1. Introduction
Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium leprae [
1], which has genetic determinants [
2], immunological [
3] and socioeconomic [
4,
5] factors linked to the risk of becoming ill. Its diagnosis remains essentially clinical [
6], so strengthening leprosy surveillance and control actions is of great importance in the early detection of new cases, which contributes to reducing physical disabilities and the stigma related to the disease [
7].
Historically neglected and still endemic in many countries, leprosy had already shown a drop in detection in recent years, which was intensified between 2019 and 2021, reaching a reduction of almost a third of global records [
8]. With the COVID-19 pandemic, health services had to reorganize (Pereira Barra et al., 2020), isolation measures, as well as the suspension of active search by services, had a strong impact on the early detection of leprosy cases [
9].
In Brazil, the COVID-19 pandemic has advanced exponentially, rapidly reaching large capitals, as well as smaller cities and more vulnerable communities [
10]. Some diseases, including leprosy, have had their care adapted with the provision of treatment extended by two or three months, consultations and remote care, in order to guarantee the home isolation of these people [
11]. In addition, reference hospitals for leprosy changed their care flows during the critical period of the pandemic, allocating 100% of their beds to care for patients affected or suspected of COVID-19, as is the case of the Eduardo de Menezes Hospital of the Minas Gerais State Hospital Foundation (FHEMIG) network [
12].
As a result of the impacts of the pandemic, in Brazil there was a reduction in the diagnosis of leprosy, as well as an increase in cases in the multibacillary clinical form, which is mainly responsible for maintaining the chain of transmission, demonstrating that control strategies were strongly impacted in the country [
13]. There was also a reduction in the assessment of the degree of physical disability among diagnosed cases [
14], which indicates significant operational weaknesses in the surveillance of physical disabilities.
Mahato, Bhattarai and Singh (2020), emphasize that the COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated the need for interventions that address social structures and are capable of effectively improving the living conditions of people affected by leprosy, by guaranteeing access to healthy and varied food, housing, sanitary and hygiene conditions, and the provision and continuity of health care services [
15].
Despite the reduction in the detection rate caused by the impact of the pandemic, Brazil is still among the three countries that diagnose the most leprosy cases in the world. In 2022, 19,635 new cases of the disease were diagnosed, of which 836 were in children under 15 and 1,917 had grade 2 physical disabilities at the time of diagnosis [
8].
In order to overcome this scenario, and in line with the WHO Global Strategy for Leprosy 2021-2030 called “Towards zero leprosy” [
16], the National Strategy for Tackling Leprosy 2024-2030 was drawn up in Brazil, with the vision of “a Brazil without leprosy” [
17]. In Minas Gerais, the Minas Gerais State Department of Health (SES-MG) proposed the “2019-2022 State Plan for Tackling Leprosy” before the pandemic, which established strategies for tackling leprosy according to the needs of each point in the care network in order to outline a horizontal and hierarchical network [
18].
Despite social determination, the “risk of becoming ill” from leprosy is strongly impacted by the operational capacity of health services to carry out programmatic health actions. This concept involves epidemiological factors that reflect the magnitude and strength of the morbidity of the endemic disease, as well as factors related to the operational capacity of health services to carry out disease control actions [
19]. In addition to the risk of becoming ill, the hidden prevalence also reflects the limitations of the health services in carrying out leprosy control actions and timely diagnosis, since the estimate is obtained from data on cases diagnosed with physical disabilities, which represents late diagnosis and in turn suggests the presence of other undetected cases [
20].
The quality of leprosy control actions has an effect on disease monitoring indicators [
7]. Based on the weaknesses exposed above, the question arises: what is the impact of the pandemic on the epidemiological scenario of leprosy in Minas Gerais?
The aim of this study was to analyze the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the epidemiological scenario of leprosy through the detection rate of new cases, risk of illness and hidden prevalence according to high-risk micro-region in Minas Gerais, Brazil.
2. Materials and Methods
This is an ecological study conducted in the health micro-regions of Minas Gerais, Brazil. The focus of the study is the state of Minas Gerais and its micro-regions classified as being at “High Risk” of becoming ill with leprosy, according to the analysis of data on notifications of new cases of the disease diagnosed between 2015 and 2023. The micro-regions were classified into different levels of risk, with “High Risk” defined as those located in the upper quartile of the index distribution.
The state of Minas Gerais is divided into 89 health micro-regions. In this study, we used the distribution of micro-regions according to the 2019 Regionalization Master Plan (PDR) [
21], since this configuration was in force from 2015 to 2023. Although the RDP was updated in 2023, this update was not considered, as it goes beyond the study period, ensuring the consistency of the data analyzed.
