1. Introduction
Pityriasis rosea (PR) is an acute self-limiting exanthematous disease associated with the endogenous systemic reactivation of human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and/or HHV-7 [
1,
2]. The causal role of the systemic active HHV-6 and HHV-7 infections in the pathogenesis of PR is supported by a large body of evidence using the most modern biological techniques [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. Among these results, the cytopathic effects revealed in culture of peripheral blood mononuclear cells [
4,
5], the detection of HHV-6 and HHV-7 DNA in plasma of PR patients and the presence of their viral antigens and mRNA expression in PR skin lesions, are all markers of active viral replication [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. In addition, the upregulation of the serum levels of interleukin- (IL-) 17, IL-22, IL-36, IFN-
γ, vascular endothelial growth factor, CX3CL1/fractalkine, and CXCL10 in PR patients compared to controls are further evidences that PR is associated with activation of cellular immunity and induction of inflammatory response against a virus [
9,
10,
11].
The cutaneous eruption of PR usually begins with a solitary erythematous papule (‘herald patch’ or ‘mother patch’) that enlarges rapidly to form an annular or oval lesion measuring between 2 and 10 cm in diameter with an erythematous, salmon-colored, scaling borders and a paler, slightly depressed center. This primary lesion remains isolated for about 2 weeks followed by a generalized secondary eruption consisting of smaller scaly papulosquamous lesions oriented with their long axis along the Langer’s lines of cleavage of the trunk in a ‘theatre curtain’ pattern [
1,
2]. The eruption is most often limited to the trunk, neck, and proximal area of the limbs, usually sparing the face. Maculo-papular and petechial oropharyngeal lesions are observed in 28% of patients [
12]. Prodromal symptoms such as general malaise, fatigue, headache, difficult to concentrate, gastrointestinal and upper respiratory symptoms, and mild fever, may precede the exanthema. The exanthem is sometimes associated with mild pruritus [
1,
2]; however, pruritus may be more severe especially if the skin lesions have been treated with a topical medication, such as antimycotic creams [
1]. The typical eruption lasts about 45 days, but a short duration of 2 weeks and persistent eruptions of several months have been described [
13]. PR affects mainly young adults and the diagnosis is entirely clinical [
1,
2,
13]. Many forms considered atypical for morphology, size, number, distribution, symptom severity, and course exist [
1,
2,
13,
14,
15]. However, it is necessary distinguish from these the PR-like eruptions, which can clinically resemble typical PR but which have a completely different pathogenesis, course, and prognosis, being a drug-induced or a vaccine-induced rash; criteria to distinguish between PR and PR-like eruptions have been described taking into account clinical, histopathologic, and virologic features [
13,
16].
The typical PR is a self-limited and frequently asymptomatic disease and the benefits associated with the use of any active intervention should therefore carefully consider any potential adverse effects and the cost of the drug. The best treatment is, therefore, reassuring the patient regarding the nature of the condition and recommending some rest [
1,
13]. However, in particular cases characterized by extensive and persistent lesions and in those associated with systemic symptoms, the disease may have a significant impact on the patient’s quality of life, and, therefore, a treatment can be prescribed [
1,
13].
Noteworthy, PR has been reported to occur more frequently in pregnancy than in the general population (18% versus 6%) [
17] and when it occurs in pregnant women it may justify some concern [
18]. Indeed, since pregnancy is a state of an altered immune response, the risk of HHV-6/7 persistent reactivation can exist and intrauterine transmission of HHV-6 and-7 after viral reactivation in the mother have been reported on several occasions [
19,
20,
21]. In fact, it has been shown that 14% of HHV-6 congenital infection results from intrauterine infections from the mother [
22]. In women developing PR during pregnancy, the most important risk factors threatening the successful outcome of pregnancy are just the high viral load of HHV-6 in the plasma. [
23,
24,
25]. The onset of PR before week 15 and the presence of oropharyngeal lesions are additional major risk factors that must be taken into account [
24]. Systemic symptoms, extensive widespread of the lesions, and PR long duration are statistically lower risk for unfavourable pregnancy outcome [
24,
25,
26,
27]. To date, there are no specific guidelines for the treatment of PR during pregnancy but there is some evidence for the benefit of acyclovir, a drug considered safe in pregnancy [
18,
24,
28,
29].
Several studies evaluated the efficacy of topical and systemic treatment for PR and found conflicting results [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42]. To date, a network meta-analysis that compares at the same time the effectiveness of several treatments for PR has never been performed. Therefore, we decided to realize pairwise and network meta-analysis comparing the effectiveness of several pharmacological treatments of PR in terms of improvement of skin eruption (reduction in number and size of the lesions and reduction of erythema and desquamation) and itch resolution within two weeks from the diagnosis. In contrast to pairwise meta-analyses, network meta-analysis can inform the simultaneous comparative performance of multiple interventions and synthesize evidence across a network of randomized control trials (RCTs), also providing a ranking of the effectiveness of the tested interventions.
The quality of evidence of our findings was also assessed and Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) criteria for network meta-analysis were used to appraise the quality of evidence [
43].
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic review was reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [
44].
