Submitted:
20 September 2024
Posted:
23 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting, and Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Socio-Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Study Participants
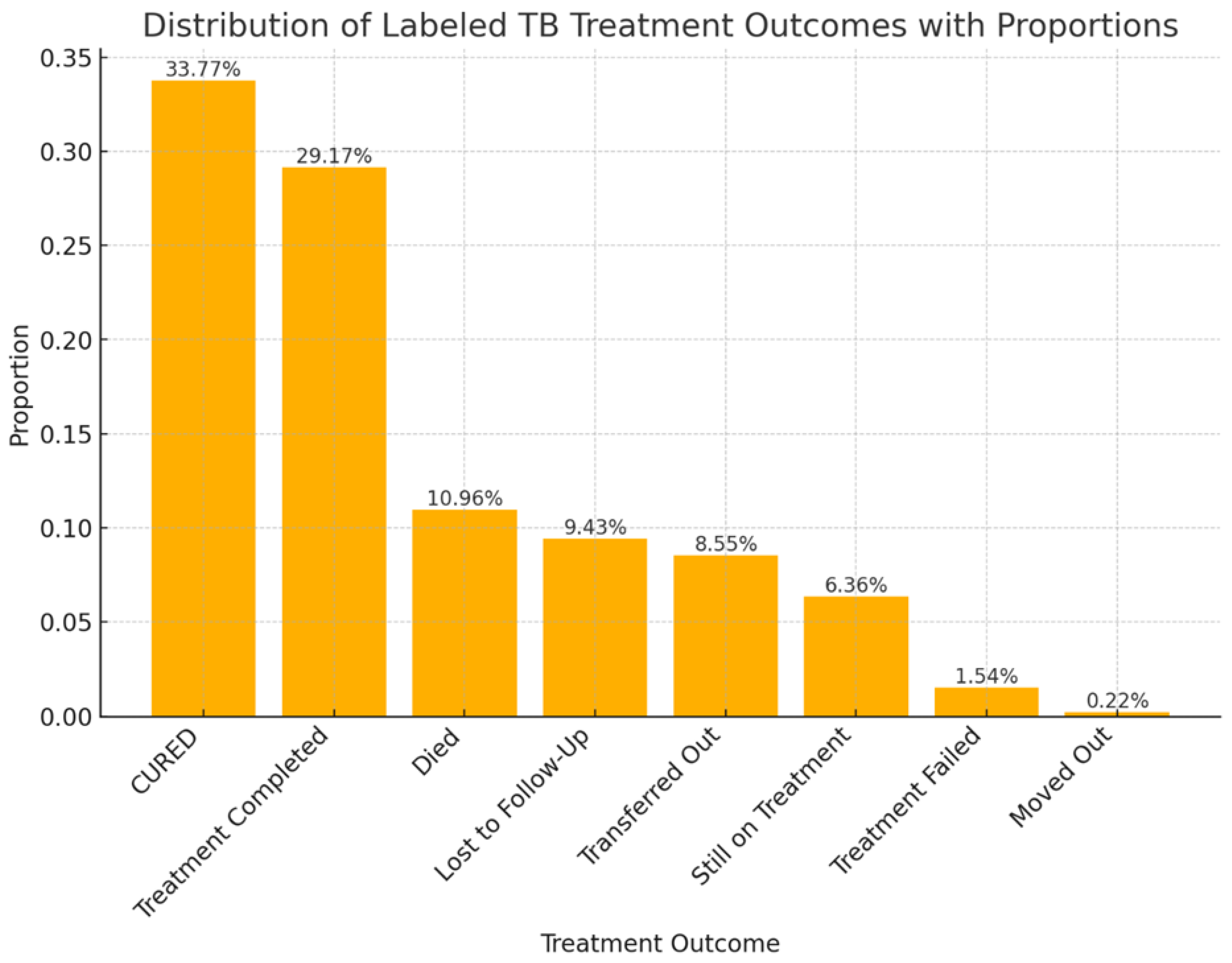
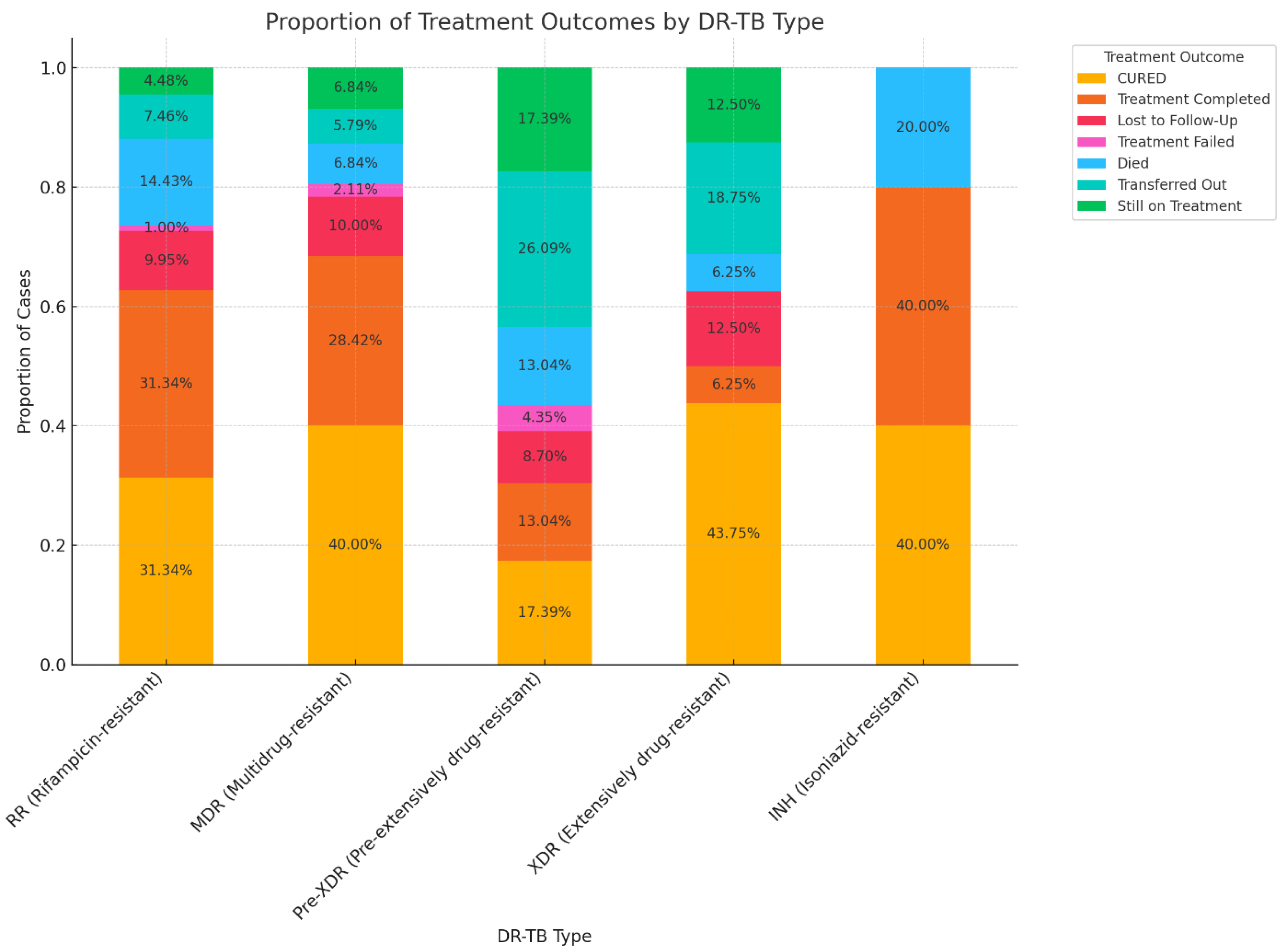
3.2. Treatment Outcomes of DR-TB
3.3. Treatment Outcomes of DR-TB Comparing COVID-19 Pre-Pandemic (2018-2019) and Pandemic (2020-2021) Periods
