1. Introduction
Burn lesions are a prominent contributor to both mortality and morbidity rates, and are considered to be a significant global health issue and socio-economic determinant. The treatment of burn injuries typically necessitates extended periods of hospitalization and rehabilitation, resulting in escalated healthcare expenditures. Infection has consistently been a significant concern in managing burn wounds. It can lead to significant complications, including the production of exudates, impaired wound healing, and abnormal collagen accumulation. The objective of burn treatment and therapy is to facilitate rapid healing and epithelization to mitigate the risk of infection. Topical therapy has a crucial role in enhancing the survival rates of individuals with significant burn injuries by effectively reducing the likelihood of burn wound infection [
1,
2,
3]. According to World Health Organization (WHO) estimates, there are approximately 11 million burn injury cases globally each year. In 2019, around 9 million cases of burns have been reported worldwide [
3]. Numerous microbes are associated with burn wound infections which include Gram-positive and negative aerobic/anaerobic bacteria, fungi and viruses [
4]. Sepsis can occur among individuals with more than 20% of their body area covered by burns. Most notably, 42% to 65% of deaths in this patient group are attributable to infection or sepsis [
5]. The WHO estimates that 180,000 people die every year from burn-associated injuries, with almost all of these deaths taking place in low- to middle-income nations [
6]. For decades, research on burns has attracted much attention, and numerous significant developments have led to improved treatment and lower fatality rates [
7].
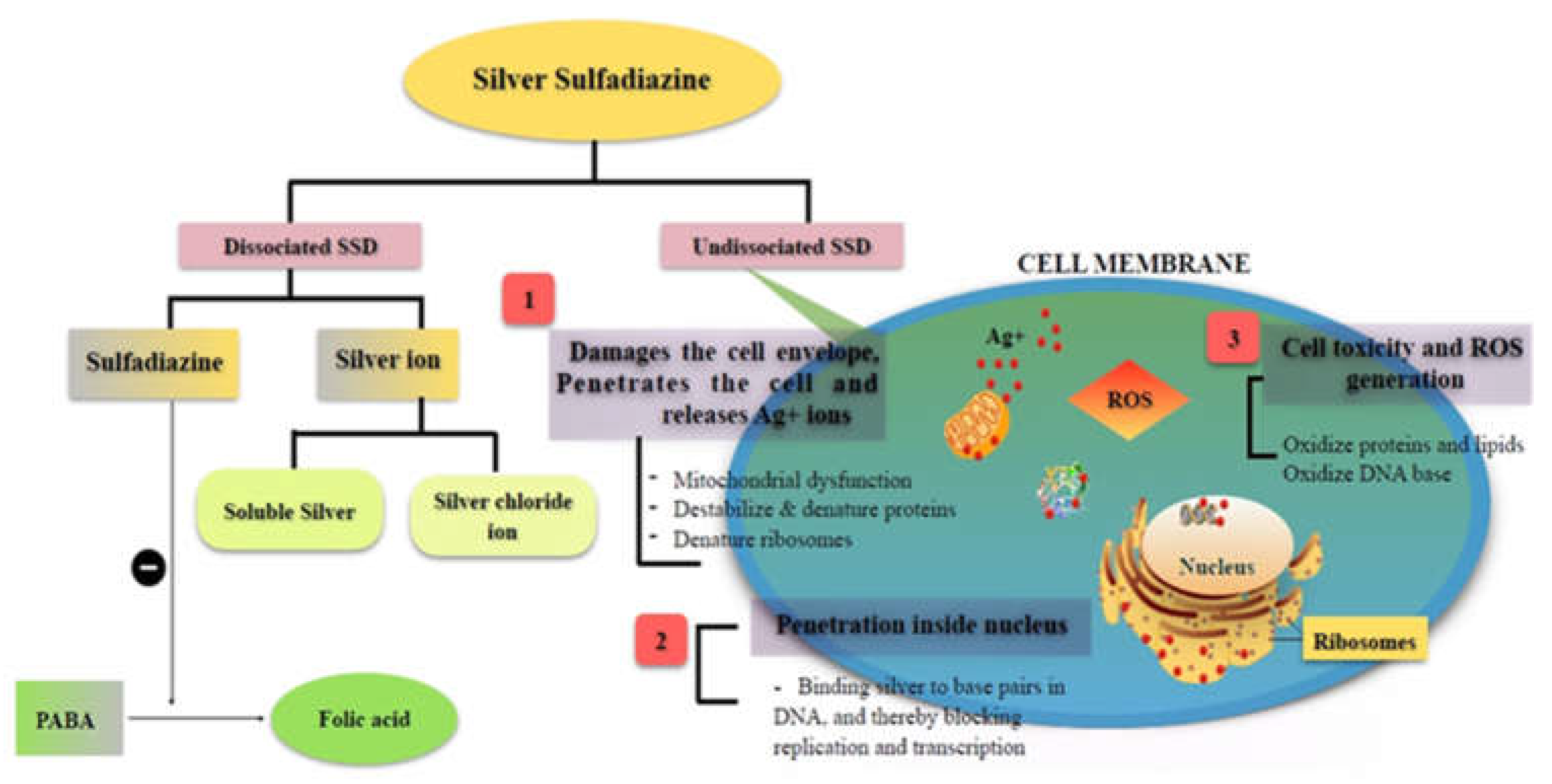
Presently, the gold standard for topical burn infections is silver sulfadiazine (SSD), a well-known bactericidal drug, for its ability to treat burn infections by targeting various cellular targets, as illustrated in
Figure 1 [
3,
8]. Silver sulfadiazine inhibits bacterial infection by attaching to the base pairs in the DNA helix and preventing the transcription process [
9]. Various SSD-based formulations are available in the market to treat burn infections [
10].
Despite immense promises, drawbacks like poor solubility, restricted bioavailability and unfavorable hematologic effects, SSD is still a good candidate for drug delivery research. Due to its low solubility and permeability, it is categorized in the biopharmaceutical classification as a class IV drug, which is the most challenging drug category [
11,
12]. Owing to these physiochemical challenges, there are biological challenges like variable absorption rate, topical bioavailability and efficacy [
13]. Using nanotechnology to address these problems appears to be a viable strategy [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. Drug delivery by nanocarrier can improve drug retention at the diseased target site inside the skin with adjustable release kinetics, enhanced permeation, and increased solubility in the biological system [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22]. For this developing a nanosuspension-based chitosan gel could be a novel strategy for the topical delivery of SSD, particularly in terms of improved drug solubility, effectiveness, uniform drug distribution on the skin, increased stability, and prolonged drug release [
23]. Chitosan is a gelling agent with good gel-forming properties, biodegradability, biocompatibility, and strong tissue adhesiveness [
24,
25]. It also provides a more uniform dispersion of SSD on the skin's surface and improves control over drug release kinetics to enhance burn wound infection control and maximize wound healing.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Silver sulphadiazine was purchased from (Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, India). Tween (20, 60, 80, and 85) and span (20, 40, 60, 80, and 85) were obtained from Hi-Media, Mumbai, India. Pluronic F-168 and F-127 were obtained from National Analytical Corporation, India. Chitosan was purchased from Panvo Organics Pvt Ltd, India. Methanol, acetonitrile, and ammonia solution were ordered from Ms.D D Patil Chemical, Jalgaon, Maharashtra, India.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of SSD Nanosuspension
The nanoprecipitation method was used to develop SSD nanosuspension [
26]. The required amount of SSD was dissolved in a 30% v/v ammonia solution. This ammonia solution was rapidly injected into a 5% w/v surfactant solution [
27]. The system was continuously stirred at 500 rpm on a magnetic stirrer. The system was neutralized using hydrochloric acid [
28]. The surfactant solution consisted of 5% (w/v) sorbitan monooleate, 5% (w/v) polysorbate 20 as a dispersing agent, and 0.5% (w/v) pluronic F68 as a co-surfactant/stabilizer.
2.2.2. Optimization of SSD Nanosuspension
Optimization of the formulation was executed using a one-factor-at-a-time approach. For optimizing the nanosuspension, the studied factors were surfactant, co-surfactant, and stabilizer. The components were optimized based on response variables such as particle size, z-average, and polydispersity index (PDI) values. Twelve different formulations were made using a mix of hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfactants in various amounts, while the drug concentration stayed the same (0.2% w/w, SSD). The batch of the developed formulation that exhibited low particle-settling behavior and the smallest particle size, together with the best stability, was selected as the optimum batch [
29].
2.2.3. Formulation of SSD-Chitosan Gel
The SSD-chitosan (SSD-CS) gel was formulated by adding an optimized SSD nanosuspension in pre-prepared high molecular weight chitosan gel. The 1.5% (w/v) chitosan was dissolved in 1% (v/v) of aqueous acetic acid and the mixture was continuously stirred at 1200 rpm using a magnetic stirrer. The SSD nanosuspension was added to the pre-prepared chitosan gel and stirred to get a smooth gel. Methyl paraben sodium salt (0.1%, w/w) as a preservative was added and stirred, and the resulting gel was sonicated to eliminate any remaining air bubbles. The developed gel was kept in closed containers at room temperature for further use [
30].
2.3. Characterization of SSD Nanosuspension and SSD-Chitosan Gel
2.3.1. Visual Observation
The optimized formulation was assessed for any visible unreconstructed particles and a distinctive opalescence of nanometric dimensions [
31].