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Our focused question on the comparative effectiveness of different pharmacological treatments for PR was addressed following the Population, Intervention, Comparator, and Outcome (PICOs) format. Included studies were parallel RCTs published as full-text papers or conference abstracts, that met the following inclusion criteria: (A) Patients: adult/adolescent/child patients with PR who underwent B) Interventions: acyclovir, antihistamine, azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin, steroids, steroids + antihistamine, (C) Comparators: placebo or compared each other, (D) Outcomes: itch resolution and rash improvement.
We excluded observational non-randomized studies, articles in which neither abstract nor text was written in the English language, and studies that did not report the outcomes at 2 weeks.
Search Strategy
A computerized bibliographic search was performed on PubMed/Medline, Scopus, and Web of Science from inception to July 2024, using the search string reported in the supplementary material (Supplementary Table 1).
The search was supplemented by checking the references of key review articles on this topic. Two investigators (GC, and FD) independently selected articles of interest based on the aforementioned inclusion and exclusion criteria. In cases of multiple publications from the same authors, only the most recent and complete article was included.
Data Abstraction and Risk of Bias Assessment
Data on study-, participant-, and intervention-related characteristics were abstracted onto a standardized form, by two investigators (GC, AF) independently; discrepancies were resolved by consensus, referring back to the original article, in consultation with a third reviewer (FD). The quality of the included studies was assessed by two authors independently (GC, FD) according to the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool 2 for assessing the risk of bias [
45].
Outcomes
Primary outcomes of interest were itch resolution within two weeks, defined as the absence of cutaneous symptoms as rated by the patient (for example through the visual analogue scale [VAS]), and improvement of the eruption within two weeks, defined as a reduction in number and size of the lesions and reduction of erythema and desquamation.
The choice of 2 weeks as the timing of the outcome assessment is due to the consideration that, although the typical PR lasts about 45 days, a shorter duration of 2 weeks has been described [
1,
2]; moreover, without any active treatment PR patients usually start having spontaneous recovery between 2 and 12 weeks [
1,
