Introduction
Oral lichen planus (OLP) is a chronic mucocutaneous inflammatory disease with lesions of varying severity and appearance. Its prevalence is about 0.5–2%. The highest incidence of the disease is in the middle-aged population, with a female predominance with a ratio of approximately 2:1(1).
OLP is clinically manifested by erythema and white lines, known as Wickham's striae, and can present in several forms such as papular, reticular, atrophic, plaque-like, erosive, and bullous. Symptoms of the erosive or atrophic types of OLP can vary from a mild burning sensation to severe pain, profoundly affecting patients' quality of life (2).
The exact cause of OLP remains unclear, however it is believed to be initiated by factors such as an genetic, autoimmune response to local antigens, cell-mediated hypersensitivity, microorganisms, drugs, infections and stress. The progression of OLP typically alternates between active phases and periods of remission (3).
Pathogenesis of OLP is a T-cell mediated autoimmune disease in which the auto-cytotoxic CD8 + T cells trigger apoptosis of the basal cells of the oral epithelium. An early event in the disease mechanism involves keratinocyte antigen expression. Followed by T cells (mostly CD8+, and some CD4 + cells) migration into the epithelium toward basal keratinocyte, these migrated CD8 + cells are activated directly by an antigen binding to major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-1 on keratinocyte or through activated CD4 + lymphocytes. In addition, the number of Langerhans cells in OLP lesions is increased along with upregulation of MHC-II expression subsequent antigen presentation to CD4 + cells and interleukin-6 activates CD4 + T helper cells which activate CD8 + T cells through receptor interaction, interferon γ (INF-γ) and IL-2. The activated CD8 +T cells in turn kill the basal keratinocytes through tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, Fas-FasL-mediated or granzyme B-activated apoptos (4)
Managing oral lichen planus medically remains challenging. The main goal of OLP treatment is to reduce painful symptoms and oral lesions, as well as to prevent lesions from turning into malignancy. The most effective treatments for this condition typically involve systemic and topical corticosteroids. Relapses may occur when steroids are discontinued. Therefore, the patients have to use medications for a long time. However, the use of corticosteroids may lead to considerable side effects, such as fungal infections and adrenal suppression. Moreover, the use of steroids is typically discouraged for breastfeeding patients or those with diabetes, and it should be approached with caution in individuals with viral hepatitis (5).
Herbal medicine is considered as an alternative monotherapy or as a complement to first-line drugs in the treatment of Oral Lichen Planus (OLP). Curcumin, a non-toxic natural compound, it possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticarcinogenic, antimutagenic, and antiproliferative properties, providing protection to both the nervous and immune systems. It is safe at very high doses (6).
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
Study design: A randomized controlled clinical trial, following the consort's guidelines (Moher et al., 2012) (7) was conducted on 30 patients diagnosed as oral lichen planus with or without cutaneous lesions. All patients were selected from the outpatients clinic of Oral Medicine Department Al-Azhar University, Assiut and Department of Dermatology, Faculty of Medicine Assiut University.
Ethical considerations:
Ethical committee of Faculty of Dental Medicine Al-Azhar University [AUAREC20240004-15] approval was obtained before the trial started and all patients gave written informed consent.
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT06605911.
Inclusion criteria
- Patients with clinical diagnosis of OLP (presence of painful bilateral oral lesions, mostly symmetrical lesions, and presence of a lace-like network of slightly raised white lines).
Exclusion criteria:
- Patients who underwent treatment for OLP within four weeks prior to the study.
- History of malignancy.
- Patients suffering from another autoimmune disease.
- Patients currently using anticoagulant or antiplatelet agents (due to curcumin's inhibitory effects on platelet aggregation).
- Patients who have been on topical, local, or systemic corticosteroid therapy in the past three months.
- Patients with a known allergy or contraindication to the medications used in the study.
- Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Patients who did not complete the trial.
The patients were classified randomly into three treatment groups, 10 patients each as follows:
Group A: ten patients with oral lichen planus were received topical triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% four times per day for six weeks.fig.(1)
Group B: ten patients with oral lichen planus were received topical cucumin 1% six times per day for six weeks. fig.(2)
Group C: ten patients with oral lichen planus were received topical triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% combiend with topical curcumin1% three times per day for each for six weeks.fig.(3).
Materials:
Therapeutic agents:
Topical corticosteroids: triamcinolone acetonide (TA) 0.1% oral gel “Kenacort-A-Orabase."
Preparation of Curcumin Gel 1%: curcumin was prepared in the department of pharmaceutics and industrial pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Assuit University.
