Submitted:
19 September 2024
Posted:
23 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
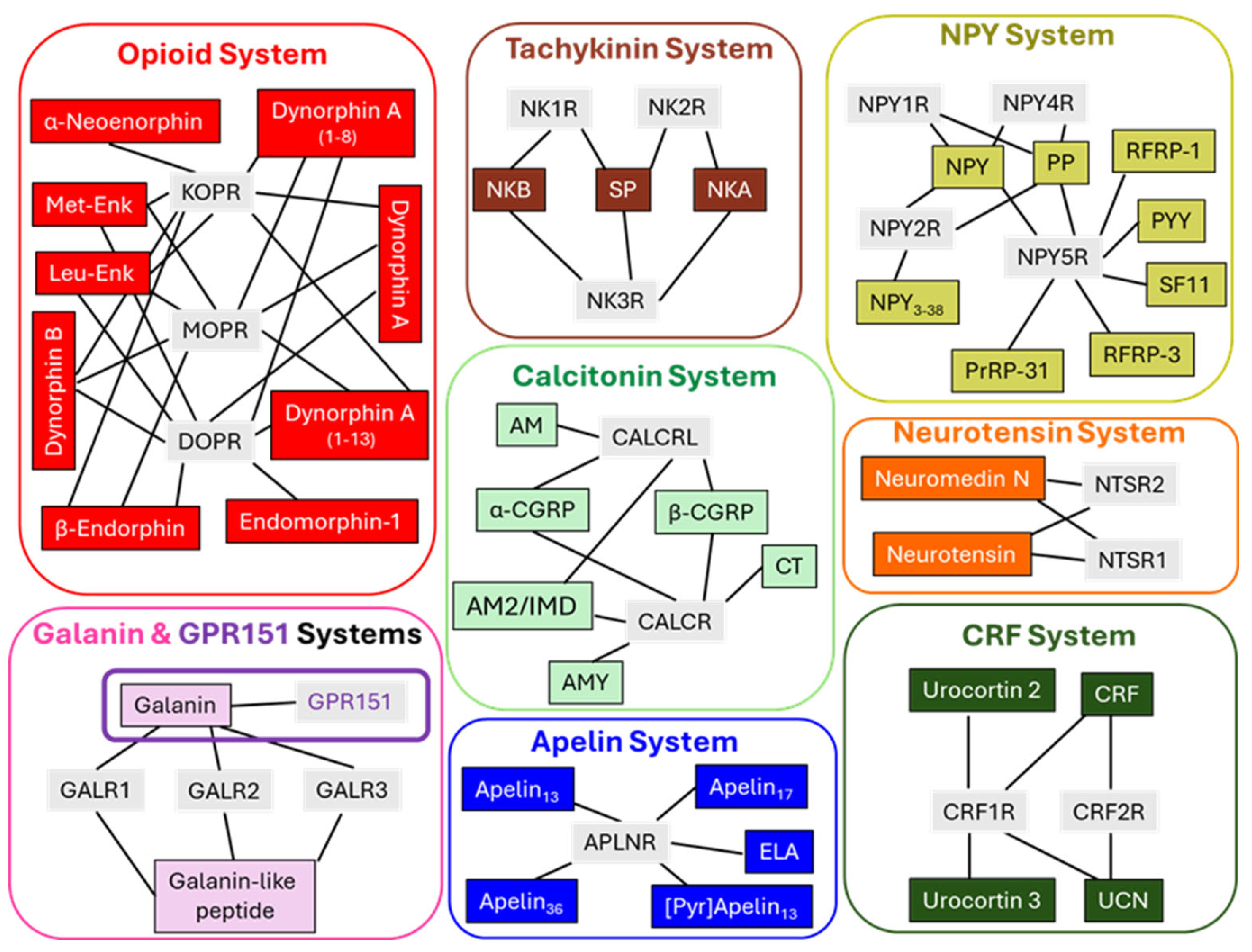
2. GPCR Peptides and Their Receptors
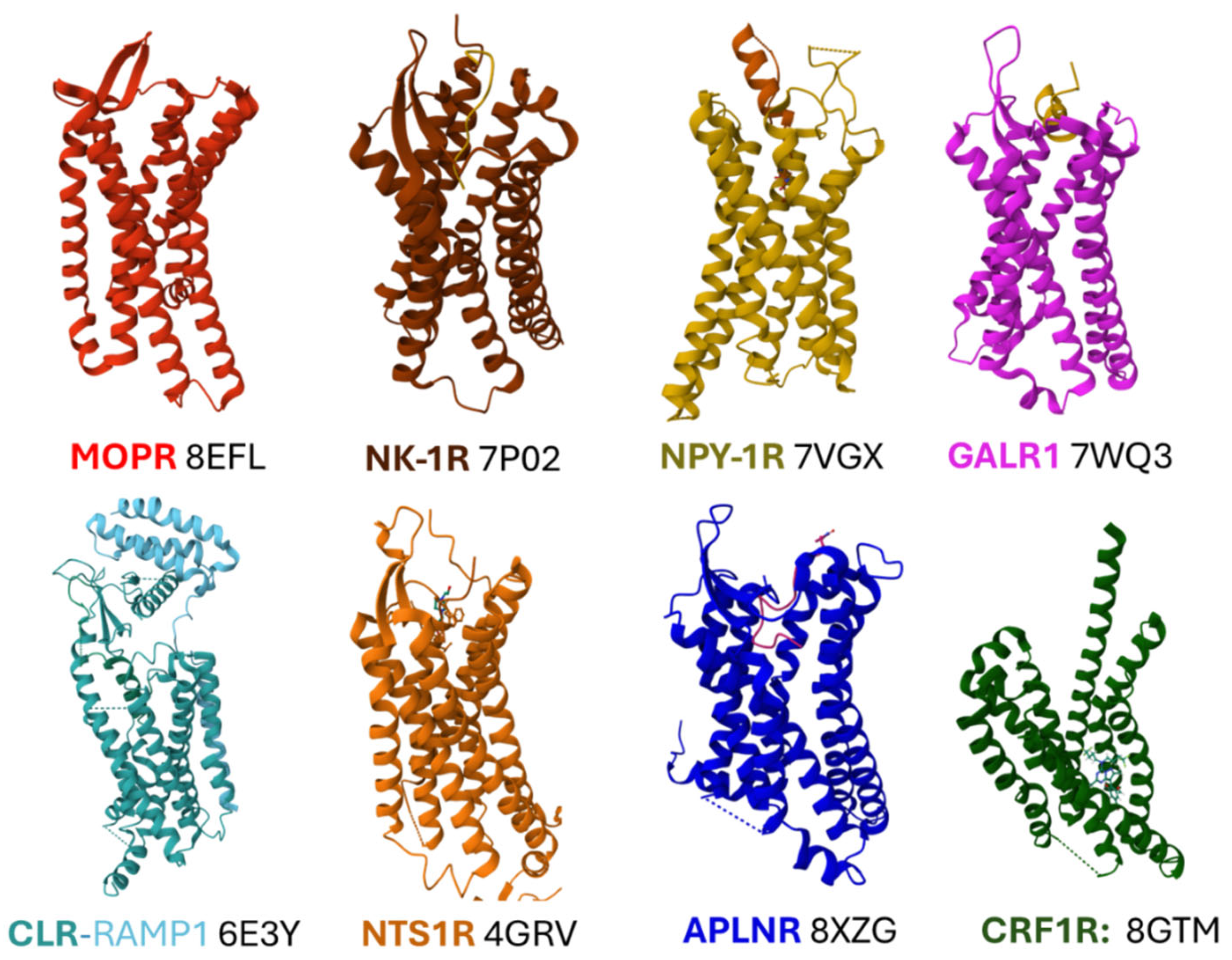
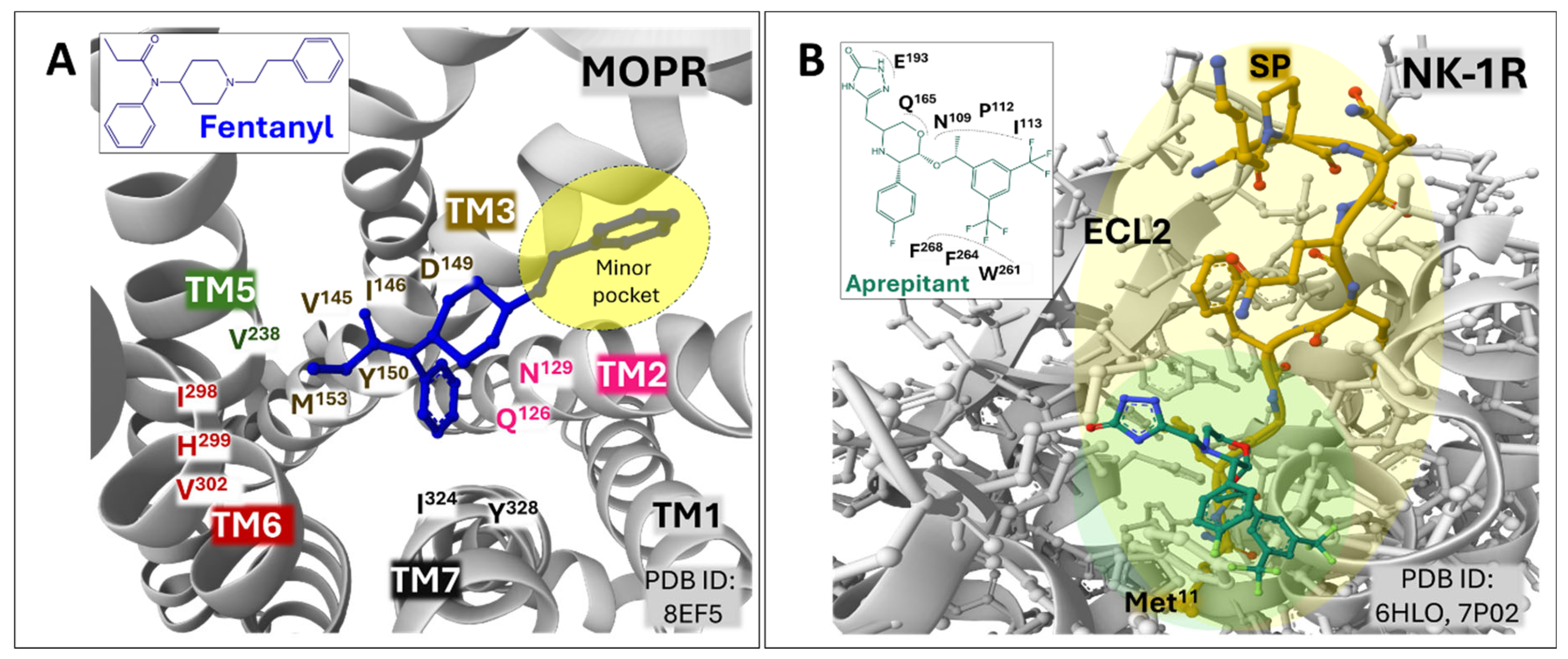
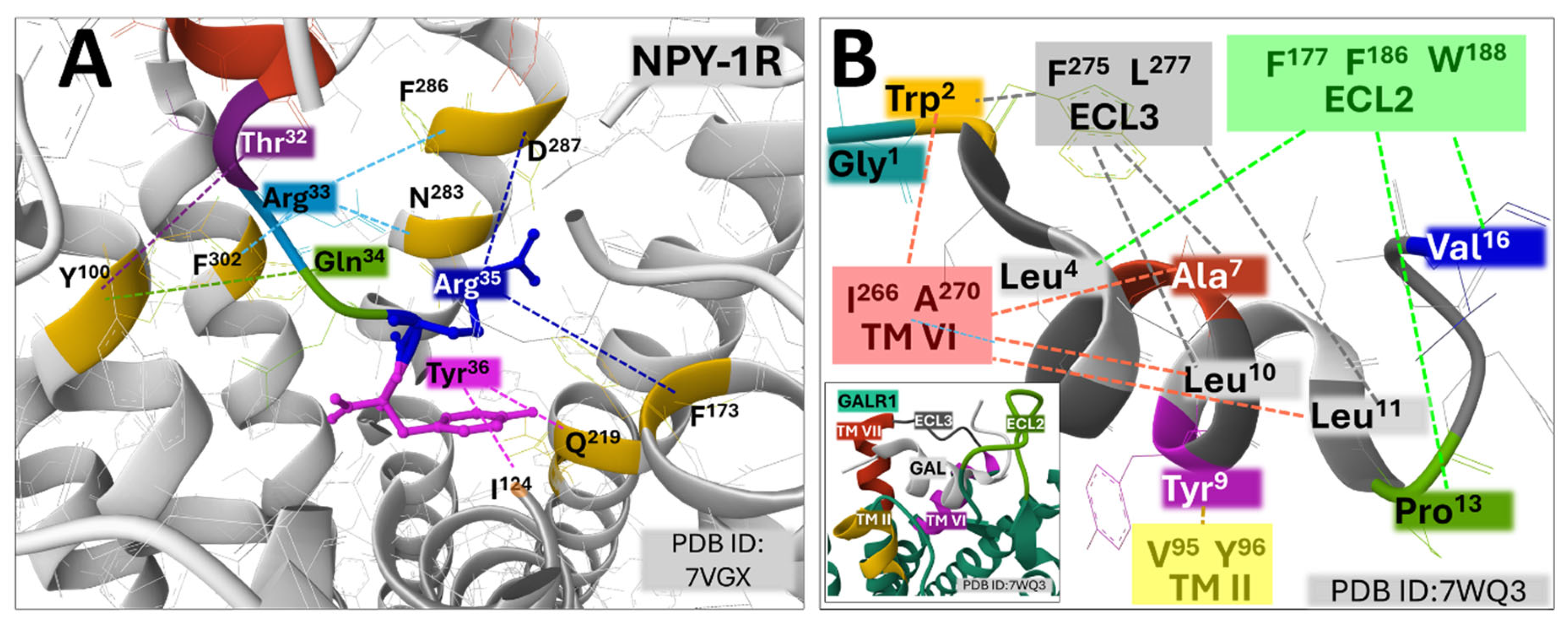
3. Peptidergic GPCR Structural Features
4. Peptidergic GPCR Signaling Circuitries and Cancer
4.1. The Opioid System
4.2. The Neurokinin System
4.3. The NPY System
4.4. The Galanin System
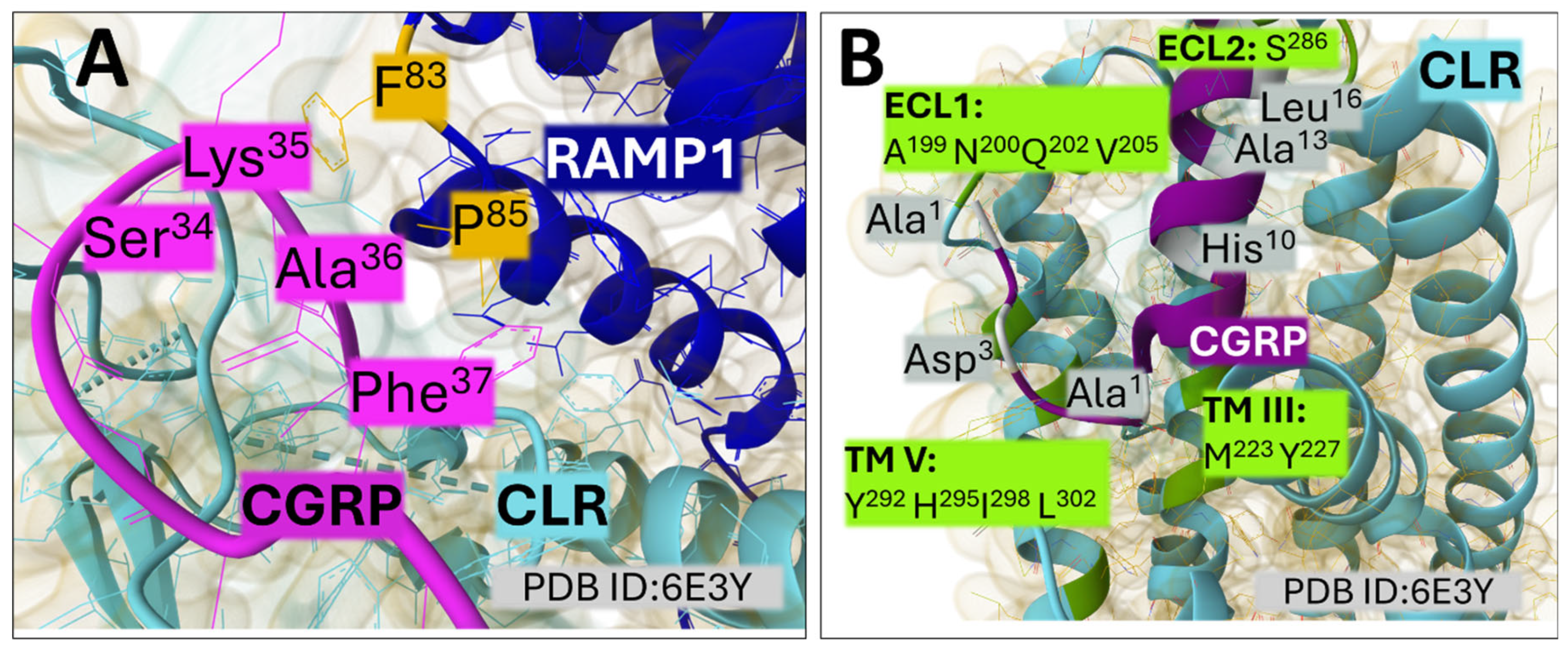
4.5. The Calcitonin System
4.6. The Neurotensin System
4.7. The Apelin System
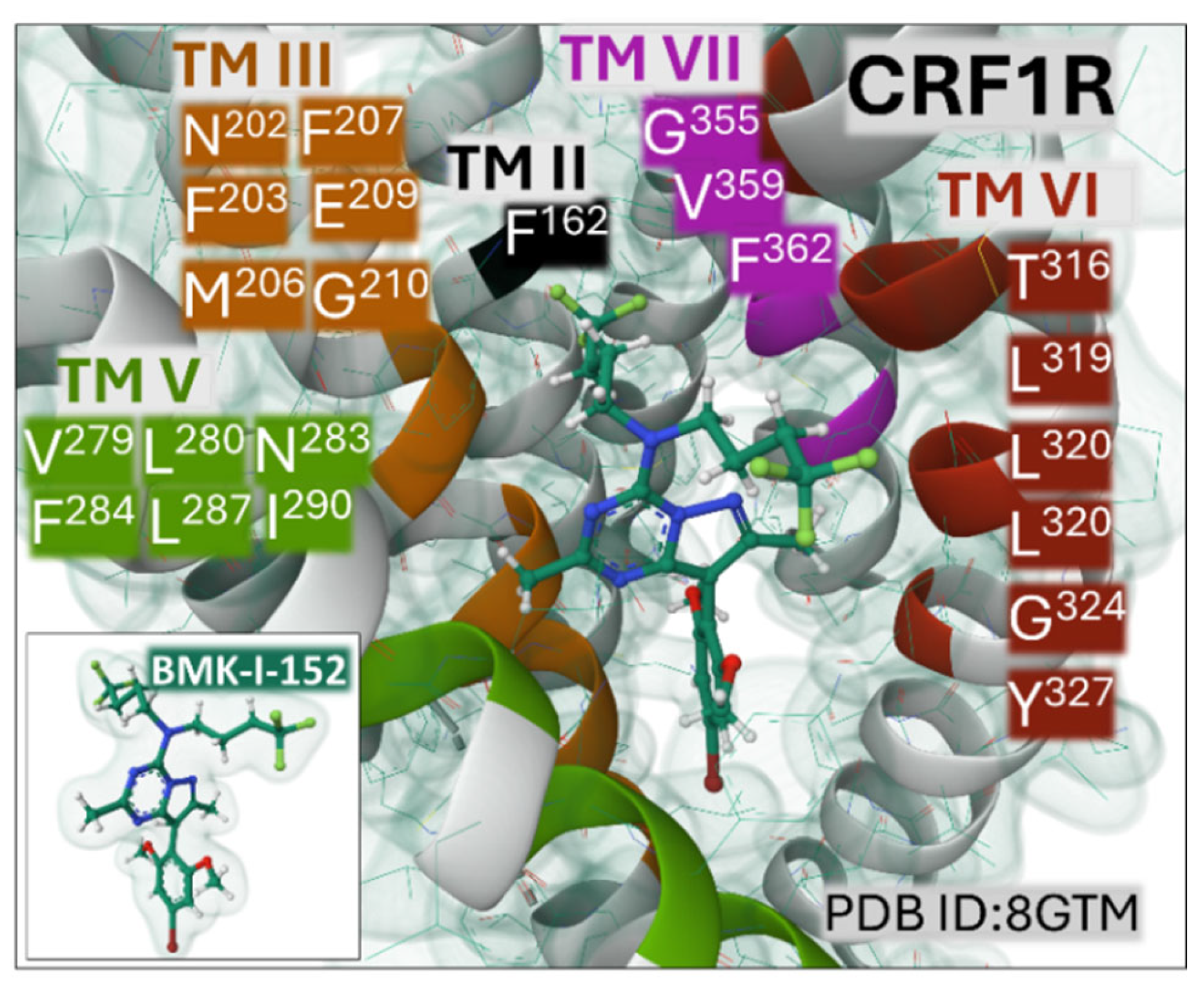
4.8. The CRF System
5. Peptidergic GPCRs as Targets for Cancer Treatment
6. Conclusion and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Golemis, E.A.; Scheet, P.; Beck, T.N.; Scolnick, E.M.; Hunter, D.J.; Hawk, E.; Hopkins, N. Molecular mechanisms of the preventable causes of cancer in the United States. Genes Dev 2018, 32, 868–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahida, A.; Buschhorn, L.; Fröhling, S.; Jost, P.J.; Schneeweiss, A.; Lichter, P.; Kurzrock, R. The coming decade in precision oncology: six riddles. Nat Rev Cancer 2023, 23, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.C.; Zaki, T.A. Changing epidemiology of colorectal cancer - birth cohort effects and emerging risk factors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2024, 21, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeagu, E.I.; Obeagu, G.U. Breast cancer: A review of risk factors and diagnosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2024, 103, e36905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, P.; Mininni, M.; Deiana, G.; Marino, G.; Divella, R.; Bochicchio, I.; Giuliano, A.; Lapadula, S.; Lettini, A.R.; Sanseverino, F. Healthy Lifestyle and Cancer Risk: Modifiable Risk Factors to Prevent Cancer. Nutrients 2024, 16, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montégut, L.; López-Otín, C.; Kroemer, G. Aging and cancer. Mol Cancer 2024, 23, 106–z. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.K.; Kim, S. An Insight into GPCR and G-Proteins as Cancer Drivers. Cells 2021, 10, 3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pándy-Szekeres, G.; Munk, C.; Tsonkov, T.M.; Mordalski, S.; Harpsøe, K.; Hauser, A.S.; Bojarski, A.J.; Gloriam, D.E. GPCRdb in 2018: adding GPCR structure models and ligands. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, D440–D446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Song, G.; de Graaf, C.; Stevens, R.C. Structure and Function of Peptide-Binding G Protein-Coupled Receptors. J Mol Biol 2017, 429, 2726–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeze, W.K.; Sassano, M.F.; Huang, X.; Lansu, K.; McCorvy, J.D.; Giguère, P.M.; Sciaky, N.; Roth, B.L. PRESTO-Tango as an open-source resource for interrogation of the druggable human GPCRome. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2015, 22, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Chiu, Y.; Pickett, J.E.; Roth, B.L. Illuminating the understudied GPCR-ome. Drug Discov Today 2024, 29, 103848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, T.; Lu, X.; Lan, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S. G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): advances in structures, mechanisms, and drug discovery. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2024, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, D.; Stevens, R.C.; Roth, B.L. How Ligands Illuminate GPCR Molecular Pharmacology. Cell 2017, 170, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.R.; Hauser, A.S.; Vedel, L.; Strachan, R.T.; Huang, X.; Gavin, A.C.; Shah, S.D.; Nayak, A.P.; Haugaard-Kedström, L.M.; Penn, R.B.; Roth, B.L.; Bräuner-Osborne, H.; Gloriam, D.E. Discovery of Human Signaling Systems: Pairing Peptides to G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Cell 2019, 179, 895–908.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beets, I.; Zels, S.; Vandewyer, E.; Demeulemeester, J.; Caers, J.; Baytemur, E.; Courtney, A.; Golinelli, L. ; Hasakioğulları, İ; Schafer, W.R.; Vértes, P.E.; Mirabeau, O.; Schoofs, L. System-wide mapping of peptide-GPCR interactions in C. elegans. Cell Rep 2023, 42, 113058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.D.; Covenas, R. Association of Neurokinin-1 Receptor Signaling Pathways with Cancer. Curr Med Chem 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jékely, G.; Melzer, S.; Beets, I.; Kadow, I.C.G.; Koene, J.; Haddad, S.; Holden-Dye, L. The long and the short of it - a perspective on peptidergic regulation of circuits and behaviour. J Exp Biol 2018, 221, jeb166710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, A.P.; Scully, C.C.G.; de Graaf, C.; Brown, A.J.H.; Maguire, J.J. Advances in therapeutic peptides targeting G protein-coupled receptors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2020, 19, 389–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrimian, A.; Kraft, T.; Pan, Y. Endogenous Opioid Peptides and Alternatively Spliced Mu Opioid Receptor Seven Transmembrane Carboxyl-Terminal Variants. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; DiBerto, J.F.; Zhou, X.E.; Schmitz, G.P.; Yuan, Q.; Jain, M.K.; Liu, W.; Melcher, K.; Jiang, Y.; Roth, B.L.; Xu, H.E. Structures of the entire human opioid receptor family. Cell 2023, 186, 413–427.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, R.J. Endogenous opiates and behavior: 2023. Peptides 2024, 179, 171268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennefather, J.N.; Lecci, A.; Candenas, M.L.; Patak, E.; Pinto, F.M.; Maggi, C.A. Tachykinins and tachykinin receptors: a growing family. Life Sci 2004, 74, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, H.; Kawada, T. Overview of the primary structure, tissue-distribution, and functions of tachykinins and their receptors. Curr Drug Targets 2006, 7, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff, M.S.; von Mentzer, B.; Geppetti, P.; Pothoulakis, C.; Bunnett, N.W. Tachykinins and their receptors: contributions to physiological control and the mechanisms of disease. Physiol Rev 2014, 94, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P.; Reichmann, F.; Farzi, A. Neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide in the gut-brain axis. Neuropeptides 2012, 46, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, Y.; Bastianetto, S.; Duranton, A.; Breton, L.; Quirion, R. Immunohistochemical distribution of neuropeptide Y, peptide YY, pancreatic polypeptide-like immunoreactivity and their receptors in the epidermal skin of healthy women. Peptides 2015, 70, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, R.; Doshi, G. Cross talk about the role of Neuropeptide Y in CNS disorders and diseases. Neuropeptides 2023, 102, 102388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.K.; Bartfai, T.; Langel, U. Galanin/GALP receptors and CNS homeostatic processes. