1. Introduction
Infection of wounds delays healing through several mechanisms: release of harmful enzymes and radicals by activated neutrophils, buildup of metabolic waste, tissue hypoxia, fragile granulation tissue, decreased fibroblast numbers, reduced collagen production, and impaired reepithelialization [
1,
2]. Microbes contaminating the wounds often form biofilms that protect them from the immune system and antibiotics, which enhances their survival and pathogenicity, promotes development of microbial resistance to treatment, and delays wound healing leading to wound chronicity [
1,
2,
3]. Microbial wound infection causes a significant burden to patients and to the health care systems [
4,
5], especially with the surge of antibiotic resistant microorganisms. Reducing microbial contamination enhances wound healing [
6].
Copper, and cuprous oxide in particular, have wide spectrum potent inherent antimicrobial properties [
7,
8,
9]. Previously we have described the
in vitro potent wide spectrum antimicrobial efficacy of copper oxide microparticles impregnated dressings [
10], hereafter termed COD. The COD are in clinical use for the management of acute and chronic wounds since 2020. Studies conducted with the COD demonstrated the capacity of the COD to stimulate wound healing, even of hard-to-heal chronic wounds that did not respond favorably to other wound management interventions [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. In the current study, we analyzed the morphological effects of the COD on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria exposed to the dressings, by using scanning electron microscopy analyses.
2. Materials and Methods
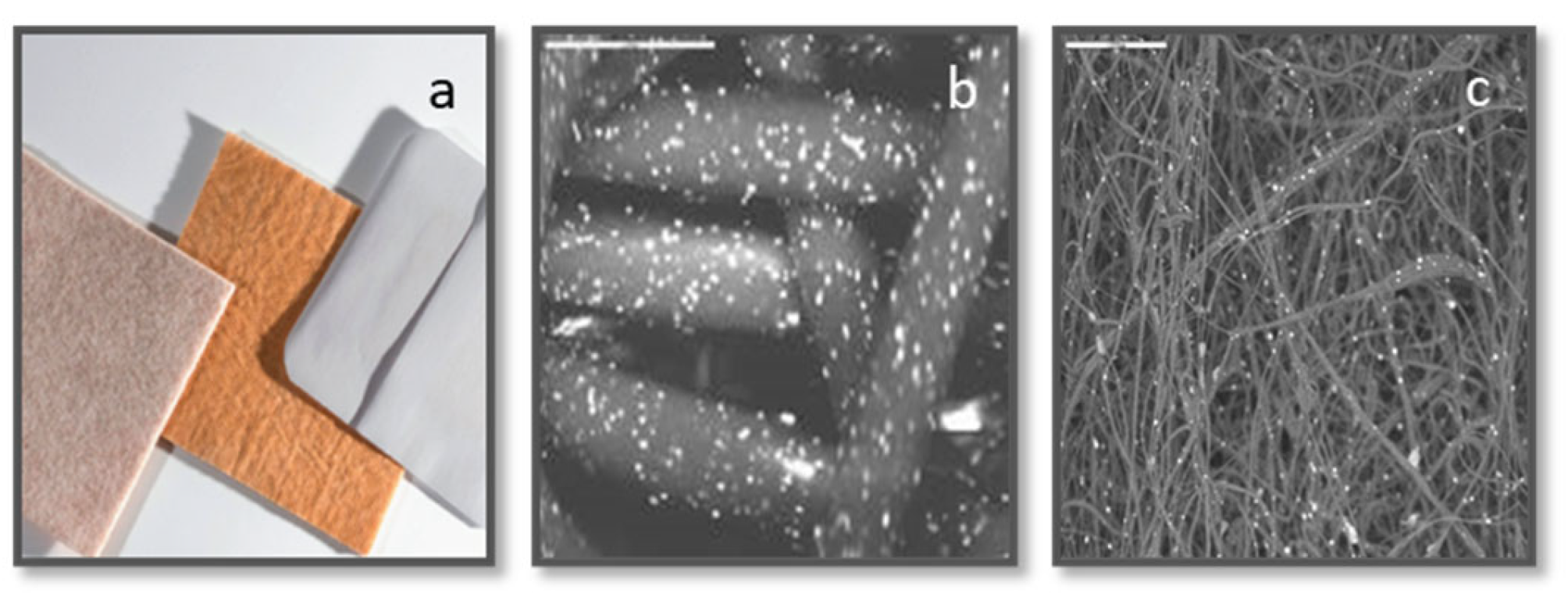
COD (
Figure 1), described previously [
10], and wound dressings without copper with a similar polymer component content and construction (3M Life Sterile Dressings; Hubei Qianjiang Kingphur Medical Materials Co Ltd, China), were used as test and control dressings, respectively.