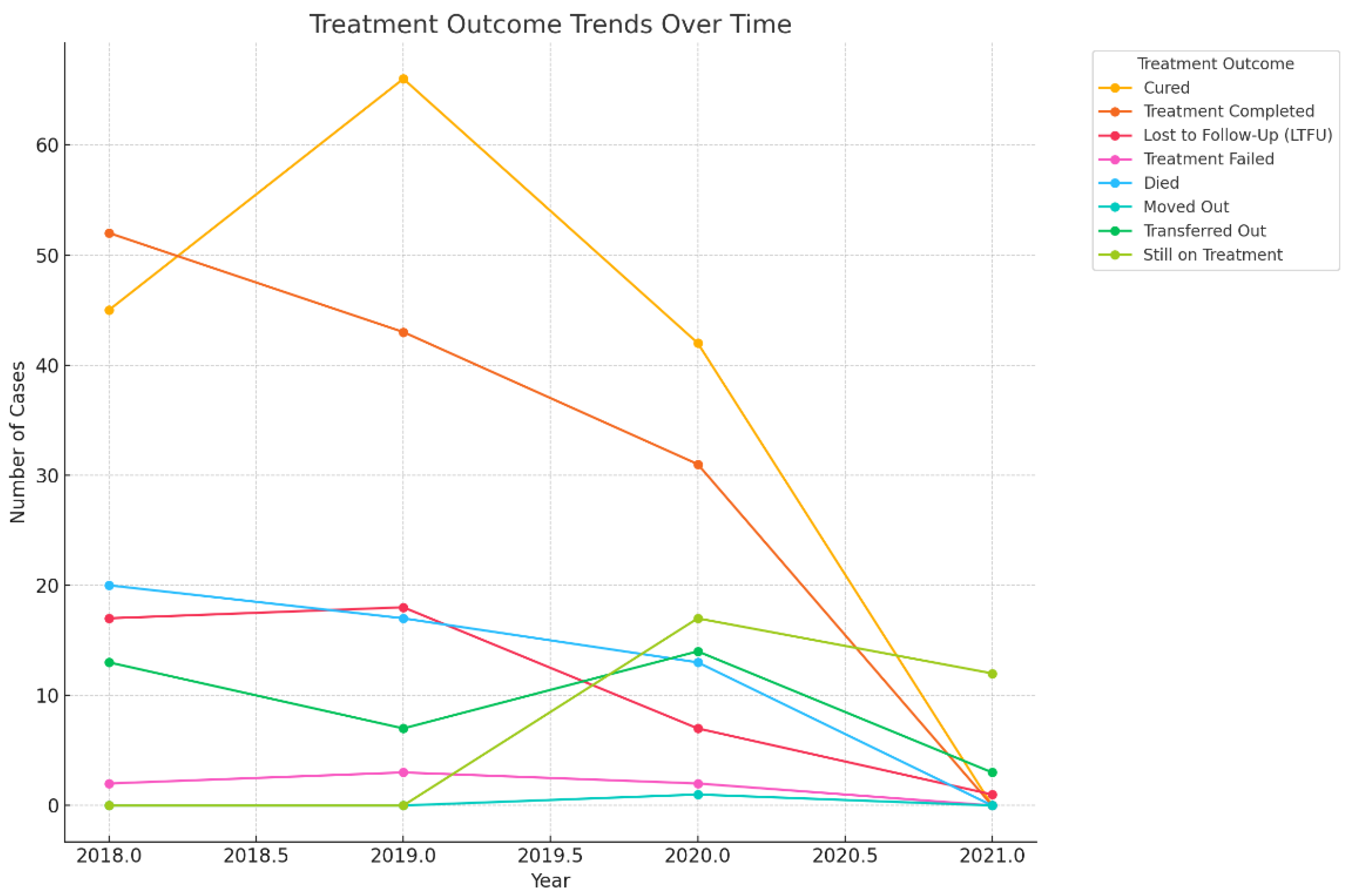
3.4. The Trend of Treatment Outcomes over Time
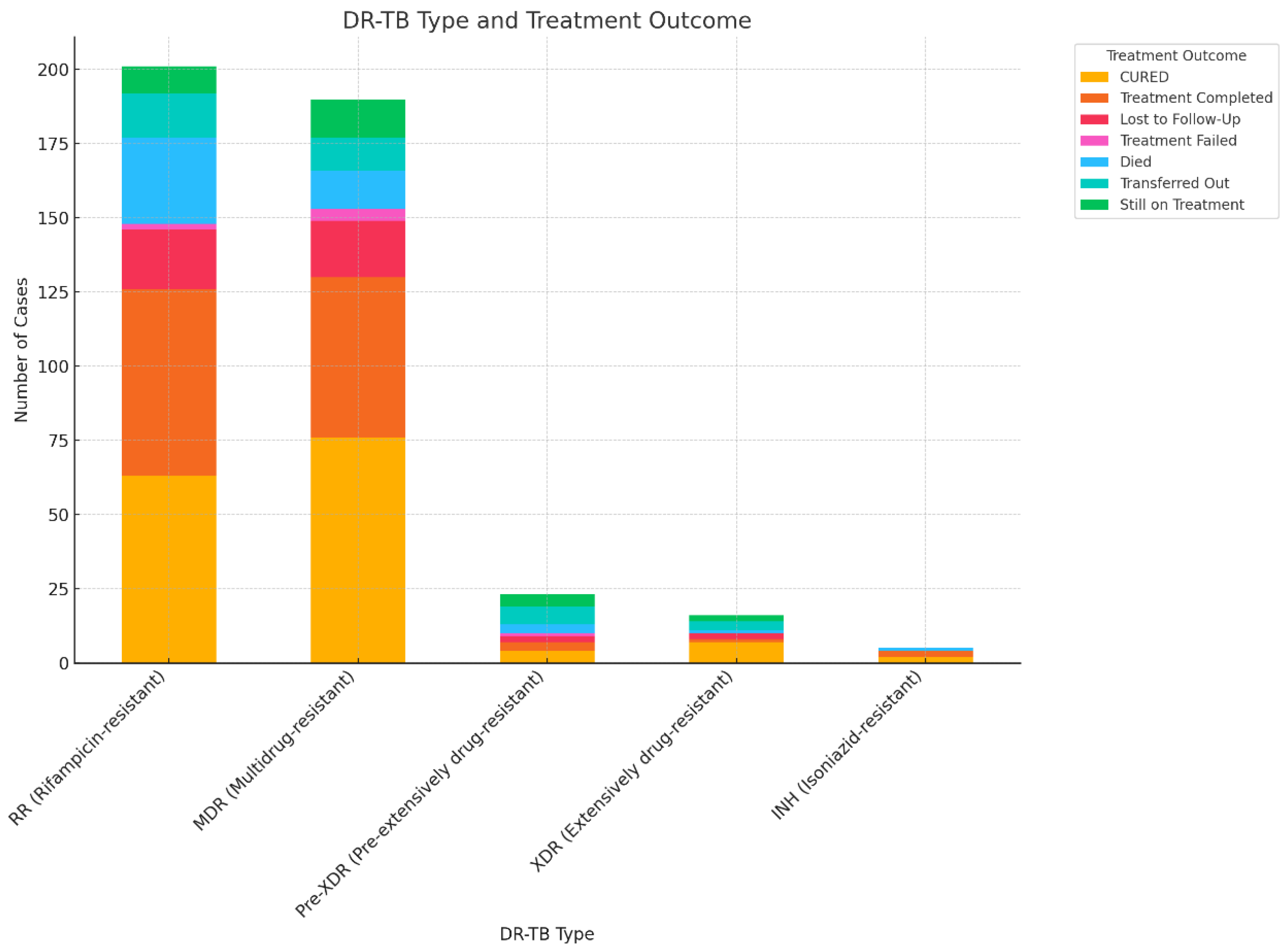
3.4. Association between DR-TB and Treatment Outcomes
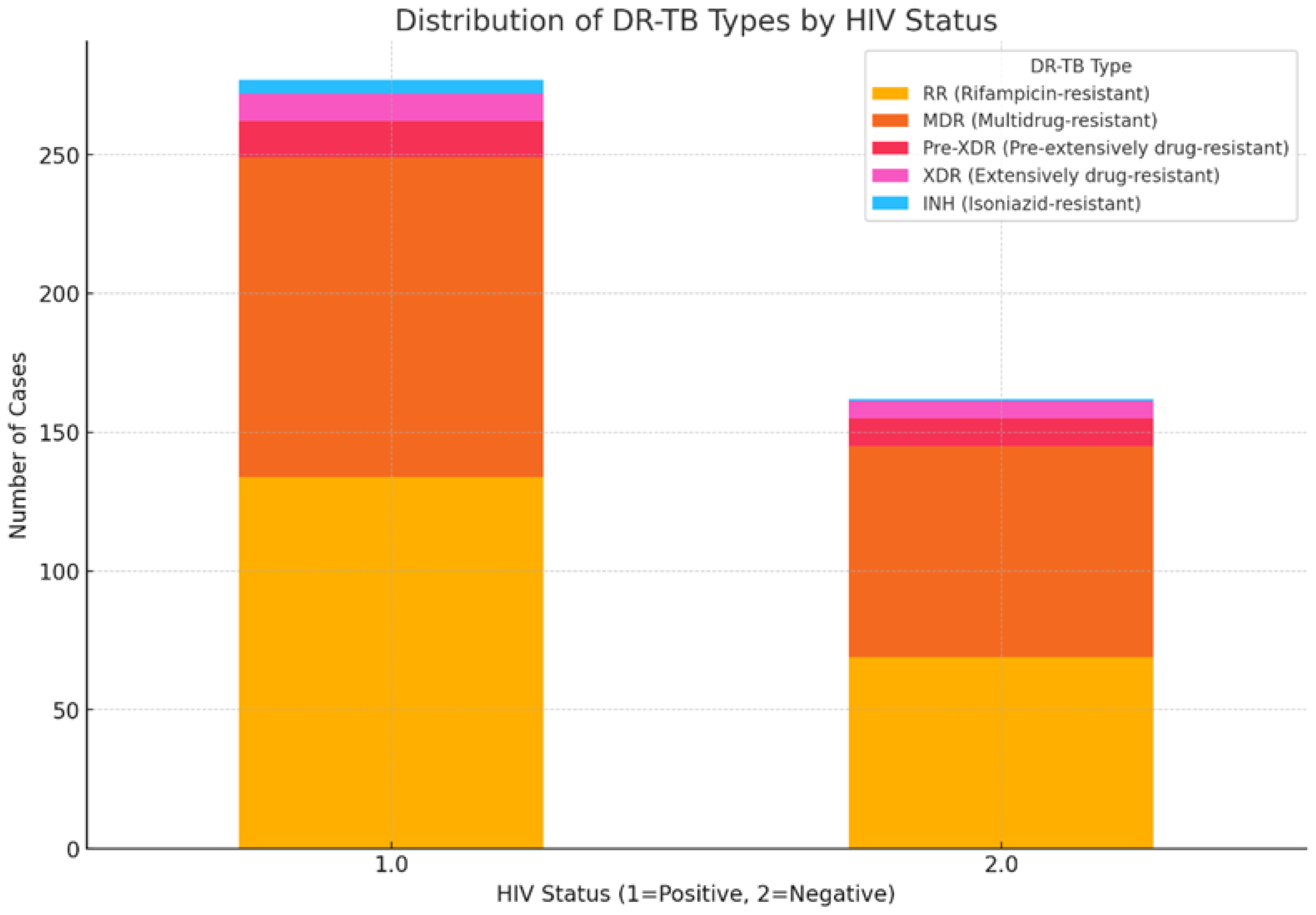
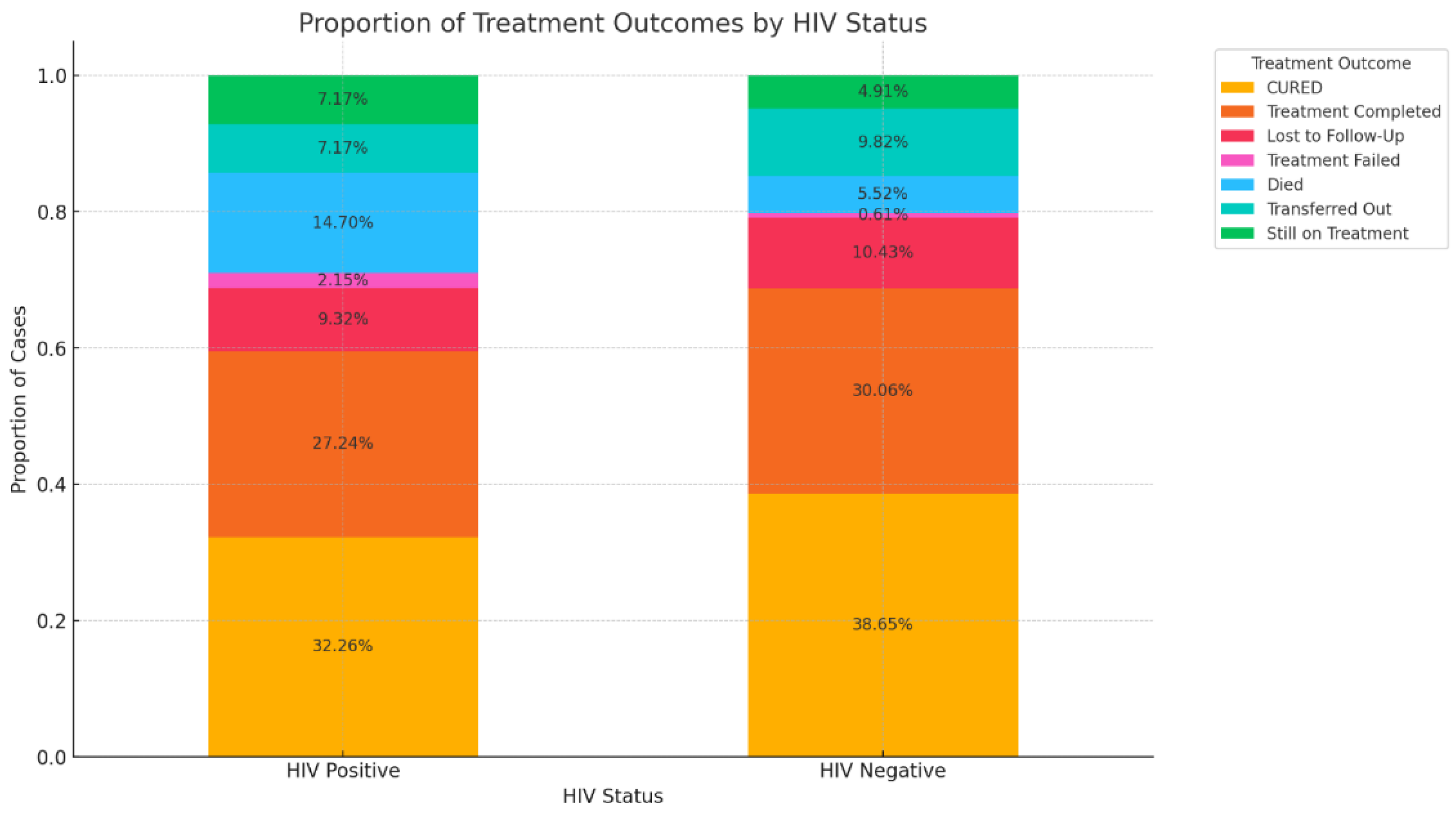
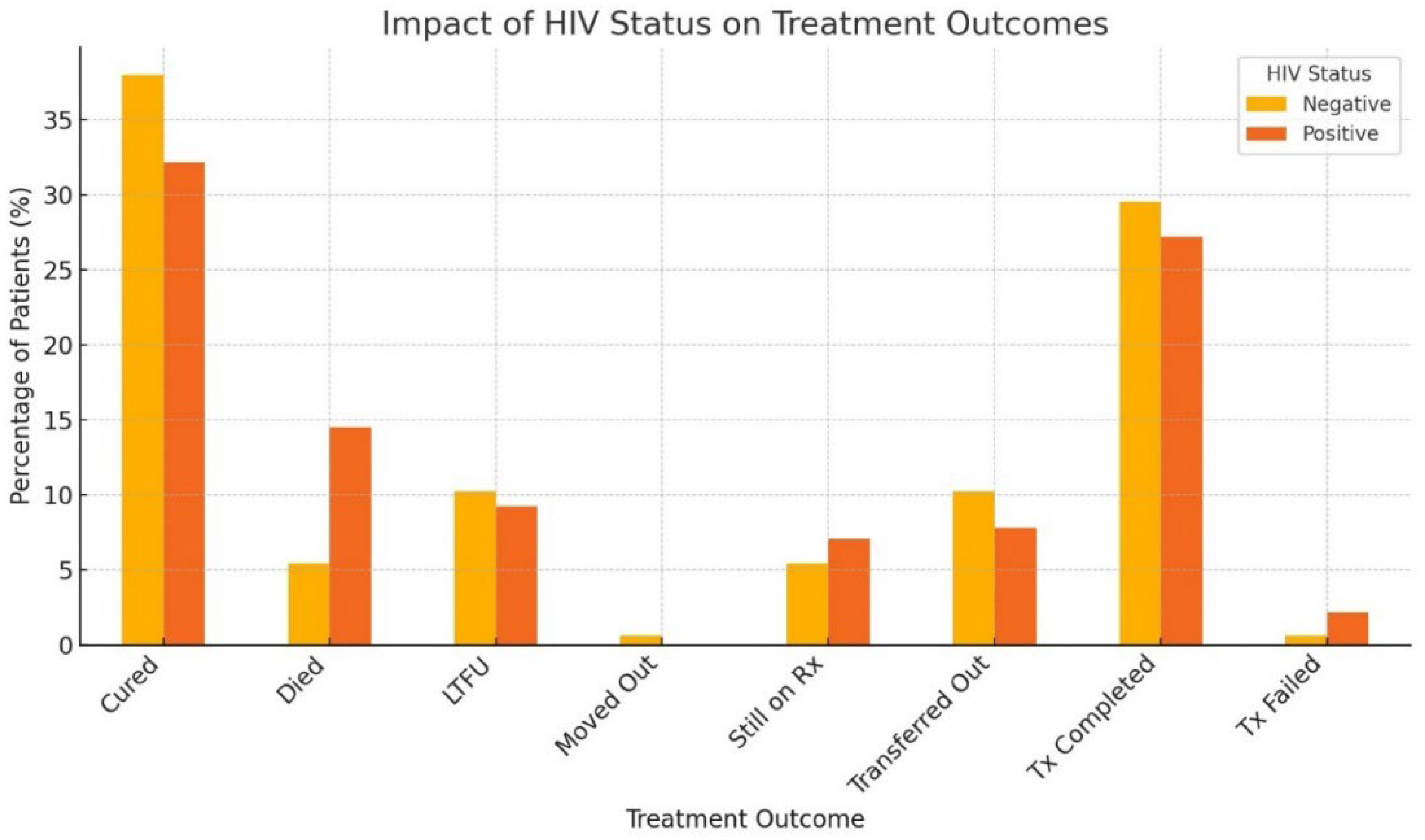
3.5. Impact of HIV Coinfection on Treatment Outcomes
