Submitted:
24 September 2024
Posted:
24 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fusarium Solani KMZW-1 Culture and Identification
2.2. Insect Collection and Rearing
2.3. Complete Genome Sequencing, Assembly and Annotation
2.3.1. Genome Sequencing
- a)
- DNA damage repair and end repair were performed followed by magnetic bead purification
- b)
- DNA fragments were ligated with adapters followed by another round of, magnetic bead purification
- c)
- Qubit flurometry was used for library quantification
- d)
- Sequencing was done using a computer based system 2.4.2.
2.3.2. Genome Assembly
2.3.3. Genome Predictions
2.3.4. Genome Protein Annotations
2.4. Comparative Genome Analysis
2.5. Pathogenicity Test of Fusarium solani KMZW-1 against Bactrocera Dorsalis
2.5.1. Conidial Suspension Preparation
2.5.2. Bioassays
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ITS-based identification of Fusarium solani KMZW-1
3.2. Genome Assembly
3.3. BUSCO evaluation
3.4. General Database Annotations
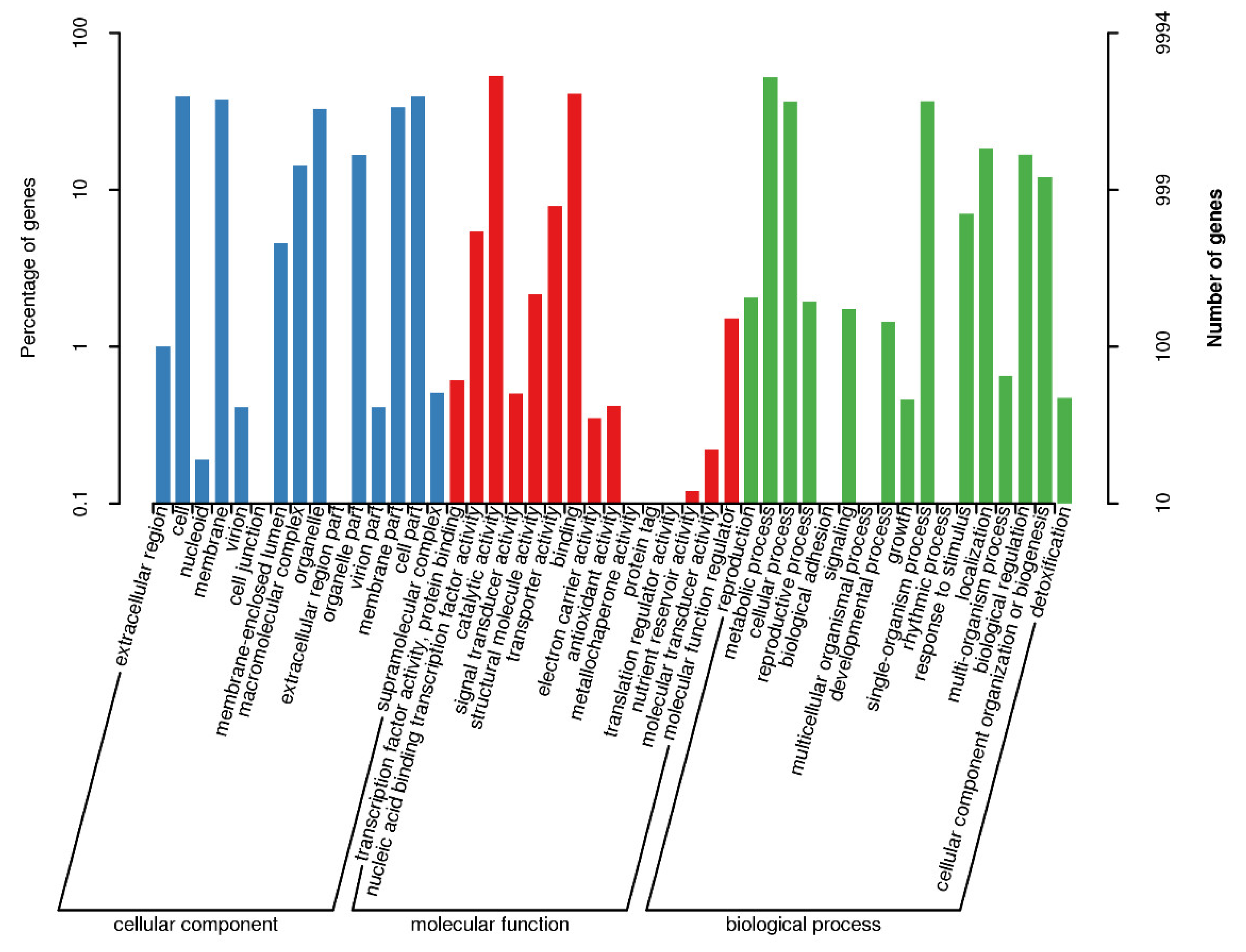
3.5. GO Annotations
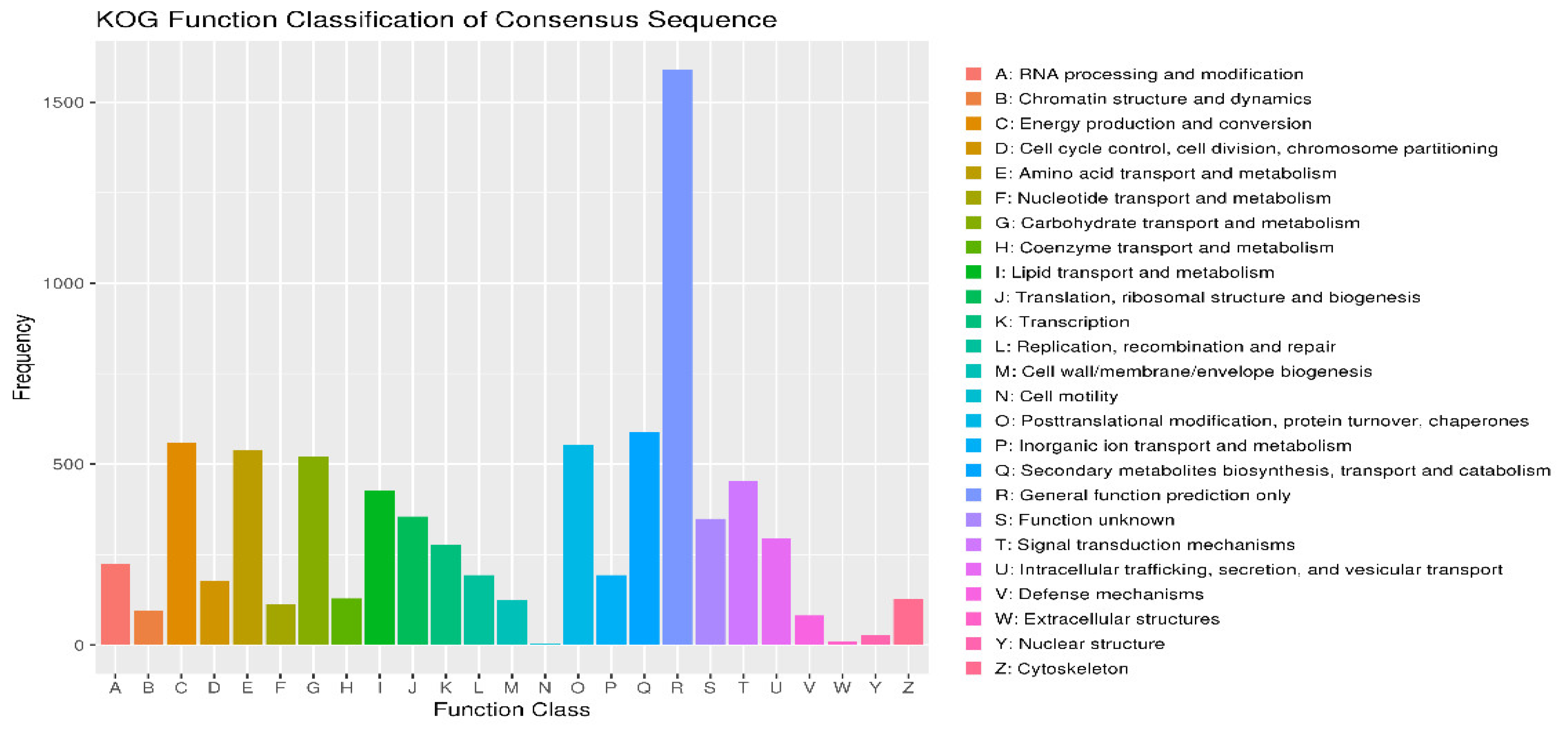
3.6. KOG Annotations
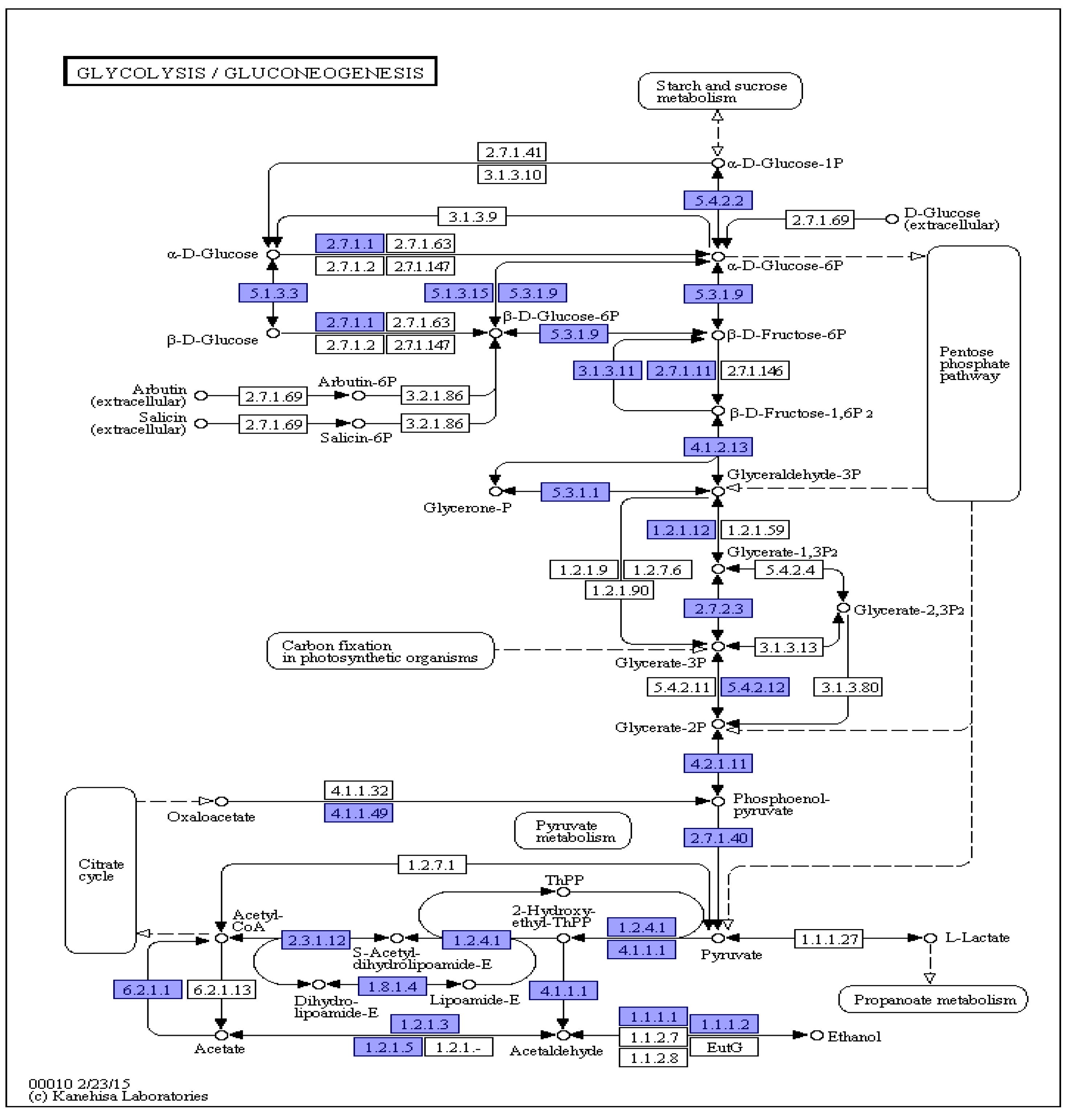
3.7. KEGG Annotations
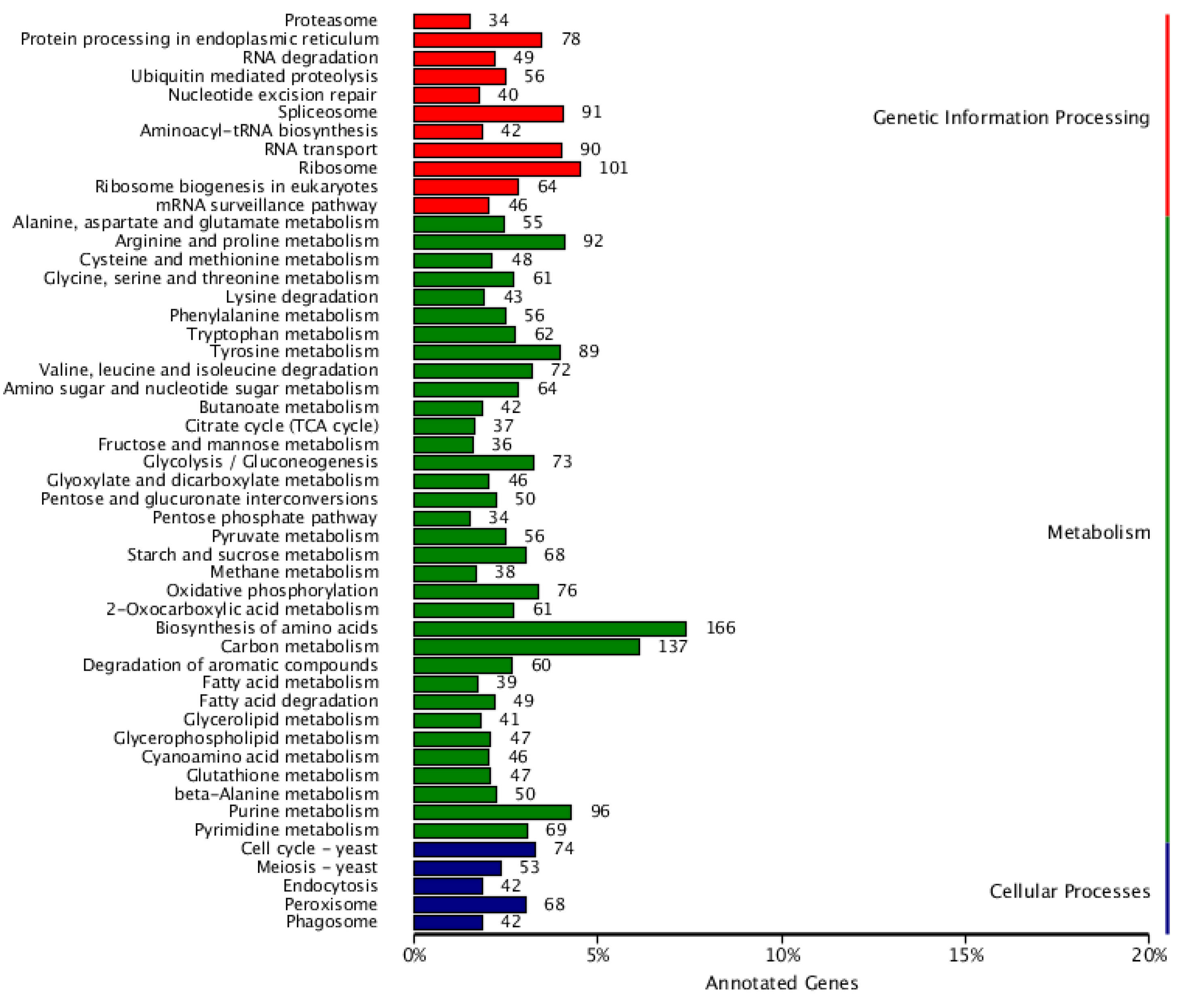
