Submitted:
26 September 2024
Posted:
27 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
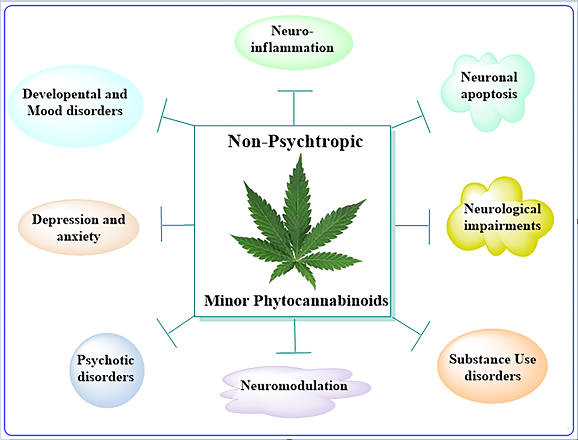
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Role of NMPs in Epilepsy
CBD
THCV
CBDV
CBG
Role of NMPs in Parkinson's Disease
CBD
THCV
CBDV
| Model | NMPs | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PD Patients | CBD | PD symptoms ↓ | [121] |
| PD Patients | CBD | Anxiety, tremor amplitude ↓ | [122] |
| Unilateral lesions rat model | CBD | hydroxydopamine-induced DA depletion | [124] |
| Sprague–Dawley rats | CBD | Neuroprotection ↑ | [125] |
| PC12 cells | CBD | Cell viability, differentiation, axonal (GAP-43), synaptophysin, and synapsin I ↑ | [126] |
| SH-SY5Y cells | CBD | Cell viability↑ Apoptosis, Bax, and caspase 3. Moreover, nuclear PARP-1↓ |
[53] |
| Mice | CBD | Cognitive dysfunction, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, Bax and Caspase-3 and NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β inflammasome pathway↓ Locomotion, 5-HT, DA, IL-10, TH, Bcl-2 ↑ |
[127] |
| Rats | CBD | SNpc, mortality rate, hippocampal neurogenesis, despair- behavior, Memory impairments, neuroinflammation↓ Neuronal maturation ↑ |
[130] |
| Mice | CBG | Motor tests , LAMP-1, TNF-α, IL-1β, nitric oxide synthase and COX2↓ | [131] |
| SH-SY5Y cells Mice (unilaterally lesioned) |
CBG | Cytoprotection, GFAP, CD68 ↓ Motor activity ↑ |
[132] |
| SH-SY5Y cells Mice (unilaterally lesioned |
CBG | TH positive neurons, Motor activity ↑ |
[133] |
| Rat | Δ9-THCV | Motor activity, TH positive neurons ↑ | [109] |
| Pitx3ak mutant mice | AIMs, horizontal and vertical activities, FosB, pAcH3, and dyskinesia ↓ | [129] | |
| C. elegans | CBDV | α-syn, DAergic neurons ↓ | [134] |
CBG
Role of NMPs in Alzheimer's Disease
CBD
| Model | NMPs | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC12 cells | CBD | Cell Survival ↑ ROS, lipid peroxidation and Caspase 3 ↓ |
[141] |
| PC12 cells | CBD | Wnt/β-catenin ↑ Tau hyperphosphorylation, p-GSK-3β ↓ |
[142] |
| MSC cells | CBD | GSK3β, CDK5, DYRK1A, CAMK2A, MAPK1, MAPK12, and MAPK14, BACE1↓, | [144] |
| N13 microglial cells Rat primary microglia Mice |
CBD |
Intracellular calcium ↓ Nitrite generation, IL-6 gene expression ↓ Spatial memory, Microglial migration ↑ |
[146] |
| APPxPS1 mice | CBD | social recognition and novel object recognition ↑ | [147] |
| AβPPSwe/PS1ΔE9 | CBD | social recognition ↑ | [148] |
| 5x FAD mice | CBD and THC | Spatial memory, beta amyloid↑ | [149] |
| SAMP8 mice | CBD | Bacteriodetes, hippocampal activated microglia shift from M1 to M2↑ and LPS ↓ | [151] |
| Male wistar rats | CBD coated by nano-chitosan | learning and memory, CB1 and CB2 protein expression ↑ Amyloid plaques ↑ |
[153] |
| Female patients | CBD | Direct contact, behavior ↑ | [155] |
| MC65 cell | CBG | Aβ aggregation ↓ | [156] |
| PC12 cells | CBG | Aβ aggregation, Aβ1-42 neurotoxicity ↓ Neuroprotection |
[157] |
| Male human subjects | THCV | Memory impairment↓ | [158] |
| In vitro assay | CBD, CBDV, CBG | AChE and BChE ↓ | [159] |
THCV
CBDV
CBG
NMPs Role in Huntington's Disease
CBD
| Model | NMPs | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| STHdh(7/7) cells | ACEA, mAEA | ATP production, BDNF-2, PGC1α CB1 mRNA levels ↑ | [165] |
