Highlights
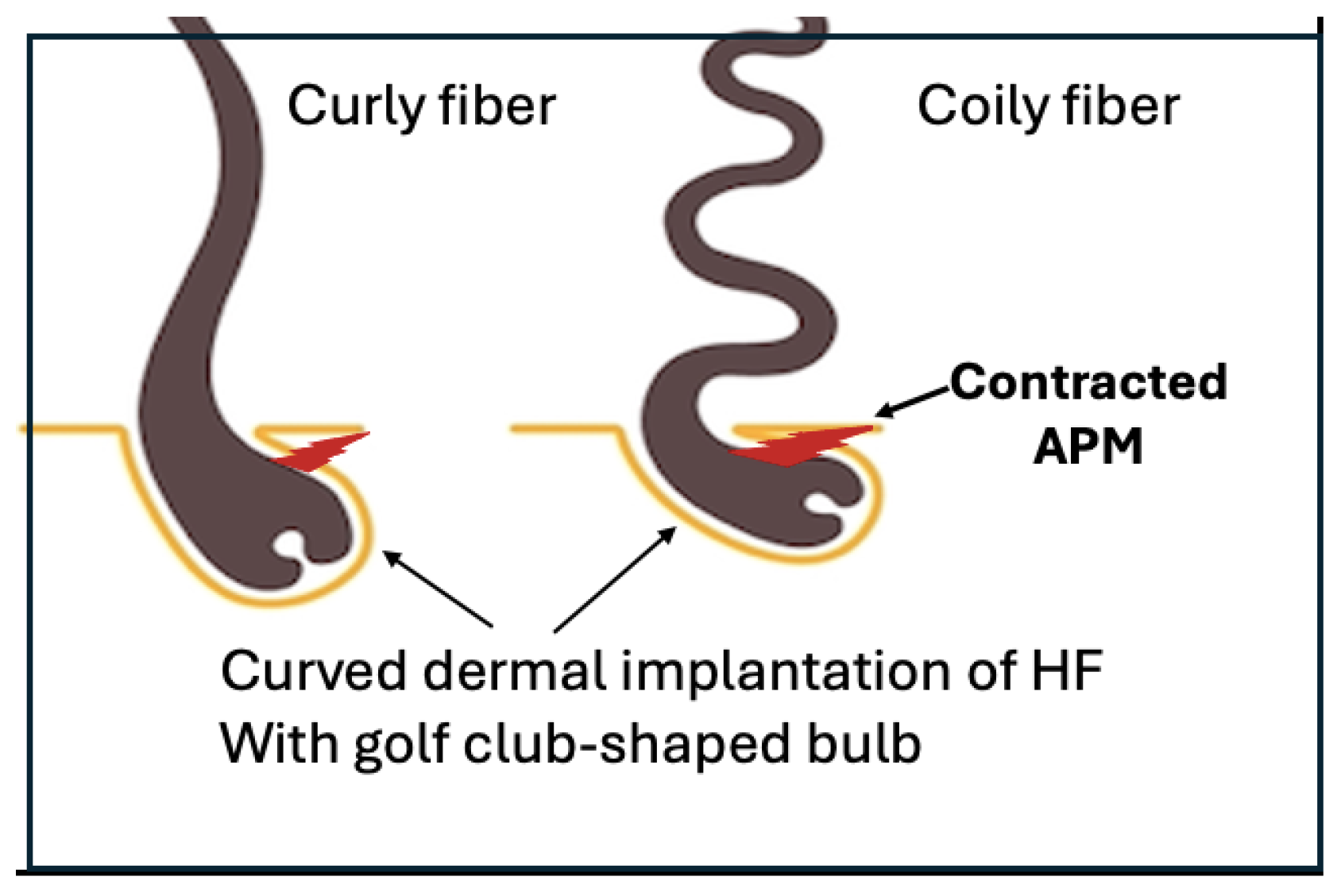
Contraction of the tiny smooth muscle of the hair follicle, the Arrector Pili, generates the mechanical force to curve the hair follicle into a golf club shape.
The Arrector Pili is a multi-unit smooth muscle, where each fiber contract independent on the other to create the enormous diversity of hair types.
As a smooth muscle, the Arrector Pili contraction can be prolonged and strong.
The Arrector Pili has a sensory function, it contracts in response to environmental factors as cold weather or emotion to produce goosebumps (piloerection).
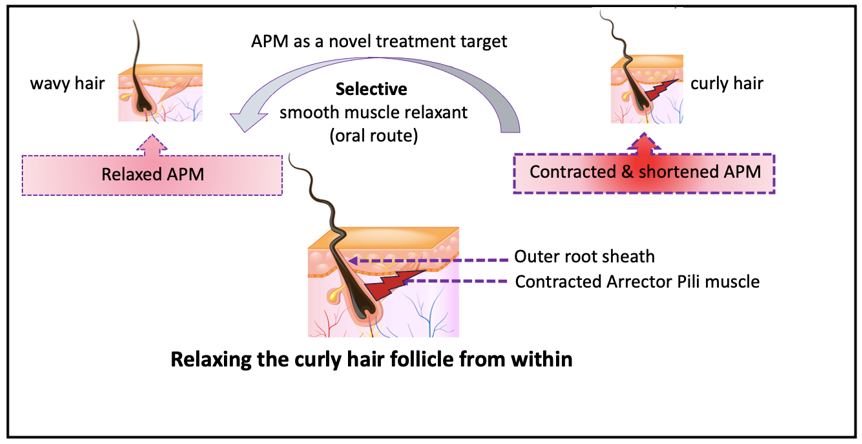
The Arrector Pili can be considered as a valid target to develop ingestible selective smooth muscle relaxing treatment to relax coily/curly hair from within to meet consumers’ needs and wants.
