1. Introduction
Disorders in the functioning of cellular signaling receptors, in particular, members of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family, lead to the development of a number of serious diseases, primarily various types of cancer. One of the effective therapeutic strategies in this case is the use of molecules that selectively bind to the malfunctioning receptor and modulate its activity in a specified manner. Besides the monoclonal immunoglobulin-based antibodies (mAbs) which are one of the key therapeutic target-specific and high-affinity binders in modern medicine [
2,
3], non-immunoglobulin based scaffold proteins (SPs) are also widely used for generation of novel specific binding agents [
4]. А robust structural scaffold of SPs allows for effective reshaping of their interaction sites for selective recognition their cellular molecular targets. Compared to mAbs, SPs display a number of advantages such as significantly smaller (up to an order of the magnitude) size and high thermal stability, which result in relative simplicity and low-cost production in bacteria [
5]. Some of SPs (Adnectins, Affibodies, Anticalins, DARPins, etc.) have already attracted close attention of the pharmaceutical industry, entering the clinical trial phase [
4,
6,
7]. Successful applications of SPs have been reported for some members of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) family that regulate the key vital cell processes including the cell growth and differentiation [
4,
6,
8]. These receptors consist of a large extracellular ligand binding domain, a single transmembrane helix, and a cytoplasmic domain with tyrosine kinase catalytic activity. Among them, one of the most important representatives is HER receptor type 2 (HER2). Its overexpression occurring in a number of cancers, including the most common breast cancer, is often associated with a high rate of cell proliferation and more aggressive disease leading to multiple distant metastases [
9,
10]. The arsenal of HER2-targeting therapy includes the substances (first of all, mAbs and SPs) that selectively bind to various epitopes of the HER2 molecule and specifically modulate its activity [
8,
11]. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that SPs can be successfully applied in radionuclide molecular imaging for detecting tumor metastases as well as control the efficacy and dynamics of chemotherapy of HER2-expressing cancers. The evaluated SP-based probes were shown to accumulate in tumors with high efficacy and help to elicit HER2-expressing cancers with high imaging contrast being well-tolerated and quite safely [
12,
13,
14].
Promising results for the future development of SP-based probes for antitumor HER2-targeting therapy were obtained in a recent study of the HER2-binding activity of SP G3 which belongs to the DARPins (Designed Ankyrin Repeat Proteins) family [
1]. The relative simplicity and rapid generation of libraries of highly specific DARPins with subnanomolar affinity for a variety of target molecules, including various kinases, made this protein scaffold a very perspective candidate for drugs [
15,
16]. Due to their physico-chemical properties, DARPins are widely used in basic research, for example, as biosensors that track the localization of proteins and interactions within the cell [
17,
18]. Like other repeat proteins, DARPin molecule is composed of repeating conserved structural motifs that mimic the tandem structure of natural Ankyrins found in many proteins involved in specific protein-protein interactions and providing cell signaling and regulation, cytoskeleton integrity, inflammatory response, and many other functions [
19].
However, one of the key problems limiting the extensive clinical trials of SP-based therapeutic agents, such as the G3 protein, is its short residence time in the bloodstream due to efficient kidney filtration [
20]. A number of strategies to extend blood residence and prevent the high accumulation of small therapeutic proteins in kidney have been proposed [
21]. Today, the dominant approaches follow the path of increasing the size of the biotherapeutics, its hydrodynamic radius and thus overcoming the renal filtration cutoff (ca. 60 kDa). An alternative strategy for extending the half-life is the fusion with the Fc region of IgG or serum albumin for recycling by the neonatal Fc receptor. Albumin is the most abundant transport protein in human serum with a very long half-life (ca.19 days) and is therefore well suited for the experiments to increase the residence time of a pharmaceutical substance in the bloodstream [
22]. Attachment of albumin-binding domains/peptides or direct fusion of albumin with a small protein binder is believed to be a promising approach to further extend the half-life due to the overlap between these two strategies [
21,
23,
24]. Among a variety of fused albumin-binding moieties, both the designed serum albumin-binding domain (ABD) of DARPin [
25] and the bacterial ABD-domain [
1,
24] can seriously increase the half-life in blood plasma, reaching the level of serum albumin. It has been was shown that the recently designed fusion construct, consisting of G3 and ABD modules, effectively modifies the activity of HER2 [
1]. To develop radionuclide imaging probes with an extended residence in the blood, reduced renal uptake and a higher accumulation degree in the tumor, the authors created and tested
in vitro and
in vivo two fusion proteins (labelled with
177Lu) containing G3 and ABD domains connected by (GS
3)
3-linker. It should be noted that the chimeras differed from each other only in the order of their domains. Variant with the ABD at the N-terminus demonstrated a loss of HER2-binding activity (but only in albumin-free medium). Nevertheless, both protein constructs have been shown to have an increased plasma lifetime compared to the G3 protein used as a control.
The molecular mechanism responsible for these unexpected effects has not been established. It should be noted that little is known about the spatial rearrangement of the modules in the absence of their target partners. Both the fact of domain interaction and /or “inappropriate” binding interfaces can seriously affect the functionality of the entire protein construct. This means that the future development of such modular proteins, specifically interacting with both HER2 (as well as with other receptors and not only from the RTK family) and the proteins performing auxiliary functions (for example, albumin, which improves the pharmacokinetic profile of the chimera) requires understanding the molecular details of the chimera’s behavior
in vivo. Furthermore, in modular proteins, the linker length and flexibility obviously affect their kinetic behavior and effective functioning [
26] and, hence, should also be taken into consideration. To proceed with this, in the present work, we explore the molecular mechanisms underlying the differences in target specificity of the ABD-G3 and G3-ABD constructs described in [
1].
