Submitted:
26 September 2024
Posted:
26 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
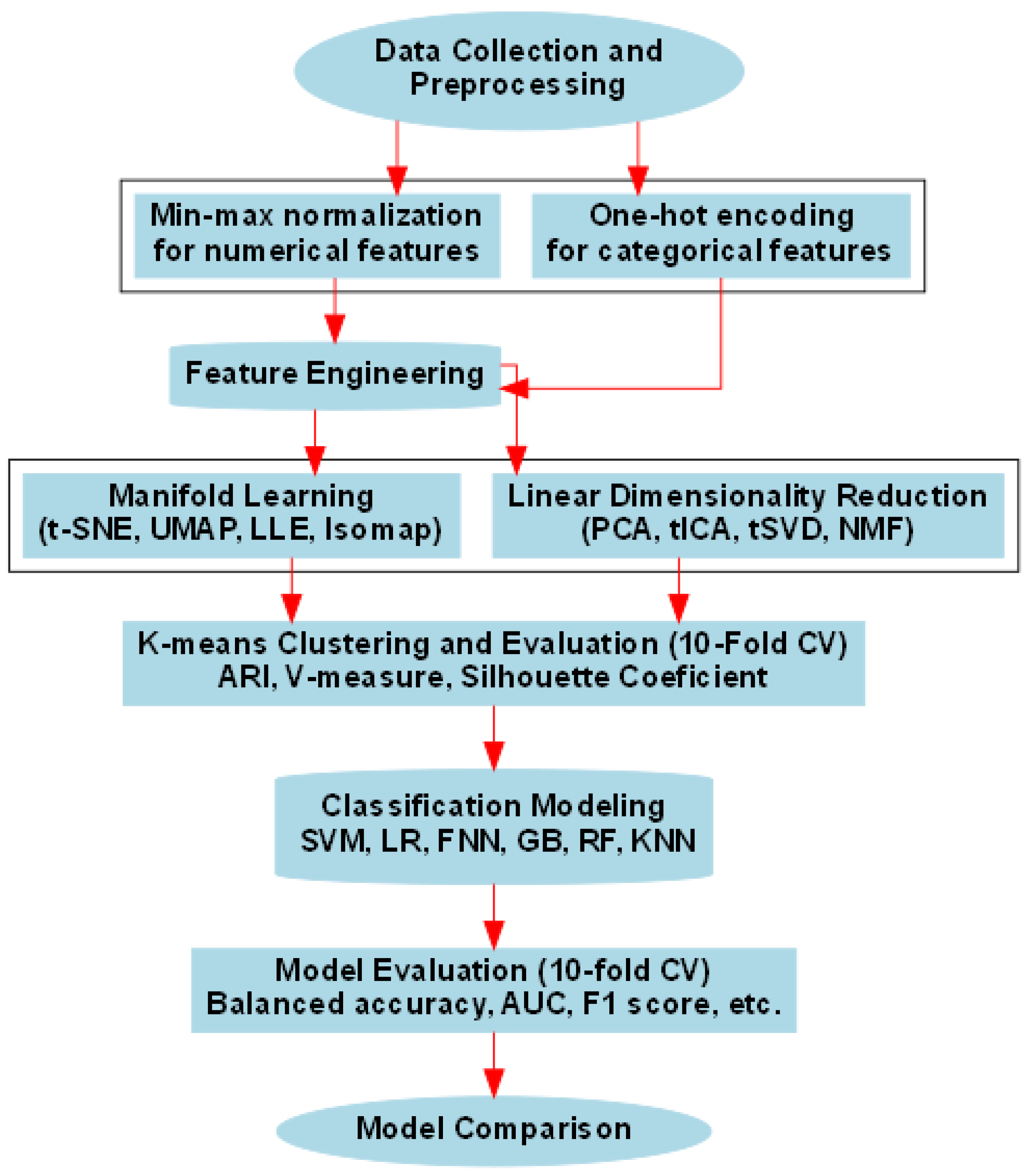
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Feature Engineering
2.3. Dimensionality Reduction Technique Evaluation and Selection for Classification Models Building.
2.4. Classification Models, Hyperparameter Tuning and Evaluation
2.5. Software and Computational Tools
3. Results and Discussion
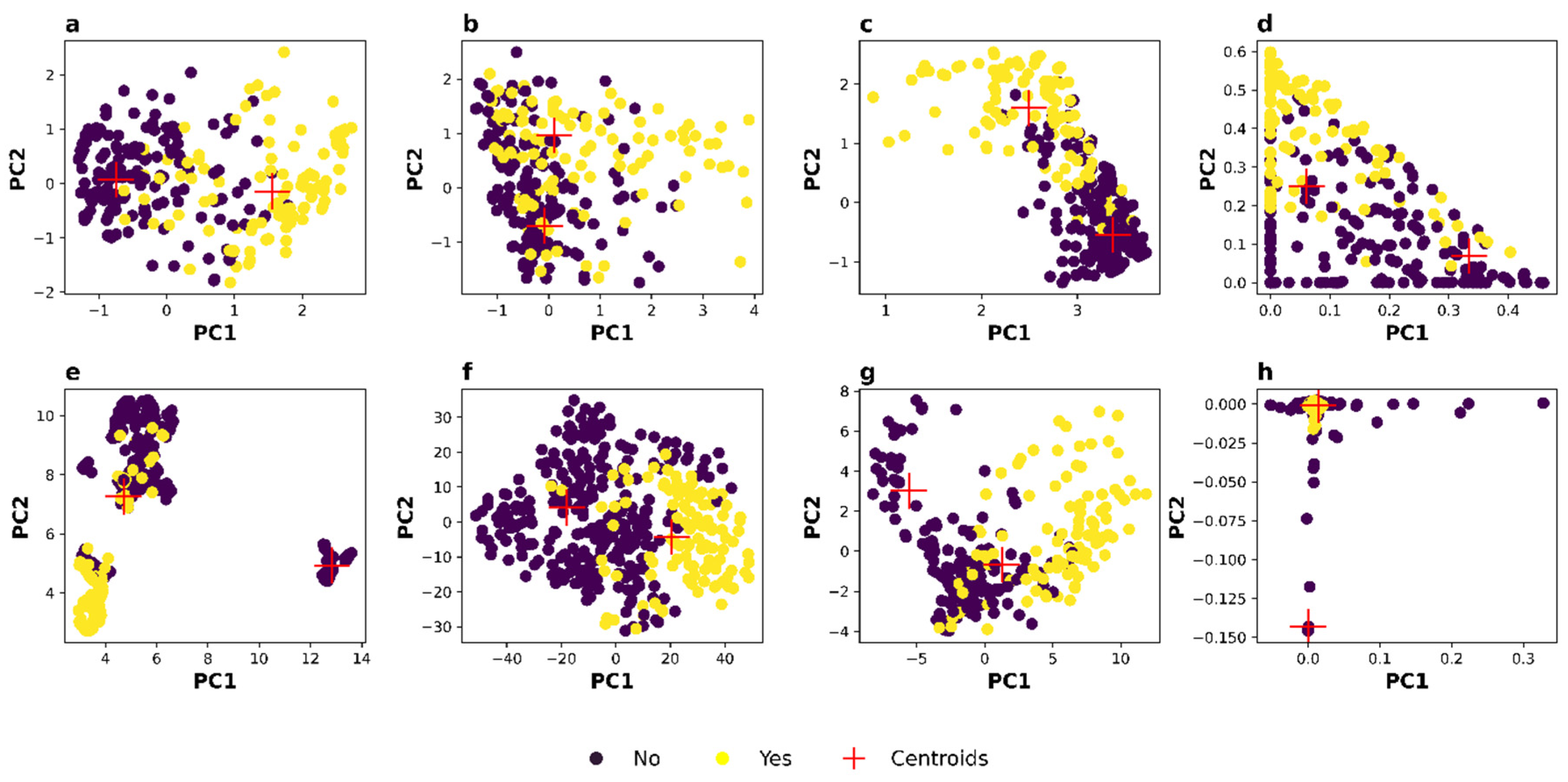
3.1. Feature Engineering Using Dimensionality Reduction
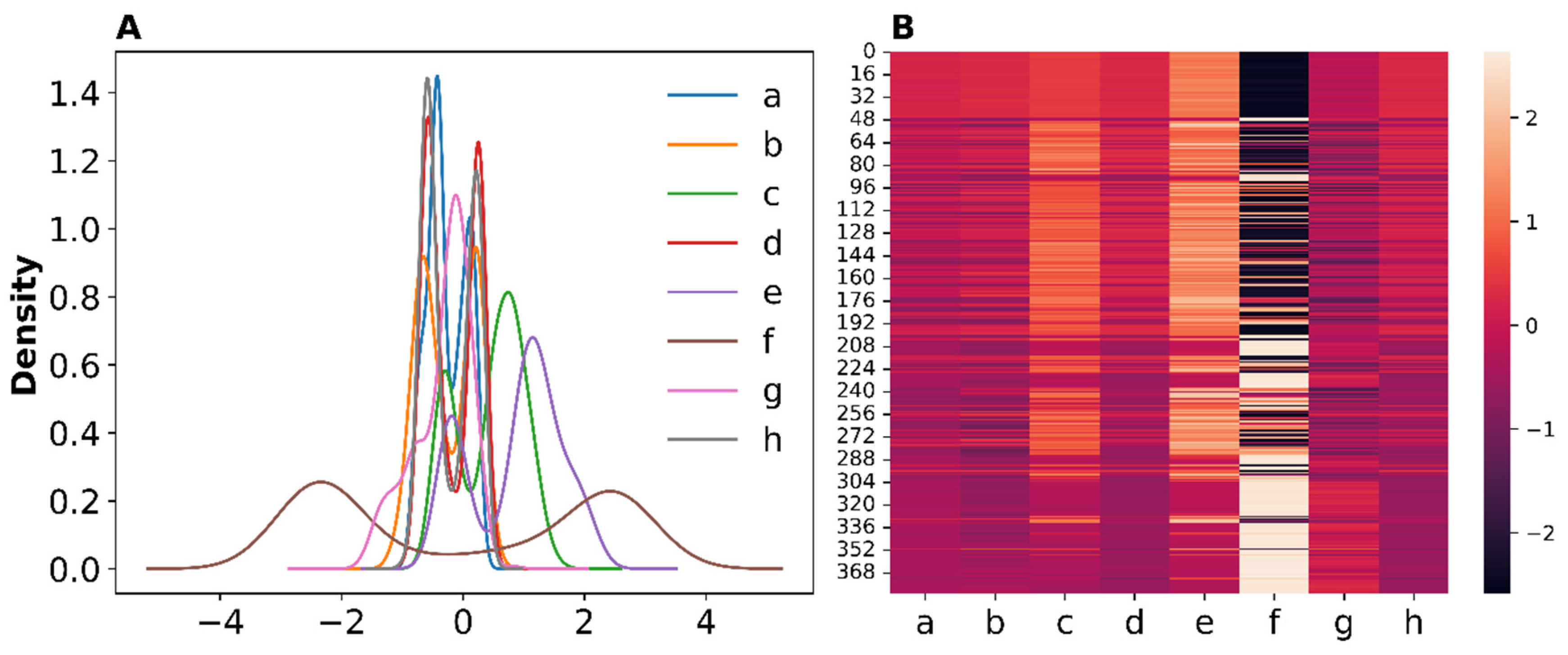
3.2. Distributions of the Engineered Features
3.3. Hyperparameter Optimization for Classification Model Pipelines
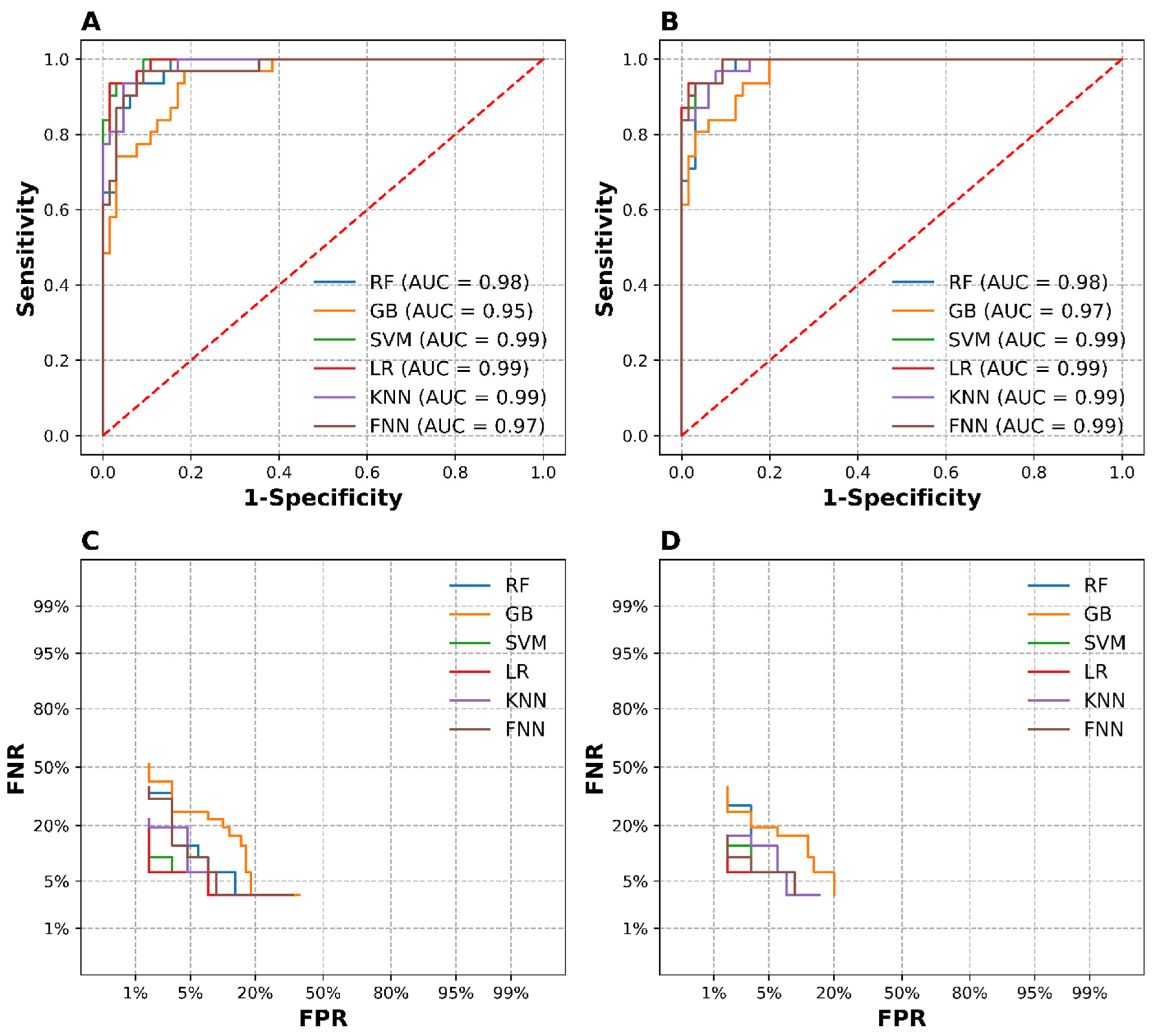
3.4. Classification Model Pipeline Evaluation
3.4.1. Performance of PCA-Model Pipelines
3.4.2. Performance of tSVD-Model Pipelines
3.5. Comparison with Other Methods
3.5.1. Advanced Dimensionality Reduction Techniques
3.5.2. Rigorous Feature Engineering and Clustering Validation
3.5.3. Diverse Machine Learning Models and Comprehensive Evaluation Metrics
3.5.4. Comparative Performance Analysis
3.6. Implications and Future Directions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miranda-Filho, A.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Bray, F.; Cao, B.; Franceschi, S.; Vaccarella, S.; Dal Maso, L. Thyroid cancer incidence trends by histology in 25 countries: a population-based study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 225–234. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, N.; M., Wang, L.; Yang, C. Author Correction: Improving the diagnosis of thyroid cancer by machine learning and clinical data. Sci Rep. 2022, 12, 13252. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayarangaiah, A.; Sidhu, G.; Brown, J.; Campbell, O. B.; McFarlane, S. I. Therapeutic options for advanced thyroid cancer, IJCEM 2019, 5, 26–34. [CrossRef]
- Medas, F.; Canu, G. L.; Boi, F.; Lai, M. L.; Erdas, E.; Calò, P. G. Predictive Factors of Recurrence in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: A Retrospective Analysis on 579 Patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 1230. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Wang, Z. Risk factors influencing the recurrence of papillary thyroid carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014, 7, 5393–5403. [PubMed]
- Hakim Tawil, J. A.; Rojas, M. F.; Santivañez, J. J.; León, L.; González Devia, D. Prognostic factors for recurrence in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Ear Nose Throat J. 2023, 1455613231158792. [CrossRef]
- Alkilany, S.; Mahfouz, E.; Mohammed, E.; Ghazawy, E.; Abdelgwad, Y.; Mohamadien, N.; Soliman, M.; Abdelrehim, M. Recurrence Risk in Thyroid Cancer Patients after Thyroidectomy. Minia Journal of Medical Research, 2024, 35, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Cho, S. W.; Park, Y. J.; Ahn, H. Y.; Kim, H. S.; Suh, Y. J.; Choi, D.; Kim, B. K.; Yang, G. E.; Park, I. S.; Yi, K. H.; Jung, C. K.; Kim, B. H. Clinicopathological Characteristics and Recurrence-Free Survival of Rare Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas in Korea: A Retrospective Study. Endocrinology and metabolism 2021, 36, 619–627. [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R. I.; Bischoff, L.; Ball, D.; Bernet, V.; Blomain, E.; Busaidy, N. L.; Campbell, M.; Dickson, P.; Duh, Q. Y., Ehya, H.; Goldner, W. S.; Guo, T.; Haymart, M.; Holt, S.; Hunt, J. P.; Iagaru, A.; Kandeel, F.; Lamonica, D. M.; Mandel, S.; Markovina, S.; … Darlow, S. Thyroid Carcinoma, Version 2.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. JNCCN, 2022, 20, 925–951. [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I. H. Machine learning: Algorithms, real-world applications, and research directions. SN Comput Sci, 2021, 2, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Borzooei, S.; Briganti, G.; Golparian, M.; Lechien, J. R.; Tarokhian, A. Machine learning for risk stratification of thyroid cancer patients: a 15-year cohort study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 281, 2095–2104. [CrossRef]
- Santos, M. S.; Soares, J. P.; Abreu, P. H.; Araújo, H.; Santos, J. Cross-validation for imbalanced datasets: Avoiding overoptimistic and overfitting approaches [Research frontier]. IEEE CIM, 2018, 13, 59–76. [CrossRef]
