1. Introduction
Soccer is an intermittent sport, which requires a high level of technical, tactical and psychological preparation, but also an equally high level of physical abilities (endurance, speed, strength, flexibility) [
1,
2]. During the game, players cover distances of more than 10 km and perform actions at very high speed (>19.8 km/h) every 70-90 seconds [
3]. For example, during the FIFA World Cup in Qatar (FIFA World Cup Qatar 2022™) [
4], teams covered an average of 108.1 km in total per match, of which 9,001m and 2,345m were covered at high intensities (>20km/h and >25km/h), respectively (FIFA, Training Center, 2022) [
5].
Youth soccer is also characterized by constant intensity changes in various actions (running, sprinting, directional changes, jumping, tackling), making it necessary to produce energy from both aerobic and anaerobic energy mechanisms [
6]. The same researchers believe that although aerobic capacity is an important factor for success in developmental ages, however, other factors, such as technique and tactics, also play an important role in youth development. For this reason, it is important for coaches in the developmental ages to use training methods that provide stimuli that meet a large part of the requirements of young players, both from a technical and tactical point of view and, also, from a fitness point of view.
A very widespread training method that is time efficient as it trains aerobic and anaerobic capacity and provides time for training other stimuli (neuromuscular skills, technique, tactics, fitness elements) necessary for the smooth development of young people is High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) [
7].
This method has been extensively applied to improve aerobic and anaerobic fitness in different populations (adults, healthy or diseased individuals, team or individual athletes), but its application to children and adolescents is not as extensive as in adults [
7]. Several studies have been conducted on adolescent soccer players with conflicting results [
8,
9,
10,
11]. Michailidis et al. [
9] implemented an 8-week HIIT program in 16-year-old adolescent soccer players that included running 2-3 sets of 4 minutes with 15 seconds of work and 15 seconds of rest at 120% of the athletes' maximum speed in the Yo-Yo Intermittent Recovery 1 test (YYIR1). Results showed a significant decrease in 10-meter speed time (9%), Illinois Agility test (3%) and a significant improvement in RSAmean (1.7%). Sperlich et al. [
10] recorded a decrease (improvement) in the speed time of young soccer players aged 13.5 years in 20, 30 and 40 meters by 4.3%, 4.4% and 2.8% respectively and in VO2max by 6.8% after a 5-week interventional HIIT program. In contrast, another study did not observe a significant improvement in speed time in the 30 m sprint and recorded a deterioration in jumping ability (CMJ and drop jump-DJ) in 16 year old elite soccer players [
8]. The conflicting results are likely to be due to the different protocols and the variables used in each, the tests (trials) or the age and competitive level of the participants.
The majority of the various studies in football have mainly used fixed intervention protocols, without periodization [
8,
12,
13,
14]. Los Arcos et al. [
12] applied 3 sets of 4 min of running with intensity at 90-95% of HRmax with a 3 min break at 50-60% of HRmax for a period of 6 weeks, while a protocol of 4 sets x 4 min was applied by Impellizzeri et al. [
13] and Impellizzeri et al. [
14] in soccer players aged 18 and 17 years, respectively.
However, based on the principle of progressive overload, it is possible that a gradual increase in load would give better results on various indicators of aerobic or anaerobic performance. Few studies seem to have applied a progressive increase in load [
9,
11], but the results of which do not seem to be in full agreement. Thus, the purpose of this study is to examine the effect of a 6-week high-intensity interval training (HIIT) program with an increase in training volume every two weeks on the physical abilities of adolescent soccer players under 15 years of age (U15).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
From the power analysis conducted prior to the study [
15], it was found that the smallest acceptable sample size would be 24 subjects for the analysis of the interaction between groups and time points of the measurements. For the above analysis, Gpower software (G*Power, version 3.1.9.2, Universität Kiel, Düsseldorf, Germany) was used with an effect size > 0.6, error probability of 0.05 and power of 0.9 for the 2 groups and 2 time points (before and after). The study inclusion criteria were defined as follows: 1) no musculoskeletal injury at least 4 months prior to the study, 2) all players participated in more than 95% of the training sessions, and 3) not taking any medication. 30 teenagers soccer players under 15 years old (U15) from an academy in Thessaloniki, who played in the developmental championships of the Macedonia Football Union in the corresponding category (U15), participated in the research. Participants were randomly divided into two subgroups: one subgroup was the control group (Control Group - C.G., n=15), while the other was the intervention group (Experimental Group - E.G., n=15). All players, and their parents, were informed about the benefits and potential risks of the study and signed a consent form for their participation. The research followed the guidelines of the Research Code of Ethics of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, in the spirit of the Declaration of Helsinki (Approval number 199/2024). The characteristics of the participants are presented in
Table 1.