| Rats | CBD | mRNA SP, mRNA NSE, mRNA SOD-2 ↑ | [60] |
| Rats | CBD | 3NP-induced GABA, Nissl-stained neurons, CB1 and IGF-1 expression and SOD-1 expression↓ Calpain expression↑ |
[171] |
| RBL-2H3 cells | CBG | Human TRPV1, rat TRPV2↓ | [89] |
| HT29 cells | CBG | COX-2 enzyme, prostaglandins ↓ | [172] |
| Mice | CBG | Reactive microgliosis, expression of COX-2, iNOS, TNF-α , Cd44, Sgk1↓ PPARγ, catalase, SOD and GSH ↑ |
[173] |
| NSC-34 | CBG |
HAP1, SLC32A1, ADCY5, AKT, ATF4, DLGAP1,DRD4, GNB4, PRKCA↑ ADCY9, CAMK2B, CLOCK, CREB1, DRD2, GNAL, PLD1, PPP3R1, PRKCB, SHANK1, SLC1A2, SLC18A1, SLC38A1 ↓ |
[174] |
THCV
CBDV
CBG
Neuroprotective Role of NMPs in Substance and Alcohol Use Disorders
Substance Use Disorders (SUD)
| Model | NMPs | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Humans | CBD (+THC) | Anxiety ↓ | [200] |
| Humans | CBD (+THC) | Satiety ↑ | [201] |
| Humans | CBD | Emotion, reward processing, effects of THC ↓ |
[203] |
| Human | CBD | Withdrawal, anxiety and dissociative symptoms ↓ | [205] |
| Human | CBD | Anxiety, cannabis use↓ Sleep ↑ |
[206] |
| Humans | CBD | Cannabis use ↓ | [207] |
| Humans | CBD | Psychological symptoms↓ Cognition ↑ | [208] |
| Human | CBD | Functional connectivity ↑ | [217] |
| Wistar rats | CBD | Morphine reward behavior ↓ | [210] |
| Rat | CBD | heroin-seeking behavior, CB1R expression ↓ |
[211] |
| Mice | CBD | Anxiety, Cnr1, Pomc ↓ Motor activity, TH expression, ↑ |
[212] |
| Mice | CBD | Gastrointestinal symptoms, Jumping behavior ↓ | [213] |
| Mice | CBD | Mechanical sensitivity, Jumping behavior ↓ | [214] |
| Rats | CBD | Locomotor Hyperactivity, MOR↓ Recognition Memory, CB1R expression ↑ |
[215] |
| Mice | CBG | Mechanical sensitivity, Aif1, Ccl2, Calca, and Tlr4↓ | [216] |
Alcohol Use Disorders (AUD)
| Model | NMPs | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rat | CBD | Anxiolytic effect ↑ | [218] |
| Rats | CBD | Social interaction ↑ | [219] |
| Rats | CBD | Neurodegeneration ↓ | [244] |
| Rats | CBD | Neurodegeneration↓ | [225] |
| Hippocampal cultures | CBD | Neuroprotection ↑ | [226] |
| Mice | CBD | Alcohol intake, TH, Oprm1, CB1R and GPR55 gene expression ↓ |
[227] |
| Humans | CBD | BrAC ↓ | [232] |
| sP Rats | CBD | Lever responses to self-administered alcohol ↓ | [233] |
| Mice | CBD (+THC) | Locomotor sensitization ↓ | [239] |
| Baboons | CBD | Alcohol seeking, self-administration, drinking patterns ↓ | [240] |
| Mice (SAW model) | CBD | Rearings, groomings, anxiogenic behavior, Cnr2, Opmr1 expression ↑ Th, Pomc gene expressions ↓ |
[234] |
| Rats | CBD | CGRP, alcohol consumption and preference ↓ | [235] |
| Rats | CBD | Corticosterone ↓ DA, postsynaptic strength ↑ |
[236] |
| Rats | CBD | Hypothermic and sedation CB1R, DRD1, DRD2 mRNA↓ CB2R gene transcription↑ |
[237] |
| Mice | CBD | Anxiety behavior, S100β and Iba1↓ | [238] |
| Mice | CBD | Cognitive deficits,TNFα IL-6 ↑ | [241] |
| Human | CBD | Disruptive behavior score↓ | [242] |
| Mice | CBD | Emotional cognitive disturbance↓ | [243] |
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
References
- Basavarajappa BS, Shivakumar M, Joshi V, Subbanna S. Endocannabinoid system in neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurochem 142(5), 624-648 (2017).