2. Results
2.1. Design of the Study
Obviously, the development, optimization and practical application of the designed specific HER2-binder (G3 DARPin domain) require the elucidation of molecular details of the structural mechanism of their interaction with the target receptor. As shown previously [
1], the fused serum albumin-binding (ABD) domain has extended the plasma life-time of the both conjugates: G3-ABD and ABD-G3. To minimize steric hindrance between domains, a sufficiently long and flexible (GS
3)
3 linker between domains was added (
Figure S1). However, the varying of the order of the domains was demonstrated to change the resulting activity. To understand possible reason of this, a comprehensive multi-stage molecular biophysical approach was applied, including NMR spectroscopy and molecular modeling. The simulations included homology modeling, molecular docking, and atomistic molecular dynamics calculations. The objectives were formulated as follows:
To establish whether the G3 and ABD domains in the conjugates are able to associate in an aqueous solution;
If so, what are the most likely interfaces in the resulting complexes? Can they affect the known G3 binding site for the HER2 receptor?
How can the effect of HSA be explained on the basis of molecular structure data?
What determines the significant difference in the action of chimeras with the "opposite orientation" - G3-ABD / ABD-G3?
In NMR studies, high resolution 1H-NMR spectra were obtained in water of both chimeras and mixtures of isolated fragments of G3 and ABD – with and without the addition of HSA. As a result, conclusions were made about the possibility of G3/ABD association, the general features of the conformational dynamics of proteins, as well as concerning the influence of HSA. In computational experiments, the propensity of domains to association was evaluated using molecular dynamics (MD) and Monte Carlo (MC) methods and possible protein-protein interactions were characterized in detail. Based on the totality of the biophysical data, we hypothesize about the possible role of the domain linker, which limits the accessibility of detected sites depending on the order of the domain in chimeric molecules.
2.2. NMR Spectroscopy
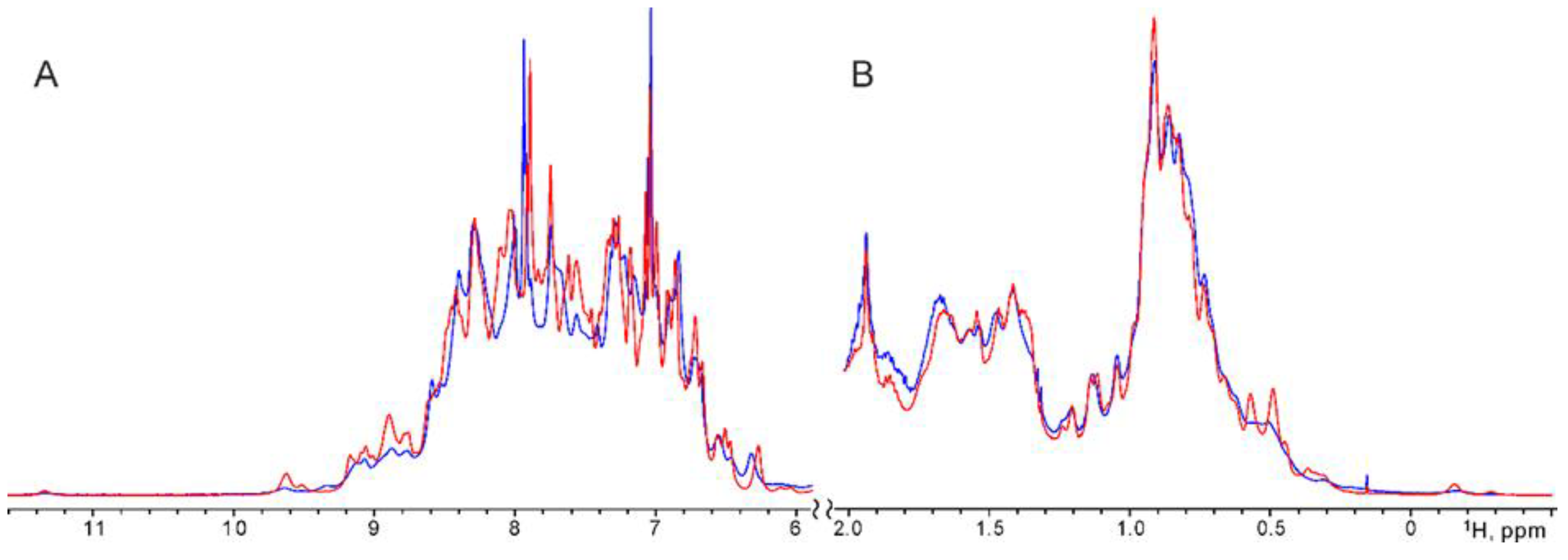
According to the characteristic signal dispersion in the
1H-NMR spectra of DARPins G3-ABD and ABD-G3 (
Figure 1,
Figure S2), both constructs have a globular structure consisting of α-helices, which were quite stable at 30°C without aggregation and denaturation at least for a week. Nevertheless, the comparison of NMR spectra revealed some differences in the overall conformation of the two constructs, associated with the alternative spatial arrangement and interaction of their G3 and ABD domains. In particular, the distribution pattern of the
1H-signal differed markedly in the regions of the amide (
Figure 1A) and methyl (
Figure 1B) groups of the spectra. In both cases, the methyl signals of Ile and Leu residues of the G3 domain were strongly shifted when G3 is linked to ABD (
Figure S2). Remarkably, in the
1H-NMR spectra of ABD-G3 a high-field
1H-signal near -0.2 ppm (
Figure 1B,
Figure S2B) of the methyl group of one Ile residue (spatially adjacent to the aromatic ring of Phe, according to the two-dimensional
1H-NMR spectra of G3) from the G3 domain was strongly split into two signals with an occupancy ratio of the major and minor components equal to ~3. A similar distinct splitting was observed for a separate low-field amide signal of the G3 subunit near 9.6 ppm (
Figure 1A) indicating that two distinct conformations of the ABD-G3 chimera exist in solution.