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2006, 5, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.; Gundlach, A.L.; Holmes, F.E.; Hobson, S.A.; Wynick, D.; Hökfelt, T.; Kofler, B. Physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of galanin peptides and receptors: three decades of emerging diversity. Pharmacol Rev 2015, 67, 118–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, M.; Całka, J. Review: Occurrence and Distribution of Galanin in the Physiological and Inflammatory States in the Mammalian Gastrointestinal Tract. Front Immunol 2021, 11, 602070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatov, A.; Hermans-Borgmeyer, I.; Schaller, H.C. Cloning and characterization of a novel G-protein-coupled receptor with homology to galanin receptors. Neuropharmacology 2004, 46, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielczyk-Maczynska, E.; Zhao, M.; Zushin, P.H.; Schnurr, T.M.; Kim, H.; Li, J.; Nallagatla, P.; Sangwung, P.; Park, C.Y.; Cornn, C.; Stahl, A.; Svensson, K.J.; Knowles, J.W. G protein-coupled receptor 151 regulates glucose metabolism and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 7408–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Galtes, D.; Wang, J.; Rockman, H.A. G protein-coupled receptor signaling: transducers and effectors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2022, 323, C731–C748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, F.E.; Kerr, N.; Chen, Y.; Vanderplank, P.; McArdle, C.A.; Wynick, D. Targeted disruption of the orphan receptor Gpr151 does not alter pain-related behaviour despite a strong induction in dorsal root ganglion expression in a model of neuropathic pain. Mol Cell Neurosci 2017, 78, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwell, J.; Gingell, J.J.; Watkins, H.A.; Archbold, J.K.; Poyner, D.R.; Hay, D.L. Calcitonin and calcitonin receptor-like receptors: common themes with family B GPCRs? Br J Pharmacol 2012, 166, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pioszak, A.A.; Hay, D.L. RAMPs as allosteric modulators of the calcitonin and calcitonin-like class B G protein-coupled receptors. Adv Pharmacol 2020, 88, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amara, S.G.; Jonas, V.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Ong, E.S.; Evans, R.M. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature 1982, 298, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimalawansa, S.J. Amylin, calcitonin gene-related peptide, calcitonin, and adrenomedullin: a peptide superfamily. Crit Rev Neurobiol 1997, 11, 167–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, T.; Kitamura, K. Translational studies of adrenomedullin and related peptides regarding cardiovascular diseases. Hypertens Res 2022, 45, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.F.; Hay, D.L. CGRP physiology, pharmacology, and therapeutic targets: migraine and beyond. Physiol Rev 2023, 103, 1565–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, S.; Basili, S.; Cangemi, R.; Yuste, J.R.; Lucena, F.; Romiti, G.F.; Raparelli, V.; Argemi, J.; D'Avanzo, G.; Locorriere, L.; Masini, F.; Calarco, R.; Testorio, G.; Spiezia, S.; Ciccozzi, M.; Angeletti, S. A Focus on the Pathophysiology of Adrenomedullin Expression: Endothelitis and Organ Damage in Severe Viral and Bacterial Infections. Cells 2024, 13, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.P.; Mazella, J.; Kitabgi, P. Neurotensin, and neurotensin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1999, 20, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gereau, G.B.; Garrison, S.D.; McElligott, Z.A. Neurotensin and energy balance. J Neurochem 2023, 166, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torruella-Suárez, M.L.; McElligott, Z.A. Neurotensin in reward processes. Neuropharmacology 2020, 167, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, F.D.; Sanchez, M.L.; Covenas, R. Neurotensin, and Alcohol Use Disorders: Towards a Pharmacological Treatment. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriatzis, G.; Khrestchatisky, M.; Ferhat, L.; Chatzaki, E.A. Neurotensin and Neurotensin Receptors in Stress-related Disorders: Pathophysiology & Novel Drug Targets. Curr Neuropharmacol 2024, 22, 916–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, M.N.; Stoyanov, D.S.; Pavlov, S.P.; Tonchev, A.B. Distribution, Function, and Expression of the Apelinergic System in the Healthy and Diseased Mammalian Brain. Genes (Basel) 2022, 13, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, C.; Nyimanu, D.; Williams, T.L.; Huggins, D.J.; Sulentic, P.; Macrae, R.G.C.; Yang, P.; Glen, R.C.; Maguire, J.J.; Davenport, A.P. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CVII. Structure and Pharmacology of the Apelin Receptor with a Recommendation that Elabela/Toddler Is a Second Endogenous Peptide Ligand. Pharmacol Rev 2019, 71, 467–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Prabhavalkar, K.S.; Bhatt, L.K. Elabela Peptide: An Emerging Target in Therapeutics. Curr Drug Targets 2022, 23, 1304–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagamajalu, S.; Rex, D.A.B.; Suchitha, G.P.; Rai, A.B.; Rainey, J.K.; Prasad, T.S.K. The network map of Elabela signaling pathway in physiological and pathological conditions. J Cell Commun Signal 2022, 16, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ji, S. Apelin/APJ system in inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol 2022, 109, 108822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, T.; Kageyama, K.; Sakihara, S.; Nigawara, T. Physiological roles of urocortins, human homologs of fish urotensin I, and their receptors. Peptides 2004, 25, 1689–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K. Distribution of urocortins and corticotropin-releasing factor receptors in the cardiovascular system. Int J Endocrinol 2012, 2012, 395284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrousos, G.P.; Zoumakis, E. Milestones in CRH Research. Curr Mol Pharmacol 2017, 10, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, I.; von Hafe, M.; Adão, R.; Leite-Moreira, A.; Brás-Silva, C. Corticotropin-releasing hormone and obesity: From fetal life to adulthood. Obes Rev 2024, 25, e13763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ji, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Cai, C.; Hu, R.; Zang, S.; Miao, L.; Xu, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, Z.; Guo, J.; Qin, J.; Shen, D.; Liang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Structure-based design of non-hypertrophic apelin receptor modulator. Cell 2024, 187, 1460–1475.