- Ferrari R, Kapogiannis D, Huey ED, Momeni P. FTD and ALS: a tale of two diseases. Curr Alzheimer Res 8(3), 273-294 (2011).
- Gibson SB, Figueroa KP, Bromberg MB, Pulst SM, Cannon-Albright L. Familial clustering of ALS in a population-based resource. Neurology 82(1), 17-22 (2014).
- Gammon K. Neurodegenerative disease: brain windfall. Nature 515(7526), 299-300 (2014).
- Kovacs GG. Concepts and classification of neurodegenerative diseases. Handb Clin Neurol 145 301-307 (2017).
- Gonzalez-Alegre P. Recent advances in molecular therapies for neurological disease: triplet repeat disorders. Hum Mol Genet 28(R1), R80-R87 (2019).
- Nopoulos PC. Huntington disease: a single-gene degenerative disorder of the striatum. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 18(1), 91-98 (2016).
- Paulson H. Repeat expansion diseases. Handb Clin Neurol 147 105-123 (2018).
- Taylor JJ, Williams NR, George MS. Beyond neural cubism: promoting a multidimensional view of brain disorders by enhancing the integration of neurology and psychiatry in education. Acad Med 90(5), 581-586 (2015).
- Hampel H, Vergallo A, Caraci F et al. Future avenues for Alzheimer's disease detection and therapy: liquid biopsy, intracellular signaling modulation, systems pharmacology drug discovery. Neuropharmacology 185 108081 (2021).
- Trinh NH, Hoblyn J, Mohanty S, Yaffe K. Efficacy of cholinesterase inhibitors in the treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms and functional impairment in Alzheimer disease: a meta-analysis. JAMA 289(2), 210-216 (2003).
- Bhushan M, Akash S, Pettarusp W. Adverse effects of medications used to treat motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease: A narrative review. Annals of Movement Disorders 6(2), 45-57 (2023).
- Hayden MR, Leavitt BR, Yasothan U, Kirkpatrick P. Tetrabenazine. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8(1), 17-18 (2009).
- Kaur N, Kumar P, Jamwal S, Deshmukh R, Gauttam V. Tetrabenazine: Spotlight on Drug Review. Ann Neurosci 23(3), 176-185 (2016).
- Sampaio C. Huntington disease - Update on ongoing therapeutic developments and a look toward the future. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 122 106049 (2024).
- Wyant KJ, Ridder AJ, Dayalu P. Huntington's Disease-Update on Treatments. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 17(4), 33 (2017).
- Mechoulam R, Fride E, Di Marzo V. Endocannabinoids. Eur J Pharmacol 359(1), 1-18 (1998).
- Di Marzo V, Melck D, Bisogno T, De Petrocellis L. Endocannabinoids: endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligands with neuromodulatory action. Trends Neurosci 21(12), 521-528 (1998).
- Peng J, Fan M, An C, Ni F, Huang W, Luo J. A narrative review of molecular mechanism and therapeutic effect of cannabidiol (CBD). Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 130(4), 439-456 (2022).
- Guindon J, Hohmann AG. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: a therapeutic target for the treatment of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Br J Pharmacol 153(2), 319-334 (2008).
- Pertwee RG. The diverse CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology of three plant cannabinoids: delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and delta9-tetrahydrocannabivarin. Br J Pharmacol 153(2), 199-215 (2008).
- Wilson RI, Nicoll RA. Endocannabinoid Signaling in the Brain. Science 296 678-682 (2002).
- Aoki J, Isokawa M. Understanding Cellular, Molecular, and Functional Specificity, Heterogeneity, and Diversity of the Endocannabinoid System. Cells 13(12), (2024).
- Basavarajappa BS. Endocannabinoid System and Alcohol Abuse Disorders. In: RECENT ADVANCES IN CANNABINOID PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY, Bukiya AN (Ed.^(Eds).Nature Springer Switzerland p.00. 25p. (2019).
- Basavarajappa BS, Subbanna S. Molecular Insights into Epigenetics and Cannabinoid Receptors. Biomolecules 12(11), (2022).
- Dallabrida KG, De Oliveira Bender JM, Chade ES, Rodrigues N, Sampaio TB. Endocannabinoid System Changes throughout Life: Implications and Therapeutic Potential for Autism, ADHD, and Alzheimer's Disease. Brain Sci 14(6), (2024).