2.2. Procedure
The study was conducted during the season (March-May) and lasted a total of 9 weeks. All participants did the same training four times a week and participated in one game. The measurements included assessment of anthropometric characteristics (height, weight) and performance indicators: 10 & 30 meters speed, change of direction (COD) (505 agility test) with both right and left foot turn, maximum oxygen uptake capacity - VO2max (30-15 Incremental Fitness test - 30-15IFT) and repeated sprint ability (RSA, 6 X 30 meters sprint). Two weeks prior to the start of the intervention program, the soccer players were familiarized with the measurement procedures to limit the learning effect error. One week before the start of the intervention, baseline measurements were taken on two different days (due to the number of trials) separated by 48 hours. At the first measurement, the anthropometric characteristics were measured as well as the speed at 10 and 30 m and the maximum oxygen uptake capacity (30-15IFT). At the second measurement, the other tests (agility test - 505 and the RSAtest) were performed. All the above mentioned procedures were repeated one week after the completion of the intervention training program for both groups in the same order. On the day of the measurements before the start of the evaluation, a 25-minute warm-up was performed, in which running exercises, neuromuscular coordination exercises, 4 repetitions of 15-meter speed and 4 repetitions with change of direction were performed, followed by a 6vs2 small sided game. The warm-up was followed by a 5 minute rest break. The entire procedure was done on synthetic turf.
2.3. Intervention Program
The intervention program took place over a six-week period, with a frequency of two training sessions per week, with the two days 48 hours apart (12 training sessions in total). The total duration of the training sessions was 90 minutes. In addition to the technical training program performed by C.G., E.G. participants performed the intervention program. The total duration of the intervention program in each training session ranged from 15 to 21 minutes (15 minutes in the first two weeks, 18 minutes in the third and fourth weeks, and 21 minutes in the last two weeks) according to the progressivity of the program. The intervention program was carried out immediately after the warm-up so that there was full neuromuscular activation. The intervention program is presented in
Table 2.
Anthropometric measurements
An electronic scale with a SECA 767 scale stadiometer (BodyScale 500, SecaGmbh&Co. Kg., Hamburg, Germany) was used to measure height and weight. During the measurements, participants were barefoot and wore only underwear.
Speed (10 & 30 m. sprint)
The 30 m sprint was used to measure speed, with an additional measurement at 10 m on synthetic turf with football boots. The footballers performed two attempts and the best time was used for statistical analysis. Photocell gates (Witty Microgate, Microgate, Bolzano, Italy) were placed at the starting point, as well as at 10 and 30 meters. The players started from an upright position, 30 cm behind the first gate. Photocells were placed at a height of 0.7 m from the ground (approximately at hip height) to record torso movement and avoid false signals caused by lower limb movement [
16]. The finish cone was placed 5 m after the 30 m photocells to eliminate the possibility of participants reducing their speed. There was complete rest between the two trials.
