1. Introduction
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a multifaceted cardiovascular disorder characterized by the abnormal thickening of the heart muscle, often leading to structural and functional abnormalities within the cardiac tissue [
1]. Despite considerable advances in cardiovascular research, the molecular mechanisms orchestrating the onset and progression of HCM remain elusive. This condition represents a significant clinical challenge due to its heterogeneity in clinical presentation, variable disease penetrance, and diverse genetic underpinnings. Notably, HCM represents the most common inherited cardiac disease, affecting individuals across all age groups, and represents a leading cause of sudden cardiac death among young athletes and individuals with familial predisposition.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in the role of exosome-derived microRNAs (miRNAs) in elucidating the molecular intricacies of HCM. Exosomes, small extracellular vesicles secreted by various cell types, have emerged as pivotal mediators of intercellular communication, facilitating the transfer of bioactive molecules, including miRNAs, between cells [
2]. Extracellular vesicles from human cardiomyocytes have demonstrated preferential uptake by human endothelial cells [
3]. In this way, these vesicles allow vesicular content including nucleic acids to be directed to their target cell type. MicroRNAs, small non-coding RNAs, have garnered considerable attention for their role in post-transcriptional gene regulation, exerting profound effects on diverse cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and metabolism. Dysregulation of miRNA expression has been implicated in numerous diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, and holds promise as potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets [
4].
This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current understanding of the involvement of exosome-derived miRNAs in the pathogenesis and progression of HCM. By synthesizing findings from both preclinical and clinical studies, we seek to delineate the complex interplay between exosome biology, miRNA signaling, and cardiac remodeling processes underlying HCM. Through this exploration, we aim to shed light on novel insights into the molecular mechanisms driving HCM pathology and identify potential avenues for diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic intervention strategies.
2. HCM
HCM is characterized by a complex array of structural, functional, and metabolic changes that collectively contribute to disease pathogenesis and progression. These changes involve alterations at the cellular and molecular levels, impacting cardiomyocyte structure and function, and myocardial remodeling. Understanding the specific mechanisms underlying these changes is crucial for the development of targeted therapies for HCM.
2.1. Hypertrophic Changes
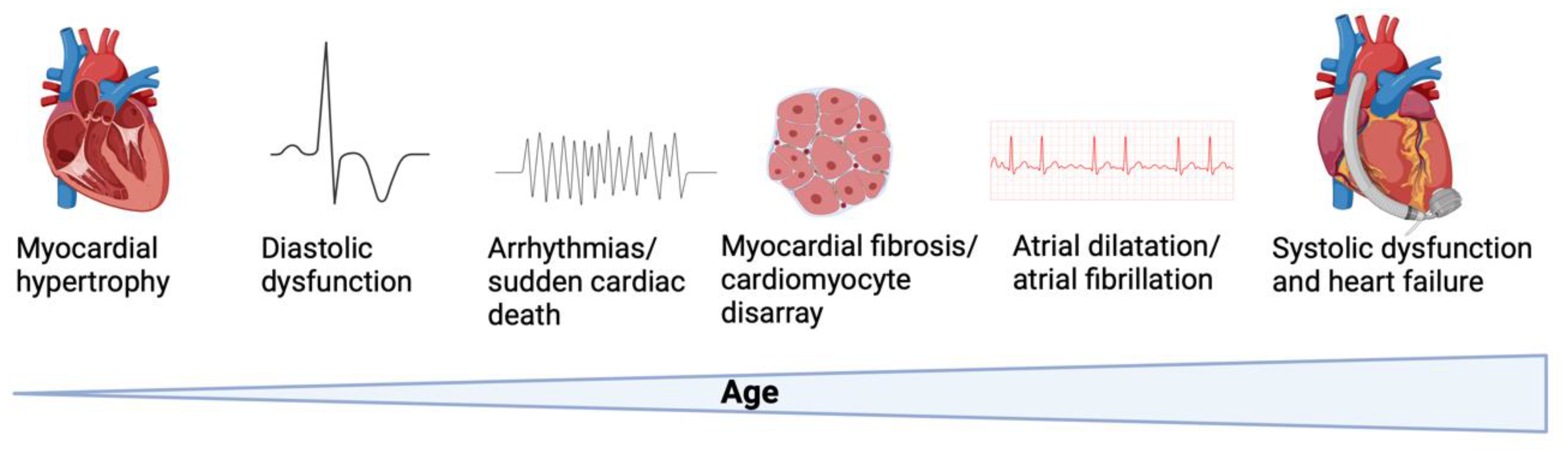
One of the hallmark features of HCM is asymmetric septal hypertrophy (
Figure 1). This condition is characterized by the uneven thickening of the interventricular septum, which can obstruct the left ventricular outflow tract during systole [
5]. This obstruction leads to increased difficulty in blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta, impacting overall cardiac function.
Figure 1.
Pathogenesis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Altered biophysical and intracellular properties cause cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, diastolic and systolic dysfunction, rhythm disturbances and histopathologic changes over time. Created with Biorender.
Figure 1.
Pathogenesis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Altered biophysical and intracellular properties cause cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, diastolic and systolic dysfunction, rhythm disturbances and histopathologic changes over time. Created with Biorender.
Additionally, HCM is marked by myocyte disarray, where cardiomyocytes within the hypertrophied myocardium are disorganized [
6]. This disorganization manifests as irregular alignment and stacking of myofibrils, contributing to impaired contractility and electrical conductivity. The structural abnormalities in the heart muscle fibers disrupt normal cardiac function and can lead to arrhythmias.
Another significant change in HCM is the increased size of cardiomyocytes. These heart cells undergo hypertrophy, characterized by an increase in cell size and protein content [
7]. This cellular enlargement is often accompanied by alterations in gene expression and changes in the structure of sarcomeres, the fundamental units of muscle contraction [
8].
In advanced stages of HCM, there is often fibrofatty replacement, where hypertrophied myocardium is replaced with fibrotic and fatty tissue [
9]. This replacement further compromises cardiac function and increases the risk of life-threatening arrhythmias, as the structural integrity and electrical pathways of the heart are altered [
10].
2.2. Fibrotic Changes
HCM involves significant fibrotic changes within the myocardium [
11]. One form of fibrosis is interstitial fibrosis, where there is excessive deposition of collagen and other extracellular matrix proteins between cardiomyocytes [
12]. This leads to myocardial stiffness, impaired relaxation, and diastolic dysfunction, as the heart muscle becomes less flexible and more resistant to filling with blood.
Another type of fibrotic change is replacement fibrosis. This occurs when areas of myocardial fibrosis replace healthy myocardium, particularly in regions affected by ischemia or infarction [
13]. Replacement fibrosis impairs the contractile function of the heart and further increases the risk of arrhythmias due to the loss of functional cardiac tissue.
Fibrotic remodeling in HCM is driven by the activation of fibroblasts [
11]. These cells become activated in response to mechanical stress and neurohormonal signaling [
14]. Once activated, fibroblasts proliferate and secrete collagen, contributing to the extensive fibrotic changes seen in the hearts of individuals with HCM.
2.3. Metabolic Changes
Cardiomyocytes in HCM also exhibit significant metabolic remodeling. There is a notable shift in substrate utilization and energy production pathways, with a preference for glycolysis over oxidative phosphorylation [
15]. This shift leads to impaired energy production and contributes to contractile dysfunction, as the heart muscle relies on less efficient energy sources.
Mitochondrial dysfunction is another critical aspect of metabolic changes in HCM. The mitochondria in hypertrophic cardiomyocytes often show altered morphology and impaired respiratory chain function [
16]. Additionally, there is increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which exacerbates energy imbalance and causes cellular damage, further impairing cardiac function [
17].
Lastly, dysregulation of calcium handling is a significant metabolic change in HCM. Proteins involved in calcium homeostasis, such as ryanodine receptors and sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca
2+-ATPase 2a (SERCA2a), are often dysfunctional [
18,
19]. This dysregulation disrupts intracellular calcium levels, leading to contractile dysfunction and increasing the risk of arrhythmogenesis, as proper calcium signaling is crucial for coordinated cardiac contraction and relaxation.
3. Exosomes: Mediators of Intercellular Communication
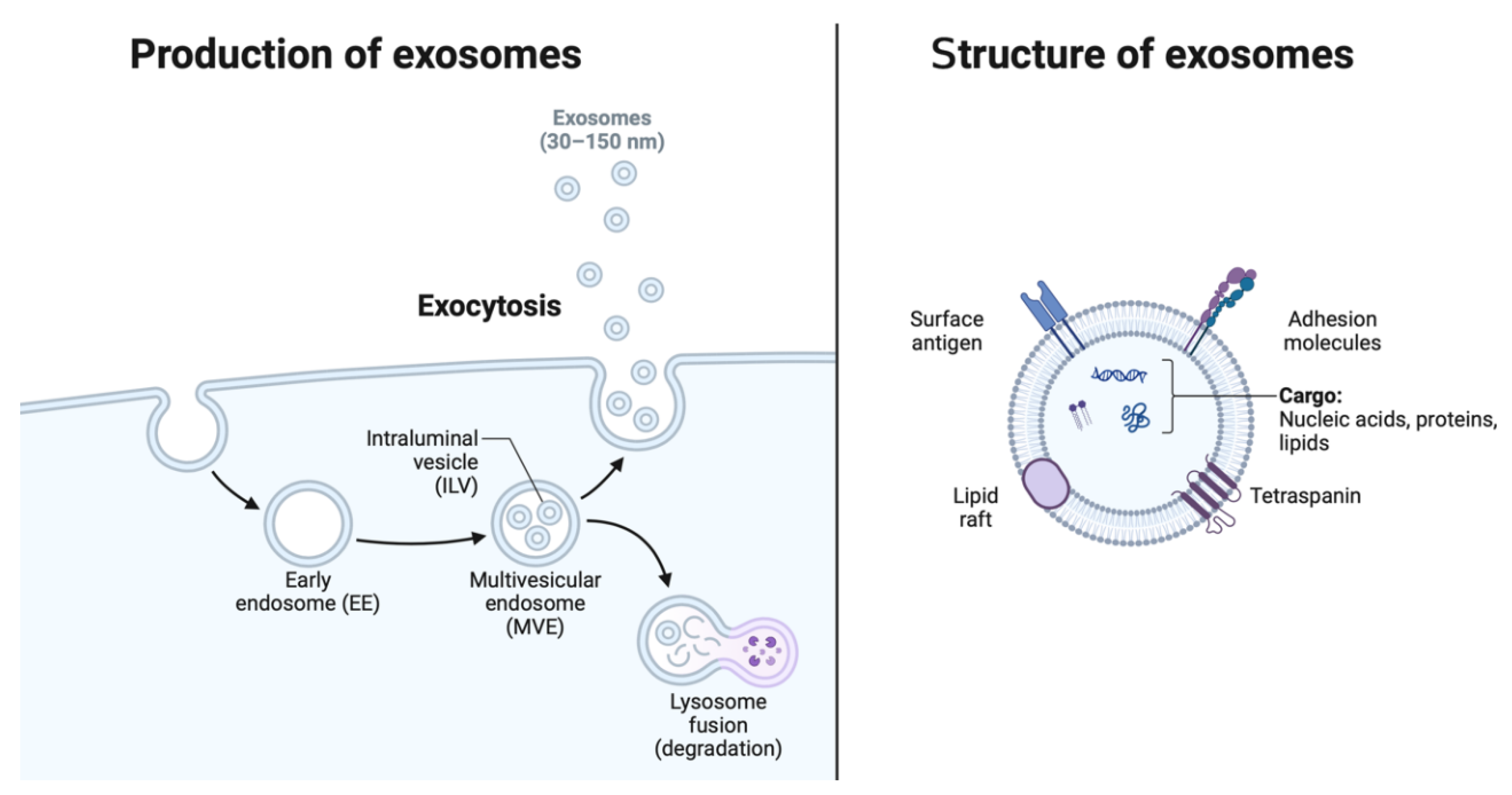
Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles with a diameter ranging from 30 to 150 nanometers, originating from the endosomal system and secreted by various cell types into the extracellular milieu. These nanovesicles serve as vital mediators of intercellular communication, facilitating the exchange of bioactive molecules between cells and modulating diverse physiological and pathological processes. The distinctive characteristics of exosomes (Figure 2), including their lipid bilayer membrane and enriched cargo composition, underpin their role as key players in cell-to-cell communication networks.