42]. Therefore, any improvement after two weeks of active treatment would make it difficult to differentiate whether the improvement is due to spontaneous recovery from the disease or to the treatment. Furthermore, not all the patients were diagnosed with PR at the onset of the disease; therefore, evaluating the outcome of a treatment more than two weeks after diagnosis would mean evaluating the patient after an indefinite number of days of spontaneous recovery.
Statistical Analysis
Pooled estimates were reported as relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI), using DerSimonian and Laird random-effects approach [
46]. We assessed statistical heterogeneity using I2 statistic, with values over 50% indicating substantial heterogeneity. Small study effects were assessed by examining funnel plot asymmetry.
We then conducted a network meta-analysis for itch resolution and improvement of the skin eruption through a frequentist approach based on a random-effects consistency model and provided a point estimate from the network along with 95% CI from the frequency distribution of the estimate [
47]. Network consistency was evaluated by comparing the direct estimates to the indirect estimates for each comparison, using a node-splitting technique. Network meta-analysis was conducted with R package netmeta (Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
We calculated the relative ranking of the interventions for achieving the aforementioned outcomes as their surface under the cumulative ranking (SUCRA). SUCRA values range between 0 when a treatment is certainly the worst, and 1 when a treatment is certainly the best [
47].
Safety data were inconsistently reported and only descriptively analysed in the Supplementary material.
Quality of Evidence
The quality of evidence for itch resolution and rash improvement derived from pairwise and network meta-analysis was judged using the GRADE framework [
48] (Supplementary Table 2). Briefly, evidence from RCTs started at high quality, and was rated down for the presence of any of the following factors – risk of bias in the literature, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, and publication bias [
48].
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
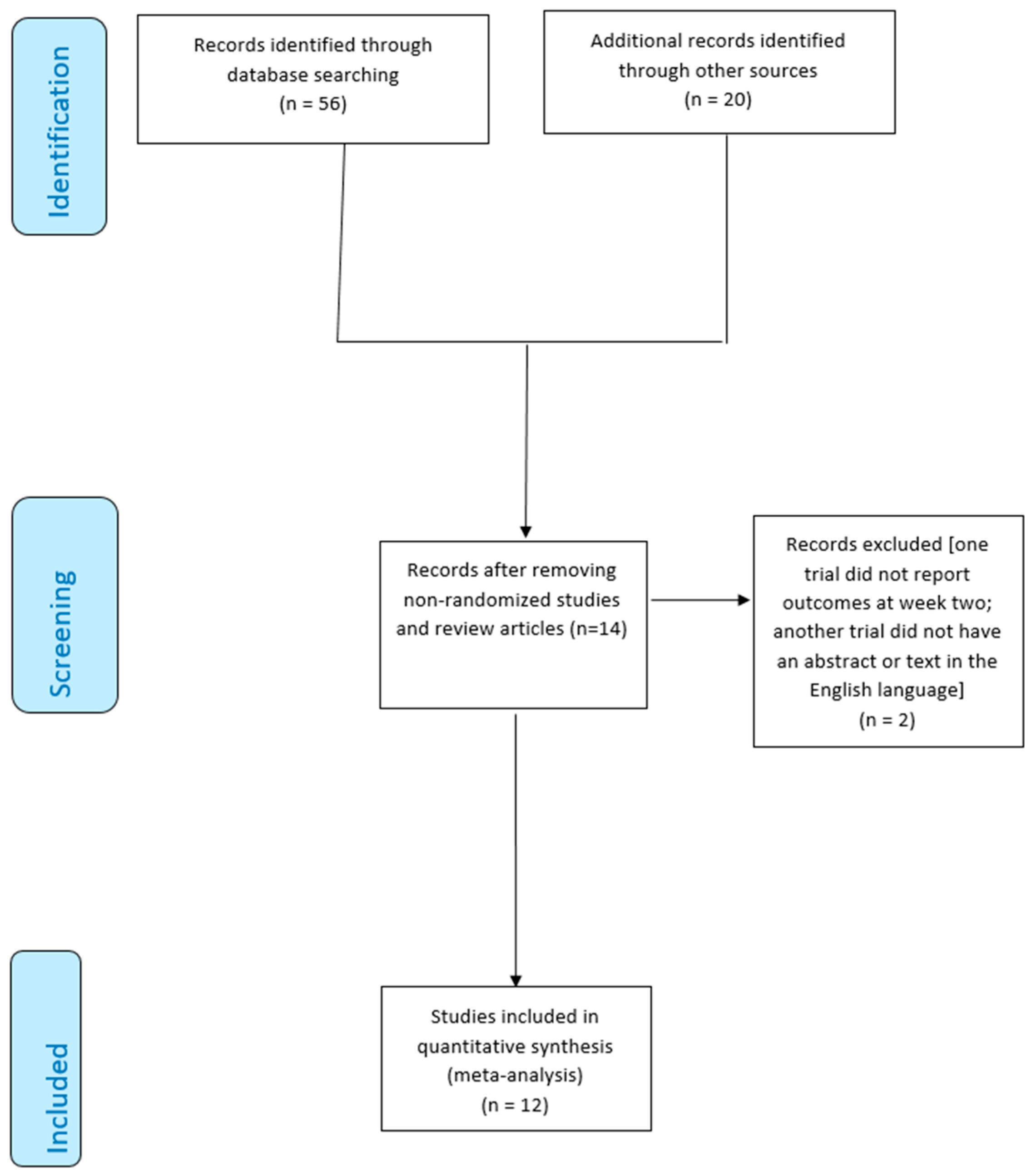
From 76 studies identified using our search strategy, 40 records were excluded based on titles, and abstracts, and 6 because they were duplication; a further 16 studies were excluded because there was no mention of randomization. The research identified 14 studies; however, we excluded one trial that did not report outcomes at week two [
49] and another trial that did not have an abstract or text in the English language [
50]. Finally, 12 RCTs [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41] (638 patients) comparing seven different treatments and placebo were included for quantitative synthesis (
Figure 1).
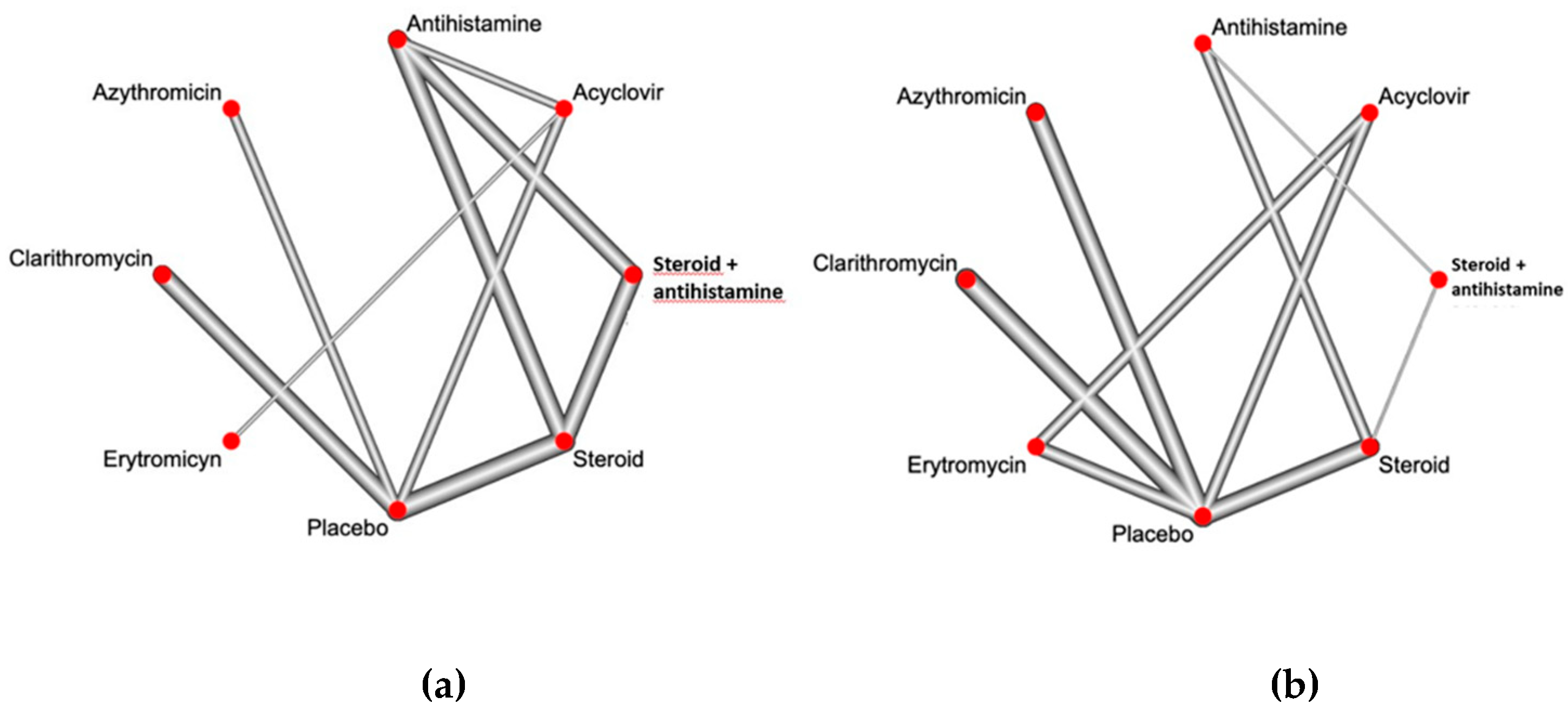
Figure 2a and
Figure 2b show the available direct comparisons and network of trials for itch resolution and improvement of the eruption, respectively.