2.3.2. Particle Size Analysis
The particle size of the optimized formulation was determined by employing the dynamic light scattering (DLS) technique using a Zetasizer (Nano–ZS, Malvern Ins. Ltd., UK). The nanosuspension (~0.1 mL) was maintained under observation at 25°C at a 90° angle after being suitably diluted with water and thoroughly blended with vigorous shaking [
32]. The aforementioned procedures were executed using DTS V–4.1 software (Malvern, UK) with the accompanying system. Three consecutive readings were recorded and reported as the mean result.
2.3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
The structural characteristics of 0.2% SSD nanosuspension were examined using transmission electron microscopy (TEM; JEM–1010, JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). The sample was analyzed using light microscopy operated at 80 kV, which had the potential to achieve point-to-point resolution. The image was magnified by a factor of 100,000. The bright field microscopy was used with increasing magnifications to construal the structure of the nanosuspension particles. A sufficiently diluted nanosuspension was placed on the holey film grid, negatively stained with a 2% solution of phosphotungstic acid, and dried before being examined under an electron microscope [
33].
2.3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
BRUKER Optik GmBH (Model ALPHA, Germany) FT-IR spectrometer was used to record and analyze the spectra of pure SSD and the SSD nanosuspension. The sample of SSD nanosuspension dispersion (~0.1 mL) was directly applied onto the KBr disc and scanned. The instrument was equipped with OPUS software version 7.8. The spectra were obtained for both samples at a resolution of 2 cm
−1, covering a scanning range of 500–4000 cm
−1 [
34].
2.3.5. Homogeneity, Physical Examination and pH
The physical examination involved visual inspection to assess the SSD-chitosan gel's separation and homogeneity. The digital pH meter (Microprocessor, pH system, Japan) was used to determine the pH of the optimized gel. All the assessments were performed in triplicate at a temperature of 25± 1ºC [
35].
2.3.6. Spreadability and Extrudability
The spreadability test was performed to determine SSD-chitosan gel's drag and slip properties. For this, the prepared gel (1g) was sandwiched between two slides, with the upper slide having a balance hook and the lower slide immobile. The time required to shift the upper slide from its original position when the weights were added to the balanced hook was recorded. All the measurements were performed in triplicate. The spreadability can be calculated by using equation 1.1 [
36].
In this context, the variables m, L, and t denote weight, fixed length, and time (measured in seconds) accordingly.
An experiment was performed to assess the extrudability of the gel from the collapsible tube by determining the weight necessary for extrusion. Briefly, the SSD-chitosan gel was filled in a collapsible tube, followed by applying incremental pressure for up to 10 seconds. The pressure or weight was recoded at which the ribbon of developed SSD-chitosan gel was extruded from the tube, reaching a distance of 0.5 cm. Extrudability was calculated using the following equation 1.2 [
37].
2.4. Ex-Vivo Skin Permeation Study
The dorsal skin was excised from a healthy Wistar female rat and used to perform the ex-vivo drug permeation study after approval from the Local Research Ethics Committee (LREC), University of Hafr Al Batin, KSA (Approval No.: UHB-005-11-2023). After the cervical dislocation of the rat for its sacrifice, the skin was taken out. The skin was cleaned three times with regular saline after the hair removal. The release of the drug was assessed from the SSD-CS gel and marketed gel cream (1%w/w) using a Franz diffusion cell. The available diffusion area of the cell was 3.14 cm2. An excised skin part was inserted between the donor and the receptor fluid of the Franz diffusion cells in such a way that the stratum corneum faces the donor, where the formulation to be examined is applied, while the dermis faces the receiver compartment. The permeation rate of the drug from the donor compartment through the skin into the receptor is determined by measuring the amount of drug permitted over time.
The diffusion medium was composed of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) of pH 7.4 and ammonium hydroxide (1:10, v/v with water) in the ratio 70:30. Ammonium hydroxide was added in the diffusion medium to uphold the sink condition. The receptor compartment of the Franz diffusion cell was filled with 10 ml of diffusion medium maintained at 32 ± 1 ºC and stirred at 30 rpm using a magnetic stirrer.
The SSD-CS gel and marketed cream were applied in infinite dose conditions (approx. 160 mg/cm
2) onto the mounted skin to determine permeation of drug across the skin barrier. At appropriate time intervals (0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 24 h), 2mL aliquot of the receptor medium was withdrawn and immediately replaced by an equal volume of the fresh diffusion medium (maintained at 32 ± 1 ºC) to ensure the sink conditions. SSD solubility in the diffusion medium was 50mg/mL, enough to guarantee sink conditions. The samples were filtered and analyzed using the HPLC method at λ
max of 254 nm. All the analyses were carried out in triplicate, and the values were averaged [
38,
39].
Permeation indicators, including flux and permeability coefficient, were computed for the SSD-CS gel and the commercially available gel cream (1%w/w). Linear regression analysis was employed to determine the flux(μg/cm
2.h) of the nanogel by analyzing the slope of the plot depicting the cumulative quantity of drug penetrated per cm
2 of the rat epidermal membrane in a steady state over time. Equation 2.1 was used to compute the drug's steady-state permeability coefficient (Kp) across the rat epidermal membrane.
In the above equation, C represents the initial drug concentration in the donor compartment, whereas J represents the flux.
2.5. Skin Irritation Study
In the skin irritation study, Wistar female rats weighing between 150 - 250 g were used. Animals were separated into four groups (n = 5). Depilatories were used to remove hair from the backs of rats, and a 4 cm
2 area was demarcated on both sides. One side is considered control, whereas the other is experimental. The animals were acclimatized for 24h, then the corresponding group received SSD-CS gel and marketed gel cream (1%) at a dose of 250 mg/rat daily for seven days. The observations were made for any sensitivity reaction. The graded sensitivity responses were as follows: A: no reaction; B: slight erythema with patches; C: slight erythema with confluent or moderate patches; D: moderate erythema; and E: severe erythema with or without edema [
40].
2.6. In-Vivo Burn Wound Study
Wistar female rats (4-6 weeks old; n=6/group) were employed for the assessment of the therapeutic potential of the developed SSD-CS gel and the marketed product using the well-established murine burn wound model [
41]. A total of twenty-four rats were housed in individual cages along with unlimited access to food (ad libitum) and water. Rats were anesthetized via intraperitoneal injection of a ketamine (50 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg) combination. Before the rats were injured, their dorsum hairs were plucked and they were then cleaned using isopropyl alcohol. Each rat was given a brass rod (10 mm x 10 mm) that had been heated in boiling water for 15 minutes, resulting in a second-degree dermal burn lesion after 45 seconds of exposure [
42]. The rats were subsequently given a subcutaneous injection of 0.9% NaCl solution. Five hours after the burn, 50 μL of an inoculum of
S. aureus containing 107 CFU/mL was administered topically to the burn site to infect. To ensure the rats' well-being, the rats were monitored twice a day. Burn wound-infected rats were divided into three groups: Group 1 served as the control (no treatment); Group 2 was treated daily for up to 10 days with 1% marketed gel cream (equivalent to 500 mg once a day) and Group 3 was treated daily for up to 10 days with SSD-CS gel (equivalent to 500 mg once a day). One group of animals was kept as a control group without any burns or treatments.
Every day, the experimental animals were observed, and the duration (measured in days) required for the wound to achieve complete epithelialization was used to calculate the healing time. Following burn wound grafting, the borders of the wound were sketched on transparent paper with a millimeter scale at 48h intervals for ten days of the experimental phase. The proportion of wound % contraction and epithelialization time accounted for total wound healing was examined. The wound area on day 0 was regarded as 100% in order to calculate the contraction of the wound (%) using the following equation Eq. (3.1).
Visual comparison analysis was conducted using images of the area affected by the burn lesion [
43].
2.7. Histopathological Study
Throughout the in-vivo burn wound model development, inflammation and edema were monitored at the burn site infected with S. aureus. The treated skin portion of rats in various groups was used to collect autopsy samples, which were then preserved in a 10% formalin solution for 24h. The samples were cleaned with tap water and then serially diluted with alcohol. After xylene was used to clean the specimens, paraffin was fixed for twenty-four hours at a temperature of 56°C. Using a sledge microtome, a slice of 4 μm regions was cut from paraffin tissue blocks. For the purpose of histopathological examination under an optical microscope, the skin tissue slices fixed on paraffin tissue blocks were placed on glass slides, deparaffinized, and then stained with hematoxylin and eosin dyes [
44].
2.8. Stability Study
Implementing the International Council for Harmonization (ICH) guidelines, the SSD-CS gel’s stability was evaluated for six months under the specified parameters of 40 ± 2˚C/75 % ± 5% RH and 25 ± 2˚C/60 % ± 5% RH under regulated conditions [
45]. The developed gel was sealed in tubes weighing 30 g (n=3) for each sampling time point (one, two, three, and six months). The tubes were then placed in a stability chamber measuring 1200 mm × 600 mm × 600 mm, which had temperature control over 20 to 60 ± 2°C and humidity control over 40% RH to 95% RH ± 5% RH. Along with the percentage drug test, the samples' pH, color change, grittiness, and viscosity were evaluated [
46].