The study population consisted of new leprosy cases notified on the Notifiable Diseases Information System (SINAN) in Minas Gerais between 2015 and 2023. Records of international, inter-municipal and inter-state transfers, readmissions and diagnostic errors were excluded.
Secondary data on the notification of new leprosy cases was taken from the SUS Information Technology Department (DATASUS) – TABWIN, Brazil. Demographic data relating to the general population, necessary for obtaining epidemiological indicators for leprosy in the micro-regions, were extracted from the IBGE database, via the DATASUS website, from the 2010 demographic census and intercensal projections. These extracted secondary data were entered into a database created using Microsoft Excel software (version 2010) to construct the study variables.
To assess the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the epidemiological scenario of leprosy, the following indicators were evaluated: annual detection rate of new cases, per 100. 000 inhabitants, which makes it possible to measure the strength of morbidity, magnitude and trend of the endemic [
22]; the Leprosy Risk Index [
19] which integrates three epidemiological indicators, making it possible, in addition to the evaluation based on the detection rate of new cases, to also evaluate the strength of recent transmission of the trend and the timely detection of new leprosy cases [
22]; and Hidden Prevalence [
23] which represents the reservoir of undetected cases [
20].
In order to assess temporal trends in the period, the Annual Percentage Change (APC) of the annual detection rate of new leprosy cases between 2015 and 2023 was calculated. The Annual Percent Change (APC) estimated from the coefficients is a summary of trends in rates over short time intervals, estimated from segmented linear regression (joinpoint regression), using the Joinpoint Regression statistical program, version 5.0.2 (Statistical Research and Applications Branch, National Cancer Institute, Rockville, MD, USA). This regression model makes it possible to estimate the average annual variation for the study period and the points (years) at which the trend changes. The program uses minimum and maximum junction points (it starts with the zero point) and tests with other junction points (until it reaches the maximum number), checking whether the changes are statistically significant. The significance test uses the Monte Carlo permutation method. This permutation tests a set of data to select junction points. This makes it possible to verify the existence of inflection points in the trend of this rate, considering the period 2015-2019 (pre-pandemic) and 2020-2023 (pandemic phase).
The estimate of Hidden Prevalence, according to the methodology proposed by Suárez and Lombardi (1997), is based on the assumption that the detection of cases with physical disabilities indicates late detection and therefore cases that should have been detected. The following epidemiological criteria were used to calculate the hidden prevalence: (a) Total new cases; (b) Total new cases assessed; (c) Total new cases with physical disabilities; (d) Percentage (%) of new cases with physical disabilities (c/b); (e) Estimate of undetected cases (d/a). The 5 years prior to the study period were taken as a reference, considering the average incubation period for leprosy.
Thus, based on the estimate of undetected cases, the Hidden Prevalence values are calculated from the sum of the 5 years prior to the estimate of undetected cases. This calculates the Expected and Actual Prevalence:
Expected prevalence = sum of the hidden prevalence and the average number of cases in the last 5 years of the study.
Actual prevalence = sum of hidden prevalence + expected prevalence.
The Disease Risk Index is a composite indicator that integrates three of the main leprosy monitoring indicators: (i) annual detection rate of new leprosy cases, (ii) annual detection rate of new leprosy cases in the population aged 0-14 and (iii) rate of new leprosy cases with grade 2 physical disability at the time of diagnosis. We chose to use this composite indicator because of the possibility of simplifying and synthesizing the indicators when there is a need for an overall assessment. The indicator was previously constructed and validated in one of the studies carried out by the Leprosy Studies and Research Center - NEPHANS [
24].
The risk of illness index was calculated for Minas Gerais and by health micro-region from the average of the epidemiological indicators for the period 2015 to 2019 and 2020 to 2023, applying the equation of transformation into scores for each indicator, using the ratio:
= [(observed value / maximum value)] = indicator score
The indicator scores were then added up and divided by three, and then transformed into an index, according to the following formula:
Index = Sum of leprosy indicator scores / number of indicators
The index values vary between 0 and 1, with “best” being the lowest (0) and “worst” being the highest (1). The values were classified as very low risk, low risk, medium risk and high risk by calculating the interquartile ranges of the indicators.
To analyze the hidden prevalence and the risk of falling ill, the study period was divided into two segments (1) 2015-2019, representing the pre-pandemic phase and (2) 2020-2023, representing the pandemic phase. From this perspective, the study variables were used considering segments 1 and 2, based on the average annual detection for each period.
