1. Introduction
Starting from the premise that in today’s observable reality the concerning finding is the transition from a decaying world to another world of knowledge and consciousness, based on the unprecedented development of science and technology, but which is still little understood, an attempt is made to outline a new path of transition that humanity is going through in the present.
This point of view highlights a nuance of societal evolution with reference to harmonization, balance, food security and planetary health as a whole, along the lines of the objectives of sustainable development and transformation of the world, starting with the exhibits specified institutionally by the Nations United [
1].
The Contemporary society largely functions in the open space delimited by the paradigm of modernity, more correctly said the one of post-post-modernity. This includes an accent on sociologic, technologic or the other conditions that distinguish the Modern Epoch from everything that followed after it, including nuances of postmodern chaos. Therefore, it is very important that researchers from interdisciplinary fields look for innovative solutions to the complex problems of today’s world. In the present society, settled postmodernism represents a set of answers of intellectual, cultural, artistic, academic or philosophic order, i.e., solutions for nowadays post-post-modernism condition [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7].
In short, it can be observed that the space of today’s society seems to be more and more a “black box”, insufficiently known, which makes the approach to understanding the world on the basis of new paradigms and transdisciplinary interpretations opportune. Thus, our approach is found along the lines of the conceptualist process, which, now more than ever, becomes opportune in the context of the general effort when humanity becomes aware of the importance of “knowledge”. This is the idea that represents the very mechanism of reporting to reality (be it theoretical, institutional, linguistic or non-linguistic) with the known expression of the Knowledge Society. In the present study we refer to a series of contributions regarding the restructuring and the perpetual harmonization of information on the concrete line of transition from the approach based on economic efficiency, to systemic effectiveness and then to a holistic dimension (which can at a given moment lead to the Society Consciousness) [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13], namely, the gradual transition towards holistic harmony at all levels and societal components. We are talking about a conceptual flow that for relatively long periods emphasized efficiency, with imbalances of systemic effectiveness and pollution with the potential for crises, but also with an ignorance of harmony, i.e., of “order, in which the different parts or functions do not oppose, which leads to a happy combination of diverse elements” (as the ancient Greeks claimed from history).
As is known, the idea of harmony is expressly found in what the Pythagoreans called “the harmony of the spheres” and persists in the thinking of modern times in Kepler, Giordano Bruno, Leibniz, Goethe (in the formulation of the pedagogical ideal, in “Wilhelm Meister”), then in German idealism. A new emphasis is given by ”harmonie préetablie„ in Leibniz’s metaphysics and in music (the science of the use of chords). Continuing on this line, with rigorous adjustments, we consider it opportune to analyse contemporary society on this troubling trajectory over time and in an adaptation to the model of planetary harmony, unjustly neglected to a great extent until now.
Knowing that things are not easy to achieve, we position ourselves in the approach of this study to encourage freedom from prejudice and sometimes ignorance, to have the chance to highlight the harmony of life and nature alike (“bio-eco-geo” type holistic harmony). So, initially based on an empirical-scientific hope, gradually the concept can be directed and then studied as a societal model, balanced in the constants of the Living Planet and universal harmony [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. The connection is actually made between the idea of dynamic balance, given by the evolution model of “living” (“bios”), with the idea of ”harmony”, thus laying the conceptual, but also etymological bases by joining the terms, in the notion of great complexity semantics of “bioharmony”.
2. The Definition and Role of Societal Bioharmony
The evolution of contemporary society is of course complicated, but in general it is connected with the unprecedented development of technology. Hence the evolution seen at the inflection of ecosystems with anthroposystems, an area where technology and biology are connected, both being evolutionary processes. Elegant arguments supporting the issue can be found in the thesis published by Ray Kurzweil in the futurological hypothesis of the Law of Accelerating Re-turns (Law of Accelerating Returns, 2005).
The 20th century brought a great scientific change with major paradigmatic impact. As is known, Einstein’s Theory of Relativity and the development of quantum mechanics led to the emergence of a new physics, capable of describing more coherently and in-depth different types of events in nature. Evolution became a unified theory when the modern synthesis reconciled Darwinian evolution with classical genetics. We recall that the molecular structure of DNA was discovered by Watson and Crick in 1953. All this makes possible new interpretations regarding natural, social and artificial phenomena, which represented, in the present case, a basis for the foundation the role of bioharmonism, which can make the connection between the natural sciences, more precisely the life sciences and the social sciences, more precisely the holistic approach to the evolution of human society.