Introduction
The scalp hair consists of two domains the shaft
and the hair follicle (HF). The human hair shaft has enormous diversity in the
degree of curvature, and the principle is now established that the hair shape
is programmed from the follicle, and that the hair fiber is a memory shape
(Thibaut et al, 2005; Thibaut et al, 2007). For many years cosmetic scientists
have attempted to develop hair typing systems by measuring the specific
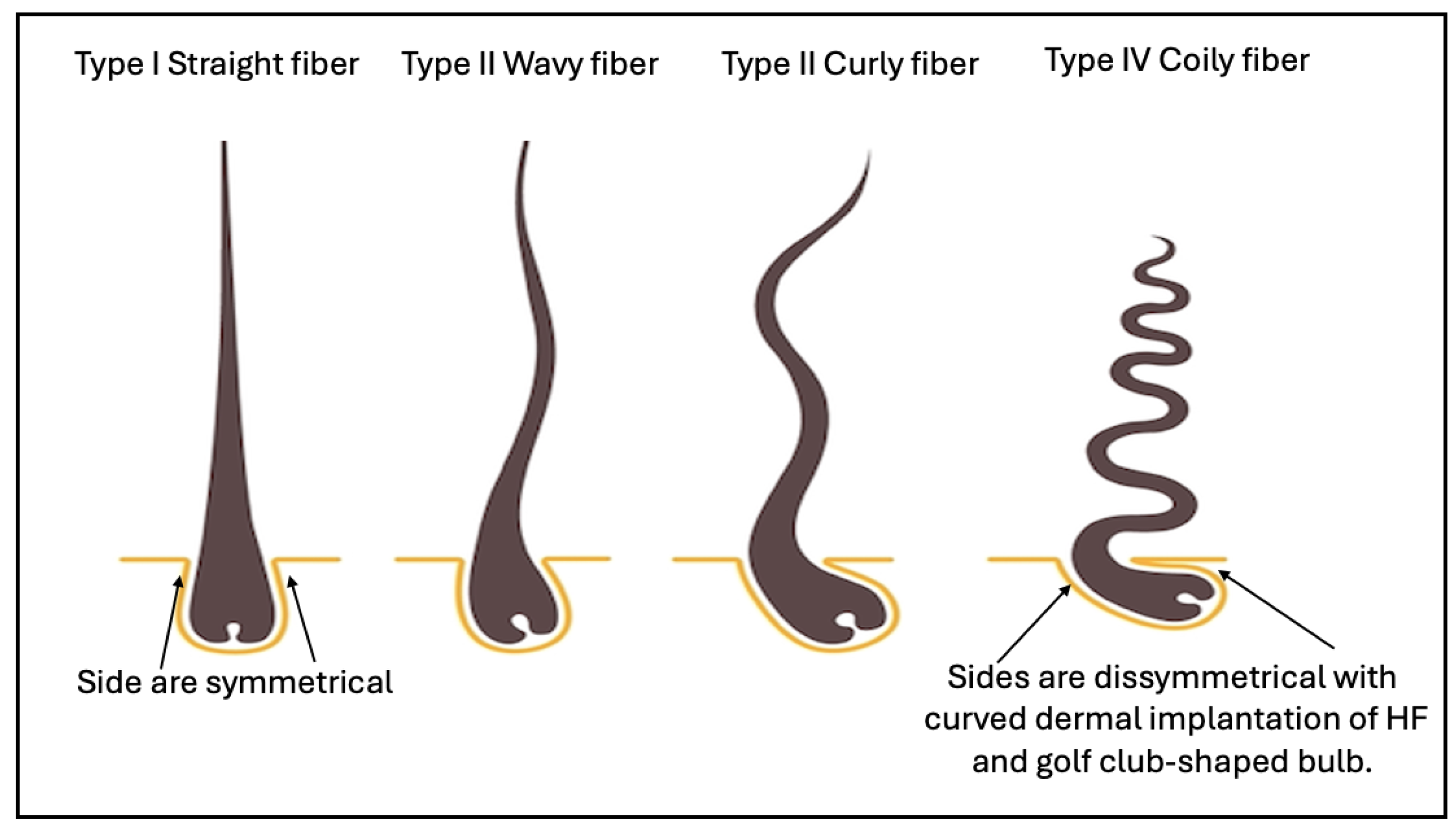
physical 3D features of human hair, including qualitative hair typing system
developed by Andre Walker, classifying hair into Type I-IV with subtypes (a-c)
(
Figure 1); Later, quantitative hair typing of STAM and modified-STAM
classification (Loussouarn et al, 2007). A high-throughput phenotyping methods
study was conducted (Zaidi et al, 2021). Recently, hair science was reimagined
to classify curly hair phenotypes using dynamic mechanical analyzer(Gaines et
al, 2022).
Human hair shape is programmed from the bulb with
the curve of the hair is created by an internal mechanical force. At the
follicular level, studies of scalp biopsies showed that the dermal implantation
of curly and coily HF have a retrocurvature at the level of the bulb, the bulb
itself was bent in the shape of a golf club. Both the outer root sheath (ORS)
and the connective tissue (dermal) sheaths were dissymmetrical. The
proliferative matrix compartment of curly hair follicle was asymmetrical, Ki-67
labelled cells being more numerous on the convex side and extending above the
Auber line. On the convex part of the follicle, the ORS was thinner.
Furthermore, some ORS cells expressed alpha-smooth muscle actin protein on the
concave side of the curvature, reflecting a mechanical stress (Thibaut et al.,
2005).