3. Results
With the data evaluated in this study, it was possible to observe: a) a reduction in the detection of new cases in most of the micro-regions evaluated, considering the average of the pre-pandemic period in relation to the pandemic period; b) an inflection point in the detection of new cases in the state rate and in some micro-regions with a positive increase in the year 2021, making it possible to suggest a resumption of diagnoses; c) a reduction in the hidden prevalence observed in certain micro-regions, which is possibly linked to a reduction in diagnoses, especially in people with an installed physical disability; d) an increase in the risk of falling ill with leprosy in the state of Minas Gerais; e) a reduction in the risk of falling ill with leprosy in some micro-regions.
The average overall detection rate for the years 2015 to 2019 was compared with the average for the years 2020 to 2023. There was a reduction in the average detection of new cases in the state rate. This same variation was observed among the micro-regions, with the exception of São Gotardo. This data is shown in
Table 1.
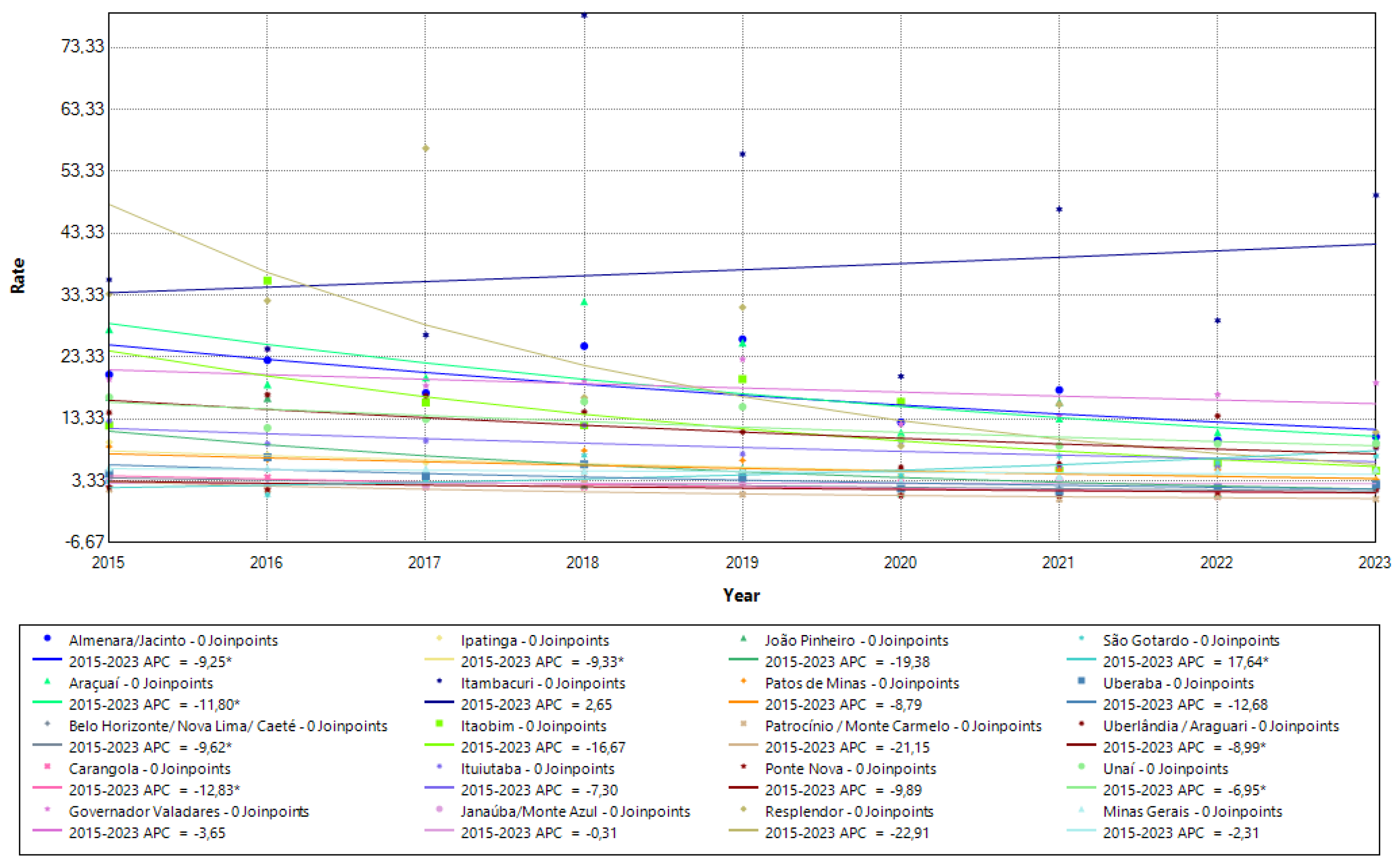
Analyzing the annual increase (APC) in the overall detection rate over the entire period (2015 to 2023), seven of these micro-regions showed a significant downward trend (p<0.05): Almenara/Jacinto (APC = -9.25; 95%CI -16.61 - -1.10), Araçuaí (APC = -11.79; 95%CI -17.85 - -5.22), Belo Horizonte/ Nova Lima/ Caeté (APC = -9.61; 95%CI -14.65 - -4.16), Carangola (APC = -12.83; 95%CI -23.67 - -0.26), Ipatinga (APC = -9.32; 95%CI -14.74 - -3.43), Uberlândia / Araguari (APC = -8.98; 95%CI -17.02 - -0.00) and Unaí (APC = -6.95; 95%CI -12.03 - -1.42).
