1. Introduction
Schizophrenia, a severe psychiatric condition, often manifests during young adulthood and can lead to significant and long-lasting deficits in patients' functionality (1). These deficits may be accompanied by elevated levels of cardiovascular (2) and metabolic (3) comorbidities, sudden death (4), and reduced life expectancy (5). Globally, schizophrenia ranks among the top 25 causes of disability (6, 7).
The concept of recovery in schizophrenia entails both symptomatic control and achieving a level of social and occupational functionality deemed acceptable. Inadequate functioning may stem from residual negative and cognitive symptoms, which many antipsychotics fail to adequately address, as they are more effective in managing positive symptomatology (8). It is widely acknowledged that sustained antipsychotic treatment is the only proven effective approach to achieving remission, maintaining it, and preventing relapses (9).
The antipsychotics currently in use span a spectrum ranging from silent antagonists of dopamine D2 receptors to nearly full agonists of the same receptors. An overly intense agonist effect may fail to treat psychosis as it cannot adequately control positive symptomatology, which is why partial agonists and silent antagonists of D2 receptors are a preferable solution. Blocking serotoninergic 5HT2A receptors, present in many atypical antipsychotics, represents an important step in improving their tolerability. Additionally, certain antipsychotics may induce partial agonism on serotoninergic 5HT1A receptors, providing additional benefits (10).
The functionality and quality of life of patients with schizophrenia have been evaluated for various antipsychotics in clinical studies comparing them to placebo and/or direct comparators (11). Additional data have been obtained through meta-analyses and systematic analyses (12, 13).
Antipsychotics differ in many parameters, such as pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, mode of administration, and/or pharmaceutical form, which entail both beneficial effects and inconveniences that can vary from one antipsychotic to another (14). These differences can certainly influence the functionality of patients with schizophrenia (15).
The present study aims to identify a theoretical parameter or index that predicts the ability of an antipsychotic to improve the functionality of patients with schizophrenia. An advantage of such a theoretical index is that it represents an attempt to supplement with theoretical information the data and findings coming from meta-analysis and systematic reviews. The theoretical index could directly compare antipsychotics, which is the focus of this work.
