Submitted:
24 September 2024
Posted:
26 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
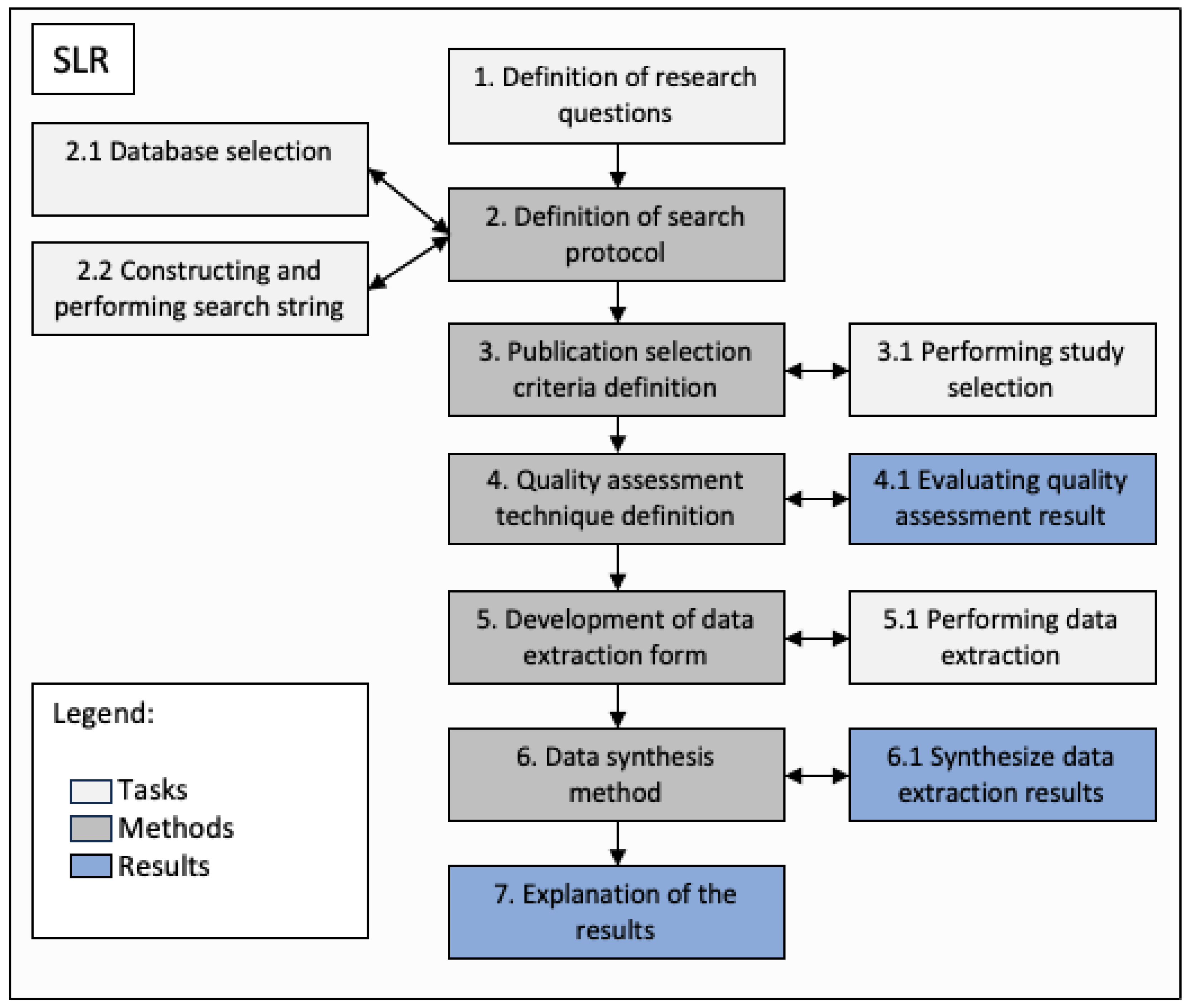
2. Methodology
2.1. Definition of Research Questions
2.2. Search Protocol
2.3. Selection criteria
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Data Synthesis
3. Results
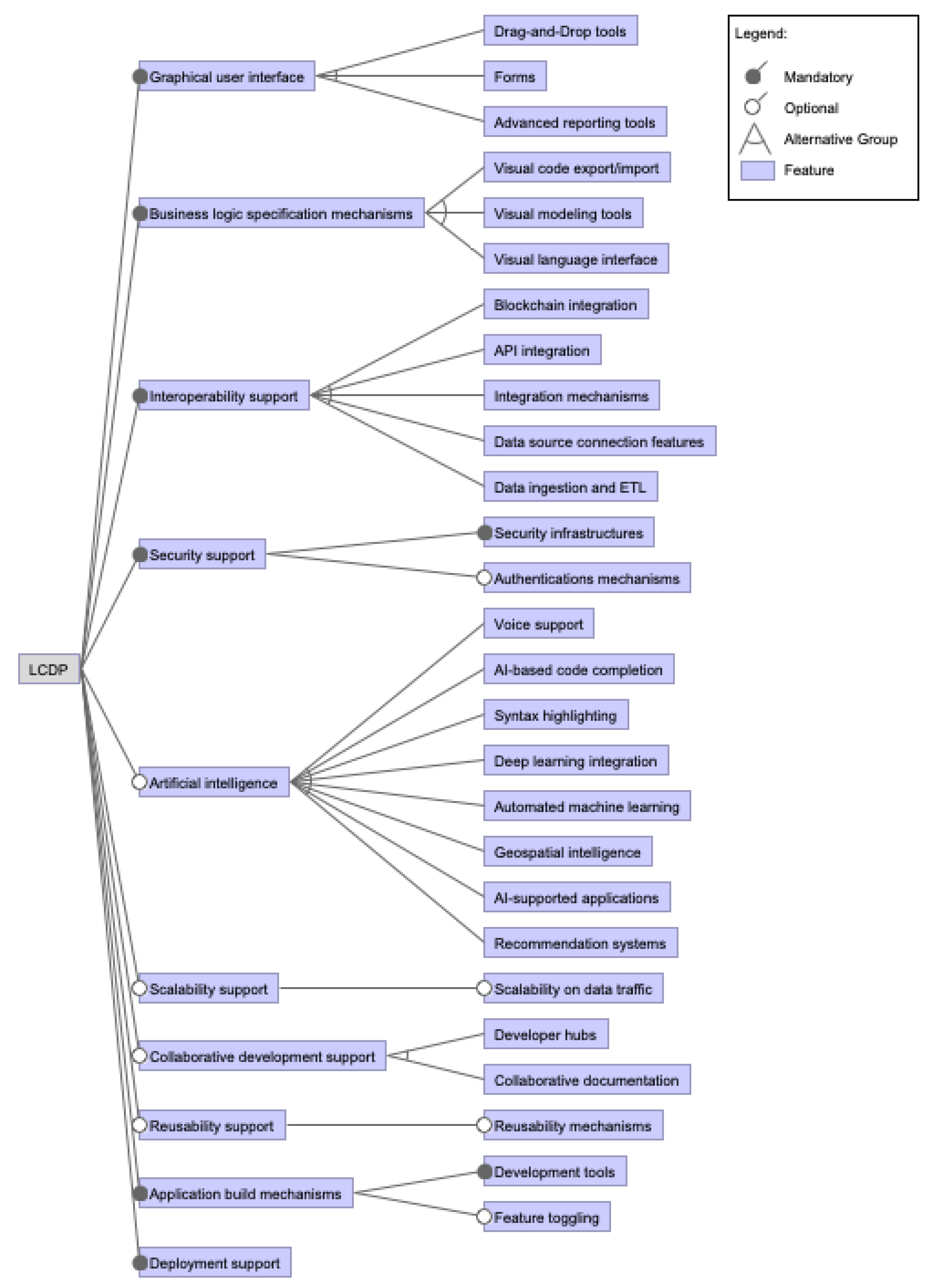
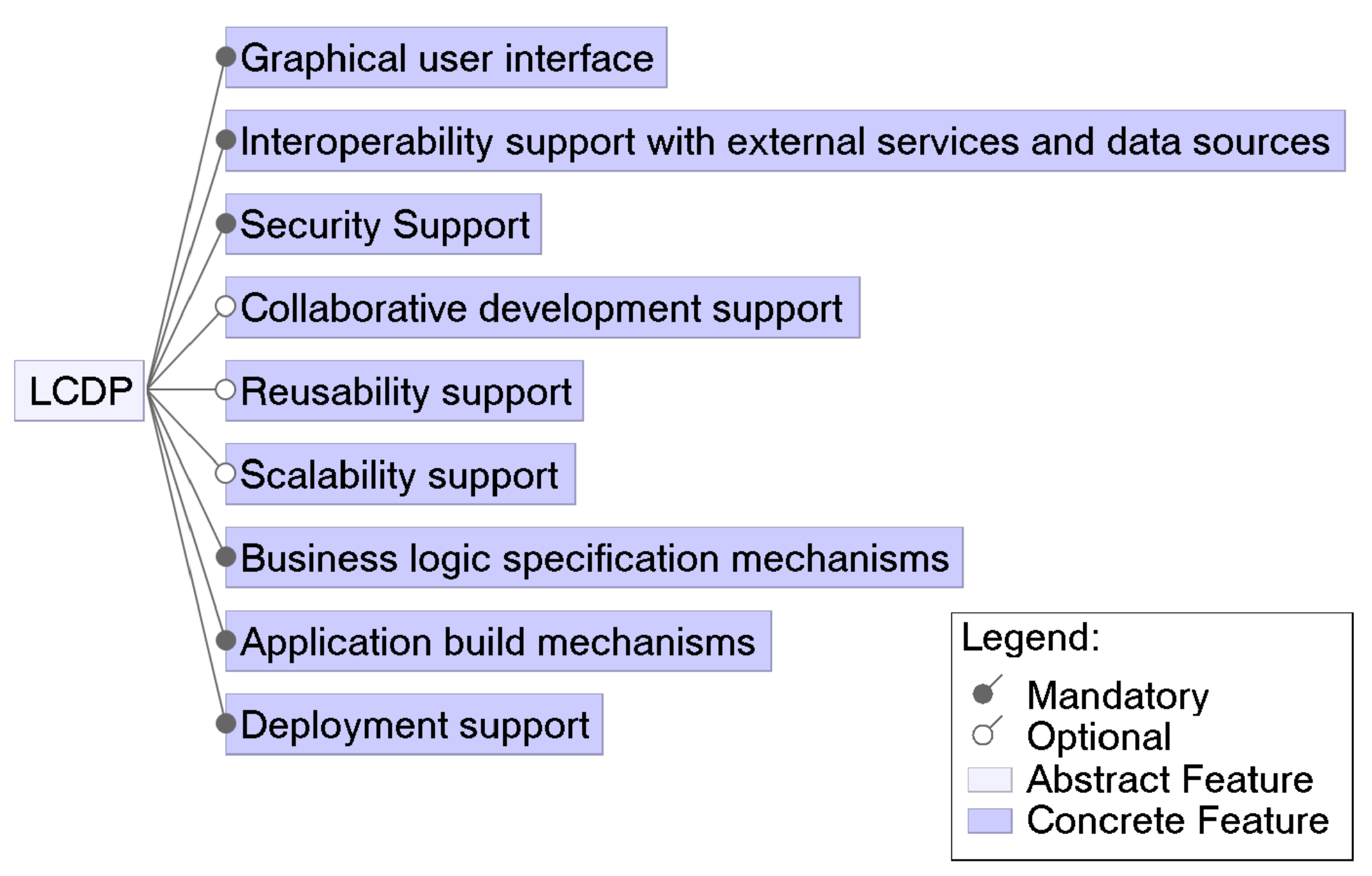
3.1. What Are the Identified Features of LCDPs?
3.1.1. Graphical User Interface (GUI) Features
3.1.2. Business Logic Specification Mechanisms
3.1.3. Interoperability Support
3.1.4. Security Support
3.1.5. Emerging AI and ML Features
3.1.6. Scalability Support
3.1.7. Collaborative Development Support
3.1.8. Reusability Support
3.1.9. Application Build Mechanisms
3.2. What Are the Objectives of LCDPs Described in Scientific Literature?
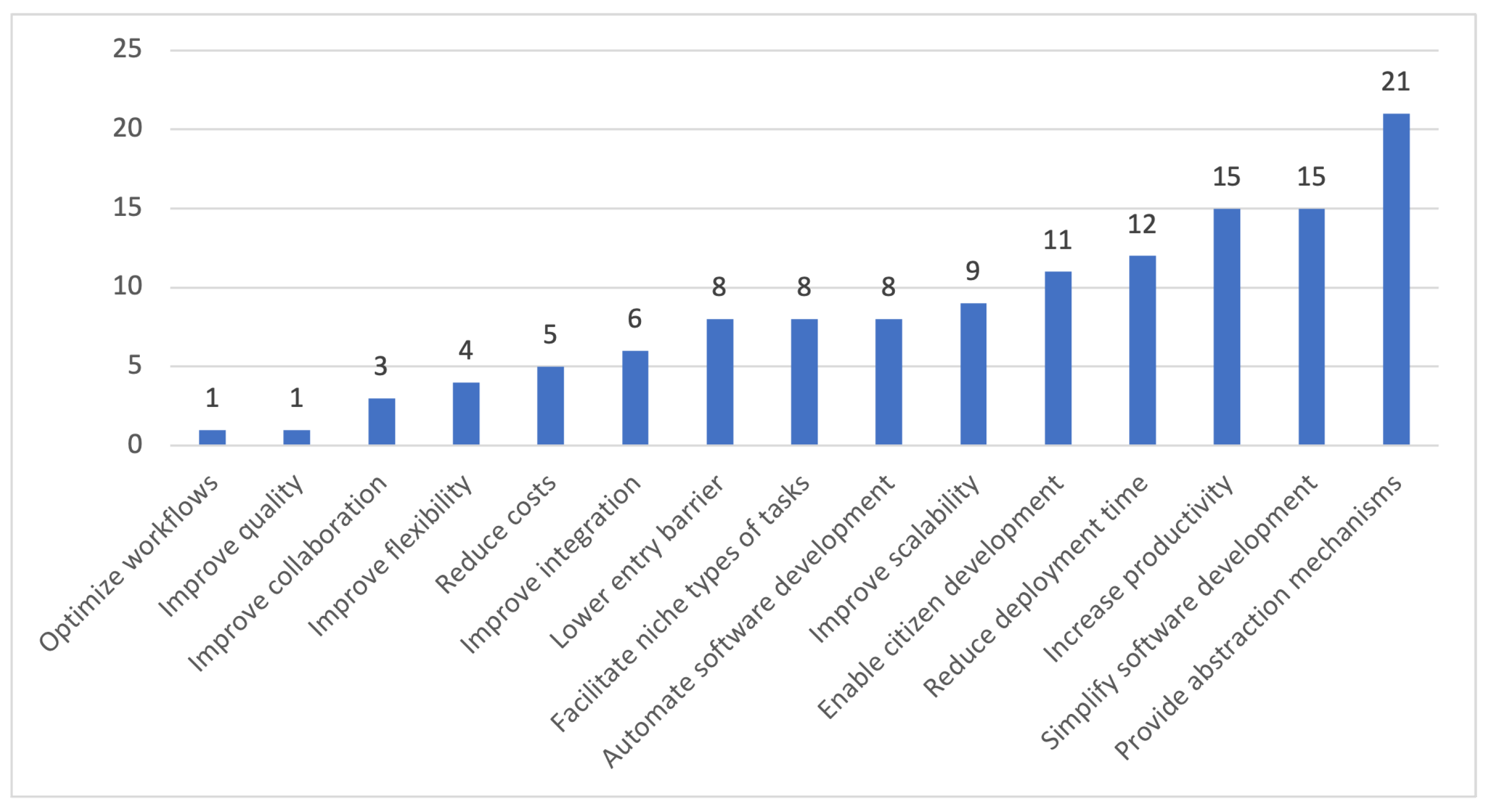
| Highlights of the results: • LCDPs encompasses various objectives, with a total of 16 primary objectives identified. • The most frequently mentioned objective is providing abstraction mechanisms. • Many of these objectives are interconnected and mutually reinforce each other. • Most objectives complementary enhance user experience. • Similar tools and techniques can be employed to achieve multiple objectives. |
| No | Objectives | Concern |
| O1 | Provide abstraction mechanisms |
With the use of LCDPs, developers can concentrate on higher-level functionality rather than detailed implementation details. As an outcome, this simplifies the development process and reduces the time required to build new applications, enabling users to focus on business value rather than technical implementation. |
| O2 | Simplify software development |
By offering pre-built components and integrations, visual modeling tools, and simplified coding interfaces, LCDPs seek to streamline the software development process. This enables developers to create applications with less complexity, improving the overall development process. |
| O3 | Increase productivity |
By providing a generative development approach that requires less coding and a shorter period to create new applications with higher value, LCDPs seek to boost productivity. As a result, developers may concentrate on tasks that generate higher economic returns like innovation, design, and user experience. |
| O4 | Reduce deployment time |
By offering pre-built components and integrations, LCDPs can shorten the time it takes for developers to build and deploy applications. This reduces the time needed to develop and test new features, enabling companies to release innovative products to market more quickly. |
| O5 | Improve scalability |
By supplying an environment where developers may quickly scale up or down applications in response to shifting business needs, LCDPs seek to increase scalability. Because of this, businesses can handle rising traffic and data processing demands without having to completely redesign their applications. |
| O6 | Enable citizen development |
By giving non-technical users the tools and resources to build applications, LCDPs intend to promote citizen development. For instance, an LCDP can offer training, intuitive instructions, guides and other resources to help non-technical users become familiar with the platform and learn how to build applications. |
| O7 | Automate software development |
