Submitted:
19 September 2024
Posted:
20 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Energy-Resolved Polarization Measurements of Prompt GRB Emission
3. New Precision Limits on LIV
4. Summary
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Samuel, S. Spontaneous breaking of Lorentz symmetry in string theory. Phys. Rev. D 1989, 39, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelino-Camelia, G.; Ellis, J.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Nanopoulos, D.V. Distance Measurement and Wave Dispersion in a Liouville-String Approach to Quantum Gravity. International Journal of Modern Physics A 1997, 12, 607–623. [arXiv:hep-th/hep-th/9605211]. [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Nanopoulos, D.V. Search for Quantum Gravity. General Relativity and Gravitation 1999, 31, 1257. [arXiv:gr-qc/gr-qc/9905048]. [CrossRef]
- Amelino-Camelia, G. Relativity: Special treatment. Nature 2002, 418, 34–35. [arXiv:gr-qc/gr-qc/0207049]. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magueijo, J.; Smolin, L. Lorentz Invariance with an Invariant Energy Scale. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 190403. [arXiv:hep-th/hep-th/0112090]. [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, J.; Morales-Técotl, H.A.; Urrutia, L.F. Loop quantum gravity and light propagation. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 65, 103509. [arXiv:hep-th/hep-th/0108061]. [CrossRef]
- Mattingly, D. Modern Tests of Lorentz Invariance. Living Reviews in Relativity 2005, 8, 5. [arXiv:gr-qc/gr-qc/0502097]. [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Nanopoulos, D.V.; Xie, D. Time delays of strings in D-particle backgrounds and vacuum refractive indices. Physics Letters B 2009, 679, 407–413. [arXiv:hep-th/0903.1303]. [CrossRef]
- Amelino-Camelia, G. Quantum-Spacetime Phenomenology. Living Reviews in Relativity 2013, 16, 5. [arXiv:gr-qc/0806.0339]. [CrossRef]
- Tasson, J.D. What do we know about Lorentz invariance? Reports on Progress in Physics 2014, 77, 062901. [arXiv:hep-ph/1403.7785]. [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.J.; Wu, X.F. Testing fundamental physics with astrophysical transients. Frontiers of Physics 2021, 16, 44300. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/2102.03724]. [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Ma, B.Q. Lorentz Symmetry Violation of Cosmic Photons. Universe 2022, 8, 323. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/2206.08180]. [CrossRef]
