Submitted:
19 September 2024
Posted:
20 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shang, J.; Chen, S.; Pang, X.; Oeltmann, J.E.; Moonan, P.K.; Chen, M. and Zhang, F. Influence of COVID-19 for delaying the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis–Tianjin, China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 937844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, N.R.; et al. The emergence of drug-resistant tuberculosis: a global perspective. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 391–392. [Google Scholar]
- Kurbatova, E.V.; Phillips, P.P.; Dorman, S.E.; Sizemore, E.E.; Bryant, K.E.; Purfield, A.E.; Ricaldi, J.; Brown, N.E.; Johnson, J.L.; Wallis, C.L.; Akol, J.P. A Standardized Approach for Collection of Objective Data to Support Outcome Determination for Late-Phase Tuberculosis Clinical Trials. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostyukova, I.; Pasechnik, O.; Mokrousov, I. Epidemiology and Drug Resistance Patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in High-Burden Area in Western Siberia, Russia. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Global Tuberculosis Report 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/global-tuberculosis-report-2021 (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Castro, D.; Maciel, E.; Sadahiro, M.; Pinto, R.; Albuquerque, B.; Braga, J. Tuberculosis incidence inequalities and its social determinants in Manaus from 2007 to 2016. Int. J. Equity Health 2018, 17, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, P.L.; Win, K.M.; Win Maung, H.M.; Show, K.L. Determinants of correct knowledge on tuberculosis transmission and self-reported tuberculosis prevalence among general population aged 15–49 years in Myanmar. Plos ONE 2023, 18, e0290470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humayun, M.; Chirenda, J.; Ye, W.; Mukeredzi, I.; Mujuru, H.A.; Yang, Z. Effect of Gender on Clinical Presentation of Tuberculosis (TB) and Age-Specific Risk of TB, and TB-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Coinfection. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022, 9, ofac512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, R. The interplay between HIV and tuberculosis: Challenges in treatment and management. J. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2020, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240061729 (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Gopalaswamy, R.; Shanmugam, S.; Mondal, R.; Subbian, S. Of tuberculosis and non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections - a comparative analysis of epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mancuso, J.; Smith, R.; Johnson, L. The evolving landscape of tuberculosis: Advances in understanding Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 36, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, A.; Beena, P.M.; Devnikar, A.V.; Mali, S. A systemic review on tuberculosis. Indian J. Tuberc. 2020, 67, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, I.; et al. Epidemiology of tuberculosis in Spain: A review of current and future challenges. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South African National Strategic Plan. National Strategic Plan for Tuberculosis Elimination; 2023–2028. Retrieved from National Department of Health. Available online: https://www.health.gov.za.
- Stop TB Partnership. TB and Human Rights. 2022. Available online: https://stoptb.org/assets/documents/global/hrtf/briefing%20note%20on%20tb%20and%20human%20rights.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Swalehe, M.A.; Obeagu, E.I. Airborne transmission of tuberculosis: Implications for public health. J. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2024, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daftary, A.; Sutherland, K.; Sweeney, S. The burden of drug-resistant tuberculosis: Global trends and implications for public health. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2021, 25, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seloma, A.; et al. Trends in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: Challenges and strategies for control. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2023, 27, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Khan, M.; Ali, S. The impact of socio-economic factors on tuberculosis treatment adherence: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2018, 22, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oga-Omenka, P.; Okwuosa, C.; Okwuosa, J. The burden of drug-resistant tuberculosis in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 92, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlatu, N.; Oladimeji, K.E.; Apalata, T. Voices from the Patients: A Qualitative Study of the Integration of Tuberculosis, Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Primary Healthcare Services in O.R. Tambo District, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Infect. Dis. Rep 2023, 15, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.L.; Gandhi, N.R.; Clennon, J.; Nelson, K.N.; Morris, N.; Ismail, N.; Allana, S.; Campbell, A.; Brust, J.C.M.; Auld, S.C.; Mathema, B.; Mlisana, K.; Moodley, P.; Shah, N.S. Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis ‘hotspots’ and sociodemographic associations in Durban, South Africa. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2019, 23, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Statistics of South Africa. 2019. Available online: http://www.statssa.gov.za (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Vanleeuw, A.; et al. The impact of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis on national TB control programs in developing countries: A review. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2022, 26, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics of South Africa. 2018. Available online: http://www.statssa.gov.za (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Dickson, L.; Le Roux, S.R.; Mitrani, L.; Hill, J.; Jassat, W.; Cox, H.; Mlisana, K.; Black, J.; Loveday, M.; Grant, A.; Kielmann, K.; Ndjeka, N.; Moshabela, M.; Nicol, M. Organisation of care for people receiving drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment in South Africa: a mixed methods study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e067121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chenciner, L.; Annerstedt, K.S.; Pescarini, J.M.; Wingfield, T. Social and health factors associated with unfavorable treatment outcome in adolescents and young adults with tuberculosis in Brazil: a national retrospective cohort study. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e1380–e1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagna, R.; Cabibbe, A.M.; Miotto, P.; Saluzzo, F.; Köser, C.U.; Niemann, S.; Gagneux, S.; Rodrigues, C.; Rancoita, P.V.M.; Cirillo, D.M. Is the new WHO definition of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis easy to apply in practice? Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2100959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohidem, N.A.; Hashim, Z.; Osman, M.; Muharam, F.M. , Elias, S.M.; Shaharudin, R. Environment as the risk factor for tuberculosis in Malaysia: a systematic review of the literature. Rev. Environ. Health 2021, 36, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nidoi, J.; Muttamba, W.; Walusimbik, S.; Imoko, J.F.; Lochoro, P.; Ictho, J.; Mugenyi, L.; Sekibira, R.; Turyahabwe, S.; Byaruhanga, R.; Putoto, G.; Villa, S.; Raviglione, M.C.; Kirenga, B. Impact of socio-economic factors on Tuberculosis treatment outcomes in north-eastern Uganda: a mixed methods study. BMC Public Health. 2021, 21, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cannon, J.; Smith, A. , & Johnson, L. The impact of socio-economic factors on healthcare access in urban populations. J. Public Health Res. 2021; 15, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielmann, K.; Vidal, N.; Riekstiņa, V.; Krutikov, M.; Werf, M.J. v. d.; Biraua, E.; Moore, D. Treatment is of primary importance, and social assistance is secondary: a qualitative study on the organisation of tuberculosis (tb) care and patients’ experience of starting and staying on tb treatment in riga, latvia. PloS ONE 2018, 13, e0203937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroof, M.; Pamei, G.; Bhatt, M.; Awasthi, S.; Bahuguna, S.C.; Singh, P.K. Drug adherence to anti-tubercular treatment during covid-19 lockdown in haldwani block of nainital district. Indian J. Community Health 2022, 34, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, S.J.; Beck, S.L.; Pearce, P.F.; Chirico, C.; Etchevarria, M.; Cardinale, D.; Rubinstein, F. Text TB: a mixed method pilot study evaluating acceptance, feasibility, and exploring initial efficacy of a text messaging intervention to support TB treatment adherence. Tuberc. Res. Treat. 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, F.; Sharma, M.; Obaid Al-Harbi, N.; Rashid Khan, M.; Qamar, W.; Iqbal, M.; Daud Ali, M.; Ali, N.; Khalid Anwar, M. The possible impact of socioeconomic, income, and educational status on adverse effects of drug and their therapeutic episodes in patients targeted with a combination of tuberculosis interventions. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021, 28, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report, 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240062006.
- Nardell, E.A. Transmission and Institutional Infection Control of Tuberculosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015, 6, a018192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Coleman, M.; Martinez, L.; Theron, G. ; Wood; R.; Marais, B. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Transmission in High-Incidence Settings-New Paradigms and Insights. Pathogens, 2022; 11, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.P.; Oeltmann, J.E.; Hill, A.N.; Tobias, J.L.; Boyd, R.; Click, E.S.; Finlay, A.; Mondongo, C.; Zetola, N.M.; Moonan, P.K. Characterizing tuberculosis transmission dynamics in high-burden urban and rural settings. Sci Rep. 2022, 12, 6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Verver, S.; Warren, R.M.; Munch, Z.; Vynnycky, E.; van Helden, P.D.; Richardsonl, M.; van der Spuy, G.D.; Enarsonk, D.A.; Borgdorff, M.W.; Behr, M.A.; Beyers, N. Transmission of tuberculosis in a high incidence urban community in South Africa. Int J Epidemiol. 2004, 33, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, B.; Morrow, C.D.; Kohls, D.; Deignan, C.; Ginsburg, S.; Wood, R. Mapping sites of high TB transmission risk: integrating the shared air and social behaviour of TB cases and adolescents in a South African township. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kootbodien, T.; Monyane, M.; Mothibe, N. The impact of socio-economic factors on tuberculosis treatment outcomes in South Africa: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youakin, A.; Smith, J.; Johnson, L. The impact of socio-economic factors on tuberculosis treatment outcomes: A systematic review. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2016, 20, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, A.Z.; Chee, C.B.E.; Wang, Y.T.; et al. Alcohol drinking and cigarette smoking in relation to risk of active tuberculosis: prospective cohort study. BMJ Open Resp Res 2017, 4, e000247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi-Naini, R.; Sharifi-Mood, B.; Metanat, M. Association between tuberculosis and smoking. Int. J. High Risk Behav. Addict. 2012, 1, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Saha, I.; Sarkar, A.; Chowdhury, R. Gender differences in notification rates, clinical forms and treatment outcome of tuberculosis patients under the RNTCP. Lung India 2012, 29, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Sane, M.; Gaikwad, S.; Sahasrabudhe, T.; Barthwal, M.; Lokhande, R.; Raskar, S.; Kagal, A.; Dharmshale, S.; Pradhan, N.; Gupte, A.; Alfarisi, O.; Gupta, A.; Dooley, K.E.; Gupte, N.; Golub, J.E.; Mave, V. Sex Differences in TB Clinical Presentation, Drug Exposure, and Treatment Outcomes in India. Chest. 2023, 163, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Murphy, M.E.; Wills, G.H.; Murthy, S.; et al. Gender differences in tuberculosis treatment outcomes: a post hoc analysis of the REMoxTB study. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msoka, E.F.; Orina, F.; Sanga, E.S.; Miheso, B.; Mwanyonga, S.; Meme, H.; Kiula, K.; Liyoyo, A.; Mwebaza, I.; Aturinde, A.; Joloba, M.; Mmbaga, B.; Amukoye, E.; Ntinginya, N.E.; Gillespie, S.H.; Sabiitim, W. Qualitative assessment of the impact of socioeconomic and cultural barriers on uptake and utilisation of tuberculosis diagnostic and treatment tools in East Africa: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e050911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baker, M.A.; et al. The role of education in the prevention of tuberculosis: a systematic review. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2018, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth, K.; Raviglione, M. Global tuberculosis control: The need for new metrics. Lancet 2016, 387, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report, 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240062006.