In the
1H-NMR spectra of G3-ABD, almost all protein signals also appeared to be doubled, but very broadened (especially those of the minor component) implying that conformation exchange, presumably, between multiple interaction modes of subunits occurred on an intermediate NMR timescale (in microseconds) for the variant G3-ABD, while the ABD-G3 construct was more rigid with better mutual folding of domains via two alternative interfaces switching at a slow NMR timescale (in milliseconds and slower). It should be also noted, that the free G3 and ABD interact via non-covalent association in a fashion that is somewhat similar to the conjugated G3-ABD, and the complex was destroyed after addition of HSA (see the Supplementary materials,
Figure S2C).
2.3. Molecular Modeling
According to the results of MD and MC simulations starting from both spatially remote domains and complexes with a hydrophobic interface (see
Section 4), G3 and ABD modules interact with each other. It is important to note that in the case of applying both computational approaches, the spatial structure of each of the individual domains remained stable (average root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) values of the backbone atoms from the starting states do not exceed 1.5 Å, see
Table S1), unlike the case of flexible linkers between them. The analysis of the ensemble of all complexes obtained showed that the G3 module interacts with ABD through two distinct types of sites spatially distant from each other. In one case, the protein-protein interface is formed by hydrophobic residues of G3 (hereinafter this nonpolar site is called “np-site”), and in the other – by predominantly polar residues (“p-site").
Detailed consideration of the both G3 sites shows the following.
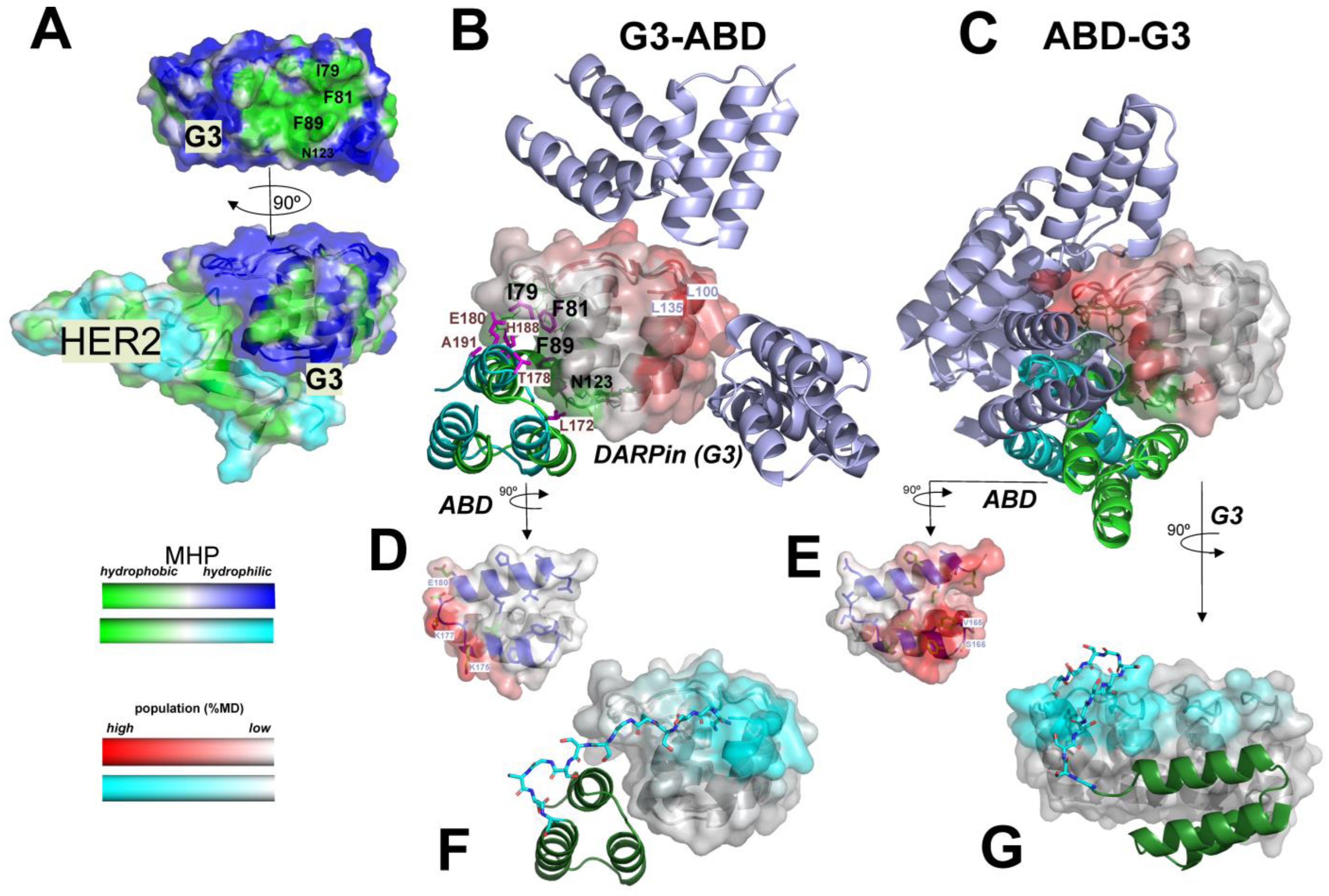
2.3.1. The HER2- and ABD-Binding Interfaces (Np-Site) on the G3 Surface Are Almost Identical
Domain packing via np-site is quite stable, since MD/MC simulations starting from both chimeras associated via this interface showed the absence of dissociation of this complex. In these cases, G3-ABD and ABD-G3 conjugates showed a high degree of similarity between the binding motif of G3 with the HER2-binding site in the experimentally obtained complexes of G3 with extracellular domains of membrane-bound HER2 receptors (PDB: 4hrn,
Figure 2A) (
Figure 2B,C). The identity of the contact areas in the predicted complexes and the experimental models is about 90%. The HER2-binding interface of G3 includes the major nonpolar pattern on its molecular surface. It contains about 20 amino acid residues, most of which are hydrophobic. Interface-forming residues of G3 are distant from each other in the sequence and belong to both ordered elements (α-helices) and β-hairpin/loop regions. Additional details of the predicted complexes are given in the Supplementary materials.