3.6. Factors Influencing Treatment Outcomes
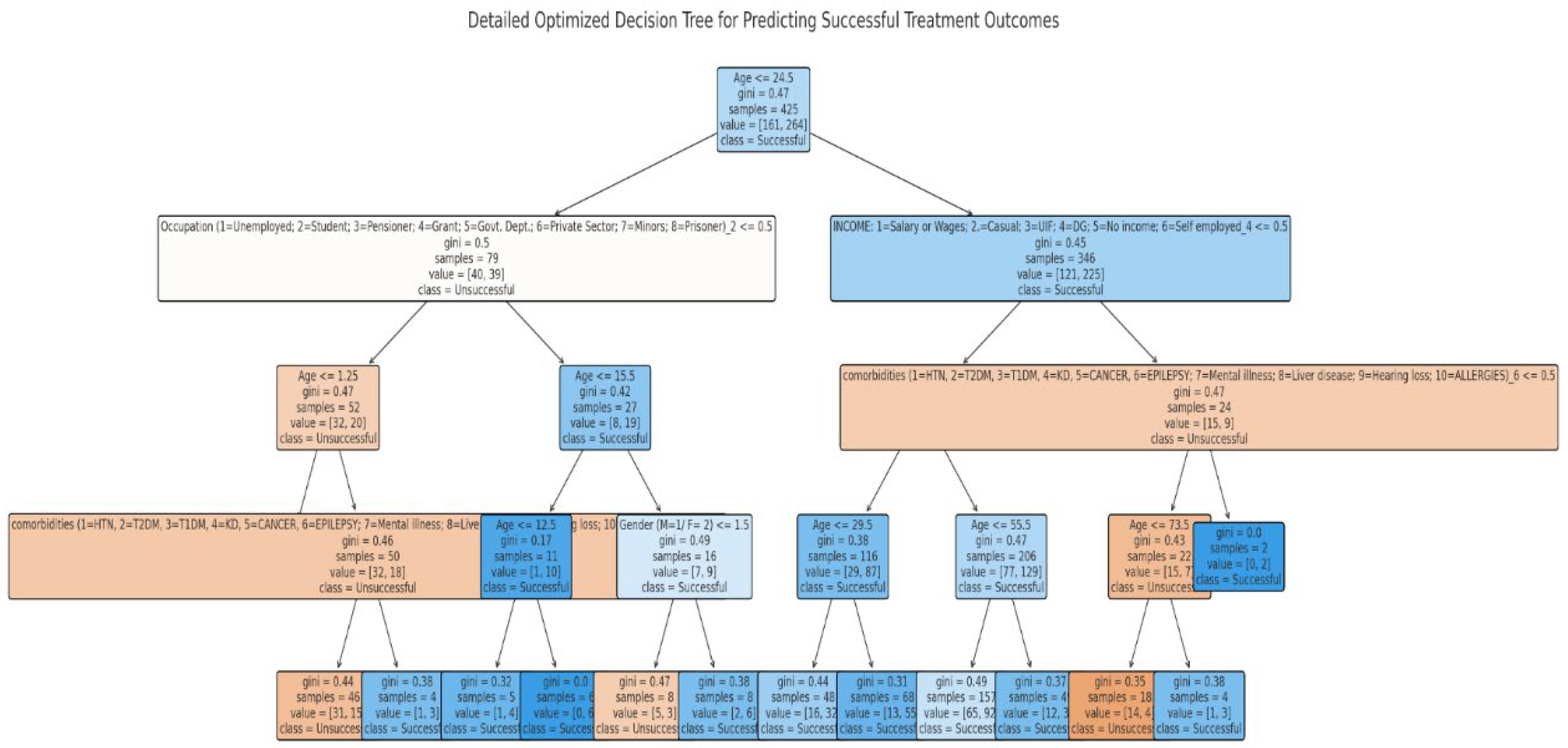
3.7. Predictors of DR-TB Successful Treatment Outcome Using a Decision Tree Classifier (Supervised Machine Learning Algorithm)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, W.M.; Guo, J.; Xu, T.T.; Li, S.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Tao, N.N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Liu, S.Q.; An, Q.Q.; Li, Y.F. Association between body mass index and newly diagnosed drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis in Shandong, China from 2004 to 2019. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, A.C.D.O.J.; Dos Santos, A.P.G.; de Medeiros, R.L.; de Oliveira Jeronymo, A.J.; Neves, G.C.; de Almeida, I.N.; de Queiroz Mello, F.C.; Kritski, A.L. Sociodemographic and clinical factors associated with treatment outcomes for drug-resistant tuberculosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 107(6), 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization 2023. Global tuberculosis report 2023. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2023. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/373828/9789240083851-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed 12 August 2024).