The main characteristics of included RCTs are reported in
Table 1.
The recruitment period ranged from March 1993 to September 2013. The two arms in the parallel RCTs were well-balanced in terms of baseline factors (mean age, sex). Five RCTs used the instrument of the VAS [
31,
38,
39,
40,
41] while four RCTs did not specify the methods of pruritus assessment [
30,
33,
34,
36]; three RCTs did not evaluate the outcome of itch [
32,
35,
37]. To evaluate the improvement of the skin eruption, only three RCTs used a standardized scale as the pityriasis rosea area and severity index (PRASI) [
40] or the pityriasis rosea severity index (PRSS) [
38,
41]; most of the RCTs assessed the rash improvement by counting the lesions at the onset of disease and at the control visit, also using digital photographs [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
39]; decrease in erythema, size, and scaling of the lesions were sometimes considered for assessing the achievement of the outcome [
35,
37].
As reported in Supplementary Table 3, a risk of bias assessment was performed in the context of the primary outcomes, and overall, studies were felt to be at low risk of bias. Even if unblinded, none of the RCTs showed deviations from the intended protocol.
3.2. Itch Resolution
As reported in
Table 2, when combining direct and indirect evidence through network meta-analysis, only oral steroids and the combination of oral steroids + antihistamine resulted significantly superior to placebo (RR placebo vs steroids 0.44, CI 0.27-0.72 and RR placebo vs steroids + antihistamine 0.47, CI 0.22-0.99), whereas none of the other interventions significantly outperformed placebo (
Table 2).
Among the other direct and indirect comparisons concerning itch resolution, antihistamines resulted significantly superior to erythromycin (RR 17.96, CI 1.07-299.68), clarithromycin and erythromycin resulted inferior to steroids (RR 0.37, CI 0.17-0.81 and RR 0.03, CI 0.01-0.58, respectively); furthermore, erythromycin was significantly inferior to the combination of oral steroids + antihistamines (RR 0.03, CI 0.01- 0.64;
Table 2).
Consequently, as reported in
Table 3, oral steroids resulted as the best option for itch resolution (SUCRA 0.90) followed by oral steroids+ antihistamines (SUCRA 0.84) and antihistamines (SUCRA 0.67). Among the other treatments, only acyclovir ranked better than placebo (SUCRA 0.45 vs 0.40), whereas erythromycin showed the poorest performance in terms of itch resolution (SUCRA score 0.02).
3.3. Improvement of the Skin Eruption
As reported in
Table 4, only acyclovir and erythromycin resulted significantly superior to placebo (RR 2.55, CI 1.81-3.58 and RR 1.69, CI 1.23-2.33, respectively).
Acyclovir outperformed all the other tested interventions (RRs ranging from 1.50 to 19.39 and CIs always beyond 1). The combination of oral steroids and antihistamines was statistically inferior to all the other treatments except clarithromycin (RR clarithromycin vs steroids+antihistamines 6.72, CI 0.95-47.2).
Among the other comparisons, clarithromycin was significantly inferior to erythromycin (RR 0.52, CI 0.34-0.77) and oral steroids (RR 0.54, CI 0.37-0.78).
Consequently, as reported in
Table 3, acyclovir ranked as the best intervention (SUCRA score 0.92), followed by erythromycin (SUCRA 0.79) and steroids (SUCRA 0.73). Clarithromycin (SUCRA 0.30) and oral steroids + antihistamines (SUCRA 0.01) were inferior to placebo (SUCRA 0.38).
3.4. Small Study Effects, Network Coherence, Safety Outcomes, and Quality of Evidence
We did not find any evidence of small study effects based on funnel plot asymmetry for the primary outcomes (data not shown). There was no significant difference between direct and indirect estimates in closed loops that allowed assessment of network coherence and where available, there was no intransitivity between results of direct and indirect meta-analysis (p-value for difference between direct and indirect estimates: p=0.31).
All the medications tested were safe and only a limited number of mild adverse effects (AEs), mainly gastrointestinal AEs, were reported, as descriptively shown in Supplementary Table 4. However, the AEs did not require discontinuation of the drugs.
The overall body of evidence was rated down for imprecision due to wide Ci crossing unity or failure to reach the optimal information size and indirectness due to the heterogeneous definition of the outcomes across the included RCTs. There was no inconsistency, risk of bias in the literature, or publication bias for any of the direct and indirect comparisons. Therefore, the overall body of evidence was rated as low quality.
