Submitted:
26 September 2024
Posted:
26 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
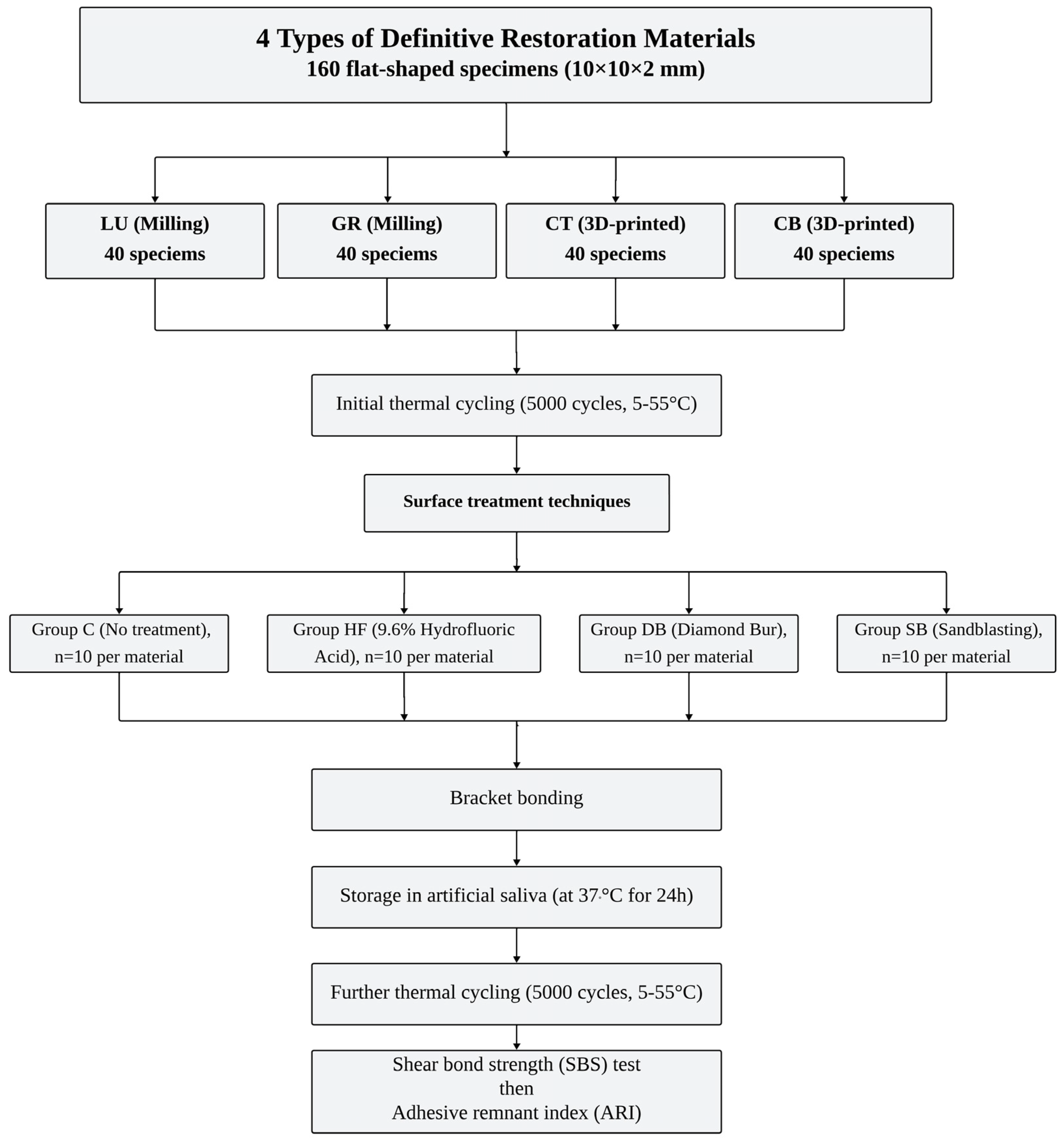
Specimen Preparation