By offering automation mechanisms, automated testing, and deployment tools, LCDPs aim to automate the production of software. This objective aims to automate various software development processes, including code generation, testing, and deployment. |
| O8 | Facilitate niche types of tasks |
By offering pre-built components, combinations of features, tools, processes, and templates for common business processes, LCDPs can support specific tasks and projects in application development. This objective aims to support particular software development tasks, e.g. creating e-commerce applications. |
| O9 | Lower entry barrier |
By enabling non-technical techniques to construct apps and minimizing the requirement for coding skills, LCDPs seek to lower the entry barrier. Users can more easily construct their own applications by using an LCDP, which can offer a visual interface for designing and configuring apps. |
| O10 | Improve integration |
By offering pre-built connectors and APIs for common business applications and services, LCDPs seek to improve integration. With the use of various integration features provided by LCDPs, including API integrations, third-party integrations, and data connectors, this objective intends to enhance the integration of diverse software applications and systems to enable seamless data interchange and communication. A low code platform might offer connectors for widely recognized CRM or ERP systems, e.g., allowing users to quickly incorporate these systems into their applications. |
| O11 | Reduce costs |
By enabling organizations to create applications with greater speed and efficiency, LCDPs can help businesses cut costs by eliminating the need for costly customized programming or third-party developers. By giving organizations access to the various cost-saving tools provided by LCDPs, such as shorter development times, streamlined development procedures, and lower development costs, this objective aims to lower the cost of software development. |
| O12 | Improve flexibility |
Rapid prototyping and iteration are made possible by LCDPs to increase flexibility. A LCDP can make it straightforward for users to update and modify their applications, add new features or integrations, and adjust to shifting business needs. By making it possible for developers to make changes quickly and easily to their applications, this objective seeks to increase the flexibility of software development. |
| O13 | Improve collaboration |
With the help of the various collaboration features provided by LCDPs, such as real-time collaboration, version control, and team collaboration tools, users can collaborate on the design and development of apps, share feedback, and monitor progress in real-time. LCDPs can help improve collaboration by offering a common platform for developers, business users, and other stakeholders to develop applications more interactively. |
| O14 | Improve quality |
By offering integrated testing and debugging tools, LCDPs can aid in enhancing the quality of software applications. With numerous mechanisms to enhance software quality, such as code reviews, testing, and quality assurance processes, this objective aims to increase the quality of software applications by lowering mistakes, defects, and other quality concerns. |
| O15 | Optimize workflows |