4. Discussion
Though self-limiting in about 6-8 weeks, PR may have a prolonged clinical course, recurrences may occur (usually within one year) and the extension of the lesions may be generalized and associated with systemic symptoms with a significant impact on the patients' quality of life [
1,
2]. Moreover, in pregnant women, PR may be associated with pregnancy complications as fetal distress, oligohydramnios, premature delivery [
26,
27] and in some cases fetal deaths, abortions, or miscarriages [
18,
23,
24]. In all these atypical course of PR, an effective treatment could be considered.
The most recent Cochrane Review on the interventions for PR included 14 trials (761 participants) and assessed the efficacy of macrolide antibiotics, acyclovir, phototherapy, oral steroids, antihistamines, and Chinese medicine. The authors concluded that oral acyclovir leads to good or excellent rash improvement [
40]. In such a study, the effectiveness of the different drugs has been compared in pairs (for example, azithromycin versus placebo, acyclovir plus antihistamine versus antihistamine, and others) [
42]. Conversely, the present work is the first network meta-analysis that simultaneously compares the performance of multiple pharmacological treatments for PR and summarises evidence across a network of RCTs, providing a ranking of the effectiveness of the treatments.
Using network meta-analysis with GRADE methodology to optimally inform and critically appraise evidence, we made several key observations.
Firstly, in terms of itch resolution, only oral steroids (alone or in combination with antihistamines) resulted significantly superior to placebo (RR placebo vs steroids 0.44, CI 0.27-0.72 and RR placebo vs steroids + antihistamines 0.47, CI 0.22-0.99), whereas none of the other interventions significantly outperformed placebo. Antihistamines alone were also effective and, although not significantly superior to placebo, they outperformed erythromycin; however, the large CI poses a note of caution in the interpretation of this finding. Oral steroids were also superior to macrolides. Overall, oral steroids alone resulted as the best intervention for itch resolution (SUCRA 0.90) followed by steroids+antihistamines (SUCRA 0.84) and antihistamines (SUCRA 0.67); among the other treatments only acyclovir ranked better than placebo in improving the itch. Macrolides showed a very poor performance in terms of itch resolution.
Of note, corticosteroids are not directly antipruritic and it is believed they exert a beneficial effect on pruritus through their reduction in skin inflammation [
51]. However, because of their immunosuppressive effects, the administration of oral steroids could be inappropriate in a disease characterized by viral reactivations, like PR. Furthermore, HHV-6 and HHV-7 reactivations may be associated, especially in immunosuppressed patients (transplant recipients, patients undergoing oncological treatments), with severe complications like hepatitis, pneumonitis, and encephalitis and, therefore, these viral reactivations can benefit of antiviral drugs rather than oral steroids [
52].
Secondly, acyclovir showed striking results concerning rash improvement with a clear superiority over all the other tested interventions. Out of the other drugs, only erythromycin was significantly superior to the placebo (RR 1.69, CI 1.23-2.33). The very poor performance of the combination of steroids and antihistamines deserves some explanation. First of all, it is based on a single small study and this result needs further validation; secondly, the immunosuppressive effect of steroids may exacerbate (instead of recover) a disease like PR associated with endogenous viral reactivations and therefore prolong its course [
52].
The present results strongly corroborate our previous studies. In 2006 Drago et al. evaluated 87 consecutive patients with PR who were treated for 1 week with either oral acyclovir (800 mg 5 times daily) or placebo; on the 7th day of observation, there were significantly fewer new lesions in patients treated in the first week from onset than in those treated later. Remarkably, on the 14th day of treatment, 79% of treated patients fully regressed compared with 4% of the placebo group. Although this trial was neither randomized nor double-blind (objectivity was achieved by counting the skin lesions), it first revealed the efficacy of acyclovir in the treatment of PR, especially in patients treated in the first week from onset when replicative viral activity of HHVs is very high [
53]. In the following years, RCTs, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses further confirm the data on the efficacy of oral acyclovir during the early course of PR [
39,
54,
55]. Among the antivirals available against human herpesviruses, ganciclovir, foscarnet, and cidofovir proved to be active both in vitro and in vivo in inhibiting HHV-6 replication. However, the use of these agents, though more active than acyclovir, is burdened by serious side effects such as myelosuppression and nephrotoxicity [
53]. Conversely, acyclovir at high doses proved to have an anti-HHV-6 effect inhibiting viral DNA synthesis and viral replication and showed easy availability and a low rate of side effects [
53,
56,
57]. A lower activity of acyclovir against HHV-7 has also been shown [
56,
57]. However, it has been demonstrated that in vivo, HHV-7 replication may precede and stimulate HHV-6 reactivation; once reactivated, HHV-6 genomes may predominate and replace the former, leading HHV-7 to disappear or impair its detection by PCR [
6,
58]. Therefore, the use of an antiviral agent like acyclovir which is mainly directed against HHV-6 is justified.