Clinical evaluations
Each patient was examined at the beginning of treatment, and then after 1and 3 months of therapy. Patients signs and symptoms were evaluated by the following parameters:
Pain was scored using the visual analogue scale (VAS), a well-documented method of pain assessment (8). The severity of pain and pain sensation were evaluated. Patients were asked to score their intensity of pain at each visit. Pain scores ranged from 0 (no pain) to 10 (extreme pain).
This scoring system was proposed in 2007 (Escudier et al) (9) to evaluate the lesion severity and activity a ‘severity score’ (0–3).
This scoring system was proposed in 2008 (Malhotra et al) (10) to evaluate the lesion sites. It divided the oral cavity into 15 sites with score system led to grades (0–III).
Biochemical Evaluation
By assessment of salivary Interleukin-6 level using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) at base line, 1 and 3 months after treatment.
Statistical analysis
All the results were tabulated and statistically analyzed using SPSS software (version 20©; SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA). Data were presented as means and SDs. The two study groups were compared using independent samples t-test. Moreover, within each group, paired sample t-test was used to determine significant changes between time points for parametric data. The significance level was set at P value less than 0.05.
Results
Analytical statistics reveal the mean ± SD, and p-values of the VAS Score, Malhotra score, Activity Escidier Score, and the treatment modalities' impact on Interleukin 6 concentrations at various intervals across all study groups A, B, C detailed in Tables [1,2]. The most common symptoms prior to treatment were burning sensations, pain, and ulceration, with the atrophic/erosive form being the most prevalent lesion type. All patients completed the treatment protocol, resulting in either complete or partial responses, or recurrence of the lesion at 3 months into the study. The study's results indicated no significant differences in the baseline evaluation periods among all groups concerning the parameters studied, P > 0.05. Post-treatment, the triamcinolone acetonide group showed highly statistically significant differences at various intervals in all scoring systems compared to baseline. There was a noticeable remission and reduction in size, color, shape, and severity of oral lesions in all cases, with highly statistically significant differences in salivary Interleukin-6 levels at different intervals post-treatment compared to baseline, as shown in Tables [1,2]. There were highly statistically significant differences in the Malhotra score, activity, and site Escidier score at different intervals post-treatment compared to baseline, as well as in salivary Interleukin-6 levels.
In this study, there were no statistically significant differences between groups (A) triamcinolone acetonide and group (B) curcumin showed comparable efficacy. In the 1% curcumin group (B), there was complete remission of pain after one month in 60% of cases and a reduction of pain in 40% of cases. After the second month, there was complete remission in 80% and a reduction of pain in 20%, and after three months, complete remission in 40% and a reduction in 60% of cases, indicating that curcumin is effective in reducing pain in OLP patients.
There was a statistically significant difference between group A (triamcinolone acetonide), group B(curcumin), and group C (combination treatment) at different intervals, with group A showing greater improvement in Malhotra and Escudier scores.
Furthermore, in group C there were a statistically significant differences between pre-treatment and one month post-treatment according to the Escudier score, and salivary interleukin-6 levels at different intervals. However, there was a highly significant difference after three months compared to pre-treatment in Malhotra score and activity Escudier scoring systems, indicating that the combination is more effective than using curcumin alone. The use of medications in all three groups led to a statistically significant decrease in pain levels as indicated by VAS values, Escudier scores, and salivary interleukin-6 concentrations (P<0.001) compared to baseline values. The differences between all groups were statistically significant at all treatment periods, favoring the combined treatment.