Concreting the relationship between biological, technological and society, we take as a benchmark the non-linear planetary harmony, expressed through life itself as an evolutionary model and a validated benchmark for contemporary society. We refer to BIOHARMONY as a scientific-philosophical approach and to BIOHARMONISM as the transposition of the ideal of bioharmony into objectives, strategies and tactics. Bioharmonism essentially aims to transform reality with anarchic tendencies into one with optimized, balanced and environmentally friendly performance, based on the principles of sustainability and the convergence of three pillars of conceptual, processual and societal reference. In short, bioharmonism aims at the emergent integration of resources and processes, becoming a suitable vehicle towards the Knowledge Society. This by outlining a new societal model of maximum systemic effectiveness and resilience, but also with ethical valences along technological, ecological, social and political lines.
Hence the role of the concept that is related to sustainability, resilience and planetary health, which indicates the need to analyse planetary bioharmony and transpose the model to the structure and functionality of human society through the complex, unitary and coherent approach of the bioharmonization process [
16,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24].
Without going into details, we specify that “bioharmonization” refers to the continuous process of optimization and objectification of the contemporary reality with the specificity of the biological revolution in the information age which, after the phase of current drift and even disintegration, will restructure society towards another world. Methodologically, bioharmonization is initially based on empirical observations, and at the phenomenological level on fragmentation mechanisms (fractal analysis), multiple integration flows (integronics), quantum approach, etc., trying to define the problem, find quantification methods and finally the non-linear interpretation of the biological-eco-informational reality phenomena, in relation to the dynamics and linear components (cause-effect) of the standard approaches so far [
4,
16].
Reality shows us concerns about the planet, but only a small step forward has been made on some issues, such as understanding how to limit global warming, to adapt to the impact of climate change, and to provide funds to achieve these goals [
25]. In other words, the problem remains, especially in the relationship with the biggest polluters of the world, which requires new practical approaches, but based on theories and concepts with the potential to be settled and of course, accepted.
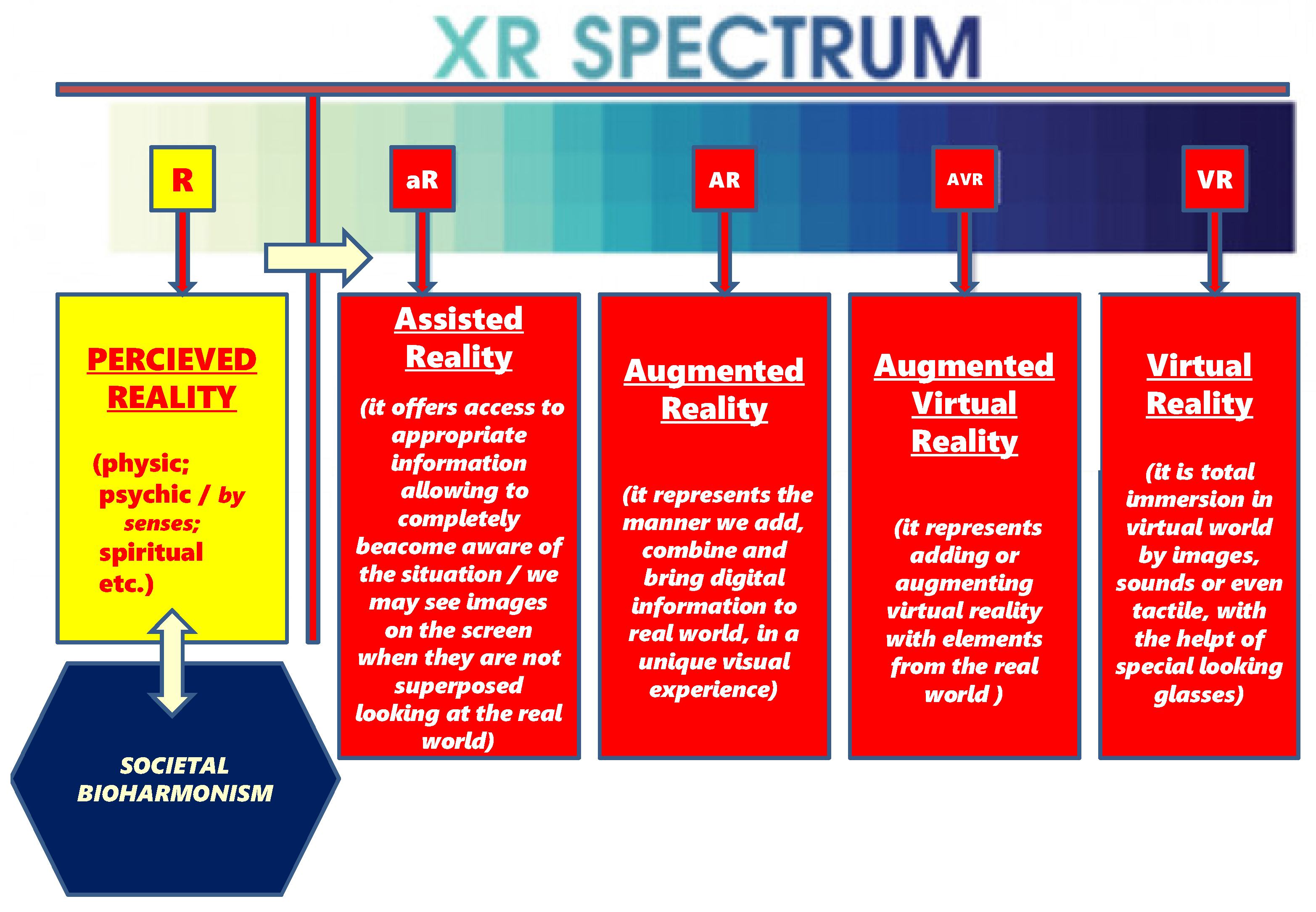
To better understand “reality” one must take into account the typologies of reality we are currently discovering (augmented and combined realities), which makes concepts from the extended bio-informational world more useful [
26]. As a benchmark we have the spectrum of realities (
Figure 1), from which it becomes essential to understand the physical, psychic (including through the senses), spiritual realities, all perceived more or less around us, as a prime mystery still little distinguished, but which can rightly support “parallel realities”, especially from the virtual world, that we are discovering in the 21st century.