The comparison between different macrolides showed a superiority of erythromycin over clarithromycin, which resulted inferior also to steroids (RR 0.54, 0.37-0.78). Consequently, acyclovir ranked as the best intervention (SUCRA score 0.92) in rash improvement, followed by erythromycin (SUCRA 0.79) and steroids (SUCRA 0.73). Clarithromycin (SUCRA 0.30) and steroids + antihistamines (SUCRA 0.01) were the poorest treatments, even inferior to placebo. The efficacy shown by some macrolide antibiotics in PR could be explained by their modest anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties [
38]. However, given the large amount of evidence on the PR viral etiology, the administration of antibiotics is not recommended.
Our study has several limitations, related to both the network meta-analysis as well as individual studies. First, there was a paucity of head-to-head trials supporting some of the comparisons, and most of the included RCTs were underpowered. Second, most of the included studies were unblinded RCTs, so prone to performance bias. However, no deviations from the intended protocol were detected in any of the included RCTs, so the evidence was not downrated for this specific item. Third, the definition of the outcome “rash improvement” and the methods to evaluate the achievement of this outcome were heterogeneous across the various trials. Conversely, as regards the itch, the outcome was evaluated as “itch resolution” (not as “itch improvement”) therefore the achievement could be evaluated objectively also without a scale.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, based on this systematic review with network meta-analysis of different interventions for PR, in terms of rash improvement, acyclovir represents the best option to consider in cases of PR characterized by extensive skin eruption and systemic symptoms and in cases with recurrent or persistent course (800 mg 5 times daily for 7 days) [
53]. Moreover, despite the absence of consensus on treatment, when PR develops during the first week's gestation showing an aggressive course with generalized lesions and systemic symptoms, after consultation with the patient’s obstetrician, treatment with acyclovir may be cautiously considered. In addition to intervening on the course of PR, this can also reassure patients particularly anxious for the pregnancy outcome. Erythromycin and oral steroids, which could represent other options, are less effective than acyclovir. The use of clarithromycin should be abandoned due to its poor efficacy. Although oral steroids and antihistamines (alone or in combination) seemed the best treatment for itch resolution, acyclovir represents a valuable alternative (better than a placebo) that does not carry the risk of immunosuppressing the patients leading to the possible systemic complications related to HHV-6/7 reactivation. Further large and adequately powered RCTs are needed to confirm these results.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Supplementary Table 1, 2, 3, 4.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.C. and A.F.; methodology, A.F.; software, A.F.; validation, G.C., F.D. and A.F.; formal analysis, A.F.; data curation, A.H.; writing—original draft preparation, G.C., F.D.; writing—review and editing, G.C., A.F. and C.F.; visualization, C.F., ; supervision, C.F. and S.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived as this study is a review of published literature.
Informed Consent Statement
As a literature-based study, approval by the Institutional Review Board and informed consent were not required.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Drago, F.; Broccolo, F.; Rebora, A. Pityriasis rosea: an update with a critical appraisal of its possible herpesviral etiology. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 61, 303-18. [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Ciccarese, G.; Merlo, G.; Trave, I.; Javor, S.; Rebora, A.; Parodi, A. Oral and cutaneous manifestations of viral and bacterial infections: Not only COVID-19 disease. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 39, 384-404. [CrossRef]
- El-Shiemy, S.; Nassar, A.; Mokhtar, M.; Mabrouk, D. Light and electron microscopic studies of pityriasis rosea. Int. J. Dermatol. 1987, 26, 237–9. [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Ranieri, E.; Malaguti, F.; Losi, E.; Rebora, A. Human herpesvirus 7 in pityriasis rosea. Lancet. 1997, 349, 1367-8. [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Ranieri, E.; Malaguti, F.; Battifoglio, M.L.; Losi, E.; Rebora, A. Human herpesvirus 7 in patients with pityriasis rosea. Electron microscopy investigations and polymerase chain reaction in mononuclear cells, plasma and skin. Dermatology. 1997, 195, 374–8. [CrossRef]
- Broccolo, F.; Drago, F.; Careddu, A.M.; Foglieni, C.; Turbino, L.; Cocuzza, C.E.; Gelmetti, C.; Lusso, P.; Rebora, A.; Malnati, M.S. Additional evidence that pityriasis rosea is associated with reactivation of human herpesvirus-6 and -7. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 1234–40. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kawamura, T.; Jacob, S.E., Aquilino, E.A.; Orenstein, J.M.; Black, J.B.; Blauvelt, A. Pityriasis rosea is associated with systemic active infection with both human herpesvirus-7 and human herpesvirus-6. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 793–7. [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, M.; Sada, E.; MacHino, H.; Fujita, S. Reactivation of human herpesvirus 6 in pityriasis rosea. Br. J. Dermatol. 1999, 140, 169-70. [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Ciccarese, G.; Broccolo, F.; Ghio, M.; Contini, P.; Thanasi, H.; Parodi, A. The Role of Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors in the Pathogenesis of Pityriasis Rosea. Mediators Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 438963. [CrossRef]