Change of Direction (COD) (505 agility test)
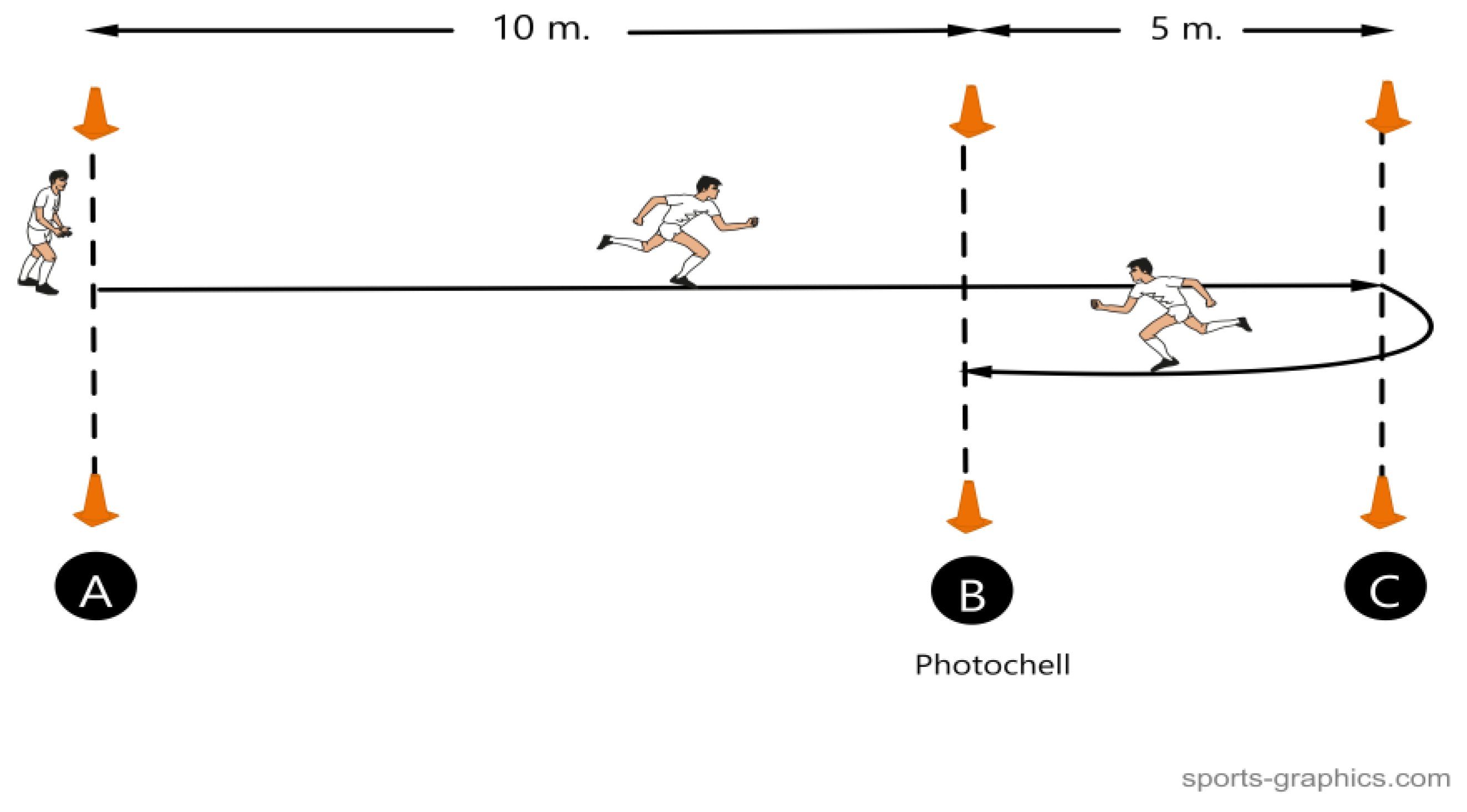
Participants started from a standing position, 30 cm behind the starting point. From position A (starting position) they sprinted to position C in which they stepped with one foot, changed direction and quickly crossed the finish line through gate B. The test was performed twice for each leg (right - left) and the best timed effort on each side was taken for statistical analysis. Position C was 15 m from position A, while position B was 5 m from C and 10 m from A. Photocell beams were placed at positions B and C to measure the time.
Figure 1 shows the test procedure.
Repeated Sprint Ability (RSA test)
The RSA test consisted of 6 × 30 m sprints with a 20-second interval between repetitions. Photocell beams were placed at the start line and the 30 m finish line at hip height (0.7 m from the ground). Each player started 30 cm before the start line and performed the first attempt whenever ready. Subsequent repetitions were performed after the examiner's signal, which was given exactly at 20 seconds, and at 15 seconds there was a readiness alert from the examiner. For statistical analysis, the total time (RSAtotal), the mean time (RSAmean) and the percentage of performance decrement (RSAdecr) were determined.
