Submitted:
22 September 2024
Posted:
23 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
- How does information security policy compliance impact data protection?
- What are the key components of an effective information security policy, and how do they contribute to reducing security breaches?
- What are the potential consequences of inadequate leadership support and organizational size on information security policy compliance?
- What is the impact of the SETA program on staff’s understanding and adherence to information security policies?
- What are the most common types of security breaches and their potential impact on organizations?
- What are the gaps in the current body of research on information security policies compliance and security breach incidence, and what future research directions should be pursued to address these gaps?
Literature Review
Methodology
| ID | Author(s) | Title | Type | Publisher | Year | Source | Method |
| 1 | A. Albarrak | Evaluation of Users Information Security Practices at King Saud University Hospitals | Article | Global Business and Management Research | 2011 | Sematic scholar | Quantitative |
| 2 | Premylla et al. | Potential measures to enhance information security compliance in the healthcare Internet of Things | Conference | Recent Trends in Data Science and Soft Computing | 2018 | Sematic scholar | Qualitative |
| 3 | Li et al. | The roles of IT strategies and security investments in reducing organizational security breaches | Article | Journal of Management Information Systems | 2021 | Taylor & Francis | Quantitative |
| 4 | Mohammad et al. | Cybersecurity in Hospitals: A Systematic, Organizational Perspective | Article | Journal of Medical Internet Rsearch | 2018 | JMIR Publications | Qualitative |
| 5 | Abdelhamid et al. | Putting the focus back on the patient: How privacy concerns affect personal health information sharing intentions | Article | Journal of Medical Internet Research | 2017 | Google scholar | Quantitative |
| 6 | Sher et al. | Compliance With Electronic Medical Records Privacy Policy: An Empirical Investigation of Hospital Information Technology Staff | Article | INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision | 2017 | Sage | Quantitative |
| 7 | Kessler et al. | Information security climate and the assessment of information security risk among healthcare employees | Article | Health informatics journal | 2020 | Sage | Quantitative |
| 8 | Chua, Hui Na et al. | Impact of employees’ demographic characteristics on the awareness and compliance of information security policy in organizations | Article | Telematics and Informatics, | 2018 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 9 | Huertas et al. | Preserving patients’ privacy in health scenarios through a multicontext-aware system | Article | Annals of Telecommunications | 2017 | Springer | Qualitative |
| 10 | Kuo et al. | Hospital Staff’s Adherence to Information Security Policy: A Quest for the Antecedents of Deterrence Variables | Article | NQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision | 2021 | Sage | Quantitative |
| 11 | Dincelli et al. | Choose your own training adventure: designing a gamified SETA artefact for improving information security and privacy through interactive storytelling | Article | European Journal of Information Systems ISSN: | 2020 | Taylor & Francis | Quantitative |
| 12 | Adel Yazdanmehr et al. | Employees’ information security policy compliance: A norm activation perspective | Article | Decision Support Systems journal | 2016 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 13 | Choi, Myeonggil &ong, Jeongseok | Social control through deterrence on the compliance with information security policy | Article | Soft Computing | 2018 | Springer | Quantitative |
| 14 | Enaizan, Odai et al. | Electronic medical record systems: decision support examination framework for individual, security and privacy concerns using multi-perspective analysis | Article | Health and Technology | 2020 | Springer | Quantitative |
| 15 | Nader Sohrabi Safa et al. | Information security policy compliance model in organizations | Article | Computer & Security | 2016 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 16 | K Kim et al. | Nurses’ and patients’ perceptions of privacy protection behaviours and information provision | Article | Nurse and ethics | 2017 | Sage | Quantitative |
| 17 | T Herath, HR Rao | Protection motivation and deterrence: a framework for security policy compliance in organisations | Article | European Journal of information systems | 2009 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 18 | C Liu et al. | Influencing factors of employees’ information systems security police compliance: Empirical research in China | Conference | E3S Web of Conferences | 2020 | e3s-conferences | Quantitative |
| 19 | SL Hepp et al. | Evaluation of the awareness and effectiveness of IT security programs in a large publicly funded health care system | Article | Health Information Management Journal | 2018 | Sage | Qualitative |
| 20 | N Humaidi, V Balakrishnan | Indirect effect of management support on users’ compliance behavior towards information security policies | Article | Health Information Management Journal | 2018 | Sage | Quantitative |
| 21 | J D’Arcy et al. | User awareness of security countermeasures and its impact on information systems misuse: A deterrence approach | Article | Information systems research | 2009 | Pubsonline | Quantitative |