- Torres, S.G.V. , Fullmer, J. and Berkowitz, L. A Case of Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Tuberculosis and HIV Co-Infection. Cureus, 2023; 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, E. The clinical profile and outcomes of drug-resistant tuberculosis in Central Province of Zambia. BMC Infect. Dis, 2024; 24, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, 2021. Global Tuberculosis Report 2021. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240037021. (Accessed 18 August 2024). 18.
- Kamara, R.F. , Saunders, M.J., Sahr, F., Losa-Garcia, J.E., Foray, L., Davies, G., Wingfield, T. Social and health factors associated with adverse treatment outcomes among people with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Sierra Leone: a national, retrospective cohort study. Lancet Glob. Health, 2022; 10, e543–e554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, A.; Diallo, B.D.; Camara, L.M.; Kounoudji, L.A.N.; Bah, B.; N’Zabintawali, F.; Carlos-Bolumbu, M.; Diallo, M.H.; Sow, O.Y. Different profiles of body mass index variation among patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis, 2020; 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daftary, A., Mondal, S.; Zelnick, J.; Friedland, G.; Seepamore, B.; Boodhram, R.; Amico, K.R.; Padayatchi, N.; O’Donnell, M.R. Dynamic needs and challenges of people with drug-resistant tuberculosis and HIV in South Africa: a qualitative study. Lancet Glob. Health, 2021, 9(4), e479-e488. [CrossRef]
- Wagnew, F.; Alene, K.A.; Kelly, M.; Gray, D. Impacts of body weight change on treatment outcomes in patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Northwest Ethiopia. Sci. Rep, 2024; 14, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.; Walzl, G.; Du Plessis, N. Therapeutic host-directed strategies to improve outcome in tuberculosis. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13(2), 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Prasad, R.; Balasubramanian, V.; Gupta, N. Drug-resistant tuberculosis and HIV infection: current perspectives. HIV/AIDS-(Auckl), 2020; 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization 2019. Global Tuberculosis Report 2019. Geneva: WHO; 2019 (WHO/CDS/TB/2019.15). Available from: https://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/. {Accessed 18 August 2024}.
- Cerrone, M.; Bracchi, M.; Wasserman, S.; Pozniak, A.; Meintjes, G.; Cohen, K.; Wilkinson, R.J. Safety implications of combined antiretroviral and anti-tuberculosis drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2020, 19(1), 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Report: Global strategy and targets for tuberculosis prevention, care, and control after 2015. http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/EB134/B134_12-en.pdf?ua=1 29 November 2013. (accessed 7 September 2024).
- World Health Organization (WHO) Report. The Global plan to stop TB 2011–2015. http://www.stoptb.org/assets/documents/global/plan/TB_GlobalPlanToStopTB2011-2015.pdf (accessed 7 September 2024).
- Zumla, A.; Petersen, E.; Nyirenda, T.; Chakaya, J. Tackling the tuberculosis epidemic in sub-Saharan Africa–unique opportunities arising from the second European Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP) programme 2015-2024. Int. J. Infect. Dis., 2015; 32, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, J.; Nussinov, R.; Zhang, Y.C.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, Z.K. Computational network biology: data, models, and applications. Phys. Rep, 2020; 846, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiffer-Smadja, N.; Rawson, T.M.; Ahmad, R.; Buchard, A.; Georgiou, P.; Lescure, F.X.; Birgand, G.; Holmes, A.H. Machine learning for clinical decision support in infectious diseases: a narrative review of current applications. Clin. Microbiol. Infect, 2020; 26, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, S. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in precision and genomic medicine. Med. Oncol, 2022; 39, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino Ferreira da Silva Barros, M.H.; Oliveira Alves, G.; Morais Florêncio Souza, L.; da Silva Rocha, E.; Lorenzato de Oliveira, J.F.; Lynn, T.; Sampaio, V.; Endo, P.T. Benchmarking machine learning models to assist in the prognosis of tuberculosis. Informatic, 2021; 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, A.A. Prediction and classification of Tuberculosis using machine learning. J. Stat. Appl. Pro. 2024, 13(3), 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, P.; Moodley D.; Pillay A.W.; Seebregts, C.J.; Oliveira, T.D. “An investigation of classification algorithms for predicting HIV drug resistance without genotype resistance testing.” In Foundations of Health Information Engineering and Systems: Third International Symposium, FHIES 2013, Macau, China, August 21-23, 2013. Revised Selected Papers 3, 236-253. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2014.