- Sanad, E.M.; Ibrahim, M.; Rachwan, M.; Shams, G.M. Serum Interleukin-36 in Pityriasis Rosea: A Potential Biomarker for Disease Severity. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 43-46. PMID: 37288282. [PubMed]
- Gangemi, S.; Cannavò, S.P.; Guarneri, F.; Merendino, R.A.; Sturniolo, G.C.; Minciullo, P.L.; Di Pasquale, G.; Valenzise, M.; Drago, F.; Rebora, A. The CX3C-chemokine fractalkine (CX3CL1) is detectable in serum of patients affected by active pityriasis rosea. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2006, 20, 1366-7. [CrossRef]
- Ciccarese, G.; Broccolo, F.; Rebora, A.; Parodi, A.; Drago. F. Oropharyngeal lesions in pityriasis rosea. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 833-837.e4. [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Ciccarese, G.; Rebora, A.; Broccolo, F.; Parodi, A. Pityriasis Rosea: A Comprehensive Classification. Dermatology. 2016, 232, 431-7. [CrossRef]
- Chuh, A.; Zawar, V.; Lee, A. Atypical presentations of pityriasis rosea: case presentations. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2005, 19, 120–6. [CrossRef]
- Bostan, E.; Jarbou, A. Atypical pityriasis rosea associated with mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 814-816. [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Broccolo, F.; Ciccarese, G. Pityriasis rosea, pityriasis rosea-like eruptions, and herpes zoster in the setting of COVID-19 and COVID-19 vaccination. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 40, 586-590. [CrossRef]
- Corson, E.F.; Luscombe, H.A. Coincidence of pityriasis rosea with pregnancy. Arch. Dermatol. Syph. 1950, 62:562-4. [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Broccolo, F.; Zaccaria, E.; Malnati, M.; Cocuzza, C.; Lusso, P.; Rebora. A. Pregnancy outcome in patients with pityriasis rosea. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, S78-83. [CrossRef]
- Katsafanas, G.C.; Schirmer, E.C.; Wyatt, L.S.; Frenkel, N. In vitro activation of human herpesviruses 6 and 7 from latency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 1996, 93, 9788-92. [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.B.; Caserta, M.T.; Schnabel, K.C.; Boettrich, C.; McDermott, M.P.; Lofthus, G.K.; Carnahan, J.A.; Dewhurst, S. Congenital infections with human herpesvirus 6 (HHV6) and human herpesvirus 7 (HHV7). J. Pediatr. 2004, 145, 472-7. [CrossRef]
- Caserta, M.T.; Hall, C.B.; Canfield, R.L.; Davidson, P.; Lofthus, G.; Schnabel, K.; Carnahan, J.; Shelley, L.; Wang, H. Early developmental outcomes of children with congenital HHV-6 infection. Pediatrics. 2014, 134, 1111-8. [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.B.; Caserta, M.T.; Schnabel, K.C.; Shelley, L.M.; Carnahan, J.A.; Marino, A.S.; Yoo, C.; Lofthus, G.K. Transplacental congenital human herpesvirus 6 infection caused by maternal chromosomally integrated virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 505-7. [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Broccolo, F.; Javor, S.; Drago, F.; Rebora, A.; Parodi, A. Evidence of human herpesvirus-6 and -7 reactivation in miscarrying women with pityriasis rosea. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 198-9. [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Ciccarese, G.; Herzum, A.; Rebora, A.; Parodi, A. Pityriasis Rosea during Pregnancy: Major and Minor Alarming Signs. Dermatology. 2018, 234, 31-36. [CrossRef]
- Rebora, A.; Ciccarese, G.; Herzum, A.; Parodi, A.; Drago, F. Pityriasis rosea and other infectious eruptions during pregnancy: Possible life-threatening health conditions for the fetus. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 38, 105-112. [CrossRef]
- Stashower, J.; Bruch, K.; Mosby, A.; Boddie, P.P.; Varghese, J.A.; Rangel, S.M.; Brodell, R.T.; Zheng, L.; Flowers, R.H. Pregnancy complications associated with pityriasis rosea: A multicenter retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021, 85, 1648-1649. [CrossRef]
- Wenger-Oehn, L.; Graier, T.; Ambros-Rudolph, C.; Müllegger, R.; Bittighofer, C.; Wolf, P.; Hofer, A. Pityriasis rosea in pregnancy: A case series and literature review. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2022, 20, 953-959. [CrossRef]
- Mother To Baby | Fact Sheets [Internet]. Brentwood (TN): Organization of Teratology Information Specialists (OTIS); 1994-. Acyclovir (Zovirax®) / Valacyclovir (Valtrex®) 2024 Feb. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK582557/.
- Heymann, W.R. Probing pityriasis rosea in pregnancy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 1413. [CrossRef]
- Lazaro-Medina, A.; Villena-Amurao, C.; Dy-Chua, N.S.; Sit-Toledo, M.S.W.; Villanueva, B. A clinico-histopathologic study of a randomized double-blind clinical trial using oral dexchlorpheniramine 4 mg, betamethasone 500 mcg and betamethasone 250 mcg with dexchlorpheniramine 2 mg in the treatment of pityriasis rosea: a preliminary report. Journal of the Philippine Dermatological Society. 1996, 5:3-7.
- Villarama, C.; Lansang, P. The efficacy of erythromycin stearate in pityriasis rosea: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. 10th Philippine Dermatological Society Resident's Research Forum. Phillipines: Phillipine Dermatological Society, 27th November 2002:1-17.
- Akhyani, M.; Mortazavi, H.; Izadi, M.; Ehsani, A.H. The efficacy of oral erythromycin in the treatment of patients with pityriasis rosea: A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Iranian Journal of Dermatology 2003, 7, 14-18.