I: Analytical Data:
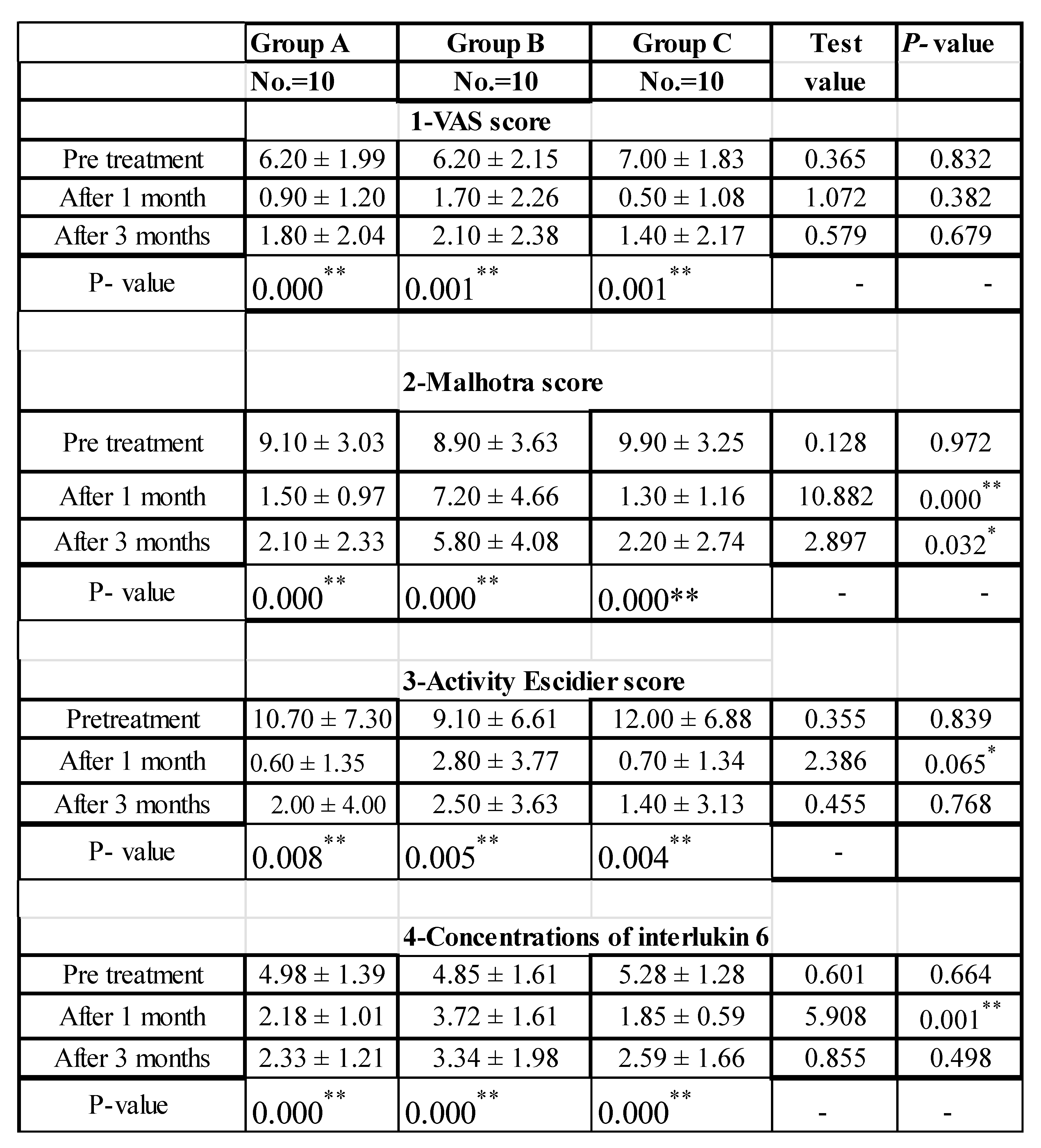
Table 1.
Comparison between the studied groups regarding VAS Score, Malhotra score, Activity Escidier score and regarding the effect of the treatment modalities on concentrations of Interlukin 6 at different intervals:.
Table 1.
Comparison between the studied groups regarding VAS Score, Malhotra score, Activity Escidier score and regarding the effect of the treatment modalities on concentrations of Interlukin 6 at different intervals:.