- Addazi, A.; Alvarez-Muniz, J.; Alves Batista, R.; Amelino-Camelia, G.; Antonelli, V.; Arzano, M.; Asorey, M.; Atteia, J.L.; Bahamonde, S.; Bajardi, F.; Ballesteros, A.; Baret, B.; Barreiros, D.M.; Basilakos, S.; Benisty, D.; Birnholtz, O.; Blanco-Pillado, J.J.; Blas, D.; Bolmont, J.; Boncioli, D.; Bosso, P.; Calcagni, G.; Capozziello, S.; Carmona, J.M.; Cerci, S.; Chernyakova, M.; Clesse, S.; Coelho, J.A.B.; Colak, S.M.; Cortes, J.L.; Das, S.; D’Esposito, V.; Demirci, M.; Di Luca, M.G.; di Matteo, A.; Dimitrijevic, D.; Djordjevic, G.; Prester, D.D.; Eichhorn, A.; Ellis, J.; Escamilla-Rivera, C.; Fabiano, G.; Franchino-Viñas, S.A.; Frassino, A.M.; Frattulillo, D.; Funk, S.; Fuster, A.; Gamboa, J.; Gent, A.; Gergely, L.Á.; Giammarchi, M.; Giesel, K.; Glicenstein, J.F.; Gracia-Bondía, J.; Gracia-Ruiz, R.; Gubitosi, G.; Guendelman, E.I.; Gutierrez-Sagredo, I.; Haegel, L.; Heefer, S.; Held, A.; Herranz, F.J.; Hinderer, T.; Illana, J.I.; Ioannisian, A.; Jetzer, P.; Joaquim, F.R.; Kampert, K.H.; Uysal, A.K.; Katori, T.; Kazarian, N.; Kerszberg, D.; Kowalski-Glikman, J.; Kuroyanagi, S.; Lämmerzahl, C.; Said, J.L.; Liberati, S.; Lim, E.; Lobo, I.P.; López-Moya, M.; Luciano, G.G.; Manganaro, M.; Marcianò, A.; Martín-Moruno, P.; Martinez, M.; Martinez, M.; Martínez-Huerta, H.; Martínez-Miravé, P.; Masip, M.; Mattingly, D.; Mavromatos, N.; Mazumdar, A.; Méndez, F.; Mercati, F.; Micanovic, S.; Mielczarek, J.; Miller, A.L.; Milosevic, M.; Minic, D.; Miramonti, L.; Mitsou, V.A.; Moniz, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Nardini, G.; Navas, S.; Niechciol, M.; Nielsen, A.B.; Obers, N.A.; Oikonomou, F.; Oriti, D.; Paganini, C.F.; Palomares-Ruiz, S.; Pasechnik, R.; Pasic, V.; Pérez de los Heros, C.; Pfeifer, C.; Pieroni, M.; Piran, T.; Platania, A.; Rastgoo, S.; Relancio, J.J.; Reyes, M.A.; Ricciardone, A.; Risse, M.; Frias, M.D.R.; Rosati, G.; Rubiera-Garcia, D.; Sahlmann, H.; Sakellariadou, M.; Salamida, F.; Saridakis, E.N.; Satunin, P.; Schiffer, M.; Schüssler, F.; Sigl, G.; Sitarek, J.; Peracaula, J.S.; Sopuerta, C.F.; Sotiriou, T.P.; Spurio, M.; Staicova, D.; Stergioulas, N.; Stoica, S.; Strišković, J.; Stuttard, T.; Cerci, D.S.; Tavakoli, Y.; Ternes, C.A.; Terzić, T.; Thiemann, T.; Tinyakov, P.; Torri, M.D.C.; Tórtola, M.; Trimarelli, C.; Trześniewski, T.; Tureanu, A.; Urban, F.R.; Vagenas, E.C.; Vernieri, D.; Vitagliano, V.; Wallet, J.C.; Zornoza, J.D. Quantum gravity phenomenology at the dawn of the multi-messenger era-A review. Progress in Particle and Nuclear Physics 2022, 125, 103948. [arXiv:hep-ph/2111.05659]. [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.J.;Wu, X.F., Tests of Lorentz Invariance. In Handbook of X-ray and Gamma-ray Astrophysics; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1–30. [CrossRef]