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöppe, J.; Ehrenmann, J.; Klenk, C.; Rucktooa, P.; Schütz, M.; Doré, A.S.; Plückthun, A. Crystal structures of the human neurokinin one receptor in complex with clinically used antagonists. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 17–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, C.; Ehrenmann, J.; Vacca, S.; Waltenspühl, Y.; Schöppe, J.; Medalia, O.; Plückthun, A. Structures of neurokinin one receptor in complex with G(q) and G(s) proteins reveal substance P binding mode and unique activation features. Sci Adv 2021, 7, eabk2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Basith, S.; Choi, S. Recent Advances in Structure-Based Drug Design Targeting Class A G Protein-Coupled Receptors Utilizing Crystal Structures and Computational Simulations. J Med Chem 2018, 61, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiden, L.E.; Goosens, K.A.; Jacobson, K.A.; Leggio, L.; Zhang, L. Peptide-Liganded G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Neurotherapeutics. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci 2020, 3, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Therapeutic peptides: current applications and future directions. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehnal, D.; Bittrich, S.; Deshpande, M.; Svobodová, R.; Berka, K.; Bazgier, V.; Velankar, S.; Burley, S.K.; Koča, J.; Rose, A.S. Mol* Viewer: modern web app for 3D visualization and analysis of large biomolecular structures. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, W431–W437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, B.; He, X.; Zhou, X.E.; Guo, S.; Rao, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Liu, W.; Jiang, X.; Yang, D.; Jiang, H.; Shen, J.; Melcher, K.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wang, M.; Xie, X.; Xu, H.E. Molecular recognition of morphine and fentanyl by the human μ-opioid receptor. Cell 2022, 185, 4361–4375.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manglik, A.; Kruse, A.C.; Kobilka, T.S.; Thian, F.S.; Mathiesen, J.M.; Sunahara, R.K.; Pardo, L.; Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K.; Granier, S. Crystal structure of the µ-opioid receptor bound to a morphinan antagonist. Nature 2012, 485, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Guo, C.; Lei, Y.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.; Cao, P.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Yang, X. Dynamic recognition of naloxone, morphine and endomorphin1 in the same pocket of µ-opioid receptors. Front Mol Biosci 2022, 9, 925404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.D.; Coveñas, R. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor: Structure Dynamics and Signaling. Receptors 2022, 1, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Kim, J.; Ko, S.; Choi, Y.K.; Jeong, H.; Woo, H.; Kang, H.; Bang, I.; Kim, S.A.; Yoon, T.; Seok, C.; Im, W.; Choi, H. Structural basis of neuropeptide Y signaling through Y1 receptor. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 853–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Shen, D.; Zhao, T.; Guo, S.; He, X.; Yin, W.; Xu, P.; Ji, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, X.; Jiang, H.; Eric Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, X.; Jiang, Y. Molecular basis for allosteric agonism and G protein subtype selectivity of galanin receptors. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 1364–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Khoshouei, M.; Deganutti, G.; Glukhova, A.; Koole, C.; Peat, T.S.; Radjainia, M.; Plitzko, J.M.; Baumeister, W.; Miller, L.J.; Hay, D.L.; Christopoulos, A.; Reynolds, C.A.; Wootten, D.; Sexton, P.M. Cryo-EM structure of the active, G(s)-protein complexed, human CGRP receptor. Nature 2018, 561, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.L.; Rodríguez, F.D.; Coveñas, R. Peptidergic Systems and Cancer: Focus on Tachykinin and Calcitonin/Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Families. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.F.; Noinaj, N.; Shibata, Y.; Love, J.; Kloss, B.; Xu, F.; Gvozdenovic-Jeremic, J.; Shah, P.; Shiloach, J.; Tate, C.G.; Grisshammer, R. Structure of the agonist-bound neurotensin receptor. Nature 2012, 490, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deluigi, M.; Klipp, A.; Klenk, C.; Merklinger, L.; Eberle, S.A.; Morstein, L.; Heine, P.; Mittal, P.R.E.; Ernst, P.; Kamenecka, T.M.; He, Y.; Vacca, S.; Egloff, P.; Honegger, A.; Plückthun, A. Complexes of the neurotensin receptor 1 with small-molecule ligands reveal structural determinants of full, partial, and inverse agonism. Sci Adv 2021, 7, eabe5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumbak, F.; Bower, J.B.; Zemmer, S.C.; Inoue, A.; Pons, M.; Paniagua, J.C.; Yan, F.; Ford, J.; Wu, H.; Robson, S.A.; Bathgate, R.A.D.; Scott, D.J.; Gooley, P.R.; Ziarek, J.J. Stabilization of pre-existing neurotensin receptor conformational states by β-arrestin-1 and the biased allosteric modulator ML314. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 3328–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yue, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Song, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Li, C.; Hanson, M.A.; Han, G.W.; Sickmier, E.A.; Swaminath, G.; Zhao, S.; Stevens, R.C.; Hu, L.A.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, M.; Xu, F. Structural Basis for Apelin Control of the Human Apelin Receptor. Structure 2017, 25, 858–866.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pioszak, A.A.; Parker, N.R.; Suino-Powell, K.; Xu, H.E. Molecular recognition of corticotropin-releasing factor by its G-protein-coupled receptor CRFR1. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 32900–32912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lim, T.; Ha, G.E.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Chang, N.