- Wright NJD. A review of the direct targets of the cannabinoids cannabidiol, Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, N-arachidonoylethanolamine and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. AIMS Neurosci 11(2), 144-165 (2024).
- Morales P, Hurst DP, Reggio PH. Molecular Targets of the Phytocannabinoids: A Complex Picture. Prog Chem Org Nat Prod 103 103-131 (2017).
- Mechoulam R, Gaoni Y. The absolute configuration of delta-1-tetrahydrocannabinol, the major active constituent of hashish. Tetrahedron Lett 12 1109-1111 (1967).
- Boychuk DG, Goddard G, Mauro G, Orellana MF. The effectiveness of cannabinoids in the management of chronic nonmalignant neuropathic pain: a systematic review. J Oral Facial Pain Headache 29(1), 7-14 (2015).
- Novack GD. Cannabinoids for treatment of glaucoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 27(2), 146-150 (2016).
- Phillips RS, Friend AJ, Gibson F et al. Antiemetic medication for prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in childhood. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2(2), CD007786 (2016).
- Pomorska DK, Do-Rego JC, Do-Rego JL, Zubrzycka M, Janecka A. Opioid and Cannabinoid System in Food Intake. Curr Pharm Des 22(10), 1361-1370 (2016).
- Mechoulam R, Peters M, Murillo-Rodriguez E, Hanus LO. Cannabidiol--recent advances. Chem Biodivers 4(8), 1678-1692 (2007).
- Borges RS, Batista J, Jr., Viana RB et al. Understanding the molecular aspects of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol as antioxidants. Molecules 18(10), 12663-12674 (2013).
- Hampson AJ, Grimaldi M, Axelrod J, Wink D. Cannabidiol and (-)Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol are neuroprotective antioxidants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(14), 8268-8273 (1998).
- Yamaori S, Ebisawa J, Okushima Y, Yamamoto I, Watanabe K. Potent inhibition of human cytochrome P450 3A isoforms by cannabidiol: role of phenolic hydroxyl groups in the resorcinol moiety. Life Sci 88(15-16), 730-736 (2011).
- Huizenga MN, Wicker E, Beck VC, Forcelli PA. Anticonvulsant effect of cannabinoid receptor agonists in models of seizures in developing rats. Epilepsia 58(9), 1593-1602 (2017).
- Cristino L, Bisogno T, Di Marzo V. Cannabinoids and the expanded endocannabinoid system in neurological disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 16(1), 9-29 (2020).
- Wallace MJ, Blair RE, Falenski KW, Martin BR, Delorenzo RJ. The endogenous cannabinoid system regulates seizure frequency and duration in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307(1), 129-137 (2003).
- Alger BE. Retrograde signaling in the regulation of synaptic transmission: focus on endocannabinoids. Progress in Neurobiology. 68 247-286 (2002).
- Schlicker E, Kathmann M. Modulation of transmitter release via presynaptic cannabinoid receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22(11), 565-572 (2001).
- Laprairie RB, Bagher AM, Kelly ME, Denovan-Wright EM. Cannabidiol is a negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Br J Pharmacol 172(20), 4790-4805 (2015).
- Russo EB, Burnett A, Hall B, Parker KK. Agonistic properties of cannabidiol at 5-HT1a receptors. Neurochem Res 30(8), 1037-1043 (2005).
- Anand U, Jones B, Korchev Y et al. CBD Effects on TRPV1 Signaling Pathways in Cultured DRG Neurons. J Pain Res 13 2269-2278 (2020).
- Shi QX, Yang LK, Shi WL et al. The novel cannabinoid receptor GPR55 mediates anxiolytic-like effects in the medial orbital cortex of mice with acute stress. Mol Brain 10(1), 38 (2017).
- Marichal-Cancino BA, Fajardo-Valdez A, Ruiz-Contreras AE, Mendez-Diaz M, Prospero-Garcia O. Advances in the Physiology of GPR55 in the Central Nervous System. Curr Neuropharmacol 15(5), 771-778 (2017).
- Armin S, Muenster S, Abood M, Benamar K. GPR55 in the brain and chronic neuropathic pain. Behav Brain Res 406 113248 (2021).
- Do Val-Da Silva RA, Peixoto-Santos JE, Kandratavicius L et al. Protective Effects of Cannabidiol against Seizures and Neuronal Death in a Rat Model of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Front Pharmacol 8 131 (2017).