By streamlining and automating repetitive tasks, reducing manual effort requirements, increasing workforce efficiency, LCDPs aim to optimize workflows. By elimination of manual work and automating routine tasks, like data entry or approvals, and providing real-time visibility into the status of the process, this objective aims to streamline and optimize business processes. |
| Study | Objectives Categories | ||||||||||||||
| O1 | O2 | O3 | O4 | O5 | O6 | O7 | O8 | O9 | O10 | O11 | O12 | O13 | O14 | O15 | |
| [46] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [36] | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||
| [39] | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||
| [31] | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| [51] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [28] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [45] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [62] | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| [52] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [49] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [42] | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||
| [27] | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||
| [63] | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| [53] | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| [59] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [56] | x | x | |||||||||||||
| [54] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [64] | x | x | |||||||||||||
| [35] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [30] | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| [40] | x | x | |||||||||||||
| [26] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [41] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [43] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [50] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [65] | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||
| [37] | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||
| [55] | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||
| [58] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [33] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [32] | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| [34] | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| [29] | x | ||||||||||||||
| [47] | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| [25] | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| [38] | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| [48] | x | x | |||||||||||||
| O1: Provide Abstraction Mechanisms | O5: Improve scalability | O9: Lower entry barriers | O13: Improve collaboration | ||||||||||||
| O2: Simplify software development | O6: Enable citizen development | O10: Improve integration | O14: Improve quality | ||||||||||||
| O3: Increase productivity O4: Reduce Deployment time |
O7: Automate software development O8: Support specific tasks |
O11: Reduce costs O12: Improve flexibility |
O15: Optimize workflows | ||||||||||||
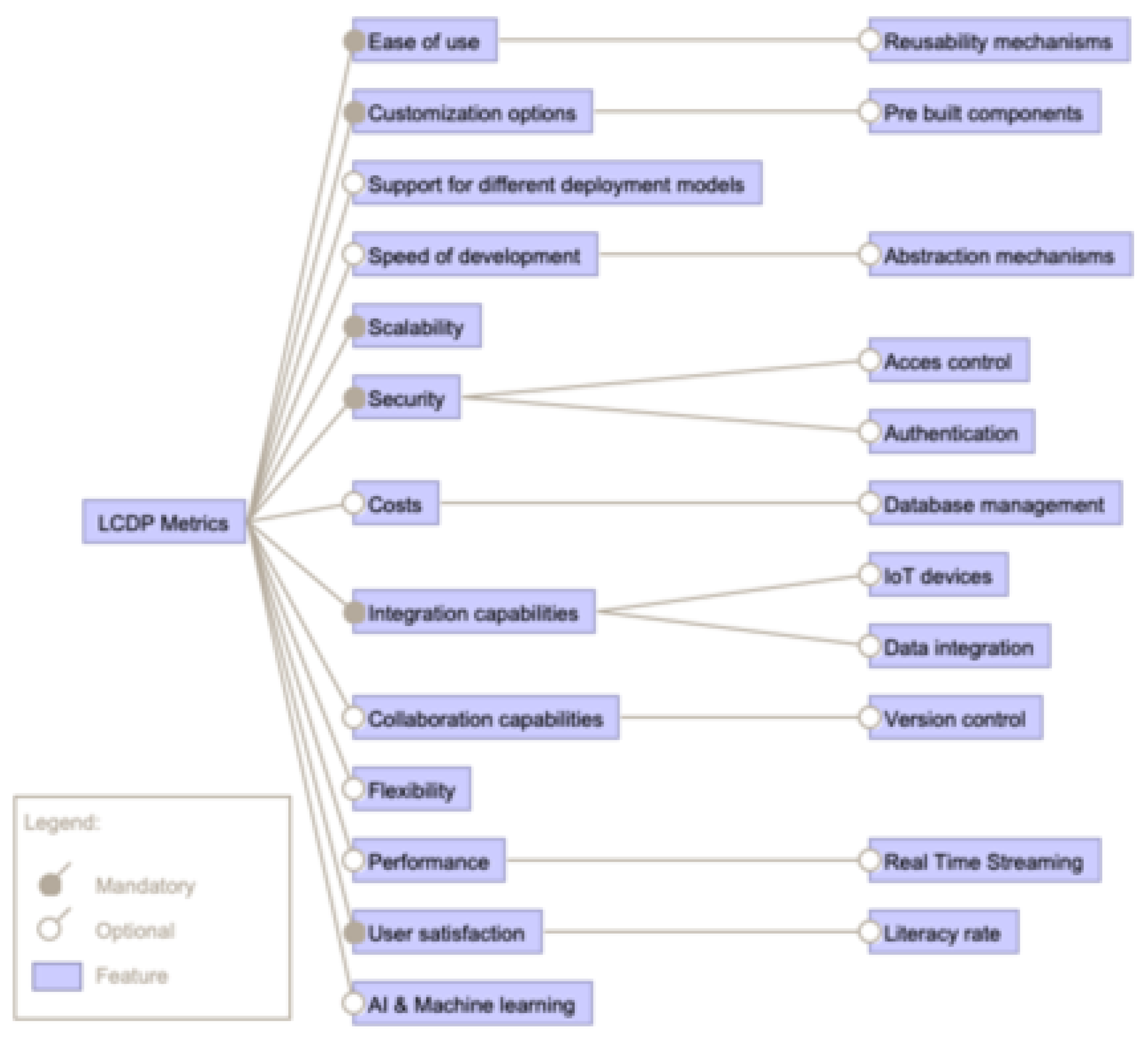
3.3. To What Extent Are the Identified LCDP Objectives Valid in the Context of PA?
3.4. What Are the Challenges That Have to Be Overcome for LCDPs in PA?
3.5. What Are the Future Research Directions for LCDP in PA?
4. LCDP for Precision Agriculture
5. Discussion