On the other hand, the São Gotardo micro-region showed a significant growth trend throughout the period, with an annual increase of 17.64 (95%CI 2.75 - 34.90). These results reinforce the variation in local transmission dynamics, with most regions showing a significant reduction, while São Gotardo went in the opposite direction. The trend in the overall detection rate in the nineteen micro-regions, as well as the state rate, is shown in
Figure 1.
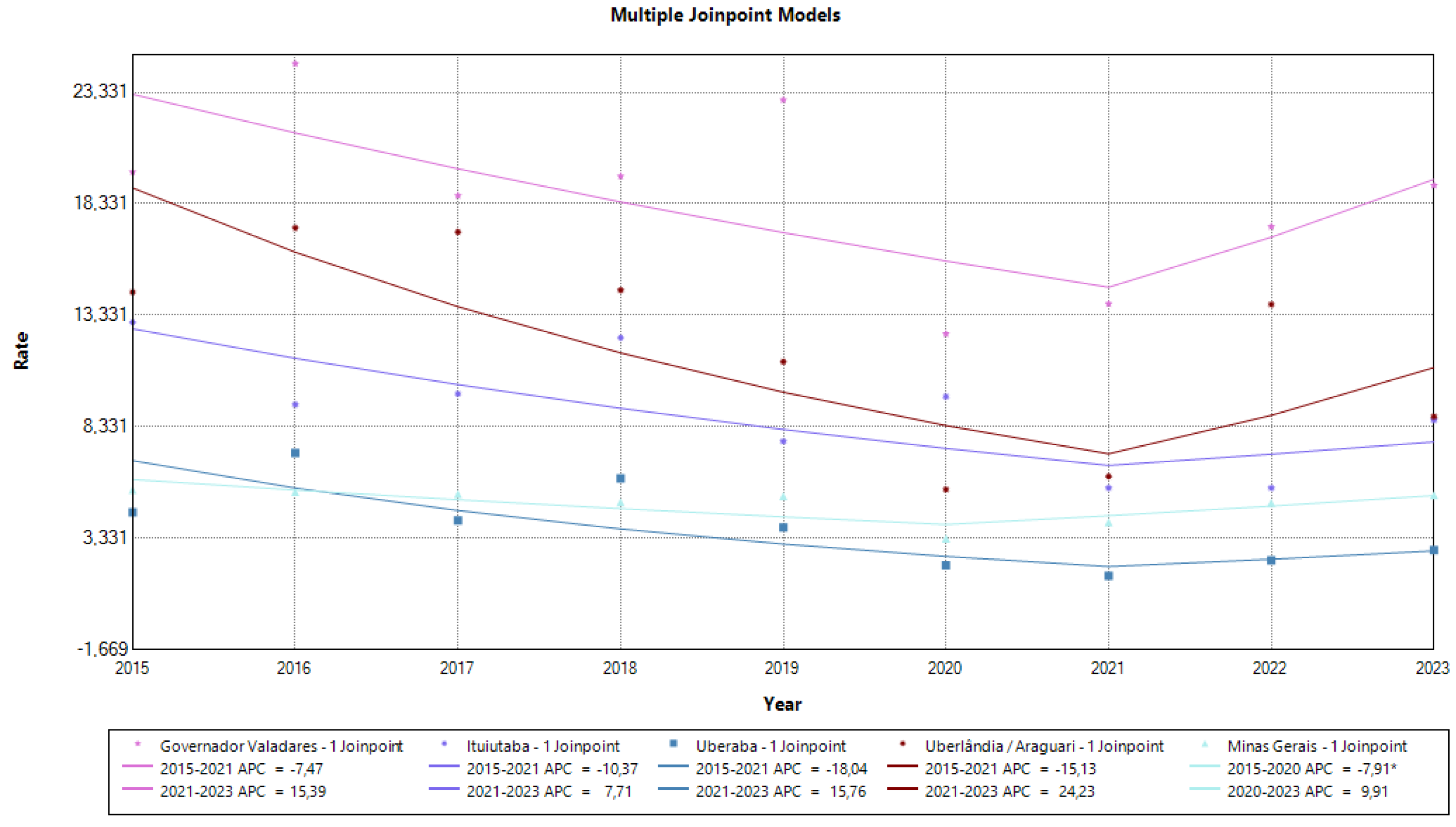
When evaluating the inflection points observed over the period, we identified a trend towards recovery. The state of Minas Gerais had been showing a significant negative annual increase between 2015 and 2020 (APC = -7.91; 95%CI -21.76 - -1.72), and in 2020 it showed an inflection point, with an annual increase of 9.91 in the period from 2020 to 2023.