Surface Treatment Application
Bracket Bonding Procedure
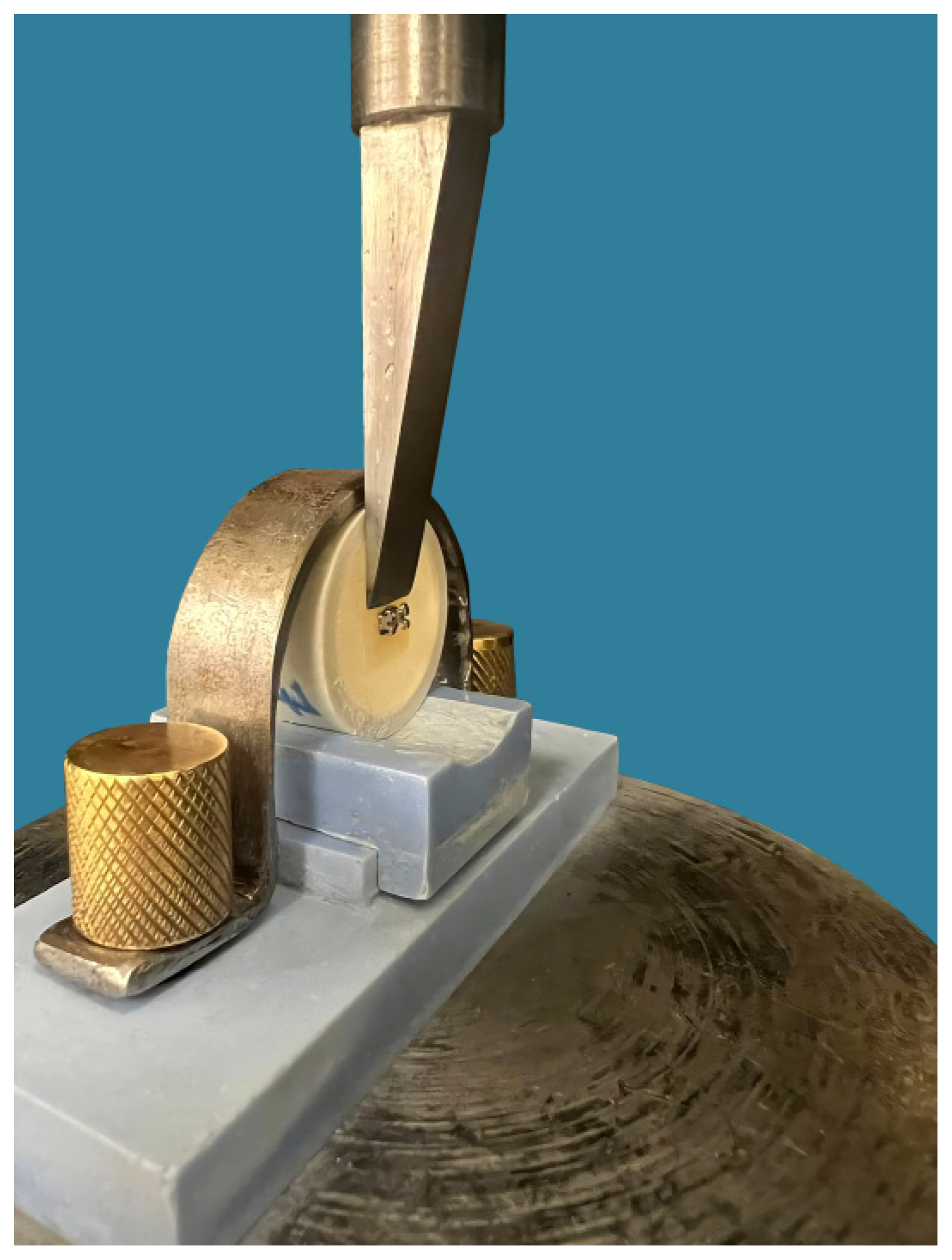
Shear Bond Strength (SBS) Test
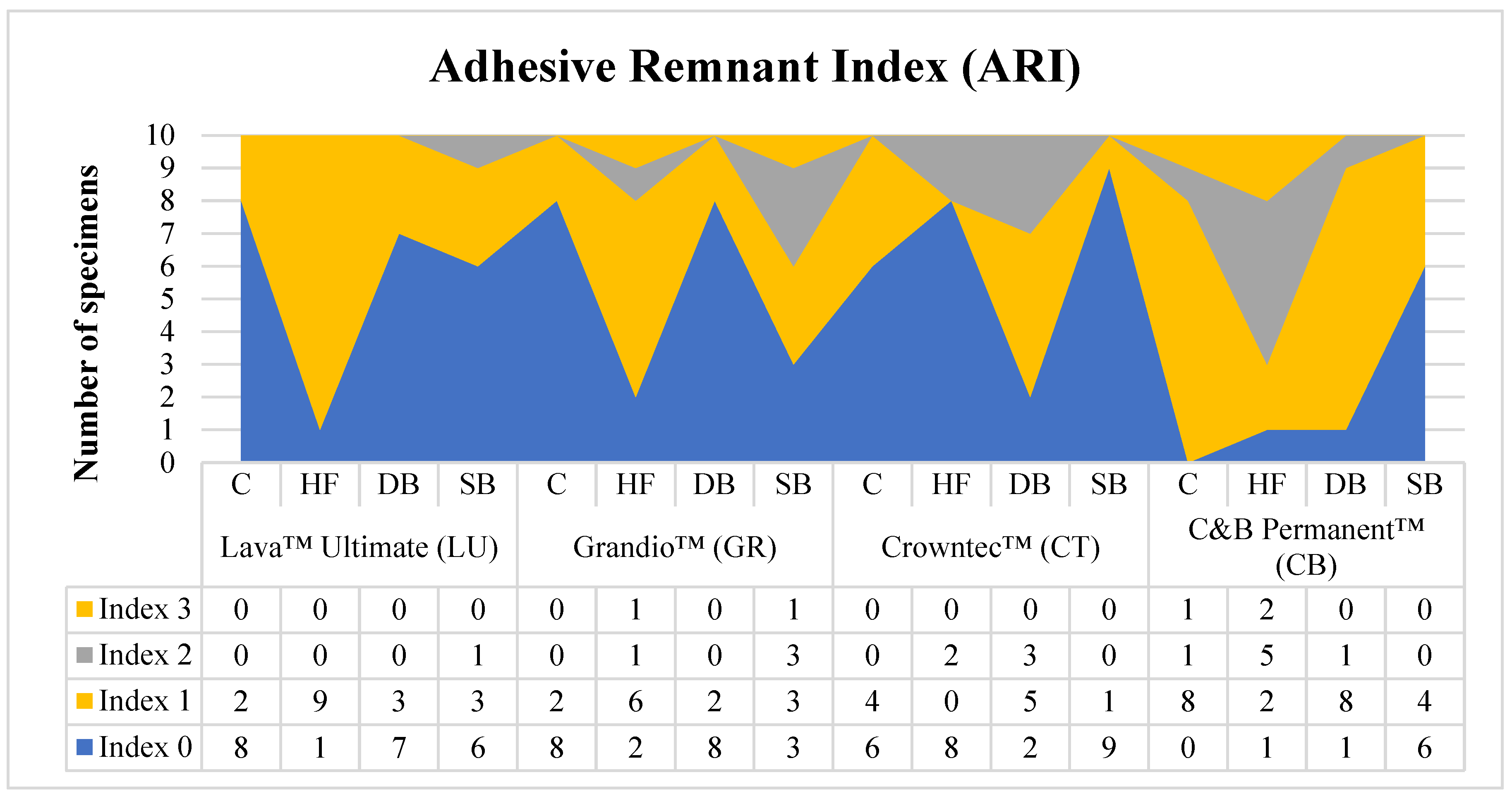
Adhesive Remnant Index (ARI) Score
- ➢
- 0: no adhesive remained on the bonded surface (Adhesive failure of the cementation with the restoration).