3.1. Definition and Characteristics of Exosomes
Exosomes are distinguished by their unique biophysical properties and molecular composition. Their biogenesis begins within the endosomal compartment, where inward budding of the endosomal membrane forms intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) within multivesicular endosomes (MVEs) [
20]. Subsequent fusion of MVEs with the plasma membrane results in the release of ILVs into the extracellular space as exosomes. These vesicles are characterized by a lipid bilayer membrane enriched in cholesterol, sphingolipids, and tetraspanin proteins (e.g., CD9, CD63, CD81), which confer stability and facilitate their uptake by recipient cells [
21]. Importantly, exosomes possess a diverse cargo of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, including miRNAs, messenger RNAs (mRNAs), and various classes of non-coding RNAs, reflecting their origin from parent cells and influencing their biological functions [
2,
22].
Figure 2.
Production and structure of exosomes. EE = early endosome, ILV = intraluminal vesicle, MVE = multivesicular endosome. Created with Biorender.
Figure 2.
Production and structure of exosomes. EE = early endosome, ILV = intraluminal vesicle, MVE = multivesicular endosome. Created with Biorender.
3.2. Biogenesis and Secretion Mechanisms
The biogenesis of exosomes is intricately regulated by a series of molecular machineries involved in endosomal sorting, membrane trafficking, and vesicle release. This process is extensively outlined elsewhere [
23]. Central to this process is the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT), which comprises multiple protein subunits (ESCRT-0, -I, -II, -III) responsible for sorting ubiquitinated cargoes into ILVs and facilitating their budding into MVEs [
24]. Additionally, ESCRT-independent mechanisms, such as the ceramide-dependent pathway and tetraspanin-enriched microdomains, also contribute to exosome biogenesis and cargo sorting [
25]. Upon fusion of MVEs with the plasma membrane, exosomes are released into the extracellular milieu through a process mediated by soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors (SNAREs) and other vesicle trafficking proteins [
26].
3.3. Cargo Composition: Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic acids
Exosomes harbor a diverse array of biomolecules derived from their parent cells, reflecting their cellular origin and physiological state. Proteomic analysis of exosome cargo has identified a plethora of proteins with diverse functions, including cell surface receptors, cytoskeletal proteins, heat shock proteins, and enzymes involved in metabolism and signaling pathways [
27]. Notably, exosomes are enriched in tetraspanins (e.g., CD9, CD63, CD81), heat shock proteins (e.g., HSP70, HSP90), and cytoskeletal proteins (e.g., actin, tubulin), which are commonly used as exosomal markers [
28,
29]. Exosomes from human cardiomyocytes have demonstrated preferential uptake by human endothelial cells, and the composition of the exosomal membrane may contribute to the selective uptake of exosomes by target cells [
3]. Furthermore, exosomes contain a repertoire of lipids, including cholesterol, sphingomyelin, phosphatidylserine, and various bioactive lipids, which contribute to their membrane stability and biophysical properties [
30]. Importantly, exosomes encapsulate nucleic acids, including miRNAs, mRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and circular RNAs, which can be transferred to recipient cells, modulating gene expression and cellular functions [
31].
4. MiRNAs: Regulators of Gene Expression
MiRNAs are a class of small non-coding RNAs, typically 19-25 nucleotides in length, that play crucial roles in post-transcriptional gene regulation [
32]. Through their interaction with the 3' untranslated region of target mRNAs, miRNAs can mediate mRNA degradation or translational repression, thereby fine-tuning gene expression profiles and influencing various cellular processes.
4.1. Biogenesis and Mechanisms of Action
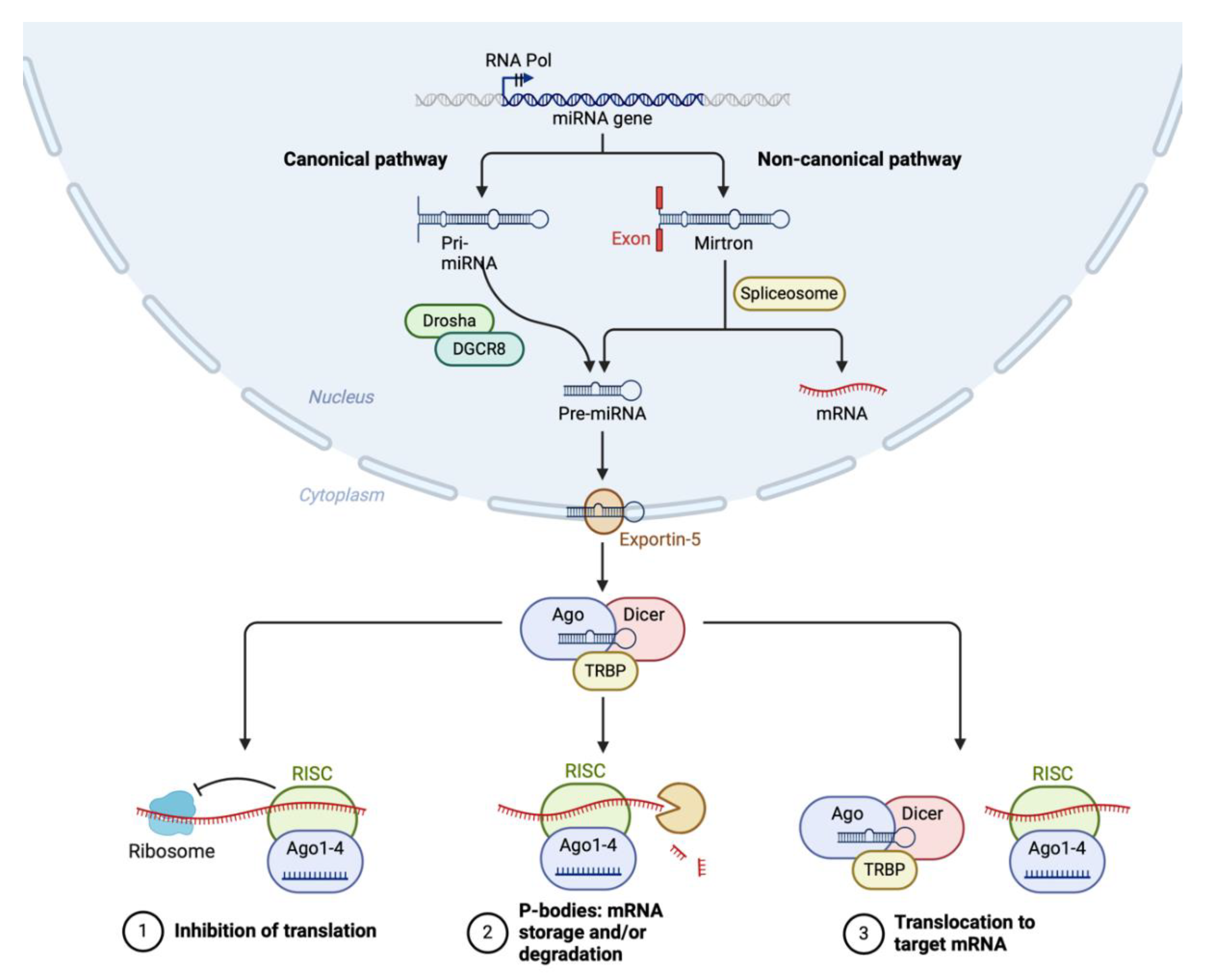
MiRNA biogenesis involves a series of coordinated steps that can be broadly categorized into the canonical and non-canonical pathways (Figure 3). Both pathways convert primary miRNA transcripts (pri-miRNAs) into mature miRNAs, which are then incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to guide gene silencing.
In the canonical pathway, miRNA biogenesis begins in the nucleus with the transcription of pri-miRNAs by RNA polymerase II [
33]. These pri-miRNAs contain a hairpin structure essential for further processing. The Microprocessor complex, composed of the RNase III enzyme Drosha and its cofactor DGCR8 (DiGeorge Syndrome Critical Region 8), cleaves the pri-miRNA near the base of the hairpin to release a precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) approximately 70 nucleotides long [
34]. The pre-miRNA is then transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm by Exportin-5 in a RanGTP-dependent manner. In the cytoplasm, the pre-miRNA is further processed by another RNase III enzyme, Dicer, in conjunction with the transactivation response RNA-binding protein [
35]. This processing results in a double-stranded miRNA duplex approximately 22 nucleotides in length.
Figure 3.
miRNA biogenesis. Created with Biorender.
Figure 3.
miRNA biogenesis. Created with Biorender.
The miRNA duplex is then loaded onto an Argonaute protein (Ago1-4) to form the core of the RISC. One strand of the duplex, known as the guide strand, is retained while the passenger strand is usually degraded. The mature RISC, guided by the miRNA, binds to complementary sequences in target mRNAs, leading to translational repression or mRNA degradation [
36]. The ribosome and spliceosome also play roles in the regulation of translation and splicing, which are influenced by miRNA activity.