3.8. Genetic Information Processing
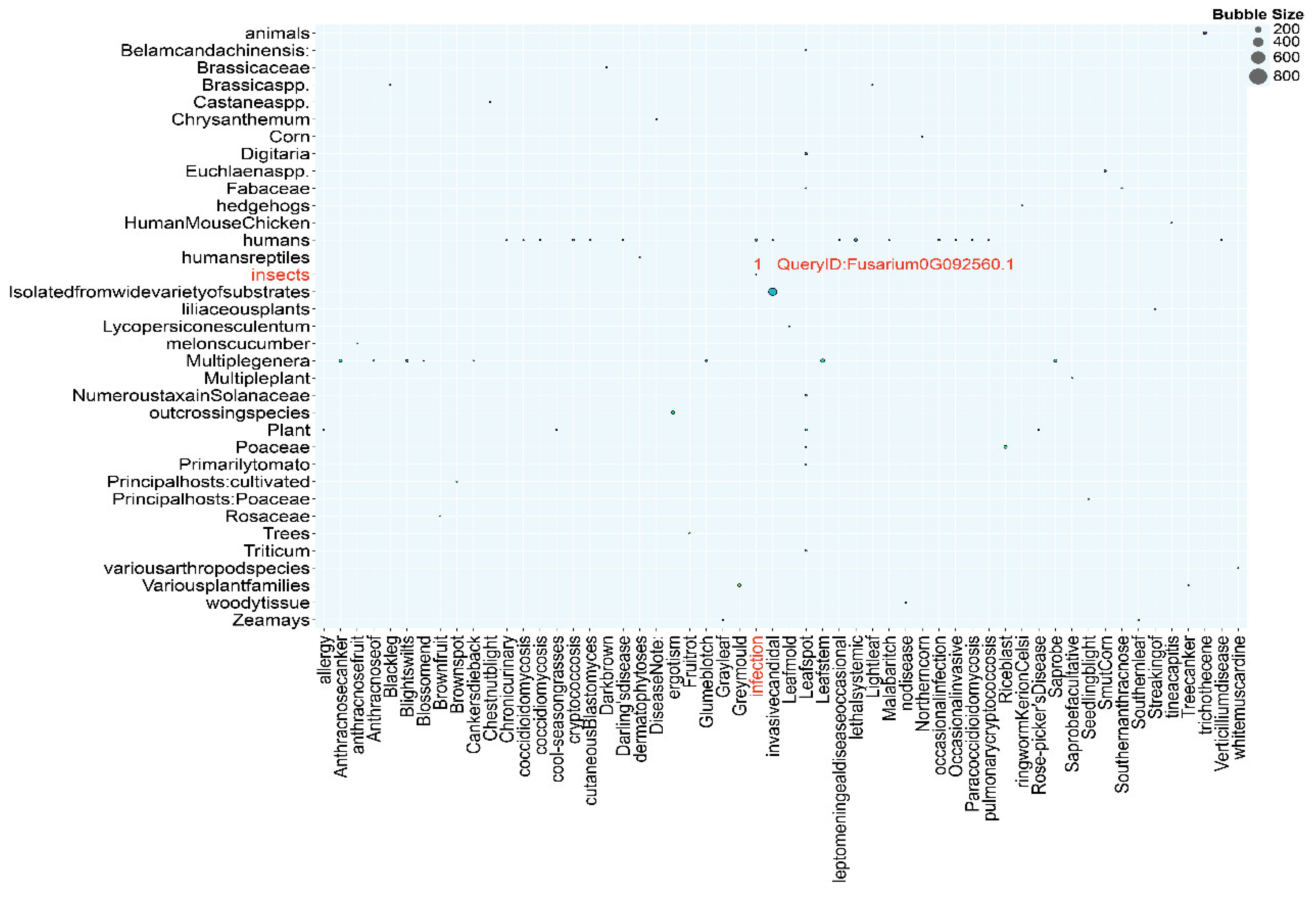
3.9. DFVF Database Annotation
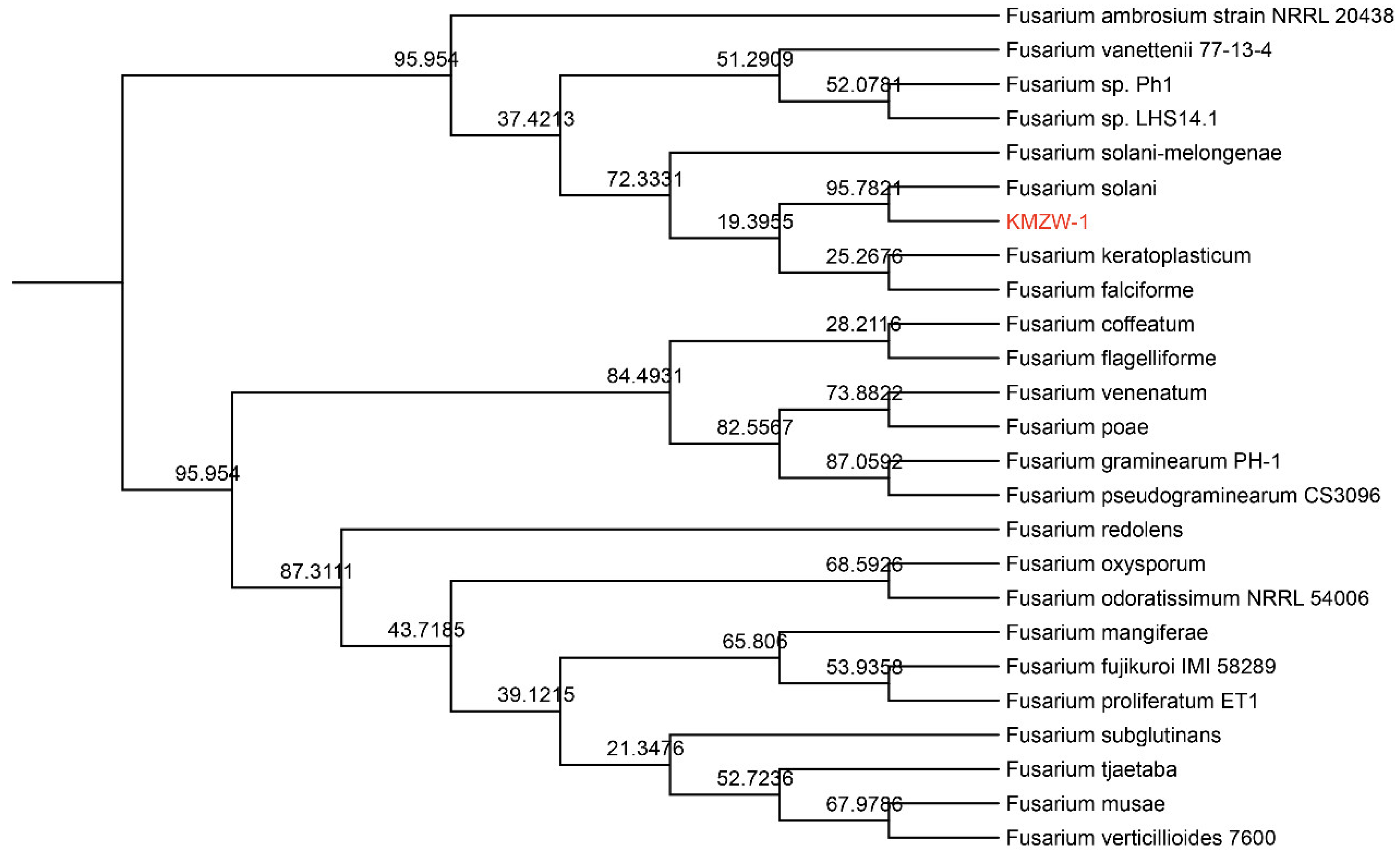
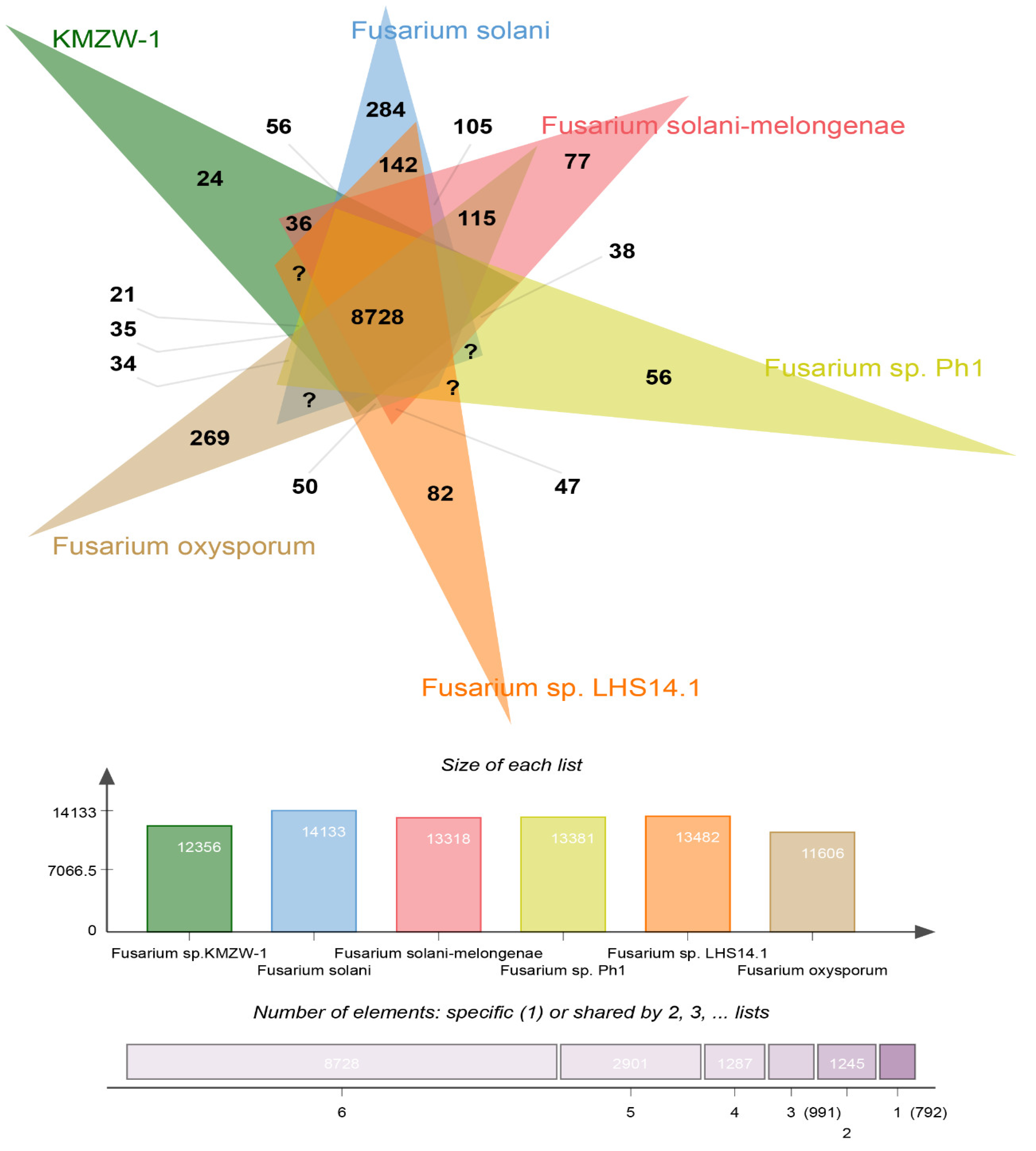
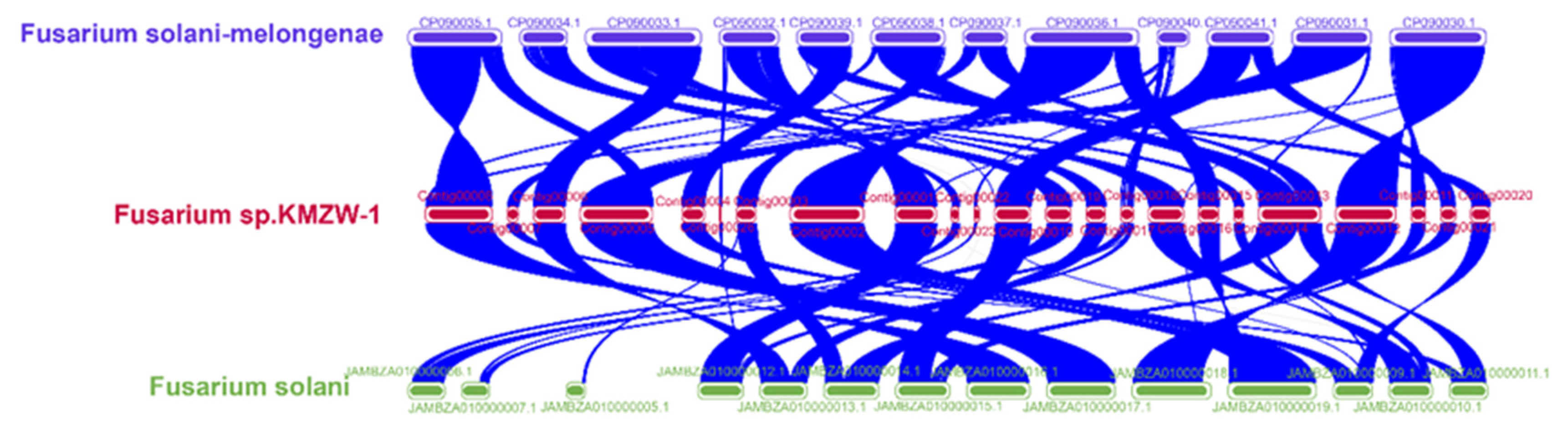
3.10. Comparative Genomic analysis
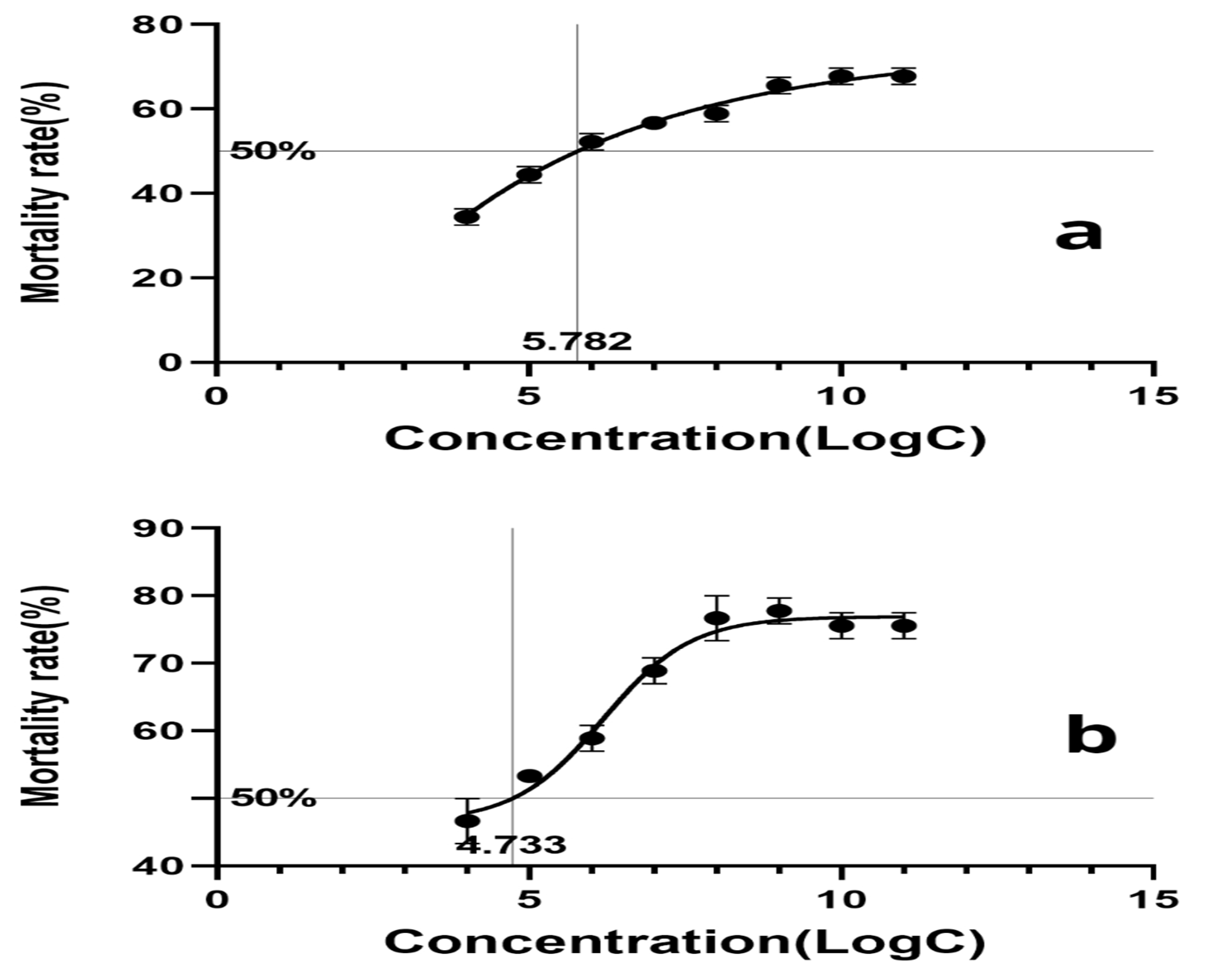
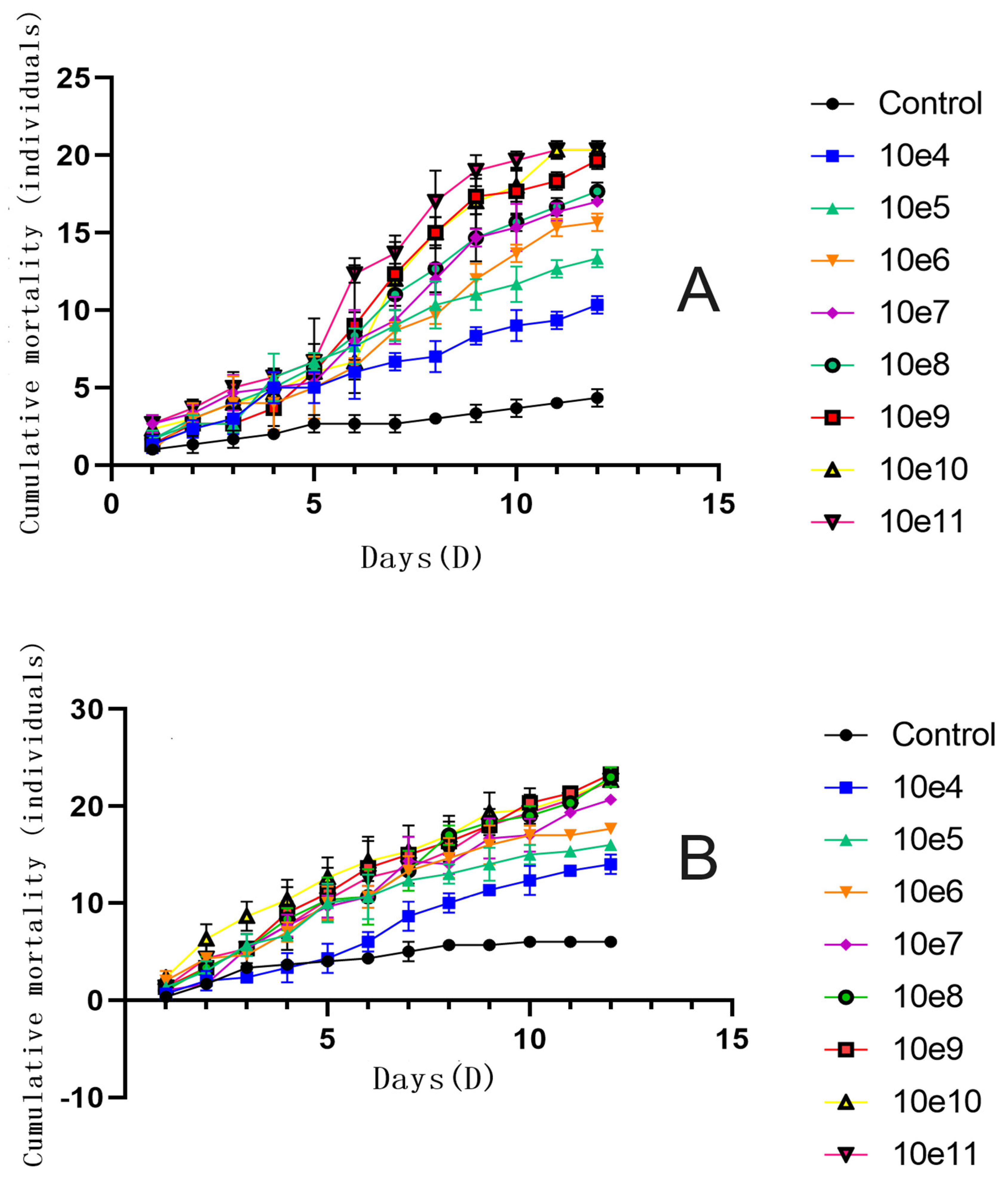
3.11. Pathogenicity Test of Fusarium solani KMZW-1 at Different Concentrations