5.1. Unveiling the Research Questions and Bridging This towards PA
5.2. Threats to Validity
6. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindblom, J.; Lundström, C.; Ljung, M.; Jonsson, A. Promoting sustainable intensification in precision agriculture: review of decision support systems development and strategies. Precision agriculture 2017, 18, 309–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, M.; Wang, N. Precision agriculture—a worldwide overview. Computers and electronics in agriculture 2002, 36, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, R.; Lowenberg-DeBoer, J. Precision agriculture and sustainability. Precision agriculture 2004, 5, 359–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisternas, I.; Velásquez, I.; Caro, A.; Rodríguez, A. Systematic literature review of implementations of precision agriculture. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2020, 176, 105626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Kaur, S. Evolution of Internet of Things (IoT) and its significant impact in the field of Precision Agriculture. Computers and electronics in agriculture 2019, 157, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdinejad, A.; Zolfaghari, B.; Azmoodeh, A.; Dehghantanha, A.; Karimipour, H.; Fraser, E.; Green, A.G.; Russell, C.; Duncan, E. A review on security of smart farming and precision agriculture: Security aspects, attacks, threats and countermeasures. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, H.S.; Brown, P.; Best, T. A systematic literature review of the factors affecting the precision agriculture adoption process. Precision Agriculture 2019, 20, 1292–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sishodia, R.P.; Ray, R.L.; Singh, S.K. Applications of remote sensing in precision agriculture: A review. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Far, S.T.; Rezaei-Moghaddam, K. Impacts of the precision agricultural technologies in Iran: An analysis experts’ perception & their determinants. Information processing in agriculture 2018, 5, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Jawad, H.M.; Nordin, R.; Gharghan, S.K.; Jawad, A.M.; Ismail, M. Energy-efficient wireless sensor networks for precision agriculture: A review. Sensors 2017, 17, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.; Larsen, M.; Nielsen, S.H.; Larsen, L.B.; Olsen, K.S.; Jørgensen, R.N. Towards an open software platform for field robots in precision agriculture. Robotics 2014, 3, 207–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Huang, N.F. Big data and ai revolution in precision agriculture: Survey and challenges. Ieee Access 2021, 9, 110209–110222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, H.; Naughton, P.; Clark, B.; Taylor, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, C.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Frewer, L. Precision agriculture in China: Exploring awareness, understanding, attitudes and perceptions of agricultural experts and end-users in China. Advances in Animal Biosciences 2017, 8, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Haley, R.; Wortman, R.; Zhang, Q. An extensible and integrated software architecture for data analysis and visualization in precision agriculture. 2012 IEEE 13th International Conference on Information Reuse & Integration (IRI). IEEE, 2012, pp. 271–278.