In this not very optimistic context, the study proposes as general goal to bring its contribution to the already established ideas referring to the understanding of the sustainability process. We refer to the objective of theorizing through an applied interpretation at a societal level, along scientific-philosophical lines of an integrative nature and the reorientation through new concepts of the evolution model of contemporary reality [
27,
28,
29,
30]. We have in view the specificity of today’s world based on disordered informational explosion and with potential to generate deep disharmonies (example the overlap of current crises). Therefore, the present study describes a series of “conceptual pillars” that aim to find mechanisms to prevent or remedy imbalances, that is, models found in the “living world”, with an effect applicable to human society. What is desired is a paradigmatic deepening necessary to generate a state that tends towards the bioharmonization of the structural elements of contemporary society, an idea briefly resumed and further defined.
BIOHARMONISM represents the concept referring to the tendency of ”systemic harmonization” and balancing of reality in the holistic organization of contemporary society, methodologically based on the agreement of the parts with the whole, with the application of the understanding of the world in relation to the model of “life” (life, existence) and planetary ”living” (live), in their complexity and interconnection with current socio-economic and info-cultural models.
3. Bioharmonism as an Argument in the Transition to Another World
The changes in contemporary society are obvious. Note the accelerated speed of science and technology and the much slower understanding of these aspects. That’s why any attempt to decode things, so that society can find its compass, is worth the effort. The theory of bioharmonism and the shaping of an ideology want to contribute to the understanding of societal reality on various levels, based especially on the types of critical, convergent and systemic thinking.
The structuring of the concept, the establishment of principles, the elaboration of rules and strategies, can make bioharmonism a benchmark for societal evolution. All this can materialize by outlining a specific methodology and establishing original notions necessary for the concise and precise expression of certain nuances, otherwise difficult to understand without their definition and elaboration, and by creating an innovative language. We cannot explain the phenomenological structural view of the material-informational reality (ortho-physics) and even more so of the biological-informational reality. In short, it becomes useful to search for notions that can explain the transition from complicated to complex, from Newtonian physics to quantum physics, from the linear to the non-linear approach specific to life (live, living) and the surrounding nature, etc. We specify that the terminology used wants to focus as correctly as possible the meaning of the way of expression, and the creation of a specific language becomes necessary, although at first sight it seems to complicate things. As examples and elements that we will describe in synthesis in this study, we can enumerate (from the Glossary of Bioharmonism Theory, 2019): bioharmony, bioharmonism, bioharmonization, emergence, ecosanogenesis, fractal, georhesia, homeoresis, homeostasis, integronic, infochronic orthoexistence, telefinality etc. [
16].