- ➢
- 1: less than 50 % of the adhesive remained on the bonded surface (Mixed Adhesive and cohesive failure of the cementation; Adhesive > Cohesive).
- ➢
- 2: more than 50 % of the adhesive remained on the bonded surface (Mixed Adhesive and cohesive failure of the cementation; Adhesive < Cohesive).
- ➢
- 3: 100 % of the adhesive remained on the bonded surface (Adhesive failure of the cementation with the bracket).
Statistical Analysis
Results
Discussion
Conclusion
- Both CAD-CAM restorative materials (milled and 3D-printed) demonstrated adequate shear bond strength (SBS) for clinical use, with milled materials (LU and GR) showing significantly higher SBS values compared to 3D-printed materials (CT and CB).
- Surface treatments significantly improved SBS, with sandblasting (SB) and hydrofluoric acid etching (HF) yielding higher SBS values than diamond bur roughening (DB).
- Adhesive failure between the bracket and the restoration was more common, with most specimens showing no adhesive or less than 50 % adhesive remaining on the surface.
- Sandblasted milled fabricated Lava Ultimate™ demonstrated the most favorable outcomes in terms of both SBS and ARI scores.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of interest
Compliance with Ethics Requirements
References
- Kollmuss M, Kist S, Goeke JE, Hickel R, Huth KC. Comparison of chairside and laboratory CAD/CAM to conventional produced all-ceramic crowns regarding morphology, occlusion, and aesthetics. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(4):791-797. [CrossRef]
- Mainjot AK, Dupont NM, Oudkerk JC, Dewael TY, Sadoun MJ. From Artisanal to CAD-CAM Blocks: State of the Art of Indirect Composites. J Dent Res. 2016;95(5):487-495. [CrossRef]
- Koenig A, Schmidtke J, Schmohl L, et al. Characterisation of the filler fraction in cad/cam resin-based composites. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(8). [CrossRef]
- Nguyen JF, Migonney V, Ruse ND, Sadoun M. Resin composite blocks via high-pressure high-temperature polymerization. Dent Mater. 2012;28(5):529-534. doi:10.1016/j.dental.2011.12.003.
- Atta I, Bourauel C, Alkabani Y, et al. Physiochemical and mechanical characterisation of orthodontic 3D printed aligner material made of shape memory polymers (4D aligner material). J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. Published online 2023:106337.
- Sharif M, Bourauel C, Ghoneima A, Schwarze J, Alhotan A, Elshazly TM. Force system of 3D-printed orthodontic aligners made of shape memory polymers: an in vitro study. Virtual Phys Prototyp. 2024;19(1):e2361857.
- Elshazly TM, Keilig L, Alkabani Y, et al. Potential Application of 4D Technology in Fabrication of Orthodontic Aligners. Front Mater 8 794536 doi 103389/fmats. Published online 2022.