| 22 | Areej Alyami et al. | Critical success factors for Security Education, Training and Awareness (SETA) programme effectiveness: an empirical comparison of practitioner perspectives | Article | Information and Computer Security | 2024 | Emerald | Qualitative |
| 23 | O Enaizan et al. | Electronic medical record systems: decision support examination framework for individual, security and privacy concerns using multi-perspective analysis | Article | Health and Technology, | 2020 | Springer | Quantitative |
| 24 | I Hwang, O Cha | Examining technostress creators and role stress as potential threats to employees’ information security compliance | Article | Computers in Human Behavior | 2018 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 25 | Xing et al. | Health information privacy concerns, antecedents, and information disclosure intention in Online surveyhealth communities | Article | Information & Management | 2018 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 26 | B Yüksel et al. | Research issues for privacy and security of electronic health services | Article | Future Generation Computer Systems | 2017 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 27 | Y Chen et al. | Organizations’ Information Security Policy Compliance: Stick or Carrot Approach? | Article | Journal of Management Information Systems | 2012 | Taylor & Francis | Quantitative |
| 28 | X Chen et al. | Sanction Severity and Employees’ Information Security Policy Compliance: Investigating mediating, moderating, and control Variables | Article | Information & Management | 2018 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 29 | D Alhuwail et al. | Information security awareness and behaviors of health care professionals at public health care facilities | Article | Applied Clinical Informatics | 2021 | thieme-connect | Quantitative |
| 30 | Mikko et al. | Compliance An Empirical Security Policies: with Information Investigation | Article | IEEE Computer Society | 2010 | Jstor | Quantitative |
| 31 | I Hwang et al. | Security Awareness: The First Step in Information Security Compliance Behavior | Article | Journal of Computer Information Systems | 2021 | Taylor & Francis | Quantitative |
| 32 | JY Han et al. | An integrative model of information security policy compliance with psychological contract: Examining a bilateral perspective | Article | Computers & Security | 2017 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 33 | ML Sher et al. | Compliance With Electronic Medical Records Privacy Policy: An Empirical Investigation of Hospital Information Technology Staf | Article | The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision | 2017 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 34 | NS Safa et al. | Information security policy compliance model in organizations | Article | computers & security, | 2016 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 35 | Hui Na Chua, et al. | Impact of Employees’ Demographic Characteristics on the Awareness and Compliance of Information Security Policy in Organizations | Article | Telematics and Informatics | 2018 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 36 | C Lee, CC Lee, S Kim | Understanding information security stress: Focusing on the type of information security compliance activity | Article | Computers & Security | 2016 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 37 | N Humaidi, V Balakrishnan | The moderating effect of working experience on health information system security policies compliance behaviour | Article | Malaysian Journal of Computer Science | 2015 | Malaysia | Quantitative |
| 38 | C Liu, N Wang, H Liang | Motivating information security policy compliance: The critical role of supervisor-subordinate guanxi and organizational commitment | Article | International Journal of Information Management | 2020 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 39 | V Kisekka, JS Giboney | The effectiveness of health care information technologies: evaluation of trust, security beliefs, and privacy as determinants of health care outcomes | Article | Journal of medical Internet research | 2018 | 0 | Quantitative |
| 40 | Inho Hwang et al. | Why not comply with information security? An empirical approach for the causes of non-compliance | Article | Online survey information review | 2017 | Elsevier | Quantitative |
| 41 | Burcu et al. | Information Security Policy Compliance: An Empirical Study of Rationality-Based Beliefs and Information Security Awareness | Article | Management Information Systems Research Cent | 2010 | Jstor | Quantitative |
| 42 | Hanifah Abdul et al. | Empirical Study on the Influence of Security Control Management and Social Factors in Deterring Information Security Misbehaviour | Conference | Journal of Physics | 2020 | 0 | Quantitative |
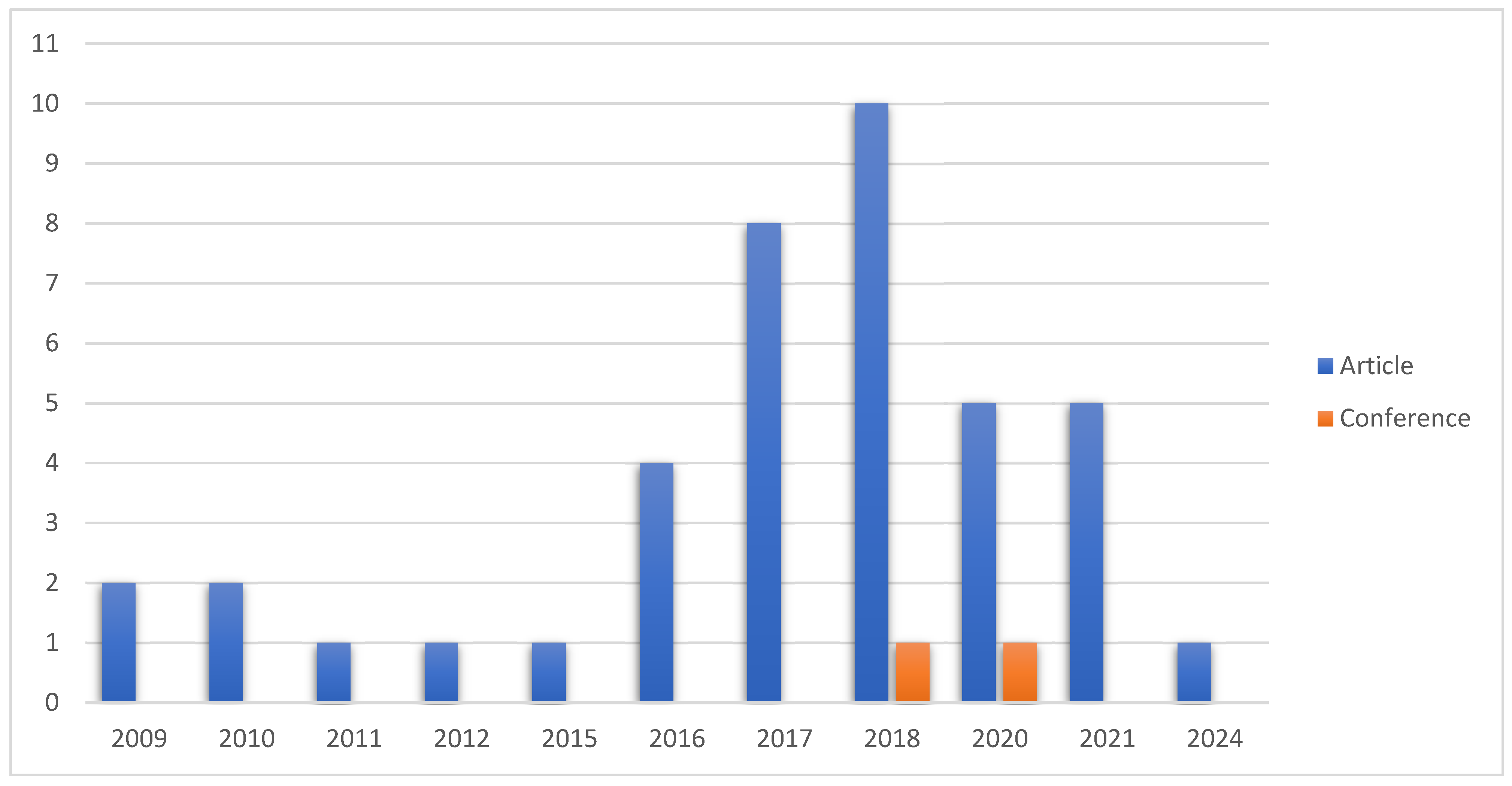
Findings
- Investments in information security, top management support, and employees' awareness contribute significantly to mitigating security incidents[56]. Implementing risk assessment methodologies and known mitigation methods can lead to a significant reduction in system downtime incidents and increase the availability of ICT systems[57]. Additionally, the implementation of security controls, such as encryption, helps organizations secure vulnerabilities and defend against data breaches, although they are not foolproof[58]. Therefore, a comprehensive ISPC readiness model is essential for organizations to effectively counter cloud threats and address compliance violations when migrating to or employing cloud computing services[19].