A bacterial mix was prepared from the following organisms: Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA; ATCC BAA-1708); Escherichia coli (ATCC 8739); Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC 4352); and Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 19439). Each microorganism was grown overnight at 37±2ºC in Tryptic soy broth (TBS; Hy laboratories Ltd., Rehovot, Israel). Then 10 µl of each of the overnight cultures were mixed in 1 mL of TBS and grown at 37±2ºC for 7 hours, in replicates, followed by centrifugation. The pellets were resuspended in 600 µl of 0.85% saline/0.1% Tween 80 (ST; Sigma Aldrich Israel Ltd.) and served as the stock bacterial mix (SBM) for the dressing inoculation.
Duplicate 0.5 cm x 0.5 cm square swatches from each test and control wound dressing were aseptically cut and each individual swatch was put in an Eppendorf tube. Fifty µl of the SBM were added to each swatch, making sure that all liquid was completely absorbed by the control and test swatch samples. The swatches were then incubated at 37±2ºC for 0, 1, 2 or 3 hours.
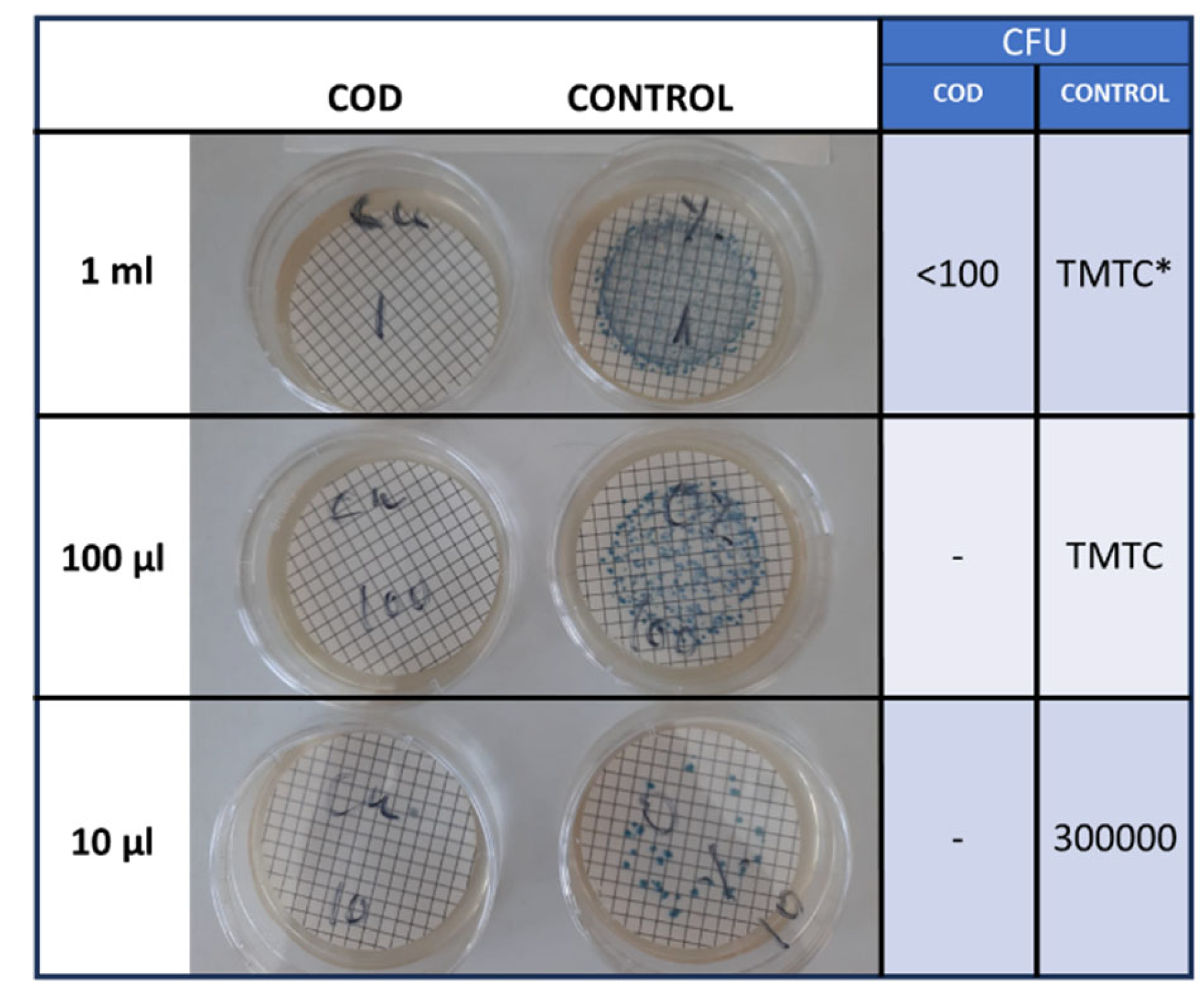
For bacterial viability determination following exposure to the dressings, duplicate sterile swatches of the control and test samples were transferred to containers with 100 mL of neutralizing solution (DeyEngley (D/E) Broth; LAB187, Lab M Limited, UK), then to sterile stomager bags (Alex Red Ltd. Mevasseret Zion, Israel). The bags were stomached for 2 minutes and 10 µl, 100 µl, and 1 mL of each liquid were filtered through 0.45 µm Cellulose Nitrate Filters (Sartorious Stedim Biotech GmbH, Germany) by using a Pall filtration device (Pall Corporation, Port Washington, New York, USA). The filters were rinsed twice with 100±5 mL of ST and then incubated on CHROMagar™ Orientation agar (
http://www.chromagar.com) at 37±2ºC for 24 hours. Colony Forming Units (CFU) were then counted.