2.3.2. Alternative p-Sites of ABD-Binding on G3 Surface Were Found in Both Chimeras and Practically Do Not Overlap
The alternative interaction interfaces (p-sites) are characterized by a significantly smaller contact area with absence of stacking interactions and fewer hydrophobic contacts. At the same time, the electrostatic interactions are more pronounced (
Table S1). In
Figure 2, the most populated spatial locations (p-sites) of the ABD domain in G3-ABD (
Figure 2B) and ABD-G3 (
Figure 2C) chimeras are shown in light-blue color and cartoon mode. In this figure, G3 surfaces with high and low frequency of involvement of the corresponding residue in contact with the ABD molecule are colored in red and white. In nine 200-ns MD trajectories, where domains were separated from each other (hereafter these MD starts are designated as “w-MD starts”), only in ~20% of MD states domains do not interact, while the starts, where the domains remain non-interacting all the time of MD calculation, it did not turn out. During w-MD, the domains are usually associated during the first 100 ns, which is not surprising, since the molecular surface of the G3 has a high net negative charge (-10). It seems likely that such p-sites are the result of random sticking of the ABD domain to the G3 domain. It should be noted that the length and location of the inter-domain linker relative to the G3 domain are very important because they limit the area of the G3 surface accessible for such a ABD “walking”. As can be seen from
Figure 2BC, potential ABD binding p-sites occupy large areas, but they practically do not overlap for two chimeras.
2.3.3. The Availability of HER2 Site Depends on the Order of the Domains in the Constructs
In all w-MD runs of ABD-G3, there is a pool of HER2 interface residues that are part of the p-sites in most of the trajectories: Y46, L48, D77, A78, I79 and F112 (
Figure 2B, hereinafter the numbering of the residues corresponds to the G3-ABD sequence). In the case of ABD-G3, “polar” variant of the domain interaction area considerably overlaps with np-site, which means that ABD domain can sterically interfere with G3 binding to HER2 (
Figure 2A,C).
On the opposite, for the G3-ABD molecule, all four w-MD trajectories show “sticking” of ABD outside the np-site zone (
Figure 2B). Such a difference is determined by the order of domains in the amino acid sequence of chimeras and by the limited linker length.
2.3.4. The Involvement of the HSA-Motif in G3 Binding Depends on Both the Type of Construct and the Binding Interface of Its Modules
Our simulation data have shown that in both chimeras, the HSA motif of ABD domain is involved in binding to G3. The HSA-binding motif elucidated from the high-resolution structures of ABD/HSA complexes (PDB ID: 2vdb) includes residues of two helices (except for the N-terminal one) and two short inter-helical loop regions which are spatially separated (
Figure 2D,E,
Figure S3). One of these loops is involved into the H-bonding (
Figure 2E) with albumin molecule, the other participate in charge interactions (
Figure 2D). Between the loops, there is a hydrophobic cluster formed by helical residues. Different types of intermolecular interactions (H-bonds, electrostatic and hydrophobic ones) provide strong binding of ABD-domain to the albumin molecule.
In MD complexes with np-sites of G3, HSA-motif is almost completely inaccessible to the solvent (ca. 70% of HSA-binding residues are on the G3-ABD interface, see
Table S1) in both chimeras and binding of HSA to such complexes is impossible. However, in complexes with p-sites of G3, this motif is shielded from water in a different extent: largely inaccessible to the solvent in ABD-G3 (
Figure 2E), but rather exposed in the G3-ABD (
Figure 2D,
Table S1). So, in one of w-MD runs of ABD-G3 all three regions (two loops and helical residues) of HSA-motif interact with G3 resulting in more than 50% of the HSA interface being inaccessible. Obviously, in this case (as in the case of the np-interface for both complexes) albumin will compete with G3 for binding to ABD.
In contrast, the C-terminal location of the ABD-domain results in a less extended area of protein-protein interface, which is characterized mainly by electrostatic interactions arising from inter-helical “charged” loop of the HSA motif carrying the corresponding residues (
Figure 2D). Thus, in all w-MD trajectories of G3-ABD, a large part (on average, more than 70%) of the HSA site remains solvent accessible. It can be assumed that in this case albumin can bind ABD-domain even within the G3-ABD complex, without its dissociation (
Figure S4). However, it is quite possible that bound HSA may sterically interfere with the effective interaction of the G3-ABD complex with the HER2 receptor (as shown in the model reconstruction of HER2/G3-ABD/HSA complex,
Figure S4).
2.3.4. Role of the Domain Linker
Analysis of the MD data revealed that the domain linker (12 residues) connecting the G3 / ABD domains affects the spatial packing of the domains. So, the number of atom-atom contacts of the linker with both domains is ~50% of domain - domain contacts in G3/ABD complex with hydrophobic interface (np-site). In case of polar interfaces (p-sites) the number of such contacts turns out to be comparable to that observed for the inter-domain interactions (see
Table S1). Analysis of w-MD starts showed that in the most populated states the linker tends to interact with neighboring helical and flexible long loop regions of G3, which are spatially distant from each other in G3-ABD and ABD-G3 (
Figure 2F,G). As a result, such linker’s behavior delimits the regions of the G3 surface available for ABD binding and may restrict an accessibility of the HER2-site depending on the chimera’s type.
Also, the domain linker can participate in additional stabilization of the conjugates’ complexes due to their interaction with the domains (mostly with G3). Thus, in the case of the ABD-G3 complexes with p-interface, the average contact area of the linker with G3 is around two times greater than in the analogous G3-ABD complexes, and the complex is additionally stabilized by a larger number of H-bonds between the linker and G3 (see
Table S1).