- Leadership support plays a crucial role in influencing employees' adherence to information security policies[23], [25]. Research indicates that factors like supportive organizational culture, security compliance leadership, and user involvement positively impact employees' attitudes towards information security policy compliance[26] [27]. Additionally, the study emphasizes the significance of management support in shaping employees' behavior to comply with information system security policies[59]. While the size of an organization was not explicitly mentioned in the contexts provided, it is essential to consider that larger organizations may have more complex structures and potentially face different challenges in ensuring policy adherence compared to smaller organizations. Therefore, effective leadership support combined with a supportive organizational culture can significantly influence employees' compliance with information security policies across organizations of varying sizes.
- Security Education, Training, and Awareness (SETA) programs play a crucial role in promoting information security awareness among staff. Research has shown that employees' perceptions of SETA programs significantly impact their commitment to security practices[30]. Factors contributing to the success of SETA programs include pedagogical approaches being more effective than communication approaches, as well as the critical success factors (CSFs) identified in the literature, such as design, development, implementation, and evaluation phases, which are essential for program effectiveness[34]. Moreover, employee security training indirectly influences security behavior through employee relations, monitoring, and accountability, highlighting the importance of holistic approaches in enhancing staff adherence to information security policies[32].
- Employee behavior plays a crucial role in the level of compliance with information security policies, with studies highlighting that employees are often the weakest link in maintaining security within organizations[32], [39], [41], [43]. Factors influencing compliance include the lack of understanding of policies, inadequate training, poor management support, and staff insensitivity towards safeguarding information[39]. Research emphasizes the importance of continuously raising awareness among users and dynamically monitoring their adherence to policies to enhance compliance levels[41]. Non-compliance with policies has been identified as a major challenge, leading to security breaches that can have severe financial implications, with estimates ranging from hundreds of billions to over one trillion dollars annually[43]. The focus on human behavior and factors affecting compliance underscores the need for robust security measures and effective strategies to prevent insider threats and mitigate security incidents within organizations.
- Additional findings, Information security policy compliance (ISPC) plays a crucial role in reducing security breaches in organizations. Studies have shown that factors like psychological contract breach (PCB) can significantly impact employees' compliance intentions, with higher PCB leading to lower ISPC[14]. Additionally, the combined effects of organizational and behavioral factors, such as accountability constructs, supportive organizational culture, and user involvement, have been found to positively influence employees' attitudes and intentions towards establishing an information security policy compliance culture[42]. Moreover, the mediating role of emotions, particularly positive emotions, between challenge information security stress and ISPC has been highlighted as a significant factor in enhancing compliance behavior intentions[60]. By addressing these factors and promoting a culture of compliance, organizations can effectively reduce security breaches through improved ISPC.
| Author | Methodology | Finding | Theoretical gap | Empirical gap | Problem |
| Chen et al. (2022) | Field quasi-experimental method used with 217 employees from Chinese companies in Shanghai and Beijing. | Challenge information security stress positively affects ISP compliance and positive emotions, while negatively affecting negative emotions. | Expands research on challenging stress in the two-dimensional model of challenge-hindrance stressor theory in organizational information security | Reveals the mediating effect of positive emotions in the relationship between challenge information security stress and ISP compliance | The study provides empirical support for the application of positive psychology in the field of management |
| Eric Amankwa, Marianne Loock( 2022) | The study utilized a questionnaire to collect data from 313 employees in Ghana | Individual measures of accountability had weak to moderate effects on employees' attitudes towards information security policy compliance, but the combined effect showed significant influence. Organizational factors like supportive culture and user involvement positively affected employees' attitudes, with attitudes having a substantial influence on establishing an information security policy compliance culture |
The study highlights the lack of previous research considering the combined application of organizational and behavioral factors to establish an information security policy compliance culture | Prior to this study, there was a gap in understanding how organizational and behavioral factors together impact compliance with information security policies in organizations | The research aimed to address the issue of non-compliance with information security policies by examining the effects of organizational and behavioral factors on establishing a culture of compliance in organizations |
| Amankwa et al.( 2021) | The study involved a field survey with 313 employees from selected Ghanaian companies | Accountability measures significantly influenced employees' attitudes and behavior intentions towards ISP compliance | Existing strategies for changing employees' behavior intentions towards compliance have not been effective, highlighting a gap in the literature. | The study validated a research model for predicting employees' compliance behavior intentions, addressing the empirical gap in understanding ISP compliance culture. | Information security policy noncompliance is a growing problem leading to security breaches in organizations, necessitating effective strategies to address this issue. |
| Hong & Xu (2021) | The study utilized hierarchical regression analysis to test hypotheses | Job satisfaction and personal responsibility positively impact Information Security Policy Compliance (ISPC). Job satisfaction promotes the formation of personal responsibility, with deterrence severity negatively moderating this relationship. Personal responsibility mediates the relationship between job satisfaction and ISP |
The study explores ISPC formation from the perspective of autonomous motivation, focusing on self-determination theory and social exchange theory | The research emphasizes the importance of organizational support in promoting employees' perceived self-determination for ISPC | The study suggests maintaining deterrence at a moderate level tailored to the organization's security strategy and specific information security environment. |
| Ghannoo & Chiniah( 2022) | The research utilized a survey among computer users in organizations in Mauritius to identify antecedents of employee compliance with information security policy. | Results showed that an employee's intention to comply is influenced by attitude, security awareness programs, and rewards, which in turn influences actual compliance to ISP. | The study addressed the gap in understanding the factors influencing employee compliance with information security policy by proposing a novel multi-theory model derived from the theory of reasoned action, cognitive evaluation theory, and hanoo. | The research aimed to fill the empirical gap in knowledge regarding the influence of attitude, security awareness programs, and rewards on employee compliance with information security policy in organizations. | The study focused on evaluating new factors influencing information security compliance among employees, recognizing them as both potential risks and assets in information security efforts. |