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.; Cho, Y.; Kim, B.W.; Abrahamsson, A.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.; Cheong, E.; Kim, B.M.; Cho, H. Structure-based drug discovery of a corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor one antagonist using an X-ray free-electron laser. Exp Mol Med 2023, 55, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nürnberg, B.; Beer-Hammer, S.; Reisinger, E.; Leiss, V. Non-canonical G protein signaling. Pharmacol Ther 2024, 255, 108589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crilly, S.E.; Puthenveedu, M.A. Compartmentalized GPCR Signaling from Intracellular Membranes. J Membr Biol 2021, 254, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. GPCR-dependent and -independent arrestin signaling. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2024, 45, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Espinoza, E.; Thomsen, A.R.B. Beneath the surface: endosomal GPCR signaling. Trends Biochem Sci 2024, 49, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauer, M.J.; Willette, B.K.A.; Tsvetanova, N.G. Functional diversification of cell signaling by GPCR localization. J Biol Chem 2024, 300, 105668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoos, A.; Gabriel, C.; Knab, V.M.; Fux, D.A. Activation of HIF-1α by δ-Opioid Receptors Induces COX-2 Expression in Breast Cancer Cells and Leads to Paracrine Activation of Vascular Endothelial Cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2019, 370, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, N.; Arab, S.S.; Doustmohammadi, A.; Daly, N.L.; Khosroushahi, A.Y. ApInAPDB: a database of apoptosis-inducing anticancer peptides. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 21341–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaly, G.; Tallima, H.; Dabbish, E.; Badr ElDin, N.; Abd El-Rahman, M.K.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Shoeib, T. Anti-Cancer Peptides: Status and Future Prospects. Molecules 2023, 28, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, G.N. Agonists of galanin subtype 2 receptor may prevent pancreatic cancer, and agonists of angiotensin II type 2 receptor may prevent colorectal cancer. Eur J Pharmacol 2024, 978, 176772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.L.; Rodríguez, F.D.; Coveñas, R. Involvement of the Opioid Peptide Family in Cancer Progression. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniak, A.; Fichna, J.; Zielińska, M. Opioids in Cancer Development, Progression and Metastasis: Focus on Colorectal Cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol 2020, 21, 6–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripolt, S.; Neubauer, H.A.; Knab, V.M.; Elmer, D.P.; Aberger, F.; Moriggl, R.; Fux, D.A. Opioids drive breast cancer metastasis through the δ-opioid receptor and oncogenic STAT3. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, T.; Sano, M.; Kajiwara, I.; Oshima, Y.; Itaya, T.; Kim, J.; Ichimaru, Y.; Kitajima, O.; Masamune, A.; Ijichi, H.; Suzuki, T. Effects of tramadol via a µ-opioid receptor on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2024, 49, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, M.; Donnini, S.; Pellegrini, C.; Coppi, E.; Bocci, G. Opioid receptors beyond pain control: The role in cancer pathology and the debated importance of their pharmacological modulation. Pharmacol Res 2020, 159, 104938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, D.; Shoffel-Havakuk, H.; Tsur, N.; Uhelski, M.L.; Gottumukkala, V.; Cata, J.P. Opioids and Cancer: Current Understanding and Clinical Considerations. Curr Oncol 2024, 31, 3086–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoir, S.; Uhelski, M.; Guerra-Londono, J.J.; Cata, J.P. The Role of Opioid Receptors in Cancer. Adv Biol (Weinh) 2023, 7, e2300102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.; Coveñas, R.; Muñoz, M. Combination Therapy of Chemotherapy or Radiotherapy and the Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist Aprepitant: A New Antitumor Strategy? Curr Med Chem 2023, 30, 1798–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coveñas, R.; Muñoz, M. Involvement of the Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptor System in Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isorna, I.; González-Moles, M. Á; Muñoz, M., Ed.; Esteban, F. Substance P and Neurokinin-1 Receptor System in Thyroid Cancer: Potential Targets for New Molecular Therapies. J Clin Med 2023, 12, 6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-García, D.; Téllez, T.; Redondo, M.; García-Aranda, M. The Use of SP/Neurokinin-1 as a Therapeutic Target in Colon and Rectal Cancer. Curr Med Chem 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.T.; Thaggikuppe Krishnamurthy, P.; Magham, S.V. Harnessing the synergistic potential of NK1R antagonists and selective COX-2 inhibitors for simultaneous targeting of TNBC cells and cancer stem cells. J Drug Target 2024, 32, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Javid, H.; Iranpour, S.; Darban, R.A.; Hashemy, S.I. Unveiling the Promising Role of Substance P/Neurokinin 1 Receptor in Cancer Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Regulation in Human Malignancies. Curr Med Chem 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalikhan, A.; Ebrahimi, S.; Aliee, A.; Mirzavi, F.; Hashemy, S.I. The combined anti-tumor effects of 5-fluorouracil and neurokinin receptor inhibitor, aprepitant, against colorectal cancer: In vitro and in vivo study. Med Oncol 2024, 41, 70–w. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei Shandiz, S.; Assaran Darban, R.; Javid, H.; Ghahremanloo, A.; Hashemy, S.I. The effect of SP/NK1R on expression and activity of glutaredoxin and thioredoxin proteins in prostate cancer cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2024, 397, 5875–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhou, P.; Miao, L.; Deng, X. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant regulates autophagy and apoptosis via ROS/JNK in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int 2024, 44, 1651–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Yuan, S.