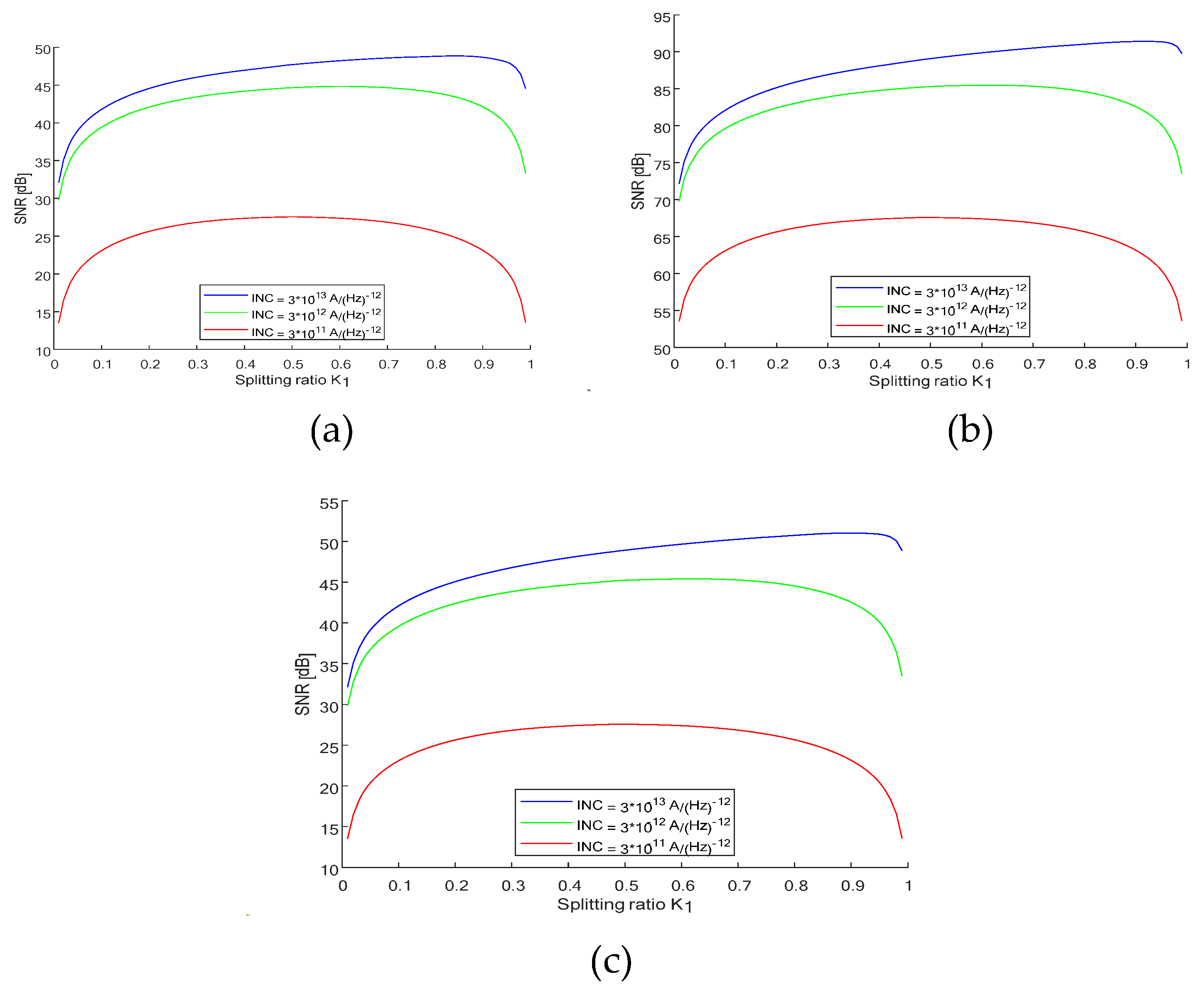
Our OCT balanced system includes four beam splitters, with attenuator, beam splitters (coupling splitting ratio coefficients (K
1, K
2, K
3, and K
4 (K
4=0.5)), sample and mirror. We plot the graph of SNR (dB) vs splitting ration K
1 for different values of NEP [
], noise equivalent power (
,
, and
). The system attenuation is 6 dB (0.2512), and the detector responsivity is one (
). The light source power is 0.1mW (
). We calculate the maximum SNR value and the optimal K
1 beam splitter value. The mirror reflectivity is set to 0.3 (
). The optimal splitting ratio K
1 is determined by
which approximated by NEP value. The graphs are plotted for three cases, (1)
,
,
(2)
,
,
, and (3)
,
,
. Couplers splitting ratio is set to 0.3 (K
1=0.3, K
2=0.3). The FWHM bandwidth of the light source is set to 62nm (
) which fit SuperLum source. The optical bandwidth of the light source (
) expression is
, whereis the speed of light in vacuum,
is the FWHM wavelength bandwidth of the source (
), and
is the light source wavelength (
) [
17,
18]. The electrical detection bandwidth is 10 kHz (
). The polarization coefficient of the light source is set to zero (