Non-canonical miRNA biogenesis pathways deviate from the canonical Drosha-DGCR8-Dicer pathway and can be categorized into several types, outlined in detail elsewhere [
37]. Mirtrons, for example, are miRNAs derived from the introns of host genes that bypass Drosha processing. Following splicing by the spliceosome, the intron lariat is debranched and refolded into a pre-miRNA-like hairpin structure, which is then exported to the cytoplasm and processed by Dicer. Similarly, simtrons are short introns processed independently of Drosha, utilizing spliceosome machinery but possibly requiring additional nucleases before Dicer processing [
38].
Certain miRNAs can be loaded directly onto Argonaute proteins without the need for Dicer cleavage, constituting another non-canonical pathway described in detail elsewhere [
39]. These pathways may involve the direct transcription of short hairpin RNAs that can be incorporated into RISC without further processing. Additionally, tRNA-derived fragments can act as miRNAs. These fragments are processed from tRNAs by specific nucleases and incorporated into RISC, bypassing the canonical miRNA processing machinery [
39]
4.2. Functions of miRNAs in Cardiovascular Biology
MiRNAs play diverse and critical roles in cardiovascular biology, influencing processes such as cardiomyocyte proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and contractility. These small regulatory molecules are involved in the maintenance of cardiac homeostasis and the response to various physiological and pathological stimuli. For instance, miR-1 and miR-133 are abundantly expressed in the heart and play key roles in cardiac development and function [
40]. MiR-1 is involved in the regulation of cardiac hypertrophy and arrhythmogenesis, while miR-133 contributes to myocyte proliferation and differentiation [
40,
41,
42]. Similarly, miR-208a, a cardiac-specific miRNA encoded within the intron of the α-myosin heavy chain gene (Myh6), is essential for cardiac conduction and contractility.
5. Exosome-Derived miRNAs in HCM: Clinical Significance
Exosomes serve as carriers of miRNAs and other bioactive molecules, reflecting the physiological and pathological status of the parent cells. MiRNAs play pivotal roles in the regulation of cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and remodeling, processes intricately linked to the pathogenesis of HCM [
43,
44,
45]. In the context of HCM, exosome-derived miRNAs have garnered significant interest due to their potential clinical significance in disease diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic intervention [
46].
5.1. Identification of Differential Expression Profiles
Numerous studies have identified differential expression profiles of exosome-derived miRNAs in patients with HCM compared to healthy individuals or those with other cardiac conditions [
47,
48]. High-throughput sequencing and quantitative PCR techniques have been employed to characterize the miRNA cargo of circulating exosomes isolated from HCM patients, revealing distinct signatures associated with disease pathogenesis and progression [
49]. These differential expression profiles highlight the potential of exosome-derived miRNAs as molecular biomarkers for HCM.
5.2. Potential Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis
Exosome-derived miRNAs hold promise as non-invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of HCM. Circulating exosomes can be isolated from various biological fluids, including blood, serum, plasma, and urine, offering a minimally invasive means of accessing disease-specific molecular signatures [
50,
51]. By analyzing the expression levels of specific miRNAs within exosomes, clinicians may be able to differentiate between HCM and other cardiac conditions, assess disease severity, and predict clinical outcomes [
52,
53,
54]. Furthermore, the stability of exosome-derived miRNAs in circulation makes them attractive candidates for longitudinal monitoring of disease progression and response to therapeutic interventions.
5.3. Therapeutic Implications
The dysregulation of exosome-derived miRNAs in HCM presents novel opportunities for therapeutic intervention. By targeting specific miRNAs implicated in disease pathogenesis, researchers aim to modulate cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and remodeling processes, ultimately ameliorating disease progression and improving clinical outcomes. Strategies for therapeutic intervention include the use of antagomirs, oligonucleotide-based inhibitors that specifically target and inhibit the function of dysregulated miRNAs, as well as the delivery of exogenous miRNAs or miRNA mimics to restore normal gene expression patterns [
55,
56,
57]. Moreover, engineered exosomes loaded with therapeutic miRNAs or other bioactive molecules represent a promising approach for targeted drug delivery to the heart, circumventing the limitations of conventional pharmacological agents [
58].
6. Exosomal miRNAs that Attenuate HCM
6.1. MiR-1 from Cardiomyocytes
MiR-1 is one of the most abundant miRNAs found in cardiomyocytes and has been shown to be highly expressed in cardiomyocyte-secreted exosomes, but its expression is reduced in the serum of patients with HCM [
59,
60]. MiR-1 has been implicated as a significant protective factor against cardiac hypertrophy by targeting several pro-hypertrophic signaling pathways [
61].
Dysregulation in calcium signaling is associated with HCM, wherein elevated intracellular Ca
2+ levels trigger hypertrophic responses within the myocardium by enhancing cardiac output [
62]. Calcineurin is a calcium-dependent enzyme shown to play a pivotal role in this process by activating the transcription factor nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFATC) 3 [
63,
64]. Studies involving human heart tissue samples and mouse cardiomyocytes have shown that increased expression of miR-1 mitigates cardiac hypertrophy by downregulating NFATC3 expression. Downregulation of NFATC3 caused a reduction in cardiomyocyte surface area and a decrease in levels of beta-myosin heavy chains (β-MHCs), a hallmark of cardiac hypertrophy [
65,
66].
Further studies have identified that exosomal miRNA-1 from cardiomyocytes may exert its anti-hypertrophic effect through modulation of Ca
2+ uptake within mitochondria. Mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter (MCU) is the core channel subunit of the mithochondrial Ca2+ uniporter complex (MCUC). MCUC plays a critical role in cardiomyocyte stress adaptation by modulating Ca
2+ uptake within mitochondria [
67]. Hypertrophic cells overexpress MCU and silencing of MCU prevents cell hypertrophy and mitochondrial dysfunction by blocking mitochondrial calcium overload, increase in mitochondrial ROS and activation of nuclear factor kappa B-dependent hypertrophic and proinflammatory signaling [
68]. A study by Zaglia and colleagues examined human cardiac biopsy specimens from individuals with cardiac hypertrophy and identified a correlation between reduced levels of miR-1 and an elevation in MCU protein content [
67]. The study showed that miR-1 is responsible for direct and selective targeting of MCU and inhibition of its translation, thereby affecting the capacity of the mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake machinery. The study also identified that treatment with β-blockers in pressure-overloaded mouse hearts prevented miR-1 down-regulation and the consequent increase in MCU content, indicating that persistent activation of ß-adrenoreceptors secondary to stress is likely one of the upstream repressors of miR-1. Ultimately, the study identified the miR-1/MCU axis as a key factor in the dynamic adaptation of cardiac cells to hypertrophy [
67].
Further studies investigating ways by which exosomal miR-1 can impose a protective role against cardiac hypertrophy have identified modulation of the cyclin D kinase 6-retinoblastoma (CDK6-Rb) pathway and thyroid hormone levels as significant mechanisms [
69,
70]. Studies involving hypertrophic rat cardiomyocytes transfected with miR-1 mimics or CDK6 siRNA demonstrated inhibition of CDK6-Rb pathway activation, a significant mechanism in regulating cell cycle progression contributing to cardiac hypertrophy [
71,
72]. Diniz and colleagues identified that overexpression of miR-1 countered thyroid hormone-induced cardiac hypertrophy, evidenced by decreased levels of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and alpha-myosin heavy chain (α-MHC), both indicators of cardiac hypertrophy [
70]. In addition, the study found that thyroid hormone induces hypertrophy by targeting histone deacetylase-4 (HDAC4), an effect mitigated by miR-1 overexpression [
70]. In this way, selective delivery of exosomal miR-1 to cardiomyocytes can prevent progression of pathogenesis in HCM.
We now know that a key downstream target of miR-1 is the cytoskeletal regulatory protein twinfilin-1 (TWF1), which governs actin dynamics, thereby influencing various cellular processes [
73,
74]. The expression pattern of TWF1 has been shown to be inversely related to miR-1 levels [
73]. Rat cardiomyocytes overexpressing miR-1 exhibit reduced cell size and suppressed TWF1 protein expression, contrasting with hypertrophic rat hearts and phenylephrine-induced hypertrophic cardiomyocytes, where downregulated miR-1 is associated with upregulated TWF1 and actin protein levels [
73].
Furthermore, insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) has emerged as one of the cardiac targets influenced by miR-1 in modulating cardiac hypertrophy [
75]. IGF-1 is recognized for its role in regulating cardiomyocyte size and contractile function [
76]. Studies utilizing the transverse aortic constriction model and Akt-transgenic animal model revealed that repression of miR-1 coincided with increased IGF-1 protein levels and its receptor, IGF-1R [
75,
77]. This finding was further supported by clinical evidence demonstrating reduced miR-1 levels in biopsies from patients with acromegaly, a condition characterized by elevated production of growth hormone and IGF-1, alongside increased cardiomyocyte size [
75].
6.2. MiR-133a from Cardiomyocytes
Similar to miR-1, miR-133a is a microRNA found in muscle tissue, demonstrated to counteract hypertrophy by affecting targets within calcium signaling, cell growth, and cell development pathways [
78,
79,
80,
81,
82,
83]. MiR-133 is highly expressed in exosomes secreted from cardiomyocytes and reduced expression in a normal adult cardiomyocyte is enough to induce cardiac hypertrophy [
84,
85,
86]. Introducing miR-133a decreases cardiac hypertrophy by reducing the expression of calcineurin [
78]. Additionally, miR-133a transfection has been found to impede cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by phenylephrine by downregulating the expression of NFATC4 [
79].
The anti-hypertrophic effects of the miR-133 family of miRNAs were observed in a rat model of triiodothyronine-induced hypertrophy, where reduced levels of miR-133 were linked, in part, to the angiotensin II receptor subtype 1 (AT1R) [
82]. AT1R plays a dual role by both decreasing miR-133 levels and increasing the expression of calcineurin and SERCA2a, both known targets of miR-133 [
82].
Recent studies have identified a potential interaction between miR-133a and α1-adrenergic receptor-mediated signaling, impacting calcium signaling dysregulation that drives cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. MiR-133a inhibits norepinephrine-induced hypertrophic changes in cardiomyocytes by downregulating protein kinase C (PKC) and Gq protein levels [
80].
Norepinephrine binding to α1-AR triggers a stress response by activating PKC and phospholipase C signaling pathways. PKC activates transcription factors linked to cardiac hypertrophy through a mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade, while phospholipase C generates inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate and diacylglycerol, activating calcium signaling and PKC, respectively [
87]. By targeting PKC and Gq, miR-133a can inhibit the rise in intracellular calcium levels and the subsequent activation of hypertrophic transcription factors such as c-Jun and c-Myc [
87].