In the sense of what was expressed, we consider bioharmonism to be, among others, a “seed for another world” [
4], through the corollary of new concepts, principles, laws and notions, which we present as an example of finding the concept in various components of reality. The analyses and examples have as a “spearhead” the main existential resource, namely food production. That is why our concerns relate mainly to examples of the agri-food axis, but also to generalizations at the level of contemporary society.
4. Examples of Application of the Pillars of Bioharmonism
In the understanding of societal bioharmony, the approaches to this problem are eloquent, both at the “macro” (holistic) theoretical level, and practically in the exemplification from this point of view, at the level of the agro-food system. Thus pragmatically, we highlight the production of food in the idea of applied biology on a large social scale and of great theoretical and practical relevance for humanity, in the context of resource depletion, current demographic dynamics and climate change.
Today’s reality indicates a postmodern society (also called the informational society, or the post-industrial society) which means the accumulation of these trends. It results in a lot of unrest and profound changes in societal groups, in scientific and technological activities, in cultural, political, etc., all of which require a solution by formulating new concepts, such as bioharmonism. The concerns regarding the paradigmatic finding and adaptation of contemporary society are based on knowledge and communication, multiculturalism, tolerance, media culture, the structuring of the great narratives of recent years, i.e., problems of the postmodernist imaginary. Let us only mention François Lyotard, Michel Foucault and Jean Baudrillard among the main philosophers who established and described the postmodern condition [
5,
31,
32].
Starting from philosophy, conceptual approaches go to economy, society, ecology and, of course, politics, covering as we all know, extremely diverse names and fields (from biology to physics, etc., to sociology or political science). We hope that the “seed” we plant through the approach centred on the integrative idea of bioarminism will be convergent with them, having a contribution with a special place [
16].
Starting from the general to the particular, the analyses in decoding or solving as much as possible the mystery of the dynamic balance model (homeoresis), from different levels of the environment and society, had for us as a holistic problem of framing bioharmonism, the general aspects of the philosophical order (“biosophy”). We are talking about a history of several decades, of theoretical approaches from various angles to create a framework that, through successive mechanisms of integration, makes possible a common element of analysis, namely, the elaboration and theorization of the “idea of bioharmonism” (
Table 1).
The pragmatic understanding of the idea of bioharmonism moves to a level of interpretation of the complexity of contemporary human society in which the excessive consumption of material products, but especially of harmful media products, of cultural products with outdated value, becomes more and more evident, which increases the disorder of society at all its levels. In this direction, as we stated previously, we focused on the primary need of the species, as world statistics show, that 70% of humanity’s needs are food. The conceptualization in the direction of the bioharmonic paradigm of the food production and processing branch made it possible to apply the theory through the aspects that we list in
Table 2 [
19,
20,
22,
23,
28].
The specifications in the tables indicate a way to try new experiments, new models, formulas and scientific, technological and economic strategies, with social and cultural impact, but especially political, respectively for the realization of public policies in a bioharmonist approach, to correlate the impact of human activity with post-modern concrete reality.
The answer to the new approaches can be found before the birth of a new cultural age (
“another world
”), with a status different from that of post-post-modernity, with a configuration and a recalibration of values, as well as new strategies that can reflect a real
“re-entry into the womb
” [
5,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40]. Highlighting, adapting to the present and finding the
“valorization
” mechanisms within contemporary society, precisely the idea of value (in many apects outdated today), becomes possible also through the approach based on the principles of bioharmonism. This through the potential to ensure the emerging transition, respectively the collective interaction of the systemic components with the purpose of the emergence of the new higher order at the level of contemporary society, i.e.