2. Methodology
In the analysis of the impact of antipsychotics on the functionality of patients with schizophrenia, aspects such as pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and pharmaceutical forms have been considered. A total of 29 antipsychotic molecules used over time in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia were analyzed: chlorpromazine, flupenthixol, fluphenazine, haloperidol, loxapine, methotrimeprazine, periciazine, perphenazine, pimozide, thioridazine, thiothixene, trifluoperazine, zuclopenthixol, asenapine, clozapine, iloperidone, sertindole, lumateperone, lurasidone, olanzapine, zotepine, paliperidone, quetiapine, amisulpride, risperidone, ziprasidone, aripiprazole, brexpiprazole, and cariprazine. Analyses were conducted to construct a new parameter called the
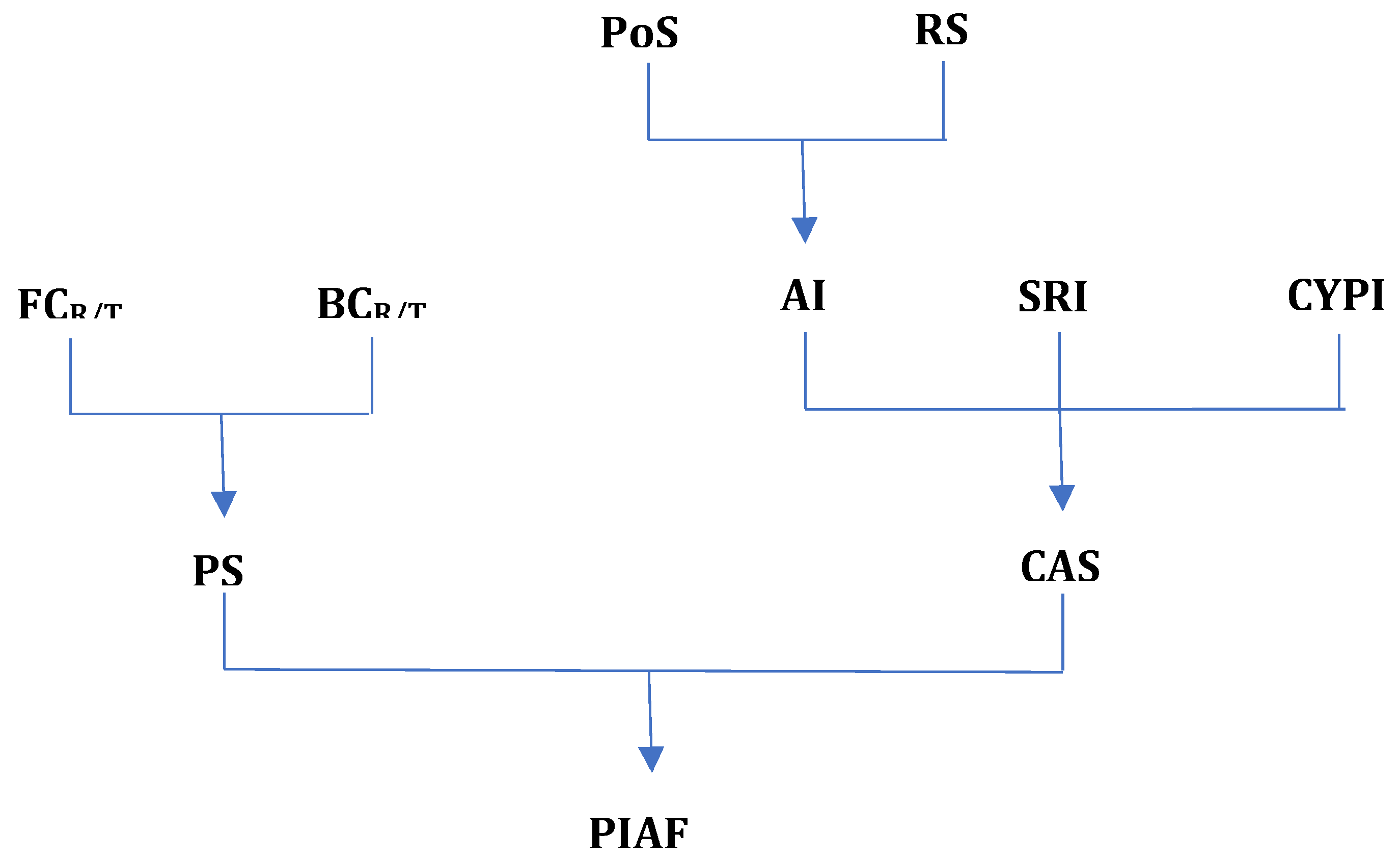
Predictive Impact of Antipsychotics on Functionality Index according to the algorithm presented in
Figure 1.
The parameter we will define as the Predictive Functionality Index of Antipsychotics considers two major aspects: pharmacodynamics and administration comfort, each expressed through other parameters which we will present next.
- A)
Pharmacodynamics: To assess the effects on functionality from a pharmacodynamic perspective, three parameters have been defined:
- 1.
Functionality coefficient (FCR/T) represents the score associated with each receptor or reuptake pump (receptor/transporter) regarding functionality according to the formula:
where F stands for Functionality.
For the calculation of
FCR/T, both beneficial actions (rated positively) and detrimental actions to functionality (rated negatively) have been considered. Thus, for beneficial actions, scoring was done based on the importance of each effect, receiving scores ranging from 3 to 1 according to
Table 1. Actions of very high importance for patient functionality (improvement of positive, negative symptoms, and aggressiveness) received each a score of 3. These were considered of utmost importance as they alleviate the core symptoms of schizophrenia patients, and in their absence, functionality remains an unattainable goal. Procognitive actions, improvement of sleep and motivation, antidepressant, anxiolytic, and antimanic actions received a score of 2, as they are also important in the overall picture of functionality but are not part of the core symptoms targeted by any antipsychotic. Additional actions (improvement of some side effects and any other additional pro-functional effects) each received a score of 1.