| Yuanxiang John Li a( 2023) | Conducted laboratory experiments to study the impact of rewards, punishments, and detection probability on information security policy compliance | Rewards or a combination of rewards and punishments are effective in improving compliance, especially with reliable violation detection | Current information security policies are based on outdated compliance models, highlighting the need for a novel behavioral-based mechanism | Demonstrated the effectiveness of small and predictable financial rewards and punishments over a punishment-focused approach in improving compliance | Addressing the challenge of improving information security policy compliance through incentivization strategies grounded in behavioral economics and externality concepts |
| Author | Methodology | Finding | Theoretical gap | Empirical gap | Problem |
| Alzahrani & Seth( 2021) | The study collected data from 171 UK employees at manufacturing SMEs using a structured questionnaire | Security training, knowledge sharing, security education, and security visibility significantly impact information security performance. | Limited studies have been conducted on the impact of organizational practices on information security management performance in small- and medium-sized enterprises in the manufacturing sector. | Previous studies have used a small number of parameters, indicating a gap in the empirical research on this topic | The research aims to evaluate the effect of security organizational practices on information security management performance with a focus on various parameters in manufacturing SMEs |
| Assefa & Tensaye,(2021) | The research used a survey research method, a quantitative approach involving counting and measuring variables | Management support, awareness and training, and accountability are key factors shaping employees' compliance with information security policy. | The study addresses the lack of knowledge about information security policies and the resulting unawareness of consequences among employees. | More than 70% of security threats come from insiders due to lack of knowledge about information security policies | Employees commonly do not comply with information security policies despite their implementation in organizations |
| Onumo et al., (2021) | The study utilized a structured questionnaire and applied structural equation modeling (SEM) to analyze survey data from public sector information technology organizations in Nigeria | Knowledge of cybersecurity and employee cognitive belief significantly influenced employees' intentions to comply with organizational cybersecurity control mechanisms. Organizational elements like leadership on employee security behavior are mediated by espoused cultural values, and the impact of employee cognitive belief is moderated by security technologies |
The research highlights the critical role of leadership and cultural values in fostering organizational adherence to prescribed security control mechanisms, contributing to behavioral security research | The study addresses the need for effective cybersecurity compliance by promoting organizational security initiatives that incorporate cybersecurity principles and practices into job descriptions, routines, and processes | The increase in cybersecurity threats necessitates the adequate addressing of adherence to organizational security control processes and procedures |
| Eric Amankwa, Marianne Loock,( 2018) | The research model was developed and validated in an empirical field survey to show how key constructs influence employees' attitudes towards establishing security policy compliance culture (ISPCC) | Supportive organizational culture and end-user involvement significantly influenced employees' attitudes towards compliance with ISP, while leadership showed the weakest influence | The study addresses the gap in research by providing insights on how to effectively address non-compliance with ISP through the establishment of ISP compliance culture, a concept not previously explored | The study's focus on nurturing ISP compliance culture through specific factors like organizational culture and end-user involvement fills an empirical gap in understanding employees' attitudes and behavioral intentions towards ISP compliance | The study aims to address employees' non-compliance with information security policy by promoting factors like supportive organizational culture, end-user involvement, and compliance leadership to influence attitudes and behavioral intentions towards ISP in organizations |
| Paliszkiewicz (2019) | The study examined the influence of trust variables on leadership in information security policy compliance. Multicollinearity among independent variables was tested using tolerance level and variance inflation factor in the model |
Leadership plays a significant role in an organization's information security. Leadership involvement significantly affects employees' behavior towards information security compliance. |
The study explores the influence of trust variables on leadership in the context of information security policy compliance, indicating a potential theoretical gap in understanding this relationship | The research highlights the importance of leadership in information security effectiveness, suggesting a potential empirical gap in the existing literature regarding the specific impact of leadership on information security practices | The study aims to investigate the impact of trust variables on leadership in the organization's information security policy compliance |
| Author | Methodology | Finding | Theoretical gap | Empirical gap | Problem |
| Hu et al. (2024) | The study utilized a factorial-based scenario survey to test the relationships through covariance-based structural equation modeling | Pedagogical approaches were found to be more effective than communication approaches in influencing employees' perceptions of the SETA program. Employees' perceptions of the SETA program explained a significant amount of variance in their commitment to SETA |
The research contributes to the theoretical knowledge of the event lens by extending it to the SETA context and exploring the relationship among three event strength components | The study enriches the SETA literature by conceptualizing a SETA program as an organizational "event," diverging from conventional approaches | The study aimed to investigate how pedagogical and communication approaches in a SETA program influence employees' perceptions and commitment to the program |
| Heyasat et al. (2023) | Qualitative approach using the case study method was applied | Middle Eastern culture significantly influences ISM. Security culture and awareness significantly impact ISM. |
Lack of attention to cultural effects in current security practices | Generic SETA programs that do not consider specific industry needs | Lack of connection between culture and awareness programs in ISM implementation |
| Alyami et al. (2024) | The study utilized a systematic inductive approach for concept development. Data was collected through semi-structured interviews with 20 key informants from various geographic locations |
11 critical success factors (CSFs) for Security Education, Training and Awareness (SETA) program effectiveness were identified. Relationships between the CSFs within and across the lifecycle phases were highlighted |
The research contributes to the first comprehensive conceptualization of the CSFs for SETA program effectiveness | The absence of empirical studies on the critical success factors for SETA program effectiveness motivated the study | The questionable effectiveness of SET SETA programs at changing employee behavior drove the investigation [ |
| Yaokumah et al.(2019) | The study utilized survey data from employees across five major industry sectors and employed structural equation modeling via SmartPLS 3.0 for analysis | Employee security training indirectly influences security behavior through its impact on employee relations, monitoring, and accountability | The study highlights the lack of consideration for the mediating role of employee relations, monitoring, and accountability in the relationship between security training and security behavior. | Previous studies have primarily focused on the direct effects of security training on behavior, neglecting the indirect effects mediated by employee relations, monitoring, and accountability. | The research aims to address the gap in understanding the comprehensive impact of security training on employee security behavior by considering the mediating factors of employee relations, monitoring, and accountability |