The Arrector Pili Muscle of the Hair Follicle: Current State of Knowledge
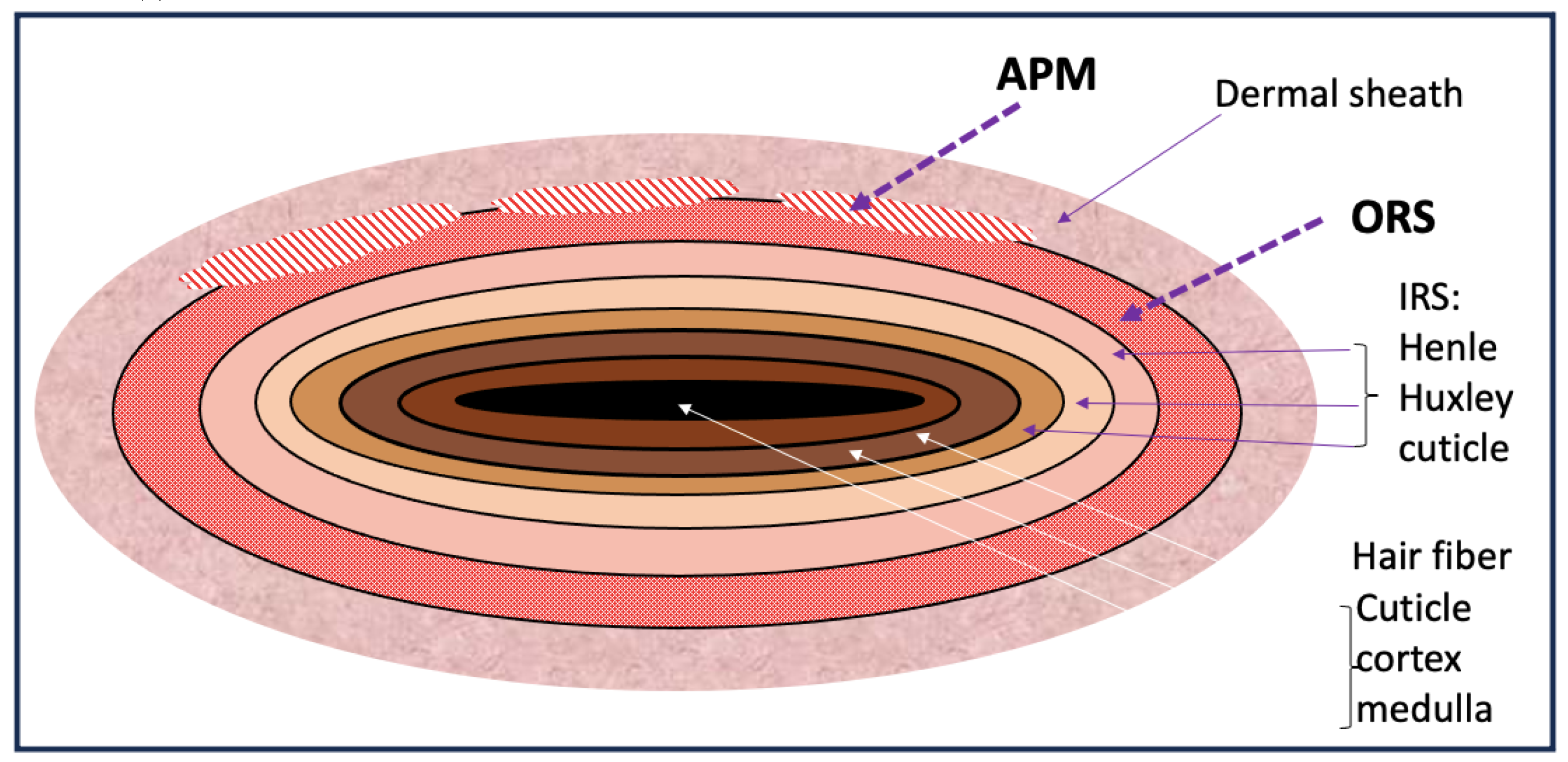
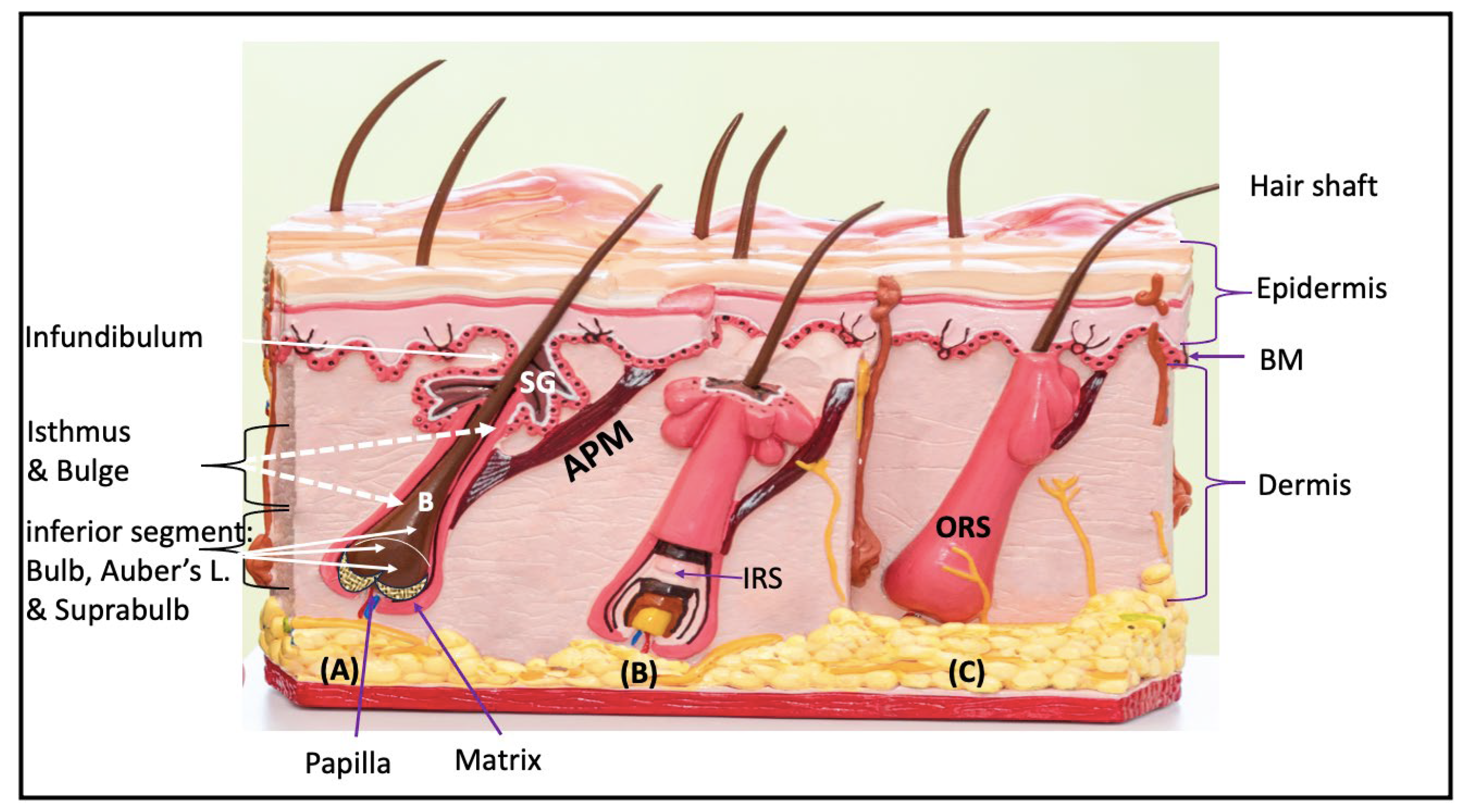
The Arrector Pili muscle (APM) is a smooth muscle
bundle that attaches to the bulge region of the follicle via elastic tendons
and extends obliquely to its superior attachment in the upper dermis at the
dermo-epidermal basement membrane (BM) (
Figure 3A).
Microscopically, one APM muscle can serve one HF
and encircle its entire circumference and attaches to the BM, or multiple APMs
from multiple follicles join together at the level of the isthmus and form a
single muscular structure known as the follicular unit (Poblet et al, 2002;
Barcaui et al, 2002). APM was thought to be vestigial in humans, but its known
functions are piloerection (goosebumps) by contracting to mediate
thermos-regulation; facilitate sebum secretion and participate in follicle
cycling. Hypothetically, APM have a possible role in maintaining the follicular
integrity and stability. It has been observed to undergo changes during in hair
loss disorders (Torkamani et al, 2014). APM was studied in abdominal wall hair
follicles using X-ray micro CT to define its fundamental 3D structure since
it is important for skin regeneration and cosmetics (Ezure et al, 2022).
Hair growth is influenced by numerous physiologic
moderators. Greater understanding of the biology of the hair follicle
facilitates the development of targeted therapy. Example is sublingual
minoxidil (Willems and Sinclair, 2021). APM was investigated mainly as
underling the mechanism of hair loss (alopecia) and an emerging therapeutic
target (Xu et al., 2023; Redmond et al, 2023). In hair transplantation surgery,
the hair is popping out of graft once the APM is cut (Garg and Garg, 2021).
The perifollicular sympathetic nerve has a