,: the emergence supported by the principles of bioharmonism. Starting from the premise that the current socio-economic and political model begins to have too many gaps, including of a cultural and educational nature [
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50],
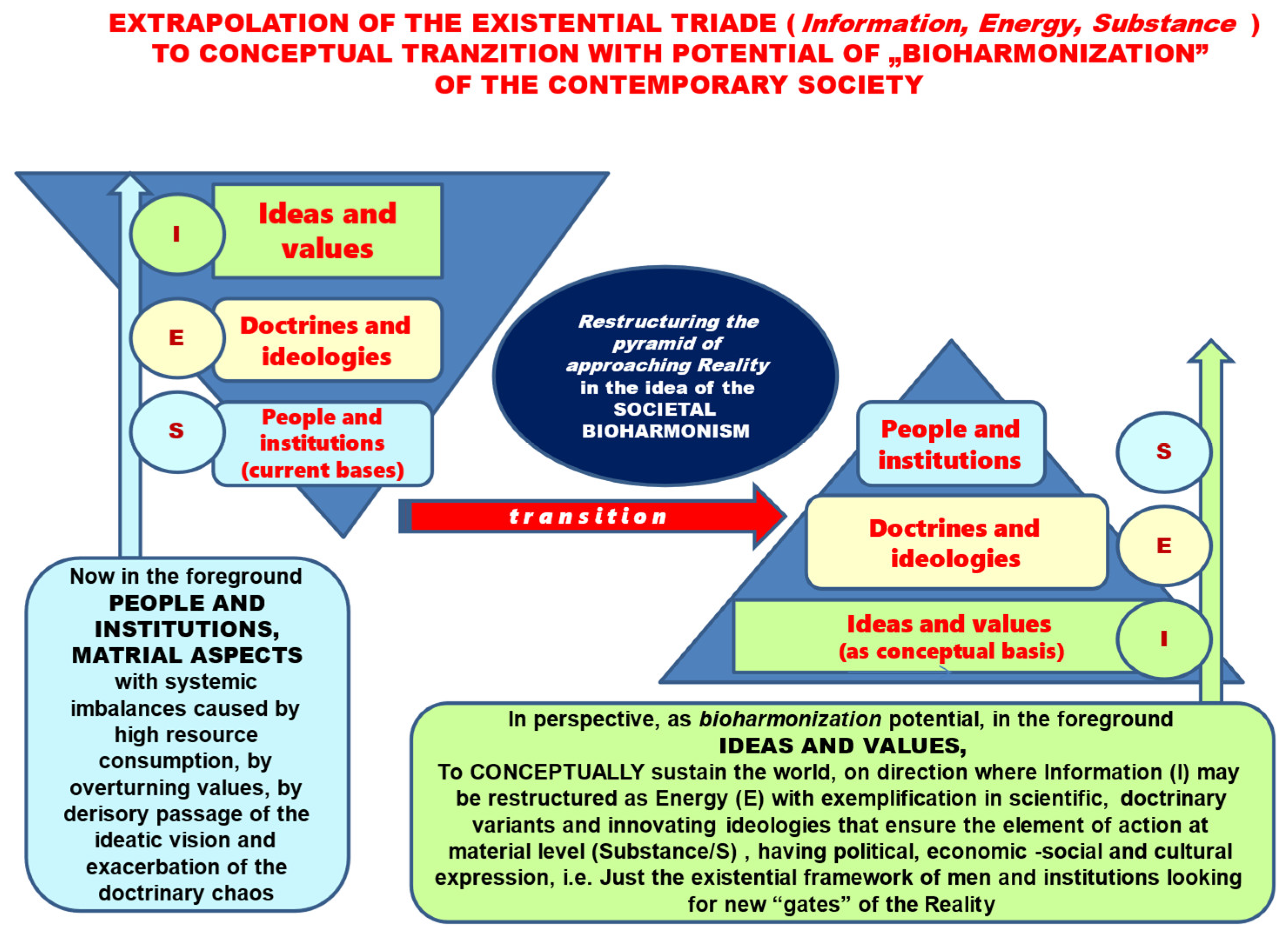
Figure 2 describes a scheme of the transition on the pillars of bioharmonism towards a society performing in dynamic balance.
That is why a better harmonized ordering with potential for avalanche restructuring of societal components (conceptual, legal and institutional reforms) is opportune in the idea of
”making peace
” with the environment, with the economy and with ourselves as individuals or society, along the lines of the fundamental reconsideration of the continuity of balanced life on Earth (
Figure 3).
The theoretical relocation through innovative concepts leads to the bioharmonization of the evolution of contemporary society which, systematically speaking, has the potential to generate “social homeoresis”. This process actually means the idea that represents the property, or state of a system, of maintaining its dynamic equilibrium. This in relation to a certain degree of antinomy to the idea of ”societal homeostasis”, respectively in the sense referring to the property of a system to maintain a static balance of the initial conditions [
16,
18,
51].
Bearing in mind, as we have emphasized on other occasions, that “routine and prejudice cannot stifle ideas indefinitely” and that “if we learn from the changes in the world, then we will see the loop of knowledge that will generate bridges by uniting between today and tomorrow ”, we are convinced that the idea of bioharmonism, with the corresponding basic pillars highlighted in this study, becomes an important landmark in the context of the accelerated changes of the world and modern human society.
5. Conclusions
Bioharmonism, through the ideational novelty, proposes a reorientation of the approach of the current society on a balanced and harmonized route in the constants and the model of the “Living Planet”, resulting in the delimitation of a variant of the socio-economic and cultural model capable of supporting the current societal resort, a society characterized mainly by the convergence of reality given by the Biological Revolution with the Information Era. It is the concept that can counteract a chaotic evolution, contrary to the planetary model that is balanced and sustainable in the perpetual evolution of life, but also with applicability and connotations regarding the harmony of the components of contemporary society.