Detrimental actions to functionality were rated negatively, with their value determined by the intensity of adverse effects resulting from action on receptors and reuptake pumps. The severity of adverse effects was rated based on the Merck Reporting Model (16). For each pharmacological mechanism, the total score of detrimental actions resulted from summing the products of the score of each type of adverse effect and their number, yielding a negative value. These were rated according to
Table 2.
PIAF – Predictive Impact of Antipsychotics on Functionality
PS – Pharmacodynamic Score
CAS – Comfort of Administration Score
FCR/T – Functionality Coefficient of Receptor/Transporter
BCR/T – Binding Coefficient of Receptor/Transporter
AI – Administration Index
SRI – Special Request Index
CYPI – CYP (Cytochrome P450) Index
PoS – Posology Score
RS – Release Score
The pro- and anti-functionality actions, their respective scores, as well as the Functionality coefficient specific to each action on receptors and reuptake pumps, are found in
Table 3.
- 2.
Binding coefficient (BCR/T) is a parameter that expresses the affinity of an antipsychotic molecule for the receptor (R) and transporter (T). This parameter was necessary because antipsychotic molecules have different affinities for these substrates, thus leading to different amplitudes of effects.
Binding coefficient () is directly proportional to the affinity of each antipsychotic molecule for receptors and transporters. Thus, these depend on the inhibition constants (
ki), being inversely proportional to them (
Table 4).
The values of ki identified for the main antipsychotics (17, 19) formed the basis of the calculation for BCR/T (Annex 1). The theoretical maximum will have BCR/T equal to 1 for receptors and transporters with positive values of FCR/T (pro-functionality), and equal to 0 for receptors and transporters with negative values of FCR/T (anti-functionality). In the case of D2 receptors, the theoretical maximum is considered to be partial agonism at this level (pro-functionality) rather than silent blockade.
- 3.
Pharmacodynamic Score (PS) is a parameter that quantifies how functionality is influenced through the pharmacodynamic mechanisms of antipsychotics. For each pharmacodynamic mechanism (action on receptor or transporter), the influence on functionality is calculated by the product . For this reason, an antipsychotic that acts through multiple mechanisms pharmacodynamic has PS as the sum of products according to the formula:
where i represents the type of receptors and/or transporters on which the respective antipsychotic acts. The PS values for the considered antipsychotics, the theoretical maximum, and the percentage values reported to the theoretical maximum, are found in
Table 5.
- B)
Comfort of Administration. To assess the effects on functionality from the perspective of administration comfort, the parameter Comfort of Administration Score (CAS) has been defined. This parameter takes into account the following criteria:
Administration Index (AI) which takes into account the frequency of administrations and the mode of release of the active substance.
- 4.
Special Requests Index (SRI) which quantifies the special requirements related to the administration of the antipsychotic.
- 5.
CYP Index (CYPI) which expresses the potential for drug interactions generated at the level of cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes.
CAS represents the sum of these parameters according to the formula:
The CAS formula equally considers the Administration Index (AI), the Special Request Index (SRI), and the CYP Index (CYPI), parameters which will be discussed below.
The Administration Index (AI) is a parameter that evaluates how the patient's comfort is influenced by the dosage and pharmaceutical form of the antipsychotic, according to the formula:
where PoS is the Posology Score, and RS is the Release Score. Considering equal importance for both PoS and RS, the calculation of AI was made as the arithmetic mean of these two.
Posology Score (PoS) quantifies how functionality is influenced by the frequency of administration of the antipsychotic. It was considered that rare administrations are more protective regarding functionality (long-acting injectable antipsychotics), while more frequent administrations generate a negative influence. The formula for this parameter is:
where NAY represents the Number of Administrations per Year, and the value
The Number of Administrations per Year (NAY) is calculated taking into account administrations once or multiple times a day (oral antipsychotics), or at a specific number of weeks, monthly, or every few months (LAI antipsychotics).