- Robert, P.C. Precision agriculture: a challenge for crop nutrition management. Progress in Plant Nutrition: Plenary Lectures of the XIV International Plant Nutrition Colloquium: Food security and sustainability of agro-ecosystems through basic and applied research. Springer, 2002, pp. 143–149.
- Schimmelpfennig, D.; Ebel, R. On the doorstep of the information age: Recent adoption of precision agriculture. Economic Research Service, Paper No. EIB-80 2011.
- Kitchenham, B.; Brereton, O.P.; Budgen, D.; Turner, M.; Bailey, J.; Linkman, S. Systematic literature reviews in software engineering–a systematic literature review. Information and software technology 2009, 51, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, H.G.; Tekinerdogan, B. Model-based testing for software safety: a systematic mapping study. Software Quality Journal 2018, 26, 1327–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köksal, Ö.; Tekinerdogan, B. Obstacles in data distribution service middleware: a systematic review. Future Generation Computer Systems 2017, 68, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummers, J.; Kassahun, A.; Tekinerdogan, B. Obstacles and features of Farm Management Information Systems: A systematic literature review. Computers and electronics in agriculture 2019, 157, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisnawijaya, N.N.K.; Tekinerdogan, B.; Catal, C.; van der Tol, R. Data analytics platforms for agricultural systems: A systematic literature review. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2022, 195, 106813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.F.; Shannon, S.E. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qualitative health research 2005, 15, 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, W.J.; Levine-Donnerstein, D. Rethinking validity and reliability in content analysis 1999.
- Sahay, A.; Indamutsa, A.; Di Ruscio, D.; Pierantonio, A. Supporting the understanding and comparison of low-code development platforms. 2020 46th Euromicro Conference on Software Engineering and Advanced Applications (SEAA). IEEE, 2020, pp. 171–178.
- Weber, I. Low-code from frontend to backend: Connecting conversational user interfaces to backend services via a low-code IoT platform. Proceedings of the 3rd Conference on Conversational User Interfaces, 2021, pp. 1–5.
- Pacheco, J.; Garbatov, S.; Goulão, M. Improving collaboration efficiency between UX/UI designers and developers in a low-code platform. 2021 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems Companion (MODELS-C). IEEE, 2021, pp. 138–147.
- Junior, A.G.D.S.; Gonçalves, L.M.G.; Caurin, G.A.D.P.; Tamanaka, G.T.B.; Hernandes, A.C.; Aroca, R.V. BIPES: Block based integrated platform for embedded systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 197955–197968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.; Kothari, D.; Salvi, A.; Mane, P.; Kolhe, V. Querylizer: An Interactive Platform for Database Design and Text to SQL Conversion. 2022 International Conference for Advancement in Technology (ICONAT). IEEE, 2022, pp. 1–6.
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Sun, P. The necessity of low-code engineering for industrial software development: a case study and reflections. 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops (ISSREW). IEEE, 2021, pp. 415–420.
- Metrolho, J.; Ribeiro, F.; Araujo, R. A strategy for facing new employability trends using a low-code development platform. INTED2020 Proceedings. IATED, 2020, pp. 8601–8606.
- Da Cruz, M.A.; de Paula, H.T.; Caputo, B.P.; Mafra, S.B.; Lorenz, P.; Rodrigues, J.J. Olp—a restful open low-code platform. Future Internet 2021, 13, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisi, M.; Mottu, J.M.; Kolovos, D.S.; De Lara, J.; Guerra, E.M.; Di Ruscio, D.; Pierantonio, A.; Wimmer, M. Lowcomote: Training the next generation of experts in scalable low-code engineering platforms. STAF 2019 Co-Located Events Joint Proceedings: 1st Junior Researcher Community Event, 2nd International Workshop on Model-Driven Engineering for Design-Runtime Interaction in Complex Systems, and 1st Research Project Showcase Workshop co-located with Software Technologies: Applications and Foundations (STAF 2019), 2019.
- Silva, C.; Vieira, J.; Campos, J.C.; Couto, R.; Ribeiro, A.N. Development and validation of a descriptive cognitive model for predicting usability issues in a low-code development platform. Human Factors 2021, 63, 1012–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qi, B.; Zhang, W.; Sun, H. A Low-Code Development Framework for Constructing Industrial Apps. Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing: 15th CCF Conference, ChineseCSCW 2020, Shenzhen, China, November 7–9, 2020, Revised Selected Papers 15. Springer, 2021, pp. 237–250.
- Metrôlho, J.; Araújo, R.; Ribeiro, F.; Castela, N. An approach using a low-code platform for retraining professionals to ICT. EDULEARN19 Proceedings. IATED, 2019, pp. 7200–7207.
- Asawa, K.; Kukreja, S.; Gondkar, R. An NCDP for developing a blockchain based dynamic supply chain management with auto-generation of smart contract. 2021 26th International Conference on Automation and Computing (ICAC). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–6.
- Salgueiro, J.; Ribeiro, F.; Metrôlho, J. Best Practices for OutSystems Development and Its Influence on Test Automation. Trends and Applications in Information Systems and Technologies: Volume 4 9. Springer, 2021, pp. 85–95.
- Zhuang, W.; Gan, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, S. Easyfl: A low-code federated learning platform for dummies. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2022, 9, 13740–13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragança, A.; Azevedo, I.; Bettencourt, N.; Morais, C.; Teixeira, D.; Caetano, D. Towards supporting SPL engineering in low-code platforms using a DSL approach. Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGPLAN International Conference on Generative Programming: Concepts and Experiences, 2021, pp. 16–28.
- Moin, A.; Mituca, A.; Challenger, M.; Badii, A.; Günnemann, S. ML-Quadrat & DriotData: a model-driven engineering tool and a low-code platform for smart IoT services. Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE 44th International Conference on Software Engineering: Companion Proceedings, 2022, pp. 144–148.
- Pantelimon, S.G.; Rogojanu, T.; Braileanu, A.; Stanciu, V.D.; Dobre, C. Towards a seamless integration of iot devices with iot platforms using a low-code approach. 2019 IEEE 5th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT). IEEE, 2019, pp. 566–571.