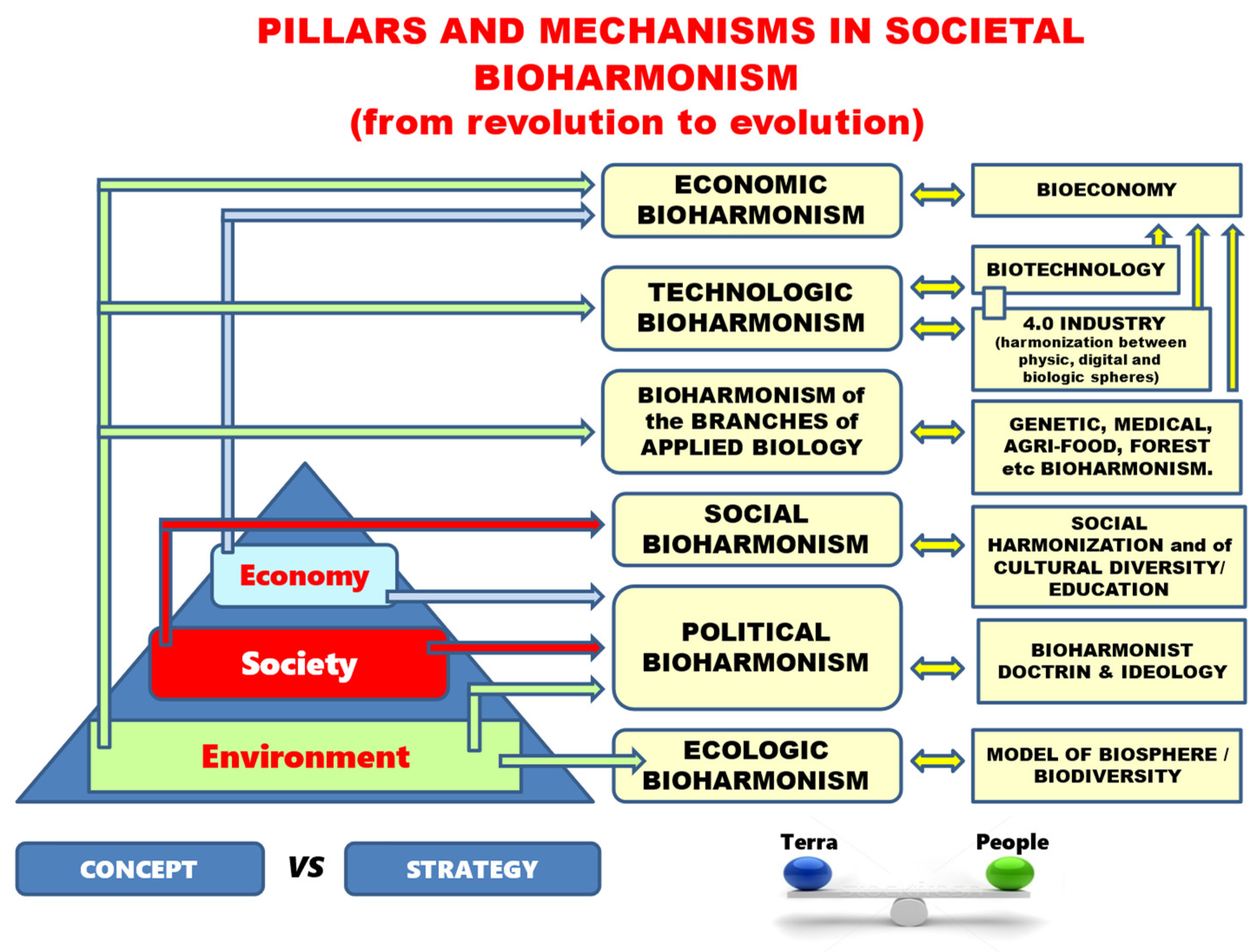
Bioharmonization processes and mechanisms aim at balanced bioeconomic and biotechnological action in relation to the creation at the level of Industry 4.0 and the corresponding cultural and psychosocial implications, essentially outlining the understanding of the development of society by taking the harmony of planetary “traditions” as a basis and analytical model, which can be supported conceptual, doctrinal and philosophical as a benchmark of the perceived Reality, specific to the current world.