- Alves Batista, R.; Amelino-Camelia, G.; Boncioli, D.; Carmona, J.M.; di Matteo, A.; Gubitosi, G.; Lobo, I.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Pfeifer, C.; Rubiera-Garcia, D.; Saridakis, E.N.; Terzić, T.; Vagenas, E.C.; Vargas Moniz, P.; Abdalla, H.; Adamo, M.; Addazi, A.; Anagnostopoulos, F.K.; Antonelli, V.; Asorey, M.; Ballesteros, A.; Basilakos, S.; Benisty, D.; Boettcher, M.; Bolmont, J.; Bonilla, A.; Bosso, P.; Bouhmadi-López, M.; Burderi, L.; Campoy-Ordaz, A.; Caroff, S.; Cerci, S.; Cortes, J.L.; D’Esposito, V.; Das, S.; de Cesare, M.; Demirci, M.; Di Lodovico, F.; Di Salvo, T.; Diego, J.M.; Djordjevic, G.; Domi, A.; Ducobu, L.; Escamilla-Rivera, C.; Fabiano, G.; Fernández-Silvestre, D.; Franchino-Viñas, S.A.; Frassino, A.M.; Frattulillo, D.; Garay, L.J.; Gaug, M.; Gergely, L.Á.; Guendelman, E.I.; Guetta, D.; Gutierrez-Sagredo, I.; He, P.; Heefer, S.; Jurić, T.; Katori, T.; Kowalski-Glikman, J.; Lambiase, G.; Levi Said, J.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Luciano, G.G.; Ma, B.Q.; Marciano, A.; Martinez, M.; Mazumdar, A.; Menezes, G.; Mercati, F.; Minic, D.; Miramonti, L.; Mitsou, V.A.; Mustamin, M.F.; Navas, S.; Olmo, G.J.; Oriti, D.; Övgün, A.; Pantig, R.C.; Parvizi, A.; Pasechnik, R.; Pasic, V.; Petruzziello, L.; Platania, A.; Rasouli, S.M.M.; Rastgoo, S.; Relancio, J.J.; Rescic, F.; Reyes, M.A.; Rosati, G.; Sakallı, İ.; Salamida, F.; Sanna, A.; Staicova, D.; Strišković, J.; Sunar Cerci, D.; Torri, M.D.C.; Vigliano, A.; Wagner, F.; Wallet, J.C.; Wojnar, A.; Zarikas, V.; Zhu, J.; Zornoza, J.D. White Paper and Roadmap for Quantum Gravity Phenomenology in the Multi-Messenger Era. arXiv e-prints 2023, p. arXiv:2312.00409. [arXiv:gr-qc/2312.00409]. [CrossRef]
- Desai, S. Desai, S., Astrophysical and Cosmological Searches for Lorentz Invariance Violation. In Recent Progress on Gravity Tests: Challenges and Future Perspectives; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2024; pp. 433–463. [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Russell, N. Data tables for Lorentz and CPT violation. Reviews of Modern Physics 2011, 83, 11–32. [arXiv:hep-ph/0801.0287]. [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.C.; Pospelov, M. Ultraviolet Modifications of Dispersion Relations in Effective Field Theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 211601. [arXiv:hep-ph/hep-ph/0301124]. [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M.; Field, G.B.; Jackiw, R. Limits on a Lorentz- and parity-violating modification of electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 1990, 41, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colladay, D.; Kostelecký, V.A. Lorentz-violating extension of the standard model. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 58, 116002. [hep-ph/9809521]. [CrossRef]