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, F. Neurokinin-1 receptor is highly expressed in cervical cancer and its antagonist induces cervical cancer cell apoptosis. Eur J Histochem 2023, 67, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Mirzavi, F.; Hashemy, S.I.; Khaleghi Ghadiri, M.; Stummer, W.; Gorji, A. The in vitro anti-cancer synergy of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist, aprepitant, and 5-aminolevulinic acid in glioblastoma. Biofactors 2023, 49, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.L.; Rodríguez, F.D.; Coveñas, R. Neuropeptide Y Peptide Family and Cancer: Antitumor Therapeutic Strategies. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 9962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigorski, D.; Wesołowski, W.; Gruszecka, A.; Gulczyński, J.; Zieliński, P.; Misiukiewicz, S.; Kitlińska, J.; Iżycka-Świeszewska, E. Neuropeptide Y and its receptors in prostate cancer: associations with cancer invasiveness and perineural spread. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2023, 149, 5803–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Mahajan, A.; Hong, S.; Galli, S.; Zhu, S.; Tilan, J.U.; Abualsaud, N.; Adnani, M.; Chung, S.; Elmansy, N.; Rodgers, J.; Rodriguez, O.; Albanese, C.; Wang, H.; Regan, M.; Zgonc, V.; Blancato, J.; Krawczyk, E.; Gallicano, G.I.; Girgis, M.; Cheema, A.; Iżycka-Świeszewska, E.; Cavalli, L.R.; Pack, S.D.; Kitlinska, J. Hypoxia-activated neuropeptide Y/Y5 receptor/RhoA pathway triggers chromosomal instability and bone metastasis in Ewing sarcoma. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 2323–x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualsaud, N.; Caprio, L.; Galli, S.; Krawczyk, E.; Alamri, L.; Zhu, S.; Gallicano, G.I.; Kitlinska, J. Neuropeptide Y/Y5 Receptor Pathway Stimulates Neuroblastoma Cell Motility Through RhoA Activation. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 8, 627090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chakrobortty, N.; Saha, A.K.; Shang, X. Identifying colon cancer stage related genes and their cellular pathways. Front Genet 2023, 14, 1120185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascetta, S.A.; Kirsh, S.M.; Cameron, M.; Uniacke, J. Pharmacological inhibition of neuropeptide Y receptors Y1 and Y5 reduces hypoxic breast cancer migration, proliferation, and signaling. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 494–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, P.J.; Pascetta, S.A.; Kirsh, S.M.; Al-Khazraji, B.K.; Uniacke, J. Expression of hypoxia inducible factor-dependent neuropeptide Y receptors Y1 and Y5 sensitizes hypoxic cells to NPY stimulation. J Biol Chem 2022, 298, 101645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakroborty, D.; Goswami, S.; Fan, H.; Frankel, W.L.; Basu, S.; Sarkar, C. Neuropeptide Y, a paracrine factor secreted by cancer cells, is an independent regulator of angiogenesis in colon cancer. Br J Cancer 2022, 127, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, I.; Kofler, B. The galanin system in cancer. Exp Suppl 2010, 102, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.L.; Coveñas, R. The Galaninergic System: A Target for Cancer Treatment. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, I.M.; Yakout, N.M.; Soliman, A.S.A.; Venkatachalam, T.; Vinod, A.; Eldohaji, L.; Nair, V.; Hareedy, A.; Kandil, A.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Hamoudi, R.; Saber-Ayad, M. Evaluation of Galanin Expression in Colorectal Cancer: An Immunohistochemical and Transcriptomic Study. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 877147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiezun, J.; Godlewski, J.; Krazinski, B.E.; Kozielec, Z.; Kmiec, Z. Galanin Receptors (GalR1, GalR2, and GalR3) Expression in Colorectal Cancer Tissue and Correlations to the Overall Survival and Poor Prognosis of CRC Patients. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, J.; Xing, N.; Xu, Z.D. Galanin suppresses proliferation of human U251 and T98G glioma cells via its subtype 1 receptor. Biol Chem 2017, 398, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros, M.C.; Liu, M.; Banerjee, R.; Bellile, E.; D'Silva, N.J.; Rossa, C.J. Galanin mediates tumor-induced immunosuppression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 2022, 45, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namsolleck, P.; Kofler, B.; Moll, G.N. Galanin 2 Receptor: A Novel Target for a Subset of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 10193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenstetter, S.; Leitner, J.; Brunner, S.M.; Rieder, T.N.; Kofler, B.; Weis, S. Galanin System in Human Glioma and Pituitary Adenoma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wende, B.; Beyer, A.L.; Ruhnke, N.; Kaemmerer, D.; Sänger, J.; Schulz, S.; Lupp, A. Expression of the Calcitonin Receptor-like Receptor (CALCRL) in Normal and Neoplastic Tissues. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, A.; Nishibata, M.; Maruyama, T.; Sunami, S.; Isono, K.; Kawamata, T. Activation of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 Is Involved in Both Pain and Tumor Growth in a Mouse Model of Cancer Pain. Neuroscience 2024, 538, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Șerban, R.; Stepan, M.; Florescu, D.N.; Boldeanu, M.; Florescu, M.; Șerbănescu, M.; Ionescu, M.; Streba, L.; Drăgoescu, N.; Christopher, P.; Obleagă, V.; Constantin, C.; Vere, C.C. Expression of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Calcitonin Receptor-like Receptor in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, S.P.A.; Lourenço, D.M.J.; Santos, M.A.; Tavares, M.R.; Toledo, R.A.; Correia-Deur, J.E.d.M. Hypercalcitoninemia is not pathognomonic of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2009, 64, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Master, S.R.; Mathias, P.M.; Burns, B. Medullary Thyroid Cancer. In StatPearlsStatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island (FL), 2024;