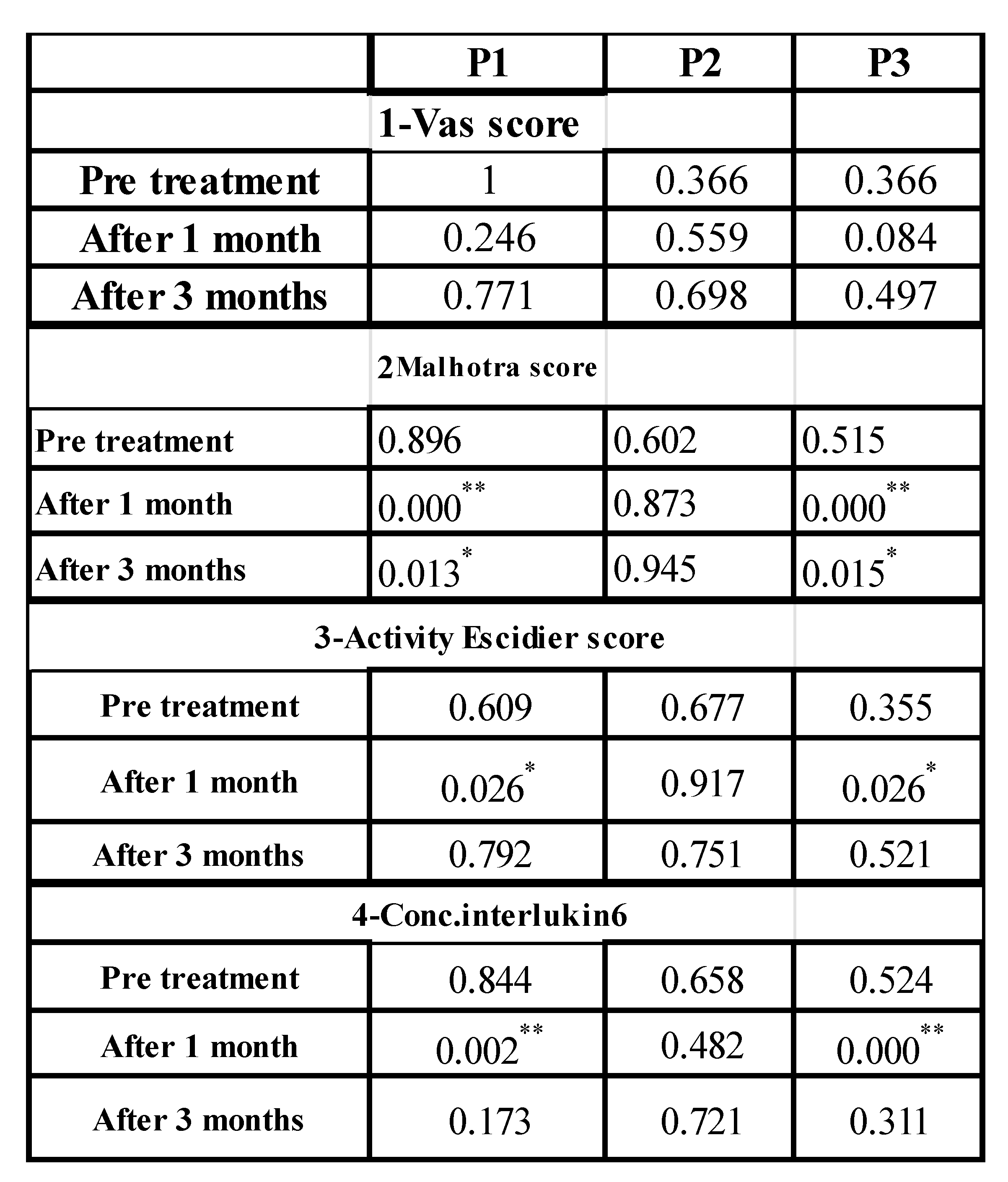
Table 2.
Showing post hoc analysis between the studied groups regarding to: VAS score, Malhotra Score, Activity Escidier score and regarding the effect of the treatment modalities on concentrations of Interlukin 6 at different intervals:.
Table 2.
Showing post hoc analysis between the studied groups regarding to: VAS score, Malhotra Score, Activity Escidier score and regarding the effect of the treatment modalities on concentrations of Interlukin 6 at different intervals:.