Societal bioharmonization expresses a system of complementary equations that holistically imposes the Environment and biodiversity in the economic equation, the Citizen in the social equation and Science in the political equation, i.e., main pillars that, through multiple integration (integronic dynamics) and emergence, induce from a systemic perspective the state of “societal homeoresis” and from a political perspective, “bioharmonist ideology” as a way to restore the rules of the game and a source of doctrinal regeneration in a changing world, including the dilution of ideological benchmarks. As secondary pillars of societal bioharmonism, with a complementary role in supporting the main pillars, we mention the conceptual contribution that considers: “ecosanogenesis” and “genetics of biocenoses” along the lines of environment and biodiversity; “integronic” dynamics on managerial direction; “modular agriculture, bioeconomic animal husbandry and gastronomic engineering” on a technological direction, applicable to the axis of the food act; as well as the omnipresence of “Information (I)” as an element of existential flow through ideational bioharmonism and the restructuring of its programs through decoding ”infogronic” flows, all in the thought corollary of “biosophy”.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.G.; methodology, R.G.; validation, R.G., L.G.; formal analysis, R.G., L.G.; writing—original draft preparation, R.G.; writing—review and editing, L.G., O.O.B.; visualization, L.G., O.O.B; supervision, R.G.; funding acquisition, R.G., L.G., O.O.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the support of Transilvania University of Brasov, Romania.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- https://www.un.org/en/exhibits/page/sdgs-17-goals-transform-world.
- Drucker, P.F. Societatea post-capitalistă, Publisher: Image, Bucharest, Romania, 1999;
- Lyon, D. Postmodernitatea, Publisher: Du Style, Bucharest, Romania, 1999;
- Munteanu, F. Semințe pentru altă lume, Publisher: Princeps, Bucharest, Romania, 2015; pp. 137-192;
- Scarlat, C. 2015: Educația postmodernă vs. Recalibrarea sistemului de valori, în Perspective, Publisher: Spiru Haret, Iași, Romania, 2015;
- Siebert, H. Învăţare autodirijată şi consilierea pentru învăţare. Noile paradigme postmoderne ale instruirii, Publisher: Institutul European, Iaşi, Romania, 2001;
- Educația și școala contemporană la granița dintre modernism și postmodernism–deziderate și extensii în practica educativă https://andreivocila.wordpress.com/2010/10/29/educatia-si-scoala-contemporana-la-granita-dintre-modernism-si-postmodernism-%E2%80%93-deziderate-si-extensii-in-practica-educativa/(Accessed on 07.09.2023);
- Albrecht, K. Inteligența socială. Noua știință a succesului, Publisher: Curtea Veche, Bucharest, Romania, 2007;
- Dasen, P., Perregaux, C., Rey, M. Educaţia interculturală. Experienţe, politici, strategii, Publisher: Polirom, Iaşi, Romania, 1999;
- Drăgănescu, M., Societatea conștiinței, Publisher: Institutul de Cercetări pentru Inteligenţă Artificială al Academiei Române, Bucharest, Romania, 2007;
- Harari, Y.N. Sapiens - Scurtă istorie a omenirii, Publisher: Polirom, Iași, Romania, 2017; pp. 296-315;
- Hawking, St. Teoria universală, Publisher: Humanitas, Bucharest, Romania, 2014; pp. 123-140;
- Wilson, E.O. Cucerirea socială a Pământului, Publisher: Humanitas, Bucharest, Romania, 2015;
- Esposito, R. Bios: Biopolitics and Philosophy, Publisher: University of Minnesota Press., USA, 2008; pp. 16;
- Frey, B.S. Economics as a Science of Human Behaviour, Towards a New Social Science Paradigm, Publisher: Kluwer Academic, Boston, USA, 1999;
- Gruia, R. Bioarmonismul, de la teorie la o nouă ideologie, Publisher: Clarion, Brașov, Romania, 2019; pp. 63-71;
- Peters, M.A. Bio-informational capitalism. Thesis Eleven 2012 110 98-111;
- Zugrăvescu, D., Munteanu, F. Planeta Pământ - Planeta vie, Institutul de Geodinamică „Sabba G. Ștefănescu” al Academiei Române, Catedra UNESCO de Geodinamică - România, Eagle Publishing House, 2011, pp. 45-47, 63-66, 90-94;