- Khan AA, Shekh-Ahmad T, Khalil A, Walker MC, Ali AB. Cannabidiol exerts antiepileptic effects by restoring hippocampal interneuron functions in a temporal lobe epilepsy model. Br J Pharmacol 175(11), 2097-2115 (2018).
- Legare CA, Raup-Konsavage WM, Vrana KE. Therapeutic Potential of Cannabis, Cannabidiol, and Cannabinoid-Based Pharmaceuticals. Pharmacology 107(3-4), 131-149 (2022).
- Vrechi TaM, Leao A, Morais IBM et al. Cannabidiol induces autophagy via ERK1/2 activation in neural cells. Sci Rep 11(1), 5434 (2021).
- Gugliandolo A, Pollastro F, Bramanti P, Mazzon E. Cannabidiol exerts protective effects in an in vitro model of Parkinson's disease activating AKT/mTOR pathway. Fitoterapia 143 104553 (2020).
- Lujan MA, Valverde O. The Pro-neurogenic Effects of Cannabidiol and Its Potential Therapeutic Implications in Psychiatric Disorders. Front Behav Neurosci 14 109 (2020).
- Lujan MA, Castro-Zavala A, Alegre-Zurano L, Valverde O. Repeated Cannabidiol treatment reduces cocaine intake and modulates neural proliferation and CB1R expression in the mouse hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 143 163-175 (2018).
- Campos AC, Ortega Z, Palazuelos J et al. The anxiolytic effect of cannabidiol on chronically stressed mice depends on hippocampal neurogenesis: involvement of the endocannabinoid system. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16(6), 1407-1419 (2013).
- Lanza Cariccio V, Scionti D, Raffa A et al. Treatment of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells with MOR and CBD Promotes Cell Survival and Neuronal Differentiation via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Int J Mol Sci 19(8), (2018).
- Giacoppo S, Pollastro F, Grassi G, Bramanti P, Mazzon E. Target regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway by cannabidiol in treatment of experimental multiple sclerosis. Fitoterapia 116 77-84 (2017).
- Renard J, Loureiro M, Rosen LG et al. Cannabidiol Counteracts Amphetamine-Induced Neuronal and Behavioral Sensitization of the Mesolimbic Dopamine Pathway through a Novel mTOR/p70S6 Kinase Signaling Pathway. J Neurosci 36(18), 5160-5169 (2016).
- Sagredo O, Ramos JA, Decio A, Mechoulam R, Fernandez-Ruiz J. Cannabidiol reduced the striatal atrophy caused 3-nitropropionic acid in vivo by mechanisms independent of the activation of cannabinoid, vanilloid TRPV1 and adenosine A2A receptors. Eur J Neurosci 26(4), 843-851 (2007).
- Jones NA, Hill AJ, Smith I et al. Cannabidiol displays antiepileptiform and antiseizure properties in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 332(2), 569-577 (2010).
- Martinez-Aguirre C, Carmona-Cruz F, Velasco AL et al. Cannabidiol Acts at 5-HT(1A) Receptors in the Human Brain: Relevance for Treating Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Front Behav Neurosci 14 611278 (2020).
- Radley JJ, Jacobs BL. Pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus increases cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of adult rats via a 5-HT1A receptor-dependent mechanism. Brain Res 966(1), 1-12 (2003).
- Schonhoff K, Von Ruden EL, Koska I, Seiffert I, Potschka H. Hippocampal and Septal 5-HT(1A) Receptor Expression in Two Rat Models of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neuroscience 465 219-230 (2021).
- Cai L, Xu Z, Luo H et al. The association between 5-HT1A binding and temporal lobe epilepsy: A meta-analysis of molecular imaging studies. Epilepsy Behav 145 109354 (2023).
- Pineda EA, Hensler JG, Sankar R, Shin D, Burke TF, Mazarati AM. Plasticity of presynaptic and postsynaptic serotonin 1A receptors in an animal model of epilepsy-associated depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 36(6), 1305-1316 (2011).
- Lazarini-Lopes W, Campos-Rodriguez C, Garcia-Cairasco N, N'gouemo P, Forcelli PA. Cannabidiol attenuates generalized tonic-clonic and suppresses limbic seizures in the genetically epilepsy-prone rats (GEPR-3) strain. Pharmacol Rep 75(1), 166-176 (2023).
- Barnes JP, Dial H, Owens W et al. Adherence and discontinuation of prescription cannabidiol for the management of seizure disorders at an integrated care center. Epilepsy Res 200 107300 (2024).
- Gill EW, Paton WD, Pertwee RG. Preliminary experiments on the chemistry and pharmacology of cannabis. Nature 228(5267), 134-136 (1970).