2.9. Statistical Analysis
After performing a Student-Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons examination, all collected data were statistically examined using GraphPad-Prism 3.0 software for a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). An indication of a significant difference was taken to be a P value less than 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Formulation of Nanosuspension and SSD-CS Nanogel
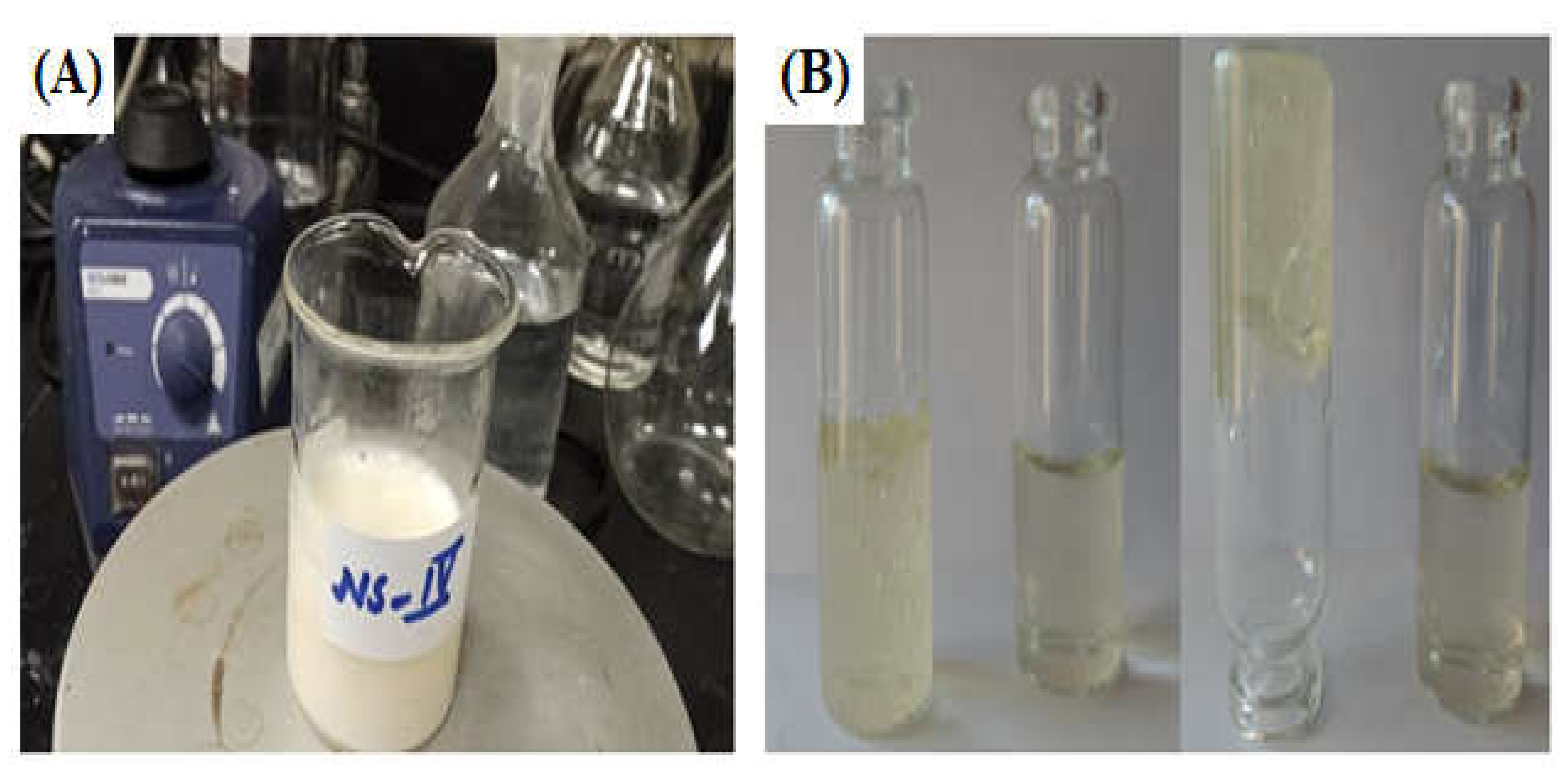
While employing an optimum blend of hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfactants together with a co-surfactant, SSD nanosuspension was developed (
Figure 2A). A combination of 5% (w/v) sorbitan monooleate, 5% (w/v) polysorbate 20, and 0.5% (w/v) pluronic F68 resulted in a more stable nanosuspension formulation with smaller particle sizes, 134.6 nm, as listed in
Table 1. The developed SSD nanosuspension was successfully incorporated into chitosan gel base (
Figure 2B), as per the process mentioned in the “MATERIALS AND METHODS" section. The developed SSD-CS nanogel was subjected to physical examinations, pH, homogeneity, spreadability, and extrudability.
3.2. Characterization of Nanosuspension and SSD-Chitosan Nanogel
3.2.1. Visual Observation
While observing a nanosuspension visually, it needs to assess some crucial factors to ensure both its stability and purity that add up to its aesthetic appeal [
47]. The nanosuspension was visually inspected for color, homogeneity, and clarity, as well as agglomeration and sedimentation [
48]. The resulting SSD nanosuspension had a distinctive opalescence that represented the dispersion of nanoparticulate drugs.
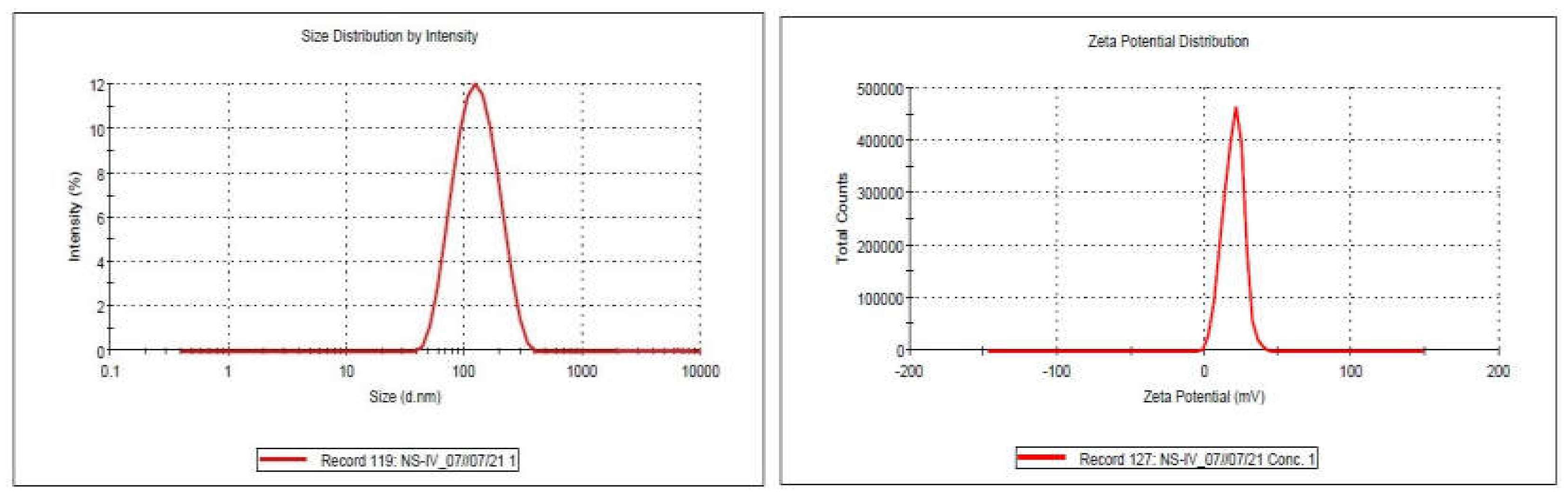
3.2.2. Determination Particle size and zeta potential
The nanosuspension's particle size measurement data is summarized in
Table 1, which shows that all of the observed dispersions had z-averages in the nanometer range. The nanodispersion exhibited a zeta potential of 19.6mv particles measuring 134.6 nm and a PDI of 0.317 (
Figure 3A,B).