In addition, exosomal miR-133a has the capability to diminish cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting the expression of serum response factor and cyclin D2 [
88]. These factors contribute to abnormal growth of heart muscle cells and subsequent heart dysfunction. Furthermore, miR-133a targets other key players in cardiac function, such as myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2), serum- and glucocorticoid-responsive kinase-1 (SGK1), and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) [
83]. When cardiomyocytes undergo hypertrophy due to glucose stimulation, there is an increase in MEF2, SGK1, and IGF-1R levels alongside a decrease in miR-133a expression. Introducing miR-133a mimics counteracted the upregulation of these hypertrophy-related molecules, suggesting that MEF2, SGK1, and IGF-1R are influenced by miR-133a in the pathological remodelling that occurs in HCM [
83].
6.3. MiR-30 from Endothelial Cells and Cardiomyocytes
The miR-30 family members, including miR-30a, miR-30b, miR-30c, and miR-30d, exert pleiotropic effects on cardiac fibrosis by targeting multiple fibrogenic pathways. These miRNAs modulate the expression of genes involved in transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling, collagen synthesis, and myofibroblast differentiation. Dysregulation of miR-30 expression has been implicated in the pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis, with therapeutic restoration of miR-30 levels attenuating fibrotic remodeling in experimental models of HCM.
Endothelial cell-derived exosomes highly express miRNA-30a and an investigation into the role that miR-30a plays in cardiac hypertrophy using male mice subjected to thoracic aortic constriction demonstrated that miR-30a expression in the myocardium is reduced in mouse models of hypertrophy [
89]. Inhibition of miR-30a markedly increased mRNA expression of cardiac hypertrophy markers such as atrial natriuretic factor and brain peptide and greatly increased cell size [
89].
MiR-30b-5p is a mRNA found highly expressed in endothelial cells and is highly expressed within plasma exosomes [
90,
91]. Computational and expressional analysis has shown that it is downregulated in cardiac hypertrophy and restoration inhibits expression of hypertrophic signaling marker Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase [
92].
A study into the role of miR-30c in high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy identified that it plays a key role in regulating the p53-p21 pathway that mediates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. MiR-30c has been identified to target p53, and expression of this miRNA was significantly decreased in high glucose-treated cardiomyocytes, together with a concomitant increase in myocardial expression of p53 and p21 genes. Overexpression of miR-30c decreased expression of p53, p21, cardiomyocyte cell size and apoptosis in high glucose-treated cardiomyocytes [
93]
Cardiomyocytes have been identified as the major cell type that expresses miR-30d and secrete them packaged in EVs [
94]. A study using murine and neonatal rat cardiomyocytes models of hypertrophy identified that miR-30d prevented pathological cardiac hypertrophy via negatively regulating its target genes MAP4K4 and GRP78 and inhibiting pro-hypertrophic NFATC [
95].
6.4. Other Exosomal MiRNAs
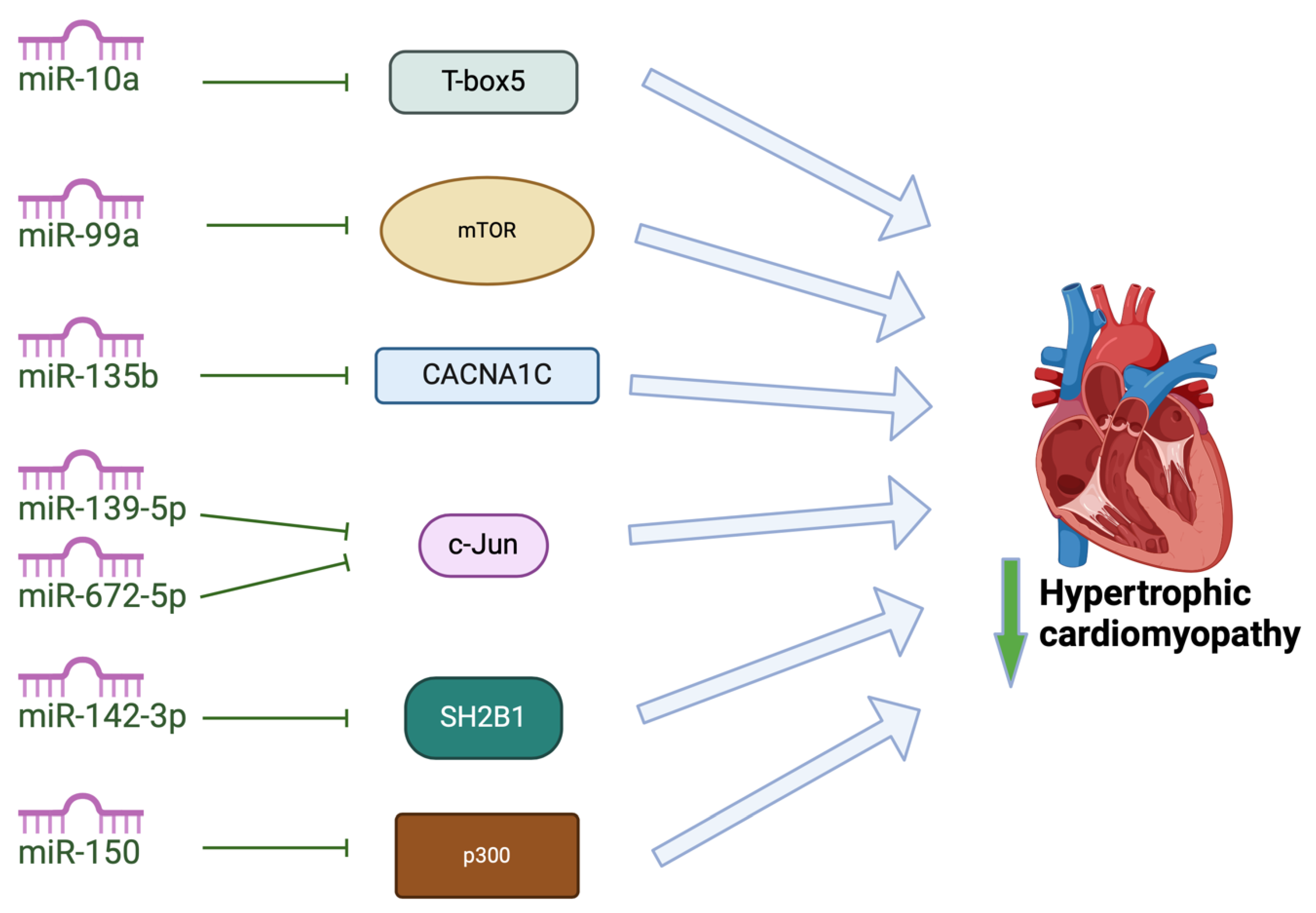
In addition to the miRNAs mentioned above, other, less-studied miRNAs attenuate cardiac hypertrophy (
Figure 4). Some of these miRNAs mediate their effects by regulating factors involved in cardiac development or factors involved in calcium signaling and energy metabolism. MiR-10a has been shown to target T-box5 in rat models, decreasing expression of natriuretic peptide A and myosin heavy chain 7 cardiac muscle beta, attenuating cardiac hypertrophy [
96]. MiR-135b overexpression has been shown to attenuate cardiac hypertrophy by targeting CACNA1C, which encodes L-type calcium channels in cardiomyocytes, attenuating hypertrophic signaling [
97]. Overexpression of miR-142-3p has been shown to inhibit Src homology 2 B adaptor protein 1. In doing so, miR-142-3p ameliorates cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction and improves mitochondrial function in rat models of HCM [
98]. Both miR-139-5p and miR-672 have recently been identified to reduce cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting expression of transcription factor JUN [
99,
100] and a study by Duan and colleagues identified that miR-150 regulates high glucose-induced cardiac hypertrophy by targeting the transcriptional co-activator p300 [
101]. Overexpression of miR-99a attenuated cardiac hypertrophy in mice models of cardiac hypertrophy induced by transverse aortic constricture, likely through downregulation of expression of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) [
102]. Further studies are required to understand the role that these miRNAs can play in therapeutic strategies for HCM.
Figure 4.
Exosomal miRNAs attenuate pathogenic changes in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy by targeting different pathways. MiRNA-10a inhibits T-box 5; miR-99a inhibits mTOR to attenuate hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes; miR-135b inhibits CACNA1C which encodes the L-type voltage-gated calcium channels; miR-139-5p and miR-672-5p inhibit c-Jun; miR-142-3p inhibits inhibit Src homology 2 (SH2) B adaptor protein 1 to improve mitochondrial function; miR-150 inhibits transcriptional co-activator p300.
Figure 4.
Exosomal miRNAs attenuate pathogenic changes in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy by targeting different pathways. MiRNA-10a inhibits T-box 5; miR-99a inhibits mTOR to attenuate hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes; miR-135b inhibits CACNA1C which encodes the L-type voltage-gated calcium channels; miR-139-5p and miR-672-5p inhibit c-Jun; miR-142-3p inhibits inhibit Src homology 2 (SH2) B adaptor protein 1 to improve mitochondrial function; miR-150 inhibits transcriptional co-activator p300.
7. Exosomal miRNAs that Promote HCM
7.1. MiR-200 from Cardiomyocytes
Exosomal miR-200 family have been implicated in the cellular crosstalk between cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells in health and pathology [
103]. One of the targets of miR-200c is dual-specific phosphatase-1 (DUSP-1). This target has been shown to prevent cardiac hypertrophy by deactivating mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), including extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 [
104]. In high-glucose-treated cardiomyocytes, miR-200c downregulates DUSP-1 expression, leading to activation of MAPK proteins, thereby inducing diabetes-associated cardiac hypertrophy [
105].
Further studies have demonstrated that exosomal miR-200c promotes cardiac hypertrophy by directly targeting myosin light chain kinase (MLCK). This enzyme is pivotal in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology [
106]. Elevated levels of miR-200c correlates with a reduction in MLCK expression [
107]. In hypertrophic models, overexpression of miR-200c causes an increase in production of ROS and apoptosis, characterised by heightened expression of pro-apoptotic markers including Bax and caspase-3 [
107]. Hypertrophic growth in the myocardium then occurs in cardiac remodeling secondary to the stress signaling.
7.2. MiR-155 from Immune Cells
Studies have indicated that exosomal miR-155 secreted from immune cells are involved in the promotion of HCM by targeting inflammation and calcium signaling pathways [
108,
109,
110,
111]. Macrophages expressing miR-155 activate the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducter and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway, thereby facilitating hypertrophic remodeling in the myocardium. MiR-155 is believed to inhibit the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1), leading to STAT3 phosphorylation [
112]. Phosphorylated STAT3 has been widely shown to initiate pro-hypertrophic signaling in cardiomyocytes. In this way, miR-155 secreted within macrophage exosomes can contribute to HCM, and therapeutic inhibition of miR-155 presents itself as a potential avenue to protect the heart from pathological cardiac hypertrophy [
108].
