Submitted:
22 September 2024
Posted:
24 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
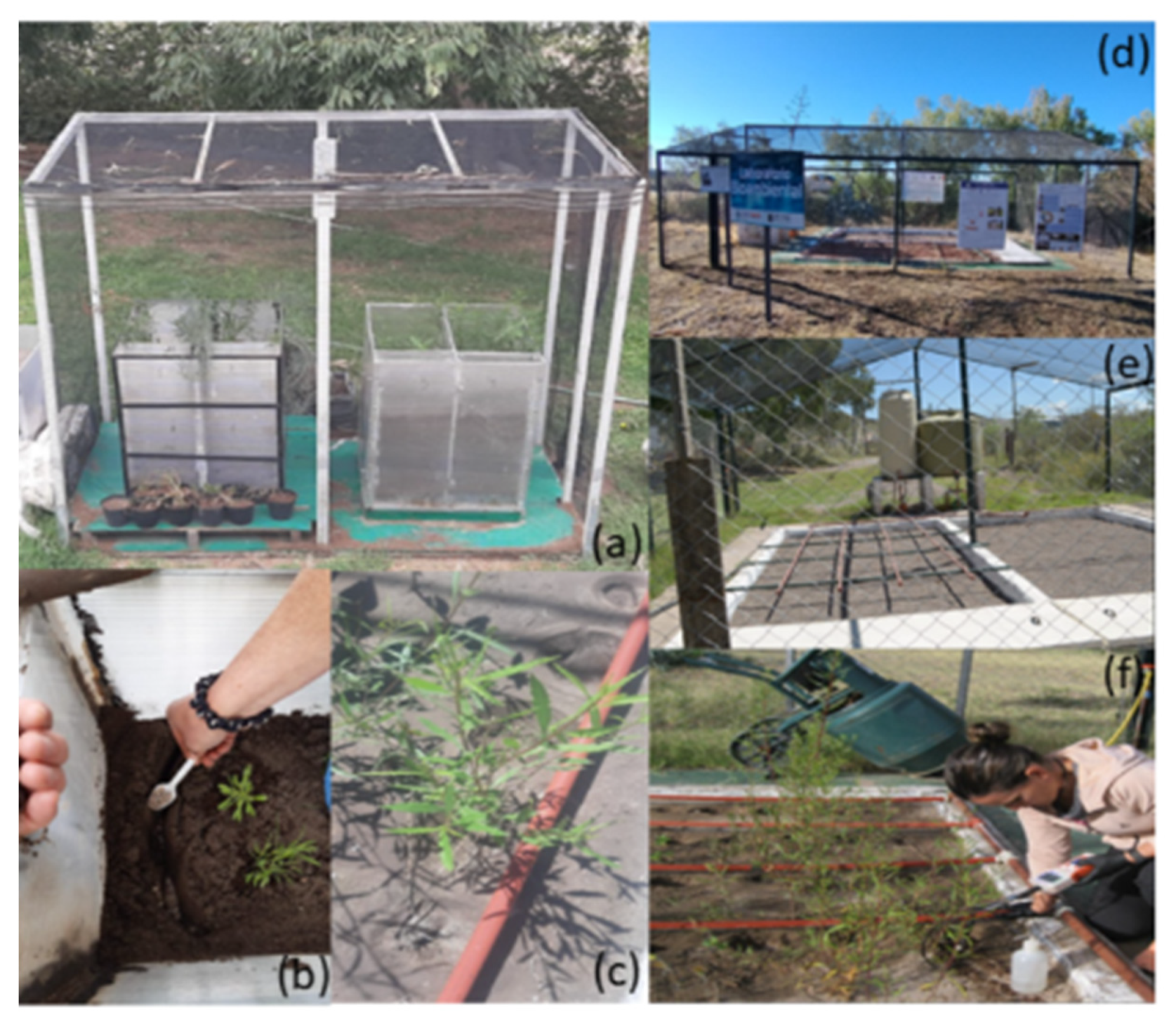
2.1. Mycorrhizal-Assisted Phytomanagement (MAPm) System
2.2. Scale-up of TRL 6, Bioreactors (TRL 4) and Vegetable Depuration Module (VDM)
2.2.1. Experiment in Bioreactors
2.2.2. Potential Scaling up of BRs to the Vegetable Depuration Module (VDM)
2.2.3. Hydraulic Calibration
- type of water entry in irrigation
- income flow (Qi)
- egress flow (Qe)
- average Qi and Qe (Q)
- liquid retention time before the exit to the collecting chamber (tc)
- permeability constant (Ks) of the stone filter and soil substrate
- the volume of the soil substrate (last layer with the soil)
- stone filter volume
- water holding capacity (WHC)
- porosity (φ)
- Darcy’s velocity (VD)
- average linear velocity (Va)
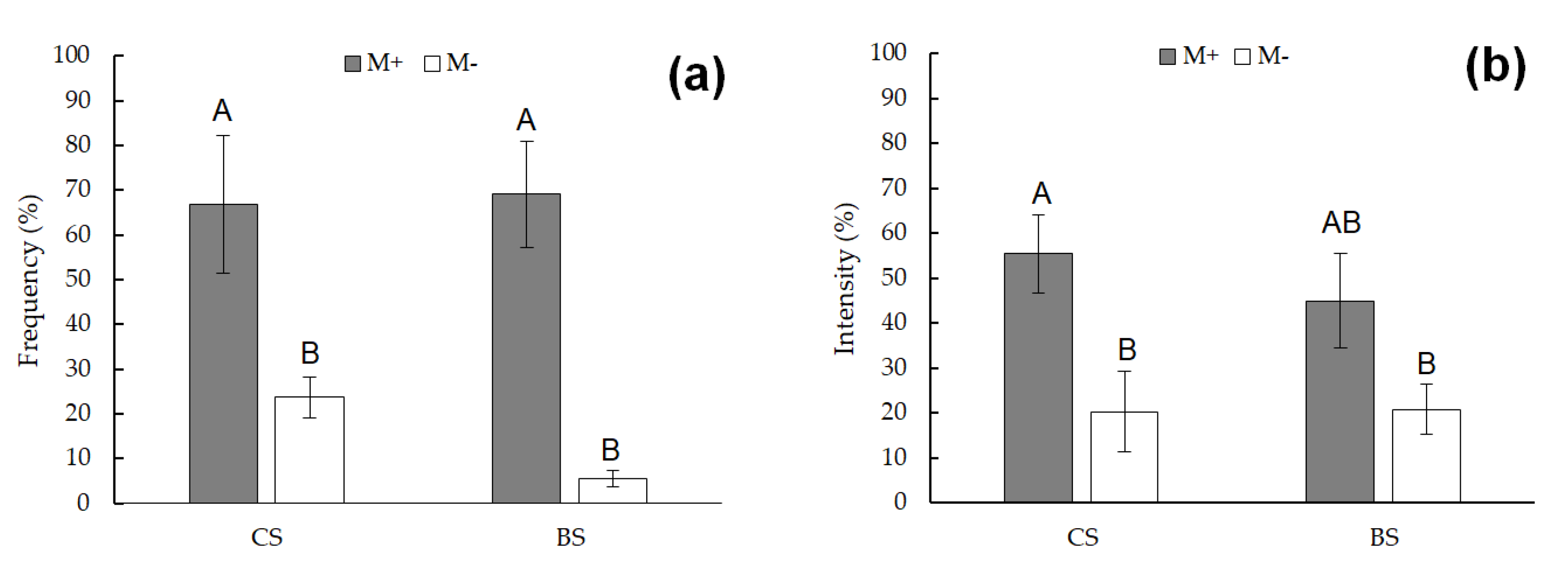
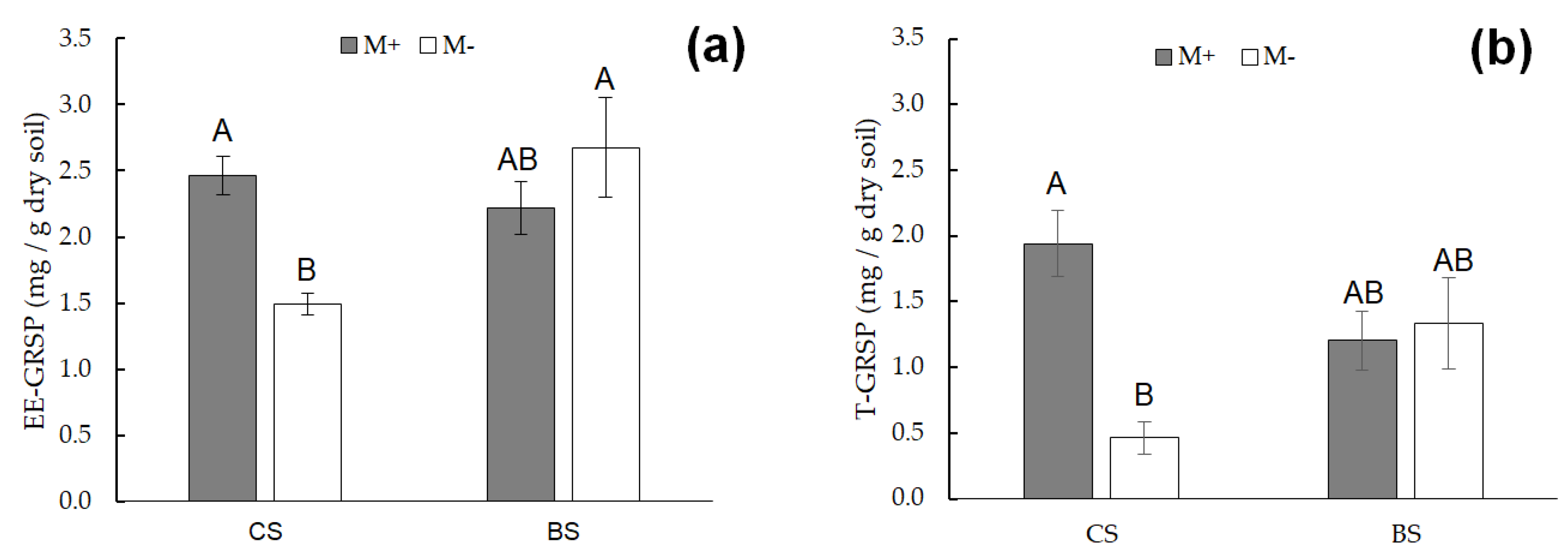
2.3. AM Fungal Parameters
2.4. Chemical Determinations
2.5. Phytomanagement Parameters Calculation
2.6. Data Analysis
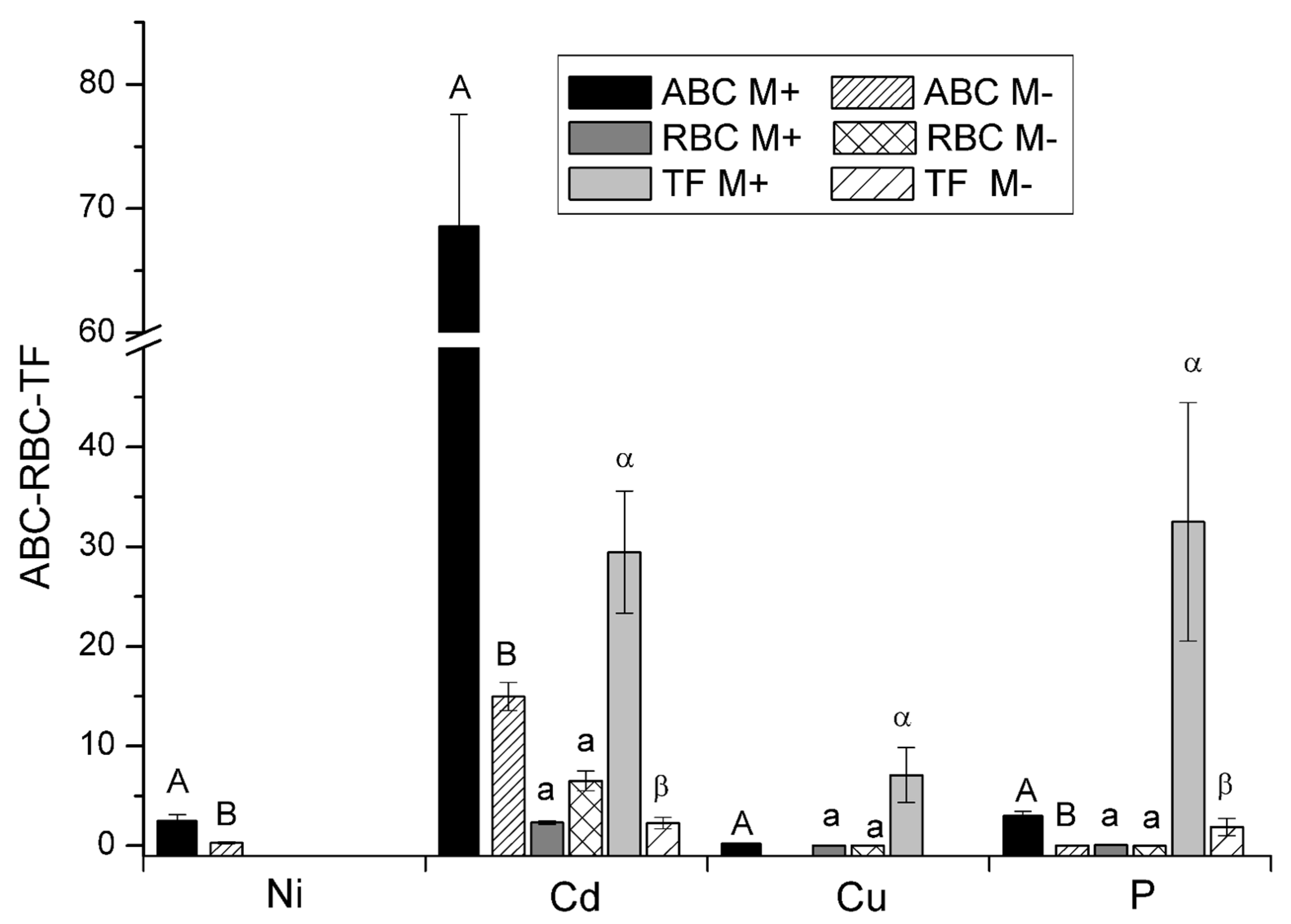