- Kohavi, R. A Study of Cross-Validation and Bootstrap for Accuracy Estimation and Model Selection. IJCAI 1995, 14, 1137–1145.
- Borzooei, Shiva; Tarokhian, Aidin. Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Recurrence. UCI Machine Learning Repository 2023. [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L. J. Principal Component Analysis. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics 2010, 2, 433–459. [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Principal Component Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer Series in Statistics: New York, 2002; pp. 338–339.
- Hyvärinen, A.; Oja, E. Independent Component Analysis: Algorithms and Applications. Neural Netw. 2000, 13, 411–430. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D. D.; Seung, H. S. Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization. Nature 1999, 401, 788–791. [CrossRef]
- van der Maaten, L. J. P.; Hinton, G. E. Visualizing high-dimensional data using t-SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2008, 9, 2579–2605.
- Tenenbaum, J. B.; de Silva, V.; Langford, J. C. A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science 2000, 290, 2319–2323. [CrossRef]
- McInnes, L., Healy, J.; Melville, J. UMAP: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction. Journal of Open Source Software 2018, 3, 861. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.03426. [CrossRef]
- Roweis, S. T.; Saul, L. K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 2000, 290, 2323–2326. [CrossRef]
- Hubert, L.; Arabie, P. Comparing partitions. Journal of Classification, 1985, 2, 193–218. [CrossRef]
- Rand, W. M. Objective Criteria for the Evaluation of Clustering Methods. JASA 1971, 66, 846–850. [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, Andrew; Hirschberg, Julia; Eisner, Jason (Bearb.). V-Measure: A Conditional Entropy-Based External Cluster Evaluation Measure. In: EMNLP-CoNLL: ACL, 2007, S. 410–420. https://aclanthology.org/D07-1043.
- Rousseeuw, P. J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 1987, 20, 53–65. [CrossRef]
- Hosmer Jr., D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression. 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ. 2013.
- Friedman, J. H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Statist. 2001, 29, 1189-1232. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining 2016, 785–794.
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Machine Learning 1995, 20, 273-297. [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Machine Learning, 2001, 45, 5–32. [CrossRef]
- Altman, N. S. An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. The American Statistician 1992, 46, 175–185. [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning. MIT Press. 2016.
- Bergstra, J.; Bengio, Y. Random Search for Hyper-Parameter Optimization. JMLR 2012, 13, 281–305.