The micro-regions of Governador Valadares, Ituiutaba, Uberaba and Uberlândia/Araguari, which had been showing a negative increase between 2015 and 2021, showed a positive annual increase in their detection rate between 2021 and 2023. These changes were not statistically significant, but they suggest a trend towards a resumption in the diagnosis of new leprosy cases in these regions. This result is illustrated in
Figure 2.
When evaluating the hidden prevalence in the micro-regions of Minas Gerais during the period from 2015 to 2023, we observed a reduction in the estimates both statewide and for several micro-regions, including Belo Horizonte/Nova Lima/Caeté, Governador Valadares, Ipatinga, Itambacuri, Itaobim, João Pinheiro, Patrocínio/Monte Carmelo, São Gotardo, Uberlândia/Araguari and Unaí, when comparing the 2015-2019 and 2020-2023 periods. In the other micro-regions, the hidden prevalence increased compared to the pre-pandemic period. As this is a composite indicator, this reduction is directly linked to the decrease in the number of new cases diagnosed, particularly those with physical disability (
Table 2).
Analysis of the risk of falling ill with leprosy between the 2015-2019 and 2020-2023 periods revealed significant changes in the classification of this indicator in nine health micro-regions in Minas Gerais. The micro-regions of Carangola, Itaobim, Ituiutaba, Patos de Minas and Resplendor, which previously had a high risk of falling ill, became medium risk during the pandemic period.
Ponte Nova and Uberaba went from high to low risk of illness, with Uberaba registering a decrease from 0.51 to 0.35. The micro-regions of João Pinheiro and Patrocínio/Monte Carmelo stood out for their even sharper reduction, going from high to very low risk of illness, with indices of 0.46 and 0.54, falling to 0.11 and 0.17, respectively. The changes in the index reflect a significant change in the pattern of illness.
While these areas showed a drop in the risk of illness, the other micro-regions evaluated maintained their high risk classification, with no significant changes between the two periods analyzed. The state as a whole showed an upward trend in the risk of illness, with the average index varying from 0.28 (medium risk) to 0.55 (high risk), showing a worrying scenario in some regions (
Table 3).
4. Discussion
The results of this study clearly demonstrate the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the epidemiological scenario of leprosy in Minas Gerais, especially in micro-regions classified as being at high risk of becoming ill. The drop in the detection rate of new cases intensified during the pandemic period, observed in several micro-regions, in line with the rates in Brazil, which in addition to the reduction in overall detection, also showed a reduction in detection among children under 15, compared to the period before the pandemic, contrasting with an increase in cases of multibacillary leprosy (MB) after the spread of Covid-19 in the country [
13]. This was a global trend that has been identified in other endemic countries, such as India, where the pandemic resulted in a 63% reduction in new cases diagnosed in the second and third quarters of 2020 [
9].
The barriers created by public health policies during the pandemic limited access to the health services needed to manage leprosy, impacting both clinical and community interventions [
15]. Thus, this decrease in the detection rate is intrinsically linked to barriers to accessing health services [
13] and the interruption of surveillance activities [
25].