- Alghazzawi TF. Advancements in CAD/CAM technology: Options for practical implementation. J Prosthodont Res. 2016;60(2):72-84. [CrossRef]
- Goodacre BJ, Goodacre CJ. Additive Manufacturing for Complete Denture Fabrication: A Narrative Review. J Prosthodont Off J Am Coll Prosthodont. 2022;31(S1):47-51. [CrossRef]
- Jain S, Sayed ME, Shetty M, et al. Physical and Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printed Provisional Crowns and Fixed Dental Prosthesis Resins Compared to CAD/CAM Milled and Conventional Provisional Resins: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(13). [CrossRef]
- Elshazly TM, Keilig L, Salvatori D, Chavanne P, Aldesoki M, Bourauel C. Effect of Trimming Line Design and Edge Extension of Orthodontic Aligners on Force Transmission: An in vitro Study. J Dent. Published online 2022:104276. [CrossRef]
- Abdelnaby YL. Effects of cyclic loading on the bond strength of metal orthodontic brackets bonded to a porcelain surface using different conditioning protocols. Angle Orthod. 2011;81(6):1064-1069. [CrossRef]
- Abu Alhaija ESJ, Abu AlReesh IA, AlWahadni AMS. Factors affecting the shear bond strength of metal and ceramic brackets bonded to different ceramic surfaces. Eur J Orthod. 2010;32(3):274-280. [CrossRef]
- Emsermann I, Eggmann F, Krastl G, Weiger R, Amato J. Influence of Pretreatment Methods on the Adhesion of Composite and Polymer Infiltrated Ceramic CAD-CAM Blocks. J Adhes Dent. 2019;21(5):433-443. [CrossRef]
- Colombo L do A, Murillo-Gómez F, De Goes MF. Bond Strength of CAD/CAM Restorative Materials Treated with Different Surface Etching Protocols. J Adhes Dent. 2019;21(4):307-317. [CrossRef]
- de Almeida RM, Hass V, Sasaki DY, Berger SB, Fernandes TM, Tonetto MR. The impact of different surface treatments on the shear bond strength of orthodontic metal brackets applied to different CAD/CAM composites. J Clin Exp Dent. 2021;13(6):608-613. [CrossRef]
- Iijima M, Ito S, Muguruma T, Saito T, Mizoguchi I. Bracket bond strength comparison between new unfilled experimental self-etching primer adhesive and conventional filled adhesives. Angle Orthod. 2010;80(6):1095-1099. [CrossRef]
- Karan S, Büyükyilmaz T, Toroǧlu MS. Orthodontic bonding to several ceramic surfaces: Are there acceptable alternatives to conventional methods? Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2007;132(2):144.e7-144.e14. [CrossRef]
- Falkensammer F, Freudenthaler J, Pseiner B, Bantleon HP. Influence of surface conditioning on ceramic microstructure and bracket adhesion. Eur J Orthod. 2012;34(4):498-504. [CrossRef]
- Reynolds IR. A Review of Direct Orthodontic Bonding. Br J Orthod. 1975;2(3):171-178. [CrossRef]
- Elsaka SE. Influence of surface treatments on bond strength of metal and ceramic brackets to a novel CAD/CAM hybrid ceramic material. Odontology. 2016;104(1):68-76. [CrossRef]
- Tezvergil A, Lassila LVJ, Vallittu PK. Composite-composite repair bond strength: Effect of different adhesion primers. J Dent. 2003;31(8):521-525. [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos K, Pahinis K, Saltidou K, Dionysopoulos D, Tsitrou E. Evaluation of the surface characteristics of dental CAD/CAM materials after different surface treatments. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(4):1-15. [CrossRef]
- Gilbert S, Keul C, Roos M, Edelhoff D, Stawarczyk B. Bonding between CAD/CAM resin and resin composite cements dependent on bonding agents: three different in vitro test methods. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(2):227-236. [CrossRef]
- Peumans M, Valjakova EB, De Munck J, Mishevska CB, Van Meerbeek B. Bonding effectiveness of luting composites to different CAD/CAM materials. J Adhes Dent. 2016;18(4):289-302. [CrossRef]
- Özcan M, Volpato CÂM. Surface Conditioning and Bonding Protocol for Nanocomposite Indirect Restorations: How and Why? J Adhes Dent. 2016;18(1):82. http://dx.doi.org/10.3290/j.jad.a35629.
- Reymus M, Roos M, Eichberger M, Edelhoff D, Hickel R, Stawarczyk B. Bonding to new CAD/CAM resin composites: influence of air abrasion and conditioning agents as pretreatment strategy. Clin Oral Investig. 2019;23(2):529-538. [CrossRef]
- Strasser T, Preis V, Behr M, Rosentritt M. Roughness, surface energy, and superficial damages of CAD/CAM materials after surface treatment. Clin Oral Investig. 2018;22(8):2787-2797. [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnaiah R, Alkheraif AA, Divakar DD, Matinlinna JP, Vallittu PK. The effect of hydrofluoric acid etching duration on the surface micromorphology, roughness, and wettability of dental ceramics. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(6). [CrossRef]
- Duzyol M, Sagsoz O, Polat Sagsoz N, Akgul N, Yildiz M. The Effect of Surface Treatments on the Bond Strength Between CAD/CAM Blocks and Composite Resin. J Prosthodont. 2016;25(6):466-471. [CrossRef]
- Frankenberger R, Hartmann VE, Krech M, et al. Adhesive luting of new CAD/CAM materials. Int J Comput Dent. 2015;18(1):9-20. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25911826.