- Wong, T. T. Performance Evaluation of Classification Algorithms by K-fold and Leave-One-Out Cross Validation. Pattern Recognition 2015, 48, 2839–2846. [CrossRef]
- Brodersen, K. H.; Ong, C. S.; Stephan, K. E.; Buhmann, J. M. The balanced accuracy and its posterior distribution. In 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition 2010, IEEE. 3121–3124.
- He, H.; Garcia, E. A. Learning from Imbalanced Data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2009, 21, 1263–1284.
- Fawcett, T. An Introduction to ROC Analysis. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2006, 27, 861–874. [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A. P. The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recognition 1997, 30, 1145–1159. [CrossRef]
- Forman, G. An Extensive Empirical Study of Feature Selection Metrics for Text Classification. JMLR 2003, 3, 1289–1305.
- Powers, D. M. Evaluation: From Precision, Recall and F-Measure to ROC, Informedness, Markedness and Correlation. J Mach Learn Technol. 2011, 2, 37–63.
- Onah, E.; Uzor, P. F.; Ugwoke, I. C.; Eze, J. U.; Ugwuanyi, S. T.; Chukwudi, I. R.; Ibezim, A. Prediction of HIV-1 protease cleavage site from octapeptide sequence information using selected classifiers and hybrid descriptors. BMC bioinformatics 2022, 23, 466. [CrossRef]
- Python Software Foundation. Python Language Reference (Version 3.8.10). 2023. https://www.python.org/.
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; Vanderplas, J.; Passos, A.; Cournapeau, D.; Brunet, M.; Duchesnay, E.; LeCun, Y.; Buitinck, L. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. JMLR, 2011, 12, 2825–2830. https://scikit-learn.org/stable/about.html.
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T. E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Brionne, J.; van der Walt, S. J.; Brett, M.; Wilson, J.; Jarrod Millman, K.; Mayorov, N.; Raw, A.; van der Meulen, M.; Certík, O.; ... Oliphant, A. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nature Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [CrossRef]
- Harris, C. R.; Millman, K. J.; van der Walt, S. J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Johansson, K.; Schulz, A.; Gribski, S.; Oliphant, T. E.; Petersen, W. K. Array programming with NumPy. Nature, 2020585, 357–362. [CrossRef]
- McKinney, W. Data Structures for Statistical Computing in Python. Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, 28 June – 3 July 2010, 56–61.
- Hunter, J. D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Computing in Science & Engineering 2007, 9, 90–95. [CrossRef]
- Waskom, M. L. Seaborn: Statistical data visualization. JOSS 2021, 6, 3021. [CrossRef]
- Berrar, D. Cross-validation. Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, 2019, 1, 542–545.
- Qiao, L.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, H.; Feng, G.; Yin, D. Machine learning based on SEER database to predict distant metastasis of thyroid cancer. Endocrine, 2024, 84, 1040–1050. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Tian, T.; Huang, R.; Qiu, J.; Tian, R. Development and validation of prediction models for papillary thyroid cancer structural recurrence using machine learning approaches. BMC cancer 2024, 24, 427. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A Density-Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise. KDD, 1996, 226–231.
- Hennig, C. Cluster-Wise Assessments of Cluster Stability. CSDA 2007, 52, 258–271. [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, M.; Lapalme, G. A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Information Processing & Management 2009, 45, 427–437. [CrossRef]
| Feature Name | Type | Description | Feature Value |