- Amer, A.; Fischer, H. Azithromycin does not cure pityriasis rosea. Pediatrics. 2006, 117, 1702-5. [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, A.; Esmaily, N.; Noormohammadpour, P.; Toosi, S.; Hosseinpour, A.; Hosseini, M.; Sayanjali, S. The comparison between the efficacy of high dose acyclovir and erythromycin on the period and signs of pitiriasis rosea. Indian J. Dermatol. 2010, 55, 246-8. [CrossRef]
- Rassai, S.; Feily, A.; Sina, N.; Abtahian, S. Low dose of acyclovir may be an effective treatment against pityriasis rosea: a random investigator-blind clinical trial on 64 patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 24-6. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; IYikhar, N.; Bashir, U.; Rizvi, S.D.; Sheikh, Z.I.; Manzur, A. Efficacy of Clarithromycin in Pityriasis rosea. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons--Pakistan (JCPSP) 2014, 24, 802-5.
- Ganguly, S. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of efficacy of oral acyclovir in the treatment of pityriasis rosea. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, YC01-4. [CrossRef]
- Pandhi, D.; Singal, A.; Vema, P.; Sharma, R. The efficacy of azithromycin in pityriasis rosea: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014, 80, 36-40. [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Sil, A.; Das, N.K.; Roy, K.; Das, A.K.; Bandyopadhyay. D. Acyclovir in pityriasis rosea: an observer-blind, randomized, controlled trial of effectiveness, safety and tolerability. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2015, 6, 181-4. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Anurag; Tiwary, N.K. Acyclovir is not effective in pityriasis rosea: Results of a randomized, triple blind, placebo-controlled trial. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016, 82, 505-9. [CrossRef]
- Sonthalia, S.; Kumar, A.; Zawar, V.; Priya, A.; Yadav, P.; Srivastava, S.; Gupta. A. Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of short-course low-dose oral prednisolone in pityriasis rosea. J Dermatolog Treat 2018, 29, 617-22. [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Ruiz, J.; Peternel, S.; Jiménez Gutiérrez, C.; Culav-Koscak, I.; Reveiz, L.; Silbermann-Reynoso, M.L. Interventions for pityriasis rosea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD005068. [CrossRef]
- Puhan, M.A.; Schünemannm, H.J.; Murad, M.H.; Li, T.; Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Singh, J.A.; Kessels, A.G.; Guyatt, G.H.; GRADE Working Group. A GRADE Working Group approach for rating the quality of treatment effect estimates from network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2014, 349, g5630. [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.P.; Fleurence, R.; Devine, B.; Itzler, R.; Barrett, A.; Hawkins, N.; Lee, K.; Boersma, C.; Annemans, L.; Cappelleri, J.C. Interpreting indirect treatment comparisons and network meta-analysis for health-care decision making: report of the ISPOR Task Force on Indirect Treatment Comparisons Good Research Practices: part 1. Value Health. 2011, 14,417-28. [CrossRef]
- Sternem J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. B.M.J. 2019, 366:l4898. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials revisited. Contemp. Clin. Trials. 2015, 45, 139-45. [CrossRef]
- White, I.R.; Barrett, J.K.; Jackson, D.; Higgins, J.P. Consistency and inconsistency in network meta-analysis: model estimation using multivariate meta-regression. Res. Synth. Methods. 2012, 3, 111-25. [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Kunz, R.; Brozek, J.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Rind, D.; Devereaux, P.J.; Montori, V.M.; Freyschuss, B.; Vist, G.; et al. GRADE guidelines 6. Rating the quality of evidence--imprecision. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 1283-93. Erratum in: J Clin Epidemiol. 2021, 137:265. [CrossRef]
- Jairath, V.; Mohan, M.; Jindal, N.; Gogna, P.; Syrty, C.; Monnappa, P.M.; Kaur, S.; Sehrawat, M.; et al. Narrowband UVB phototherapy in pityriasis rosea. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2015, 6, 326-9. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.Y. The observation of curative effects of glycyrrhizin in treating pityriasis rosea. Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 1992, 21, 43.
- Patel, T.; Yosipovitch, G. Therapy of pruritus. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 1673-82. [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Ciccarese, G.; Parodi, A. Atypical exanthems related to human herpesvirus-6 reactivations in transplant recipients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2016, 18, 639-40. [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Vecchio, F.; Rebora, A. Use of high-dose acyclovir in pityriasis rosea. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, 82-5. [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Sung, C.W.; Lin, M.H. The efficacy of oral acyclovir during early course of pityriasis rosea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2019, 30, 288-293. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Zuniga, M.; Torres, N.; Garcia-Perdomo, H. Effectiveness of acyclovir in the treatment of pityriasis rosea. A systematic review and meta-analysis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2018, 93, 686-695. [CrossRef]
- Burns, W.H.; Sandford, G.R. Susceptibility of human herpesvirus-6 to antivirals in vitro. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 162:634-7. [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Yamada, M.; Tsukazaki, T.; Chatterjee, S.; Lakeman, F.D.; Nii, S.; Whitley, R.J. Comparison of antiviral compounds against human herpesvirus 6 and 7. Antiviral Res. 1998, 40, 73-84. [CrossRef]
- Katsafanas, G.C.; Schirmer, E.C.; Wyatt, L.S.; Frenkel, N. In vitro activation of human herpesvirus 6 and 7 from latency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996, 93, 9788-92. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).