For morphological analysis of the bacteria exposed to the dressings, 1 mL of ST was added to the remaining swatches, and bacteria were recovered by 3 minutes of centrifugation at 1200 rpm. The swatches were removed and the bacterial pellets were transferred to circular glass coverlips placed in a 96-well plate and pretreated with 0.01% poly-l-lysine (Sigma-Aldrich Chemie Gmbh, USA) for 60 minutes in order to attach the bacteria to the plates. The bacteria were then fixed with 2% glutaraldehyde and 2% formaldehyde in 0.1M phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) for 1 hour at room temperature. The fixatives were rinsed out by 3 consecutive washes every 10 minutes with 200 µl 0.1M phosphate buffer (pH 7.2). The bacteria were then dehydrated by exposing them to increasing ethanol concentrations (20%, 50% 70%, 90%, 95%) each two times for 10 minutes, and finally 100% ethanol concentration four times for 10 minutes. The samples were then dried in a Critical Point Dryer (Quorum, K850) in which the ethanol was replaced by liquid CO2 at 5°C, followed by heating at 36°C, so the liquid CO2 transitions to gas and was released slowly, leaving the samples dry. Then the samples were sputter-coated with gold-palladium (Quorum, Q150T ES).
The samples were examined by a scanning electron microscope (JEOL model JSM-7800F for high resolution or IT-100 for standard). The images were taken with an accelerating voltage of 1-2 kV for high resolution and 20 kV for standard. Bacteria length and width were measured based on the electron microscope scaler.
Statistical Analysis
To investigate the effect of COD on the average width and length of the bacteria, we conducted t-tests on the size measurements. Prior to analysis, we checked the assumptions of the t-test, including normality and equal variances.
The statistical differences between the microbial titers obtained at each time point between the COD and the negative control dressing were examined using t-tests.
A significance level of 0.05 was selected to determine statistical significance, and all tests were two-sided. Analyses were performed using JMP® Pro, Version 16.
3. Results
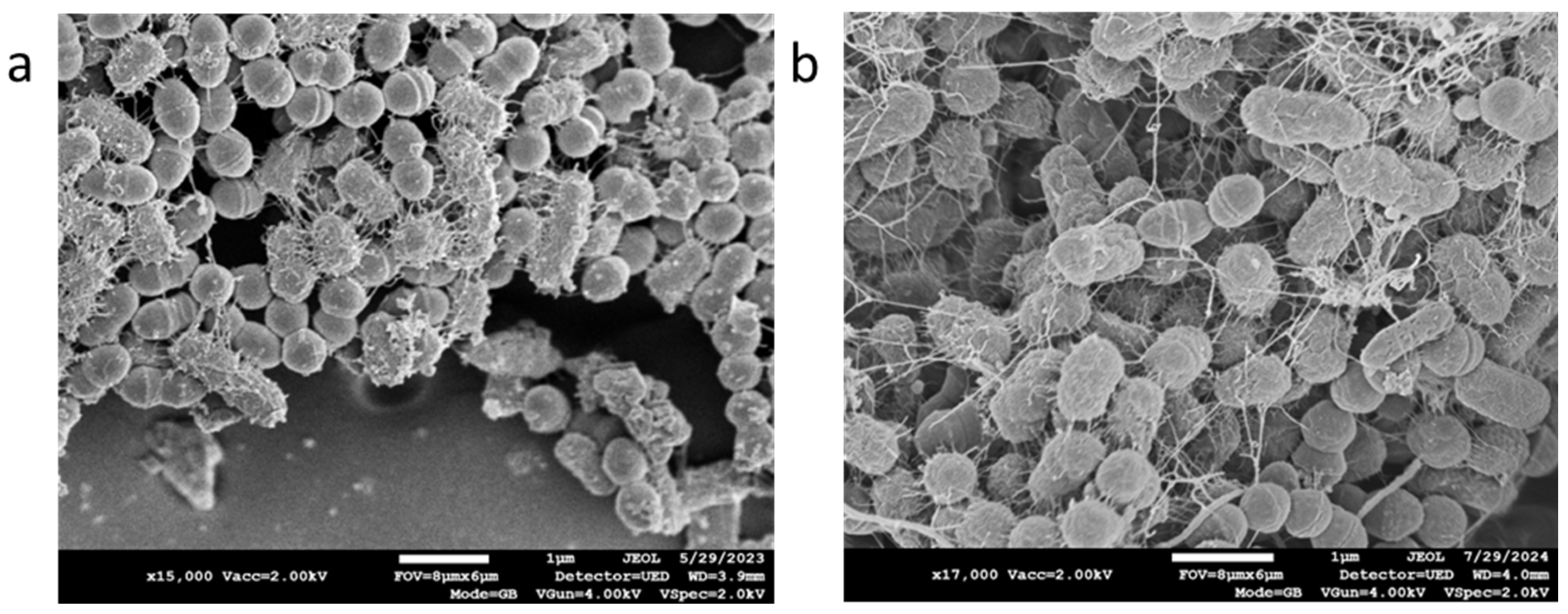
The bacterial mix grown for 7 hours at 37±2ºC were viable and produced biofilm (
Figure 2a). Exposure of the bacterial mix to the COD and their immediate recovery by centrifugation (Time 0) did not have a visible effect on the bacteria (
Figure 2b).