3.2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
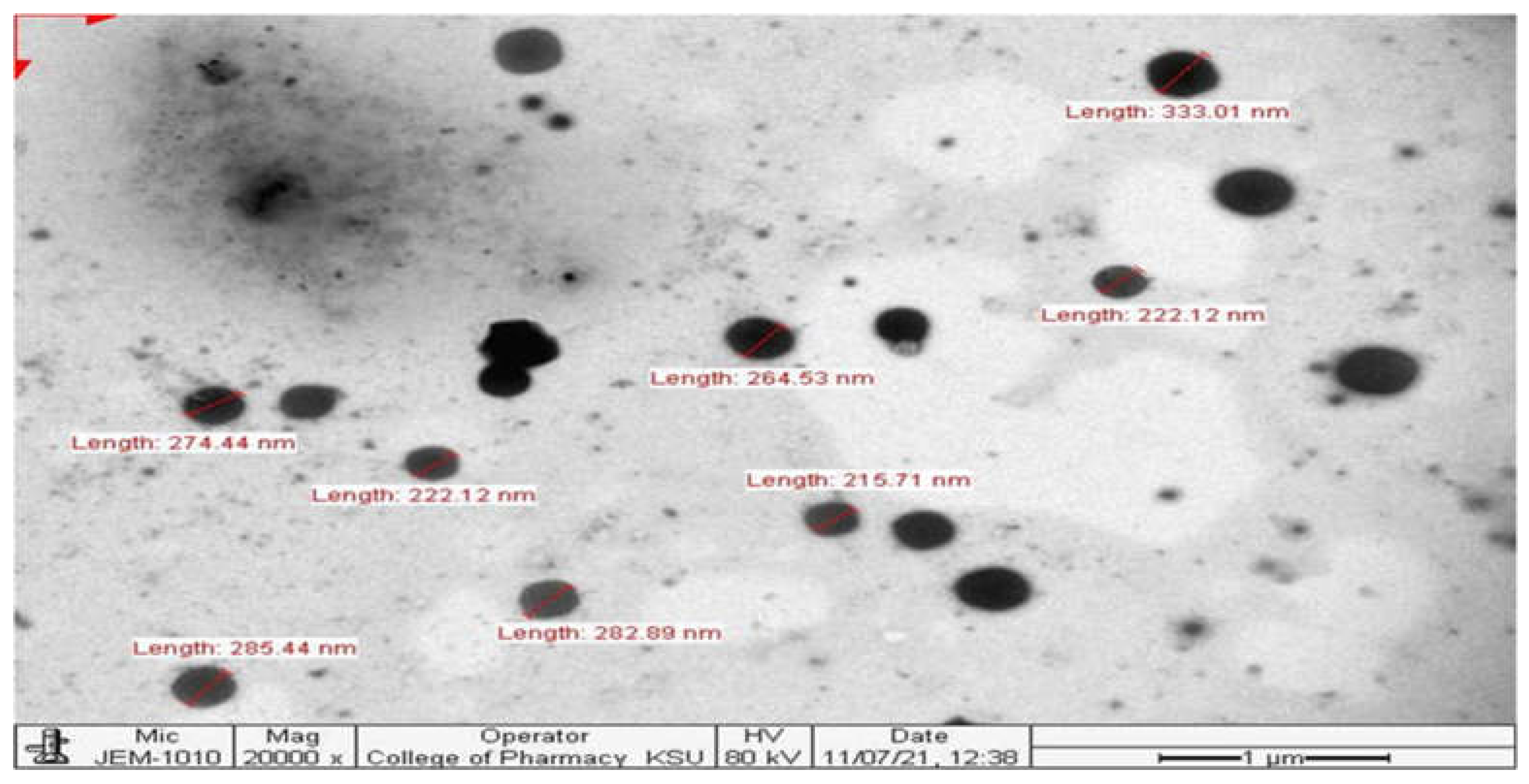
A uniform particle size distribution and a somewhat spherical surface were seen in the TEM picture of the SSD nanosuspension. The transmission electron micrograph was in consonance with the result of DLS, confirming the size range of SSD nanosuspension (
Figure 4).
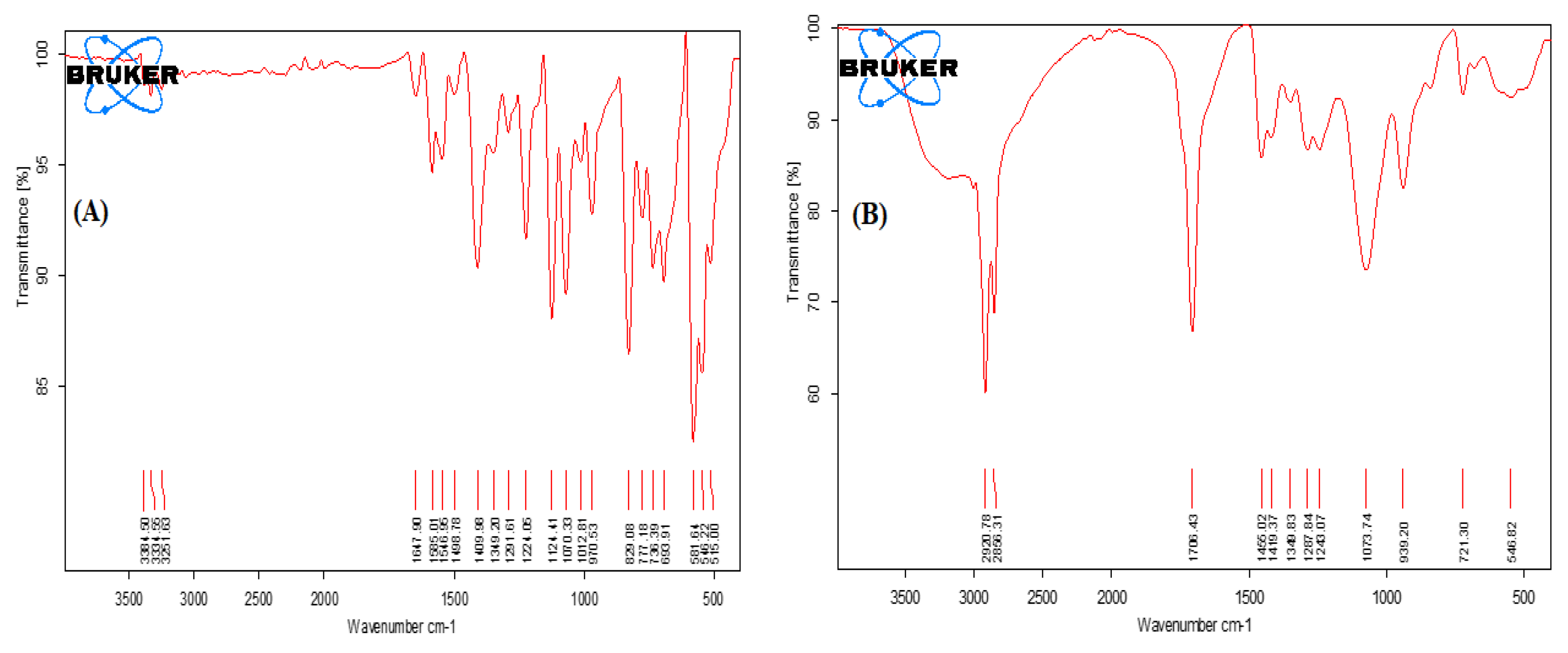
3.2.4. FTIR Studies
The FT-IR absorption spectra of SSD exhibit characteristic absorption bands, as shown in
Figure 5A. The primary peaks of SSD alone were observed at 3384.50 cm
−1, 3334.55 cm
−1, 3251.63 cm
−1, 1647 cm
−1, 1498.78 cm
−1, 1124.41 cm
−1, 970.53 cm
−1, 829.08 cm
−1 and 581.64 cm
−1 that confirmed the purity of drug sample as per established reports [
49]. In the FT-IR spectra of 0.2% SSD nanosuspension formulation (
Figure 5B), the major peaks of SSD were masked due to the overlapping with excipient peaks.
3.2.5. Determination of pH and Physical Evaluation of Nanogel
The developed SSD-CS nanogel does not show any sign of phase separation or cracking and exhibits a smooth texture as well as a slightly yellowish white homogenous colour. Also, the pH of the SSD-CS nanogel was found to be 7.02± 0.021 at 25 ± 1ºC temperature. The pH value ensured that the developed gel would be well tolerated by the skin [
50]. These findings demonstrate the gel's stability and their suitability for topical application.
3.2.6. Extrudability and Spreadability
The extrudability of prepared nanogel was observed to be 152.27±0.22g, which represents the easy extrusion of the nanogel from the tube. The spreadability of the nanogel was observed to be 5.21±0.38g.