For example, for an antipsychotic administered twice daily (BID), the formula becomes:
For LAI antipsychotics, this parameter has the highest values (close to 1). The resulting values for each antipsychotic are found in Annex 2. It is important to mention that in the analysis conducted, it was assumed that a patient loses personal comfort proportionally to the number of administrations. The ideal antipsychotic for which the final comparison is made is one that does not create any discomfort related to administration, which theoretically means zero administrations and a PoS = 1, a fact currently impossible but necessary as a reference level for the analysis at hand.
The Release Score (RS) quantifies the patient's comfort regarding the medication's release form. It starts from the premise that orally administered immediate-release substances can generate adverse effects due to greater plasma concentration fluctuations, unlike orally administered modified-release forms (extended release), or injectable forms with prolonged release (LAI), for which the smallest plasma fluctuations have been observed. An example would be quetiapine, which is available in both immediate-release and extended-release forms, and it is known that it is much better tolerated and easier to titrate in the extended-release form. Therefore, RS has the values: immediate release = 0, extended release = 0.5, and LAI = 1. The ideal antipsychotic automatically receives a score of 1. The RS values are found in Annex 2.
The Special Requests Index (SRI) quantifies the presence or absence of special administration requirements (e.g., monitoring for 3 hours after LAI olanzapine administration, ECG monitoring for sertindole, platelet monitoring for clozapine, etc.), which in turn influence the patient's comfort. Thus, the presence of special administration requirements received a score of 0, while their absence was scored with 1. The ideal antipsychotic also received a score of 1 for this parameter (Annex 2).
The CYP Index (CYPI) analyses how an antipsychotic can influence the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP). If an antipsychotic affects the activity of cytochrome enzymes by inhibiting or inducing them, this will represent an obstacle or will require dosage adjustment of other concomitant medications metabolized by the same enzymatic system. Therefore, influencing cytochrome enzymes, regardless of the direction in which it occurs, received a score of 0, while the absence of influence received a score of 1. The ideal antipsychotic will not influence the cytochrome enzymatic system and is rated with 1 (Annex 2).