- Iyer, C.K.; Hou, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Oh, K.; Ganguli, S.; Pandey, V. Trinity: A No-Code AI platform for complex spatial datasets. Proceedings of the 4th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Workshop on AI for Geographic Knowledge Discovery, 2021, pp. 33–42.
- Philippe, J.; Coullon, H.; Tisi, M.; Sunyé, G. Towards transparent combination of model management execution strategies for low-code development platforms. Proceedings of the 23rd ACM/IEEE International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems: Companion Proceedings, 2020, pp. 1–10.
- El-Sappagh, S.H.A.; Hendawi, A.M.A.; El Bastawissy, A.H. A proposed model for data warehouse ETL processes. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences 2011, 23, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sipio, C.; Di Ruscio, D.; Nguyen, P.T. Democratizing the development of recommender systems by means of low-code platforms. Proceedings of the 23rd ACM/IEEE international conference on model driven engineering languages and systems: companion proceedings, 2020, pp. 1–9.
- Almonte, L.; Cantador, I.; Guerra, E.; de Lara, J. Towards automating the construction of recommender systems for low-code development platforms. Proceedings of the 23rd ACM/IEEE International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems: Companion Proceedings, 2020, pp. 1–10.
- Waszkowski, R. Low-code platform for automating business processes in manufacturing. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotas, C.; Chatzidimitriou, K.C.; Symeonidis, A.L. RESTsec: a low-code platform for generating secure by design enterprise services. Enterprise Information Systems 2018, 12, 1007–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indamutsa, A.; Di Ruscio, D.; Pierantonio, A. A low-code development environment to orchestrate model management services. IFIP International Conference on Advances in Production Management Systems. Springer, 2021, pp. 342–350.
- Pichidtienthum, S.; Pugsee, P.; Cooharojananone, N. Developing Module Generation for Odoo Using Concept of Low-Code Development Platform and Automation Systems. 2021 IEEE 8th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Applications (ICIEA). IEEE, 2021, pp. 529–533.
- Daniel, G.; Cabot, J.; Deruelle, L.; Derras, M. Xatkit: a multimodal low-code chatbot development framework. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 15332–15346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Costa, C. Web Platform for Medical Deep Learning Services. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1727–1732.
- Lethbridge, T.C. Low-code is often high-code, so we must design low-code platforms to enable proper software engineering. Leveraging Applications of Formal Methods, Verification and Validation: 10th International Symposium on Leveraging Applications of Formal Methods, ISoLA 2021, Rhodes, Greece, –29, 2021, Proceedings 10. Springer, 2021, pp. 202–212. 17 October.
- Marek, K.; Śmiałek, M.; Rybiński, K.; Roszczyk, R.; Wdowiak, M. BalticLSC: low-code software development platform for large scale computations. Computing and Informatics 2021, 40, 734–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schötteler, S.; Laumer, S.; Schuhbauer, H.; Scheidthauer, N.; Seeberger, P.; Miethsam, B. A no-code platform for tie prediction analysis in social media networks. Innovation Through Information Systems: Volume II: A Collection of Latest Research on Technology Issues. Springer, 2021, pp. 475–491.
- Lourenço, H.; Ferreira, C.; Seco, J.C. OSTRICH-a type-safe template language for low-code development. 2021 ACM/IEEE 24th International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems (MODELS). IEEE, 2021, pp. 216–226.
- Martins, R.; Caldeira, F.; Sa, F.; Abbasi, M.; Martins, P. An overview on how to develop a low-code application using OutSystems. 2020 International Conference on Smart Technologies in Computing, Electrical and Electronics (ICSTCEE). IEEE, 2020, pp. 395–401.
- Sharma, U.; Gupta, D. Email Ingestion Using Robotic Process Automation for Online Travel Agency. 2021 9th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions)(ICRITO). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–5.
- Lopes, B.; Amorim, S.; Ferreira, C. Solution discovery over feature toggling with built-in abstraction in outsystems. 2021 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems Companion (MODELS-C). IEEE, 2021, pp. 47–56.
- Sanchis, R.; García-Perales, Ó.; Fraile, F.; Poler, R. Low-code as enabler of digital transformation in manufacturing industry. Applied Sciences 2019, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phalake, V.S.; Joshi, S.D. Low code development platform for digital transformation. Information and Communication Technology for Competitive Strategies (ICTCS 2020) Intelligent Strategies for ICT. Springer, 2021, pp. 689–697.
- Fernandes, J.P.; Araújo, R.; Zenha-Rela, M. Achieving scalability in project based learning through a low-code platform. Proceedings of the XXXIV Brazilian Symposium on Software Engineering, 2020, pp. 710–719.
- Jyothi, S.; Rajeswari, T. Accelerating SQL with Complex Visual Querying. 2022 Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Energy (ICAIS). IEEE, 2022, pp. 1126–1131.
- Martin, J. Rapid application development; Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1991.
- Sahay, A.; Di Ruscio, D.; Pierantonio, A. Understanding the role of model transformation compositions in low-code development platforms. Proceedings of the 23rd ACM/IEEE International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems: Companion Proceedings, 2020, pp. 1–5.