- Thomas A, Stevenson LA, Wease KN et al. Evidence that the plant cannabinoid Delta9-tetrahydrocannabivarin is a cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 146(7), 917-926 (2005).
- Franco R, Rivas-Santisteban R, Reyes-Resina I et al. Pharmacological potential of varinic-, minor-, and acidic phytocannabinoids. Pharmacol Res 158 104801 (2020).
- Muller C, Morales P, Reggio PH. Cannabinoid Ligands Targeting TRP Channels. Front Mol Neurosci 11 487 (2018).
- Cascio MG, Zamberletti E, Marini P, Parolaro D, Pertwee RG. The phytocannabinoid, Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabivarin, can act through 5-HT(1)A receptors to produce antipsychotic effects. Br J Pharmacol 172(5), 1305-1318 (2015).
- Garcia-Garcia AL, Newman-Tancredi A, Leonardo ED. 5-HT(1A) [corrected] receptors in mood and anxiety: recent insights into autoreceptor versus heteroreceptor function. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 231(4), 623-636 (2014).
- Glikmann-Johnston Y, Saling MM, Reutens DC, Stout JC. Hippocampal 5-HT1A Receptor and Spatial Learning and Memory. Front Pharmacol 6 289 (2015).
- Anavi-Goffer S, Baillie G, Irving AJ et al. Modulation of L-alpha-lysophosphatidylinositol/GPR55 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling by cannabinoids. J Biol Chem 287(1), 91-104 (2012).
- Dennis I, Whalley BJ, Stephens GJ. Effects of Delta9-tetrahydrocannabivarin on [35S]GTPgammaS binding in mouse brain cerebellum and piriform cortex membranes. Br J Pharmacol 154(6), 1349-1358 (2008).
- Pertwee RG, Thomas A, Stevenson LA et al. The psychoactive plant cannabinoid, Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, is antagonized by Delta8- and Delta9-tetrahydrocannabivarin in mice in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 150(5), 586-594 (2007).
- Bolognini D, Costa B, Maione S et al. The plant cannabinoid Delta9-tetrahydrocannabivarin can decrease signs of inflammation and inflammatory pain in mice. Br J Pharmacol 160(3), 677-687 (2010).
- Janssens A, Silvestri C, Martella A, Vanoevelen JM, Di Marzo V, Voets T. Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabivarin impairs epithelial calcium transport through inhibition of TRPV5 and TRPV6. Pharmacol Res 136 83-89 (2018).
- Hill AJ, Weston SE, Jones NA et al. Delta(9)-Tetrahydrocannabivarin suppresses in vitro epileptiform and in vivo seizure activity in adult rats. Epilepsia 51(8), 1522-1532 (2010).
- Ma YL, Weston SE, Whalley BJ, Stephens GJ. The phytocannabinoid Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabivarin modulates inhibitory neurotransmission in the cerebellum. Br J Pharmacol 154(1), 204-215 (2008).
- Allendorfer JB, Szaflarski JP. Neuroimaging studies towards understanding the central effects of pharmacological cannabis products on patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 70(Pt B), 349-354 (2017).
- Gaston TE, Friedman D. Pharmacology of cannabinoids in the treatment of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 70(Pt B), 313-318 (2017).
- Husni AS, Mccurdy CR, Radwan MM et al. Evaluation of Phytocannabinoids from High Potency Cannabis sativa using In Vitro Bioassays to Determine Structure-Activity Relationships for Cannabinoid Receptor 1 and Cannabinoid Receptor 2. Med Chem Res 23(9), 4295-4300 (2014).
- Rosenthaler S, Pohn B, Kolmanz C et al. Differences in receptor binding affinity of several phytocannabinoids do not explain their effects on neural cell cultures. Neurotoxicol Teratol 46 49-56 (2014).
- Navarro G, Varani K, Lillo A et al. Pharmacological data of cannabidiol- and cannabigerol-type phytocannabinoids acting on cannabinoid CB(1), CB(2) and CB(1)/CB(2) heteromer receptors. Pharmacol Res 159 104940 (2020).
- Zagzoog A, Mohamed KA, Kim HJJ et al. In vitro and in vivo pharmacological activity of minor cannabinoids isolated from Cannabis sativa. Sci Rep 10(1), 20405 (2020).
- De Petrocellis L, Ligresti A, Moriello AS et al. Effects of cannabinoids and cannabinoid-enriched Cannabis extracts on TRP channels and endocannabinoid metabolic enzymes. Br J Pharmacol 163(7), 1479-1494 (2011).