nutritional and regulatory effect on the growth, development and physiologic
cycle of HF. The sympathetic nerve forms a tight connection with the APM being
enwrapped and penetrated by sympathetic nerve, APM provide stable anchors to
the sympathetic nerve supply. Recent progress in the understanding demonstrated
that the nerve-effect factor norepinephrine affects HF stem cell and growth and
modulate hair stem cell activity (Zhang et al, 2021).
Shaping the hair is under developmental and
molecular control. The creation of the highly complex biomaterial in the HF,
and how these confer mechanical function on the fiber so formed is a topic that
remains relatively unexplained thus far. We are still a very long way from
understanding the complete biological and biophysical mechanisms that produce
such a wide range of curled, coiled, kinky and wavy hair fiber (Westgate et al,
2017).
Hypothesis of Hypersensitive Contracted Arrector Pili Muscle
In this hypothesis, I am proposing that the
mechanical force that curves the hair follicle and produce the micropatterns of
curly or coily hair is generated by the contracted fibers of the APM; squeezing
its ORS attachment site at the bulge producing a zone of “APM molding and
sculpting”; the attachment site become concave with different shapes and
degrees of curvatures; pushing the proliferating keratinocytes away to overfill
the opposite side to make it convex; deviate the axis of rotation; impact keratin
filament alignment and orientation during the time of keratinization and
hardening; sculpturing the young hair fiber in this 3D mold; producing a
dissymmetrical HF and a curly/coily hair fiber (
Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6).
If this mechanical force can be relaxed by a
selective smooth muscle relaxing treatment, then the curved HF will be
relaxed; and the curly hair fiber will be relaxed from within.