7.3. MiR-21 from Immune Cells and Cardiac Fibroblasts
Exosomal miR-21 has drawn considerable attention in recent years for the role it may play in HCM [
113,
114]. MiR-21 is abundantly expressed in immune cells such as T cells and macrophages as well as in cardiac fibroblasts. To date, several genes have been identified as miR-21 targets involved in cardiomyopathy. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) and phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome 10 (PTEN) are the two most recognised target genes involved in anti-apoptosis [
115,
116]. PTEN acts as a negative regulator of the phosphatidyl-3 kinase (PI3K)/Akt/mammalian target of the rapamycin (mTOR) pathway, pivotal in cardiac function [
117]. By targeting these genes, as well as other negative regulators of hypertrophic signaling including sprout homolog 1 (SPRY1), immune cell- and fibroblast-derived exosomes enriched with miR-21 can promote cardiomyocyte hypertrophy [
118,
119].
While primarily associated with hypertrophic signaling, mir-21 also plays a crucial role in cardiac fibrosis in HCM. MiR-21 promotes fibroblast activation and extracellular matrix deposition [
119]. MiR-21 promotes fibroblast activation and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting inhibitors of the TGF-β pathway, such as SMAD7 [
120]. Exosomes enriched with miR-21 have been implicated in the transmission of pro-fibrotic signals to fibroblasts, exacerbating fibrotic remodeling in the hypertrophic heart and a decrease of miR-21 by antagomir-21 prevents fibrosis following myocardial injury [
121].
7.4. MiR-22 from Smooth Muscle Cells
MiR-22 is highly expressed by smooth muscle and mesenchymal stromal cells and exosomal transfer of these miRNAs is hypothesised to play a pivotal role in crosstalk with cardiomyocytes [
122]. MiR-22 has been shown to be upregulated during myocardial differentiation and cardiac hypertrophy [
123]. Similar to miR-155, miR-22 is implicated in promoting HCM by targeting the calcineurin pathway, as loss of miR-22 represses calcineurin-induced cardiac hypertrophy [
123]. Inhibition of miR-22 or observing cardiomyocytes from miR-22 knockout mice led to heightened levels of HDAC4 and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) [
123]. Both are known to play protective roles against cardiac hypertrophy [
124,
125].
Further studies have also demonstrated that miR-22-induced hypertrophy may involve modulation of the PTEN pathway. Overexpression of miR-22 in HCM leads to reduced PTEN protein levels, accompanied by increased cell surface area and expression of cardiac hypertrophy markers (126). This inverse relationship between miR-22 and PTEN in cardiac hypertrophy was further supported by another study, demonstrating that atorvastatin, a cholesterol-lowering medication known for its anti-hypertrophic effects, reversed the consequences of miR-22 overexpression by elevating PTEN levels (127). Nonetheless, clinical evidence regarding the impact of atorvastatin on human patients with cardiac hypertrophy remains scarce and further studies are required to delineate the mechanisms by which it attenuates cardiac hypertrophy.
7.5. MiR-21 from Cardiomyocytes
MiR-217 is highly expressed in cardiomyocytes and cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes containing miR-217 has been shown to enhance proliferation of fibroblasts in vitro (128). MiR-217 appears to function similarly to miR-22 regarding its involvement in HCM, particularly through its interaction with PTEN. Overexpression of miR-217 leads to cardiac hypertrophy, which can be mitigated by restoring PTEN expression, as evidenced by decreased levels of hypertrophic markers such as ANP and β-MHC (129).
Further genes implicated in miR-217-mediated promotion of pathological cardiac hypertrophy are euchromatic histone–lysine N-methyltransferases EHMT1 and EHMT2 (130). Experimental induction of pathological HCM, such as through abdominal aortic banding in rat models, results in increased expression of miR-217 and subsequent suppression of EHMT1/2 mRNA levels. These enzymes are crucial for heart development in the prenatal stage and for the catalysis of histone 3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) (131). The concurrent decrease in EHMT1/2 and H3K9m2 levels triggers the re-expression of fetal-associated transcripts, ultimately leading to pathological hypertrophy. This was supported by the finding that inhibition of miR-217 activity prevents the downregulation of EHMT1/2 and reverses the onset of hypertrophy (130). These findings suggest that exosomal miR-217, through its ability to modulate methylation processes, presents a promising therapeutic target for managing and treating cardiac hypertrophy.
7.6. MiR-208 from Cardiac Stem Cells
MiR-208, specifically encoded by Myh6, plays a crucial role in cardiac remodeling and hypertrophic responses. miRNA-208 expression is markedly increased in the serum exosomes of patients with cardiac disease compared to control (132). Importantly, the sensitivity of exosome miR-208a is superior to that of exosome miR-208a. Exosomal miR-208a therefore presents itself as a potential important marker of cardiac stress during development of HCM.
Expression of pro-hypertrophic β-MHC is increased following upregulation of miR-208a. This upregulation of miR-208a precedes switch from α- to β-MHC isoforms and the development of systolic and diastolic dysfunction (133). Inhibition of this miRNA prevented β-MHC activation and the subsequent hypertrophic response, thus demonstrating the potential for miR-208a inhibition as a therapeutic avenue in HCM.
7.7. Other MiRNAs
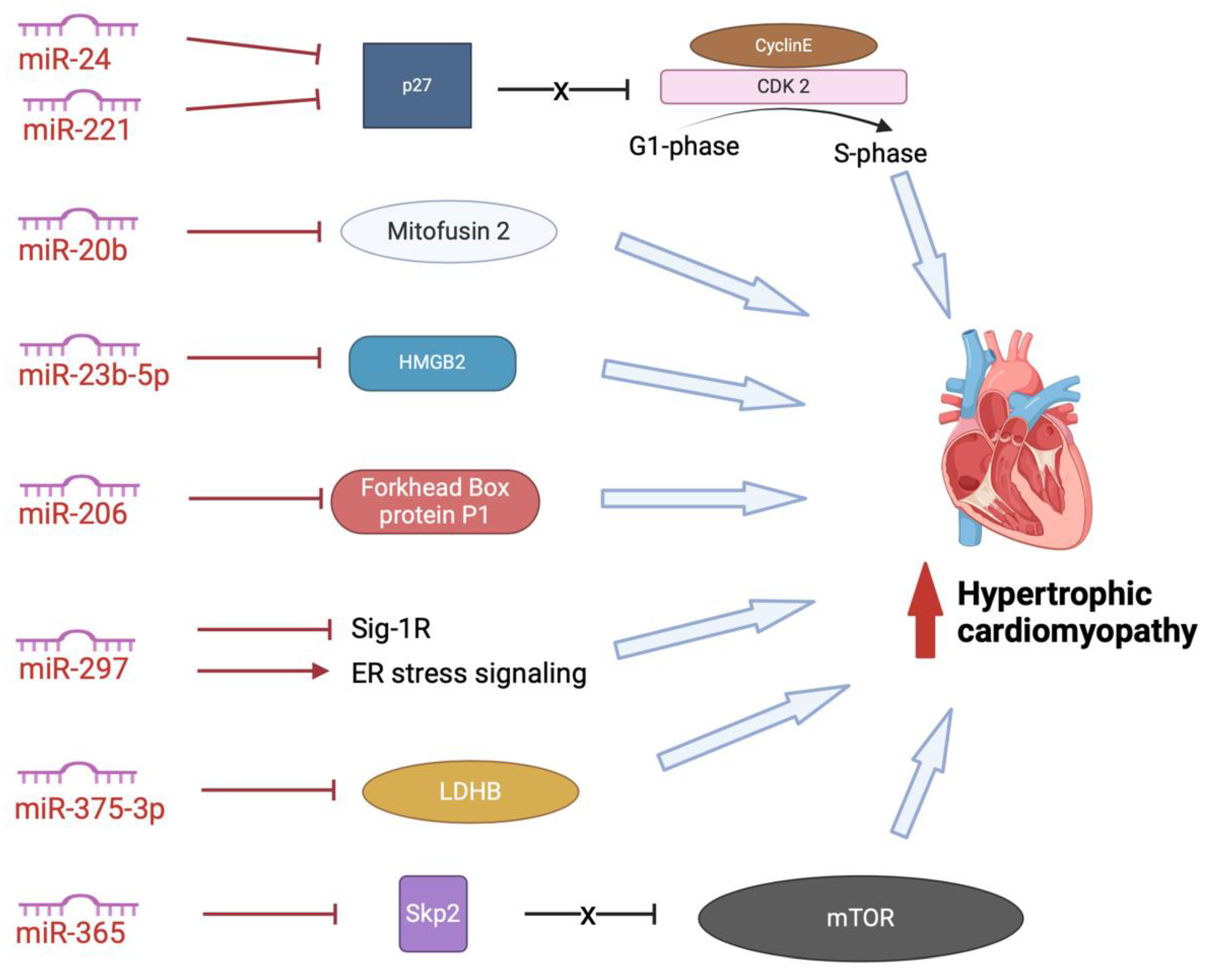
In addition to the exosomal miRNAs described above, other, less-studied exosomal miRNAs promote HCM (Figure 5). These miRNAs promote dysfunction in cardiac structure, function, or metabolism (134–141). MiR-24 and miR-221 both inhibit CDK inhibitor p27, thus disinhibiting CDK2 and allowing progression of cell cycling from G1 to S phase (138,141). This activity has led to exosomal miR-24 and miR-221 being investigated for their role in carcinomas and cancer metastasis, but with limited studies into hypertrophic remodelling (142,143).
Another potentially important miRNA in the pathogenesis of HCM is miR-20b. MiR-20b inhibits mitofusin 2-mediated inter-organelle calcium crosstalk, promoting hypertrophic remodelling (140). MiR-23b-5p blocks HMGB2, promoting cardiac dysfunction, however the relationship between miR-23b-5p and remodelling in HCM has not yet been investigated (135). MiR-206 plays an essential role in mediating cardiac hypertrophy by negatively regulates forkhead box protein P1 (137). It has also been demonstrated that circulating exosomes, containing miR-206, are taken up by the heart leading to sympathetic dysinnervation and increased arrhythmogenesis, an important feature of HCM pathogenesis (144). MiR-297 inhibits expression of sigma-1 receptor and activates ER stress signaling, promoting cardiac hypertrophy (134). However, we are yet to delineate the role of exosomal miR-297 and differentiate this from serum miR-297. MiR-375-3p inhibits expression of lactate dehydrogenase B chain, promoting cardiac hypertrophy (139). Again, although exosomal miR-375-3p has been implicated in the pathogenesis of carcinomas of the gastrointestinal tract, we are still yet to fully delineate the role of serum and exosomal miRNA-375-3p in HCM.