3. Results
| CRM and SRM | Concentration | Bioextractive Potential | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoots* - Roots (ppm) |
Mass/plant (mg) |
Total/ BR (mg) |
Total/VDM (g) |
|
| Ni | 16.32* | 16.32 | 11.63 | 1.16 |
| Cd | 153.69*-5.21 | 8.12 | 97.5 | 9.75 |
| Cu | 37.27* - 5.46 | 2.00 | 24.00 | 2.40 |
| P | 3358.52*-103.9 | 177.6 | 2131 | 213.1 |
| Qi (m3/d) |
Qe (m3/d) |
Q (m3/d) |
Ks (m3/d/m2) |
Tc (seg) |
VD (m/d) |
Va (m/d) |
φ | WHC (kg) |
pH | Eh | GRSP T (g) EE (g) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR | 2.64 | 0.83 | 1.74 | 192.9 | 32 | 11.57 | 28.94 | 0.4 | 0.14 | 7.1 | 256 | 0.054 | 0.071 |
| VDM | 264 | 83 | 174 | 193 | 3200 | 11.57 | 28.94 | 0.4 | 14 | 7.1 | 225 | 5641 | 7150 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ubaldini, S.; Guglietta, D.; Vegliò, F.; Giuliano, V. Valorization of Mining Waste by Application of Innovative Thiosulphate. Leaching for Gold Recovery. Metals 2019, 9, 274 (1-12) . [CrossRef]