3. Discussion
As it was shown in vitro [
1], binding of ABD-G3 to human serum albumin (HSA) was substantially weaker as compared to G3-ABD. Moreover, without albumin the specific binding of ABD-G3 to HER2 is lost. Here, we explain these results at the molecular level based on NMR and modeling data. As revealed by the NMR spectra, G3 and ABD mutually associate both in conjugates and in free states via at least two distinct alternative interfaces with the occupancy ratio ~3:1. This agrees perfectly well with the results of modeling, where both constructs reveal high potential for G3/ABD interaction: two types of binding interfaces (the so-called np- and p–sites) were identified in the G3 domain. The hydrophobic contact region of G3 (np-site) is validated by NMR-data showing that apolar side chains of Tyr, Leu and Ile residues (spatially adjacent to one of phenylalanines) from G3 participate directly in G3/ABD interaction. Indeed, two pairs of Ile/Phe (I79/F81 and I79/F112), as well as a number of Leu (L48, L53, L86) and Y46 were found in the np-site observed in simulations and in the experimentally derived HER2-binding site. It is important that in complexes with such a hydrophobic interface, the contact regions in G3 and ABD domains are almost identical to the known HER2- and HSA-binding sites, respectively. Comparing to the hydrophobic np-site, the spontaneously formed domain complexes observed in MD/MC simulations started from non-interacting protein domains have a much smaller and more polar contact areas (p-sites). It should be noted, the alternative inter-domain interfaces for both conjugates were also detected by NMR.
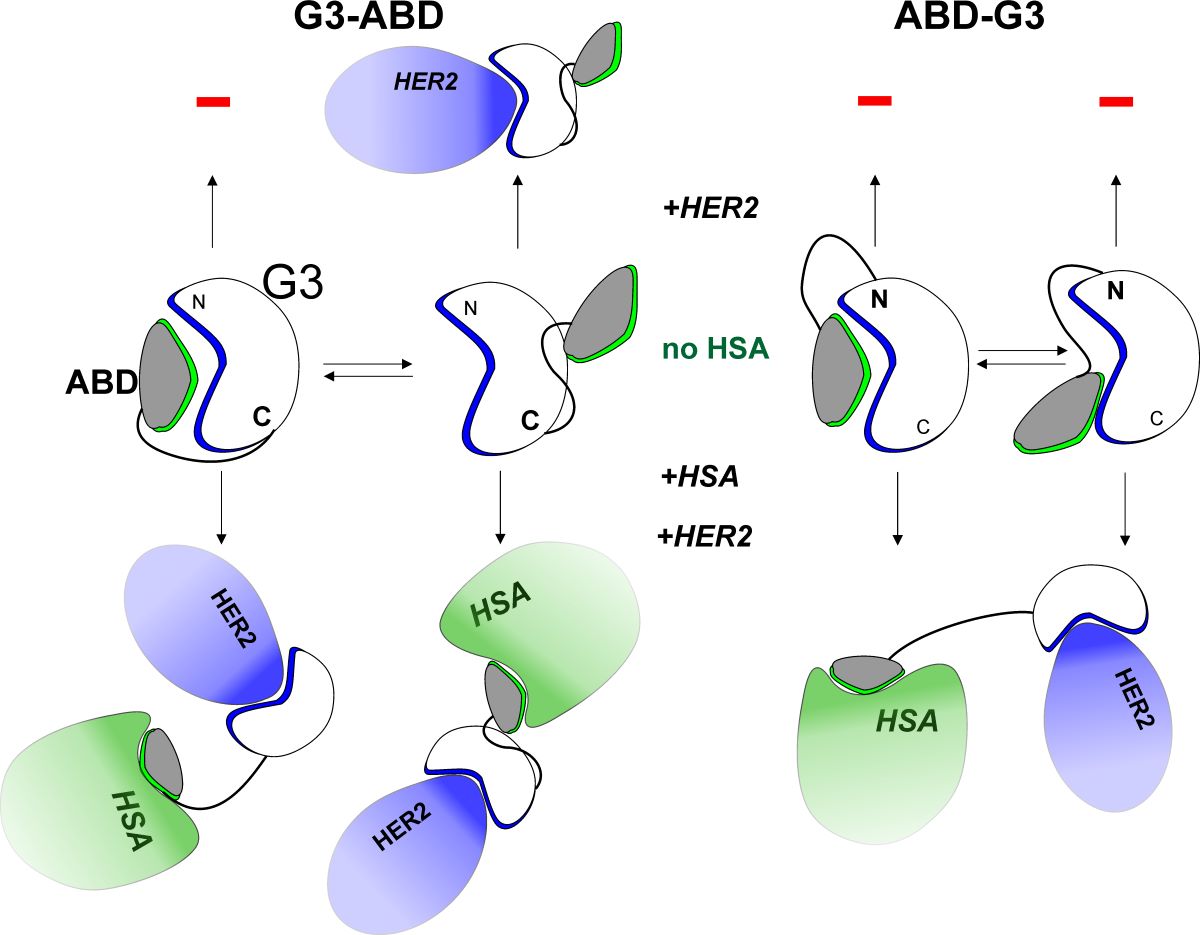
Based on the experimental and modeling data we propose the following scenario explaining the detected changes in the
in vitro activity of ABD-fused conjugates depending on the order of their domains. The main findings are summarized and presented schematically in the diagram (
Figure 3). Depending on the chimera, the alternative ABD binding sites (p-sites) on G3 surface have significantly different locations (
Figure 3A). The computational results prove that the inter-domain linker delimits the regions of the G3 surface (
Figure 2) available for ABD binding depending on its C- or N-terminal location in the sequence and affects the accessibility of the HER2-site. Importantly, p-sites in G3-ABD do not overlap with the HER2/np-site. Thus, the HER2-binding site in G3-ABD remains free and capable of interacting with the receptor. Opposite situation is observed in ABD-G3, where the region of overlapping interfaces (np- and p-sites) includes residues Ile and Phe (found on the interfaces in all simulations). Thus, regardless of the occupancies of the G3/ABD binding interfaces, ABD-G3 is likely to be sterically constrained to interact with HER2 and lose activity in an albumin-free medium (
Figure 3A).