Another miRNA which shows promise as a potential marker and therapeutic target in cardiac disease is miRN-365. MiR-365 has been found abundantly in the exosomes extracted from pericardial fluid samples from heart failure patients (145). It has been identified as a circulatory cardiovascular-related miRNA, upregulated after exercise in human (146). MiR-365 blocks Skp2, uninhibiting mTOR, triggering autophagy and cardiac hypertrophy (136). However, we are yet to understand the role that exosomal miRNA-365 plays in HCM in humans.
Figure 5.
Pro-hypertrophic miRNAs augment cardiac hypertrophy by targeting different pathways. miR-24 and miR-221 inhibit p27, promoting cell cycling; miR-20b inhibits mitofusin 2-mediated inter-organelle calcium crosstalk; miR-23b-5p blocks HMGB2; miR-206 inhibits forkhead box protein P1; miR-297 inhibits the expression of Sig-1R and activates ER stress signaling; miR-375-3p inhibits expression of LDHB, miR-365 downregulates expression of Skp2. ER: endoplasmic reticulum; HMGB2: high-mobility group box 2; LDHB: lactate dehydrogenase B chain; Sig-1R: sigma-1 receptor; Skp2: S-phase kinase-associated protein 2.
Figure 5.
Pro-hypertrophic miRNAs augment cardiac hypertrophy by targeting different pathways. miR-24 and miR-221 inhibit p27, promoting cell cycling; miR-20b inhibits mitofusin 2-mediated inter-organelle calcium crosstalk; miR-23b-5p blocks HMGB2; miR-206 inhibits forkhead box protein P1; miR-297 inhibits the expression of Sig-1R and activates ER stress signaling; miR-375-3p inhibits expression of LDHB, miR-365 downregulates expression of Skp2. ER: endoplasmic reticulum; HMGB2: high-mobility group box 2; LDHB: lactate dehydrogenase B chain; Sig-1R: sigma-1 receptor; Skp2: S-phase kinase-associated protein 2.
8. Exosomal MiRNAs That Both Attenuate and Promote HCM
8.1. MiRNAs from Cardiac Fibroblasts
MiR-29 family members, including miR-29a, miR-29b, and miR-29c, have garnered significant attention for their regulatory role in cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy. Interestingly, early investigations have demonstrated that miR-29 family members show mixed activity that both promote and attenuate HCM.
MiR-29a is the most stable and most abundantly expressed member of the miR-29 family. MiR-29a and -29b-1 are encoded on human chromosome 7q32.3 and mir-29b-2 and -29c are found on chromosome 1q32.2. Cardiac fibroblasts have been identified as the primary cell type responsible for miR-29 expression in the heart, and treatment of isolated mouse cardiac fibroblasts with TGF-β reduced expression of miR-29a, miR-29b and miR-29c (147).
A study by Liu and colleagued used mouse models and human tissues samples to identify a protective role of miR-29 family members in HCM (148). This study found that endothelin-1 (ET1) signaling, known to be upregulated in early HCM, increases ROS in cardiomyocytes, stimulating the secretion of TGF-β and suppressing miR-29a expression. This suppression of miR-29a contributes to increased collagen production in fibroblasts, promoting fibrosis (148). Therefore, modulation of miR-29a to increase expression via exosomal transfer has been identified as a potential therapeutic target.
In addition, miR-29 has been shown to exhibit a cardioprotective effect in isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting a nuclear receptor, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ (149). Additionally, a study by Li and colleagues suggests a potential role of miR-29a-3p in attenuating endothelin-1-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by inhibiting NFATc4 expression, although this finding was derived from an in vitro study using H9c2 cells (150).
However, despite these studies that support the concept that enhancing miR-29 would be a promising anti-fibrotic therapy for heart disease, there is also growing evidence that the miR-29 family are potent inducers of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy (151). A study by Sassi and colleagues investigated the role of miR-29 in myocardial remodeling identified that miR-29 promotes cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in vivo and increases, rather than decreases, cardiac fibrosis (152). This was supported by their finding that pharmacological inhibition or genetic deletion of miR-29 prevented both cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis in mice models. The study identified that the activity was through regulation of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling in cardiomyocytes, eliciting hypertrophic growth in these cells and secretion of profibrotic proteins that signal towards cardiac fibroblasts. Hence, further investigations are warranted to elucidate the precise involvement of miR-29 in cardiac remodeling.
8.2. MiR-146a From Immune Cells
MiR-146a, expressed in various immune cell subsets, serves as a critical regulator of inflammatory signaling pathways in the myocardium and has been shown exerts significant influence over cardiac hypertrophy. Genetic deletion or therapeutic inhibition of miR-146a during pressure overload diminishes the hypertrophic response and improves cardiac function (153). This effect is attributed to miR-146a's modulation of dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase (DLST), a mitochondrial protein involved in energy metabolism. Overexpression of DLST counteracts pressure overload-induced hypertrophy, underscoring its role as a potential therapeutic target.
Research indicates that miR-146a plays a crucial role in fibrosis regulation in HCM. Studies in mouse models of pressure overload and patients with aortic stenosis reveal upregulation of miR-146a. Inhibition of miR-146a during pressure overload attenuates fibrosis. Although the exact mechanisms are not fully elucidated, it is suggested that miR-146a may impact fibrosis indirectly via its effects on cardiac metabolism (153).
The impact of miR-146a extends to metabolic alterations in cardiomyocytes. MiR-146a knockout cells exhibit preserved glucose and fatty acid oxidation under pressure overload conditions, indicating a favorable metabolic profile (153). DLST, targeted by miR-146a, plays a crucial role in regulating mitochondrial ATP production, thereby influencing cardiomyocyte metabolism. Therapeutic strategies targeting miR-146a may normalize metabolic changes associated with HCM, offering potential therapeutic benefits. A study into the role that exosomal-miR-146a-5p plays in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy identified only a minor fraction of the plasma miR-146a was encapsulated in exosomes (154). However, there are limitations in exosome isolation that affects our ability to quantify exosomal-miRNA, which will be discussed in the next section.
9. Challenges and Future Directions
9.1. Methodological Limitations and Technical Challenges
Despite significant advancements in our understanding of exosome-derived miRNAs in HCM, several methodological limitations and technical challenges hinder comprehensive research in this field. One major challenge lies in the isolation and characterization of exosomes from complex biological samples, such as blood or cardiac tissue. Current isolation methods often suffer from low yield, contamination, and lack of standardization, leading to variability in experimental results (155). Moreover, the heterogeneity of exosomes, both in terms of size and cargo composition, poses a challenge for accurate characterization and functional analysis.
Furthermore, the identification and quantification of specific miRNAs within exosomes remain technically demanding. Existing techniques, such as next-generation sequencing and quantitative PCR, have inherent limitations, including sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility issues. Improved methodologies for profiling exosomal miRNAs are necessary to accurately delineate their roles in HCM pathogenesis.
9.2. Unravelling Specific Signaling Pathways and Targets
A deeper understanding of the specific signaling pathways and molecular targets regulated by exosome-derived miRNAs is crucial for elucidating their roles in HCM. While studies have identified several miRNAs implicated in hypertrophic signaling cascades, the precise mechanisms underlying their effects remain incompletely understood. Unraveling the intricate interplay between exosomal miRNAs and target genes/pathways in cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and immune cells will provide insights into the pathophysiology of HCM.
Moreover, deciphering the context-dependent effects of exosomal miRNAs in different stages of HCM progression is essential. It is likely that miRNA-mediated signaling networks vary dynamically during the course of the disease, influenced by factors such as disease etiology, comorbidities, and therapeutic interventions. Integrative approaches, combining experimental models, omics technologies, and computational analyses, are needed to unravel the complexity of miRNA-mediated regulation in HCM.
9.3. Translational Potential for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies
Despite the challenges, exosome-derived miRNAs hold significant promise as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for HCM. The unique stability and cell-type specificity of exosomal miRNAs make them attractive candidates for non-invasive biomarker discovery and disease monitoring. However, the translation of exosomal miRNA-based diagnostic assays into clinical practice requires rigorous validation in large, well-characterized patient cohorts.
Furthermore, exosome-mediated delivery of miRNA-based therapeutics offers a novel approach for targeting pathological pathways in HCM. Engineered exosomes loaded with specific miRNA mimics or inhibitors could be employed to modulate hypertrophic signaling cascades, attenuate fibrotic remodeling, and improve cardiac function in HCM patients. However, challenges related to targeted delivery, off-target effects, and safety must be addressed before clinical implementation.
Abbreviations
ANP atrial natriuretic peptide
CDK6-Rb cyclin D kinase 6-retinoblastoma
DGCR8 DiGeorge Syndrome Critical Region 8
DLST dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase
ESCRT endosomal sorting complex required for transport
HCM Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
HDAC4 histone deacetylase-4
IGF-1 insulin-like growth factor-1
IGF-1R insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
ILV intraluminal vesicle
MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinases
MCU mithochondrial Ca2+ uniporter
MCUC mithochondrial Ca2+ uniporter complex
MEF2 myocyte enhancer factor 2
MHC myosin heavy chain
miRNA microRNA
MLCK myosin light chain kinase
mRNA messenger RNA
mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin
MVE multivesicular endosome
Myh6 α-myosin heavy chain gene
NFATC transcription factor nuclear factor of activated T cells
PKC protein kinase C
Pre-miRNA precursor miRNA
Pri-miRNA primary miRNA
RISC RNA-induced silencing complex
ROS reactive oxygen species
SERCA2a sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 2a
SGK1 glucocorticoid-responsive kinase-1
SNARE soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein re-
ceptor
TGF-β transforming growth factor-beta
TWF1 twinfilin-1
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.X.W; writing—B.X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Marian AJ, Braunwald E (2017) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Genetics, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and therapy. Circ Res 121:749–770. [CrossRef]
- Di Bella MA (2022) Overview and Update on Extracellular Vesicles: Considerations on Exosomes and Their Application in Modern Medicine. Biology (Basel) 2022:804. [CrossRef]
- Zwi-Dantsis L, Winter CW, Kauscher U, et al (2020) Highly purified extracellular vesicles from human cardiomyocytes demonstrate preferential uptake by human endothelial cells. Nanoscale 12:19844–19854. [CrossRef]
- Zhou SS, Jin JP, Wang JQ, et al (2018) MiRNAS in cardiovascular diseases: Potential biomarkers, therapeutic targets and challenges review-article. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39:1073–1084.