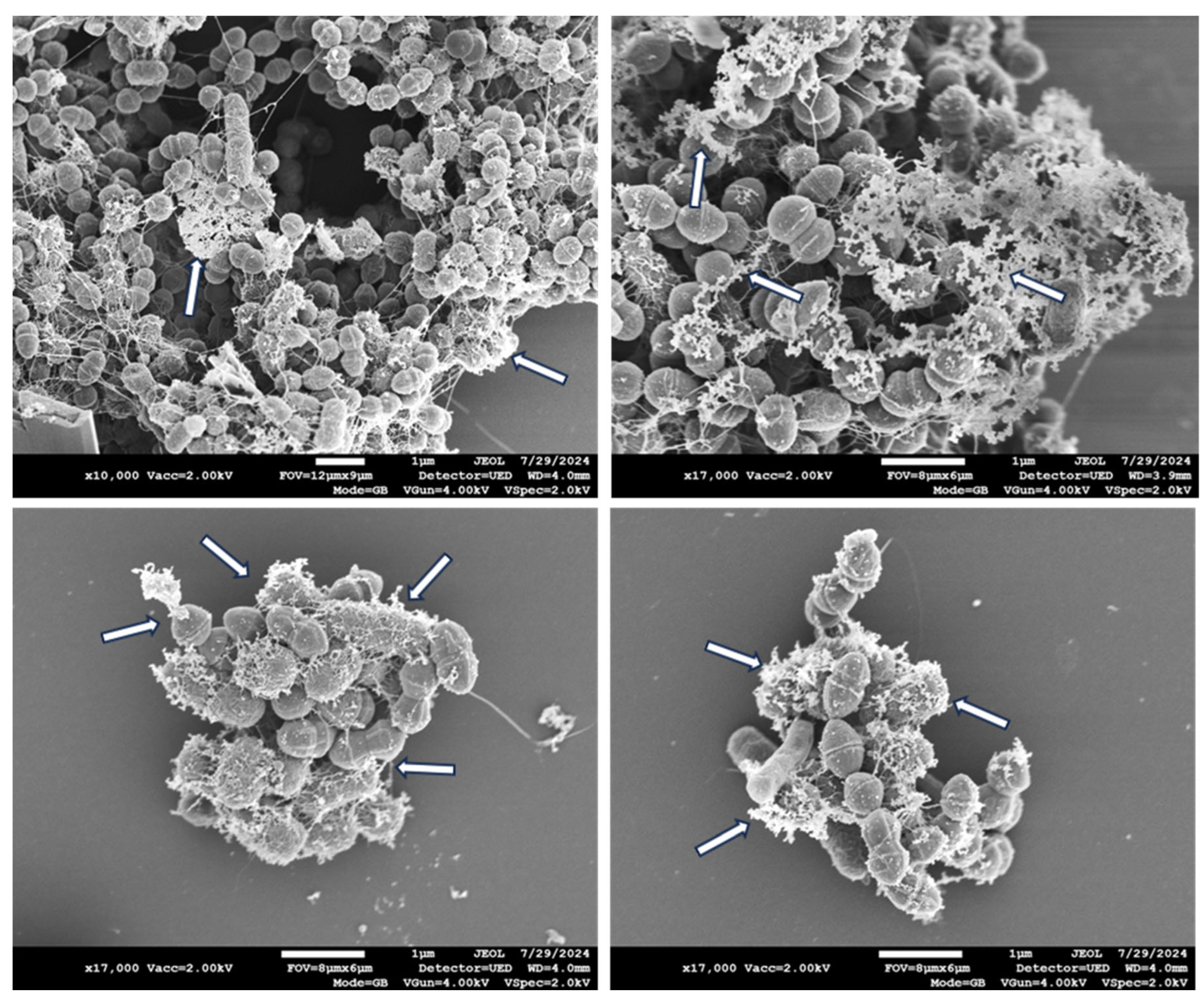
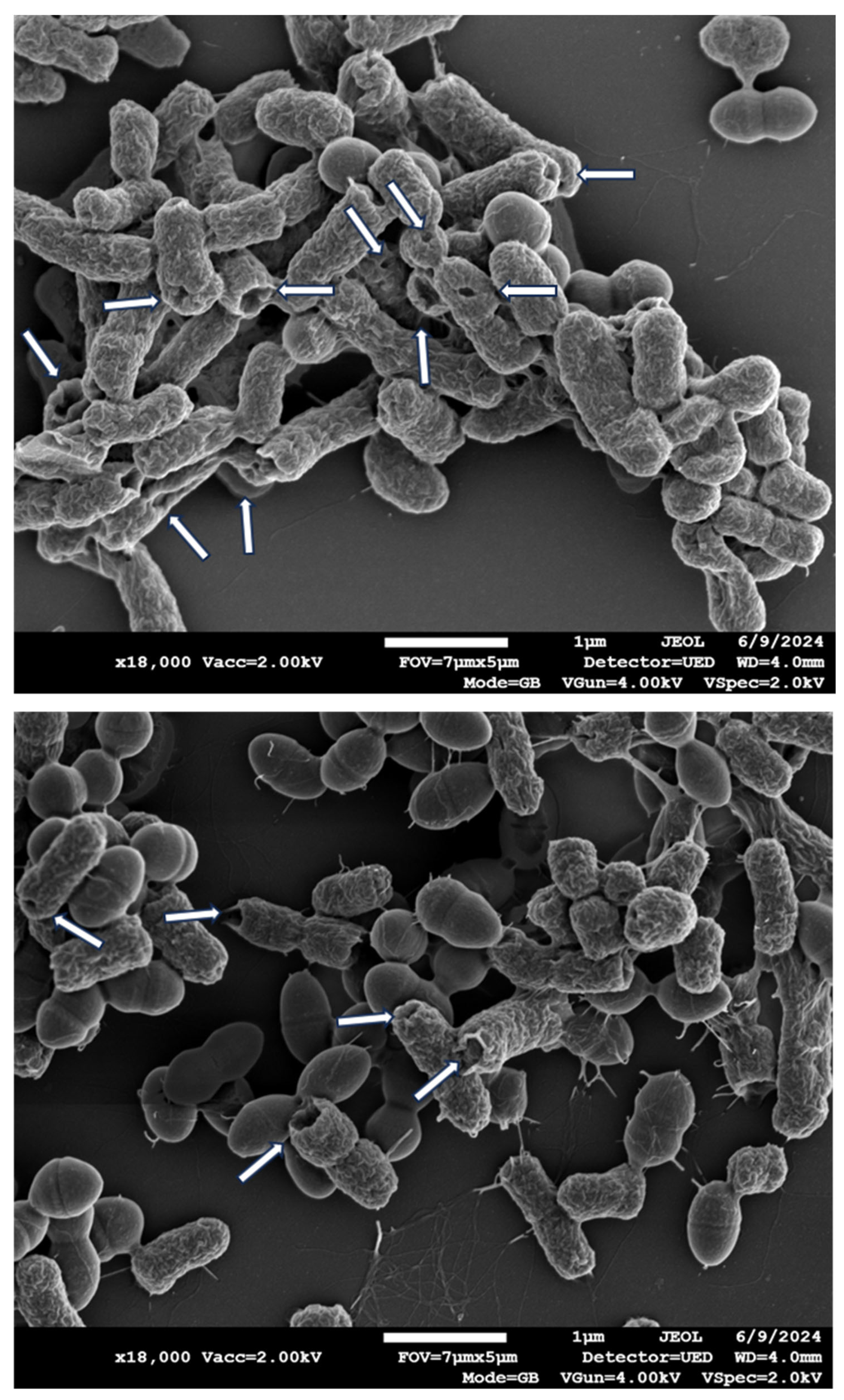
In contrast, exposure of the bacterial mix to the COD for 1 hour resulted in secretion of bacterial cytoplasmic content, as shown in some representative Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) pictures in
Figure 3.
Accordingly, there was more than 99% reduction (p<0.001) in the viable bacterial titers as compared to the control dressings (
Figure 4).
Two hours exposure of the bacteria to the COD resulted in similar extracellular content secretion by the bacteria (
Figure 5), with more than 99% reduction (p<0.001) in the bacterial viability (data not shown).