Because both chimeras contain ABD module - the high-affinity binder of HSA - albumin added to the medium strongly competes for interaction with G3. This results in dissociation of the G3/ABD complexes (
Figure 3B), exposure of the HER2/np-site and restoring binding of ABD-G3 to HER2 (
Figure 3C). The differences in dissociation rates of the complexes with p- and np-interfaces can play a significant role in reducing the affinity of ABD-G3 for HSA observed in experiments. As can be seen in the diagram (
Figure 3A), direct binding of albumin to ABD-G3 is not possible due to the total (in case of np-site) or substantial (p-sites) inaccessibility of the HSA-site in ABD domain. Moreover, as revealed by NMR, the domains in ABD-G3 are better packed than in G3-ABD and reveal slower (milliseconds and slower) transitions between alternative association modes. Taking into account modeling data, we also suggest that the domain linker contributes to the additional stabilization of the complexes with p-interfaces. In contrast to ABD-G3, the energy barrier between the major and minor conformational states of G3-ABD is apparently substantially less, resulting in fast switching between these interaction modes (on a microsecond NMR timescale). As a result, both HSA and HER2 sites are more exposed and available for interaction with albumin and HER2 receptor. In addition, based on the significantly lower involvement of the HSA motif in minor states of G3-ABD complexes (with p-interfaces), it can be assumed that the interaction of this complex with both targets (HSA and HER2) can occur without dissociation of the complex (
Figure 3B).
Shortly, we found that the targeting properties of the ABD-fused construct are sensitive to a number of structural and dynamic factors, which, in turn, depend on the order of the domains in the molecule. These include the location of the G3/ABD interaction interfaces, the overlap between different types of interfaces, the ratio of populations of complexes with alternative interfaces, and the degree of involvement of the HSA-motif in domain interactions. So, a change in the order of the domains in the polypeptide chain can significantly affect the spatial packing of domains, shifting the equilibrium distribution of possible types of ABD/G3 complexes which leads to changes in their biological activity.
Finally, it is important to note that the aim of this work was not to determine the exact (with high resolution) spatial structure(s) of the complex of G3 and ABD domains constituting the chimeras. The solution of this problem lies beyond the scope of this study, since it requires a lot of effort both experimentally and computationally. In the first case, this is due to the need for complete attribution of signals in the spectra, the use of isotopic labeling, etc. In the second case, it is necessary to have a set of structural constraints taken from experiments (for example, NMR) and required to scan the conformational phase space when searching for the most energetically favorable states of G3/ABD packing.
4. Materials and Methods
The amino acid sequences of G3, G3-ABD and ABD-G3 conjugates are given in the Supplementary materials (
Figure S1). Expression, isolation and purification of the proteins was performed according to the methodology described earlier [
1]. Most of the chemicals used in the study were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Sweden AB (Stockholm, Sweden).
4.1. NMR Studies
The 1H-NMR spectra were acquired at 30°C on a 600 MHz AVANCE III spectrometer (Bruker BioSpin, Germany) equipped with 5 mm pulsed-field gradient triple-resonance cryoprobe. NMR samples of DARPins G3-ABD (120 µM) and ABD-G3 (140 µM), as well as the equimolar mixture of separated G3 and ABD (150 µM) were prepared in 5 mm shigemi NMR tubes using 20 mM phosphate buffer with pH 7.4 containing 200 mM NaCl and 10% D2O. The 1 mM tris (2-carboxyethyl) phosphine (TCEP) was used as a reducing agent to break the inter-molecular S-S bridge between the C-terminal residues of G3-ABD and ABD-G3.
4.2. Modeling of Interaction between DARPin G3 and ABD
4.2.1. Building Up the Starting Spatial Models of G3-ABD and ABD-G3
The spatial structure of DARPin module (residues: 12-136) was taken from the Protein Data Bank (PDB ID: 2jab). Hereinafter, the numbering of domains' residues is given for G3 -ABD molecule. NMR-model of albumin binding domain of protein G from
Streptococcus sp (PDB ID: 1gjs, residues: 20-65) was selected as a structural template for ABD module (residues: 149-194). Sequences of the template and ABD domain are very similar (>85% identity, only 7 amino acid residue replacements, see
Figure S3). The homology model of ABD was built using Modeller software [
27]. The final spatial structures of the entire G3-ABD and ABD-G3 molecules (200 and 196 amino acids, respectively,
Figure S1) including 12-mer polypeptide linker between G3 and ABD modules were constructed with Modeller (version 9v9) and Maestro (version 9.3.5, Schrödinger, USA) software.
To assess the interaction potential of DARPin (G3) – ABD modules, all-atom MD simulations were carried out in explicit water solution. The following variants of starting G3 and ABD mutual arrangement in both G3 -ABD and ABD-G3 molecules were prepared:
Starting model of this complex was obtained using protein-protein docking procedure and ZDOCK program (
https://zdock.wenglab.org/ accessed on 16 September 2024). Before, the distribution of hydrophobic/hydrophilic properties on the molecular surfaces of the corresponding protein modules was calculated using the molecular hydrophobicity potential (MHP) approach implemented in the PLATINUM software [
28]. Then, some hydrophobic residues (G3: F89, I90; ABD: F168, Y169) from the central part of the major hydrophobic patterns were selected as “contacting” for rescoring of the top docking solutions such a way that the specified residues being in the binding site.
4.2.2. MD Simulations
A number of 200 ns MD simulations in water solution were carried out for G3 -ABD and ABD-G3 proteins. MD calculations were performed using the GROMACS package (versions 2020.4/6) [
29] and the all-atom force field CHARMM36 [
30]. In all calculations, the tip3p [
31] water model and 3D periodic boundary conditions were employed. A spherical cutoff function (12 Å) and the particle mesh Ewald (PME) algorithm [
32] (with a 12 Å cutoff) were used to treat van der Waals and electrostatic interactions, respectively. The preparation stages included system minimization and heating from 5 to 310 K. Finally, MD production runs (duration of 200 ns each) were conducted in an NPT ensemble at a constant temperature of 310 K with an integration step of 2 fs. A brief description of the starting systems, and the number of MD trajectories is given in
Table S1.