Hidden prevalence, an indicator used to estimate the presence of undiagnosed cases, showed a drop in several micro-regions. This result indicates that there are fewer existing cases going undiagnosed in these locations. However, this reduction may not represent an advance in leprosy control, but rather the consequence of underreporting, especially with regard to disabled cases, during the pandemic period [
26,
27]. The proportion of cases reported without having the degree of physical disability assessed increased significantly during the pandemic [
14]. The lack of assessment of physical disability among new cases and the consequent lack of registration of those possibly disabled interferes with the result of the hidden prevalence, meaning that this indicator may not reflect the real situation of missed diagnoses.
In other micro-regions, there was an increase in hidden prevalence in the period following the most critical phase of the pandemic. This may be related to the greater detection of cases with a degree of disability already in place [
28], emphasizing the vulnerability of these regions in leprosy control and pointing to the need for more incisive active search actions in order to reduce hidden prevalence and prevent the perpetuation of uncontrolled transmission chains [
26].
With regard to the risk of falling ill, the data also shows a heterogeneous impact of the pandemic in the different micro-regions of Minas Gerais. Some remained at high risk of falling ill, while in others the risk fell to medium, low and even very low. These results should be interpreted with caution, considering the pandemic context in which delays in diagnosing new cases and underreporting have already been identified in the country [
29]. The decrease in the number of diagnoses, resulting from underreporting, may mask the real severity of leprosy in these regions, and the perception of improvement may be illusory.
The reduction in notifications may not reflect a real drop in transmission, but rather a problem in the surveillance system, which has been severely impacted by the restrictions imposed by the pandemic [
30]. Therefore, even in regions where there has been a reduction in the risk of illness, it is important to monitor this indicator, as well as others that portray the epidemiological scenario of leprosy as surveillance and diagnosis activities are resumed at full capacity.
The risk indicator is calculated from three epidemiological indicators of leprosy [
24]. In this way, regions that have remained at high risk of falling ill should be monitored as areas of greater concern, especially those where there has been a drop in detection, as it indicates that the risk of falling ill is being impacted by the other two indicators, which represent detection in children under 15 and with grade 2 physical disability installed.
In these areas, the resumption of health services must be accompanied by an intensification of surveillance strategies, as well as training for professionals so that control actions are carried out in a targeted manner, thus contributing to early diagnosis [
31], thus avoiding the worsening of leprosy and its late complications.
There was no significant upturn in the detection of new leprosy cases in any of the micro-regions evaluated, nor in the state rate. However, Minas Gerais as a whole, and the micro-regions Governador Valadares, Ituiutaba, Uberaba and Uberlândia/Araguari showed a positive increase in this rate from 2021 onwards. This result suggests a resumption of leprosy surveillance actions.
When evaluating the initial resumption of detection in conjunction with the other indicators discussed in this study, it can be seen that in Governador Valadares and Uberlândia, the risk of becoming ill remained high and there was a reduction in the hidden prevalence. These data can be seen as positive, since the risk is possibly being impacted by the increase in detection, which can be both general and in children under 15, which indicates active transmission of the disease. However, the reduction in hidden prevalence indicates that cases are being diagnosed without physical disabilities.
On the other hand, in Ituiutaba and Uberaba there was a resumption of detection with a reduction in the risk of becoming ill, but the hidden prevalence increased. This result suggests that services need to pay more attention to resuming leprosy surveillance actions, since the estimate of hidden prevalence is strongly affected by the identification of disabled cases. In this way, it indicates the existence of trapped cases, as well as the need to strengthen health services and train professionals in the early identification of new cases of the disease [
29,
31].
The findings of this study show the complex interaction between the change in the detection rate and the indicators of risk of illness and hidden prevalence. The numerous difficulties imposed by the pandemic period, such as difficulty in accessing health services [
32], culminating in underdiagnosis and late diagnosis [
29] have an even greater impact on the variations in these indicators.
The limitations of this study include the use of secondary SINAN data, which may contain inconsistencies, as well as the complex interpretation of hidden prevalence during periods of interruption. Finally, the temporal interference of the pandemic in previous leprosy trends makes it difficult to separate the pandemic effects from the natural variations in the disease. It should be noted that the analysis of the time trend, carried out by calculating the Annual Percentage Change (APC), could be more robust over a longer period of time.
5. Conclusions
The pandemic has had a considerable impact on the detection of new cases in Minas Gerais and in the micro-regions evaluated. The heterogeneous results of both the risk of illness and the hidden prevalence indicate that, even with the resumption of health services, there is still a long way to go to achieve the elimination of leprosy as a public health problem. It is imperative to implement public health policies that prioritize the early identification of cases, as well as ensuring that vulnerable populations are monitored.