30-15 Intermittent Fitness Test (30-15IFT)
The 30-15 Intermittent Fitness Test (30-15
IFT) [
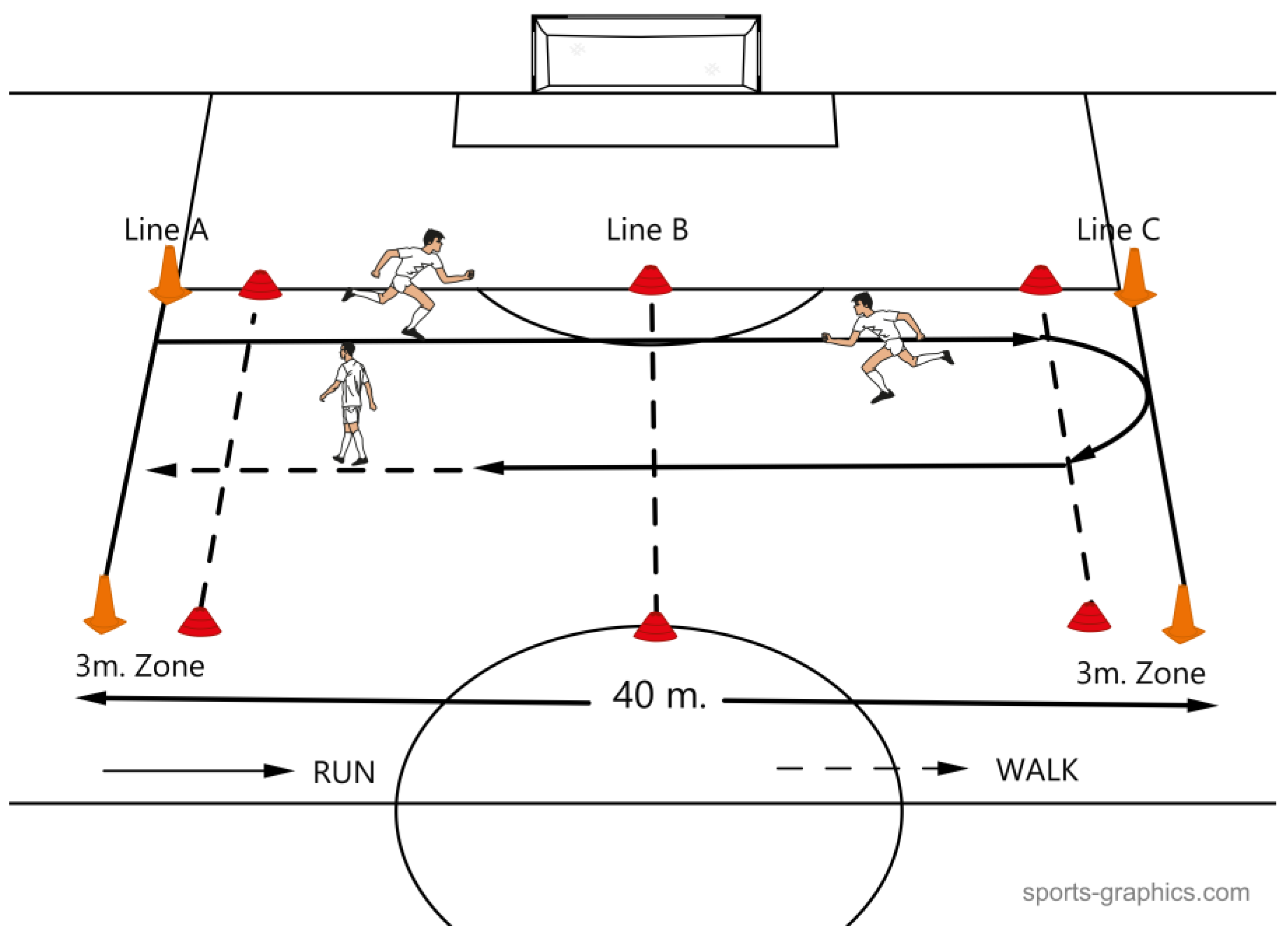
17] is a progressively increasing intermittent test consisting of 30-second runs interrupted by 15-second periods of passive recovery. The test was conducted in the standard 40-meter version proposed for soccer [
17]. The 40 m distance is defined by two lines A and C and separated in the middle by another line B. Before lines A and C two zones of 3 m length each are defined. Footballers ran back and forth between the two lines A and C at a pace determined by recorded sound signals (beeps) at appropriate time intervals that helped them to adjust their running speed by entering the 3-meter zones and the middle line B when the short duration sound signals were heard (
Figure 2). The players started at a speed of 8 km/h, which increased by 0.5 km/h every 45 seconds. The 30-15
IFT app was used to implement the test, which was "downloaded" to the mobile phone via the Apple Appstore and has the genuine recording of the test's sound signals. During the 15-second recovery period, the footballers walked to the nearest line (A, B or C) depending on the point where they stopped their 30-second run, from which they started the next stage of running. The test was completed for each player when they could not maintain the given speed or could not reach the 3-meter zones at the moment of the sound signal for 3 consecutive times. The speed at which the player was running at the given moment was considered the maximum running speed [
17] and was used to run the intervention program.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and confidence intervals (CI) (95%) were calculated. The 1-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to test the normal distribution of our data. The results of this test showed that it was not necessary to use non-parametric statistical methods. 2-way (group and time) ANOVA with repeated measures was used for statistical analysis. Partial eta square was used for effect size and this was classified as small (0.01-0.059), medium (0.06-0.137) and large (>0.138) [Richardson, 2011]. The significance level was set at p<0.05. SPSS version 25.0 was used for all analyses (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
The two groups did not differ in age, body measurements and fitness tests at baseline. Also, soccer training and the intervention program did not affect the anthropometric characteristics of the participants.