- Harrisson, L.; Smith, J. Socio-economic determinants of tuberculosis treatment outcomes: A systematic review. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2020, 24, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei, D.; et al. Barriers to tuberculosis treatment adherence in low-income communities: A qualitative study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, D.; et al. The impact of poverty on tuberculosis treatment outcomes: A systematic review. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2012, 16, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, M.; et al. The impact of malnutrition on tuberculosis susceptibility: A systematic review. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Ali, S.; Rahman, A. Socio-economic determinants of tuberculosis treatment adherence: A cross-sectional study in urban settings. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2021, 25, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhedhi, S.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, R. Nutritional status and its impact on drug-resistant tuberculosis: A study from a tertiary care center. J. Clin. Tuberc. Other Mycobact. Dis. 2022, 25, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M.; et al. The impact of socio-economic factors on tuberculosis treatment adherence: A systematic review. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2016, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.; Rylance, J.; Makumbirofa, S.; Meffert, S.M.; Vu, T.A.; Clayton, J.M.; Metcalfe, J. Chronic lung disease in adult recurrent tuberculosis survivors in Zimbabwe: a cohort study. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2019, 23, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havir, E.; Smith, J.; Johnson, L. The impact of socio-economic factors on tuberculosis treatment outcomes: A systematic review. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.R.; Mousnad, M.A. Systematic review of the impact of food provision on adherence to the tuberculosis treatment. Health Prim. Care 2019, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Treatment Guidelines for Isoniazid-Resistant Tuberculosis: Supplement to the WHO Treatment Guidelines for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Wu, S.; Litvinjenko, S.; Magwood, O.; Wei, X. Defining tuberculosis vulnerability based on an adapted social determinants of health framework: a narrative review. Global Public Health 2023, 18, 2221729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, D.; Maciel, E.; Sadahiro, M.; Pinto, R.; Albuquerque, B.; Braga, J. Tuberculosis incidence inequalities and its social determinants in manaus from 2007 to 2016. Int. J. Equity Health 2018, 17, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, K.; Toonsiri, C. Factors related to the successful treatment of tuberculosis: a literature review. Belitung Nurs. J. 2019, 5, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, S.A.; Lewin, S.A.; Smith, H.J.; Engel, M.E.; Fretheim, A.; Volmink, J. Patient adherence to tuberculosis treatment: a systematic review of qualitative research. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hussain, H.; Mori, A.T.; Khan, A.J.; et al. The cost-effectiveness of incentive-based active case finding for tuberculosis (TB) control in the private sector Karachi, Pakistan. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2019, 19, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaleta, K.; Gizachew, M.; Gelaw, B.; Tesfa, H.; Getaneh, A.; Biadgo, B. Rifampicin-resistant <em>mycobacterium tuberculosis</em> among tuberculosis-presumptive cases at university of gondar hospital, northwest ethiopia. Infect. Drug Resist. 2017, 10, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Hill, A.; Kurbatova, E.; Walt, M.; Kvasnovsky, C.; Tupasi, T.; Cegielski, P. Estimating the future burden of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in india, the philippines, russia, and south africa: a mathematical modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misyatin, D.; Soeroto, A.; Ferdian, F. Distribution of rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis patients based on presumptive drug-resistant tuberculosis criteria at dr. hasan sadikin hospital 2016–2019. Althea Med. J. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baéz-Saldaña, R.; Delgado-Sánchez, G.; García-García, L.; Cruz-Hervert, L.; Montesinos-Castillo, M.; Ferreyra-Reyes, L.; Ponce-de-León, A. Isoniazid mono-resistant tuberculosis: impact on treatment outcome and survival of pulmonary tuberculosis patients in Southern Mexico 1995-2010. Plos One 2016, 11, e0168955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, B.; Edwards, J.; Cooper, R.; Kunimoto, D.; Somayaji, R.; Fisher, D. Incidence, treatment, and outcomes of isoniazid mono-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis infections in alberta, canada from 2007-2017. Plos One 2020, 