The contracted APM muscle hypothesis can answer
several questions the science doesn’t have the answer for- yet. This hypothesis
can answer how multiple curl types are present in one textured head, why
multiple 3D shapes are present within the same coil type and subtype and
whether an individualized curly hair pattern is possible. In addition, it set
the stage for developing a selective smooth muscle relaxing treatment
Scientific Support for the Contracted APM Hypothesis
1.1. Diving into the General Biology of Smooth Muscle
There are limited studies on the biology of the
APM. Therefore, we dive in the general biology of the human smooth muscle to
get more insight and apply this knowledge to APM.
1.1.1 Smooth muscles (SM) are found throughout
the body where it serves to regulate function of internal organs. For example,
in the respiratory tract it regulates the airway diameter, in the blood vessels
it regulates vascular resistance, in the eye it functions as a sensory organ,
dilating and constricting the pupil in response to light, and in the skin where
it raises the hair in response to cold weather and emotions (goosebumps).
1.1.2 There are two physiologic variants of SM, a
single-unit and multi-unit, wherein the single-unit can be stimulated by only
one synaptic input to produce a synchronous contraction, while in the
multi-unit SM each cell receives its synaptic input to allow a much finer
controlled physiologic function. Multi-unit SM are found in the skin (APM), the
eye (ciliary muscle) and the airways. SM have the ability to be contracted and
controlled involuntarily and are capable of maintain tone for extended periods.
The autonomic nervous system uses hormones, neurotransmitters, and other
receptors to control smooth muscle contraction. The use of SM-relaxing
treatment is an approach to treat hypersensitive airways and other conditions
(Hafen et al., 2023).
1.1.3 The emotional and physiological
(non-emotional) correlates of piloerection in humans were studied by Jonathon
and Zickfeld (2022). Their analysis revealed that indices of sympathetic
activation are abundant, suggesting emotional piloerection occurs with
increased (phasic) skin conductance.
1.1.4 An interesting hypothesis about SM is that
they have sculpturing function on the epithelial lining of internal organs
during embryonic development. Organs involved are hollow organs lined by
epithelial mucous membrane; stiffness over a variety of cell lengths makes SM
cells especially poised for directing epithelial morphogenesis (Jaslove and
Nelson, 2018). Morphogenesis is defined as a mechanical process involving force
that generate mechanical stress, strain, and movement of cells, and can be
induced by genetic programs according to spatial patterning of cells within
tissues(Bidhendi et al., 2019). It became clear that these properties make SM
an effective tool for changing the shape and lumen diameter of the internal
organ lining. Furthermore, investigating how nature uses SM as a morphogenic
tool may help us understand how to repurpose it for engineering organs in
clinical application ((Jaslove and Nelson, 2018).
1.1.5 Pierard-Franchimont et al. (2011) offered a
hypothesis that, the hair shape in part depends on the organization of the cell
proliferation in the hair matrix. This review gathers observations supporting
the involvement of cell tensegrity in shaping the hair shaft. Cell tensegrity
encompasses all intrinsic and extrinsic forces responsible for the
three-dimensional arrangement of intracellular macromolecules.
1.2. How Does APM Differ from Other Smooth Muscles? Personal Observations
During my study of the published articles on the
morphology and function of the different types of muscles in human body I have
noticed that APM share some characteristics with skeletal muscles (
Table 1).
APM fibers are longitudinal and have origin and insertion, hence the direction
of force can be to “pull upward” the follicle in the direction of the APM
attachment at the dermo-epidermal basement membrane. This might explain
previous observations that a curly HF penetrates the epidermis at an angle,
tilted in the shape of golf club with dissymmetrical follicle.
The functional similarity the SM of internal organs
might explain how a slow, strong contraction of APM can be sustained for a long
time to create muscle tone that can sculpture the HF. This contraction is
Involuntary, self-working and self-regulated.
1.3. Neurologic Pathways of the Hypersensitive APM
Hypersensitive APM is referring to an increased response of the muscle fibers to different environmental factors including light, ultraviolet rays, heat, or other spasmogens that might be involved. The environmental factors act directly on the outer layer of the skin, the epidermis; it induces a nerve impulse transmitted to the deep layer of the skin, the dermis. It has been established that dermal-epidermal interactions regulate HF activities.
1.3.1 Two neural networks innervate hair and HF, and both contain sensory nerve fibers and sympathetic nerve fibers that regulate involuntary physiologic processes (N1 and N2). One of the neural networks surrounds the neck of the HF, and the second encircle the midsection of the HF. The APM is innervated also by the nearby nerves (
Figure 4) (Murphrey et al, 2023).
1.3.2 In a scanning electron microscopic study, it has been observed that repeated contraction of the APM produce groove-like depressions and ring -like elevations of the ORS: In the bulge area of scalp follicles there are many knob-like or villous projections either located on one side or around the entire circumference of the follicle. These projections were thought to represent the anchoring points of the branched follicular end of the arrector muscles. Ring-like elevations with groove-like depressions above and below were also observed surrounding the entire follicle. These were thought to represent the track of circum-follicular arrector muscles which depressed the ORS when they repeatedly contracted (Narisawa et al, 1995).
1.3.3 The most amazing research finding is that the external light entering the eye stimulate the retina and can activates HF stem cells through sympathetic neural pathway (Mai-Yi Fan et al., 2017).
1.3.4 Neurotransmitters are released from axons and diffuse to the SM cells. The ability of the nerve to initiate an action potential depends on the amount of neurotransmitter released and the amount of depolarization required to reach threshold. Therefore, it is reasonable to hypothesize that an individualized response can explain the individual hair curl pattern!