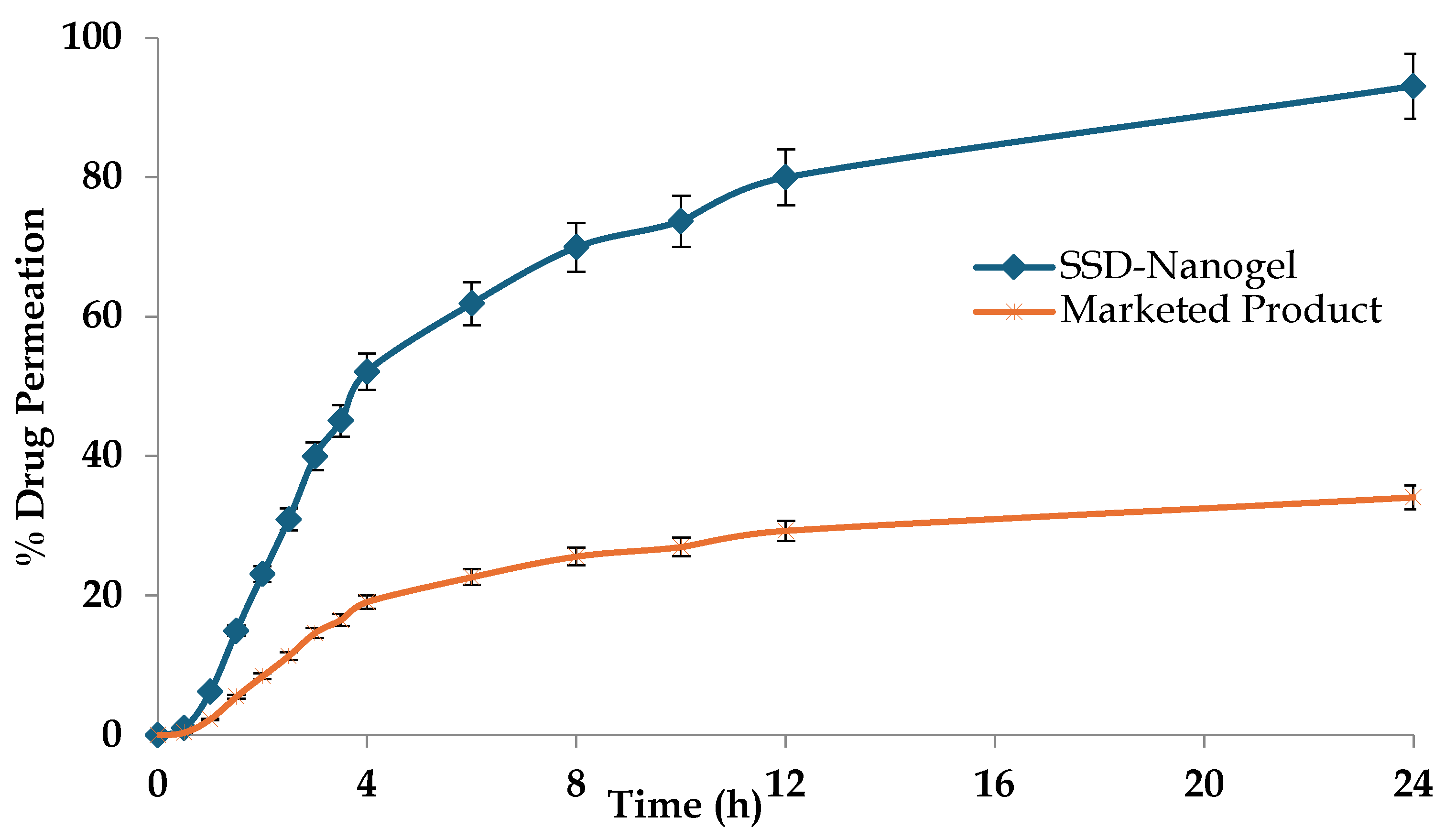
3.3. Ex-Vivo Skin Permeation Study
This study was performed in order to compare release profiles of SSD-CS nanogel and 1% marketed gel cream. In comparison with the commercial formulation, the prepared nanogel formulation exhibits a superior drug release profile (
Figure 6). The difference in the drug permeation profile is vivid across the excised rat skin. It has been observed that after 8 hours the drug permeation from the SSD-CS nanogel was 69.96 ± 2.32 %, significantly higher than the cream-based marketed product (25.63 ± 1.27%; p<0.05). The higher skin permeation of silver sulphadiazine may be attributed to several variables, such as the improved adhesion and penetration aided by the addition of chitosan gel, as well as the nano-scale size of the dispersion. The chitosan probably strengthened the contact with the skin and maybe accelerated the transportation of the drug, resulting in an improved administration of silver sulfadiazine via the skin. The average permeation flux values for SSD across the mouse skin were found to be 12.35 μg cm
2/h and 4.52 μg cm
2/h, respectively for the developed nanogel and the marketed product. The significant difference in the release flux shows the promises of the novel materials and carriers over the conventional dosage forms.
3.4. Skin Irritation Study
The primary irritation index of the SSD-CS nanogel was noted to be A; no reaction/no irritation was observed on the skin of the rats, while in the case of the marketed formulation, the primary irritation index was noted to be B. This may indicate that the SSD-CS nanogel is safe and compatible when applied to the skin [
51,
52].
3.5. In-Vivo Burn Wound Study
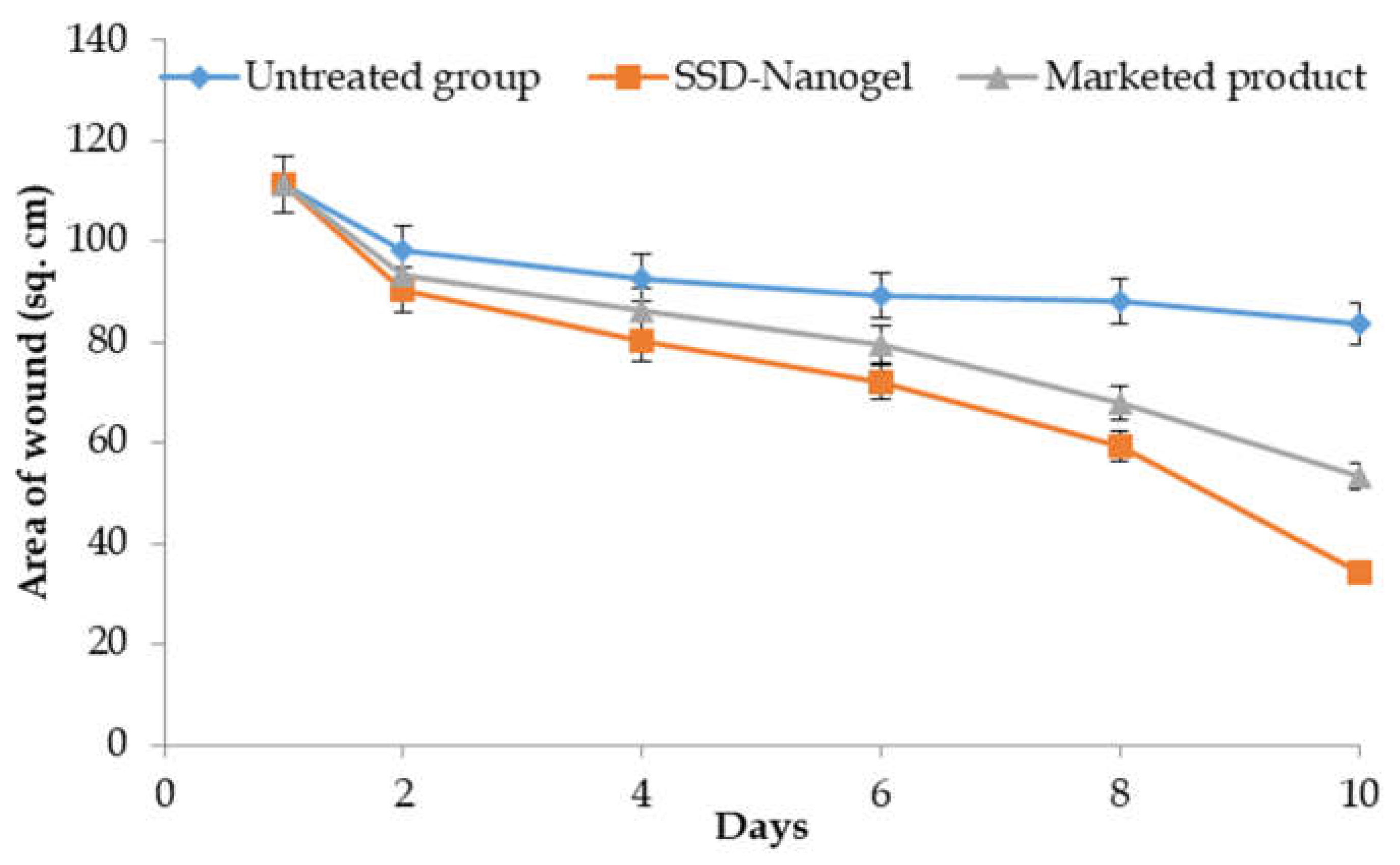
The results of the variation of the average lesion area of the wound on various days of the study are shown in
Figure 7. As clear from the picture, the wound area in the untreated rats group also decreased with time, however, the pace of recovery was relatively low. On the other hand, the developed nanogel resulted in fast shrinkage and re-epithelialization of the wound. There was around 25% wound constriction in the control group over the period of the study, i.e., 75 % of wound area was still there. On the other hand, the group receiving the marketed product exhibited 52% of wound constriction and the developed nanogel offered 69% of the wound healing at the end of the 10-day study. The better permeation and retention of the drug by means of the designed system resulted in a better localization of the drug and a better re-epithelialization process. The marketed product also offered promising results, though of lower magnitude than the developed formulation, owing to differences in the architectural framework that have resulted in relatively poorer permeation and retention, as vouched by permeation studies.