- Gleiser, R.J.; Kozameh, C.N. Astrophysical limits on quantum gravity motivated birefringence. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 083007. [gr-qc/0102093]. [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Mewes, M. Cosmological Constraints on Lorentz Violation in Electrodynamics. Physical Review Letters 2001, 87, 251304. [hep-ph/0111026]. [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Mewes, M. Sensitive Polarimetric Search for Relativity Violations in Gamma-Ray Bursts. Physical Review Letters 2006, 97, 140401. [hep-ph/0607084]. [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Mewes, M. Lorentz-Violating Electrodynamics and the Cosmic Microwave Background. Physical Review Letters 2007, 99, 011601. [astro-ph/0702379]. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Mewes, M. Constraints on Relativity Violations from Gamma-Ray Bursts. Physical Review Letters 2013, 110, 201601. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1301.5367]. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrofanov, I.G. Astrophysics (communication arising): A constraint on canonical quantum gravity? Nature 2003, 426, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, T.; Liberati, S.; Mattingly, D.; Stecker, F.W. New Limits on Planck Scale Lorentz Violation in QED. Physical Review Letters 2004, 93, 021101. [astro-ph/0309681]. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.Z.; Wei, D.M.; Xu, D. γ-ray burst ultraviolet/optical afterglow polarimetry as a probe of quantum gravity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 376, 1857–1860. [astro-ph/0702006]. [CrossRef]
- Gubitosi, G.; Pagano, L.; Amelino-Camelia, G.; Melchiorri, A.; Cooray, A. A constraint on Planck-scale modifications to electrodynamics with CMB polarization data. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 8, 021. [arXiv:astro-ph.CO/0904.3201]. [CrossRef]
- Laurent, P.; Götz, D.; Binétruy, P.; Covino, S.; Fernandez-Soto, A. Constraints on Lorentz Invariance Violation using integral/IBIS observations of GRB041219A. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 121301. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1106.1068]. [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W. A new limit on Planck scale Lorentz violation from γ-ray burst polarization. Astroparticle Physics 2011, 35, 95–97. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1102.2784]. [CrossRef]