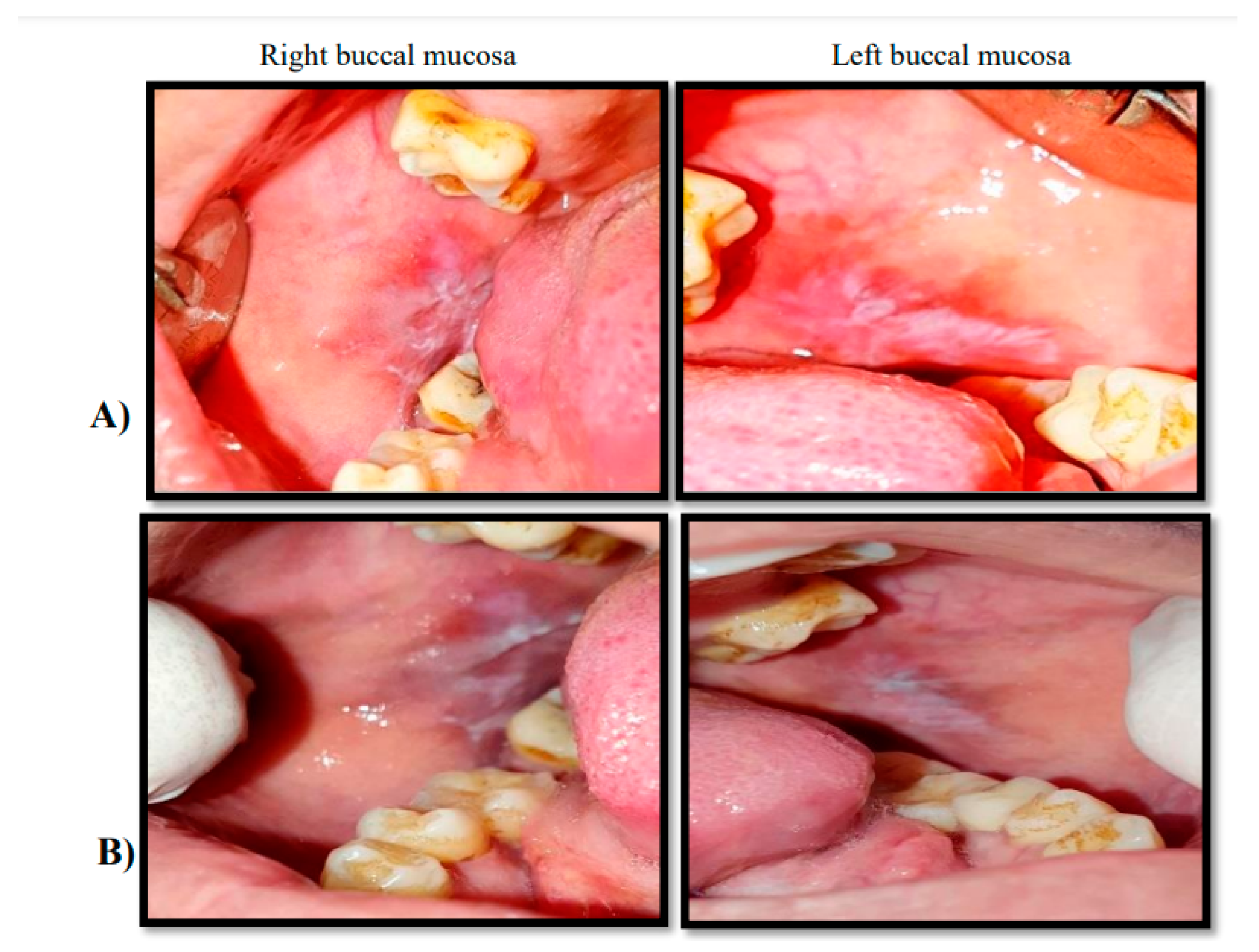
Figure 1.
Clinical phtographs showing a 53 years femal patient diagnosed with OLP on right and left buccal mucossa she recived topical trimicenolone acetonide 0.1% oral gel. Group(A).
Figure 1.
Clinical phtographs showing a 53 years femal patient diagnosed with OLP on right and left buccal mucossa she recived topical trimicenolone acetonide 0.1% oral gel. Group(A).
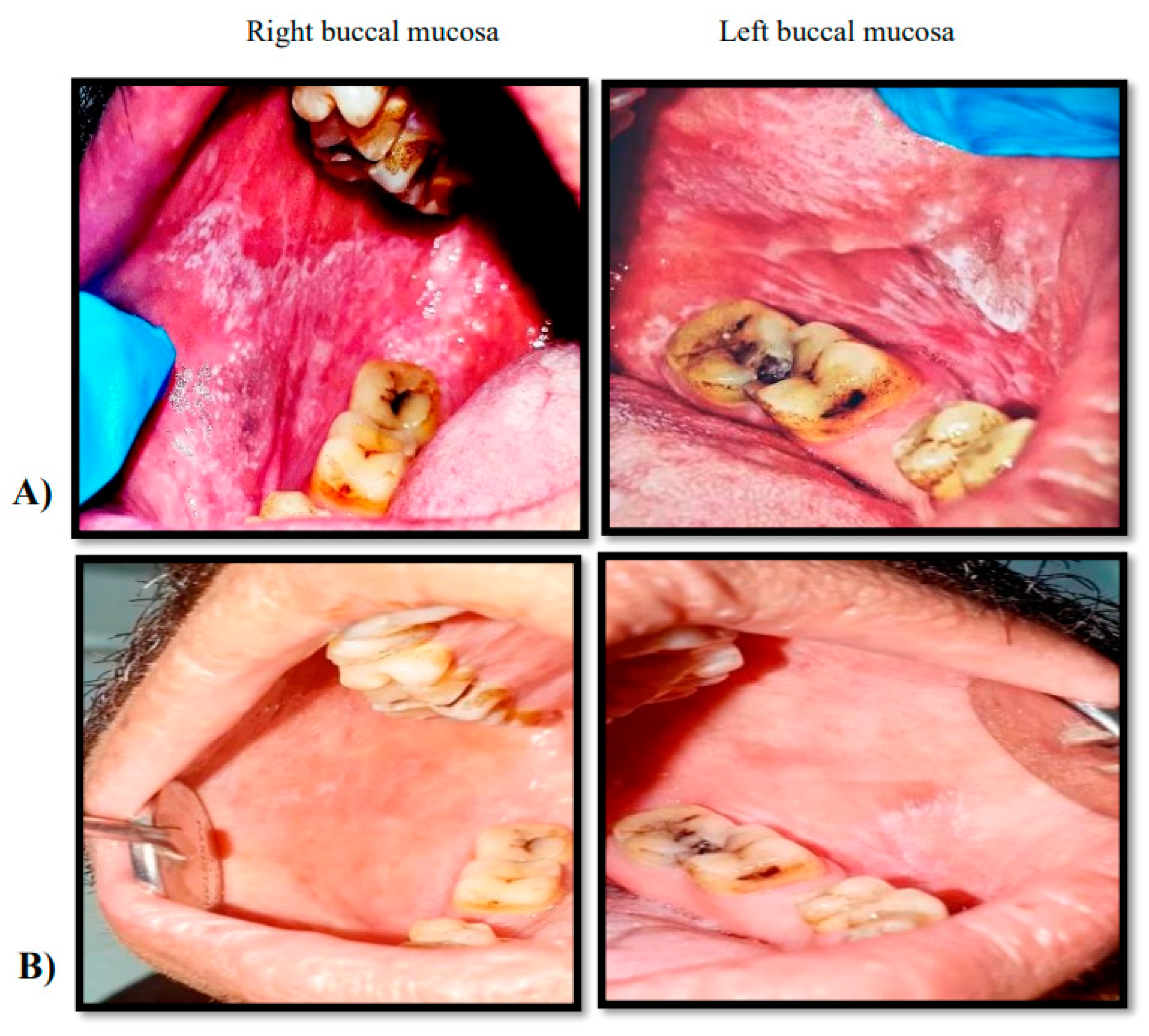
Figure 2.
Clinical phtographs showing a 46 years femal patient diagnosed with OLP on right and left buccal mucossa she recived topical curcumin 1% oral gel. Group(B). A:pretreatment, B: after treatment
Figure 2.
Clinical phtographs showing a 46 years femal patient diagnosed with OLP on right and left buccal mucossa she recived topical curcumin 1% oral gel. Group(B). A:pretreatment, B: after treatment
Figure 3.
Clinical phtographs showing a 43 years male patient diagnosed with OLP on right and left buccal mucossa he recived topical curcumin1% oral gel combined with triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% oral gel. Group(C). A: pretreatment, B: after treatment. .
Figure 3.
Clinical phtographs showing a 43 years male patient diagnosed with OLP on right and left buccal mucossa he recived topical curcumin1% oral gel combined with triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% oral gel. Group(C). A: pretreatment, B: after treatment. .
Discussion
Oral Lichen Planus (OLP) is an immune-mediated mucocutaneous condition with an unknown cause. It predominantly affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, with the average age of participants in this study being 48.44 ± 11.40 years, which is consistent with the typical age range of OLP patients. The majority of participants are female (31 out of 33 patients in the clinical trial), corroborating the commonly reported female-to-male ratio of around 2:1. OLP was known for its variable clinical manifestations, ranging from moderate to severe, and for its pattern of flare-ups followed by symptom-free periods, significantly impacting the quality of life of patients. Due to the low risk of malignant transformation, continuous clinical monitoring is crucial. Pharmacological treatment offers benefits for symptomatic individuals (12).
Pathogenesis of OLP characterized by T-cell mediated chronic inflammation of the oral mucosa that locally present in the involved tissue causing release cytokines like interleukin-6 (IL-6), which contributes to the pathogenesis of OLP. Therefore, levels of IL-6 in the saliva of OLP patients are considered as reliable indicators of therapeutic response to predict disease severity and monitor disease activity (13,14).