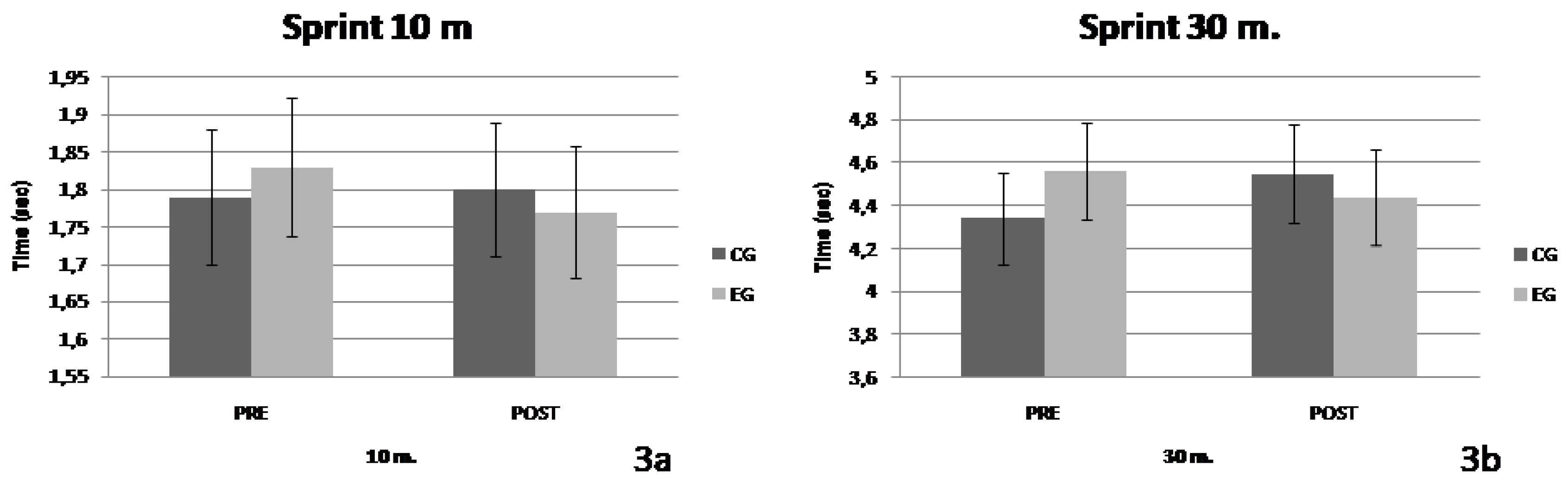
The results of the analysis on the 10 m sprint performance showed a significant interaction of the factors "group x time" (F=6.053, p=0.027, η
2=0.302). In contrast, no significant effect of the factor "group" (F=0.030, p=0.864, η
2=0.002) nor of the factor "time" (F=6.053, p=0.066, η
2=0.221) was observed. Also, no significant interaction of the factors "group x time" (F=2.566, p=0.131, η
2=0.155) was observed on 30m sprint performance. No significant effect of the factor "group" (F=0.220, p=0.646, η
2=0.015) nor of the factor "time" (F=0.167, p=0.689, η
2=0.012) was observed. The variations of the parameters values are presented in
Figure 3a & b.