- Fugazzola, L. Medullary thyroid cancer - An update. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2023, 37, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Lin, B.; Xu, T.; Jiang, J.; Luo, S.; Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Xiang, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, S.; Lv, W.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, H. The neurotransmitter calcitonin gene-related peptide shapes an immunosuppressive microenvironment in medullary thyroid cancer. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 5555–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Sánchez-López, C.M.; Marcilla, A.; Barone, R.; Caruso Bavisotto, C.; Graziano, F.; Conway de Macario, E.; Macario, A.J.L.; Bucchieri, F.; Cappello, F.; Campanella, C.; Rappa, F. Hsp70 and Calcitonin Receptor Protein in Extracellular Vesicles from Glioblastoma Multiforme: Biomarkers with Putative Roles in Carcinogenesis and Potential for Differentiating Tumor Types. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhu, H.; Sheng, L.; Mu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Z.; Wu, A.; Ouyang, G. CALCRL knockdown suppresses cancer stemness and chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3-ITD and DNM3TA-R882 double mutations. Drug Dev Res 2024, 85, e22137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, N.H.; Inoue, K.; Lewis, P.K.; Khan, A.; Hwang, J.H.; Chokshi, V.; Dabovic, B.B.; Selvaraj, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Dubeykovskaya, Z.; Pinkerton, N.M.; Bunnett, N.W.; Loomis, C.A.; Albertson, D.G.; Schmidt, B.L. Calcitonin Related Polypeptide Alpha Mediates Oral Cancer Pain. Cells 2023, 12, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Cho, J.; Bae, S.; Jung, H.S.; Kang, C.M.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, C.; Kim, H.; Jo, D.; Paik, Y. Inhibition of the Alternative Complement Pathway May Cause Secretion of Factor B, Enabling an Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer. J Proteome Res 2024, 23, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jailani, A.B.A.; Bigos, K.J.A.; Avgoustou, P.; Egan, J.L.; Hathway, R.A.; Skerry, T.M.; Richards, G.O. Targeting the adrenomedullin-2 receptor for the discovery and development of novel anti-cancer agents. Expert Opin Drug Discov 2022, 17, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; Cui, H.; Xu, M.; Yi, L. Oncogenic role of neurotensin and neurotensin receptors in various cancers. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2017, 44, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Pellino, G.; Fiorentino, F.; Rasheed, S.; Darzi, A.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. A Review of the Role of Neurotensin and Its Receptors in Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2017, 2017, 6456257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, S.; Qiu, S.; Fiorentino, F.; Simillis, C.; Rasheed, S.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. The role of Neurotensin and its receptors in non-gastrointestinal cancers: a review. Cell Commun Signal 2020, 18, 68–y. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou, N.; Blondy, S.; David, V.; Verdier, M.; Lalloué, F.; Jauberteau, M.; Mathonnet, M.; Perraud, A. Neurotensin pathway in digestive cancers and clinical applications: an overview. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11, 1027–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, T.W.; Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Jensen, R.T. Adding of neurotensin to non-small cell lung cancer cells increases tyrosine phosphorylation of HER3. Peptides 2022, 156, 170858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.L.; Coveñas, R. The Neurotensinergic System: A Target for Cancer Treatment. Curr Med Chem 2022, 29, 3231–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Tian, H.; Niu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, N.; Wen, S.; Chen, X.; Ren, S.; Xu, C.; Chang, C.; Flores-Morales, A.; Shang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Niu, Y. Neurotensin and its receptors mediate neuroendocrine transdifferentiation in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 4875–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaryńska, M.; Olejniczak-Kęder, A.; Podpłońska, K.; Prahl, A.; Iłowska, E. Bradykinin and Neurotensin Analogues as Potential Compounds in Colon Cancer Therapy. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.; Wang, H.; Hsu, S.; Wang, L.; Tsai, Y.; Su, Y.; Hung, W.; Chen, L. Neuron-derived neurotensin promotes pancreatic cancer invasiveness and gemcitabine resistance via the NTSR1/Akt pathway. Am J Cancer Res 2024, 14, 448–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhlef, L.; Yassine, M.; Chandouri, B.; Rivière, L.; Naves, T.; Dmytruk, N.; Gachard, N.; Jauberteau, M.; Gallet, P. Targeting the NTSR2/TrkB oncogenic pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 6084–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoumi, J.; Jafarzadeh, A.; Khorramdelazad, H.; Abbasloui, M.; Abdolalizadeh, J.; Jamali, N. Role of Apelin/APJ axis in cancer development and progression. Adv Med Sci 2020, 65, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinstead, C.; Yoon, S. Apelin, a Circulating Biomarker in Cancer Evaluation: A Systematic Review. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, L. Roles of apelin/APJ system in cancer: Biomarker, predictor, and emerging therapeutic target. J Cell Physiol 2022, 237, 3734–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hayashi, Y.; Kidoya, H.; Takakura, N. Endothelial cell-derived Apelin inhibits tumor growth by altering immune cell localization. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 14047–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, F.S.; Güneş, C.E.; Yavuz, E.; Kurar, E. Apelin triggers macrophage polarization to M2 type in head and neck cancer. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Q.; Jiao, X.; Ye, J.; Hao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Ma, G.; Hao, C.; Cui, B. APLN promotes the proliferation, migration, and glycolysis of cervical cancer through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 2024, 755, 109983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effenberger, M.; Grander, C.; Hausmann, B.; Enrich, B.; Pjevac, P.; Zoller, H.; Tilg, H. Apelin and the gut microbiome: Potential interaction in human MASLD. Dig Liver Dis 2024, 56, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Hong, Y.; Dai, L.; Qian, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wu, B.; Li, S. CRH promotes human colon cancer cell proliferation via IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway and VEGF-induced tumor angiogenesis. Mol Carcinog 2017, 56, 2434–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Li, S. Role of CRH in colitis and colitis-associated cancer: a combinative result of central and peripheral effects? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2024, 15, 1363748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Wen, H.; Dai, L.; Lou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yi, Y.; Yan, X.; Wu, Y.; Sun, W.; Chen, P.; Yang, S.