Longer exposure of 3 hours of the bacteria to the COD resulted also in the clear appearance of holes in the gram-negative bacteria (
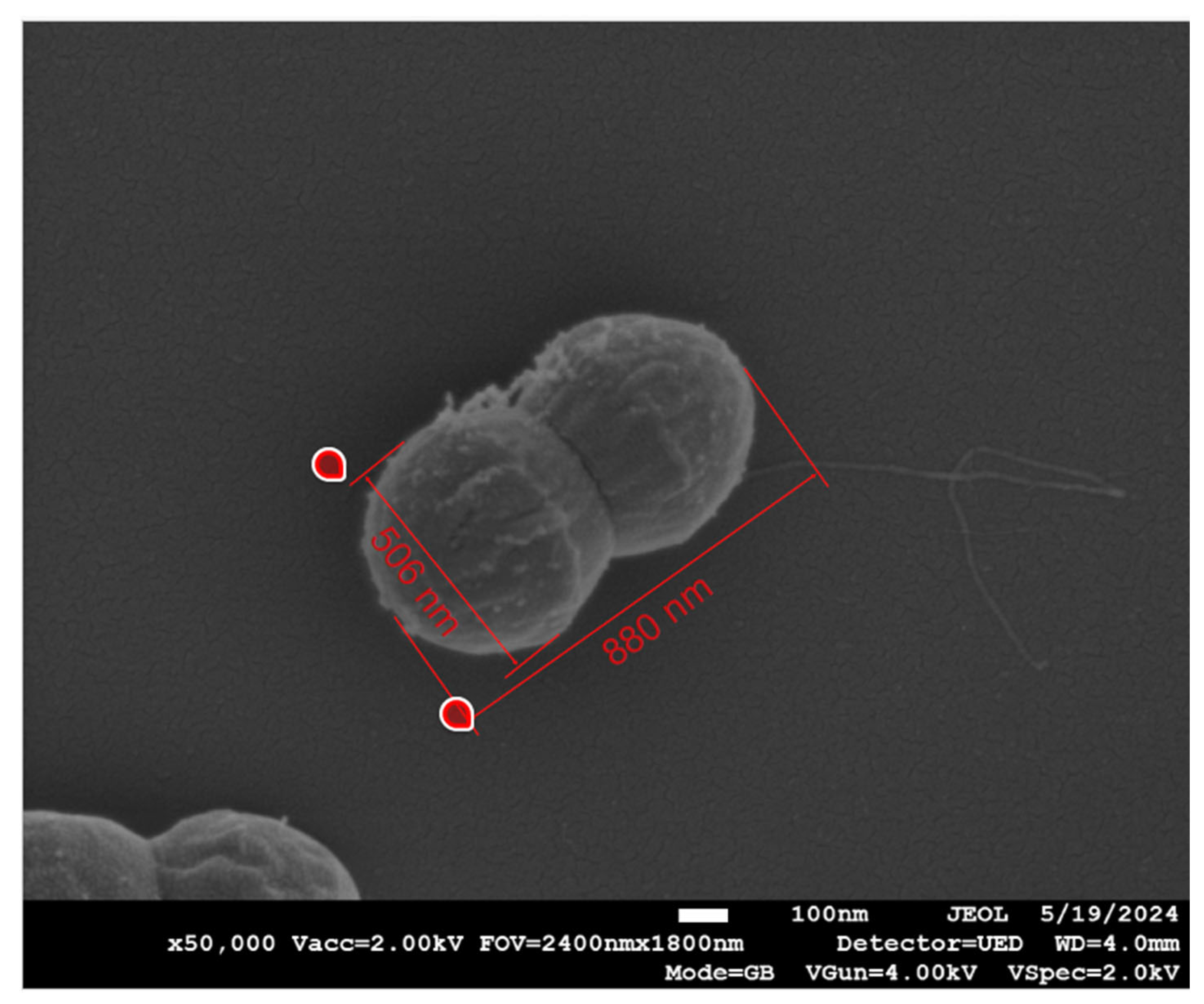
Figure 6), but not visible in the gram-positive bacteria. However, in the gram-positive, measurement of the width and length of the bacteria, as shown in a representative example in
Figure 7, showed a statistically significant reduction (p<0.001) in the width, but not in the length of the bacteria that were exposed to the COD as compared to the bacteria exposed to the control dressings (
Table 1).
4. Discussion
The COD possess potent antimicrobial efficacy, as previously demonstrated [
10]. In the current study, we used scanning electron microscopy analyses to study the effect that the COD have on the bacteria exposed to it. We used a mixture of known wound gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial pathogens [
3], including of an antibiotic resistant bacterium (MRSA), to more closely imitate the natural scenario in which a wound is exposed and colonized at any given time by a mixture of bacteria [
3,
18]. Furthermore, as bacterial biofilms are common in chronic wounds where they impede the wound healing process [
19], we grew the mix of bacteria for 7 hours at 37±2ºC in a rich culture medium to allow the bacteria mix to form biofilm, as shown in
Figure 2, before exposing them to the COD.