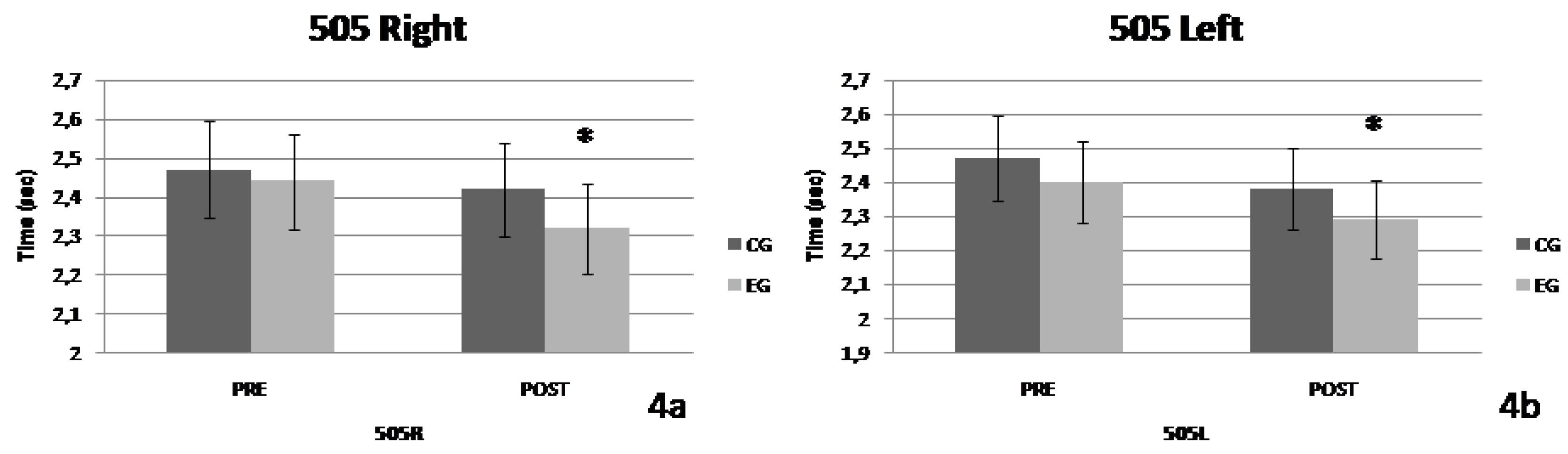
The results about the 505 test performance on the right leg showed no significant interaction of the factors "group x time" (F=1.591, p=0.228, η
2=0.102). There was no significant effect of the factor "group" (F=1.702, p=0.213, η
2=0.108). However, a significant effect of the factor "time" was observed (F=10.882, p=0.005, η
2=0.437). Similar results concerning the performance in test 505 on the left leg did not show a significant interaction of the factors "group x time" (F=0.106, p=0.749, η
2=0.008). There was no significant effect of the factor "group" (F=2.405, p=0.143, η
2=0.680), but there was a significant effect of the factor "time" (F=29.766, p=0.00 η
2=0.680). The variations of the parameters values are presented in
Figure 4 a & b.
In the 30-15
IFT test and VO
2max performance, no significant interaction of the factors "group x time" was observed (F=0.3.949, p=0.067, η
2=0.22). No significant effect of the factor "group" was observed (F=0.443, p=0.516, η
2=0.031), but a significant effect of the factor "time" was observed (F=7.619, p=0.015, η
2=0.352). The changes in the values of the parameter are shown in
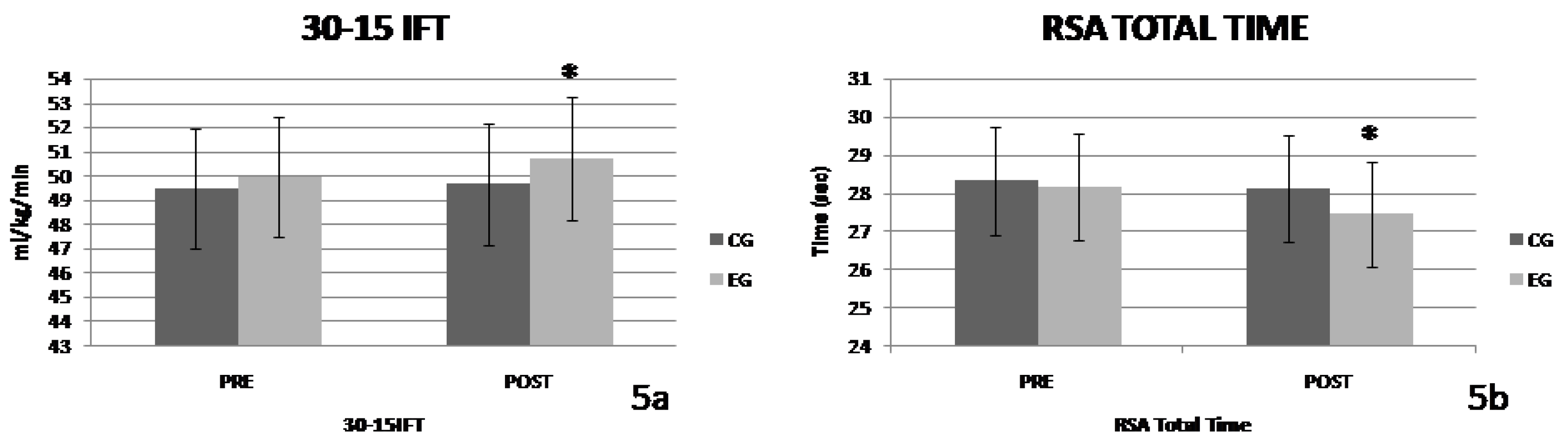
Figure 5a.