- Guglietta, D.; Belardi, G.; Cappai, G.; Casentini, B.; Godeas, A.; Milia, S.; Passeri, D.; Salvatori, R.; Scotti, A.; Silvani, V. Toward a Multidisciplinary Strategy for the Classification and Reuse of Iron and Manganese Mining Wastes. Chem. J. Mold 2020, 15, 21–30.
- European Commission, Directorate-General for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs, Grohol, M., Veeh, C., Study on the critical raw materials for the EU 2023 – Final report, Publications Office of the European Union. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2873/725585. Accessed on 12 September 2024. [CrossRef]
- Scotti, A.; Silvani, V.; Milia, S.; Cappai, G.; Ubaldini, S.; Ortega, V.; Colombo, R.; Godeas, A.; Gómez, M. Chapter title: Scale-up of Mycorrhizal-Assisted Phytoremediation (MAPm) system from TRL6 to TRL 7: cost-benefits within a circular economy context. In book title: Soil Science - Emerging Technologies, Global Perspectives and Applications. Aide, M. and Braden, I. Publisher: IntechOpen, London, United Kingdom, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Advanced Materials Initiative. Available online:https://www.ami2030.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Ami2030-Dossier-2.pdf Accessed on 12 September 2024.
- Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A. European development trends in innovative advanced materials area. International Scientific Journal Innovations 2024,2,36-39.
- Dinh, T.; Dobo, Z.; Kovacs, H. Phytomining of noble metals—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131805 (1-14). [CrossRef]
- Ubaldini, S.; Guglietta, D.; Trapasso, F.; Carloni, S.; Passeri, D.; Scotti, A. Treatment of Secondary Raw Materials by Innovative Processes. Chem. J. Mold. 2019, 14, 32–46. [CrossRef]
- 9. COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) 2023/915 of April 25 2023 on maximum levels for certain contaminants in food and repealing Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32023R0915. Accessed on 12 September 2024.
- Fontagro. Bioproceso reductor de la solubilidad del cadmio (Cd) rizosférico. Available online: https://www.fontagro.org/new/proyectos/bioproceso-cd/es. Accessed on 12 September 2024.