1.4. New Zone of APM Molding of the Young Hair Root
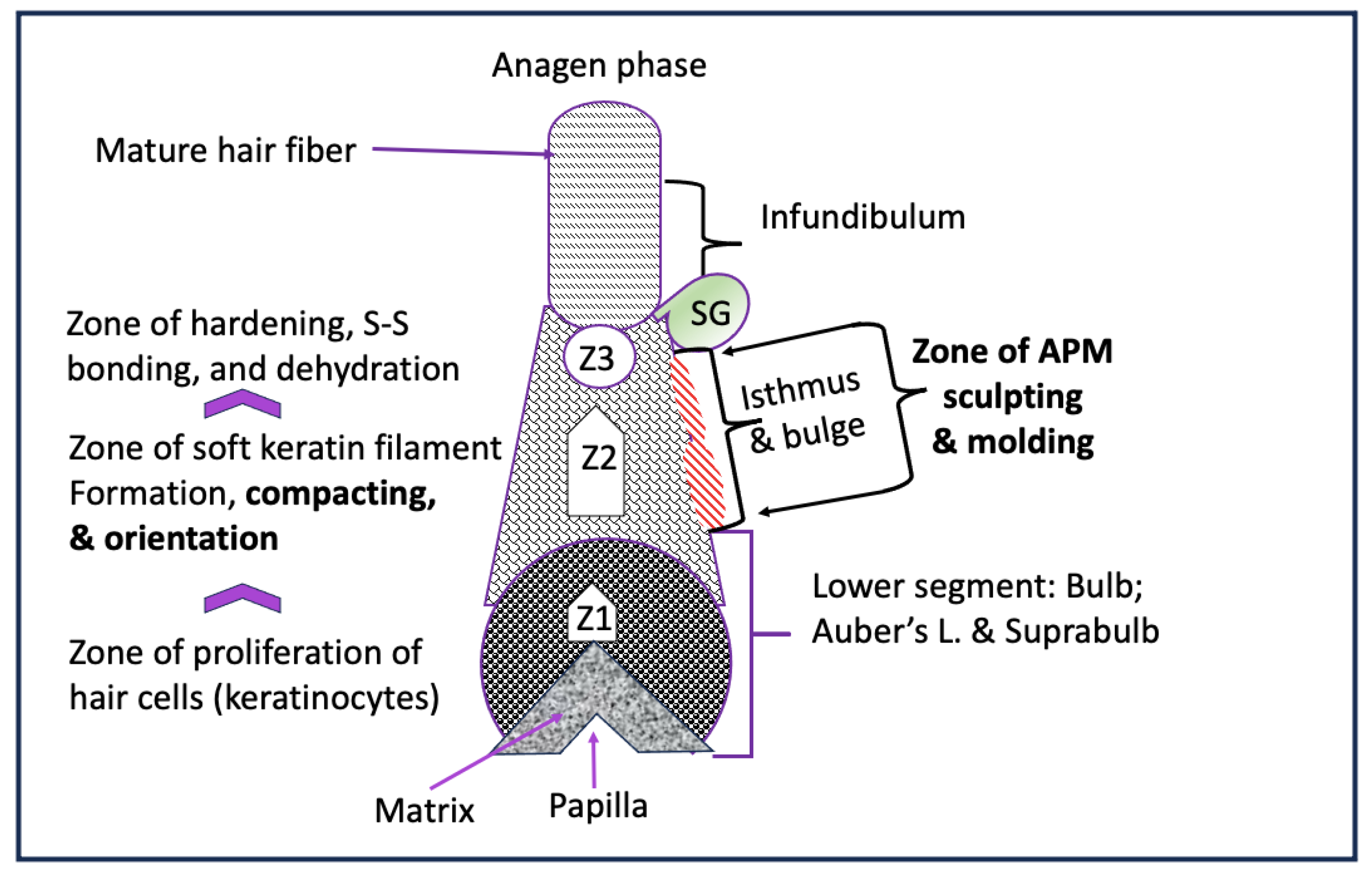
Hair keratinization was described as orderly series occurring at the molecular level. The hierarchical structure of the hair is alpha-keratin coiled-coil protein that form a tetramer; profilaments; intermediate filaments until they aggregate together to form microfilament surrounded by matrix to form the basic unit of hair cortical cell (Yang et al., 2014). The architecture of human hair intermediate filament was studied in relation to the longitudinal organization of the molecule within the filament, lateral interfilament packing and described “nonordered” organization inside hard alpha-keratin intermediate fibers (Rafik et al., 2004). On the other hand, curl in the hair was hypothesized to derive primarily from “inhomogenous” distribution of different cell types across the fiber cross-section as a result of subtle biochemical engineering by the follicle (Wortmann and Wortmann, 2013). Further, the gradual stiffening of the hair fiber tetramer structure over the course of the entire keratinization process was studied, and the process was divided into four “zones” starting above the bulb is the elongation zone; keratinization ; hardening concomitant with their continuous compaction and parallel orientation and post-hardening zones (Bornschlögl et al, 2016).
In our contracted APM hypothesis (
Figure 6), we are proposing that there is a “zone of sculpting and molding,” where each APM muscle fibers contracts individually to create an asymmetrical 3D mold for the young soft hair root. The APM mold is located under the muscle attachment to the ORS. This mold can physically constrain the space available for the proliferating keratinocytes sufficient to produce dissymmetrical (nonordered and inhomogenous) placement of the keratinocyte, and physically influence the compacting and alignment of the developing keratin filaments to produce individualized curly hair pattern
. This process involves forces that generate mechanical stress, strain, and movement of cells, and can be induced by genetic programs according to the spatial patterning of cells within tissues.