On Repeated Sprint Ability performance and especially on Total Time variable, a significant interaction of the "group x time" factors was observed (F=5.781, p=0.031, η
2=0.22). No significant effect of the factor "group" was observed (F=0.382, p=0.546, η
2=0.031), while a significant effect of the factor "time" was observed (F=18.491, p=0.001, η
2=0.352). The changes in the values of the parameter are presented in
Figure 5b.
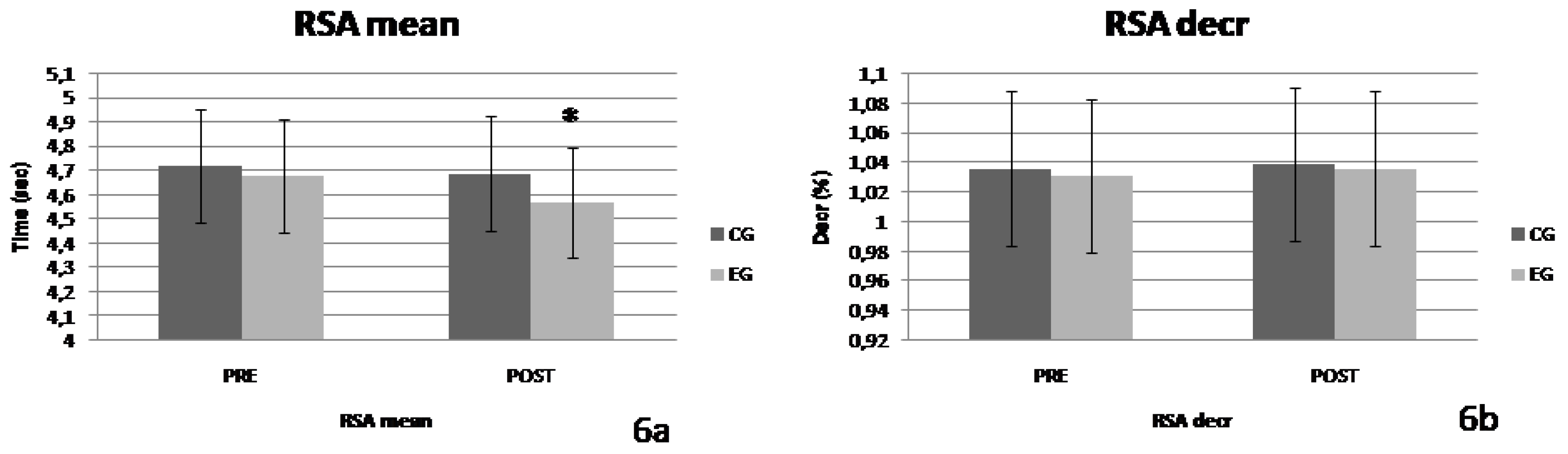
Similar results were recorded in the performance on Repeated Sprint Ability and the RSA
mean variable. A significant interaction of the "group x time" factors was observed (F=5.963, p=0.028, η
2=0.299). No significant effect of the "group" factor was observed (F=0.387, p=0.544, η
2=0.027), while a significant effect of the "time" factor was observed (F=17.817, p=0.001, η
2=0.560). Finally, in the performance on RSA
decr no significant interaction was observed neither between the factors "group x time" (F=0.099, p=0.758; η
2=0.007), nor any significant effect of both the factor "group" (F=0.227, p=0.641, η
2=0.016) and the factor "time" (F=1.240, p=0.284, η
2=0.081). The changes in the values of the two parameters are presented in
Figure 6 a & b.