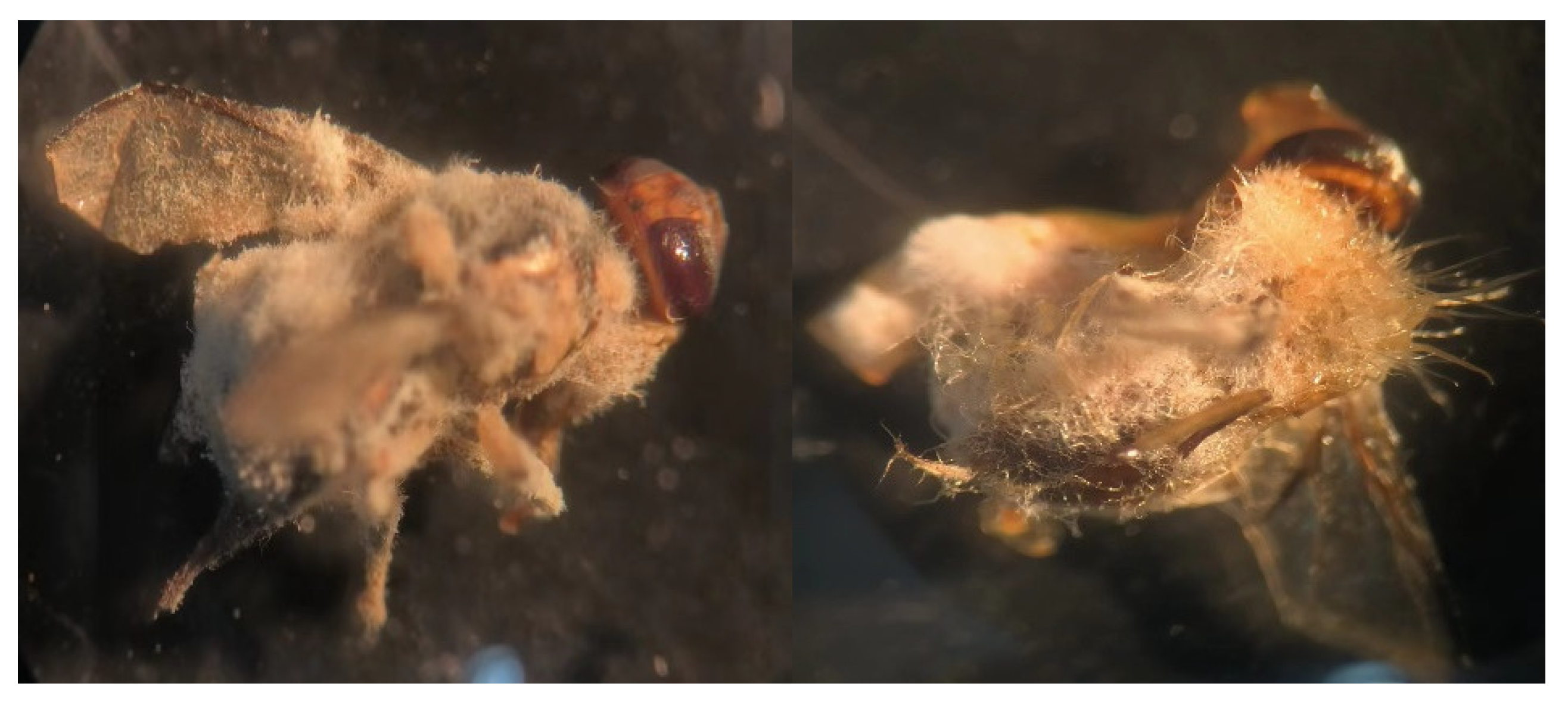

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, L.W.; Yuan, G.R.; Lu, X.P.; Jing, T.X.; Zheng, L.S.; Yong, H.X.; Wang, J.J. Two delta class glutathione S-transferases involved in the detoxification of malathion in Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Pest Management Science. 2019, 75, 1527–1538. [CrossRef]
- Li XL, Zhang JJ, Li DD, Cai XY, Qi YX, Lu YY. Toxicity of Beauveria bassiana to Bactrocera dorsalis and effects on its natural predators. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2024 May 2;15:1362089. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang L, Chen X, Hou Q, Et Al. 2018. Genome Sequencing And Comparative Genomics Reveal The Potential Pathogenic Mechanism Of Cercospora Sojina Hara On Soybean. Scientific Reports [J], 8: 1796.