15, e0229691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senbeto, M.; Tadesse, S.; Tadesse, T.; et al. Appropriate health-seeking behavior and associated factors among people who had cough for at least two weeks in northwest Ethiopia: a population-based cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelner, J.L.; Murray, M.B.; Becerra, M.C.; Galea, J.; Lecca, L.; Calderon, R.; Yataco, R.; Contreras, C.; Zhang, Z.; Manjourides, J.; Grenfell, B.T.; Cohen, T. Identifying Hotspots of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Transmission Using Spatial and Molecular Genetic Data. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 287–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- MacNeil, A.; Glaziou, P.; Sismanidis, C.; Date, A.; Maloney, S.; Floyd, K. Global Epidemiology of Tuberculosis and Progress Toward Meeting Global Targets—Worldwide, 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2018, 69, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndjeka, N.; Campbell, J.R.; Meintjes, G.; Maartens, G.; Schaaf, H.S.; Hughes, J.; Padanilam, X.; Reuter, A.; Romero, R.; Ismail, F.; Enwerem, M.; Ferreira, H.; Conradie, F.; Naidoo, K.; Menzies, D. Treatment outcomes 24 months after initiating short, all-oral bedaquiline-containing or injectable-containing rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis treatment regimens in South Africa: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022, 22, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cioboata, R.; Biciusca, V.; Olteanu, M.; Vasile, C.M. COVID-19 and Tuberculosis: Unveiling the Dual Threat and Shared Solutions Perspective. J Clin Med. 2023, 12, 