| Age | Integer | The age of the patient in years. | Any positive integer value (e.g., 20, 45, 60) |
| Gender | Categorical | The gender of the patient. | Male or Female |
| Smoking | Categorical | Indicates whether the patient is a current smoker. | Yes or No |
| Hx Smoking | Categorical | History of smoking. | Yes or No |
| Hx Radiothreapy | Categorical | History of receiving radiotherapy, particularly in the head and neck area. | Yes or No |
| Thyroid Function | Categorical | The functional status of the thyroid gland (e.g., Normal, Hyperthyroidism, Hypothyroidism). | Euthyroid, Clinical Hyperthyroidism, Subclinical Hypothyroidism, Clinical Hypothyroidism, or Subclinical Hyperthyroidism, |
| Physical Examination | Categorical | Findings from a physical examination of the patient. | Multinodular goiter, Single nodular goiter-right, Single nodular goiter-left, Normal or Diffuse goiter |
| Adenopathy | Categorical | Presence of swollen or enlarged lymph nodes, indicating potential spread of cancer. | No, Right, Bilateral, Left, Extensive, or Posterior |
| Pathology | Categorical | Histopathological findings from a biopsy of the thyroid tissue (e.g., Papillary, Follicular). | Papillary, Micropapillary, Follicular, or Hurthel cell |
| Focality | Categorical | Indicates whether the cancer is unifocal (single tumor) or multifocal (multiple tumors). | Uni-Focal or Multi-Focal |
| Risk | Categorical | Overall risk assessment based on various factors like tumor size, lymph node involvement, etc. | Low, Intermediate or High |
| T | Categorical | Tumor (T) stage in the TNM classification system, describing the size and extent of the primary tumor. | T2, T3a, T1a, T1b, T4a, T3b, or T4b |
| N | Categorical | Node (N) stage in the TNM classification system, indicating lymph node involvement. | N0, N1b, or N1a |
| M | Categorical | Metastasis (M) stage in the TNM classification system, indicating whether cancer has spread distantly. | M0 or M1 |
| Stage | Categorical | Overall cancer stage determined by combining T, N, and M stages (I, II, III, IV). | I, II, III, IVA or IVB |
| Response | Categorical | Indicates the patient's response to treatment (e.g., Complete, Partial, Stable, Progressive). | Excellent, Indeterminate, Structural Incomplete, or Biochemical Incomplete |
| Recurred | Categorical | Target variable indicating whether the thyroid cancer has recurred after treatment. | Yes or No |
| Dataset | Method | ARI | V-Measure | Silhouette Coefficient | PC1 Variance |
| BaseData | PCA* | 0.557 | 0.451 | 0.489 | 1.200 |
| tICA | 0.179 | 0.165 | 0.318 | 1.001 | |
| tSVD* | 0.558 | 0.459 | 0.537 | 0.537 | |
| NMF | 0.013 | 0.102 | 0.352 | 0.156 | |
| UMAP | -0.076 | 0.093 | 0.604 | 2.565 | |
| t-SNE | 0.258 | 0.277 | 0.362 | 22.727 | |
| Isomap | 0.258 | 0.292 | 0.334 | 4.477 | |
| LLE | -0.081 | 0.083 | 0.633 | 0.049 |
| Model | Hyperparameter | PCA-Model Pipeline | tSVD-Model Pipeline |
| RF | criterion | log_loss | entropy |
| max_depth | None | None | |
| class_weight | {0:1, 1:3} | {0:1, 1:3} | |
| min_sample_leaf | 4 | 2 | |
| sample_split | 4 | 5 | |
| n_estimators | 400 | 400 | |
| max_features | log2 | log2 | |
| GB | criterion | squared_error | friedman_mse |
| learning_rate | 0.36 | 0.35 | |
| loss | Exponential | log_loss | |
| max_depth | 5 | 5 | |
| n_estimators | 152 | 150 | |
| SVM | C | 0.12 | 0.25 |
| kernel | Sigmoid | sigmoid | |
| LR | C | 0.35 | 0.1 |
| solver | Liblinear | Liblinear | |
| max_iter | 5000 | 5000 | |
| penalty | l2 | l2 | |
| KNN | n_neighbors | 17 | 18 |
| weight | distance | Distance | |
| p | 2 | 4 | |
| FNN | alpha | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| activation | relu | Identity | |
| hidden_layer_size | (100, 100) | (125,155) | |
| learning_rate | constant | Adaptive | |
| solver | sgd | Sgd | |