- Toma, K.; Mukohyama, S.; Yonetoku, D.; Murakami, T.; Gunji, S.; Mihara, T.; Morihara, Y.; Sakashita, T.; Takahashi, T.; Wakashima, Y.; Yonemochi, H.; Toukairin, N. Strict Limit on CPT Violation from Polarization of γ-Ray Bursts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 241104. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1208.5288]. [CrossRef]
- Götz, D.; Covino, S.; Fernández-Soto, A.; Laurent, P.; Bošnjak, Ž. The polarized gamma-ray burst GRB 061122. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, 3550–3556. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1303.4186]. [CrossRef]
- Götz, D.; Laurent, P.; Antier, S.; Covino, S.; D’Avanzo, P.; D’Elia, V.; Melandri, A. GRB 140206A: the most distant polarized gamma-ray burst. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 444, 2776–2782. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1408.4121]. [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.N.; Li, X.; Chang, Z. Gamma-ray burst polarization reduction induced by the Lorentz invariance violation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 463, 375–381. [arXiv:hep-ph/1609.00193]. [CrossRef]
- Kislat, F.; Krawczynski, H. Planck-scale constraints on anisotropic Lorentz and C P T invariance violations from optical polarization measurements. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 083013. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1701.00437]. [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.S.; Leon, D.; Crowley, K.D.; Johnson, D.; Teply, G.; Tytler, D.; Keating, B.G.; Cole, G.M. Constraints on Lorentz invariance and C P T violation using optical photometry and polarimetry of active galaxies BL Lacertae and S5 B 0716 +714. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 035045. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1809.08356]. [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.J. New constraints on Lorentz invariance violation with polarized gamma-ray bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 485, 2401–2406. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1905.03413]. [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.S.; Gerasimov, R.; Leon, D.; Stevens, W.; Tytler, D.; Keating, B.G.; Kislat, F. Improved constraints on anisotropic birefringent Lorentz invariance and C P T violation from broadband optical polarimetry of high redshift galaxies. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 043008. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/2003.00647]. [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.J.; Wu, X.F. Testing the weak equivalence principle and Lorentz invariance with multiwavelength polarization observations of GRB optical afterglows. European Physical Journal Plus 2020, 135, 527. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/2006.11528]. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Q.; Yi, S.X.; Wei, J.J.; Wu, X.F. Constraints on Lorentz Invariance Violation with Multiwavelength Polarized Astrophysical Sources. Galaxies 2021, 9, 44. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/2106.05733]. [CrossRef]