2. APM as a Target to Develop New Curl Relaxing Treatment
The hypothesis set the stage to identify the structure of a smooth muscle target, including cell surfaces receptor, that is involved or upregulated and functions to induce APM contraction. If such a receptor is found, Then a computer-aided in silico preliminary studies can be performed to find small molecules with the potential to modulate the activity of this receptor.
Testing the Contracted APM Hypothesis
Our hypothesis can be challenged by studying the 3-dimesional (3D) quantitative characteristics of AMP of curly hair follicle. The 3D studies include APM volume, mean length, muscle angle with the basement membrane and its orientation. It is more informative to calculate the ratio of APM volume/whole follicle volume in curly hair and compare it to other hair types. The technology used in published research include X-ray micro CT (Azure et al. 2022), very high-frequency ultrasound (Wortsman et al., 2018), or computer-based 3D reconstruction (Jimenez-Acosta et al., 2006). Coiled coil predictions are often used to interpret biochemical data and are part of in-silico functional genome annotation (Simm et al., 2021).
Later, it is desirable to evaluate APM as a target for the development of new treatment that relax the HF using in-silica computer-aided target identification.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we propose, and try to support, the hypothesis that APM play a critical role in molding the HF and shaping the hair shaft, and as a consequence propose the search for selective smooth muscle relaxing small molecules as a possible treatment to relax curly hair from within. This mechanistic hypothesis can explain why there are a wide range of hair fiber shapes, that can’t be explained on genetic studies or other hypotheses.
Author and Affiliation: Dr Nedaa Al Jasim, MD, Founder and CEO of Apex Medical Device Design company, Dublin, Ohio, USA.
Intellectual property
The author is the inventor of the US patent publication number US 2024/0307474 A1 (PCT patent application # WO2023/283277 A1), titled: Fermented uni-sourced nanoemulsion of Nigella sativa or Cannabis sativa for use in medical, cosmetic, and recreational indications with a method of its production and use.
Competing interest
None declared.
Funding
This study has not supported by any external funding.
Acknowledgement
I would like to thank Noor Ahmed for assisting in the preparation and submission of this article.
References
- Agarwal R, Katare OP, Vyas SP. The pilosebaceous unit: a pivotal route for topical drug delivery. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2000 Mar;22(2):129-33. doi: 10.1358/mf.2000.22.2.796082. PMID: 10849897.
- Anil Garg and Seema Garg. Overview of follicular extraction. Indian J Plast Surg 2021; 54: 456-462. DOI https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1739244.
- Anneliese Willems and Rodney Sinclair. Alopecia in humans: biology, pathomechanisms and emerging therapies. Veterinary Dermatology, 2021; 32(6): 596-e 159. https://doi.org/10.1111/vde.13014.
- Ezure T, Amano S, Matsuzaki K. Quantitative characterization of 3D structure of vellus hair arrector pili muscles by micro CT. Skin Res Technol. 2022 Sep;28(5):689-694. doi: 10.1111/srt.13168. Epub 2022 Jun 21. PMID: 35726958; PMCID: PMC9907649.
- Bidhendi Amir J., Altarttouri Bara, Gosselin Frederick P, et al. Mechanical stress initiates and sustains the morphogenesis of wavy leaf epidermal cells. Cell Reports, 2019; 28(5): 1237-1250. Doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.006.
- C. B. Barcaui, J. Pineiro-Maceira, M. M. De Avelar Alchorne. Arrector pili muscle: evidence of proximal attachment variant in terminal follicles of the scalp. British Journal of Dermatology. 2002. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04541.x.
- Cloete Elsabe, Khumalo Nonhlanhla, Ngoepe Malebogo N. The what, why and how of curly hair: a review. Proc. R. Soc., 2019; A.475: 20190516. http://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.2019.0516.
- Enrique Poblet MD, Francisco Ortega MD, Francisco Jimenez MD. The Arrector Pili Muscle and the Follicular Unit of the Scalp: A Microscopic Anatomy Study. Dermatologic Surgery, 2002; 28(9): 800-803. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.02038.x.
- Francisco Jimenez-Acosta, WC Song, WJ Hwang et al. From the literature: A new model for the morphology of the Arrector Pili muscle in the follicular unit based on three-dimensional reconstruction. Hair Transplant Forum International September 2006, 16(5): 186. DOI: https://doi.org/10.33589/16.5.0186.
- Gillian E. Westgate, Rebecca S. Ginger, and Martin R. Green. The biology and genetics of curly hair. Experimental Dermatology, 2017; 26: 483-490. DOI: 10.1111/exd.13347.
- Hafen BB, Shook M, Burns B. Anatomy, Smooth Muscle. [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532857/.
- Jaslove Jacob M and Nelson Celeste M. Smooth muscle: a stiff sculptor of epithelial shapes. Phil. Trans. R. Soc, 2018; B373(1759): 2017031820170318 http://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2017.0318.
- Jiarui Zhang, Rousi Chen, Lihong Wen, et al. Recent progress in the understanding of the effect of sympathetic nerve on HF growth. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021: Sec. Stem Cell Research; 9: article #736738. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.736738.
- Jonathon McPhetres and Janis H. Zickfeld. The physiological study of emotional piloerection: A systematic review and guide for future research. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 2022; 179: 6-20.
- Joseph N. Nissimov and Asit Baran Das Chaudhuri. Hair curvature: A natural dialectic and review. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 2014: 89(3): DOI:10.1111/brv.12081.
- Juan Carlos Fonseca Mata, modified by Maria Victoria Gonzaga. Biology Online Dictionary. https://www.biologyonline.com/dictionary/smooth-muscle. Last visited Aug. 18, 2023.