- Ofori-Agyemang, F.; Burges, A.; Waterlot, C.; Lounès-Hadj Sahraoui; A.; Tisserant, B.; Mench, M.; Oustrière, N. Phytomanagement of a metal-contaminated agricultural soil with Sorghum bicolor, humic/fulvic acids and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi near the former Pb/Zn metaleurop Nord smelter. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142624. [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Bhandari, P. Cadmium toxicity in crop plants and its alleviation by arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi: An overview. Plant Biosystems - An International Journal Dealing with all Aspects of Plant Biology 2014, 148(4), 609-621. [CrossRef]
- Ubaldini, S. Advanced Technologies in Bio/Hydrometallurgy for Recovery and Recycling of Metals. Metals 2023, 13, 1105. [CrossRef]
- Ubaldini, S. Leaching Kinetics of Valuable Metals. Metals 2021, 11, 173. [CrossRef]
- Seuring, S.; Müller, M. From a literature review to a conceptual framework for sustainable supply chain management. Journal of Cleaner Production 2008, 16(15),1699-1710. [CrossRef]
- Scotti, A.; Milia, S.; Silvani, V.; Cappai, G.; Guglietta, D.; Trapasso, F.; Tempesta, E. ;Passeri, D.; Godeas, A.; Gómez, M.; Ubaldini, S. Sustainable Recovery of Secondary and Critical Raw Materials from Classified Mining Residues Using Mycorrhizal-Assisted Phytoextraction. Metals 2021, 11(8), 1163. [CrossRef]
- Scotti, A.; Silvani, V.A.; Juarez, N.A.; Godeas, A.M.; Ubaldini, S. The Role of Mycorrhizal-Assisted Phytomining in the Recovery of Raw Materials from Mine Wastes. Metals 2022, 12(11), 1828. [CrossRef]
- FAO, UN Water. Progress on the Level of Water Stress: Global Status and Acceleration Needs for SDG Indicator 6.4.2; 444 FAO; United Nations Water (UN Water): Rome, Italy, 2021; p 95.
- Scotti, A.; Godeas, A.; Silvani, V. Procedimiento para Aumentar la Capacidad Biorremediadora de Plantas Hiperacumuladoras a Través de Hongos Formadores de Micorrizas Arbusculares (HMA) para Tratamiento de Suelos y/o Aguas Contaminados. Patent AR090183 B1130100620, 2022.
- Silvani, V.A.; Bidondo, L.F.; Bompadre, M.J.; Colombo, R.P.; Pérgola, M.; Bompadre, A.; Fracchia, S.; Godeas, A. Growth dynamics of geographically different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal isolates belonging to the ‘Rhizophagus clade’ under monoxenic conditions. Mycologia 2014, 106(5), 963-75. [CrossRef]
- Castaño, A.R.; Scotti, A.; Silvani, V.A.; Ubaldini, S.; Trapasso, F.; Tempesta, E.; Plá, R.R.; Giuffré, M.; Juarez, N.A.; Guglietta, D. Remote Sensing and Mycorrhizal-Assisted Phytoremediation for the Management of Mining Waste: Opportunities and Challenges to Raw Materials Supply. Minerals 2023, 13(6), 765. [CrossRef]
- Scotti, A.; Silvani, V.; Cerioni, J.; Visciglia, M.; Benavidez, M.; Godeas, A. Pilot testing of a bioremediation system for water and soils contaminated with heavy metals: vegetable depuration module. International Journal of Phytoremediation 2019, 21(9), 899-907. [CrossRef]
- Declerck, S.; D’Or, D.; Bivort, C.; De Souza, F.A. Development of extraradical mycelium of Scutellospora reticulata under root-organ culture: spore production and function of auxiliary cells. Mycological Research 2004, 108(1), 84-92. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; He, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Chu, G.; Tang, X. Accumulation of glomalin-related soil protein benefits soil carbon sequestration: Tropical coastal forest restoration experiences. Land Degradation & Development 2022, 33(10), 1541–1551. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, T.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Glomalin Play a Crucial Role in Soil Aggregate Stability in Pb-Contaminated Soil. IJERPH 2022, 19(9), 5029. [CrossRef]
- US EPA O. EPA Method 3050B: Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, and Soils. 2019. https://www.epa.gov/esam/epa-method-3050b-acid-digestion-sediments-sludges-and-soils. Accessed on 12 September 2024.
- US EPA O. SW-846 Test Method 3005A: Acid Digestion of Waters for Total Recoverable or Dissolved Metals for Analysis by Flame Atomic Absorption (FLAA) or Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) Spectroscopy. 2015. https://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-test-method-3005a-acid-digestion-waters-total-recoverable-or-dissolved-metals. Accessed on 12 September 2024.
- Zagal, E. and Sadzawka, A. Protocolo de métodos de análisis para suelos y lodos. Universidad de Concepción, Servicio Agrícola y Ganadero: Santiago, Chile, 2007, 10-18.
- Olsen SR. Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. US Department of Agriculture. 1954; 939, 18-19.
- Ibáñez, J. Niveles de madurez de la tecnología [Technology readiness levels: TRLS]: Una introducción. Econ. Indus 2014, 393, 165–171.