As demonstrated before [
10] and as confirmed in this study, exposure of the bacteria to the COD, even for 1 hour, reduces their viability by more than 99%. The COD are impregnated with copper oxide microparticles that are not released from the dressing, but they serve as a reservoir of copper ions. These ions are slowly and constantly released in the presence of humidity [
13], endowing the wound dressing with prolonged and stable biocidal properties for at least 7 consecutive days that protect the dressings from bio-contamination and reduction of passage of viable microorganism through them from the exterior environment into the wound bed.
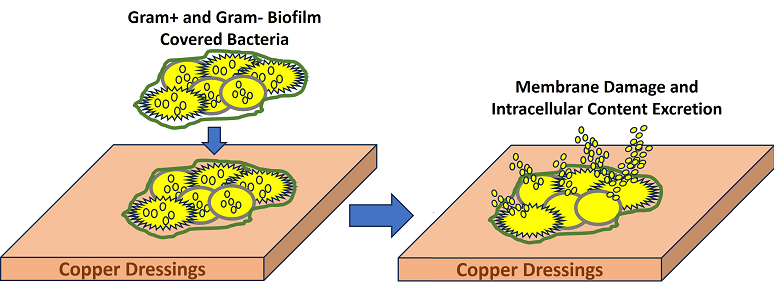
We found that the effect of the dressing on the bacteria included the disruption of the bacterial cell membrane, causing the leakage of cellular content, as clearly seen after 1 and 2 hours of the bacterial exposure to the COD. After 3 hours of exposure of the bacteria to the COD, holes were observed in the gram-negative bacteria, but not in the gram-positive bacteria. The cellular secreted content was almost not seen any more at 3 hours of exposure; apparently most of it was completely detached from the bacteria and washed away during the centrifugation steps. We could not clearly distinguish between MRSA and the enterococcus bacteria. We thus measured the width and length of the gram-positive bacteria as a group, and found a statistically significant reduction in the width of the gram-positive bacteria. We did not notice a reduction in the length of the gram-positive bacteria. Bacterial width is generally more stable and less influenced by the bacterial cell cycle, making it a more reliable metric for comparative studies between treatments. Measuring width can help minimize variability due to natural growth processes and focus more on the effects of the treatments being studied. Similar observations were found with copper-based metal–organic frameworks against
Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and
Lactobacillus [
20,
21]. The release of the internal content of bacteria when exposed to copper ions is similar to what has been described for silver nanoparticles [
22].
The capacity of copper nanoparticles to inhibit the formation of biofilm was demonstrated [
23,
24]. However, bacteria in wounds are in many cases already covered by biofilm when covered with wound dressings. Importantly, in the current study, we demonstrate that the bacteria are killed even when they are already covered by biofilm. The capacity of the dressings to reduce bioburden in an infected diabetic foot ulcer was already shown using real-time fluorescence imaging device [
25]. Our findings are in accordance with previous studies that demonstrated the capacity of copper nanoparticles and other nanoparticles to have an antimicrobial effect on biofilms, through the generation of reactive oxygen species [
26], and are in accordance with clinical observation of management of wound infection in acute and chronic wounds by the COD [
14,
16,
27].
5. Conclusions
The current study demonstrates the capacity of COD to kill bacteria even when they are already covered by biofilm. It shows that part of the killing mechanism is through the damage of the bacterial cell wall of the bacteria exposed to the dressings, leading to the secretion of the cytoplasmic content from the bacteria. Further studies are needed to determine if the bacteria are killed when exposed to the copper ions even before the loss of the cytoplasmic content occurs.
Author Contributions
G.B., T.R. and E.Z. designed the studies. T.R. performed the experiments, and T.R., E.Z. and T.K. performed the microscopy analyses. All authors contributed to the writing of the article.
Funding
This research was funded by MedCu Technologies Ltd.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
G.B. is the Chief Scientist of MedCu. T.R. is a current employee of MedCu. MedCu is the company that developed the COD. E.Z. and T.K. have no conflict of interests.