| Author | Methodology | Finding | Theoretical gap | Empirical gap | Problem |
| Addae & Simpson( 2019) | Data was collected from 329 employees in the top-performing banks in Ghana and analyzed using PLS-SEM | Security education training, top-management's commitment, and peer non-compliance behavior influence the information security climate. Information security climate, punishment severity, and certainty of deterrent influence employees' intention to comply with ISP |
The study examines information security compliance from the perspective of general deterrence theory and information security climate, addressing gaps in understanding ISP compliance | The study contributes empirical evidence on the factors influencing information security policy compliance behavior in organizations, particularly in the banking sector in Ghana | Organizations face challenges in understanding and improving employees' compliance with information security policies, given the identified weaknesses in internal employee behavior leading to security breaches |
| Sarmoen et al.(2019) | The research methodology involves identifying factors related to human behavior that led to information breaches. The study aims to understand the root causes of confidential information leakages through individual attitudes, awareness programs, and management efforts |
The study aims to fill the gap in understanding the severity of factors influencing information leakages. The research hypotheses propose significant relationships between behavior, awareness programs, understanding of law and policy, and management roles in protecting information security |
The theoretical model proposed highlights the influence of behavior, awareness programs, understanding of law and policy, and management roles on information security compliance | The research aims to enhance awareness and knowledge regarding information security among employees and cultivate a culture of safeguarding confidential information in the workplace | The study addresses the lack of understanding of information policy, training, poor management support, and staff insensitivity towards safeguarding information as factors leading to information breaches |
Discussion
| Author | Methodology | Finding | Theoretical gap | Empirical gap | Problem |
| Rusetskaya (2023) | The article analyzes the concept of compliance and its main components in the context of information security | The article discusses the advantages of automated compliance over traditional methods and provides examples of existing developments in compliance automation. | The article does not explicitly mention a theoretical gap in the study of compliance in information security. | The article does not explicitly mention an empirical gap in the study of compliance in information security | The main focus of the article is on studying the organization of compliance in ensuring information security, the tasks of compliance control in Russian organizations, and the importance of compliance automation in information security. |
| Amankwa et al.( 2022) | The study collected data from 313 employees in Ghana using a questionnaire | Individual accountability measures had varying effects on employees' attitudes towards information security policy compliance, with a significant combined effect observed | Previous research lacked consideration of the combined impact of organizational and behavioral factors on establishing an information security policy compliance culture | Prior to this study, there was a gap in understanding how organizational and behavioral factors together influence compliance with information security policies in organizations | The research aimed to address non-compliance with information security policies by examining the effects of organizational and behavioral factors on establishing a culture of compliance in organizations |
| Asfoor et al.( 2022) | The authors used grounded theory in a comprehensive literature review | Compliance increased for both internal and external causes, as well as for protection. The outcomes showed that the procedures currently used to ensure compliance are inadequate |
The literature lacks a complete grasp of the elements that change employees' non-compliance to compliance | The research investigated an ISP's PMT and IT vision conflict, studying IT vision conflict mediation's impact on PMT components and ISP noncompliance attitudes | Most security professionals develop information security policies generically, leading to non-compliance |
| Nord et al. (2022) | The study utilized an instrument with 5 constructs administered electronically to employees in the U.S.A. | Supportive organizational culture and role values were the most influential predictors of ISP compliance. | The study aimed to build on the existing literature on ISP compliance by creating a prediction model with specific predictor variables. | The research analyzed data using multiple regression analysis to determine the significance of the predictor variables in predicting ISP compliance. | The study sought to identify which predictor variables, including leadership, engagement, supportive organizational culture, and role values, were most influential in predicting ISP compliance |
| A. Alzahrani et al.( 2018) | The study utilized self-determination theory (SDT) to investigate employees' information security policy (ISP) compliance intentions | Autonomy, competence, and relatedness positively affect employees' intentions to comply with ISP. Perceived value congruence had a negative effect on ISP compliance intentions The perceived legitimacy construct did not affect employees' intentions to comply with ISP |
The study highlights the value of SDT in researching employees' ISP compliance intentions | The research provides empirical support for the model through data obtained from a survey in a Fortune 600 organization in Saudi Arabia | Investigating the role of intrinsic motivation towards policy compliance in the organization was the main focus of the study |
| Author | Methodology | Finding | Theoretical gap | Empirical gap | Problem |
| Chin & Chua (2021) | The study applies the Theory of Interpersonal Behavior (TIB) to predict Information Security Policy (ISP) compliance in a Malaysian context | Government effectiveness significantly influences ISP compliance, and TIB shows strong explanatory power in predicting ISP compliance | Previous studies did not explore the role of government effectiveness in enforcing data protection regulations on individuals' intention to comply with ISP, creating a theoretical gap | The integration of government effectiveness with TIB to explain ISP compliance in a Malaysian context represents an empirical gap that this study aims to address. | Employees' compliance with ISP is crucial for minimizing information security threats, and understanding the factors influencing ISP compliance behavior is a major concern for organizations. |
| J. Kim & Mou(2020) | The research employed Two-Stage Structural Equation Modeling to investigate factors influencing information security policy compliance behavior based on TPB | All three factors of TPB significantly influenced behavioral intention, with overall fit indices of the structural model exhibiting a satisfactory level | The research aimed to fill the gap in understanding the factors influencing information security policy compliance behavior based on TPB through meta-analysis | The research aimed to fill the gap in understanding the factors influencing information security policy compliance behavior based on TPB through meta-analysis | The study addressed the critical need to understand and improve information security policy compliance behavior in organizations with the widespread use of information technologies |
| Trang & Brendel,( 2019) | The study utilized a random-effects model to control for sampling and measurement errors | Sanctions have an overall effect on deviant behavior, with contextual factors influencing this relationship. Deterrence theory better predicts deviant behavior in malicious contexts, high power distance cultures, and high uncertainty avoidance cultures |