- Huang S, Zhao X, Luo Z, Tang X, Zhou Y, Keyhani N, Zhang Y. Fungal co-expression network analyses identify pathogen gene modules associated with host insect invasion. Microbiology Spectrum. 2023 Sep 1;11(5):e0180923. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cao Y, Wang Y, Feng M G 2020. Whole-Genome Sequence Of Lecanicillium Attenuatum Strain Lec8, An Entomopathogenic Fungus With High Potential As A Biocontrol Agent. *Microbiology Resource Announcements [J],9:E01480-01499. [CrossRef]
- Xie S Y, Ma T, Zhao N, Zhang X, Fang B, Huang L. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Comparative Genome Analysis of Fusarium solani-melongenae Causing Fusarium Root and Stem Rot in Sweet potatoes. Microbiology Spectrum. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0068322. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Weems, Jr., Howard V., John B. Heppner, Thomas R. Fasulo, and James L. Nation. 2004. “Caribbean Fruit Fly, Anastrepha Suspensa (Loew) (Insecta: Diptera: Tephritidae): EENY196/IN353, 3/2001”. EDIS 2004 (5). Gainesville, FL. [CrossRef]
- Vargas R.I., Piñero J.C., Leblanc L. An Overview Of Pest Species Of Bactrocera Fruit Flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) And The Integration Of Biopesticides With Other Biological Approaches For Their Management With A Focus On The Pacific Region. Insects. 2015;6:297–318. [CrossRef]
- Usman M., Gulzar S., Wakil W., Piñero J.C., Leskey T.C., Nixon L.J., Oliveira-Hofman C., Wu S., Shapiro-Ilan D. Potential Of Entomopathogenic Nematodes Against The Pupal Stage Of The Apple Maggot Rhagoletis Pomonella (Walsh) (Diptera:Tephritidae)Journal of Nematology. 2020 52:E2020–E2079. [CrossRef]
- Gulzar S., Wakil W., Shapiro-Ilan D.I. Combined Effect Of Entomopathogens Against Thrips Tabaci Lindeman (Thysanoptera: Thripidae): Laboratory, Greenhouse And Field Trials. Insects. 2021;12:456. [CrossRef]
- Wakil W., Tahir M., Al-Sadi A.M., Shapiro-Ilan D. Interactions Between Two Invertebrate Pathogens: An Endophytic Fungi And Externally Applied Bacterium. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2020;11:2624. [CrossRef]
- Tahir M., Wakil W., Ali A., Sahi S.T. Pathogenicity Of Beauveria Bassiana, And Metarhizium Anisopliae Isolates Against Larvae Of The Polyphagous Pest Helicoverpa Armigera. Entomologia Generalis. 2019;38:225–242. [CrossRef]
- Usman M, Wakil W, Piñero JC, Wu S, Toews MD, Shapiro-Ilan DI. Evaluation of Locally Isolated Entomopathogenic Fungi against Multiple Life Stages of Bactrocera zonata and Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae): Laboratory and Field Study. Microorganisms. 2021 Aug 23;9(8):1791. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology. [J] 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403-10. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker B J, Abeel T, Shea T, Et Al. 2014. Pilon: An Integrated Tool For Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection And Genome Assembly Improvement. Plos One [J], 9: E112963. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Durbin R 2009. Fast And Accurate Short Read Alignment With Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics [J], 25: 1754-1760. oi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324.
- Simão F A, Waterhouse R M, Ioannidis P, Et Al. 2015. BUSCO: Assessing Genome Assembly And Annotation Completeness With Single-Copy Orthologs. Bioinformatics [J], 31: 3210-3212. [CrossRef]
- Xu Z, Wang H 2007. LTR_FINDER: An Efficient Tool For The Prediction Of Full-Length LTR Retrotransposons. Nucleic Acids Reserch [J], 35: W265-268. [CrossRef]
- Han Y, Wessler S R 2010. Mite-Hunter: A Program For Discovering Miniature Inverted-Repeat Transposable Elements From Genomic Sequences. Nucleic Acids Research [J], 38: E199. [CrossRef]
- Price A L, Jones N C, Pevzner P A 2005. De Novo Identification Of Repeat Families In Large Genomes. Bioinformatics [J], 21 Suppl 1: I351-358. [CrossRef]
- Edgar R C, Myers E W 2005. PILER: Identification And Classification Of Genomic Repeats. Bioinformatics [J], 21 Suppl 1: I152-158. [CrossRef]
- Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Et Al. 2009. Reply: A Unified Classification System For Eukaryotic Transposable Elements Should Reflect Their Phylogeny. Nature Review Genetics. [J], 10: 276-276. [CrossRef]
- Jurka J, Kapitonov V V, Pavlicek A, Et Al. 2005. Repbase Update, A Database Of Eukaryotic Repetitive Elements. Cytogenetic And Genome Research. 110: 462-467. [CrossRef]
- Tarailo-Graovac M, Chen N 2009. Using Repeatmasker To Identify Repetitive Elements In Genomic Sequences. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics [J], Chapter 4: 4.10.11-14.10.14. [CrossRef]
- Burge C, Karlin S 1997. Prediction Of Complete Gene Structures In Human Genomic DNA. Journal of Molecular Biology. [J], 268: 78-94. [CrossRef]
- Stanke M, Waack S 2003. Gene Prediction With A Hidden Markov Model And A New Intron Submodel. Bioinformatics [J], 19: Ii215-Ii225. [CrossRef]
- Majoros W H, Pertea M, Salzberg S L 2004. Tigrscan And Glimmerhmm: Two Open Source Ab Initio Eukaryotic Gene-Finders. Bioinformatics [J], 20: 2878-2879. [CrossRef]
- Alioto T, Blanco E, Parra G, Et Al. 2018. Using Geneid To Identify Genes. Current Protoc Bioinformatics [J], 64: E56. [CrossRef]
- Keilwagen J, Wenk M, Erickson J L, Et Al. 2016. H: Using Intron Position Conservation For Homology-Based Gene Prediction. Nucleic Acids Research [J], 44: E89-E89. [CrossRef]
- Haas B J, Salzberg S L, Zhu W, Et Al. 2008. Automated Eukaryotic Gene Structure Annotation Using Evidencemodeler And The Program To Assemble Spliced Alignments. Genome Biology [J], 9: R7. [CrossRef]
- Lowe T M, Eddy S R 1997. Trnascan-SE: A Program For Improved Detection Of Transfer RNA Genes In Genomic Sequence. Nucleic Acids Research. [J], 25: 955-964. [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki E P, Eddy S R 2013. Infernal 1.1: 100-Fold Faster RNA Homology Searches. Bioinformatics [J], 29: 2933-2935. [CrossRef]
- She R, Chu J S C, Wang K, Et Al. 2009. Genblasta: Enabling BLAST To Identify Homologous Gene Sequences. Genome Research. [J], 19: 143-149. [CrossRef]
- Birney E, Clamp M, Durbin R 2004. Genewise And Genomewise. Genome Research. [J], 14: 988-995. [CrossRef]
- Blin K, Shaw S, Kloosterman A M, Et Al. 2021. Antismash 6.0: Improving Cluster Detection And Comparison Capabilities. Nucleic Acids Research. [J], 49: W29-W35. [CrossRef]
- Altschul S F, Madden T L, Schäffer A A, Et Al. 1997. Gapped BLAST And PSI-BLAST: A New Generation Of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Research. [J], 25: 3389-3402. [CrossRef]
- Deng Y Y, Li J Q, Wu S F 2006. Integrated Nr Database In Protein Annotation System And Its Localization. J]. Comput Engineerig [J], 32: 71-74. [CrossRef]
- Boeckmann B, Bairoch A, Apweiler R, Et Al. 2003. The SWISS-PROT Protein Knowledgebase And Its Supplement Trembl In 2003. Nucleic Acids Research. [J], 31: 365-370. [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Et Al. 2004. The KEGG Resource For Deciphering The Genome. Nucleic Acids Research. [J], 32: D277-280. [CrossRef]
- Tatusov R L, Galperin M Y, Natale D A, Et Al. 2000. The COG Database: A Tool For Genome-Scale Analysis Of Protein Functions And Evolution. Nucleic Acids Research. [J], 28: 33-36. [CrossRef]
- Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez J, Et Al. 2004. Blast2GO: A Universal Annotation And Visualization Tool For Functional Genomics Research. Bioinformatics. 15;21(18):3674-6. [CrossRef]
- Eddy S R 1998. Profile Hidden Markov Models. Bioinformatics [J]: 755-763. [CrossRef]
- Cantarel B L, Coutinho P M, Rancurel C, Et Al. 2009. The Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes Database (Cazy): An Expert Resource For Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Research [J]: D233-D238. [CrossRef]
- Saier M H, JR., Tran C V, Barabote R D 2006. TCDB: The Transporter Classification Database For Membrane Transport Protein Analyses And Information. Nucleic Acids Research. [J], 34: D181-186. [CrossRef]
- Winnenburg R 2006. PHI-Base: A New Database For Pathogen Host Interactions. Nucleic Acids Research. [J], 34: D459-D464. [CrossRef]
- Fischer M, Knoll M, Sirim D, Et Al. 2007. The Cytochrome P450 Engineering Database: A Navigation And Prediction Tool For The Cytochrome P450 Protein Family. Bioinformatics [J], 23: 2015-2017. [CrossRef]
- Lu T, Yao B, Zhang C 2012. DFVF: Database Of Fungal Virulence Factors. Database [J], 2012: Bas032-Bas032. [CrossRef]
- Petersen T N, Brunak S, Von Heijne G, Et Al. 2011. Signalp 4.0: Discriminating Signal Peptides From Transmembrane Regions. Nature Methods [J], 8: 785-786. [CrossRef]
- Krogh A, Larsson B, Von Heijne G, Et Al. 2001. Predicting Transmembrane Protein Topology With A Hidden Markov Model: Application To Complete Genomes. Journal of Molecular Biology. [J], 305: 567-580. [CrossRef]
- Sperschneider J, Gardiner D M, Dodds P N, Et Al. 2016. Effectorp: Predicting Fungal Effector Proteins From Secretomes Using Machine Learning. New Phytologist. [J], 210: 743-761. [CrossRef]
- Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2021 Jun 25;38(7):3022-3027. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Emms D M , Kelly S . OrthoFinder: solving fundamental biases in whole genome comparisons dramatically improves orthogroup inference accuracy[J].Genome biology, 2015, 16(157):157. [CrossRef]
- Chen C., Wu Y., Li J., Wang X., Zeng Z., Xu J., Liu Y., Feng J., Chen H., He Y., and Xia R. (2023). TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Molecular Plant. 16,1733–1742. [CrossRef]
- He W, Yang J, Jing Y, Xu L, Yu K, Fang X. NGenomeSyn: an easy-to-use and flexible tool for publication-ready visualization of syntenic relationships across multiple genomes. Bioinformatics. 2023 Mar 1;39(3):btad121. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Keyhani, N.O.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J. Infection of the Western Flower Thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis, by the Insect Pathogenic Fungus Beauveria bassiana. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1910. [CrossRef]
- Taylor J.W., Fisher M.C. Fungal multilocus sequence typing: It’s not just for bacteria. Current Opinion in Microbiology. 2003;6:351–356. [CrossRef]
- Kim JC, Park SE, Lee SJ, Kim JS. Whole-Genome Sequence of Beauveria bassiana JEF-350, a Strain with High Insecticidal Activity against Melon Thrips (Thrips palmi). Microbiology Resource Announcements. 2022 Sep 15;11(9):e0047022. [CrossRef]
- Lee G, Ibal JC, Park T, Kim M, Choi S, Shin J. 2024. Whole-genome sequencing of Beauveria bassiana KNU-101 using the hybrid assembly approach. Microbiology Resource Announcment. 13:e00681-23. [CrossRef]
- Altimira F, Arias-Aravena M, Jian L, Real N, Correa P, González C, Godoy S, Castro JF, Zamora O, Vergara C, et al. Genomic and Experimental Analysis of the Insecticidal Factors Secreted by the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria pseudobassiana RGM 2184. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(3):253. [CrossRef]
- Iwanicki NSA, Botelho ABRZ, Klingen I, Júnior ID, Rossmann S, Lysøe E. Genomic signatures and insights into host niche adaptation of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium humberi. G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Feb 4;12(2):jkab416. [CrossRef]
- Binneck E, Lastra CCL, Sosa-Gómez DR. Genome Sequence of Metarhizium rileyi, a Microbial Control Agent for Lepidoptera. Microbiology Resource Announcements. 2019 Sep 5;8(36):e00897-19. [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.-S., Lee, D.-H., Lee, K. H., Park, H.-M. in Bae, K. S. (1998). Cloning and phylogenetic analysis of chitin synthase genes from the insect pathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae var. anisopliae. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 159(1), 77-84. [CrossRef]
- Guo, W., Wang, W., Tang, J., Li, T. in Li, X. (2023). Genome analysis and genomic comparison of a fungal cultivar of the nonsocial weevil Euops chinensis reveals its plant decomposition and protective roles in fungus-farming mutualism. Frontiers in Microbiology, 14, 1048910. [CrossRef]
- Cherry A J, Moore D 2006. Infection Of The Non-Target Invertebrate Pests Bactrocera Dorsalis And Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Diptera: Tephritidae) With Metarhizium Anisopliae And Beauveria Bassiana. Biocontrol Science And Technology [J], 16: 701-713.
- Mantzoukas, S.; Kitsiou, F.; Lagogiannis, I.; Eliopoulos, P.A. Potential Use of Fusarium Isolates as Biological Control Agents: Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8918. [CrossRef]
- Jackson M A, Dunlap C A 2012. Laboratory Evaluation Of Isaria Fumosorosea CCM 8367 For Controlling Bactrocera Dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). Florida Entomologist [J], 95: 62-69. [CrossRef]
- Murtaza G, Naeem M, Manzoor S, Khan HA, Eed EM, Majeed W, Ahmed Makki H, Ramzan U, Ummara UE. Biological control potential of entomopathogenic fungal strains against peach Fruit fly, Bactrocera zonata (Saunders) (Diptera: Tephritidae). PeerJ. 2022 Apr 22;10:e13316. [CrossRef]
| Concentration | Female Insect | Male Insect |
|---|---|---|
| 1×104 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×105 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×106 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×107 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×108 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×109 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×1010 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×1011 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| Control | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| Total (Insect) | 810 | 810 |
| Contig Length (bp). | Contig Number | Contig N50 (bp) | Contig N90 (bp) | GC content (%) | Gaps Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 47,239,278 | 27 | 2,751,789 | 1,018,923 | 51.16 | 0 |
| Complete BUSCOs(C) | Complete and single-copy BUSCOs(S) | Complete and duplicated BUSCOs(D) | Fragmented BUSCOs(F) | Missing BUSCOs(M) | Total Lineage BUSCOs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 284 (97.93%) | 281 (96.90%) | 3 (1.03%) | 4 (1.38%) | 2 (0.69%) | 290 |
| Database | Number | 100<=length<300 | length>=300 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GO_Annotation | 9,994 | 2,279 | 7,603 |
| KEGG_Annotation | 3,775 | 913 | 2,788 |
| KOG_Annotation | 7,059 | 1,422 | 5,575 |
| Pfam_Annotation | 10,510 | 2,346 | 8,076 |
| Swissprot_Annotation | 8,390 | 1,692 | 6,608 |
| TrEMBL_Annotation | 13,862 | 3,729 | 9,992 |
| nr_Annotation | 13,864 | 3,730 | 9,993 |
| All_Annotated | 13,867 | 3,733 | 9,993 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