According to the World Health Organization's (WHO) 2030 agenda, the goal of global leprosy elimination implies reducing the incidence to less than 1 case per 10,000 inhabitants. In addition, its long-term vision is to eliminate physical disabilities, infection, the disease and the stigma associated with it. Considering the impact of the pandemic and the recovery observed, it is estimated that, without more effective additional interventions, the state of Minas Gerais could face significant challenges in reaching this target within the established timeframe.
The results of this study highlight the need for strategic post-pandemic interventions to mitigate the effects of interrupted services and ensure continuity of care. reinforcing the need for more robust surveillance and active search strategies, especially in historically underdiagnosed areas, to mitigate the negative impact caused by the health crisis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.L., S.V., D.L. and I.M; Methodology, S.V., D.L., I.M., I.L., A.C. and F.L.; Software, S.V. and I.L.; Validation, F.L, A.C. and I.L.; Formal Analysis, S.V., D.L., I.M., I.L., A.C. and F.L.; Investigation, F.L., S.V. and D.L.; Data Curation, F.L., S.V., D.L. and I.L; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, S.V., D.L., I.M., I.L., A.C. and F.L.; Writing—Review & Editing, S.V., D.L., I.M., I.L., A.C. and F.L.; Supervision, F.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Postgraduate Program in Nursing at UFMG through the granting of scholarships to support the training of high-level human resources sponsored by the Coordination Foundation for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), a Brazilian government agency.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study meets the criteria of Resolution 466/12 of the National Research Ethics Council, which deals with studies with human beings, and was approved by the UFMG Ethics Committee, under opinion no. 4.322.580.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Hastings RC, Gillis TP, Krahenbuhl JL, Franzblau SG. Leprosy. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988; 1:330–48.
- Alter A, Grant A, Abel L, Alcaïs A, Schurr E. Leprosy as a genetic disease. Mammalian Genome [Internet]. 2011 [citado 3 de setembro de 2024]; 22:19–31.
- Nath I, Saini C, Valluri VL. Immunology of leprosy and diagnostic challenges. Clin Dermatol. 2015; 33:90–8.
- Leano HA de M, Araújo KM da FA, Bueno I de C, Niitsuma ENA, Lana FCF. Fatores socioeconômicos relacionados à hanseníase: revisão integrativa da literatura. Rev Bras Enferm [Internet]. 2019; 72:1405–15.
- Nery JS, Ramond A, Pescarini JM, Alves A, Strina A, Ichihara MY, et al. Socioeconomic determinants of leprosy new case detection in the 100 Million Brazilian Cohort: a population-based linkage study. Lancet Glob Health [Internet]. 2019; 7:e1226–36.
- Brasil. Protocolo Clínico e Diretrizes Terapêuticas da Hanseníase. Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de ciência tecnologia, inovação e insumos estratégicos em saúde., organizadores. Brasília: Ministério da Saúde; 2022.
- Vieira NF, Martínez-Riera JR, Lana FCF. Primary care quality and its effects on leprosy monitoring indicators. Rev Bras Enferm [Internet]. 2020; 73:e20190038.
- World Health Organization. Weekly epidemiological record. 2023; 98:409–30.
- De Arquer GR, Kumar A, Singh RK, Satle N, Mamidi R, Biswas P. COVID-19 and leprosy new case detection in India. Lepr Rev. 2021; 92:88–91.
- Dantas RCC, De Campos PA, Rossi I, Ribas RM. Implications of social distancing in Brazil in the COVID-19 pandemic. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol [Internet]. 2022; 43:953.
- Brasil. Conselho Nacional de Saúde - RECOMENDAÇÃO No 030, DE 27 DE ABRIL DE 2020. Recomenda medidas que visam a garantia dos direitos e da proteção social das pessoas com doenças crônicas e patologias [Internet]. http://conselho.saude.gov.br/recomendacoes-cns/1143-recomendacao-n-030-de-27-de-abril-de-2020. 2020.
- Minas Gerais. Eduardo de Menezes é o primeiro hospital mineiro integralmente destinado ao atendimento de pacientes Covid-19 | Secretaria de Estado de Saúde de Minas Gerais [Internet]. https://www.saude.mg.gov.br/component/gmg/story/12436-eduardo-de-menezes-e-o-primeiro-hospital-mineiro-integralmente-destinado-ao-atendimento-de-pacientes-covid-19. 2020.