The present study was designed to evaluate the effectiveness of Curcumin as Alternative or Complementary to Triamcinolone Acetonate in treatment of OLP patients. Curcumin is a polyphenol derived from curcuma longa plant, commonly known as turmeric. The components of turmeric are named curcuminoids, which include mainly curcumin (diferuloyl methane), demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxy-curcumin, it is nontoxic and has variety of therapeutic properties including antioxidant, analgesic, antiinflammatory, antiseptic activity, antimicrobial, anticarcinogenic, antimutagenic, and antiproliferative properties and protects nervous and immune systems(15,16).
Our study results indicate that the use of medications in the three groups led to statistically significant decrease in pain scores as indicated by VAS values (P<0.001) as compared to baseline values. The differences between the three groups were statistically significant at all treatment periods in favor to the combined treatment group (C). Curcumin did not significantly affect erythema in OLP, consistent with the findings of Bakhshi et al (17), Keshari et al. (18), Thomas et al.(19), and Chainani-Wu et al. (20), who also observed no significant impact on erythema in OLP patients. However, there was a marked reduction in lesion size at the 12-week treatment point, unlike the 2- and 4-week marks. In a similar vein, Kapoor and Arora (21) noted a significant reduction in lesion size after a 12-week period. Curcumin is not effective as triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% in reducing burning sensation erythema and lesion changes (22).
There was a statistically significant reduction of the mean interlukin 6 values that continued down to the end of the study with both treatment modalities in groups A, C. The mean difference of interlukin 6 between the three treatment groups A, B, C were statistically significant at one month while there was statistically significant difference between the three treatment modalities in favor to group C combined treatment at 3 months respectively.
The use of a combination of topical triamcinolone acetonide in orabase and curcumin to triamcinolone in orabase alone (GI) led to a decrease in the size of lesions. The decrease in the size of the lesions was greater in the test group (C) compared to the control group (A, B). It was shown that oral curcumin could be effective in preventing the recurrence of OLP lesions after treatment and initial control; in addition, the dose of curcumin is more important than the duration of the treatment (23).
Topical curcumin has been found effective in controlling the signs and symptoms of oral lichen planus (OLP). The parameters studied, including pain, erythema, and ulceration, showed statistically significant improvement with topical curcumin therapy. Additionally, topical curcumin was safe at the prescribed dose, which is 99% curcumin in a gel base, with no adverse effects reported compared to patients treated with triamcinolone acetonide 0.1%, who developed a superadded candida infection as a side effect and tacrolimus group ,whose developed burning sensation, nephrotoxicity, hypertension and high cost (24).
The research indicates that topical curcumin might be an alternative to conventional corticosteroid therapy for suppressing the immune response in the treatment of OLP. This could lessen reliance on medications with more severe side effects. The study revealed that topical curcumin has shown promising results in managing OLP and combining it with another medication like Triamcinolone Acetonate could enhance the treatment efficacy for OLP symptoms.
Conclusion
Curcumin, a compound known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory properties, may offer potential benefits for various inflammatory diseases. Its clinical efficacy and safety in treating oral lichen planus (OLP) have been observed.
Topical application of curcumin as an alternative therapy for OLP may be less effective than triamcinolone acetonide when used alone.
Combining curcumin with triamcinolone acetonide could potentially enhance the treatment's efficacy for oral lichen planus symptoms compared to triamcinolone acetonide alone.
IL-6 is a significant biomarker in the pathogenesis of OLP and is used to predict disease severity and monitor disease activity.
Limitation
Further research with a larger sample size and evaluation of histological parameters before and after treatment is necessary to confirm the efficacy of topical curcumin in the management of OLP at the cellular level.
Funding
no external funding.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to express their profound gratitude to Professor Dr. Dina Fathalla Mohamed, pharmaceutical department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Assiut University, for her significant contributions to the preparation of the topical curcumin formulation.
Ethics Statement
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the ethical committee Faculties of dental medicine, Al-Azhar University, Assiut Branch. (approval AUAREC20240004-15). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT06605911.
Statement of informed consent
were taken from all patients about the method of trial and the suspected publishing.