The study highlights the importance of contextual and methodological moderators in understanding deterrence theory in information security policy compliance research | The analysis reveals no significant differences between scenario-based and behavior-specific measurement methods in deterrence studies | The research aims to examine the applicability of deterrence theory in information security policy compliance and address inconsistencies in empirical findings |
| Kajtazi et al. (2021) | The study reviews 11 theories related to information security behavior models and empirically compares them in Study. The unified model of information security policy compliance (UMISPC) is proposed and empirically tested in Study 2 |
Preliminary empirical support for the UMISPC model was provided in Study 2 | The UMISPC aims to examine the similarities and differences in constructs across existing models in information security behavior research | Future research is needed to determine the extent to which the UMISPC can explain different types of information systems security behaviors and violations | The UMISPC is intended to inspire further research to theorize and demonstrate differences between rival theories in the information systems security context that are not currently captured by existing measures |
| Njenga & Lowry( 2018) | Qualitative Grounded Theory approach is used to examine causes of violations and generate unique insights on intent | Identified counterfactual balances of norms, commitment, and attachment leading to tensions and IS policy violations | Emphasis on 'intent' of violations rather than 'effect' in information security policy violations research | Lack of cognitive consonance, relational imbalance, and unstable disposition identified as outcomes of counterfactual balances | Employees often do not follow recommended information security policies despite awareness levels, leading to violations |
| Nasir et al.(2017) | The paper proposed a conceptual framework for Information Security Policy (ISP) compliance behavior based on seven comprehensive dimensions of Information Security Culture (ISC) and integrates the Theory of Planned Behavior | The framework aims to provide a deeper understanding of the relationship between ISC and ISP compliance behavior | Addresses the lack of a comprehensive framework integrating ISC dimensions and behavioral theory in the context of ISP compliance | Seeks to enhance the accuracy of findings on ISC's influence on ISP compliance behavior through the proposed multidimensional ISC framework | Emphasizes the importance of employees' adherence to ISP for reducing information security risks and highlights the influence of ISC on ISP compliance |
| Yazdanmehr & Wang (2016) | The paper proposed a conceptual framework for Information Security Policy (ISP) compliance behavior based on seven comprehensive dimensions of Information Security Culture (ISC) and integrates the Theory of Planned Behavior | The framework aims to provide a deeper understanding of the relationship between ISC and ISP compliance behavior | Addresses the lack of a comprehensive framework integrating ISC dimensions and behavioral theory in the context of ISP compliance | Seeks to enhance the accuracy of findings on ISC's influence on ISP compliance behavior through the proposed multidimensional ISC framework | Emphasizes the importance of employees' adherence to ISP for reducing information security risks and highlights the influence of ISC on ISP compliance |
Conclusions
- Investigating how organizational context factors such as industry, size, and security maturity might moderate the ISPC-security breach relationship.
- Research comparing the relative effectiveness of different ISPC enhancement strategies (e.g. training, incentives, enforcement) in driving behavioral change and security outcomes.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis of ISPC: Future research could focus on conducting comprehensive cost-benefit analyses to determine the financial implications of implementing various ISPC measures and their return on investment.
- The majority of this review are quantitative studies in the future research qualitative studies to gain deeper insights into the social, psychological, and organizational dynamics underlying employee security behaviors and ISPC.
Supplementary Materials
References
- S. Hina and P. D. D. Dominic, “Information security policies’ compliance: a perspective for higher education institutions,” J. Comput. Inf. Syst., vol. 60, no. 3, pp. 201–211, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Angraini, R. A. Alias, and Okfalisa, “Affecting Factors in Information Security Policy Compliance: Combine Organisational Factors and User Habits,” Lect. Notes Data Eng. Commun. Technol., vol. 72, no. Bongiovanni 2019, pp. 826–836, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. F. Ali, P. D. D. Dominic, S. E. A. Ali, M. Rehman, and A. Sohail, “Information security behavior and information security policy compliance: a systematic literature review for identifying the transformation process from noncompliance to compliance,” Appl. Sci., vol. 11, no. 8, 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Rostami, F. Karlsson, and S. Gao, “Policy components – a conceptual model for modularizing and tailoring of information security policies,” Inf. Comput. Secur., vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 331–352, 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Höne and J. H. P. Eloff, “What makes an effective information security policy?,” Netw. Secur., vol. 2002, no. 6, pp. 14–16, 2002. [CrossRef]
- A. Ahmad, K. C. Desouza, S. B. Maynard, H. Naseer, and R. L. Baskerville, “How integration of cyber security management and incident response enables organizational learning,” J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol., vol. 71, no. 8, pp. 939–953, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Shah and B. M. Mehtre, “An overview of vulnerability assessment and penetration testing techniques,” J. Comput. Virol. Hacking Tech., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 27–49, 2015. [CrossRef]
- C. S. Jackson, “CYBERSECURITY POLICY: EXPLORING LEADERSHIP STRATEGIES THAT INFLUENCE INSIDER COMPLIANCE,” 2017.
- Q. Hu, T. Dinev, P. Hart, and D. Cooke, “Managing Employee Compliance with Information Security Policies: The Critical Role of Top Management and Organizational Culture,” Decis. Sci., vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 615–660, 2012. [CrossRef]
- T. Stefaniuk, “Training in shaping employee information security awareness,” Entrep. Sustain. Issues, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 1832–1846, 2020. [CrossRef]
- B. Zheng, D. Tse, J. Ma, X. Lang, and Y. Lu, “An Empirical Study of SETA Program Sustaining Educational Sector’s Information Security vs. Information Systems Misuse,” Sustain., vol. 15, no. 17, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. A. Hamid and N. R. S. M. Dali, “Empirical Study on the Influence of Security Control Management and Social Factors in Deterring Information Security Misbehaviour,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., vol. 1551, no. 1, 2020. [CrossRef]
- D. Sikolia and B. Biros, “Motivating Employees to Comply with Information Security Policies,” J. Midwest Assoc. Inf. Syst., vol. 2016, no. 2, pp. 7–25, 2016. [CrossRef]
- D. Lee, H. S. Lallie, and N. Michaelides, “The impact of an employee’s psychological contract breach on compliance with information security policies: intrinsic and extrinsic motivation,” Cogn. Technol. Work, vol. 25, no. 2–3, pp. 273–289, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. J. Li and E. Hoffman, “Designing an incentive mechanism for information security policy compliance: An experiment,” J. Econ. Behav. Organ., vol. 212, pp. 138–159, 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. J. Zandona and J. M. Thompson, “Going beyond Compliance: A Strategic Framework for Promoting Information Security in Hospitals,” Health Care Manag. (Frederick)., vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 364–371, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Jalali and J. P. Kaiser, “Cybersecurity in hospitals: A systematic, organizational perspective,” J. Med. Internet Res., vol. 20, no. 5, 2018. [CrossRef]
- P. Jeremiah, G. N. Samy, B. Shanmugam, K. Ponkoodalingam, and S. Perumal, Potential measures to enhance information security compliance in the healthcare internet of things, vol. 843. Springer International Publishing, 2019.