- Flores, K.R.; de Carvalho, L.V.F.M.; Reading, B.J.; Fahrenholz, A.; Ferket, P.R.; Grimes, J.L. Machine learning and data mining methodology to predict nominal and numeric performance body weight values using Large White male turkey datasets. J. Appl. Poult. Res, 2023; 32, 100366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, G.; Khalilzadeh, O.; Michalski, M.; Do, S.; Samir, A.E.; Pianykh, O.S.; Geis, J.R.; Pandharipande, P.V.; Brink, J.A.; Dreyer, K.J. Current applications and future impact of machine learning in radiology. Radiology, 2018; 288, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, E.J. High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat Med., 2019, 25:44-56. [CrossRef]
- Abràmoff, M.D.; Lavin, P.T.; Birch, M.; Shah, N.; Folk, J.C. Pivotal trial of an autonomous AI-based diagnostic system for detection of diabetic retinopathy in primary care offices. NPJ digital medicine, 2018, 39. [CrossRef]
- Zazzi, M.; Cozzi-Lepri, A. Prosperi MCF. Computer-aided optimization of combined anti-retroviral therapy for HIV: new drugs, new drug targets and drug resistance. Curr HIV Res, 2016; 14, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macesic, N.; Polubriaginof, F.; Tatonetti, N.P. Machine learning: novel bioinformatics approaches for combating antimicrobial resistance. Curr Opin Infect Dis, 2017; 30, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Satola, S.W.; Read, T.D. Genome-based prediction of bacterial antibiotic resistance. J Clin Microbiol, 201, 8. [CrossRef]
- Durrant, J.D.; Amaro, R.E. Machine-learning techniques applied to antibacterial drug discovery. Chem Biol Drug Des, 2015; 85, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Lee, M.W.; Fulan, B.M.; Ferguson, A.L.; Wong, G.C.L. What can machine learning do for antimicrobial peptides, and what can antimicrobial peptides do for machine learning? Interface Focus 2017, 7, 20160153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sips, M.E.; Bonten, M.J.M.; van Mourik, M.S.M. Automated surveillance of healthcare-associated infections: state of the art. Curr Opin Infect Dis, 2017; 30, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.A.; Battegay, M.; Juchler, F.; Vogt, J.E.; Widmer, A.F. Introduction to machine learning in digital healthcare epidemiology. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol, 2018; 39, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evora, L.H.R.A.; Seixas, J.M.; Kritski, A.L. Neural network models for supporting drug and multidrug resistant tuberculosis screening diagnosis. Neurocomputing, 2017; 265, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Bhandari, K.; Sah, S.P.; Anitha, V.; Mane, Y.D.; Punithavel, R.; Banerjee, S. AI in Healthcare: Predicting Patient Outcomes using Machine Learning Techniques. Afr.J.Bio.Sc. 2024; 6. [Google Scholar]
- Revell, A.D.; Wang, D.; Wood, R.; Morrow, C. ’ Tempelman, H.; Hamers, R.L.; Alvarez-Uria, G.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Ene, L.; Wensing, A.M.J.; DeWolf, F. Computational models can predict response to HIV therapy without a genotype and may reduce treatment failure in different resource-limited settings. J. Antimicrob. Chemother, 2013; 68, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Statistics South Africa. Census 2022; Stats SA: Pretoria, South Africa, 2022. Available online: http://www.statssa.gov.za (accessed 21 April 2023).
- Berhan, A.; Berhan, Y.; Yizengaw, D. A meta-analysis of drug-resistant tuberculosis in Sub-Saharan Africa: how strongly associated with previous treatment and HIV co-infection? Ethiopian J. Health Sci., 2013; 23, 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Nachega, J.B.; Kapata, N.; Sam-Agudu, N.A.; Decloedt, E.H.; Katoto, P.D.; Nagu, T.; Mwaba, P.; Yeboah-Manu, D.; Chanda-Kapata, P.; Ntoumi, F.; Geng, E.H. Minimizing the impact of the triple burden of COVID-19, tuberculosis and HIV on health services in sub-Saharan Africa. Int. J. Infect. Dis, 2021; 113, S16–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seloma, N.M.; Makgatho, M.E.; Maimela, E. Evaluation of drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment outcome in Limpopo province, South Africa. Afri. J. Prim. Health Care Fam. Med, 2023; 15, 3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hamdouni, M.; Bourkadi, J.E.; Benamor, J.; Hassar, M.; Cherrah, Y.; Ahid, S. Treatment outcomes of drug-resistant tuberculosis patients in Morocco: Multi-centric prospective study. BMC Infect Dis. 2019, 19(1), 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramma, L.; Cox, H.; Wilkinson, L.; Foster, N.; Cunnama, L.; Vassall, A.; Sinanovic, E. Patients’ costs associated with seeking and accessing treatment for drug-resistant tuberculosis in South Africa. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis, 2015; 19, 1513–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Ismail, F.; Omar, S.V.; Blows, L.; Gardee, Y.; Koornhof, H. Drug-resistant tuberculosis in Africa: Current status, gaps and opportunities. Afr. J. Lab. Med, 2018; 7, 781. [Google Scholar]
- Przybylski, G.; Dąbrowska, A.; Pilaczyńska-Cemel, M.; Krawiecka, D. Unemployment in TB patients–ten-year observation at regional center of pulmonology in Bydgoszcz, Poland. Med. Sci. Monit. : Inter. Medical J. Exp. Clin. Res, 2014; 20, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mphande-Nyasulu, F.A.; Puengpipattrakul, P.; Praipruksaphan, M.; Keeree, A.; Ruanngean, K. Prevalence of tuberculosis (TB), including multi-drug-resistant and extensively-drug-resistant TB, and association with occupation in adults at Sirindhorn Hospital, Bangkok. IJID regions, 2022; 2, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limenh, L.W.; Kasahun, A.E.; Sendekie, A.K.; Seid, A.M.; Mitku, M.L.; Fenta, E.T.; Melese, M.; Workye, M.; Simegn, W.; Ayenew, W. Tuberculosis treatment outcomes and associated factors among tuberculosis patients treated at healthcare facilities of Motta Town, Northwest Ethiopia: a five-year retrospective study. Sci. Rep, 2024; 14, 7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, J.K.; Porter, J.D.; Conradie, H.H.; Boyles, T.H.; Gaunt, C.B.; Dimanda, S.; Cort, D. Treating drug-resistant tuberculosis in an era of shorter regimens: Insights from rural South Africa. South Afr. Med. J. 2023, 113(11), 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faye, L.M.; Hosu, M.C.; Iruedo, J.; Vasaikar, S.; Nokoyo, K.A.; Tsuro, U.; Apalata, T. Treatment outcomes and associated factors among tuberculosis patients from selected rural eastern cape hospitals: An ambidirectional study. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis, 2023; 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyare, S.A.; Osei, F.A.; Odoom, S.F.; Mensah, N.K.; Amanor, E.; Martyn-Dickens, C.; Owusu-Ansah, M.; Mohammed, A.; Yeboah, E.O. Treatment Outcomes and Associated Factors in Tuberculosis Patients at Atwima Nwabiagya District, Ashanti Region, Ghana: A Ten-Year Retrospective Study. Tuberc. Res. Treat, 2021; 9952806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariem, C.N.; Odumosu, P.; Dapar, M.P.; Musa, J.; Ibrahim, L.; Aguiyi, J. Tuberculosis treatment outcomes: A fifteen-year retrospective study in Jos-North and Mangu, Plateau State, North-Central Nigeria. BMC Public Health, 2020; 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofoegbu, O.S.; Odume, B.B. Treatment outcome of tuberculosis patients at National Hospital Abuja Nigeria: A five-year retrospective study. S. Afr. Fam. Pract, 2015; 57, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getie, A; Alemnew B. Tuberculosis treatment outcomes and associated factors among patients treated at Woldia General Hospital in NortheastEthiopia: An institution-based cross-sectional study. Infect. Drug Resist., 2020, 13:3423–3429.