4.2.3. MC Conformational Search
The protein conformational space was explored via MC search in torsion angles space and in the presence of implicit water-mimic solvent as described elsewhere [
33]. Two starting models of protein complex G3-ABD were employed: i) included as randomly placed non-interacting domains; ii) associated domains with the hydrophobic binding interface (initial as MD-state taken (from MD run) of the associated domains with hydrophobic binding interface. MC simulations were performed using all-atom ЕСЕРР/2 force field [
34]. The distance-dependent dielectric permeability ɛ =4
× r and an adaptive-temperature schedule protocol were applied. After each MC step, the structures were subjected to conjugate gradients energy minimization. Other details of MC simulation’s protocol are given in [
33]. Further analysis of the obtained G3/ABD binding modes was carried out for the resulting ensemble of low-energy MC states in the energy range: E
min., E
min.+ 20 kcal/mol, where E
min is the minimal potential energy of the system obtained via MC simulations.
4.2.4. Data Analysis
Analysis of MD/MC data included detailed analysis of the interaction interface between DARPin and ABD modules in G3-ABD and ABD-G3 molecules. MD data were analyzed and averaged over the resulting MD trajectories. The latter were sampled at time intervals of 100−1000 ps. Conformational mobility and intermolecular contacts (including hydrophobic, electrostatic and stacking interactions) were delineated using GROMACS [
29] tools and in-house software. The distribution of hydrophobic/hydrophilic properties on the molecular surfaces of the peptides was calculated using the MHP approach [
35]. Mapping the hydrophobic properties of the peptides’ surfaces was estimated with the PLATINUM software [
28]. The accessible surface area (“contact area”) was calculated by
naccess version 2.1.1 program (
http://www.bioinf.manchester.ac.uk/naccess/ accessed on 16 September 2024). Molecular graphics were rendered using PyMOL v. 2.5 (
http://pymol.org accessed on 16 September 2024).
5. Conclusions
As shown earlier, fusion of anti-HER2 DARPins with ABD increases their retention time of in the blood and leads to a higher accumulation in the tumor due to high bioavailability of the targeting agent. The main finding of this work is that the effect of merging SP with ABD depends strongly on the order of domains in the construct and is most likely caused by the domain-domain association and by different conformation/positioning of linkers with respect to the domains, which affects the domain-linker interactions. This suggests that the future design of antitumor conjugates based on DARPin-ABD fusion and related chimeras requires careful evaluation of various protein architecture using molecular biophysics methods.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, Figure S1: Amino acid sequences of DARPin constructions: G3-ABD, ABD-G3 and G3; Figure S2:
1H-NMR spectra of the DARPins conjugates and free G3; Figure S3: Protein sequence alignment of ABD-module with its structural template (1gjs) and albumin-binding domain (from
Finegoldia magna) as part of the complex with albumin (2vdb); Figure S4: MD simulations: molecular reconstruction of HER2/G3-ABD/HSA complex; Table S1: Structural parameters of binding interfaces of G3 /ABD complexes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G.K., E.V.B., S.M.D., and R.G.E.; investigations: A.G.K. and R.G.E. performed the simulations, E.V.B. carried out NMR experiments; resources, A.A.S., E.V.K; writing—original draft preparation, A.G.K., E.V.B., and R.G.E.; writing—review and editing, A.G.K., E.V.B., S.M.D., and R.G.E.; supervision, S.M.D., V.T., and R.G.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (Agreement No. 075-15-2024-536).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the article and the
Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Supercomputer calculations were supported within the framework of the HSE University Basic Research Program. Access to computational facilities of the Supercomputer Center “Polytechnical” at the St. Petersburg Polytechnic University and IACP FEB RAS Shared Resource Center “Far Eastern Computing Resource” equipment (https://cc.dvo.ru) is gratefully appreciated.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Deyev, S.M.; Oroujeni, M.; Garousi, J.; Gräslund, T.; Li, R.; Rosly, A.H.B.; Orlova, A.; Konovalova, E.; Schulga, A.; Vorobyeva, A.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of HER2-Targeting DARPin G3: Impact of Albumin-Binding Domain (ABD) Fusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullard, A. FDA Approves 100th Monoclonal Antibody Product. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.-M.; Hwang, Y.-C.; Liu, I.-J.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsai, H.-Z.; Li, H.-J.; Wu, H.-C. Development of Therapeutic Antibodies for the Treatment of Diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedler, M.; Skerra, A. Non-Antibody Scaffolds as Alternative Therapeutic Agents. In Handbook of Therapeutic Antibodies; Dübel, S., Reichert, J.M., Eds.; Wiley, 2014; pp. 435–474 ISBN 978-3-527-32937-3.