4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Muhammad Dayyab, F.; Iliyasu, G.; Garba Ahmad, B.; Aliyu Umar, I.; Musa Shuaib, N.; Bajehson, M.; Muhammad Daiyab, I.; Akpala, O.; Remilekun, O.; Garba Habib, A. For Kano TB Concilium Experts: Emerging threat of drug-resistant tuberculosis and trends in the era of COVID-19: A descriptive study from northwestern Nigeria. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis 2022, 28, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aznar, M.L.; Espinosa-Pereiro, J.; Saborit, N.; Jové, N.; Martinez, F.S.; Pérez-Recio, S.; Vitoria, A.; Sanjoaquin, I.; Gallardo, E.; Llenas-García, J.; Pomar, V. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on tuberculosis management in Spain. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liu, J. A united model for diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis with random forest and artificial neural network. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1094099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouchaki, S.; Yang, Y.; Lachapelle, A.; Walker, T.M.; Walker, A.S.; CRyPTIC Consortium; Peto TEA.; Crook, D.W.; Clifton, D.A. Multi-Label Random Forest Model for Tuberculosis Drug Resistance Classification and Mutation Ranking. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 667. 2020, 11, 667. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedaso, M.H.; Kalil, F.S. Trends of Drug Resistance Tuberculosis from 2014 to 2018, Bale Zone, Oromia Region, Ethiopia. Infect Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rodrigues, M.M.S.; Barreto-Duarte, B.; Vinhaes, C.L.; Araújo-Pereira, M.; Fukutani, E.R.; Bergamaschi, K.B.; Kristki, A.; Cordeiro-Santos, M.; Rolla, V.C.; Sterling, T.R.; Queiroz, A.T.L.; Andrade, B.B. Machine