- De Petrocellis L, Vellani V, Schiano-Moriello A et al. Plant-derived cannabinoids modulate the activity of transient receptor potential channels of ankyrin type-1 and melastatin type-8. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325(3), 1007-1015 (2008).
- Laun AS, Shrader SH, Song ZH. Novel inverse agonists for the orphan G protein-coupled receptor 6. Heliyon 4(11), e00933 (2018).
- Devinsky O, Cilio MR, Cross H et al. Cannabidiol: pharmacology and potential therapeutic role in epilepsy and other neuropsychiatric disorders. Epilepsia 55(6), 791-802 (2014).
- Hill AJ, Mercier MS, Hill TD et al. Cannabidivarin is anticonvulsant in mouse and rat. Br J Pharmacol 167(8), 1629-1642 (2012).
- Huizenga MN, Sepulveda-Rodriguez A, Forcelli PA. Preclinical safety and efficacy of cannabidivarin for early life seizures. Neuropharmacology 148 189-198 (2019).
- Vigli D, Cosentino L, Raggi C, Laviola G, Woolley-Roberts M, De Filippis B. Chronic treatment with the phytocannabinoid Cannabidivarin (CBDV) rescues behavioural alterations and brain atrophy in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Neuropharmacology 140 121-129 (2018).
- Zamberletti E, Gabaglio M, Piscitelli F et al. Cannabidivarin completely rescues cognitive deficits and delays neurological and motor defects in male Mecp2 mutant mice. J Psychopharmacol 33(7), 894-907 (2019).
- Hill TD, Cascio MG, Romano B et al. Cannabidivarin-rich cannabis extracts are anticonvulsant in mouse and rat via a CB1 receptor-independent mechanism. Br J Pharmacol 170(3), 679-692 (2013).
- Amada N, Yamasaki Y, Williams CM, Whalley BJ. Cannabidivarin (CBDV) suppresses pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced increases in epilepsy-related gene expression. PeerJ 1 e214 (2013).
- Brodie MJ, Czapinski P, Pazdera L et al. A Phase 2 Randomized Controlled Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of Cannabidivarin as Add-on Therapy in Participants with Inadequately Controlled Focal Seizures. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res 6(6), 528-536 (2021).
- Hurley EN, Ellaway CJ, Johnson AM et al. Efficacy and safety of cannabidivarin treatment of epilepsy in girls with Rett syndrome: A phase 1 clinical trial. Epilepsia 63(7), 1736-1747 (2022).
- Navarro G, Varani K, Reyes-Resina I et al. Cannabigerol Action at Cannabinoid CB(1) and CB(2) Receptors and at CB(1)-CB(2) Heteroreceptor Complexes. Front Pharmacol 9 632 (2018).
- Nadal X, Del Rio C, Casano S et al. Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is a potent PPARgamma agonist with neuroprotective activity. Br J Pharmacol 174(23), 4263-4276 (2017).
- Cascio MG, Gauson LA, Stevenson LA, Ross RA, Pertwee RG. Evidence that the plant cannabinoid cannabigerol is a highly potent alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist and moderately potent 5HT1A receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 159(1), 129-141 (2010).
- Hill AJ, Jones NA, Smith I et al. Voltage-gated sodium (NaV) channel blockade by plant cannabinoids does not confer anticonvulsant effects per se. Neurosci Lett 566 269-274 (2014).
- Anderson LL, Heblinski M, Absalom NL et al. Cannabigerolic acid, a major biosynthetic precursor molecule in cannabis, exhibits divergent effects on seizures in mouse models of epilepsy. Br J Pharmacol 178(24), 4826-4841 (2021).
- Ghovanloo MR, Estacion M, Higerd-Rusli GP, Zhao P, Dib-Hajj S, Waxman SG. Inhibition of sodium conductance by cannabigerol contributes to a reduction of dorsal root ganglion neuron excitability. Br J Pharmacol 179(15), 4010-4030 (2022).
- Milligan CJ, Anderson LL, Mcgregor IS, Arnold JC, Petrou S. Beyond CBD: Inhibitory effects of lesser studied phytocannabinoids on human voltage-gated sodium channels. Front Physiol 14 1081186 (2023).
- Iannotti FA, Hill CL, Leo A et al. Nonpsychotropic plant cannabinoids, cannabidivarin (CBDV) and cannabidiol (CBD), activate and desensitize transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channels in vitro: potential for the treatment of neuronal hyperexcitability. ACS Chem Neurosci 5(11), 1131-1141 (2014).