- Tanue, E.A.; Nsagha, D.S.; Njamen, T.N.; Assob, N.J.C. Tuberculosis treatment outcome and its associated factors among people living with HIV and AID in Fako Division of Cameroon. PLoS One, 2019; 14, e0218800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapata, N.; Grobusch, M.P.; Chongwe, G.; Chanda-Kapata, P.; Ngosa, W.; Tembo, M.; Musonda, S.; Katemangwe, P.; Bates, M.; Mwaba, P.; Zumla, A. Outcomes of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Zambia: a cohort analysis. Infection, 2017; 45, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soedarsono, S.; Mertaniasih, N.M.; Kusmiati, T.; Permatasari, A.; Juliasih, N.N.; Hadi, C.; Alfian, I.N. Determinant factors for loss to follow-up in drug-resistant tuberculosis patients: the importance of psycho-social and economic aspects. BMC Pulm. Med., 2021; 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adepoju, V.A.; Adelekan, A.; Adejumo, A.O. Timing and reasons for lost to follow-up among patients on 6-month standardized anti-TB treatment in Nigeria. J Pre-Clin Clin Res, 2022; 16, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO) African Region. Low funding, COVID-19 curtail tuberculosis fight in Africa. https://www.afro.who.int/news/low-funding-covid-19-curtail-tuberculosis-fight-africa. (Accessed 5 September 2024).
- Abdul, J.B.P.A.A.; Adegbite, B.R.; Ndanga, M.E.D.; Edoa, J.R.; Mevyann, R.C.; Mfoumbi, G.R.A.I.; De Dieu, T.J.; Mahoumbou, J.; Biyogho, C.M.; Jeyaraj, S.; Niemann, S. Resistance patterns among drug-resistant tuberculosis patients and trends-over-time analysis of national surveillance data in Gabon, Central Africa. Infection, 2023; 51, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabunda, T.E.; Ramalivhana, N.J.; Dambisya, Y.M. . Mortality associated with tuberculosis/HIV co-infection among patients on TB treatment in the Limpopo province, South Africa. Afr. Health Sci, 2014; 14, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, M.A. , Yesuf, A., Girma, F., Adugna, F., Melak, K., Biru, M., Seyoum, M., Abiye, T. Impact of HIV-AIDS on tuberculosis treatment outcome in Southern Ethiopia–a retrospective cohort study. J. Clin. Tuberc. Other Mycobact. Dis., 2021, 25, 100279. 2021; 25, 100279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngari, M.M.; Rashid, M.A.; Sanga, D.; Mathenge, H.; Agoro, O.; Mberia, J.K.; Katana, G.G.; Vaillant, M.; Abdullahi, O.A. ; Burden of HIV and treatment outcomes among TB patients in rural Kenya: a 9-year longitudinal study. BMC Infect. Dis, 2023; 23, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, O.S.; Olaleye, S.A.; Mohsin, M.; Toivanen, P. Investigating machine learning methods for tuberculosis risk factors prediction: a comparative analysis and evaluation. Proceedings of the 37th International Business Information Management Association (IBIMA). ISBN: 978-0-9998551-6-4, 1-2 April 2021, Cordoba, Spain.
- Kalhori, S.R.N.; Zeng, X.J. Evaluation and comparison of different machine learning methods to predict outcome of tuberculosis treatment course. J. Intell. Learn. Syst. Appl. 2013, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | N | % |
|---|---|---|
|
Gender Male Female |
256 200 |
56.1 43.9 |
|
Age groups (years) 0-18 19-35 36-50 51-65 >66 |
32 185 142 65 21 |
7.2 41.6 31.9 14.6 4.7 |
|
Occupation Unemployed Employed (govt. and private) Student Pensioner Grant recipient Minors |
331 34 35 20 8 6 |
76.3 7.8 8.1 4.6 1.8 1.4 |
|
Type of TB PTB EPTB NR |
446 6 4 |
97.8 1.3 0.9 |
|
Type of resistance Monoresistance Polyresistance NR |
207 237 12 |
45.4 52.0 2.6 |
|
Type of drug resistance RR MDR Pre-XDR XDR INH-R NR |
205 194 23 17 6 11 |
45.0 42.5 5.0 3.7 1.3 2.4 |
|
Previous drug history New PT1 PT2 Unk NR |
226 178 43 1 8 |
49.6 39.0 9.4 0.2 1.75 |
|
HIV status Positive Negative NR |
281 165 10 |
61.6 36.2 2.2 |
| DR-TB type | Age groups (years) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-18 | 19-35 | 36-50 | 51-65 | >66 | |
| RR | 15 | 85 | 67 | 24 | 14 |
| MDR | 12 | 84 | 62 | 31 | 5 |
| Pre-XDR | 3 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 1 |
| XDR | 2 | 11 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| INH-R | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