- H. Li, S. Yoo, and W. J. Kettinger, “The Roles of IT Strategies and Security Investments in Reducing Organizational Security Breaches,” J. Manag. Inf. Syst., vol. 38, no. 1, pp. 222–245, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. I. Albarrak, “Evaluation of Users Information Security Practices at King Saud University Hospitals.,” Glob. Bus. Manag. Res., vol. 3, no. 1, p. 1, 2011.
- E. H. Yuanxiang John Li a, “Designing an incentive mechanism for information security policy compliance: An experiment,” J. Econ. Behav. Organ., 2023.
- J. A. Addae and G. Simpson, “Factors Influencing Information Security Policy Compliance Behavior,” 2019 Int. Conf. Cyber Secur. Internet Things, pp. 43–47, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Angraini, R. A. Alias, and Okfalisa, “Information Security Policy Compliance: An Exploration of User Behaviour and Organizational Factors,” Lect. Notes Data Eng. Commun. Technol., vol. 127, pp. 641–650, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Y. Chin and H. N. Chua, “Using the theory of interpersonal behavior to predict information security policy compliance,” 2021 8th Int. Conf. eDemocracy eGovernment, ICEDEG 2021, pp. 80–87, 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Amankwa, M. Loock, and E. Kritzinger, “The determinants of an information security policy compliance culture in organisations: the combined effects of organisational and behavioural factors,” Inf. Comput. Secur., vol. 30, no. 4, pp. 583–614, 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Alzahrani and K. P. Seth, “The impact of organizational practices on the information security management performance,” Inf., vol. 12, no. 10, 2021. [CrossRef]
- T. Assefa and A. Tensaye, “Factors influencing information security compliance: an institutional perspective,” SINET Ethiop. J. Sci., vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 108–118, 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. J. Knapp, T. E. Marshall, R. K. Rainer, and F. N. Ford, “Information security: Management’s effect on culture and policy,” Inf. Manag. Comput. Secur., vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 24–36, 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. Choi, “Leadership of information security Manager on the effectiveness of information systems security for secure sustainable computing,” Sustain., vol. 8, no. 7, 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Hu, C. Hsu, and Z. Zhou, “Understanding employees’ perceptions of SETA events: the role of pedagogical and communication approaches,” Internet Res., vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 294–319, 2024. [CrossRef]
- H. Heyasat, S. Mubarak, and N. Evans, “Security Culture and Security Education, Training and Awareness (SETA) Influencing Information Security Management,” Lect. Notes Networks Syst., vol. 721 LNNS, pp. 332–343, 2023. [CrossRef]
- O. de Casanove, N. Leleu, and F. Sèdes, “Applying PDCA to Security, Education, Training and Awareness Programs,” IFIP Adv. Inf. Commun. Technol., vol. 658 IFIP, pp. 39–48, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Yaokumah, D. O. Walker, and P. Kumah, “SETA and Security Behavior,” J. Glob. Inf. Manag., vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 102–121, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Alyami, D. Sammon, K. Neville, and C. Mahony, “The critical success factors for Security Education, Training and Awareness (SETA) program effectiveness: a lifecycle model,” Inf. Technol. People, vol. 36, no. 8, pp. 94–125, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. L. Kim, H. B. S. Choi, and J. Han, “Leader power and employees’ information security policy compliance,” Secur. J., vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 391–409, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. I. Merhi and V. Midha, “The impact of training and social norms on information security compliance: A pilot study,” Int. Conf. Inf. Syst. ICIS 2012, vol. 5, pp. 4183–4193, 2012.
- N. A. A. Md Azmi, A. P. Teoh, A. Vafaei-Zadeh, and H. Hanifah, “Predicting information security culture among employees of telecommunication companies in an emerging market,” Inf. Comput. Secur., vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 866–882, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Asker and A. Tamtam, “An Investigation of the Information Security Awareness and Practices among Third Level Education Staff, Case Study in Nalut Libya,” Eur. Sci. J. ESJ, vol. 16, no. 15, pp. 20–32, 2020. [CrossRef]
- N. Sarmoen, H. Khalid, S. Z. Abd Rasid, S. A L Baskaran, and R. Basiruddin, “Understanding Human Behaviour in Information Security Policy Compliance in a Malaysian Local Authority Organization,” Bus. Manag. Strateg., vol. 10, no. 2, p. 64, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Tsohou and M. Karyda, “Information Security Policy Compliance Competences,” Encycl. Cryptogr. Secur. Priv., vol. 50011, pp. 1–3, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Alotaibi, S. Furnell, and N. Clarke, “Information security policies: A review of challenges and influencing factors,” 2016 11th Int. Conf. Internet Technol. Secur. Trans. ICITST 2016, pp. 352–358, 2017. [CrossRef]
- E. Amankwa, M. Loock, and E. Kritzinger, “Information security policy compliance culture: Examining the effects of accountability measures,” Int. J. Technol. Hum. Interact., vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 75–91, 2021. [CrossRef]
- D. Sikolia, “A Thematic Review of User Compliance With Information Security Policies Literature,” J. Digit. Forensics, Secur. Law, no. 2, pp. 101–104, 2013, [Online]. Available: http://search.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.liv.ac.uk/login.aspx?direct=true&db=tsh&AN=92505415&site=eds-live&scope=site.