- Maron BJ, Gardin JM, Flack JM, et al (1995) Prevalence of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in a General Population of Young Adults. Circulation 92:785–789. [CrossRef]
- Marian AJ (2000) Pathogenesis of diverse clinical and pathological phenotypes in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The Lancet 355:58–60. [CrossRef]
- Eduardo Carreño J, Apablaza F, Ocaranza MP, Jalil JE (2006) Cardiac Hypertrophy: Molecular and Cellular Events. Revista Española de Cardiología (English Edition) 59:473–486. [CrossRef]
- Crocini C, Gotthardt M Cardiac sarcomere mechanics in health and disease. [CrossRef]
- Corrado D, Zorzi A, Cipriani A, et al (2023) Scarring/arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. European Heart Journal, Supplement 25:C144–C154. [CrossRef]
- van der Voorn SM, te Riele ASJM, Basso C, et al (2020) Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: Pathogenesis, pro-arrhythmic remodelling, and novel approaches for risk stratification and therapy. Cardiovasc Res 116:1571–1584.
- Schlittler M, Pramstaller PP, Rossini A, De Bortoli M (2023) Myocardial Fibrosis in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A Perspective from Fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci 24.
- Frangogiannis NG (2021) Cardiac fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res 117:1450–1488.
- Frangogiannis NG (2020) Transforming growth factor–ß in tissue fibrosis. Journal of Experimental Medicine 217.
- Hartupee J, Mann DL (2016) Role of inflammatory cells in fibroblast activation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 93:143–148.
- Van Der Velden J, Tocchetti CG, Varricchi G, et al (2018) Metabolic changes in hypertrophic cardiomyopathies: Scientific update from the working group of myocardial function of the European Society of Cardiology. Cardiovasc Res 114:1273–1280.
- Nollet EE, Duursma I, Rozenbaum A, et al (2023) Mitochondrial dysfunction in human hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is linked to cardiomyocyte architecture disruption and corrected by improving NADH-driven mitochondrial respiration. Eur Heart J 44:1170–1185. [CrossRef]
- Wijnker PJM, Sequeira V, Kuster DiWD, Van Der Velden J (2019) Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A Vicious Cycle Triggered by Sarcomere Mutations and Secondary Disease Hits. Antioxid Redox Signal 31:318–358.
- Periasamy M, Huke S (2001) SERCA Pump Level is a Critical Determinant of Ca2+Homeostasis and Cardiac Contractility. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33:1053–1063. [CrossRef]
- Robinson P, Liu X, Sparrow A, et al (2018) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations increase myofilament Ca2 buffering, alter intracellular Ca2 handling, and stimulate Ca2-dependent signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry 293:10487–10499. [CrossRef]
- Beach A, Zhang HG, Ratajczak MZ, Kakar SS (2014) Exosomes: An overview of biogenesis, composition and role in ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res 7.
- Gurung S, Perocheau D, Touramanidou L, Baruteau J (2021) The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Communication and Signaling 19.
- O’Brien K, Breyne K, Ughetto S, et al (2020) RNA delivery by extracellular vesicles in mammalian cells and its applications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21:585–606.
- Krylova S V., Feng D (2023) The Machinery of Exosomes: Biogenesis, Release, and Uptake. Int J Mol Sci 24.
- Ju Y, Bai H, Ren L, Zhang L (2021) The role of exosome and the escrt pathway on enveloped virus infection. Int J Mol Sci 22.
- Tschuschke M, Kocherova I, Bryja A, et al (2020) Inclusion biogenesis, methods of isolation and clinical application of human cellular exosomes. J Clin Med 9.
- Xu M, Ji J, Jin D, et al (2023) The biogenesis and secretion of exosomes and multivesicular bodies (MVBs): Intercellular shuttles and implications in human diseases. Genes Dis 10:1894–1907.
- Burtenshaw D, Regan B, Owen K, et al (2022) Exosomal Composition, Biogenesis and Profiling Using Point-of-Care Diagnostics—Implications for Cardiovascular Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol 10.
- Andreu Z, Yáñez-Mó M (2014) Tetraspanins in extracellular vesicle formation and function. Front Immunol 5:. [CrossRef]
- Doyle LM, Wang MZ (2019) Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells 8.
- Zhang Y, Liu Y, Liu H, Tang WH (2019) Exosomes: Biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci 9.
- Li C, Ni YQ, Xu H, et al (2021) Roles and mechanisms of exosomal non-coding RNAs in human health and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6.
- Ranganathan K, Sivasankar V (2014) MicroRNAs - Biology and clinical applications. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology 18:229–234.
- B: L-A, Murphy PR (2010) MicroRNA, 2010; 33. Macfarlane L-A, Murphy PR (2010) MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer.
- Han J, Lee Y, Yeom KH, et al (2004) The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing. Genes Dev 18:3016–3027. [CrossRef]
- Bohnsack MT, Czaplinski K, Görlich D (2004) Exportin 5 is a RanGTP-dependent dsRNA-binding protein that mediates nuclear export of pre-miRNAs. RNA 10:185–191. [CrossRef]
- Medley JC, Panzade G, Zinovyeva AY (2021) microRNA strand selection: Unwinding the rules. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 12.
- Annese T, Tamma R, De Giorgis M, Ribatti D (2020) microRNAs Biogenesis, Functions and Role in Tumor Angiogenesis. Front Oncol 10.
- Havens MA, Reich AA, Duelli DM, Hastings ML (2012) Biogenesis of mammalian microRNAs by a non-canonical processing pathway. Nucleic Acids Res 40:4626–4640. [CrossRef]
- Su Z, Wilson B, Kumar P, Dutta A (2020) Noncanonical Roles of tRNAs: TRNA Fragments and beyond. Annu Rev Genet 54:47–69.
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Fibroblast Cultures by Defined Factors. Cell 126:663–676. [CrossRef]
- 41. Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, et al Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines Derived from Human Somatic Cells.
- Nakagawa M, Koyanagi M, Tanabe K, et al (2008) Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells without Myc from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nat Biotechnol 26:101–106. [CrossRef]
- Dudek J, Cheng IF, Balleininger M, et al (2013) Cardiolipin deficiency affects respiratory chain function and organization in an induced pluripotent stem cell model of Barth syndrome. Stem Cell Res 11:806–819. [CrossRef]
- Nasilli G, Verkerk AO, O’Reilly M, et al (2024) Chronic Mexiletine Administration Increases Sodium Current in Non-Diseased Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Biomedicines 12:. [CrossRef]
- Nasilli G, Yiangou L, Palandri C, et al (2023) Beneficial effects of chronic mexiletine treatment in a human model of SCN5A overlap syndrome. Europace 25:. [CrossRef]
- Novak A, Barad L, Zeevi-Levin N, et al (2012) Cardiomyocytes generated from CPVT D307H patients are arrhythmogenic in response to β-adrenergic stimulation. J Cell Mol Med 16:468–482. [CrossRef]
- Sasaki K, Makiyama T, Yoshida Y, et al (2016) Patient-specific human induced pluripotent stem cell model assessed with electrical pacing validates S107 as a potential therapeutic agent for catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. PLoS One 11:. [CrossRef]
- Lan F, Lee ASS, Liang P, et al (2013) Abnormal Calcium Handling Properties Underlie Familial Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Pathology in Patient-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 12:101–113. [CrossRef]
- Jiang Y, Habibollah S, Tilgner K, et al (2014) An Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Model of Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) Reveals Multiple Expression and Functional Differences in HLHS-Derived Cardiac Myocytes. Stem Cells Transl Med 3:416–423. [CrossRef]
- Ebert AD, Kodo K, Liang P, et al (2014) Characterization of the molecular mechanisms underlying increased ischemic damage in the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 genetic polymorphism using a human induced pluripotent stem cell model system. Sci Transl Med 6:255ra130-255ra130. [CrossRef]
- Lauriol J, Kontaridis MI (2011) PTPN11-Associated Mutations in the Heart: Has LEOPARD Changed Its RASpots? Trends Cardiovasc Med 21:97–104.
- Moretti A, Bellin M, Welling A, et al (2010) Patient-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem-Cell Models for Long-QT Syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 363:1397–1409. [CrossRef]
- Yazawa M, Hsueh B, Jia X, et al (2011) Using induced pluripotent stem cells to investigate cardiac phenotypes in Timothy syndrome. Nature 471:230–236. [CrossRef]
- Davis RP, Casini S, Van Den Berg CW, et al (2012) Cardiomyocytes derived from pluripotent stem cells recapitulate electrophysiological characteristics of an overlap syndrome of cardiac sodium channel disease. Circulation 125:3079–3091. [CrossRef]
- Lahti AL, Kujala VJ, Chapman H, et al (2012) Model for long QT syndrome type 2 using human iPS cells demonstrates arrhythmogenic characteristics in cell culture. Dis Model Mech 5:220–230. [CrossRef]
- Limpitikul WB, Dick IE, Tester DJ, et al (2017) A Precision Medicine Approach to the Rescue of Function on Malignant Calmodulinopathic Long-QT Syndrome. Circ Res 120:39–48. [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti M, Sala L, Dreizehnter L, et al (2017) Elucidating arrhythmogenic mechanisms of long-QT syndrome CALM1-F142L mutation in patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res 113:531–541. [CrossRef]
- Adams WJ, Zhang Y, Cloutier J, et al (2013) Functional vascular endothelium derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Reports 1:105–113. [CrossRef]
- Liu C, Shen M, Tan WLW, et al (2023) Statins improve endothelial function via suppression of epigenetic-driven EndMT. Nature Cardiovascular Research 2:467–485. [CrossRef]
- Matrone G, Thandavarayan RA, Walther BK, et al (2019) Dysfunction of iPSC-derived endothelial cells in human Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome. Cell Cycle 18:2495–2508. [CrossRef]
- Richardson SE, Ghazanfari R, Chhetri J, et al (2021) In vitro differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into the B lineage using OP9-MS5 co-culture. STAR Protoc 2:. [CrossRef]
- Fan F, Yu Y, Sun L, et al (2018) Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocyte Toxicity by Supernatant of Long Term-Stored Red Blood Cells in Vitro. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 46:1230–1240. [CrossRef]
- Haro-Mora JJ, Uchida N, Demirci S, et al (2020) Biallelic correction of sickle cell disease-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) confirmed at the protein level through serum-free iPS-sac/erythroid differentiation. Stem Cells Transl Med 9:590–602. [CrossRef]
- Ge X, Ren Y, Bartulos O, et al (2012) Modeling supravalvular aortic stenosis syndrome with human induced pluripotent stem cells. Circulation 126:1695–1704. [CrossRef]
- Granata A, Serrano F, Bernard WG, et al (2017) An iPSC-derived vascular model of Marfan syndrome identifies key mediators of smooth muscle cell death. Nat Genet 49:97–109. [CrossRef]
- Lyra-Leite DM, Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez Ó, Wang M, et al (2022) A review of protocols for human iPSC culture, cardiac differentiation, subtype-specification, maturation, and direct reprogramming. STAR Protoc 3.