Data Availability
Public available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Payeras, M.R.; Cherubini, K.; Figueiredo, M.A.; Salum, F.G. Oral lichen planus: Focus on etiopathogenesis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Jawanda, M. Oral lichen planus: An update on etiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis and management. Indian J. Dermatol. 2015, 60, 222–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.-S.L.; Gould, A.; Kurago, Z.; Fantasia, J.; Muller, S. Diagnosis of oral lichen planus: a position paper of the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Oral Surgery, Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2016, 122, 332–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roopashree, M.R.; Gondhalekar, R.V.; Shashikanth, M.C.; George, J.; Thippeswamy, S.H.; Shukla, A. Pathogenesis of oral lichen planus - a review. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2010, 39, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, R.-C.; Lin, H.-P.; Sun, A.; Wang, Y.-P. Prompt healing of erosive oral lichen planus lesion after combined corticosteroid treatment with locally injected triamcinolone acetonide plus oral prednisolone. J. Formos. Med Assoc. 2013, 112, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kia, S.J.; Basirat, M.; Mortezaie, T.; Moosavi, M.-S. Comparison of oral Nano-Curcumin with oral prednisolone on oral lichen planus: a randomized double-blinded clinical trial. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Hopewell, S.; Schulz, K.F.; Montori, V.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Devereaux, P.; Elbourne, D.; Egger, M.; Altman, D.G. CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Int. J. Surg. 2012, 10, 28–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekorn L, Sererat T Taweesap W. Relative efficacy of fluocinolone acetonide compared with triamcinolone acetonide in treatment of oral lichen planus. J Oral Pathol Med. 1992; 21:456–8.
- Escudier, M.; Ahmed, N.; Shirlaw, P.; Setterfield, J.; Tappuni, A.; Black, M.; Challacombe, S. A scoring system for mucosal disease severity with special reference to oral lichen planus. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, A.K.; Khaitan, B.K.; Sethuraman, G.; Sharma, V.K. Betamethasone oral mini-pulse therapy compared with topical triamcinolone acetonide (0.1%) paste in oral lichen planus: A randomized comparative study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffari, H.R.; Sharifi, R.; Sadeghi, M. Interleukin-6 levels in the serum and saliva of patients with oral lichen planus compared with healthy controls: a meta-analysis study. Central Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 43, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrashdan, M.S.; Cirillo, N.; McCullough, M. Oral lichen planus: a literature review and update. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2016, 308, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel S, Marwah A, Kaushik S, et al.: Role of serum interleukin-6 in deciding therapy for multidrug resistant orallichen planus. J Clin Exp Dent2015; 7:477-82.
- Kaur J, Jacobs R: Proinflammatory cytokine levels in oral lichen planus, oral leukoplakia, and oral submucousfibrosis. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.2015; 41: 171-175.
- Sneha S, Ul Nisa S, Mhapuskar A. Curcumin - A Novel Ayurvedic treatment for oral Lichen Planus. Int J Curr Med Pharm Res. 2017; 3:1507–11.
- Purushothaman, A.; Rose, K.T.; Jacob, J.M.; Varatharaj, R.; Shashikala, K.; Janardanan, D. Curcumin analogues with improved antioxidant properties: A theoretical exploration. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, M.; Gholami, S.; Mahboubi, A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Namdari, M. Combination Therapy with 1% Nanocurcumin Gel and 0.1% Triamcinolone Acetonide Mouth Rinse for Oral Lichen Planus: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial. Dermatol. Res. Pr. 2020, 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshari, D.; Patil, K.; Guledgud, M.V. Efficacy of topical curcumin in the management of oral lichen planus: A randomized controlled-trial. J. Adv. Clin. Res. Insights 2015, 2, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas AE, Varma B, Kurup S, Jose R, Chandy ML, Kumar SP, et al. Evaluation of efficacy of 1% curcuminoids as local application in management of oral Lichen Planus – Interventional Study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11 :89–93.
- Chainani-Wu, N.; Madden, E.; Lozada-Nur, F.; Silverman, S. High-dose curcuminoids are efficacious in the reduction in symptoms and signs of oral lichen planus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 66, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor S, Arora P. Effect of curcumin in management of potentially malignant disorders-A comparative study. Oncol Radiotherapy. 2019;1: 001–4.
- Lv K-j, Chen T-c, Wang G-h, Yao Y-n. Clinical safety and efficacy of Curcumin Use for oral Lichen Planus: a systematic review. J Dermatological Treat. 2018;30: 605–11.
- Naik DR, Nazneen DL, Dhobley DA, Sharma Thombre DA, Saxena DU, Kosta DS. Curcumin alone and curcumin with prednisone in management oral Lichen Planus patients. Eur J Mol Clin Med. 2021;8(3).
- Anju elizabeth thomas, beena varma, seema kurup, renju jose, marina lazar chandy, sreeja p kumar et al. Evaluation of Efficacy of 1% Curcuminoids as Local Application in Management of Oral Lichen Planus. J Clin Diagn Res.2017;11(4): ZC89–ZC93.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.a |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).