- Abbasi, R.; Martinez, P.; Ahmad, R. The digitization of agricultural industry–a systematic literature review on agriculture 4.0. Smart Agricultural Technology 2022, 2, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneveld, D.; Tekinerdogan, B.; Garousi, V.; Catal, C. A domain-specific language framework for farm management information systems in precision agriculture. Precision Agriculture 2021, 22, 1067–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdouw, C.; Tekinerdogan, B.; Beulens, A.; Wolfert, S. Digital twins in smart farming. Agricultural Systems 2021, 189, 103046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriga, J.A.; Clemente, P.J.; Sosa-Sánchez, E.; Prieto, Á.E. SimulateIoT: Domain Specific Language to design, code generation and execute IoT simulation environments. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 92531–92552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzworth, D.P.; Snow, V.; Janssen, S.; Athanasiadis, I.N.; Donatelli, M.; Hoogenboom, G.; White, J.W.; Thorburn, P. Agricultural production systems modelling and software: current status and future prospects. Environmental Modelling & Software 2015, 72, 276–286. [Google Scholar]
- Shafi, U.; Mumtaz, R.; García-Nieto, J.; Hassan, S.A.; Zaidi, S.A.R.; Iqbal, N. Precision agriculture techniques and practices: From considerations to applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Riquelme, J.; Pavón-Pulido, N.; Navarro-Hellín, H.; Soto-Valles, F.; Torres-Sánchez, R. A software architecture based on FIWARE cloud for Precision Agriculture. Agricultural water management 2017, 183, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkilä, R.; Seilonen, I.; Koskinen, K. Software architecture for farm management information systems in precision agriculture. Computers and electronics in agriculture 2010, 70, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantalaki, N.; Souravlas, S.; Roumeliotis, M. Data-driven decision making in precision agriculture: The rise of big data in agricultural systems. Journal of agricultural & food information 2019, 20, 344–380. [Google Scholar]
- Pogorelskaia, I.; Várallyai, L. Agriculture 4.0 and the role of education. Journal of Agricultural Informatics/Agrárinformatika Folyóirat 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, K.; Borrero, A.N.; Vasuian, F.; Bryceson, K.P. Experiences in building an IoT infrastructure for agriculture education. Procedia Computer Science 2018, 135, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.R.; Razdari, A.M.; others. Application of GIS and GPS in precision agriculture (a review). International Journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research 2015, 3, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Gawankar, S.A. Achieving sustainable performance in a data-driven agriculture supply chain: A review for research and applications. International Journal of Production Economics 2020, 219, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, K.G.; Busato, P.; Moshou, D.; Pearson, S.; Bochtis, D. Machine learning in agriculture: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutter, T.; Tiemann, S.; Siebert, R.; Fountas, S. The role of communication and co-operation in the adoption of precision farming. Precision Agriculture 2011, 12, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baio, F.H.; Silva, S.P.d.; Camolese, H.d.S.; Neves, D.C. Financial analysis of the investment in precision agriculture techniques on cotton crop. Engenharia Agrícola 2017, 37, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.B.; do Vale, S.M.L.R.; Pinto, F.A.; Müller, C.A.; Moura, A.D. The economic feasibility of precision agriculture in Mato Grosso do Sul State, Brazil: a case study. Precision Agriculture 2007, 8, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenberg-DeBoer, J.; Erickson, B. Setting the record straight on precision agriculture adoption. Agronomy Journal 2019, 111, 1552–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilaris, A.; Kartakoullis, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X. A review on the practice of big data analysis in agriculture. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2017, 143, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Jain, A.; Gupta, P.; Chowdary, V. Machine learning applications for precision agriculture: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access 2020, 9, 4843–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrullah, A.; OZERDEM, M.S.; USTUNDAG, B.B. Machine learning based regression model for prediction of soil surface humidity over moderately vegetated fields. 2019 8th International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics (Agro-Geoinformatics). IEEE, 2019, pp. 1–4.
- Wolfert, S.; Goense, D.; Sørensen, C.A.G. A future internet collaboration platform for safe and healthy food from farm to fork. 2014 annual SRII global conference. IEEE, 2014, pp. 266–273.
- Aceto, G.; Persico, V.; Pescapé, A. A survey on information and communication technologies for industry 4.0: State-of-the-art, taxonomies, perspectives, and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2019, 21, 3467–3501. [Google Scholar]
- Arcury, T.A.; Estrada, J.M.; Quandt, S.A. Overcoming language and literacy barriers in safety and health training of agricultural workers. Journal of agromedicine 2010, 15, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fomenko, T.; Bilotserkovets, M.; Klochkova, T.; Statsenko, O.; Sbruieva, A.; Kozlova, O.; Kozlov, D. Overcoming barriers in intercultural communication: a case study on agricultural idioms in English, Ukrainian and Chinese. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies 2020, 9, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, J.V. Implementing precision agriculture in the 21st century. Journal of agricultural engineering research 2000, 76, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Shao, X.F.; Wu, C.H.; Qiao, P. A systematic literature review on applications of information and communication technologies and blockchain technologies for precision agriculture development. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 298, 126763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, D.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z. Path Tracking Control for Four-Wheel-Independent-Driven Agricultural High Clearance Sprayer with New Front-Rear-Dual-Steering-Axle. 2020 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC). IEEE, 2020, pp. 2966–2972.
- Torky, M.; Hassanein, A.E. Integrating blockchain and the internet of things in precision agriculture: Analysis, opportunities, and challenges. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2020, 178, 105476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfert, S.; Ge, L.; Verdouw, C.; Bogaardt, M.J. Big data in smart farming–a review. Agricultural systems 2017, 153, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L.; Wiegman, C.; Davis, J.; Shearer, S. Confidence-driven hierarchical classification of cultivated plant stresses. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2021, pp. 2503–2512.
- Nicoletti, J.V.M.; De Miranda, J.H.; Cooke, R.; Christianson, L.E.; De Oliveira, L.A. Efficiency analysis of machine learning models for simulating nitrate movement in soils from Illinois State. 2021 ASABE Annual International Virtual Meeting. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, 2021, p. 1.
- Bosona, T.; Gebresenbet, G. Food traceability as an integral part of logistics management in food and agricultural supply chain. Food control 2013, 33, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, N.; Wortman Jr, M.S.; Mathias, E.D. Dominant factors impacting the development of business-to-business (B2B) e-commerce in agriculture. The International Food and Agribusiness Management Review 2001, 4, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadi, A.; Kamble, S.S.; Mani, V.; Benkhati, I.; Touriki, F.E. An ensemble machine learning approach for forecasting credit risk of agricultural SMEs’ investments in agriculture 4.0 through supply chain finance. Annals of Operations Research 2021, pp. 1–29.
- Kyriazi, F.; Thomakos, D.D.; Guerard, J.B. Adaptive learning forecasting, with applications in forecasting agricultural prices. International Journal of Forecasting 2019, 35, 1356–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucaioni, A.; Cicchetti, A.; Ciccozzi, F. Modelling in low-code development: a multi-vocal systematic review. Software and Systems Modeling 2022, 21, 1959–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, N.; Rentrop, C.; Huber, M. Low-Code Development Platforms-A Literature Review. AMCIS, 2021.
- Alsaadi, H.A.; Radain, D.T.; Alzahrani, M.M.; Alshammari, W.F.; Alahmadi, D.; Fakieh, B. Factors that affect the utilization of low-code development platforms: survey study. Romanian Journal of Information Technology & Automatic Control/Revista Română de Informatică și Automatică 2021, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, A.C.; Frank, U. Low-code platform. Business & Information Systems Engineering 2021, 63, 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Van Geest, M.; Tekinerdogan, B.; Catal, C. Design of a reference architecture for developing smart warehouses in industry 4.0. Computers in industry 2021, 124, 103343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Huang, X. A map of threats to validity of systematic literature reviews in software engineering. 2016 23rd Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference (APSEC). IEEE, 2016, pp. 153–160.