- Paz WS, Souza MR, Tavares DS, de Jesus AR, Santos AD, Carmo RF, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the diagnosis of leprosy in Brazil: An ecological and population-based study. The Lancet Regional Health – Americas, 2022.
- Matos TS, do Nascimento VA, do Carmo RF, Moreno de Oliveira Fernandes TR, de Souza CDF, da Silva TFA. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the diagnosis of new leprosy cases in Northeastern Brazil, 2020. Int J Dermatol. 2021; 60:1003–6.
- Mahato S, Bhattarai S, Singh R. Inequities towards leprosy-affected people: A challenge during COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2020.
- Organização Mundial da Saúde. Estratégia Global de Hanseníase 2021–2030 – “Towards Zero Leprosy” [Internet]. 2021 [cited sep 3, 2024]. Available from: https://www.who.int/pt/publications/i/item/9789290228509.
- Brasil. Estratégia Nacional para Enfrentamento à Hanseníase 2024-2030. Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde e Ambiente, Departamento de Doenças Transmissíveis. Brasília: Ministério da Saúde; 2024.
- Minas Gerais. Plano de Enfrentamento da Hanseníase em Minas Gerais, 2019-2022. Secretaria de Estado de Saúde de Minas Gerais. Coordenadoria Estadual de Controle da Hanseníase. Belo Horizonte; 2019.
- Bueno I de C, Lages D dos S, Lana FCF. Spatial analysis of the epidemiological risk of leprosy in the municipalities of Minas Gerais. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023; 17:e0011381.
- Ignotti E, Rodrigues AM, Andrade VLG de, Valente JG. Aplicação de métodos de estimativa da prevalência de hanseníase no Estado de Mato Grosso. Revista Brasileira de Epidemiologia. 2004; 7:155–66.
- Minas Gerais. Deliberação CIB-SUS/MG No 3.013, de 23 de Outubro de 2019. 2019.
- Brasil. Diretrizes para vigilância, atenção e eliminação da Hanseníase como problema de saúde pública: manual técnico-operacional. Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde, Departamento de Vigilância das Doenças Transmissíveis, organizadores. Brasília: Ministério da Saúde; 2016.
- Lombardi C, Suárez R. Epidemiologia da Hanseníase. Em: Talhari S, Neves RG, organizadores. Hanseníase. 3o. Manaus: Gráfica Tropical; 1997. p. 127–36.
- Araújo KM da FA, Gomes LCF, Lana FCF. Análise espacial do risco de adoecimento da hanseníase em um estado do nordeste Brasileiro. Revista Baiana de Enfermagem, 34: e37902, 2020.
- Thangaraju P, Arulmani M, Venkatesan S, Gurunthalingam M, Thangaraju E. COVID-19 and leprosy-hurdles and possible solutions. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2020; 13:472.
- da Cunha VP, Botelho GM, de Oliveira AHM, Monteiro LD, de Barros Franco DG, da Costa Silva R. Application of the ARIMA Model to Predict Under-Reporting of New Cases of Hansen’s Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic in a Municipality of the Amazon Region. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 19:415.
- Dominic S, Sasidharanpillai S, Gangan R, Minu U, Sneha KS, Hameed J, et al. Impact of Lockdown Restrictions on Treatment of Leprosy. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2022; 13:370–4.
- Souza CDF de, Santos FGB. Prevalência da hanseníase, taxa de grau II de incapacidade física e proporção de casos multibacilares: Um paradoxo que evidencia diagnóstico tardio e prevalência oculta? Revista de Epidemiologia e Controle de Infecção. 2019; 9.
- Ziembowicz H, Souza I, Peruzzo JV, Subtil L de C, Onófrio LG, Vaucher MB. As consequências da pandemia de Sars-CoV-2 sobre a educação médica no combate à hanseníase. Revista de Epidemiologia e Controle de Infecção. 2022.
- Pschichholz, L. Impacto da pandemia de sars-cov-2 na incidência de hanseníase no brasil: comparação com os últimos 5 anos. The Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2022; 26:102307.
- Vieira NF, Lanza FM, Martínez-Riera JR, Nolasco A, Lana FCF. Orientación de la atención primaria en las acciones contra la lepra: factores relacionados con los profesionales. Gac Sanit. 2020; 34:120–6.
- de Barros B, Lambert SM, Negera E, de Arquer GR, Sales AM, Darlong J, et al. An assessment of the reported impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on leprosy services using an online survey of practitioners in leprosy referral centres. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2021; 115:1456–61.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).