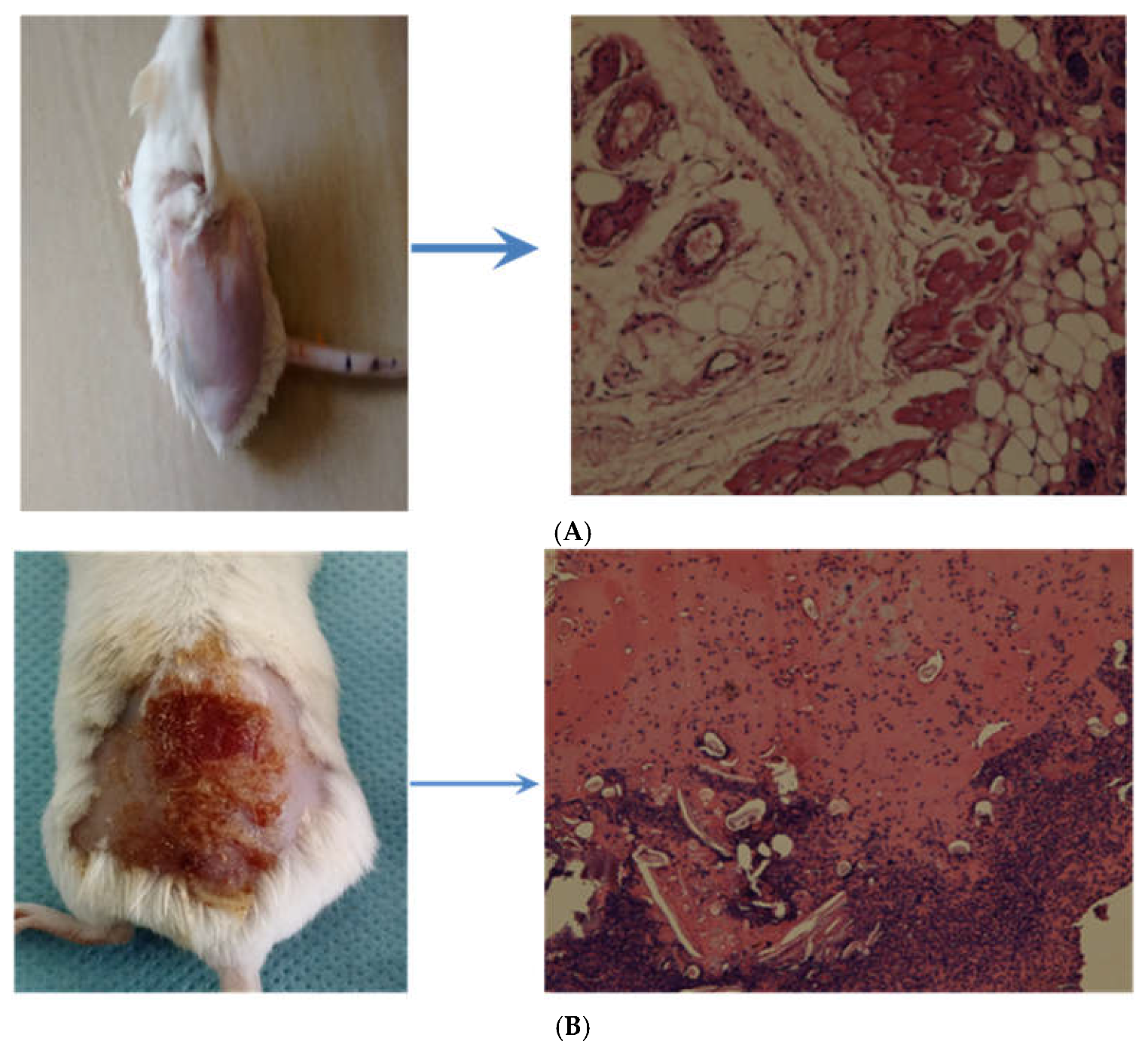
Figure 8A shows the images of the skin of a normal rat without any deviation from the normal histopathology.
Figure 8B shows the disease-induced skin lesions of the wound and the signs of skin damage.
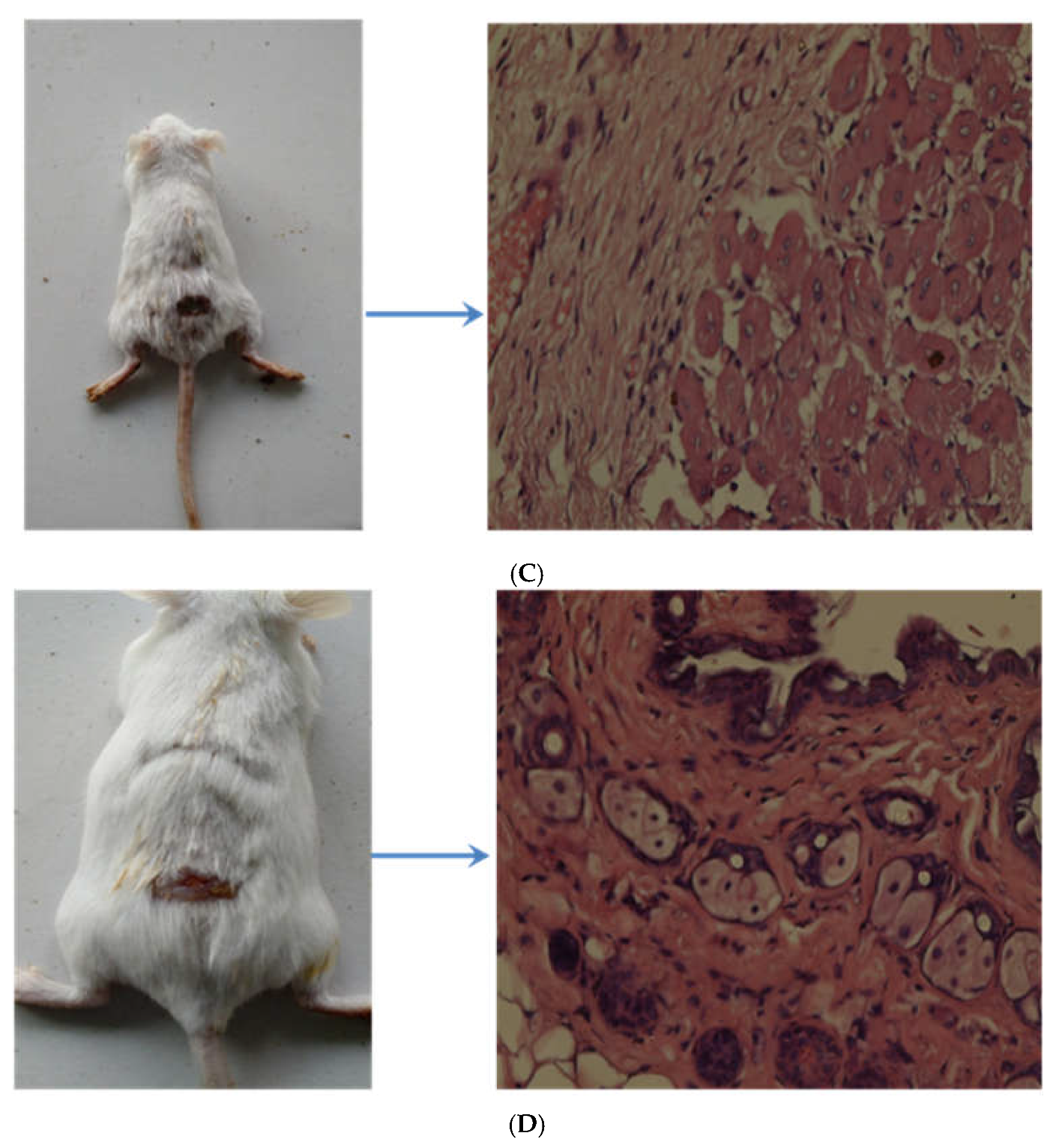
Figure 8C shows the 10th day slide of the rat, where there are conspicuous signs of re-epithelialization and wound healing induced by the marketed product and the same has been further improved by the developed nanogel system as depicted in
Figure 8D.
3.6. Stability Study
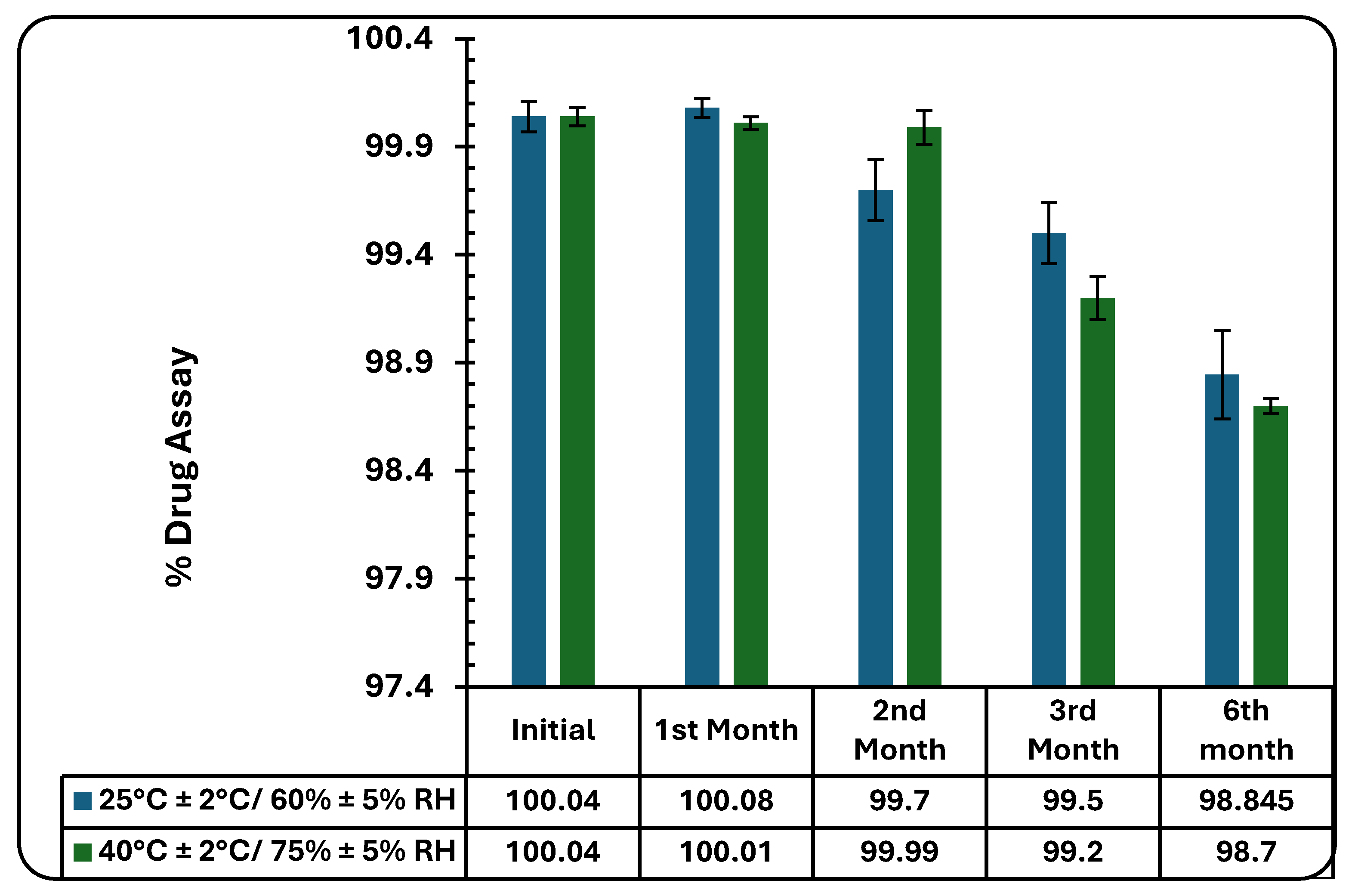
The results obtained from the stability studies of the developed nanogel at ICH prescribed conditions of 40˚C ± 2˚C/75 % ± 5% RH and the controlled conditions of 25˚C ± 2˚C/60 % ± 5% RH have been shown in
Figure 9 and
Table 2.