- Salas-Luévano, M.A.; Mauricio-Castillo, J.A.; González-Rivera, M.L.; Vega-Carrillo, H.R.; Salas-Muñoz, S. Accumulation and phytostabilization of As, Pb and Cd in plants growing inside mine tailings reforested in Zacatecas, Mexico. Environ Earth Sci. 2017, 76(23), 806. [CrossRef]
- Hard, H.R.; Brusseau, M.; Ramirez-Andreotta, M. Assessing the feasibility of using a closed landfill for agricultural graze land. Environ Monit Assess 2019, 191(7), 458. [CrossRef]
- Kadukova, J.; Manousaki, E.; Kalogerakis, N. Pb and Cd Accumulation and Phyto-Excretion by Salt Cedar (Tamarix Smyrnensis Bunge). International Journal of Phytoremediation 2008, 10(1), 31-46. [CrossRef]
- Colombo, R.P.; Silvani, V.A.; Benavidez, M.E.; Scotti, A.; Godeas, A.M. Different behavior of two strains of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus intraradices on Senecio bonariensis Hook. & Arn. against heavy metal soil pollution: a pilot-scale test. International Journal of Phytoremediation 2024, 26 (11), 1741–1748. [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Singh, S.; Kashyap, L. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Heavy Metal Tolerance in Plants: An Insight into Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms. In: Varma, A., Prasad, R., Tuteja, N. (eds) Mycorrhiza - Nutrient Uptake, Biocontrol, Ecorestoration, springer, Cham. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Haider, F.U.; Maqsood, M.F.; Mohy-Ud-Din, W.; Shabaan, M.; Ahmad, M.; Kaleem, M.; Ishfaq, M.; Aslam, Z.; Shahzad, B. Recent Advances in Microbial-Assisted Remediation of Cadmium-Contaminated Soil. Plants 2023, 12(17), 3147. [CrossRef]
- Herath, B.M.M.A.; Madushan, K.W.A.; Lakmali, J.P.D.; Yapa, P.N. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as a potential tool for bioremediation of heavy metals in contaminated soil. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews 2021, 10(03), 217–228. [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Polle, A.; Rennenberg, H.; Luo, Z-B. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of heavy metal accumulation in nonmycorrhizal versus mycorrhizal plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 1087–1103. [CrossRef]
- Ubaldini, S.; Povar, I.; Lupascu, T.; Spinu, O.; Trapasso, F.; Passeri, D.; Carloni, S.; Guglietta, D. Application of Innovative Processes for Gold Recovery from Romanian Mining Wastes. Chem. J. Mold. 2020, 15, 29–37. [CrossRef]
- Ubaldini, S.; Massidda, R.;Veglio’, F.; Beolchini, F. Gold stripping by hydro-alcoholic solutions from activated carbon: Experimental results and data analysis by a semi-empirical model. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 81, 40-44. [CrossRef]
- Luptakova, A.; Ubaldini, S.; Fornari, P.; Mačingova, E. Physical-chemical and biological-chemical methods for treatment of acid mine drainage. Chemical Engineering Transactions 2012, 28, 115-120. [CrossRef]