The final CAS values for each antipsychotic are also found in Annex 2.
The Predictive Impact of Antipsychotics on Functionality (PIAF) is a predictive parameter that expresses, in percentage, the capacity of an antipsychotic to improve the functionality of patients compared to an ideal antipsychotic (theoretical maximum). As mentioned earlier, this index takes into account the two parameters that can express the improvement in patient functionality, namely Pharmacodynamic Score (PS) and Comfort of Administration Score (CAS), according to the formula:
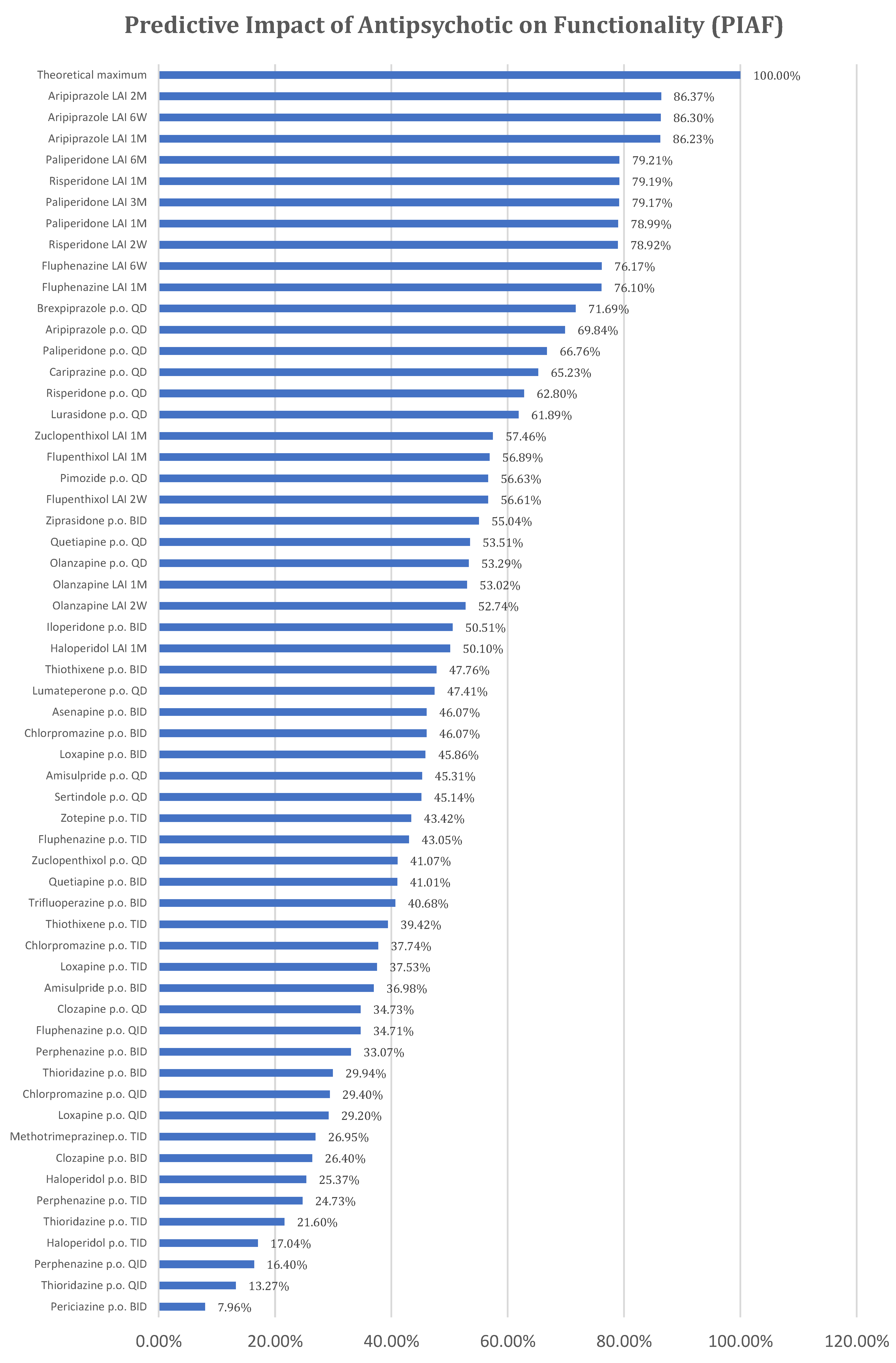
In the above formula, equal weights (arithmetic mean) have been considered for the two scores because both have major importance in patient functionality. The following PIAF results have been obtained and are presented in Annex 3 and
Figure 2.
3. Discussions
Within this concept, in terms of Pharmacodynamic Score (PS), brexpiprazole, asenapine, aripiprazole, and cariprazine were the best classified regarding patient functionality. It was expected that partial agonists of D2 receptors would be the most favorable for functionality due to their particular mode of action, which counterbalances the specific dopaminergic imbalances of the disease, thus offering efficacy and tolerability, essential aspects of functionality. The classification of asenapine among partial D2 agonists is justified by its favorable receptor profile, having maximum affinity for 5-HT2A receptors (the highest-rated pro-functionality receptor), 5-HT2C, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7, as well as very good affinity, almost at maximum, for D3 receptors, 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, which are also favorable for patient functionality. Atypical antipsychotics were generally positioned better compared to typical antipsychotics, with some exceptions such as amisulpride, quetiapine, clozapine, and olanzapine. The latter, although proven effective in schizophrenia, are not the most favorable for functionality due to a less favorable pro- and anti-functionality ratio.