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G. A brain-tumor neural circuit controls breast cancer progression in mice. J Clin Invest 2023, 133, e167725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hamada, Y.; Narita, M.; Sato, D.; Tanaka, K.; Mori, T.; Tezuka, H.; Suda, Y.; Tamura, H.; Aoki, K.; Kuzumaki, N.; Narita, M. Elucidation of the mechanisms underlying tumor aggravation by the activation of stress-related neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Mol Brain 2023, 16, 18–0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, R.; Zhou, F.; Hong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C.; Jin, L.; Li, S. CRH upregulates supervillin through ERK and AKT pathways to promote bladder cancer cell migration. Cell Biol Int 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimas, A.; Goussia, A.; Papoudou-Bai, A.; Politi, A.; Paschopoulos, M.; Navrozoglou, I.; Makrigiannakis, A.; Vrekoussis, T. The expression of corticotropin-releasing hormone family peptides in premalignant and malignant vulvar lesions. Clin Transl Oncol 2024, 26, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Motoi, F.; Tajiki, H.; Kawaguchi, K.; Ohtsuka, H.; Takadate, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Takagi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Katayose, Y.; Fukudo, S.; Unno, M. Expression of Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone and Its Receptors May Be Associated With Survival Rate in Pancreatic Cancer. Gastro Hep Adv 2022, 2, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitakis, K.; Koufakis, T.; Kotsa, K.; Germanidis, G. How Far beyond Diabetes Can the Benefits of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Go? A Review of the Evidence on Their Effects on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faggiano, A. Long-acting somatostatin analogs and well differentiated neuroendocrine tumors: a 20-year-old story. J Endocrinol Invest 2024, 47, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, J. Bradykinin stimulates IL-6 production and cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep 2014, 32, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.L.; Mangas, A.; Coveñas, R. Glioma and Peptidergic Systems: Oncogenic and Anticancer Peptides. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.D.; Coveñas, R. Antitumor Strategies Targeting Peptidergic Systems. Encyclopedia 2024, 4, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, H.; Tan, L.; Siu, K.T.H.; Guan, X. Exploring treatment options in cancer: Tumor treatment strategies. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2024, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; You, Y.; Griffin, N.; Feng, J.; Shan, F. Low-dose naltrexone (LDN): A promising treatment in immune-related diseases and cancer therapy. Int Immunopharmacol 2018, 61, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Yan, L.; Shan, F.; Wang, X.; Qu, N.; Handley, M.K.; Ma, M. Low-dose naltrexone plays antineoplastic role in cervical cancer progression through suppressing PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Transl Oncol 2021, 14, 101028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, N.; Meng, Y.; Handley, M.K.; Wang, C.; Shan, F. Preclinical and clinical studies into the bioactivity of low-dose naltrexone (LDN) for oncotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 96, 107714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, J.; Haddad, T.; Gupta, K.; Sauers, J.; Yee, D. An open label phase II study of safety and clinical activity of naltrexone for treatment of hormone refractory metastatic breast cancer. Invest New Drugs 2023, 41, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciwun, M.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A.; Pawlak, D. Low-Dose Naltrexone as an Adjuvant in Combined Anticancer Therapy. Cancers (Basel) 2024, 16, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Assaran Darban, R.; Javid, H.; Esparham, A.; Hashemy, S.I. The anti-tumoral role of Hesperidin and Aprepitant on prostate cancer cells through redox modifications. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2023, 396, 3559–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coveñas, R.; Rodríguez, F.D.; Robinson, P.; Muñoz, M. The Repurposing of Non-Peptide Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonists as Antitumor Drugs: An Urgent Challenge for Aprepitant. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 15936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishibe-Toyosato, S.; Ando, Y.; Torii, Y.; Ichikawa, R.; Owaki, A.; Miyamura, H.; Nishio, E.; Matsuda, H.; Tsujii-Fujii, N.; Shimato-Isobe, A.; Mukaiji, K.; Ito, K.; Hayashi, T.; Fujii, T.; Yamada, S. Comparing Injection Site Reactions of Aprepitant and Fosaprepitant in Gynecologic Cancer Chemotherapy. In Vivo 2024, 38, 2374–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivia, V.; Recio, R.; Lerena, P.; Pozo, E.; Serrano, R.; Calero, R.; Pintado, C.; Leal, M.P.; Moreno-Rodríguez, N.; Organero, J. Á; Khiar, N.; Fernández, I. Biological evaluation of carbohydrate-based aprepitant analogs for neuroblastoma treatment. Eur J Med Chem 2024, 264, 116021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirith, I.; Renz, B.W.; Mudusetti, S.; Ring, N.S.; Kolorz, J.; Koch, D.; Bazhin, A.V.; Berger, M.; Wang, J.; Angele, M.K.; D'Haese, J.G.; Guba, M.O.; Niess, H.; Andrassy, J.; Werner, J.; Ilmer, M. Identification of the Neurokinin-1 Receptor as Targetable Stratification Factor for Drug Repurposing in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Lee, M.; Gao, Y.; Bu, P.; Coarfa, C.; Miles, B.; Sreekumar, A.; Creighton, C.J.; Ayala, G. Neuropeptide Y nerve paracrine regulation of prostate cancer oncogenesis and therapy resistance. Prostate 2021, 81, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, A.; Balaskó, M.; Pétervári, E.; Koller, A.; Brunner, S.M.; Moll, G.N.; Kofler, B. Intranasal Delivery of a Methyllanthionine-Stabilized Galanin Receptor-2-Selective Agonist Reduces Acute Food Intake. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 2737–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deigin, V.; Linkova, N.; Vinogradova, J.; Vinogradov, D.; Polyakova, V.; Medvedev, D.; Krasichkov, A.; Volpina, O. The First Reciprocal Activities of Chiral Peptide Pharmaceuticals: Thymogen and Thymodepressin, as Examples. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, A.; Rid, R.; Beyreis, M.; Bianchini, R.; Holub, B.S.; Lang, A.; Sternberg, F.; Brodowicz, B.; Velickovic, O.; Jakab, M.; Kerschbaum, H.; Önder, K.; Kofler, B. In vitro toxicity of the galanin receptor 3 antagonist SNAP 37889. Neuropeptides 2016, 56, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgoustou, P.; Jailani, A.B.A.; Zirimwabagabo, J.; Tozer, M.J.; Gibson, K.R.; Glossop, P.A.; Mills, J.E.J.; Porter, R.A.; Blaney, P.; Bungay, P.J.; Wang, N.; Shaw, A.P.; Bigos, K.J.A.; Holmes, J.L.; Warrington, J.I.; Skerry, T.M.; Harrity, J.P.A.; Richards, G.O. Discovery of a First-in-Class Potent Small Molecule Antagonist against the Adrenomedullin-2 Receptor. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci 2020, 3, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirimwabagabo, J.; Jailani, A.B.A.; Avgoustou, P.; Tozer, M.J.; Gibson, K.R.; Glossop, P.A.; Mills, J.E.J.; Porter, R.A.; Blaney, P.; Wang, N.; Skerry, T.M.; Richards, G.O.; Harrity, J.P.A. Discovery of a First-In-Class Small Molecule Antagonist against the Adrenomedullin-2 Receptor: Structure-Activity Relationships and Optimization. J Med Chem 2021, 64, 3299–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluexam, T.; Grandits, A.M.; Schlerka, A.; Nguyen, C.H.; Etzler, J.; Finkes, T.; Fuchs, M.; Scheid, C.; Heller, G.; Hackl, H.; Harrer, N.; Sill, H.; Koller, E.; Stoiber, D.; Sommergruber, W.; Wieser, R. CGRP Signaling via CALCRL Increases Chemotherapy Resistance and Stem Cell Properties in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, 5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Sheng, D.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y. Neuronal calcitonin gene-related peptide promotes prostate tumor growth in the bone microenvironment. Peptides 2021, 135, 170423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suekane, A.; Ichikawa, T.; Saito, Y.; Nakahata, S.; Morishita, K. The CGRP Receptor Antagonist MK0974 Induces EVI1(high) AML Cell Apoptosis by Disrupting ERK Signaling. Anticancer Res 2022, 42, 4743–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Agopiantz, M.; Poupon, J.; Wu, Z.; Just, P.; Borghese, B.; Ségal-Bendirdjian, E.; Gauchotte, G.; Gompel, A.; Forgez, P. Neurotensin Receptor 1 Antagonist SR48692 Improves Response to Carboplatin by Enhancing Apoptosis and Inhibiting Drug Efflux in Ovarian Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2017, 23, 6516–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C.; Ehrlich, L.; Venter, J.; O'Brien, A.; White, T.; Zhou, T.; Dang, T.; Meng, F.; Invernizzi, P.; Bernuzzi, F.; Alpini, G.; Lairmore, T.C.; Glaser, S. Inhibition of the apelin/apelin receptor axis decreases cholangiocarcinoma growth. Cancer Lett 2017, 386, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Ying, H.; Yu, Z.; Chang, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Chang, S.; Qiu, Y.; Lin, X. Apelin Receptor Can Act as a Specific Marker and Promising Therapeutic Target for Infantile Hemangioma. J Invest Dermatol 2023, 143, 566–577.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, S.R.; Yi, X.; Lei, J.T.; Wen, B.; Zhao, H.; Liao, Y.; Jaehnig, E.J.; Somes, L.K.; Shafer, P.W.; Lee, T.D.; Fu, Z.; Dou, Y.; Shi, Z.; Gao, D.; Hoyos, V.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, B. Pan-cancer proteogenomics expands the landscape of therapeutic targets. Cell 2024, 187, 4389–4407.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusardi, M.; Signorello, M.G.; Russo, E.; Caviglia, D.; Ponassi, M.; Iervasi, E.; Rosano, C.; Brullo, C.; Spallarossa, A. Structure-Activity Relationship Studies on Highly Functionalized Pyrazole Hydrazones and Amides as Antiproliferative and Antioxidant Agents. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Aref, A.R.; Sethi, G.; Ertas, Y.N. Peptide-functionalized, -assembled and -loaded nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today 2024, 29, 103981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, V.; Bardhan, M.; Dave, T.; Shamim, M.A.; Suresh, D.; Satish, P.; Dhakal, B.; Bhonsale, A.; Roy, P.; Padhi, B.K.; Monteith, T. Zavegepant for Acute Treatment of Migraine: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin Neuropharmacol 2024, 47, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerra, V.S.; Ramachandran, B.; Shareef, S.; Carrillo-Bermejo, A.; Sundararaj, R.; Venkatesan, S. Molecular docking aided machine learning for the identification of potential VEGFR inhibitors against renal cell carcinoma. Med Oncol 2024, 41, 198–0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caronna, E.; Alpuente, A.; Torres-Ferrus, M.; Pozo-Rosich, P. CGRP monoclonal antibodies and CGRP receptor antagonists (Gepants) in migraine prevention. Handb Clin Neurol 2024, 199, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Antitumoral compounds | Receptor | Tumor | References |
Naltrexone (antagonist)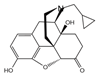
|
OPR | Metastatic breast cancer (phase II study) Gastrointestinal cancer Cervical cancer |
[163,164,165,166,167] |
Aprepitant (antagonist)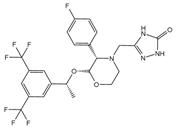
|
NK-1R | Gall bladder cancer Colorectal cancer Gynecologic cancer Cholangiocarcinoma Neuroblastoma Prostate cancer Thyroid cancer Pancreatic cancer |
[96,102,168,169,170,171,172] |
BIP3226 (antagonist)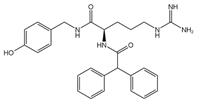 L152,804 (antagonist) 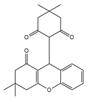
|
NPY1R (BIBP 3226), NPY5R (L152,804)- |
Breast cancer Colon cancer Prostate cancer |
[105,110,112,173] |
| M89b, a galanin analogue (agonist) Amino acid sequence: pEWNLNAAGYLLATHACG (pE stands for pyro-Glu) |
GAL2R | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Colorectal cancer |
[114,119,174,175] |
SNAP 37889 (antagonist)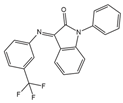
|
GAL3R | Promyelocytic leukemia cells | [176] |
Indolinone Compound 25 (antagonist)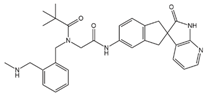
|
CLR-RAMP3 (AM2R) |
Human pancreatic cancer cell lines In vivo models of breast cancer |
[132,177,178] |
Olcegepant (antagonist)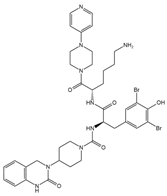 Telcagepant or MK0974) (antagonist) 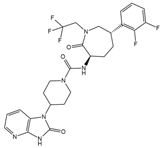
|
CLR-RAMP1 | Prostate cancer Acute myeloid leukemia |
[179,180,181] |
SR 48692 (antagonist)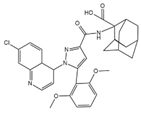
|
NTS1R | Ovarian cancer | [182] |
ML 221 (antagonist)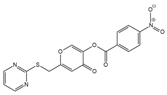
|
APLNR | Cholangiocarcinoma Breast cancer Infantile hemangioma |
[143,183,184] |
BMK-I-152 (antagonist)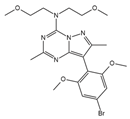
|
CRFR1 | Not tested in cancer therapy* Tested for major depression |
[77] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