- Benavidez, M.E.; De La Fournière, E.M.; Colombo, R.P.; Silvani, V.A.; Debray, M.E.; Scotti, A.; Godeas, A.M. Micro PIXE mapping proves a differential distribution and concentration of trace elements in fungal structures of Rhizophagus intraradices. Fungal Biology 2024, 128(7), 2089-93. [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Castro, C.; Prieto-Fernández, A.; Alvarez-Lopez, V.; Monterroso, C.; Cabello-Conejo, M.I.; Acea, M.J.; Kidd, P.S. Nickel solubilizing capacity and characterization of rhizobacteria isolated from hyperaccumulating and non-hyperaccumulating subspecies of Alyssum serpyllifolium. Int J Phytoremediation 2011, 13 Suppl 1, 229-244. PMID: 22046762. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li; K.; Li, W.; Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ban, Y. The positive effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation and/or additional aeration on the purification efficiency of combined heavy metals in vertical flow constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2022, 29, 68950–68964. [CrossRef]
- Guittonny-Philippe, A.; Masotti, V.; Höhener, P.; Boudenne, J.L.; Viglione, J.; Laffont-Schwob, I. Constructed wetlands to reduce metal pollution from industrial catchments in aquatic Mediterranean ecosystems: A review to overcome obstacles and suggest potential solutions. Environment International 2014, 64, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Akratos, C.S.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Effect of temperature, HRT, vegetation and porous media on removal efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecological Engineering 2007, 29(2), 173-91. [CrossRef]
- Mena, J.; Rodriguez, L.; Nuñez, J.; Fernández, F.J.; Villaseñor, J. Design of horizontal and vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands treating industrial wastewater. Water Pollution IX 2008, 111, 555-564. [CrossRef]
- Husson, O. Redox potential (Eh) and pH as drivers of soil/plant/microorganism systems: a transdisciplinary overview pointing to integrative opportunities for agronomy. Plant Soil 2013, 362(1-2), 389-417. [CrossRef]
- Göhre, V.; Paszkowski, U. Contribution of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis to heavy metal phytoremediation. Planta 2006, 223(6), 1115-22. [CrossRef]

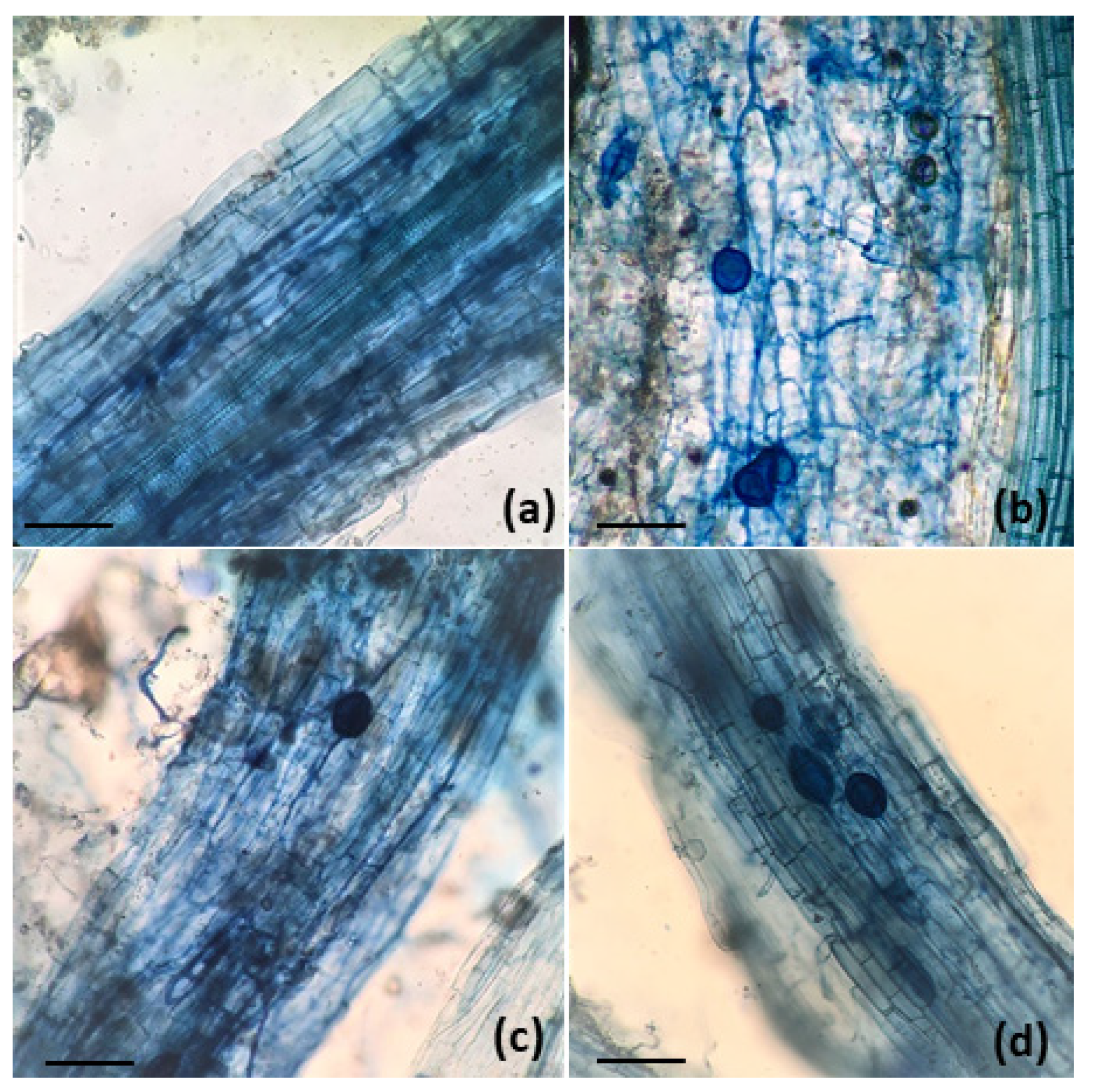
| Element | Essential | Natural sources | Anthropogenic sources | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arsenic | No | Dust storms. Volcanic eruptions. Geothermal/hydrothermal activity. Forest fires. Arsenic-rich minerals. |
Metal mining and smelting. Coal mining and burning of arsenic-rich coals. Pesticide. Timber industry. Pyrotechnics. |
Wood preservatives. Additive to veterinarian drugs (poultry). Doping agent in semiconductors. |
| Cadmium | No | Zinc and lead minerals. Phosphates rocks. |
Electroplating. Metal industry (non-ferrous metals and steel). Automobile exhaust. Phosphate mineral fertilizer |
Pigments in paints, ceramics, plastics, etc. Cd impurities in Zn coatings used on metal structures. |
| Chromium | Yes | Chromium minerals. | Metal industry. Electroplating. Industrial sewage. |