From the perspective of administration comfort (CAS), the best-ranked antipsychotics are those that achieve optimal administration with minimal frequency, release methods that do not lead to large fluctuations in plasma concentrations, absence of special administration requirements, and lack of interactions with cytochrome enzyme systems. Thus, the best-ranked antipsychotics were long-acting injectables (LAI) (paliperidone every 6 months, paliperidone every 3 months, aripiprazole every 2 months, and aripiprazole every 6 weeks, respectively). Antipsychotics with unfavourable CAS were those with oral administration multiple times a day, immediate release, special administration requirements, or significant influence on the cytochrome enzyme system. In the case of thioridazine (p.o. QID) and perphenazine (p.o. QID), negative values were recorded because they met three of the four conditions mentioned earlier, namely frequent daily administrations, immediate release, and inhibition of the CYP2D6 enzyme.
The Predictive Impact of Antipsychotics on Functionality (PIAF) is higher for antipsychotics with both high Pharmacodynamic Scores (PS), which are correlated only with the active substance, and good Comfort of Administration Scores (CAS), which are correlated with both the pharmaceutical forms of antipsychotics and the active substance. Consequently, the best ranking was obtained by the only partial agonist dopaminergic D2 antipsychotic with LAI formulation (aripiprazole LAI), followed by the atypical LAI antipsychotic with the rarest administrations (paliperidone LAI 6M). Given this ranking, a better antipsychotic would result from the combination of a partial dopaminergic agonist with the lowest possible administration frequency.
Although risperidone and paliperidone are pharmacodynamically close, the profile of risperidone is more favorable to functionality, making risperidone with monthly administration better positioned than paliperidone with administration every 3 months and 1 month.
Flupenthixol LAI ranks among atypical antipsychotics in the final PIAF ranking, combining a favorable PS score (the best among typical antipsychotics) with administration every 6 weeks and 1 month, the absence of special administration requirements, and no influence on cytochrome enzyme systems. In its oral administration variant, flupenthixol no longer maintains the same favorable position for functionality.
Strictly analysing oral antipsychotics, brexpiprazole is the most favorable for functionality, with the best PS, followed by aripiprazole, paliperidone, cariprazine, risperidone, and lurasidone.
Interestingly, oral olanzapine (QD) is better positioned compared to olanzapine LAI administered monthly or every 2 weeks, with the explanation lying in the special requirements for olanzapine LAI administration (monitoring for 3 hours after administration). (21, 22)
The challenge of this theoretical, predictive concept lay in referencing existing data in the specialized literature, including meta-analyses and systematic reviews, which scrutinized reported clinical studies. It was crucial to confront prediction with observation. Consequently, we noted that in the meta-analysis by Leucht et al. in 2017, in terms of quality of life, aripiprazole, quetiapine, lurasidone, cariprazine, olanzapine, and paliperidone were identified as the most effective, while in terms of social functioning, thioridazine, lurasidone, olanzapine, risperidone, paliperidone, brexpiprazole, and aripiprazole were the best ranked. In the meta-analysis conducted by Huhn et al. in 2019, aripiprazole and paliperidone topped the rankings in terms of quality of life, whereas in terms of social functioning, thioridazine, olanzapine, paliperidone, quetiapine, lurasidone, and brexpiprazole were the most effective antipsychotics.