), unpolarized. The K
1 beam splitter value is changed from 1% to 99% and we calculate parameters
,
,
and
for each specific value of K
1. I
dc value, noise, and SNR are calculated for each K
1 beam splitter. We create a linearly spaced vector of splitting factor
, the row vector
of 99 points linearly spaced between 0.01 to 99, including 0.01 and 99. We get the maximum SNR value and the optimal
value for three cases. (1)
,
, SNRmax = 48.8269 and K1_opt = 83 (
Figure 7a) (2)
,
, SNRmax = 91.4207 and K1_opt = 92 (
Figure 7b), and (3)
,
, SNRmax = 51.0380 and K1_opt = 91 (
Figure 7c). The expressions for noise and SNR as a function of
K1are
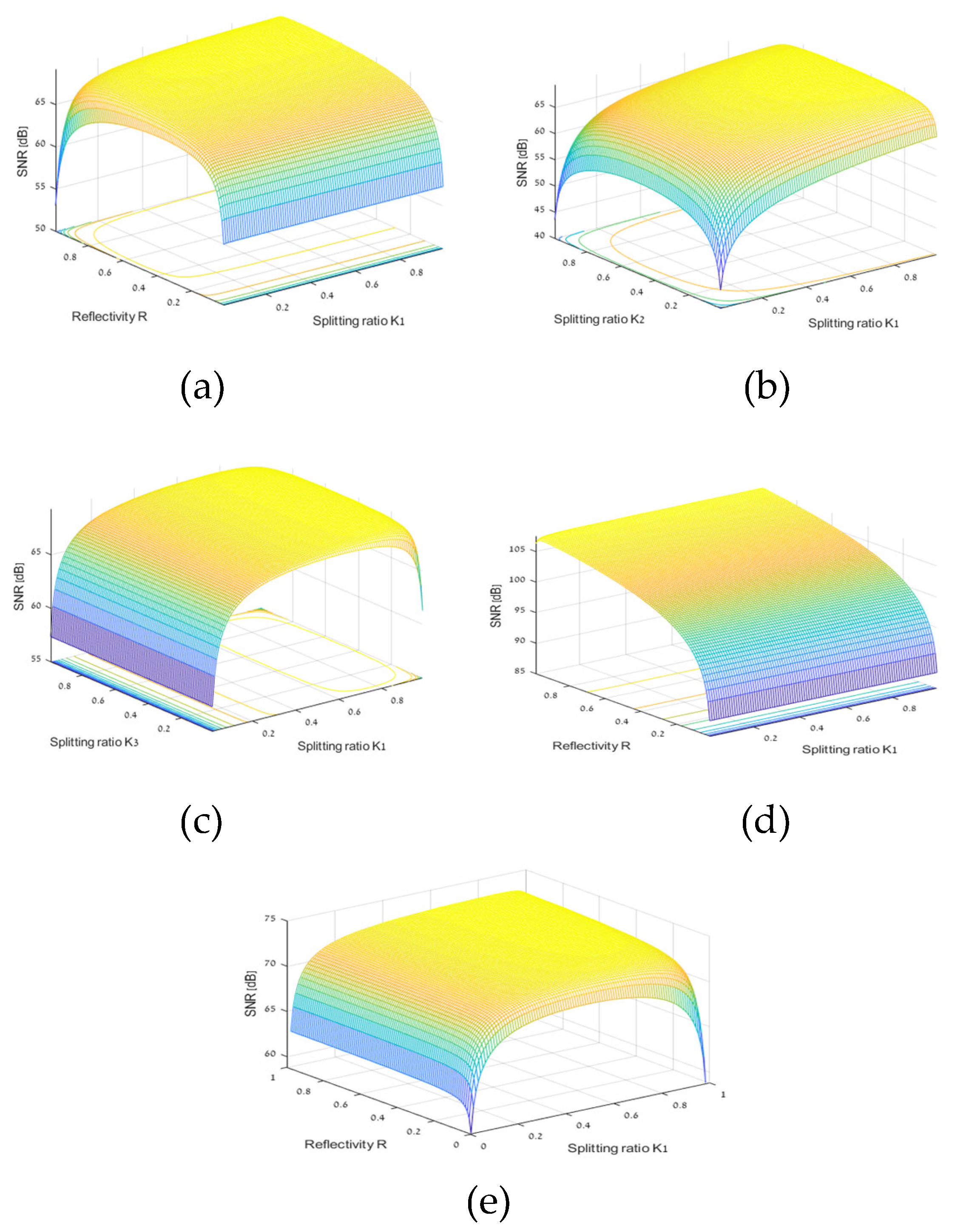
We plot 3D graphs of SNR as a function of mirror reflectivity (R) and K1 splitting ratio for our OCT balanced system with four splitters and attenuator.. The overall system parameters are as follow:
(10 dB) attenuator, detector responsivity (
), light source power
(
), noise equivalent power (NEP) is
, reflection coefficients
, couplers splitting ratio
,
, FWHM wavelength bandwidth of the source
(
). The optical bandwidth of the source
is calculated by the formula
,
is the speed of light in vacuum,
is the light source wavelength