- Ampatzoglou, A.; Bibi, S.; Avgeriou, P.; Verbeek, M.; Chatzigeorgiou, A. Identifying, categorizing and mitigating threats to validity in software engineering secondary studies. Information and Software Technology 2019, 106, 201–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catal, C.; Giray, G.; Tekinerdogan, B. Applications of deep learning for mobile malware detection: A systematic literature review. Neural Computing and Applications 2022, pp. 1–26.
| RQ | Question | Aim |
| 1 | What are the identified features of LCDPs? |
The aim is to identify and compare existing LCDPs capabilities and suitability for a particular development task |
| 2 | What are the objectives of LCDPs described in scientific literature? |
The aim is to identify the specific goals and purposes for which LCDPs are employed in different software development projects and settings. |
| 3 | To what extent are the identified LCDP objectives and features applicable for PA? |
The aim is to gain understanding in the agricultural industries and technical application of LCDPs implemented across the PA domain. |
| 4 | What are the challenges that have to be overcome for LCDPs in PA? |
The aim is to identify and define the obstacles, difficulties, and deficiencies that arise during LCDP adoption in PA. Furthermore, the aim of this question is to understand and emphasize the techniques, best practices, and suggestions provided in academic research to address the challenges identified. |
| 5 | What are the future directions for LCDPs in PA? |
The aim is to explore potential developments and trends in LCDPs and provide insights on where the technology may be advancing for PA. |
| Sources | After automated and manual search |
After applying selection criteria |
| ACM Digital Library | 42 | 9 |
| IEEE Xplore | 42 | 20 |
| Science Direct | 121 | 1 |
| Scopus | 141 | 22 |
| Wiley Online Library | 26 | 0 |
| Manual search | 33 | 8 |
| Total | 405 | 60 |
| Total after removing duplicates |
44 |
| Selection criteria | |
| 1 | Papers that do not have full text available |
| 2 | Papers which not written in English |
| 3 | The duplicate publication that found in multiple sources |
| 4 | Papers that are brief in information (less than 4 pages) |
| 5 | Papers do not relate to software development |
| 6 | Papers do not relate to low code development platforms |
| 7 | Papers do not validate the proposed study |
| 8 | Papers which are experience and survey papers |
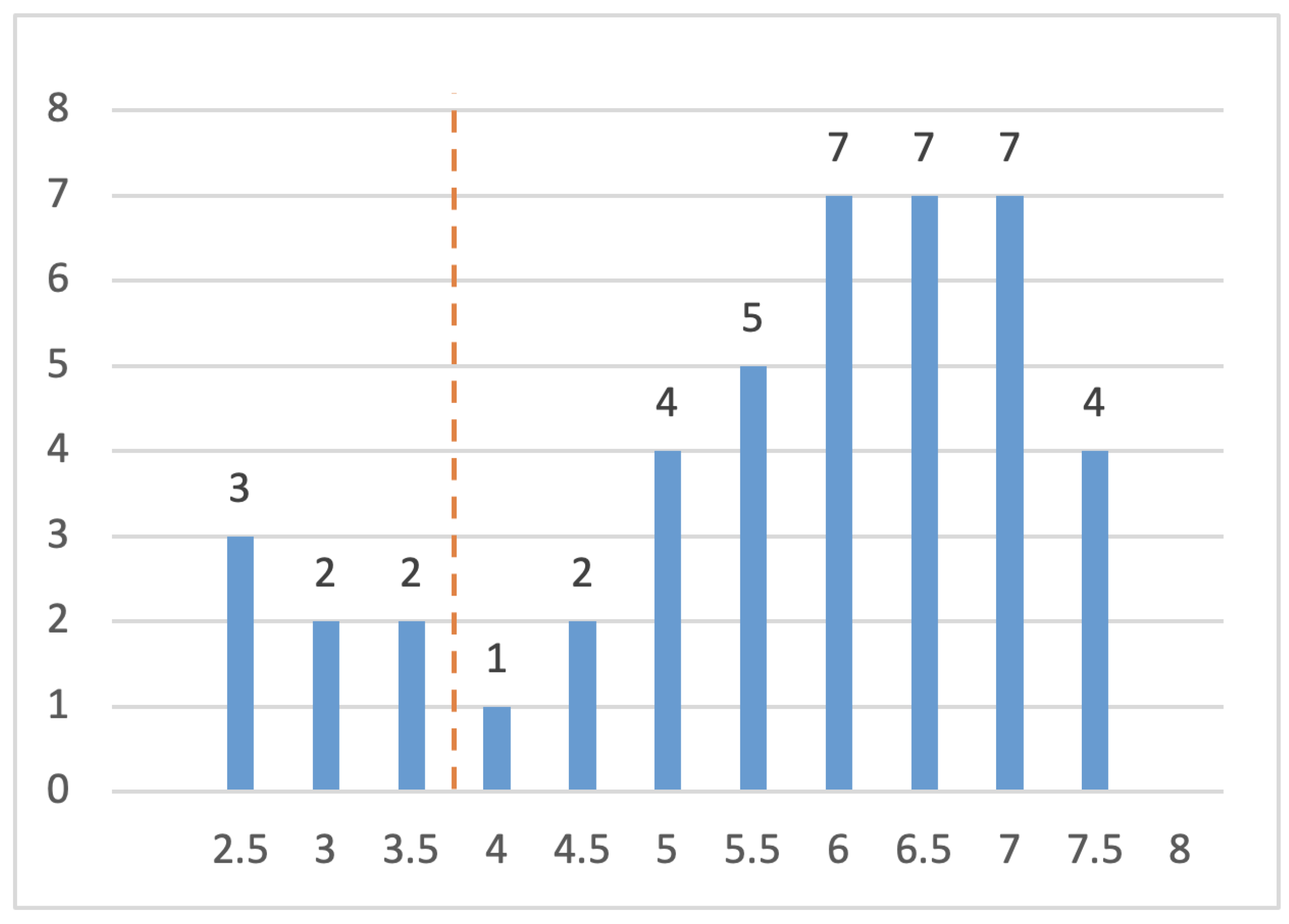
| Question | Yes (1) |
Partial (0.5) |
No (0) |
|
| 1 | Aims clearly stated | |||
| 2 | Scope and Context clearly defined | |||
| 3 | Variables valid and reliable | |||
| 4 | Research process documented adequately | |||
| 5 | All study questions answered | |||
| 6 | Negative findings presented | |||
| 7 | The main findings clearly stated | |||
| 8 | Conclusions relate to the aim of the purpose of the study |
| Study | Year | Study | Year | Study | Year |
| Almonte et al. | 2020 | Lethbridge | 2021 | Sahay et al. | 2020 |
| Asawa et al. | 2021 | Lopes et al. | 2021 | Salgueiro et al. | 2021 |
| Braganca et al. | 2021 | Lourenco et al. | 2021 | Schötteler et al. | 2021 |
| Da Cruz et al. | 2021 | Marek et al. | 2021 | Sharma and Gupta | 2021 |
| Daniel et al. | 2020 | Martins et al. | 2020 | Silva et al. | 2021 |
| Deshpande et al. | 2022 | Metrôlho et al. | 2019 | Tisi et al. | 2019 |
| Di Sipio et al. | 2020 | Metrôlho et al. | 2020 | J.Wang et al. | 2021 |
| Fernandes et al. | 2020 | Moin et al. | 2022 | Y.Wang et al. | 2021 |
| Ferreira and Costa | 2021 | Pacheco et al. | 2021 | Waszkowski | 2019 |
| Indamutsa et al. | 2021 | Pantelimon et al. | 2019 | Weber | 2021 |
| Iyer et al. | 2021 | Philippe et al. | 2020 | Zhuang et al. | 2022 |
| Junior et al. | 2020 | Pichidtienthum et al. | 2021 | Zolotas et al. | 2018 |
| Jyothi and Rajeswari | 2022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