- D. Olifer, N. Goranin, A. Kaceniauskas, and A. Cenys, “Controls-based approach for evaluation of information security standards implementation costs,” Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ., vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 196–219, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. Rusetskaya, “Compliance in Information Security,” RSUH/RGGU Bull. Ser. Inf. Sci. Inf. Secur. Math., no. 2, pp. 70–80, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Chen, M. Liu, and T. Lyu, “Understanding employees’ information security–related stress and policy compliance intention: the roles of information security fatigue and psychological capital,” Inf. Comput. Secur., vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 751–770, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. H. Asfoor, H. Kasim, A. B. A. Latif, R. A. Razali, Z.-A. Ibrahim, and A. Shanneb, “Identifying Factors of Non-Compliance, Compliance with Information Security Policy, and Behavior Change to Compliance: Literature Review,” J. Hunan Univ. Nat. Sci., vol. 49, no. 12, pp. 274–288, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Brunel, F. Cuppens, N. Cuppens, T. Sans, and J. P. Bodeveix, “Security policy compliance with violation management,” FMSE’07 - Proc. 2007 ACM Work. Form. Methods Secur. Eng., pp. 31–40, 2007. [CrossRef]
- Nord, C. S. Sargent, A. Koohang, and A. Marotta, “Predictors of Success in Information Security Policy Compliance,” J. Comput. Inf. Syst., vol. 62, no. 4, pp. 863–873, 2022. [CrossRef]
- P. Kuppusamy et al., “Systematic Literature Review of Information Security Compliance Behaviour Theories,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., vol. 1551, no. 1, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Alexei, P. Nistiriuc, and A. Alexei, “ANALYSIS OF SECURITY FRAMEWORKS IMPLEMENTED IN HEI’s,” InterConf, pp. 347–359, 2021. [CrossRef]
- D. Zellhofer, “Information security policies in organizations: How convention theory can serve as a framework to inform information security research and HR practice,” Lect. Notes Inf. Syst. Organ., vol. 28, pp. 49–62, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Y. Kurii and I. Opirskyy, “Analysis and Comparison of the NIST SP 800-53 and ISO/IEC 27001:2013,” CEUR Workshop Proc., vol. 3288, pp. 21–32, 2022.
- A. M. K. Erick. O. Otieno, Agnes N. Wausi, “A Theoretical Model For Information Security Policy Compliance Culture,” Int. J. Appl. Inf. Syst., vol. 12, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Al-Omari, A. Deokar, O. El-Gayar, J. Walters, and H. Aleassa, “Information security policy compliance: An empirical study of ethical ideology,” Proc. Annu. Hawaii Int. Conf. Syst. Sci., pp. 3018–3027, 2013. [CrossRef]
- H. Lee, E. Kwon, K. Yoo, and S. Chai, “An impact of information security investment on information security incidents: A case of Korean organizations,” ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser., vol. 17-19-Augu, 2016. [CrossRef]
- H. Očevčić, K. Nenadić, K. Šolić, and T. Keser, “The impact of information system risk management on the frequency and intensity of security incidents,” Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. Syst., vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 41–46, 2017. [CrossRef]
- G. O. M. Yee, “Towards Reducing the Impact of Data Breaches,” Fourteenth Int. Conf. Emerg. Secur. Information, Syst. Technol., no. c, pp. 75–81, 2020.
- E. K. Eric Amankwa, Marianne Loock, “Establishing information security policy compliance culture in organizations,” Inf. Comput. Secur., vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 302–316, 2018.
- Chen, Z. Xie, J. Zhen, and K. Dong, “The Impact of Challenge Information Security Stress on Information Security Policy Compliance: The Mediating Roles of Emotions,” Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag., vol. 15, no. April, pp. 1177–1191, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Chen, “Information security management: compliance challenges and new directions,” J. Inf. Technol. Case Appl. Res., vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 243–249, 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Amankwa, M. Loock, and E. Kritzinger, “Information Security Policy Compliance Culture: Examining the Effects of Accountability Measures,” Int. J. Technol. Hum. Interact., vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 75–91, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Hong and M. Xu, “Autonomous motivation and information security policy compliance: Role of job satisfaction, responsibility, and deterrence,” J. Organ. End User Comput., vol. 33, no. 6, 2021. [CrossRef]
- F. Ghannoo and A. Chiniah, “A Multi-Theory Model to evaluate new factors influencing Information Security Compliance,” Int. J. Secur. Networks, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 1, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Onumo, I. Ullah-Awan, and A. Cullen, “Assessing the Moderating Effect of Security Technologies on Employees Compliance with Cybersecurity Control Procedures,” ACM Trans. Manag. Inf. Syst., vol. 12, no. 2, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Paliszkiewicz, “Information Security Policy Compliance: Leadership and Trust,” J. Comput. Inf. Syst., vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 211–217, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Alyami, D. Sammon, K. Neville, and C. Mahony, “Critical success factors for Security Education, Training and Awareness (SETA) programme effectiveness: an empirical comparison of practitioner perspectives,” Inf. Comput. Secur., vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 53–73, 2024. [CrossRef]
- S. MERAL and H. İ. BÜLBÜL, “Kamu Kurumlarının Bilgi Güvenliği Politikalarının Kurumsal Bilgi Güvenliğinin Sağlanması Açısından Etkinliğinin Analiz Edilmesi,” Gazi Üniversitesi Fen Bilim. Derg. Part C Tasarım ve Teknol., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 314–329, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Alzahrani, C. Johnson, and S. Altamimi, “Information security policy compliance: Investigating the role of intrinsic motivation towards policy compliance in the organisation,” 2018 4th Int. Conf. Inf. Manag. ICIM 2018, pp. 128–132, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Kim and J. Mou, “Meta-analysis of Information Security Policy Compliance Based on Theory of Planned Behavior,” J. Digit. Converg., vol. 18, no. 11, pp. 169–176, 2020, [Online]. Available: . [CrossRef]
- S. Trang and B. Brendel, “A Meta-Analysis of Deterrence Theory in Information Security Policy Compliance Research,” Inf. Syst. Front., vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 1265–1284, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Kajtazi, S. Sarker, B. Johansson, N. Holmberg, C. Keller, and O. Tona, “Toward a Unified Model of Information Security Policy Compliance: A Conceptual Replication Study,” AIS Trans. Replication Res., vol. 7, pp. 1–15, 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. Njenga and P. B. Lowry, “Information security policy violations: A Grounded Theory approach to counterfactual balance and tensions,” Proc. Dewald Roode Work. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2018, pp. 14–15, 2018.
- A. Nasir, R. A. Arshah, and M. R. Ab Hamid, “Information security policy compliance behavior based on comprehensive dimensions of information security culture: A conceptual framework,” ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser., vol. Part F1282, pp. 56–60, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Yazdanmehr and J. Wang, “Employees’ information security policy compliance: A norm activation perspective,” Decis. Support Syst., vol. 92, pp. 36–46, 2016. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