- Burridge PW, Matsa E, Shukla P, et al (2014) Chemically defned generation of human cardiomyocytes. Nat Methods 11:855–860. [CrossRef]
- Moretti A, Laugwitz KL, Dorn T, et al (2013) Pluripotent stem cell models of human heart disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 3:. [CrossRef]
- Parameswaran S, Kumar S, Verma RS, Sharma RK (2013) Cardiomyocyte culture — an update on the in vitro cardiovascular model and future challenges. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 91:985–998. [CrossRef]
- Li D, Wu J, Bai Y, et al (2014) Isolation and Culture of Adult Mouse Cardiomyocytes for Cell Signaling and <em>in vitro</em> Cardiac Hypertrophy. Journal of Visualized Experiments 2–9. [CrossRef]
- 1995; 71. Wang Q, Shen J, Splawski I, et al (1995) SCN5A Mutations Associated with an Inherited Cardiac Arrhythmia, Long QT Syndrome.
- Funke BH (2016) Development of a Comprehensive Sequencing Assay for Inherited Cardiac Condition Genes. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 9:1–2.
- Moretti A, Bellin M, Welling A, et al (2010) Patient-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem-Cell Models for Long-QT Syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 363:1397–1409. [CrossRef]
- Skinner JR, Winbo A, Abrams D, et al (2019) Channelopathies That Lead to Sudden Cardiac Death: Clinical and Genetic Aspects. Heart Lung Circ 28:22–30.
- Zhang M, D’Aniello C, Verkerk AO, et al (2014) Recessive cardiac phenotypes in induced pluripotent stem cell models of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: Disease mechanisms and pharmacological rescue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:E5383–E5392. [CrossRef]
- Tabish AM, Azzimato V, Alexiadis A, et al (2017) Genetic epidemiology of titin-truncating variants in the etiology of dilated cardiomyopathy. Biophys Rev 9:207–223.
- Hinson JT, Chopra A, Nafissi N, et al (2015) Titin mutations in iPS cells define sarcomere insufficiency as a cause of dilated cardiomyopathy. Science (1979) 349:982–986. [CrossRef]
- Eisner DA, Caldwell JL, Kistamás K, Trafford AW (2017) Calcium and excitation-contraction coupling in the heart. Circ Res 121:181–195. [CrossRef]
- El-Battrawy I, Lan H, Cyganek L, et al (2018) Modeling Short QT syndrome using human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. J Am Heart Assoc 7:. [CrossRef]
- Kolanu ND (2024) CRISPR–Cas9 Gene Editing: Curing Genetic Diseases by Inherited Epigenetic Modifications. Glob Med Genet 11:113–122. [CrossRef]
- Asif M, Khan WJ, Aslam S, et al (2024) The Use of CRISPR-Cas9 Genetic Technology in Cardiovascular Disease: A Comprehensive Review of Current Progress and Future Prospective. Cureus. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Tov D, Mafessoni F, Cucuy A, et al (2024) Uncovering the dynamics of precise repair at CRISPR/Cas9-induced double-strand breaks. Nat Commun 15:. [CrossRef]
- Jacinto F V., Link W, Ferreira BI (2020) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing: From basic research to translational medicine. J Cell Mol Med 24:3766–3778.
- Garg P, Oikonomopoulos A, Chen H, et al (2018) Genome Editing of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells to Decipher Cardiac Channelopathy Variant. J Am Coll Cardiol 72:62–75. [CrossRef]
- King O, Kermani F, Wang B, et al (2019) Endothelial Cell Regulation of Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Myocardium. Biophys J 116:153a. [CrossRef]
- Wang BX, Nicastro L, Couch L, et al (2022) Extracellular Vesicles from Human Cardiac Fibroblasts Modulate Calcium Cycling in Human Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Cells 11:. [CrossRef]
- Pinto AR, Ilinykh A, Ivey MJ, et al (2016) Revisiting cardiac cellular composition. Circ Res 118:400–409. [CrossRef]
- Lewis-Israeli YR, Wasserman AH, Aguirre A (2021) Heart organoids and engineered heart tissues: Novel tools for modeling human cardiac biology and disease. Biomolecules 11.
- Brassard JA, Lutolf MP (2019) Engineering Stem Cell Self-organization to Build Better Organoids. Cell Stem Cell 24:860–876.
- Lancaster MA, Knoblich JA (2014) Organogenesisin a dish: Modeling development and disease using organoid technologies. Science (1979) 345.
- Yang KC, Breitbart A, De Lange WJ, et al (2018) Novel Adult-Onset Systolic Cardiomyopathy Due to MYH7 E848G Mutation in Patient-Derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. JACC Basic Transl Sci 3:728–740. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Fu W, Guo G, et al (2021) A heterozygous MYH7 (c. 2156G > A) mutant human induced pluripotent stem cell line (ZZUNEUi020-A) generated from a patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Stem Cell Res 51:. [CrossRef]
- Buono MF, Boehmer L von, Strang J, et al (2020) Human cardiac organoids for modeling genetic cardiomyopathy. Cells 9:1–19. [CrossRef]
- 2018; 94. Long C, Li H, Tiburcy M, et al (2018) Correction of diverse muscular dystrophy mutations in human engineered heart muscle by single-site genome editing.
- Marini V, Marino F, Aliberti F, et al (2022) Long-term culture of patient-derived cardiac organoids recapitulated Duchenne muscular dystrophy cardiomyopathy and disease progression. Front Cell Dev Biol 10:. [CrossRef]
- Duan D, Goemans N, Takeda S, et al (2021) Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7.
- Gao QQ, McNally EM (2015) The dystrophin complex: Structure, function, and implications for therapy. Compr Physiol 5:1223–1239. [CrossRef]
- Jabbour R, Owen T, Reinsch M, et al (2019) Development and preclinical testing of upscaled engineered heart tissue for use in translational studies. Eur Heart J 40:0345–0345.
- Stoppel WL, Kaplan DL, Black LD (2016) Electrical and mechanical stimulation of cardiac cells and tissue constructs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 96:135–155.
- Wang K, Schriver BJ, Aschar-Sobbi R, et al (2023) Human engineered cardiac tissue model of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy recapitulates key hallmarks of the disease and the effect of chronic mavacamten treatment. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 11:. [CrossRef]
- Braunwald E, Saberi S, Abraham TP, et al (2023) Mavacamten: a first-in-class myosin inhibitor for obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 44:4622–4633.
- Kane C, Terracciano CM (2018) Human cardiac fibroblasts engage the sarcoplasmic reticulum in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte excitation–contraction coupling. J Am Coll Cardiol 72:1061–1063. [CrossRef]
- Sheikh F, Ross RS, Chen J (2009) Cell-Cell Connection to Cardiac Disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med 19:182–190.
- Giacomelli E, Meraviglia V, Campostrini G, et al (2020) Human-iPSC-Derived Cardiac Stromal Cells Enhance Maturation in 3D Cardiac Microtissues and Reveal Non-cardiomyocyte Contributions to Heart Disease. Cell Stem Cell 26:862-879.e11. [CrossRef]
- Israeli-Rosenberg S, Manso AM, Okada H, Ross RS (2014) Integrins and integrin-associated proteins in the cardiac myocyte. Circ Res 114:572–586.
- Wang BX, Kane C, Nicastro L, et al (2022) Integrins Increase Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Activity for Excitation—Contraction Coupling in Human Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Int J Mol Sci 23:. [CrossRef]
- Jefferies JL (2013) Barth syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 163:198–205. [CrossRef]
- Ross Pennington E, Funai K, Brown DA, et al (2019) The role of cardiolipin concentration and acyl chain composition on mitochondrial inner membrane molecular organization and function HHS Public Access Author manuscript. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1039–1052. [CrossRef]
- Wang G, McCain ML, Yang L, et al (2014) Modeling the mitochondrial cardiomyopathy of Barth syndrome with induced pluripotent stem cell and heart-on-chip technologies. Nat Med 20:616–623. [CrossRef]
- Karakikes I, Ameen M, Termglinchan V, Wu JC (2015) Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes: Insights into Molecular, Cellular, and Functional Phenotypes. Circ Res 117:80–88. [CrossRef]
- Gherghiceanu M, Barad L, Novak A, et al (2011) Cardiomyocytes derived from human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells: Comparative ultrastructure. J Cell Mol Med 15:2539–2551. [CrossRef]
- Du DTM, Hellen N, Kane C, Terracciano CMN (2015) Action potential morphology of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes does not predict cardiac chamber specificity and is dependent on cell density. Biophys J 108:1–4. [CrossRef]
- Bernardo BC, Weeks KL, Pretorius L, McMullen JR (2010) Molecular distinction between physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy: experimental findings and therapeutic strategies. Pharmacol Ther 128:191–227. [CrossRef]
- Wang B, Kit-Anan W, Terracciano C (2018) Many Cells Make Life Work—Multicellularity in Stem Cell-Based Cardiac Disease Modelling. Int J Mol Sci 19:3361. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Wilson GF, Soerens AG, et al (2009) Functional cardiomyocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Circ Res 104:e30-41. [CrossRef]
- Zwi L, Caspi O, Arbel G, et al (2009) Cardiomyocyte differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Circulation 120:1513–1523. [CrossRef]
- Hanft LM, McDonald KS (2010) Length dependence of force generation exhibit similarities between rat cardiac myocytes and skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol 588:2891–2903. [CrossRef]
- Wheelwright M, Win Z, Mikkila JL, et al (2018) Investigation of human iPSC-derived cardiac myocyte functional maturation by single cell traction force microscopy. PLoS One 13:e0194909. [CrossRef]
- Kamakura T, Makiyama T, Sasaki K, et al (2013) Ultrastructural maturation of human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in a long-term culture. Circ J 77:1307–1314.
- Schick R, Mekies L, Shemer Y, et al (2017) P3496Functional abnormalities in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes generated from titin-mutated dilated cardiomyopathy patients. Eur Heart J 38:1–25. [CrossRef]
- Dorn GW, Vega RB, Kelly DP (2015) Mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics in the developing and diseased heart. Genes Dev 29:1981–1991. [CrossRef]
- Dai D-F, Danoviz ME, Wiczer B, et al (2017) Mitochondrial Maturation in Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Cardiomyocytes. Stem Cells Int 2017:5153625. [CrossRef]
- Schaper J, Meiser E, Stammler G (1985) Ultrastructural morphometric analysis of myocardium from dogs, rats, hamsters, mice, and from human hearts. Circ Res 56:377–391.
- Lopaschuk GD, Spafford MA, Marsh DR (1991) Glycolysis is predominant source of myocardial ATP production immediately after birth. Am J Physiol 261:H1698-705. [CrossRef]
- Lundy SD, Zhu W-Z, Regnier M, Laflamme MA (2013) Structural and Functional Maturation of Cardiomyocytes Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells Dev 22:1991–2002. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).