. The electrical detection bandwidth is
(
). The polarization coefficient is set to zero (
), un polarized. We change R and
values between 1% and 99%, and calculate the system parameters
,
,
,
,
, noise, and
, (
Figure 8a). We calculate the maximum SNR value and the optimal
and
values (
,
, and
) [
19,
20].
We get our OCT balanced system four beam splitter and Attenuator, SNR (dB) as a function of splitting ratios K
1, K
2 for
,
,
,
, ratios K
1 , K
2 is changed between 1% to 99%,
, and
,
,
, and
,
(
Figure 8b), (
,
, and
).
We get our OCT balanced system with four beam splitter and Attenuator, SNR (dB) as a function of splitting ratios K
1, K
3 for
,
,
,
, ratios K
1 , K
3 is changed between 1% to 99%,
, and
,..,
,
, and
(
Figure 8c), (
,
, and
) [
21,
22].
We get our OCT balanced system four beam splitter and attenuator SNR (dB) as a function of splitting ratios K
1 , R for
,
,
,
, ratios K
1 , R is changed between 1% to 99%,
,
,
,
,
,
(
Figure 8d), (
,
, and
).
We get our OCT balanced system four beam splitter and attenuator SNR (dB) as a function of splitting ratios K
1 , R for
,
,
,
, ratios K
1 , R is changed between 1% to 99%,
,
,
,
,
,
(
Figure 8e), (
,
, and
).