The STAR study, comparing oral antipsychotics, found that switching to oral aripiprazole from other oral antipsychotics led to improvements in negative symptoms, somnolence, weight gain, cognitive function, vitality, and mood. (24)
Naber et al. 2015 and Naber et al. 2018 provide additional data regarding the functional benefits following treatment with LAI antipsychotics, namely aripiprazole LAI (1M) and paliperidone LAI (1M). In these studies, aripiprazole LAI demonstrated greater favourability in improving functional outcomes in patients with schizophrenia, particularly in the age group under 35 years old. (25, 26)
Ifteni et al. (2021) proposes the ROLIN scale with the aim of identifying patients who would benefit the most from LAI treatment. This tool considers a range of predictors of good or poor therapeutic outcomes, including age, duration of illness, number of relapses, therapeutic response to oral antipsychotics, social support for the patient, pharmaceutical form of the antipsychotic, and therapeutic adherence. Some of these predictors overlap with those considered in calculating the PIAF index, thus the combined use of the ROLIN scale and the PIAF index by the psychiatrist could potentially provide additional benefits in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia. (9)
Although the theoretical predictive index presented in this paper cannot perfectly align with the data resulting from these studies and meta-analyses, we cannot overlook the fact that in the resulting classification, aripiprazole, paliperidone, risperidone, brexpiprazole, cariprazine, and lurasidone are ranked at the top. An advantage of the predictive index could be that it also considers the pharmaceutical form in which the antipsychotic molecule is presented. Thus, two different methods, one theoretical that directly compares antipsychotics and the other based on important clinical data, lead to comparable results.
Limitations
Within this concept, only adverse reactions determined by pharmacodynamic action were considered, not those based on reports, adverse reactions mentioned in the summary of product characteristics (SPC) of each antipsychotic individually. Although a rigorous analysis of the adverse reactions mentioned in the SPC was conducted, it could not be used because it led to paradoxical results, namely a superior safety profile of typical antipsychotics compared to second-generation (atypical) ones. The reason for this is that reporting adverse reactions during the development of atypical antipsychotics and thereafter their marketing was much more rigorously done in accordance with stricter pharmacovigilance legislation. Therefore, in this work, their inclusion in the final calculation was abandoned, thus remaining in the theoretical and predictive parameter zone.
4. Conclusions
According to the theoretical predictive index developed, the most favourable for the functionality of patients with schizophrenia are atypical LAI antipsychotics. Among these, the partial agonist mechanism of D2 dopamine represents an advantage.
Based on this functionality index, the clinical psychiatrist could select either from the beginning or during the treatment, the most suitable antipsychotic for their patient, with the ultimate goal of achieving their individual maximum potential.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
References
- Patel KR, Cherian J, Gohil K, and Atkinson D. Schizophrenia: Overview and Treatment Options. P&T September 2014 Vol. 39 No. 9; 638-645.
- Correll CU, Solmi M, Croatto G, Schneider LK, Rohani-Montez SC, Fairley L, Smith N, Bitter I, Gorwood P, Taipale H, Tiihonen J. Mortality in people with schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of relative risk and aggravating or attenuating factors. World Psychiatry 2022;21:248–271.
- Pillinger T, McCutheon RA, Vano L, Mizuno Y, Arumuham A, Hindley G, Beck K, Natesan S, Efthimiu O, Cipriani A, Howes OD. Comparative effects of 18 antipsychotics on metabolic function in patients with schizophrenia, predictors of metabolic dysregulation, and association with psychopathology: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2020; 7: 64–77.
- Scorza FA, de Almeida A-CG, Scorza CA, Cysneiros RM and Finsterer J. Sudden death in schizophrenia: pay special attention and develop preventive strategies. Curr Med Res Opin. 2021;37(1):109–121.
- Hjorthøj C, Stürup AE, McGrath JJ, Nordentoft M. Years of potential life lost and life expectancy in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2017; 4: 295–301.
- Boland R, Verduin ML, Ruiz P. 2022. Kaplan & Sadock's Synopsis of Psychiatry 12th edition. Wolters Kluwer.
- Switaj P, Anczewska M, Chrostek A, Sabariego C, Cieza A, Bickenbach J, and Chatterji S. Disability and schizophrenia: a systematic review of experienced psychosocial difficulties. BMC Psychiatry. (2012) 12:193. [CrossRef]
- Correll CU. Using Patient-Centered Assessment in Schizophrenia Care: Defining Recovery and Discussing Concerns and Preferences. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry Volume: 81 Issue: 3 Pages: MS19053BR2C. [CrossRef]
- Ifteni P, Petric P-S and Teodorescu A (2021) Rating Opportunity for Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotic Initiation Index (ROLIN). Front. Psychiatry 12:767756. [CrossRef]
- Stahl SM. Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific Basis and Practical Applications - 5th ed. 2021 ISBN 978-1-108-83857-3.