learning algorithms using national registry data to predict loss to follow- up during tuberculosis treatment. BMC Public Health. 2024, 24, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
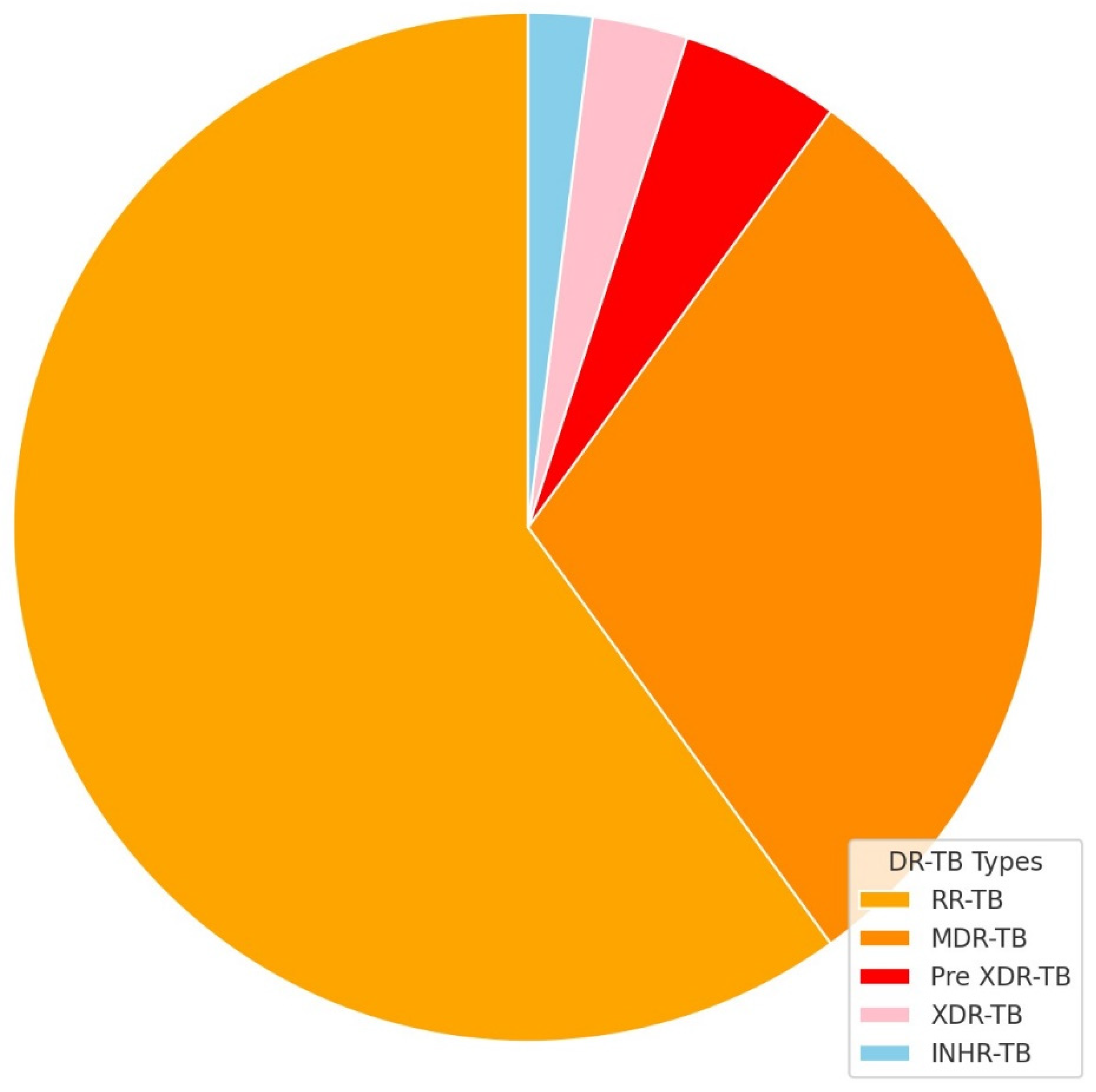
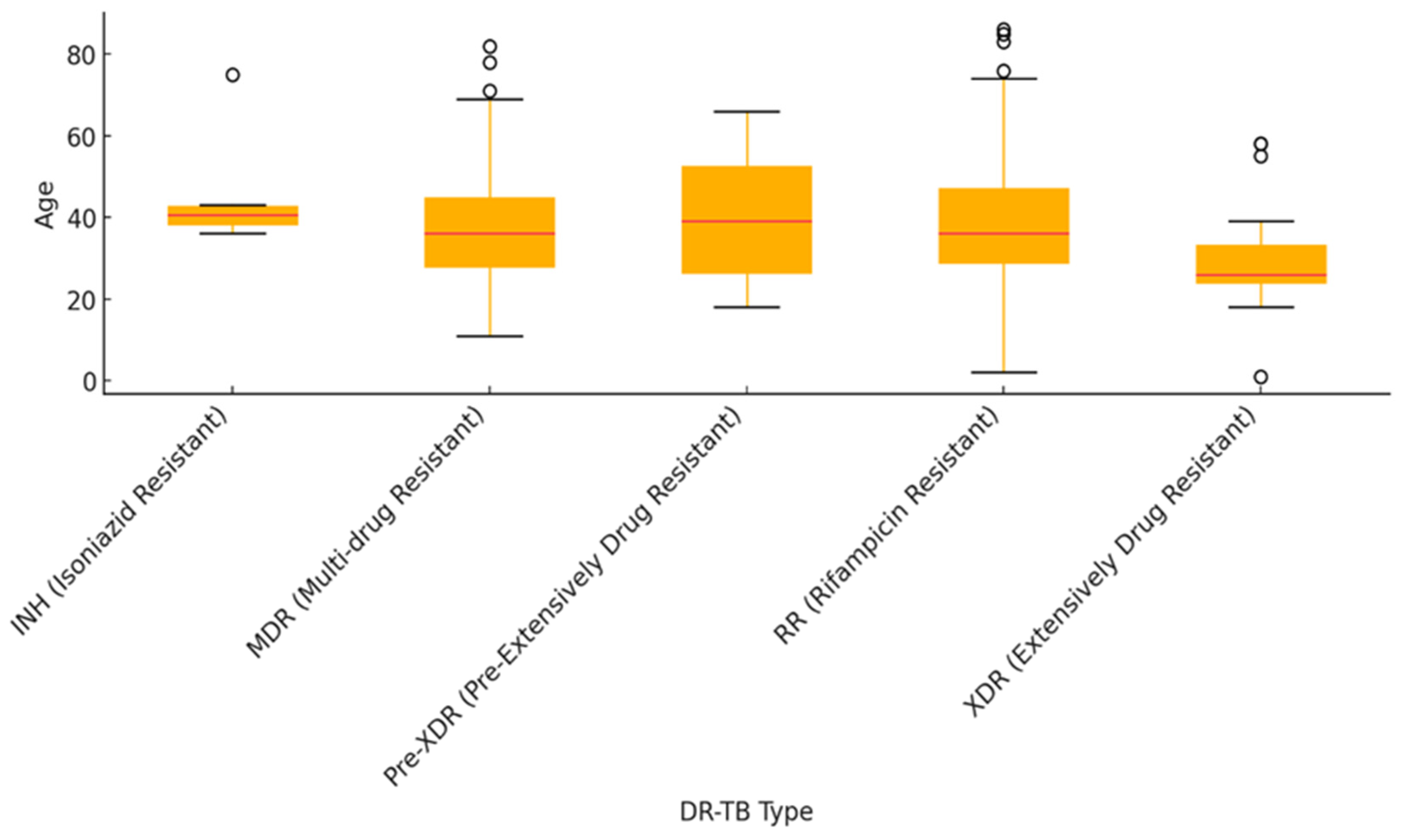
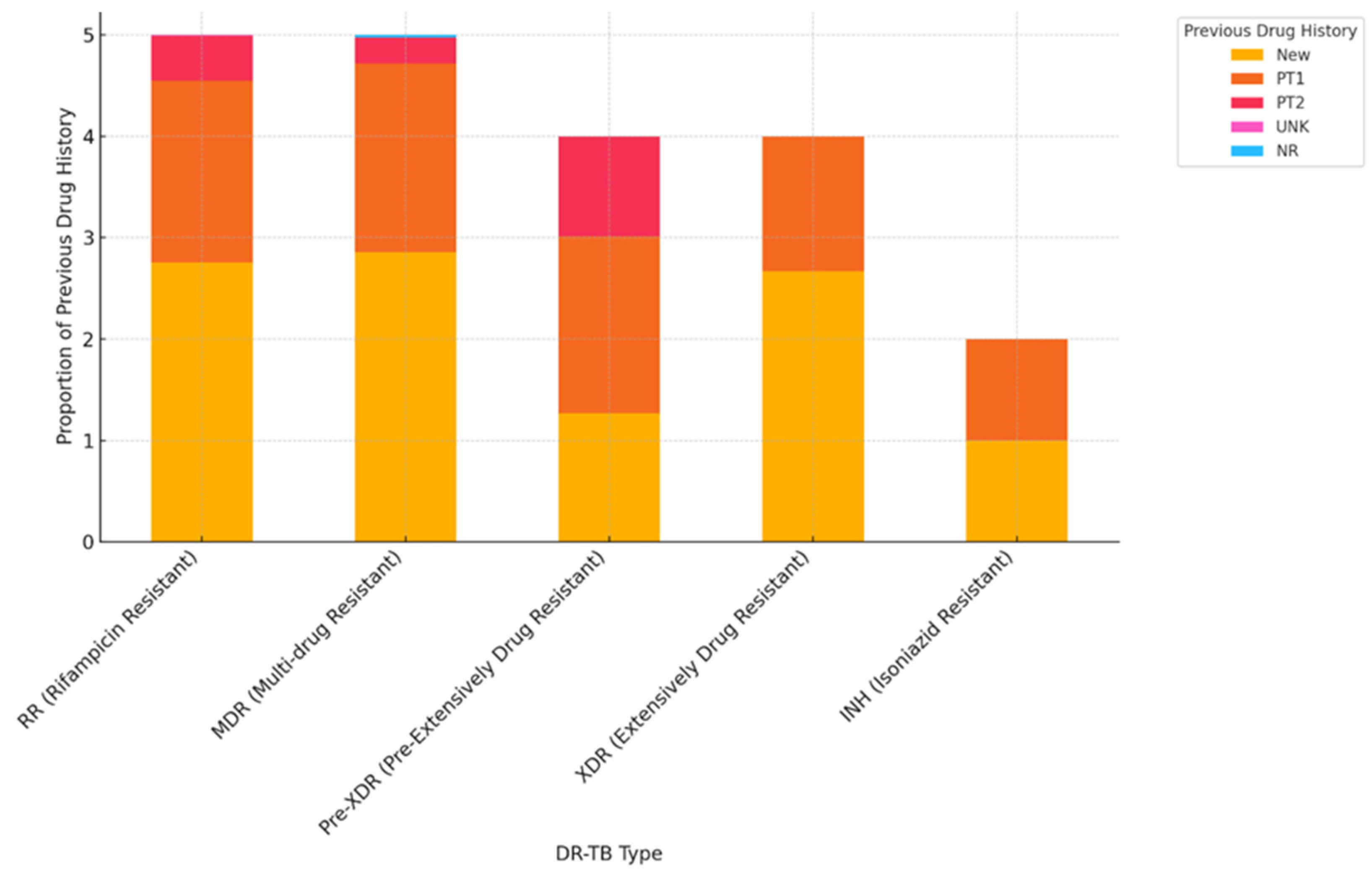
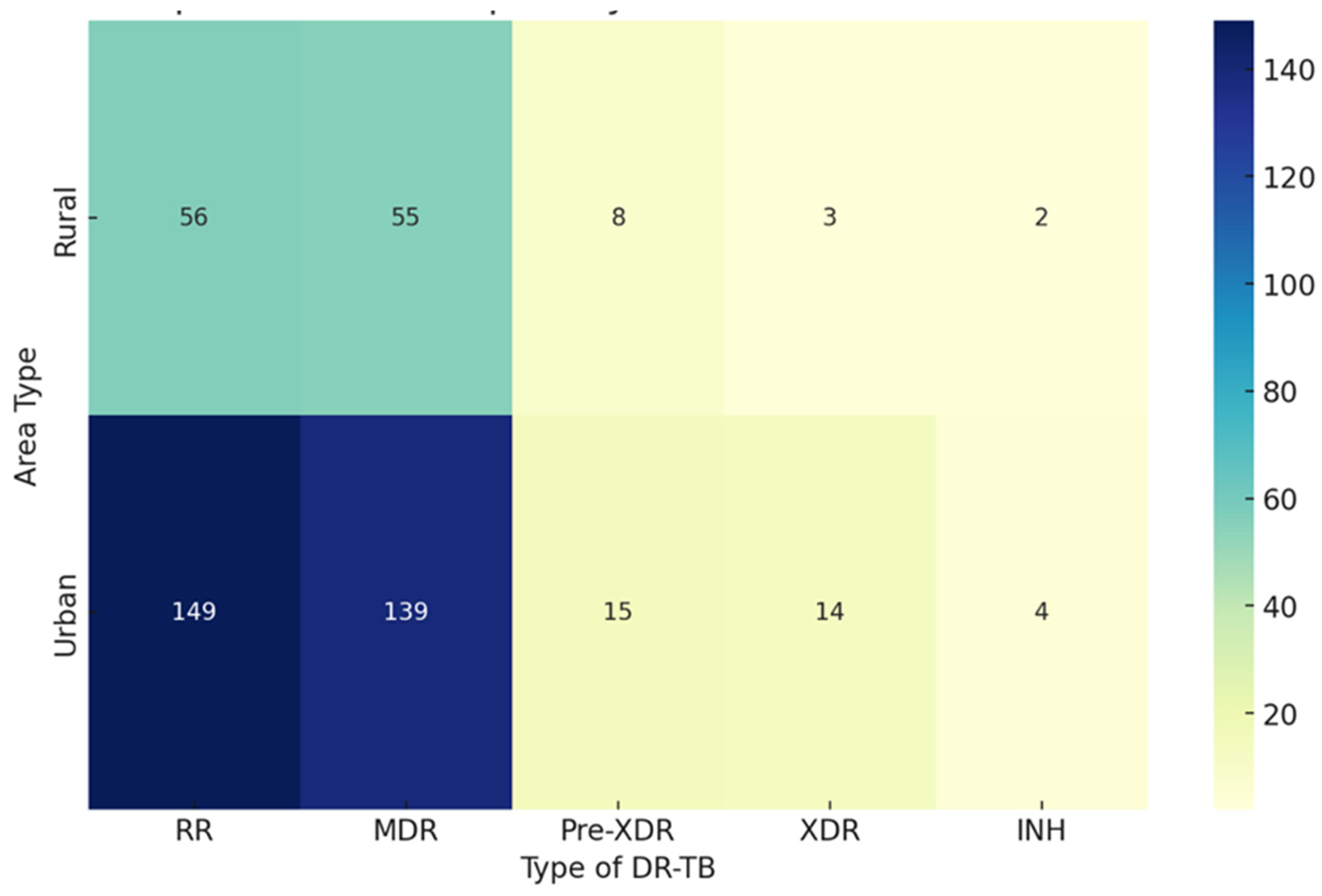
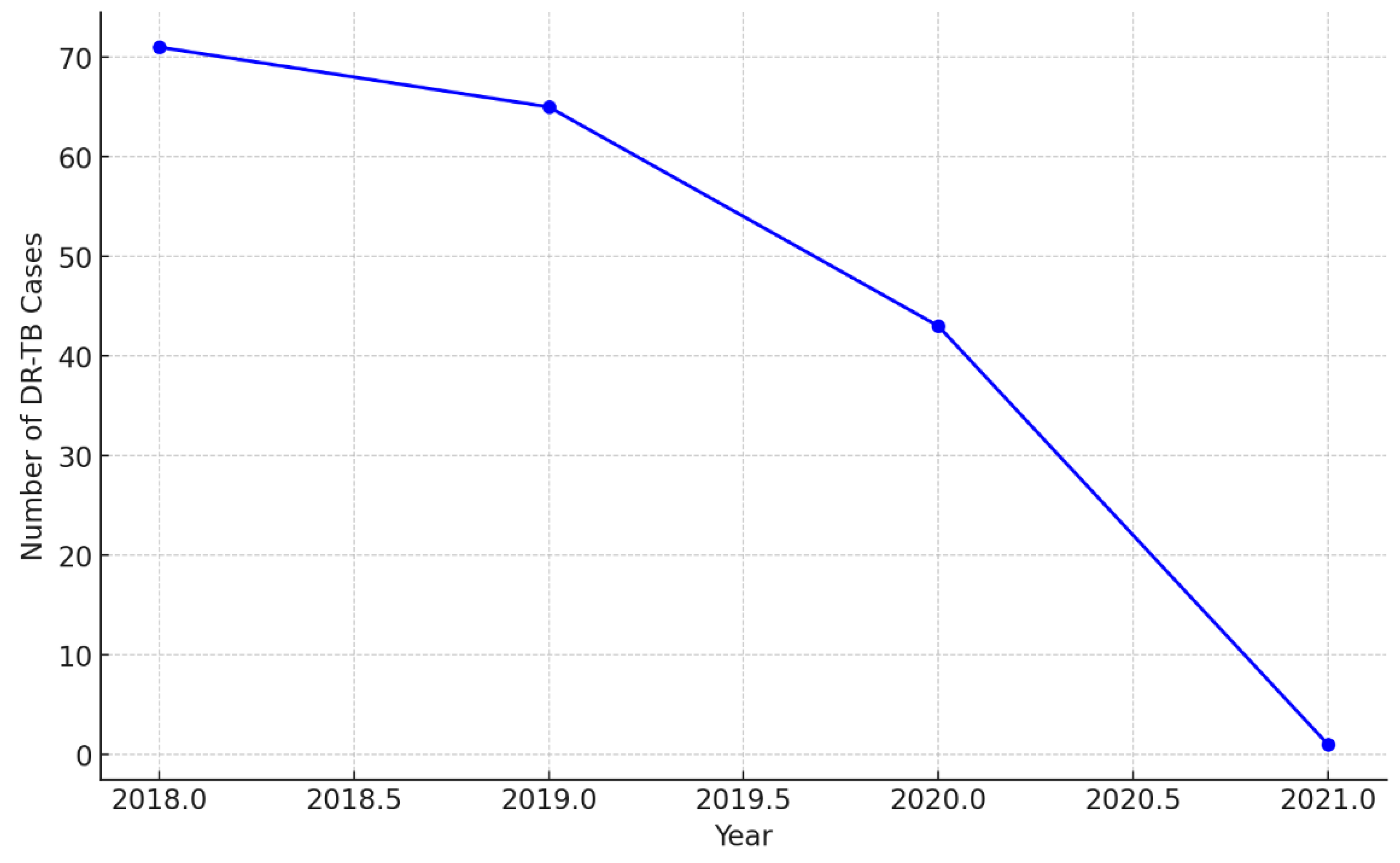
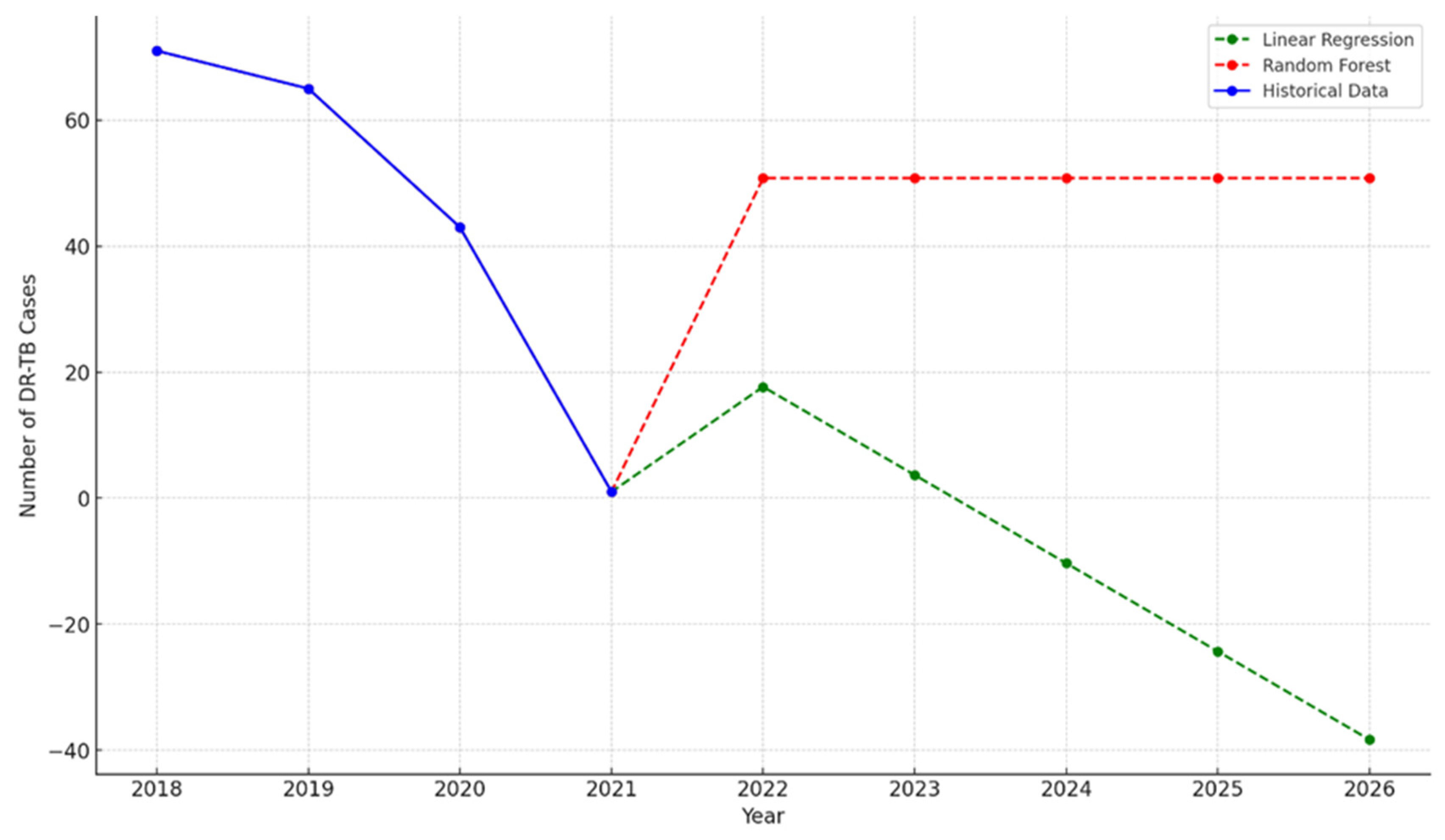
| Characteristics of Interest |
Enrolled DR-TB Patients (n=456) (%) |
O.R. Tambo population (n=1 514 306) % | Difference % | [95% CI] | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics |
|||||
|
Age (years) <20 20-49 50-59 >60 |
30.0 50.0 15.0 5.0 |
52.0 36.0 5.0 7.0 |
-22.0 14.0 10.0 -2.0 |
[-22.04; -21.96] [13.96; 14.04] [9.97; 10.03] [-2.02; -1.98] |
<0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001 0.0597 |
|
Gender Female |
44.04 |
53.3 |
-9.26 |
[-9.30; -9.21] |
0.000035 |
|
Level of education No Education Primary Education Secondary Education Tertiary Education |
19.78 22.92 47.87 9.21 |
10 30 50 10 |
+9.78 -7.08 -2.13 -0.79 |
[9.75%, 9.81%] [-7.12%, -7.04%] [-2.17%, -2.09%] [-0.82%, -0.76%] |
<0.0001 0.00033 0.3407 0.5488 |
|
Income category No Income Salary or Wages Casual UIF Disability Grant |
56.85 19.15 15.96 1.54 3.08 |
40 25 20 5 5 |
+16.85 -5.85 -4.04 -3.46 -1.92 |
[16.81%, 16.89%] [-5.89%, -5.81%] [-4.07%, -4.01%] [-3.48%, -3.44%] [-1.94%, -1.90%] |
<0.0001 0.0016 0.0187 0.00036 0.0292 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