The % assay of the developed gel decreased from 100.04 ± 5.16% to 98.85 ± 3.19% at 25 ± 2˚C/60 % ± 5% RH and to 98.70 ± 2.73% at 40 ± 2˚C/75 % ± 5% RH over a period of six months. The changes in the drug assays at both the studied conditions were non-significant (p<0.05). Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3).
4. Discussion
SSD nanosuspension-based chitosan-derived nanogel was prepared using nanoprecipitation and ultrasonication methods. The optimized formulation was characterized by particle size in the nanometric range. The results confirmed a sub-micron nanodispersion in accordance with the published literature [
53]. The positive surface charge is ascribable to the protonated amine group and silver ions of SSD [
54]. The PDI was also in the range vouching for the reliability of the dispersed system micromeritic profile [
53]. The homogenous nature of the nanosuspension was highlighted by the TEM image, which showed a uniform and well-defined particle size distribution. The stability and quality of the nanosuspension were further highlighted by the lack of anomalies or agglomerations [
55].
Furthermore, FTIR spectra of plain drug and formulation suggest that no chemical interaction between the drug and excipients was found. The formulation spectra exhibited most of the characteristic peaks with insignificant shifts and lesser intensities as compared to the pure drug. These results demonstrated that SSD gets transformed into nanosuspension and is not involved in any chemical interaction with the nanosuspension's constituent parts. The surfactants' ability to maintain the structural integrity of SSD also reflected its ability to maintain its effectiveness [
56]. In addition, the outcome of the spreadability examination shows that the prepared gel could be easily spread onto the skin. A topical formulation's spreadability is an important factor since it directly affects the product's efficacy and application experience. Based on the measured value, it appears that the SSD-CS nanogel has good spreading properties that allow for an even and smooth application throughout the skin's surface [
57]. Besides that, the stability of the developed nanogel was assessed as per ICH guidelines. There was no crystal formation and color changes observed in the gel, indicating that the developed system exhibits substantial chemical and physical stability. No odor developed after storage and no gas formation was observed even after sealed pack storage at these two conditions for six months. During this study, the developed gel maintained its consistency and was devoid of weeping, oozing, and grittiness. The stability studies confirmed that the developed gel offered substantial chemical stability to the SSD and also exhibited appreciable physical stability over a period of 6 months in an accelerated as well as controlled environment [
58].
Ex-vivo skin permeation and in-vivo burn wound studies showed the potential of formulation in improved therapeutic efficacy and burn wound healing. In comparison with the marketed formulation, nanosuspension-based nanogel has shown a better drug release profile. The possible reasons for the better skin permeation of the SSD could be due to the better adhesion and permeation owing to chitosan incorporated in the gel and the nano-size of the developed dispersion. The chitosan might have enhanced the contact with the skin and plausibly assisted in the transport of the drug resulting in the enhanced topical delivery of SSD. Moreover, the efficacy of SSD(0.2%w/v) nanosuspension-based chitosan nanogel was more pronounced than the 1% marketed product and the safety was enhanced. The better permeation and retention of the drug by means of the designed system resulted in a better localization of the drug and a better re-epithelialization process. The nanosized SSD having a large surface area helps in faster interaction with bacteria.3 Hence, SSD-CS nanogel shows higher efficacy in contrast to marketed preparation with micron-sized drug particles. The outcomes obtained from the in vivo study are agreeable with the literature.
We can make a conclusion that in contrast to the marketed formulation, the release of SSD from nanogel was enhanced, which would likely improve antimicrobial activity toward infection. Therefore, SSD nanosuspension-based chitosan-derived nanogel has a high potential to improve the outcomes in the treatment of burn wound infections.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.B and H.A.H; methodology, H.B and H.A.H; software, H.B, M.A.B, and R.A.; validation, H.B, M.A.B. and H.A.H; formal analysis, H.A.H and R.A; investigation, H.B.; resources, H.B.; data curation, H.B and R.A; writing—original draft preparation, H.B and M.A.B; writing—review and editing, H.A.H and R.A; visualization, M.A.B.; supervision, H.A.H and R.A; project administration, H.AH; funding acquisition, H.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by Local Research Ethics Committee (LREC), University of Hafr Al Batin, KSA (Approval No.: UHB-005-11-2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
None.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest.
References
- Chaudhary NA, Munawar MD, Khan MT, et al. Epidemiology, Bacteriological Profile, and Antibiotic Sensitivity Pattern of Burn Wounds in the Burn Unit of a Tertiary Care Hospital. Cureus. 2019;11(6):e4794. [CrossRef]
- Jeschke MG, van Baar ME, Choudhry MA, Chung KK, Gibran NS, Logsetty S. Burn injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6(1):11. [CrossRef]
- Abul Barkat H, Abul Barkat M, Ali R, Hadi H, Kasmuri AR. Old Wine in new Bottles: Silver Sulfadiazine Nanotherapeutics for Burn Wound Management. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2023:15347346231166980. [CrossRef]
- Maitz J, Merlino J, Rizzo S, McKew G, Maitz P. Burn wound infections microbiome and novel approaches using therapeutic microorganisms in burn wound infection control. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023;196:114769. [CrossRef]
- Kelly EJ, Oliver MA, Carney BC, Shupp JW. Infection and Burn Injury. European Burn Journal. 2022; 3(1):165-179. [CrossRef]
- Zhang P, Zou B, Liou YC, Huang C. The pathogenesis and diagnosis of sepsis post burn injury. Burns Trauma. 2021;9:tkaa047. [CrossRef]
- Hamblin MR. Novel pharmacotherapy for burn wounds: what are the advancements. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019;20(3):305-321. [CrossRef]
- Levin NJ, Erben Y, Li Y, Brigham TJ, Bruce AJ. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Comparing Burn Healing Outcomes Between Silver Sulfadiazine and Aloe vera. Cureus. 2022;14(10):e30815. [CrossRef]
- Thakur K, Mahajan A, Sharma G, et al. Implementation of Quality by Design (QbD) approach in development of silver sulphadiazine loaded egg oil organogel: An improved dermatokinetic profile and therapeutic efficacy in burn wounds. Int J Pharm. 2020;576:118977. [CrossRef]
- Elshamy AI, Ammar NM, Hassan HA, et al. Topical Wound Healing Activity of Myricetin Isolated from Tecomaria capensis v. aurea. Molecules. 2020;25(21):4870. [CrossRef]
- Fatima Q-ua, Ahmed N, Siddiqui B, Rehman Au, Haq Iu, Khan GM, Elaissari A. Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Sulfadiazine Cosmetotherapeutic Nanolotion for Burn Infections. Cosmetics. 2022; 9(5):93. [CrossRef]
- Orbay H, Ziembicki JA, Yassin M, Egro FM. Prevention and Management of Wound Infections in Burn Patients. Clin Plast Surg. 2024;51(2):255-265. [CrossRef]
- Ezike TC, Okpala US, Onoja UL, et al. Advances in drug delivery systems, challenges and future directions. Heliyon. 2023;9(6):e17488. [CrossRef]
- Kim EA, Park JS, Kim MS, et al. High-Payload Nanosuspension of Centella asiatica Extract for Improved Skin Delivery with No Irritation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:7417-7432. [CrossRef]
- Abruzzo A, Parolin C, Rossi M, Vitali B, Cappadone C, Bigucci F. Development and Characterization of Azithromycin-Loaded Microemulsions: A Promising Tool for the Treatment of Bacterial Skin Infections. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022;11(8):1040. [CrossRef]
- Raza K, Kumar M, Kumar P, et al. Topical delivery of aceclofenac: challenges and promises of novel drug delivery systems. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:406731. [CrossRef]
- Katare OP, Raza K, Singh B, Dogra S. Novel drug delivery systems in topical treatment of psoriasis: rigors and vigors. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2010;76(6):612-621. [CrossRef]
- Jo JK, El-Fiqi A, Lee JH, Kim DA, Kim HW, Lee HH. Rechargeable microbial anti-adhesive polymethyl methacrylate incorporating silver sulfadiazine-loaded mesoporous silica nanocarriers. Dent Mater. 2017;33(10):e361-e372. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian S, Ghorbani M, Mahmoodzadeh F. Silver sulfadiazine-loaded electrospun ethyl cellulose/polylactic acid/collagen nanofibrous mats with antibacterial properties for wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;162:1555-1565. [CrossRef]