The confidence intervals of all variables are presented in
Table 3.
4. Discussion
Based on the results of the present study, it is evident that the intervention group after the program implemented improved their performance in change of direction (COD), ability to perform repeated sprints (RSA) as well as aerobic capacity (VO2max). In contrast, no significant difference was observed in 10 and 30 m speed.
The performance on the COD ability, as assessed by the 505 agility test in the present study, improved for the intervention group (3%).Conflicting results are recorded in the literature regarding the effect of HIIT on the COD ability [
9,
18,
19,
20].The results of Fernandez-Fernandez et al. [
19] in tennis athletes and Fang & Jiang [
18] in male and female basketball athletes are consistent with the results of the present study. Similarly, Michailidis et al. [
9] recorded an improvement in the ability to COD in 16-year-old soccer players. In contrast, Wen et al. [
20] did not record a significant improvement in the performance of adult female soccer players after an interventional 8-week HIIT program. The differences in results are likely to be due to the age of the participants, the different tests, and the different characteristics of the protocols (duration, intensity, density, interval). Kyranoudis et al. [
21] report an improvement in the ability to COD with increasing age. Direction change actions include accelerations and decelerations and therefore the use of the stretch-shortening cycle (SSC) effect is critical for performance [
22]. The improvement in the performance of COD ability can be attributed to an increase in muscle metabolites (phosphocreatine) as a result of HIIT training, which can enhance energy availability during high intensity activities [
9].Several mechanisms, such as increased muscle fibre recruitment, firing frequency and timing of motor units, are thought to be responsible for improving athletic performance in burst-type activities [
23]. These adaptations enhance the ability of the muscular system to generate force and respond more rapidly to motor stimuli, which is critical for sports that require explosiveness, speed and power, such as soccer [
9].
Significant improvement in the RSA ability and especially in the variables RSA
total and RSA
mean was recorded by the intervention group compared to the control group. In contrast, there does not seem to be a significant improvement in RSA
dec. Similar results in RSA
mean were recorded by Chtara et al. [
24] in soccer athletes of similar age to the participants in the present study. The ability to perform repetitive sprints (RSA) depends on metabolic, neural and mechanical factors [
25]. Improving one or more factors by implementing training programs leads to improvements in the above mentioned ability [
9]. Although there are no measurements available in the present study, we hypothesize that possible improvements in glycolysis and the phosphagen system, the percentage of oxidative muscle fibers and the ability of muscle homeostasis and lactic acid management may have led to improvements in the ability of repetitive sprinting [
26,
27].
HIIT is a form of training that improves aerobic capacity [
28]. The results of the study confirm this view, as there was a significant improvement in the maximum oxygen uptake (VO
2max) of the participants in the intervention group compared to the control group. Improvement in VO
2max after implementation of HIIT programs was recorded by Milanovic et al. [
29] in their meta-analysis involving 723 adult athletes of various sports. A 4.3% and 7% improvement was also observed by Arslan et al. [
30] and Sperlich et al. [
10], respectively, in adolescent soccer players under 15 years of age using HIIT protocols of 5 weeks duration. The improvement observed following the application of HIIT training protocols is likely due to the fact that training at high intensities (VO
2max) induces peripheral adaptations (increase in muscle mitochondrial and capillary density) and central adaptations (increase in pulse volume and cardiac output) [
31].
The physical ability that did not seem to have significant improvement after the HIIT protocol was speed, both at 10 m and 30 m. The results of the present study contradict those of Arslan et al. [
30], who reported an improvement in acceleration speed (-5%) in 14-year-old adolescent soccer players and Michailidis et al. [
9] who report an improvement in 10 m speed (9%), also in adolescent football players, but in an older category (U17). On the other hand, the lack of improvement in 30 m speed seems to be in line with the results of Michailidis et al. [
9] but not with those of Arslan et al. [
30] who recorded an improvement in the performance of adolescent footballers. Engel et al. [
7] in their review and meta-analysis study report a large positive effect of HIIT training on 5-40 m speed ability. However, the participants in the different studies included in the meta-analysis were not all football players and the age and protocols were different.