- Planck Collaboration. ; others. Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6. [arXiv:astro-ph.CO/1807.06209]. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Pandey, S.B.; Gupta, S.; Chattopadhayay, T.; Bhattacharya, D.; Bhalerao, V.; Castro-Tirado, A.J.; Valeev, A.; Ror, A.K.; Sharma, V.; Racusin, J.; Aryan, A.; Iyyani, S.; Vadawale, S. A Detailed Time-resolved and Energy-resolved Spectro-polarimetric Study of Bright Gamma-Ray Bursts Detected by AstroSat CZTI in Its First Year of Operation. Astrophys. J. 2024, 972, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesani, D.; de Ugarte Postigo, A.; de Pasquale, M.; Kann, D.A.; Cano, Z.; Perley, D.A.; Izzo, L.; Thoene, C.C.; Butler, N.; Watson, A.M.; Kutyrev, A.; Lee, W.H.; Richer, M.G.; Fox, O.; Prochaska, J.X.; Bloom, J.S.; Cucchiara, A.; Troja, E.; Littlejohns, O.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; de Diego, J.A.; Georgiev, L.; Gonzalez, J.; Roman-Zuniga, C.; Gehrels, N.; Moseley, H.; Capone, J.; Golkhou, V.Z.; Toy, V. GRB 160623A: optical astrometry, photometry, and redshift. GRB Coordinates Network 2016, 19708, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yonetoku, D.; Murakami, T.; Nakamura, T.; Yamazaki, R.; Inoue, A.K.; Ioka, K. Gamma-Ray Burst Formation Rate Inferred from the Spectral Peak Energy-Peak Luminosity Relation. Astrophys. J. 2004, 609, 935–951. [arXiv:astro-ph/astro-ph/0309217]. [CrossRef]
- Nava, L.; Salvaterra, R.; Ghirlanda, G.; Ghisellini, G.; Campana, S.; Covino, S.; Cusumano, G.; D’Avanzo, P.; D’Elia, V.; Fugazza, D.; Melandri, A.; Sbarufatti, B.; Vergani, S.D.; Tagliaferri, G. A complete sample of bright Swift long gamma-ray bursts: testing the spectral-energy correlations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 421, 1256–1264. [arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1112.4470]. [CrossRef]
- Foreman-Mackey, D.; Hogg, D.W.; Lang, D.; Goodman, J. emcee: The MCMC Hammer. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2013, 125, 306. [arXiv:astro-ph.IM/1202.3665]. [CrossRef]
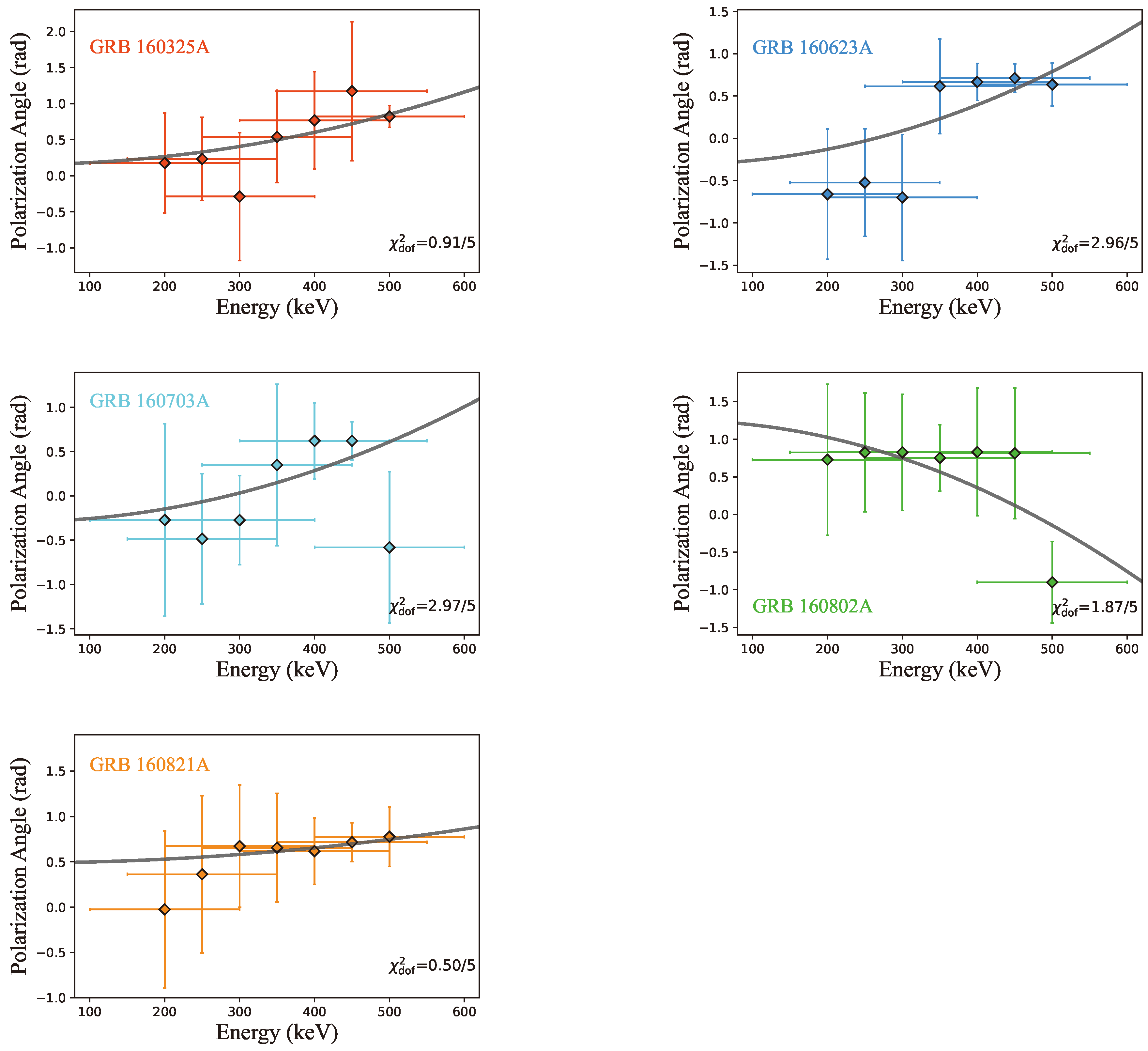
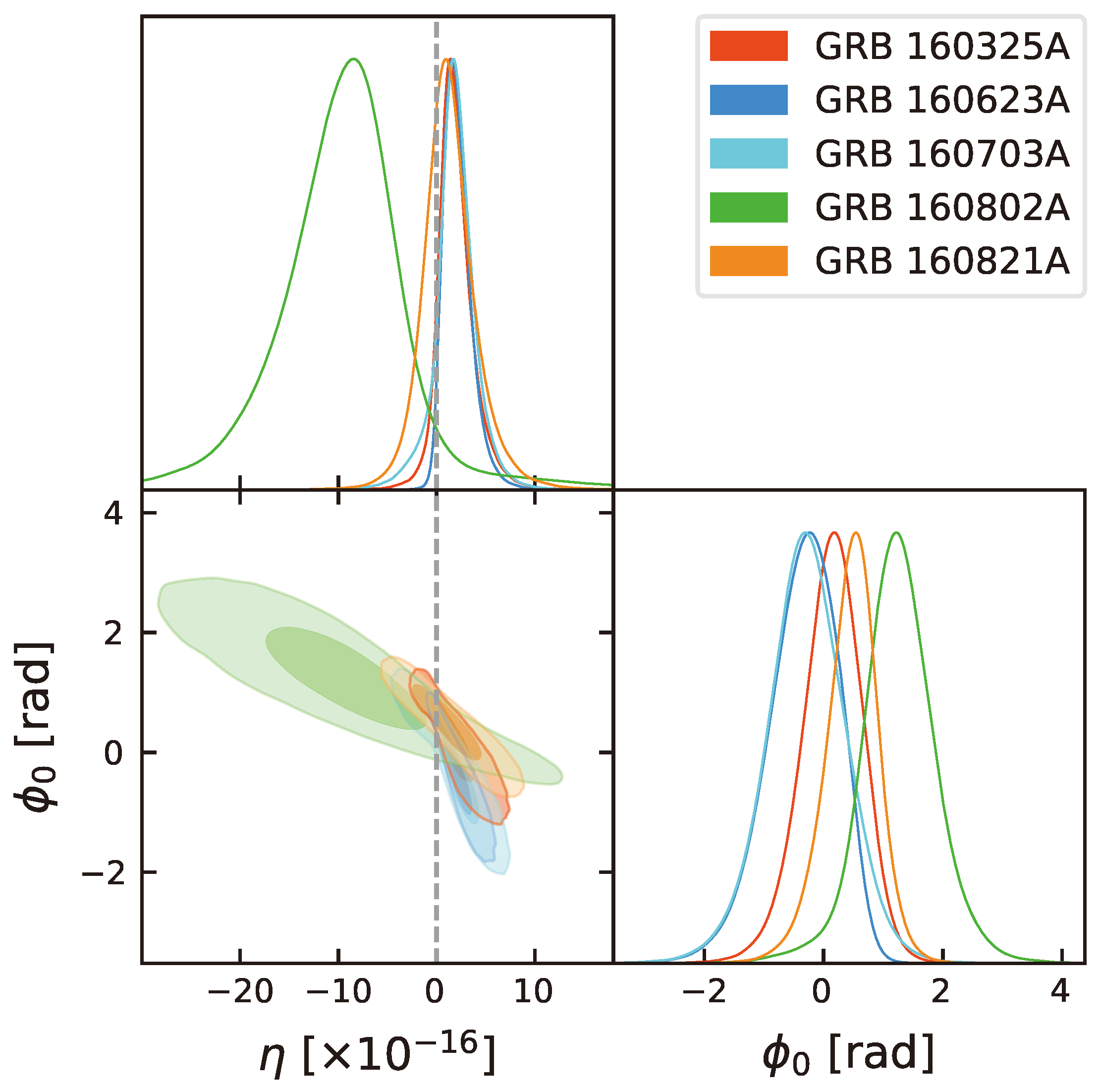
| Source | z | ||
| GRB 160325A | 0.2671 | ||
| GRB 160623A | 0.367 | ||
| GRB 160703A | 0.3161 | ||
| GRB 160802A | 0.1021 | ||
| GRB 160821A | 0.1531 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