- Nqakala ZB, Sibuyi NRS, Fadaka AO, Meyer M, Onani MO, Madiehe AM. Advances in Nanotechnology towards Development of Silver Nanoparticle-Based Wound-Healing Agents. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(20):11272. [CrossRef]
- Bhandari S, Rathore K.S. Formulation and evaluation of nano-ethogel of silver sulfadiazine for treatment of topical burns. IP Int. J. Compr. Adv. Pharmacol. 2023;7:195–202. [CrossRef]
- El-Feky GS, El-Banna ST, El-Bahy GS, Abdelrazek EM, Kamal M. Alginate coated chitosan nanogel for the controlled topical delivery of Silver sulfadiazine. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;177:194-202. [CrossRef]
- Shen C, Shen B, Liu X, Yuan H. Nanosuspensions based gel as delivery system of nitrofurazone for enhanced dermal bioavailability. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2018;43:1–11. [CrossRef]
- Shariatinia Z, Jalali AM. Chitosan-based hydrogels: Preparation, properties and applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;115:194-220. [CrossRef]
- Thakur CK, Thotakura N, Kumar R, et al. Chitosan-modified PLGA polymeric nanocarriers with better delivery potential for tamoxifen. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;93(Pt A):381-389. [CrossRef]
- Koca M, Sevinç Özakar R, Ozakar E, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Nanosuspensions of Triiodoaniline Derivative New Contrast Agent, and Investigation into Its Cytotoxicity and Contrast Properties. Iran J Pharm Res. 2022;21(1):e123824.s. [CrossRef]
- Özdemir S, Üner B, Karaküçük A, Çelik B, Sümer E, Taş Ç. Nanoemulsions as a Promising Carrier for Topical Delivery of Etodolac: Formulation Development and Characterization. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(10):2510. [CrossRef]
- Mou D, Chen H, Wan J, Xu H, Yang X. Potent dried drug nanosuspensions for oral bioavailability enhancement of poorly soluble drugs with pH-dependent solubility. Int J Pharm. 2011;413(1-2):237-244. [CrossRef]
- Gajera BY, Shah DA, Dave RH. Development of an amorphous nanosuspension by sonoprecipitation-formulation and process optimization using design of experiment methodology. Int J Pharm. 2019;559:348-359. [CrossRef]
- Oktay AN, Ilbasmis-Tamer S, Han S, Uludag O, Celebi N. Preparation and in vitro / in vivo evaluation of flurbiprofen nanosuspension-based gel for dermal application. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020;155:105548. [CrossRef]
- Aldeeb MME, Wilar G, Suhandi C, Elamin KM, Wathoni N. Nanosuspension-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Topical Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:825-844. [CrossRef]
- Ho HN, Le TG, Dao TTT, et al. Development of Itraconazole-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticle Dermal Gel for Enhanced Antifungal Efficacy, J. Nanomater. 2020;2020. [CrossRef]
- Zaid Alkilani A, Hamed R, Abdo H, et al. Formulation and Evaluation of Azithromycin-Loaded Niosomal Gel: Optimization, In Vitro Studies, Rheological Characterization, and Cytotoxicity Study. ACS Omega. 2022;7(44):39782-39793. [CrossRef]
- Barkat MA, Harshita, Ahmad I, et al. Nanosuspension-Based Aloe vera Gel of Silver Sulfadiazine with Improved Wound Healing Activity. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017;18(8):3274-3285. [CrossRef]
- Dantas MG, Reis SA, Damasceno CM, et al. Development and Evaluation of Stability of a Gel Formulation Containing the Monoterpene Borneol. ScientificWorldJournal. 2016;2016:7394685. [CrossRef]
- Kola-Mustapha AT, Yohanna KA, Ghazali YO, Ayotunde HT. Design, formulation and evaluation of Chasmanthera dependens Hochst and Chenopodium ambrosioides Linn based gel for its analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities. Heliyon. 2020;6(9):e04894. [CrossRef]
- Oktay AN, Ilbasmis-Tamer S, Uludag O, Celebi N. Enhanced Dermal Delivery of Flurbiprofen Nanosuspension Based Gel: Development and Ex Vivo Permeation, Pharmacokinetic Evaluations. Pharm Res. 2021;38(6):991-1009. [CrossRef]
- Elshall AA, Ghoneim AM, Abdel-Mageed HM, Osman R, Shaker DS. Ex vivo permeation parameters and skin deposition of melatonin-loaded microemulsion for treatment of alopecia, Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022;8:28. [CrossRef]
- Tas C, Ozkan Y, Okyar A, Savaser A. In vitro and ex vivo permeation studies of etodolac from hydrophilic gels and effect of terpenes as enhancers. Drug Deliv. 2007;14(7):453-459. [CrossRef]
- Rahman SA, Abdelmalak NS, Badawi A, Elbayoumy T, Sabry N, El Ramly A. Formulation of tretinoin-loaded topical proniosomes for treatment of acne: in-vitro characterization, skin irritation test and comparative clinical study. Drug Deliv. 2015;22(6):731-739. [CrossRef]
- Rahman MS, Islam R, Rana MM, et al. Characterization of burn wound healing gel prepared from human amniotic membrane and Aloe vera extract. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19(1):115. Published 2019 Jun 3. [CrossRef]
- Ito K, Saito A, Fujie T, et al. Sustainable antimicrobial effect of silver sulfadiazine-loaded nanosheets on infection in a mouse model of partial-thickness burn injury. Acta Biomater. 2015;24:87-95. [CrossRef]
- Tazeze H, Mequanente S, Nigussie D, Legesse B, Makonnen E, Mengie T. Investigation of Wound Healing and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Leaf Gel of Aloe trigonantha L.C. Leach in Rats. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:5567-5580. Published 2021 Oct 28. [CrossRef]
- Ali Khan B, Ullah S, Khan MK, Alshahrani SM, Braga VA. Formulation and evaluation of Ocimum basilicum-based emulgel for wound healing using animal model. Saudi Pharm J. 2020;28(12):1842-1850. [CrossRef]
- González-González O, Ramirez IO, Ramirez BI, et al. Drug Stability: ICH versus Accelerated Predictive Stability Studies. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(11):2324. [CrossRef]
- Sah A, Aggarwal G, Jain GK, Zaidi SMA, Naseef PP, Kuruniyan MS, Zakir F. Design and Development of a Topical Nanogel Formulation Comprising of a Unani Medicinal Agent for the Management of Pain. Gels. 2023; 9(10):794. [CrossRef]
- Aghajani MH, Pashazadeh AM, Mostafavi SH, et al. Size Control in the Nanoprecipitation Process of Stable Iodine (¹²⁷I) Using Microchannel Reactor-Optimization by Artificial Neural Networks. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015;16(5):1059-1068. [CrossRef]
- Uma Maheswari R, Mullaicharam AR. Development and in-vitro evaluation of nanosuspension formulation containing acyclovir for the treatment of ocular infections, Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2013;4:463–480.
- Yaşayan G, Chitosan films and chitosan/pectin polyelectrolyte complexes encapsulating silver sulfadiazine for wound healing, İstanbul J. Pharm. 2020;50:1–7. [CrossRef]
- Lukić M, Pantelić I, Savić SD. Towards Optimal pH of the Skin and Topical Formulations: From the Current State of the Art to Tailored Products. Cosmetics. 2021; 8(3):69. [CrossRef]
- Sindhu RK, Gupta R, Wadhera G, Kumar P. Modern Herbal Nanogels: Formulation, Delivery Methods, and Applications. Gels. 2022; 8(2):97. [CrossRef]
- Guzmán E, Ortega F, Rubio RG. Chitosan: A Promising Multifunctional Cosmetic Ingredient for Skin and Hair Care. Cosmetics. 2022; 9(5):99.
- Alkholifi FK, Alam A, Foudah AI, Yusufoglu HS. Phospholipid-Based Topical Nano-Hydrogel of Mangiferin: Enhanced Topical Delivery and Improved Dermatokinetics. Gels. 2023;9(3):178. [CrossRef]
- Martins AF, Facchi SP, Follmann HD, Pereira AG, Rubira AF, Muniz EC. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan derivatives containing N-quaternized moieties in its backbone: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(11):20800-20832. [CrossRef]
- He J, Han Y, Xu G, et al. Preparation and evaluation of celecoxib nanosuspensions for bioavailability enhancement, RSC Adv. 2017;7:13053–13064. [CrossRef]
- Shadab NA, Alhakamy S, Akhter ZAY, et al. Development of polymer and surfactant based naringenin nanosuspension for improvement of stability, antioxidant, and antitumour activity, J. Chem. 2020;2020. [CrossRef]
- Niu J, Yuan M, Gao P, et al. Microemulsion-Based Keratin-Chitosan Gel for Improvement of Skin Permeation/Retention and Activity of Curcumin. Gels. 2023;9(7):587. [CrossRef]
- Aghrbi I, Fülöp V, Jakab G, Kállai-Szabó N, Balogh E, Antal I. Nanosuspension with improved saturated solubility and dissolution rate of cilostazol and effect of solidification on stability, J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021;61:102165. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).