- Gruia, R. Gastronomic engineering, a distinct direction within food engineering. J. of EcoAgriTourism 2008 4, 10-16;
- Gruia, R. Modular agriculture – paradigm of globalization dynamics within the context of climatic and scientific changes. EEMJ 2010 9, 1601-1606; [CrossRef]
- Gruia, R. Bazele managementului si directiile viitoare de evolutie, Publisher: Lux Libris, Brașov, Romania, 2013; pp. 163-197;
- Gruia, R. Zootehnia bioeconomică, Publisher: Lux Libris Brașov, Romania, 2016; pp. 5-364;
- Gruia, R. Resurse genetice în fermele agroturistice, Publisher: Clarion, Brașov, Romania, 2017; pp. 147-188;
- Gruia, R. Ideologia bioarmonistă, Publisher: Clarion Brașov, Romania, 2019; pp. 3-50;
- COP26 Climate Change Conference in Glasgow,1-12, Nov. 2021 https://web.cvent.com/event (Accessed on 12.08.2023);
- Ce este Realitatea Augmentată? https://www.inas.ro/ro/blog-arhive/ce-este-realitatea-augmentata (Accessed on 03.06.2023);
- Buican, D. Biognoseologie, evoluție și revoluție în cunoaștere, Publisher: All, Bucharest, Romania, 1993;
- Gruia, R. Managementul eco-fermelor, Publisher: Ceres Bucharest, Romania, 1998; pp. 68-85;
- Gruia, R. Ecoemergetic theory in sustainable development, Publisher: Universitatea Transilvania Braşov, Romania, 2002;
- Păun, E., Potolea, D. Pedagogie. Fundamentări teoretice și demersuri aplicative, Publisher: Polirom, Iași, Romania, 2002;
- Barry, R.J.J. Globalisation and Interdependence in the International Political Economy, Rethoric and reality, Pinter Publishers, London, 1995; pp. 50-75.
- Fukuyama, F. The End of History and the Last Man, Publisher: The Free Press, New York, USA, 1992; [CrossRef]
- Gaceu L., Gruia R. Sisteme informatice în management, Publisher: Infomarket, Braşov, Romania, 2006;
- Ginman, M. Information culture and business performance. IATUL Quarterly: A Journal of Library Management and Technology, 1998 2 93-106;
- Kuhn, Th. Structura revoluţiilor ştiinţifice, Publisher: Humanitas, Bucharest, Romania, 2008;
- Lemke, T. Biopolitics: An Advanced Introduction, Publisher: NYU Press, 2011; pp. 9–10;
- Mignerot, V., Transition- Réformer l’écologie pour nous adapter à la réalité, Publisher: Association Adrastia, 2017;
- Pillet, G. Economie de l’environnement et du patrimoine naturel. Rev. econ. 1990 41, 321-333;
- Smith, D.E. The Social Construction of Documentary Reality, Sociol. Inq. 1974 44, 257-268; [CrossRef]
- Soran, V., Şerban, M.E. Bioeconomia – o nouă ştiinţă de graniţă, Publisher: Ştiinţifică şi enciclopedică, Bucharest, Romania, 1980;
- Antonovics, J., 1978: The input of population genetics,” The new ecological genetics”, Syst. Bot. 1978, 1, 233-243;
- Bache, M.C., 2000: Anima mundi - Ecological crisis and death of the ego of the species: speculation on the future, JTP, 2000, 32, 25-32;
- Ball,T., Dagger,R. Ideologii politice și idealul democratic, Publisher: Polirom, Bucharest, Romania, 2000; pp. 17-33;
- Bell, D. The End of Ideology. On the Exhaustion of Political Ideas in the Fifties, Publisher: Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Mass, UK 2001;
- Brown, L. The Evolution of Public Sector Strategy, Public Administration Review, Wiley 2010, 70;
- Fukuyama, F. The Great Disruption. Human Nature and the Reconstruction of Social Order. Publisher: The Free Press, New York, USA, 1999;
- Georgescu-Roegen, N. The entropy law and the economic process. Publisher: Harvard Univ. Press, Cambridge, Mass., UK, 1971;
- Georgescu-Roegen, N. Legea entropiei, Publisher: Politică, Bucharest, Romania, 1979;
- Vlăsceanu, L. 2002: Şcoala la răscruce. Schimbare şi continuitate în curriculumul învăţământului obligatoriu. Studiu de impact, Publisher: Polirom, Iaşi, Romania, 2002;
- Werner, W. Which Socio-economic Model for Europe? Inter Econ. 2006 41, p. 4–23;
- Munteanu, F. Studiu asupra abordării procesului de geostazie planetară, XI-th ed. Of the Annual Conference ASTR, Bucharest, Romania, 2017; pp. 200-205;
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).