References
- Uberoi, A.; McCready-Vangi, A.; Grice, E.A. The wound microbiota: Microbial mechanisms of impaired wound healing and infection. Nat Rev Microbiol 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswary, T.; Nurul, A.A.; Fauzi, M.B. The Insights of Microbes’ Roles in Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, K.; Saleha, S.; Zhu, X.; Huo, L.; Basit, A.; Franco, O.L. Bacterial Contribution in Chronicity of Wounds. Microb. Ecol 2017, 73, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badia, J.M.; Casey, A.L.; Petrosillo, N.; Hudson, P.M.; Mitchell, S.A.; Crosby, C. Impact of surgical site infection on healthcare costs and patient outcomes: A systematic review in six European countries. J Hosp Infect 2017, 96, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hsia, H.C. The Impact of Microbial Communities on Wound Healing: A Review. Ann. Plast. Surg 2018, 81, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, J.; Rajan, V.K.; Biswas, R.; Jayakumar, R. Controlled Delivery of Bioactive Molecules for the Treatment of Chronic Wounds. Curr Pharm. Des 2017, 23, 3529–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G. Using copper to fight microorganisms. Curr Chem Biol 2012, 6, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Salvatori, R.; Kanmukhla, V.K. Drastic Reduction of Bacterial, Fungal and Viral Pathogen Titers by Cuprous Oxide Impregnated Medical Textiles. J Funct. Biomater 2021, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Sidwell, R.W.; Smee, D.F.; Barnard, D.L.; Morrey, J.D.; Lara-Villegas, H.H.; Shemer-Avni, Y.; Gabbay, J. Neutralizing viruses in suspensions by copper oxide based filters. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2007, 51, 2605–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Roth, T.; Kalinkovich, A. Wide spectrum potent antimicrobial efficacy of wound dressings impregnated with cuprous oxide microparticles. Microbiology Research 2022, 13, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Melamed, E. Copper, an abandoned player returning to the wound healing battle. In Recent Advances in Wound Healing, 1st ed.; Shahin, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gorel, O.H.M.; Feldman, I.; Kucyn-Gabovich, I. Enhanced healing of wounds that responded poorly to silver dressing by copper wound dressings: Prospective single arm treatment study. Health Science Reports 2024, 7, e1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, E.; Borkow, G. Continuum of care in hard-to-heal wounds by copper dressings: A case series. J Wound Care 2023, 32, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, E.; Kiambi, P.; Okoth, D.; Honigber, I.; Tamir, E.; Borkow, G. Healing of Chronic Wounds by Copper Oxide-Impregnated Wound Dressings-Case Series. Medicina (Kaunas.) 2021, 57, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, E.; Rovitsky, A.; Roth, T.; Assa, L.; Borkow, G. Stimulation of Healing of Non-Infected Stagnated Diabetic Wounds by Copper Oxide-Impregnated Wound Dressings. Medicina (Kaunas.) 2021, 57, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, E.; Rovitsky, A.; Roth, T.; Borkow, G. Anterior ankle full thickness skin necrosis treated with copper oxide dressings without debridment and skin graft a case report. Arch. Clin. Med. Case Rep. 1980, 6, 501–510. [Google Scholar]
- Weitman, C.C.; Roth, T.; Borkow, G. Copper dressings to the wound rescue after everything else failed: Case report. Arch. Clin. Med. Case Rep 2022, 6, 466–473. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, S.Y.; Manikam, R.; Muniandy, S. Prevalence and antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria from acute and chronic wounds in Malaysian subjects. J Infect Dev. Ctries 2015, 9, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, I.; Sivori, F.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Abril, E.; Pontone, M.; Di Domenico, E.G.; Pimpinelli, F. Bacterial Biofilm in Chronic Wounds and Possible Therapeutic Approaches. Biology (Basel) 2024, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmehrath, S.; Ahsan, K.; Munawar, N.; Alzamly, A.; Nguyen, H.L.; Greish, Y. Antibacterial efficacy of copper-based metal-organic frameworks against Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus. RSC Adv 2024, 14, 15821–15831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangzhen Zhang, J.B.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Peng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Weng, J.; Zhi, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X. Constructing a highly efficient multifunctional carbon quantum dot platform for the treatment of infectious wounds. Regenerative Biomaterials 2024, rbae105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, V.P.S.; Loke, M.F.; Jagadheesan, A.; Marsili, E.; MubarakAli, D.; Velusamy, P.; Vadivelu, J. Biogenic synthesis, characterization of antibacterial silver nanoparticles and its cell cytotoxicity. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2017, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahire, J.J.; Hattingh, M.; Neveling, D.P.; Dicks, L.M. Copper-Containing Anti-Biofilm Nanofiber Scaffolds as a Wound Dressing Material. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehabeldine, A.M.; Amin, B.H.; Hagras, F.A.; Ramadan, A.A.; Kamel, M.R.; Ahmed, M.A.; Atia, K.H.; Salem, S.S. Potential Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Properties of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles: Time-Kill Kinetic Essay and Ultrastructure of Pathogenic Bacterial Cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2023, 195, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Rao, A.; Oropallo, A.; Gawlik, S.; Haight, J. Use of Copper Nanoparticles to Reduce Bioburden in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Eplasty 2022, 22, QA4. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, M.; Baranska-Rybak, W. Nanomaterials as a Successor of Antibiotics in Antibiotic-Resistant, Biofilm Infected Wounds? Antibiotics (Basel) 2021, 10, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Melamed, E. Copper, an abandoned player returning to the wound healing battle. In Recent Advances in Wound Healing; Aghaei, S., Ed.; IntechOpen London: 5 Princes Gate Court, London, SW7 2QJ, UK, 2021; pp. 165–184. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).