- Ishigooka J, Nakagome K, Ohmori T, Iwata N, Inada K, Iga J-I, Kishi T, Fujita K, Kikuchi Y, Shichijo T, Tabuse H, Koretsune S, Terada H, Terada H, Kishimoto T, Tsutsumi Y, Kanda Y, Ohi K and Sekiyama K. Discontinuation and remission rates and social functioning in patients with schizophrenia receiving second-generation antipsychotics: 52-week evaluation of JUMPs, a randomized, open-label study. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 76: 22–31, 2022.
- Leucht S, Leucht C, Huhn M, Chaimani A, Mavridis D, Helfer B, Samara M, Rabaioli M, Bächer S, Cipriani A, Geddes JR, Salanti G, Davis JM. Sixty Years of Placebo-Controlled Antipsychotic Drug Trials in Acute Schizophrenia: Systematic Review, Bayesian Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression of Efficacy Predictors. [CrossRef]
- Huhn M, Nikolakopoulou A, Schneider-Thoma J, Krause M, Samara M, Peter N, Arndt T, Bäckers L, Rothe P, Cipriani A, Davis J, Salanti G, Leucht S. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 32 oral antipsychotics for the acute treatment of adults with multi-episode schizophrenia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet 2019; 394: 939–51. [CrossRef]
- Stahl SM, Djokic G. Comparing the pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of antipsychotics: Choosing an antipsychotic and dosing a long-acting injectable. European Neuropsychopharmacology 73 (2023) 108–118.
- de Filippis R, De Fazio P, Gaetano R, Steardo L, Cedro C, Bruno A, Zoccali RA and Muscatello MRA (2021) Current and emerging long-acting antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia, Expert Opinion on Drug Safety, 20:7, 771-790. [CrossRef]
-
https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/drugs/adverse-drug-reactions/severity-of-adverse-drug-reactions.
- Procyshyn RM, Bezchlibnyk-Butler KZ, Kim DD. Clinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs 25th edition. 2023 Hogrefe Publishing ISBN 978-0-88937-474-4.
- Procyshyn RM, Bezchlibnyk-Butler KZ, Jeffries JJ. Clinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs 23rd edition. 2019 Hogrefe Publishing ISBN 978-0-88937-474-4.
- PDSP ki Database https://pdsp.unc.edu/databases/kidb.php.
- Correll CU, Kim E, Sliwa JK, Hamm W, Gopal S, Mathews M, Venkatasubramanian R, Saklad SR. Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics for Schizophrenia: An Overview. CNS Drugs (2021) 35:39–59. [CrossRef]
-
https://www.medscape.com.
-
https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h479.htm.
-
https://nomenclator.anm.ro/medicamente.
- Kerwin R, Millet B, Herman E, Banki CM, Lublin H, Pans M, Hanssens L, L’Italien G, McQuade RD, Beuzen J-N. A multicentre, randomized, naturalistic, open-label study between aripiprazole and standard of care in the management of community-treated schizophrenic patients Schizophrenia Trial of Aripiprazole: (STAR) study. European Psychiatry 22 (2007) 433-443.
- Naber D, Hansen K, Forray C, Baker RA, Sapin C, Beillat M, Peters-Strickland T, Nylander A-G, Hertel P, Andersen HS, Eramo A, Loze J-Y, Potkin SG. Qualify: a randomized head-to-head study of aripiprazole once-monthly and paliperidone palmitate in the treatment of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 168 (2015) 498-504.
- Naber D, Baker RA, Eramo A, Forray C, Hansen K, Sapin C, Peters-Strickland T, Nylander A-G, Hertel P, Schmidt SN, Loze J-Y, Potkin SG. Long-term effectiveness of aripiprazole once-monthly for schizophrenia is maintained in the QUALIFY extension study. Schizophrenia Research 192 (2018) 205-210.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).