- Özcan M, Valandro LF, Amaral R, Leite F, Bottino MA. Bond strength durability of a resin composite on a reinforced ceramic using various repair systems. Dent Mater. 2009;25(12):1477-1483. [CrossRef]
- Bayram M, Yeşilyurt C, Kuşgöz A, Ülker M, Nur M. Shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets to aged resin composite surfaces: effect of surface conditioning. Eur J Orthod. 2011;33(2):174-179. [CrossRef]
- Valandro LF, Ozcan M, Bottino MC, Bottino MA, Scotti R, Bona A Della. Bond strength of a resin cement to high-alumina and zirconia-reinforced ceramics: the effect of surface conditioning. J Adhes Dent. 2006;8(3):175-181.
- Yüzbaşıoğlu E, Sayar-Torun G, Özcan M. Adhesion of orthodontic brackets to indirect laboratory-processed resin composite as a function of surface conditioning methods and artificial aging. J Adhes Sci Technol. 2016;30(23):2565-2572. [CrossRef]
- Alavi S, Shirani F, Zarei Z, Raji S. Effect of different surface treatment with panaviaV5 on shear bond strength of metal brackets to silver amalgam. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2021;18(1). [CrossRef]
- Asiry MA, AlShahrani I, Alaqeel SM, Durgesh BH, Ramakrishnaiah R. Effect of two-step and one-step surface conditioning of glass ceramic on adhesion strength of orthodontic bracket and effect of thermo-cycling on adhesion strength. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;84(March):22-27. [CrossRef]
| Material | Material type | Composition | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filler | Polymer | |||
| Lava Ultimate™ (LU) | Milling block nanoceramic composite resin | 80 wt.% fillers of silica (size 20 nm), zirconia (size 4-11 nm) nanoparticles | 20 wt. % Bis-GMA, UDMA, Bis-EMA, TEGDMA | 3MTM ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA |
| Grandio™ (GR) | Milling block nanohybrid composite resin | 86 wt.% nanohybrid fillers (particle size 20-60 nm) | 14 wt. % UDMA, DMA | VOCO GmbH, Cuxhaven, Germany |
| Crowntec™ (CT) | 3D-printed composite resin | 30–50 wt.% fillers (particle size 0.7 μm) silanized dental glass, pyrogenic silica | Esterification products of 4,4′-isopropylidiphenol, ethoxylated and 2-methylprop-2enoic acid | Saremco Dental AG, Rebstein, Switzerland |
| C&B Permanent™ (CB) | 3D-printed composite resin | N/A | Diurethane dimethacrylate, 2-Propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, (1-methylethylidene) bis (4,1-phenyleneoxy(1-methyl-2,1-ethanediyl)) ester, 2-HEMA, diphenyl (2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphine oxide, and additives | ODS, Seoul, Korea |
| Material | Surface treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | HF | DB | SB | |
| Lava™ Ultimate (LU) | 14.8 ±1.2 Ac | 19.6 ±1.8 Cc | 17.2 ±1.4 Bc | 20.4 ±1.5 Cc |
| Grandio™ (GR) | 13.9 ±0.7 Ac | 19.7 ±1.6 Cc | 17.5 ±1.6 Bc | 20.0 ±1.0 Cc |
| Crowntec™ (CT) | 5.7 ±0.7 Aa | 16.1 ±1.5 Ca | 9.7 ±0.7 Ba | 15.5 ±0.6 Ca |
| C&B Permanent™ (CB) | 11.5 ±1.4 Ab | 17.4 ±1.3 Cb | 14.8 ±1.2 Bb | 18.2 ±0. 9 Cb |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