| max_iter | 8000 | 15000 |
| Model | PCA-Model Pipeline | |||||||||||
| Test set Performance | 10-fold CV Performance | |||||||||||
| B. Acc. | F1 score | AUC | Sen. | Spec. | Prec. | B. Acc. |
F1 Score |
AUC | Sen. | Spec. | Prec. | |
| RF | 0.906 | 0.853 | 0.977 | 0.935 | 0.877 | 0.784 | 0.882 | 0.867 | 0.966 | 0.862 | 0.902 | 0.779 |
| GB | 0.849 | 0.794 | 0.948 | 0.806 | 0.892 | 0.781 | 0.868 | 0.873 | 0.946 | 0.797 | 0.939 | 0.856 |
| SVM | 0.929 | 0.892 | 0.992 | 0.935 | 0.923 | 0.853 | 0.873 | 0.861 | 0.960 | 0.845 | 0.902 | 0.776 |
| LR | 0.952 | 0.935 | 0.992 | 0.935 | 0.969 | 0.935 | 0.850 | 0.849 | 0.967 | 0.779 | 0.920 | 0.798 |
| KNN | 0.912 | 0.885 | 0.985 | 0.871 | 0.954 | 0.900 | 0.872 | 0.881 | 0.960 | 0.788 | 0.957 | 0.883 |
| FNN | 0.938 | 0.896 | 0.971 | 0.968 | 0.908 | 0.833 | 0.903 | 0.897 | 0.961 | 0.871 | 0.935 | 0.855 |
| tSVD-Model Pipeline | ||||||||||||
| Test set Performance | 10-fold CV Performance | |||||||||||
| B. Acc. | F1 score | AUC | Sen. | Spec. | Prec. | B. Acc. |
F1 Score |
AUC | Sen. | Spec. | Prec. | |
| RF | 0.937 | 0.886 | 0.986 | 0.912 | 0.938 | 0.861 | 0.889 | 0.892 | 0.965 | 0.844 | 0.949 | 0.871 |
| GB | 0.896 | 0.853 | 0.978 | 0.853 | 0.938 | 0.853 | 0.884 | 0.886 | 0.957 | 0.825 | 0.938 | 0.858 |
| SVM | 0.928 | 0.879 | 0.992 | 0.853 | 0.963 | 0.906 | 0.846 | 0.848 | 0.961 | 0.780 | 0.916 | 0.789 |
| LR | 0.944 | 0.933 | 0.994 | 0.903 | 0.985 | 0.966 | 0.854 | 0.859 | 0.965 | 0.770 | 0.931 | 0.832 |
| KNN | 0.908 | 0.885 | 0.987 | 0.853 | 0.963 | 0.906 | 0.860 | 0.868 | 0.952 | 0.770 | 0.949 | 0.862 |
| FNN | 0.912 | 0.903 | 0.989 | 0.824 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.859 | 0.870 | 0.963 | 0.762 | 0.967 | 0.906 |
| Study | Model | Dataset/Features | AUC | Sen. | Spec. | Comment |
| Our Study | SVM | PCA/tSVD pipelines | 99.2% | 93.5% (PCA), 85.3% (tSVD) | >92% | Confirms SVM's effectiveness; aligns with Borzooei et al. |
| KNN | PCA/tSVD pipelines | >98.4% | >85% | >95% | Suggests improved predictive ability with high-variance features. | |
| RF | PCA/tSVD pipelines | >97% | 93.5% (PCA), 91.2% (tSVD) | 87.7% (PCA), 93.8% (tSVD) | Consistent with Borzooei et al.; reliable performance. | |
| FNN | PCA/tSVD pipelines | >97% | 96.8% (PCA), 82.4% (tSVD) | 90.8% (PCA), 100% (tSVD) | Comparable performance with Borzooei et al.’ ANN model; high spec and sen. | |
| LR | PCA/tSVD pipelines | >99% | 93.5% (PCA), 90.6% (tSVD) | >96% | Superior performance to Wang et al. LR | |
| Borzooei et al. (2024) [11] | SVM | 13 clinicopathologic features | 99.71 | 99.33% | 97.14% | High performance; aligns with your tSVD-based SVM (AUC: 99.2%). |
| KNN | 13 clinicopathologic features | 98.44 | 83% | 97.14% | Our KNN models in PCA/tSVD pipelines show slightly higher AUC (>98%) and sensitivity (>85%). | |
| RF | 13 clinicopathologic features | 99.38 | 99.66% | 94.28% | Comparable to our RF models with AUC >97% in both PCA and tSVD pipelines. | |
| ANN | 13 clinicopathologic features | 99.64 | 96.6% | 95.71% | High performance comparable to our FNN model. | |
| Qiao et al. (2024) [51] | RF | Distant metastasis dataset | 0.960 | 92.9% | N/A | High performance similar to our RF model's performance. |
| Wang et al. (2024) [52] | RF | Larger cohort (2244 patients), perioperative variables | 0.766 | 0.757 | 0.682 | Lower performance than our study; variation may be due to different feature sets. |
| LR | Larger cohort (2244 patients), perioperative variables | 0.738 | 0.865 | 0.495 | Lower performance than our LR; variation may be due to different feature sets. | |
| SVM | Larger cohort (2244 patients), perioperative variables | 0.752 | 0.568 | 0.903 | Lower performance than our SVM but with comparable spec. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