Electroplating. Metal alloys. Anticorrosive products. Pesticides, detergents |
| Cooper | Yes | Sulfides, oxides, carbonates | Domestic and industrial waste, mining waste, and manure (pig and poultry). Car breaks. Metal industry. Copper-based fungicides. |
Electric supplies, electric conductor. Electroplating. Fungicides. Plant residues treated with fungicides are used as soil amendments. Timber treatment chemicals. Copper piping and guttering. Vehicle brake linings. |
| Lead | No | Lead minerals | Battery manufacturing facilities. Private and industrial waste. Rifle ranges and military facilities. Leaded paints and leaded fuel addition. Insecticides. |
Batteries. Alloys, bullets, and other munitions. |
|
Mercury |
No |
Mercury sulfide ores. Volcanoes. Forest fires. Ocean emissions |
Artisanal and small-scale gold mining. Chemical industry. Fossil fuels (coal and petroleum) combustion. Nonferrous metals production |
Catalysts, electrical switches. Batteries, fluorescent lights, felt production, thermometers, and barometers. Alloy for dental fillings. Bright-red paint pigments. |
| Nickel | Yes | Nickels mineral. | Metalworks, battery plants, electronics. Industrial waste. |
Metal alloys, batteries, electronics. |
| Zinc | Yes | Minerals. | Battery plants. Metal industry. Phosphate fertilizers. |
Batteries. Alloys. Construction anticorrosive planting. Tire rubber. Additives in veterinary drugs and pesticides. |
| Description | Ni | Cd | Cu | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BS M+ shoot | BDL | BDL | 10.45ab (1.42) | 2750.07c (284.63) |
| BS M+ roots | BDL | BDL | 16.08b (1.60) | 1717.71b (200.15) |
| BS M- shoot | 2.06a (0.63) | BLD | 1.09a (0.15) | 34.86a (9.41) |
| BS M- roots | BDL | BLD | BDL | 153.95a (10.79) |
| CS M+ shoot | 16.32b (1.32) | 153.69c(16.71) | 37.27c (4.61) | 3358.52c (297.3) |
| CS M+ roots | BDL | 5.21a( 0.3) | 5.46a (1.04) | 103.91a (13.72) |
| CS M- shoot | 1.93a (0,20) | 31.14b (2.5) | BDL | 38.57a (10.79) |
| CS M- roots | BDL | 13.55ab (1.9) | 6.84ab(1.43) | 19.54a (1.82) |
| BS initial | 3.00c (0.35) | BDL | 11.75d (1.75) | 1000.58e (100.42) |
| BS M+ final | 3.13c(0.81) | BDL | 15.38d (4.48) | 1129.99e (137.29) |
| BS M- final | 3.00c (1.04) | BDL | 25.50d (6.31) | 1047.57e (105.31) |
| CS initial | 7.13d (1.22) | 2.62d (0,09) | 245.38g (1.65) | 585.07d (107.20) |
| CS M+ final | 6.50d (1.04) | 2.24e (0.05) | 175.25f(5.81) | 1123.82e (83.10) |
| CS M- final | 6.25d (1.00) | 2.08e (0.03) | 229.0g (11.05) | 1231.02e (61.50) |
| Leached M- | 0.26f (0.02) | BDL | 1.18h (0.05) | 1.27f (0.01) |
| Leached M+ | 0.44g (002) | BDL | 1.39h (0.08) | 1.59g (0.03) |
| Treatment | Shoot Biomass (g) | Root Biomass (g) |
Total plant Biomass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS M+ | 52.67 (33.53) | 6.75 (5.91) | 59,42 (34,04) |
| CS M- | 37.67 (28.31) | 9 (7.21) | 46,66 (29,21) |
| BS M+ | 30.00 (22.72) | 5.50 (4.20) | 35,50 (23,10) |
| BS M- | 35.75 (24.06) | 7.25 (2.87) | 43,00 (24,23) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