- Julianna L. Martel, Julia H. Miao, Talel Badri. Anatomy, Hair follicle. [Updated 2022 Oct 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls publishing; last updated June 22, 2024. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470321/.
- Kiyokazu Morioka, Mary Arai, and Setsunosuke Ihara. Steady and temporary expression of smooth muscle actin in hair, vibrissa, arrector pili muscle, and other hair appendages of developing rats. Acta Histochem, 2011; 44(3): 141-153. doi:10.1267/ahc.11013.
- Lasisi, T., Zaidi, A.A., Webster, T.H. et al. High-throughput phenotyping methods for quantifying hair fiber morphology. Sci Rep 11, 11535 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-90409-x.
- Leah C. Redmond, Summik Limbu, Bassan Farjo, et al. Male pattern hair loss: can developmental origins explain the pattern? Experimental Dermatology, 2023; 23(7): 1174-1181. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.14839.
- Loussouarn G, Garcel AL, Lozano I, Collaudin C, et al. Worldwide diversity of hair curliness: a new method of assessment. Int J Dermatol., 2007;46(1) :2-6. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2007.03453.x.
- Mériem Er Rafik, Jean Doucet, and Fatima Briki. The intermediate filament architecture as determined by X-ray diffraction modeling of hard alpha-keratin. Biophysical journal, 2004; 86: 3893-3904.
- Michelle Gaines, Imani Page, Nolan Miller, et al., Reimagining hair science: a new approach to classify curly hair phenotypes via new quantitative geometrical and structural mechanical parameters. ChemRxiv, 2022, 10 November: Version 1. DOI 10.26434/chemrxiv-2022-35bt7.
- Murphrey MB, Agarwal S, Zito PM. Anatomy, Hair. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513312/.
- Nadia Khaveh, Kathrin Schachler, Jan Berghofer, et al. Altered hair root gene expression profiles highlight calcium signaling and lipid metabolism pathways to be associated with curly hair initiation and maintenance in Mangalitza pigs. Front. Genet., 2023; 14: http://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2023.1184015.
- Piérard-Franchimont C, Paquet P, Quatresooz P, et al. J Cosmet Dermatology, 2011; 10(2): 163-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1473-2165.2011.00553.x.
- Sabrina Mai-Yi Fan, Yi-Ting Chang, Chih-Lung Chen et al. External light activates hair follicle stem cells through eyes via an ipRGC–SCN–sympathetic neural pathway. PNAS, 2017; 115 (29) E6880-E6889: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1719548115.
- Sebastien Thibaut, O Gaillard, P Bouhanna, et al., Human hair is programmed from the bulb. British Journal of Dermatology, 2005; 152(4): 632-8. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06521.x.
- Sebastien Thibaut, Philippe Barbarat, Frederic Leroy, and Bruni A Bernard. Human Hair Keratin Network and Curvature. International Journal of Dermatology, 2007; 46(1(S1): 7-10. http://doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2007.03454.x.
- Silva LMA, Hsieh R, Lourenço SV, Rocha BO, Romiti R, et al. (2019) Revisiting Hair Follicle Embryology, Anatomy and the Follicular Cycle. J Cosmo Trichol 5(1): 1000141. doi:10.4172/2471-9323.1000141 (https://www.hilarispublisher.com/open-access/revisiting-hair-follicle-embryology-anatomy-and-the-follicular-cycle.pdf.
- Simm, D., Hatje, K., Waack, S. et al. Critical assessment of coiled-coil predictions based on protein structure data. Sci Rep 11, 12439 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91886-w.
- Teresa Matama, Cristiana Costa, Bruno Fernandes et al. Changing human hair fibre colour and shape from the follicle. J Adv Res. 2023 Nov 13:S2090-1232(23)00350-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.11.013.
- Thibaut S, Bruno Bernard, Philippe Barbarat, and Dominique Bernard. Patent: Method for shaping keratin fibers. Inventor: Filed by L’oreal. Application PCT/FR2005/002466, WO200604044A1.
- Thomas Bornschlögl, Lucien Bildstein, Sébastien Thibaut, et al. Keratin network modification lead to mechanical stiffening of the hair follicle fiber. PNAS, 2016; 113(21): 5940-5945. www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pmas.1520302113.
- Tomonobu Ezure, Satoshi Amano, Kyoichi Matsuzaki. Quantitative characterization of 3D structure of vellus hair arrector pili muscle by micro CT. Skin Res Technol, 2022; 28: 689-694. DOI: 10.1111/srt.13168.
- Wen Xu, Sheng Wan, Bo Xie, et al. Novel therapeutic target for alopecia areata. Frontiers of Immunology, 2023; 14: 1148359. http://doi.10.3389/fimmu.2023.1148359.
- Xiangyu Lin, Liang Zhu, and Jing He. Morphogenesis, Growth Cycle and Molecular Regulation of Hair Follicles. Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 2022; 10: Article 899095. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.899095.
- Ximena Wortsman, Laura Carreño, Camila Ferreira-Wortsman, et al. Ultrasound characteristics of the hair follicle and tracts, sebaceous glands, Montgomery glands, apocrine glands, and arrector pili muscles. J of Ultrasound in Medicine, 2018; 38(8): 1995-2004. DOI: 10.1002/jum.14888.
- Yutaka Narisawa, Ken Hashimoto and Hiromu Kohda. Scanning electron microscopic observations of extracted terminal hair follicles of the adult human scalp and eyebrow with special reference to bulge area. Archives of Dermatological Research, 1995; 287: 599-607. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00374083.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).