- Binz, H.K.; Stumpp, M.T.; Forrer, P.; Amstutz, P.; Plückthun, A. Designing Repeat Proteins: Well-Expressed, Soluble and Stable Proteins from Combinatorial Libraries of Consensus Ankyrin Repeat Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 332, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hober, S.; Lindbo, S.; Nilvebrant, J. Bispecific Applications of Non-Immunoglobulin Scaffold Binders. Methods 2019, 154, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurch, T.; Pierré, A.; Depil, S. Novel Protein Scaffolds as Emerging Therapeutic Proteins: From Discovery to Clinical Proof-of-Concept. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Iqbal, N. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) in Cancers: Overexpression and Therapeutic Implications. Mol. Biol. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Parker, B.A.; Schwab, R.; Kurzrock, R. HER2 Aberrations in Cancer: Implications for Therapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amisha, F.; Malik, P.; Saluja, P.; Gautam, N.; Patel, T.H.; Roy, A.M.; Singh, S.R.K.; Malapati, S.J. A Comprehensive Review on the Role of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) as a Biomarker in Extra-Mammary and Extra-Gastric Cancers. Onco 2023, 3, 96–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, E.; Shan, K.; Dalal, S.; Vu, D.; Milillo-Naraine, A.; Guaqueta, D.; Ergle, A. Molecular Targeting of the Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-2 (HER2) Genes across Various Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahnd, C.; Kawe, M.; Stumpp, M.T.; De Pasquale, C.; Tamaskovic, R.; Nagy-Davidescu, G.; Dreier, B.; Schibli, R.; Binz, H.K.; Waibel, R.; et al. Efficient Tumor Targeting with High-Affinity Designed Ankyrin Repeat Proteins: Effects of Affinity and Molecular Size. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragina, O.; Chernov, V.; Schulga, A.; Konovalova, E.; Garbukov, E.; Vorobyeva, A.; Orlova, A.; Tashireva, L.; Sörensen, J.; Zelchan, R.; et al. Phase I Trial of 99mTc-(HE)3-G3, a DARPin-Based Probe for Imaging of HER2 Expression in Breast Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolmachev, V.; Bodenko, V.; Oroujeni, M.; Deyev, S.; Konovalova, E.; Schulga, A.; Lindbo, S.; Hober, S.; Bragina, O.; Orlova, A.; et al. Direct In Vivo Comparison of 99mTc-Labeled Scaffold Proteins, DARPin G3 and ADAPT6, for Visualization of HER2 Expression and Monitoring of Early Response for Trastuzumab Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amstutz, P.; Koch, H.; Binz, H.K.; Deuber, S.A.; Plückthun, A. Rapid Selection of Specific MAP Kinase-Binders from Designed Ankyrin Repeat Protein Libraries. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2006, 19, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahnd, C.; Wyler, E.; Schwenk, J.M.; Steiner, D.; Lawrence, M.C.; McKern, N.M.; Pecorari, F.; Ward, C.W.; Joos, T.O.; Plückthun, A. A Designed Ankyrin Repeat Protein Evolved to Picomolar Affinity to Her2. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 369, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, J.R.; Benk, A.S.; Schaefer, J.V.; Dreier, B.; Hermann, L.O.; Plückthun, A.; Missirlis, D.; Spatz, J.P. Designed Ankyrin Repeat Proteins as Actin Labels of Distinct Cytoskeletal Structures in Living Cells. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 8919–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, M.; Batyuk, A.; Klenk, C.; Kummer, L.; De Picciotto, S.; Gülbakan, B.; Wu, Y.; Newby, G.A.; Zosel, F.; Schöppe, J.; et al. Generation of Fluorogen-Activating Designed Ankyrin Repeat Proteins (FADAs) as Versatile Sensor Tools. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 1272–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, L.K.; Cammett, T.J.; Desrosiers, D.C.; Peng, Z. The Ankyrin Repeat as Molecular Architecture for Protein Recognition. Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meibohm, B. Pharmacokinetics and Half-Life of Protein Therapeutics. In Therapeutic Proteins; Kontermann, R., Ed.; Wiley, 2012; pp. 23–38 ISBN 978-3-527-32849-9.
- Kontermann, R.E. Half-Life Extended Biotherapeutics. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, A.; Emami, J.; Tuszynski, J.A.; Lavasanifar, A. The Uniqueness of Albumin as a Carrier in Nanodrug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 1862–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Shin, G.; Lim, S.I. Human Serum Albumin Binders: A Piggyback Ride for Long-Acting Therapeutics. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, J.T.; Pehrson, R.; Tolmachev, V.; Daba, M.B.; Abrahmsén, L.; Ekblad, C. Extending Half-Life by Indirect Targeting of the Neonatal Fc Receptor (FcRn) Using a Minimal Albumin Binding Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5234–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, D.; Merz, F.W.; Sonderegger, I.; Gulotti-Georgieva, M.; Villemagne, D.; Phillips, D.J.; Forrer, P.; Stumpp, M.T.; Zitt, C.; Binz, H.K. Half-Life Extension Using Serum Albumin-Binding DARPin® Domains. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2017, 30, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, D.M.; Turowski, V.R.; Murakami, M.T. Effects of the Linker Region on the Structure and Function of Modular GH5 Cellulases. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Protein Structure Modeling with MODELLER. In Structural Genomics; Chen, Y.W., Yiu, C.-P.B., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer US: New York, NY, 2021; ISBN 978-1-07-160891-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pyrkov, T.V.; Chugunov, A.O.; Krylov, N.A.; Nolde, D.E.; Efremov, R.G. PLATINUM: A Web Tool for Analysis of Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic Organization of Biomolecular Complexes. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1201–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauda, J.B.; Venable, R.M.; Freites, J.A.; O’Connor, J.W.; Tobias, D.J.; Mondragon-Ramirez, C.; Vorobyov, I.; MacKerell, A.D.; Pastor, R.W. Update of the CHARMM All-Atom Additive Force Field for Lipids: Validation on Six Lipid Types. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 7830–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Tirado-Rives, J. Potential Energy Functions for Atomic-Level Simulations of Water and Organic and Biomolecular Systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2005, 102, 6665–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A Smooth Particle Mesh Ewald Method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremov, R.G.; Nolde, D.E.; Vergoten, G.; Arseniev, A.S. A Solvent Model for Simulations of Peptides in Bilayers. I. Membrane-Promoting α-Helix Formation. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 2448–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemethy, G.; Pottle, M.S.; Scheraga, H.A. Energy Parameters in Polypeptides. 9. Updating of Geometrical Parameters, Nonbonded Interactions, and Hydrogen Bond Interactions for the Naturally Occurring Amino Acids. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 1883–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremov, R.G.; Alix, A.J.P. Environmental Characteristics of Residues in Proteins: Three-Dimensional Molecular Hydrophobicity Potential Approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1993, 11, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).