- Garcia C, Palomo-Garo C, Garcia-Arencibia M, Ramos J, Pertwee R, Fernandez-Ruiz J. Symptom-relieving and neuroprotective effects of the phytocannabinoid Delta(9)-THCV in animal models of Parkinson's disease. Br J Pharmacol 163(7), 1495-1506 (2011).
- Nalls MA, Blauwendraat C, Vallerga CL et al. Identification of novel risk loci, causal insights, and heritable risk for Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol 18(12), 1091-1102 (2019).
- Mack JM, Schamne MG, Sampaio TB et al. Melatoninergic System in Parkinson's Disease: From Neuroprotection to the Management of Motor and Nonmotor Symptoms. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016 3472032 (2016).
- Braak H, Del Tredici K. Neuropathological Staging of Brain Pathology in Sporadic Parkinson's disease: Separating the Wheat from the Chaff. J Parkinsons Dis 7(s1), S71-S85 (2017).
- Yasuda T, Nakata Y, Mochizuki H. alpha-Synuclein and neuronal cell death. Mol Neurobiol 47(2), 466-483 (2013).
- Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rub U, Bratzke H, Del Tredici K. Stages in the development of Parkinson's disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res 318(1), 121-134 (2004).
- Garcia C, Palomo-Garo C, Gomez-Galvez Y, Fernandez-Ruiz J. Cannabinoid-dopamine interactions in the physiology and physiopathology of the basal ganglia. Br J Pharmacol 173(13), 2069-2079 (2016).
- Oz M, Jaligam V, Galadari S, Petroianu G, Shuba YM, Shippenberg TS. The endogenous cannabinoid, anandamide, inhibits dopamine transporter function by a receptor-independent mechanism. J Neurochem 112(6), 1454-1464 (2010).
- Pisani A, Fezza F, Galati S et al. High endogenous cannabinoid levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of untreated Parkinson's disease patients. Ann Neurol 57(5), 777-779 (2005).
- Van Laere K, Casteels C, Lunskens S et al. Regional changes in type 1 cannabinoid receptor availability in Parkinson's disease in vivo. Neurobiol Aging 33(3), 620 e621-628 (2012).
- Song L, Yang X, Ma Y, Wu N, Liu Z. The CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonist reduces L-DOPA-induced motor fluctuation and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Drug Des Devel Ther 8 2173-2179 (2014).
- Gomez-Galvez Y, Palomo-Garo C, Fernandez-Ruiz J, Garcia C. Potential of the cannabinoid CB(2) receptor as a pharmacological target against inflammation in Parkinson's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 64 200-208 (2016).
- Chagas MH, Zuardi AW, Tumas V et al. Effects of cannabidiol in the treatment of patients with Parkinson's disease: an exploratory double-blind trial. J Psychopharmacol 28(11), 1088-1098 (2014).
- De Faria SM, De Morais Fabricio D, Tumas V et al. Effects of acute cannabidiol administration on anxiety and tremors induced by a Simulated Public Speaking Test in patients with Parkinson's disease. J Psychopharmacol 34(2), 189-196 (2020).
- Peball M, Krismer F, Knaus HG et al. Non-Motor Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease are Reduced by Nabilone. Ann Neurol 88(4), 712-722 (2020).
- Garcia-Arencibia M, Gonzalez S, De Lago E, Ramos JA, Mechoulam R, Fernandez-Ruiz J. Evaluation of the neuroprotective effect of cannabinoids in a rat model of Parkinson's disease: importance of antioxidant and cannabinoid receptor-independent properties. Brain Res 1134(1), 162-170 (2007).
- Lastres-Becker I, Molina-Holgado F, Ramos JA, Mechoulam R, Fernandez-Ruiz J. Cannabinoids provide neuroprotection against 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity in vivo and in vitro: relevance to Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 19(1-2), 96-107 (2005).
- Santos NA, Martins NM, Sisti FM et al. The neuroprotection of cannabidiol against MPP(+)-induced toxicity in PC12 cells involves trkA receptors, upregulation of axonal and synaptic proteins, neuritogenesis, and might be relevant to Parkinson's disease. Toxicol In Vitro 30(1 Pt B), 231-240 (2015).
- Wang L, Wu X, Yang G et al. Cannabidiol Alleviates the Damage to Dopaminergic Neurons in 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine-Induced Parkinson's Disease Mice Via Regulating Neuronal Apoptosis and Neuroinflammation. Neuroscience 498 64-72 (2022).
- Mattos BA, Bonato JM, Splendor MC, Del Bel E, Milani H, Oliveira RMW. Cannabidiol improves nonmotor symptoms, attenuates neuroinflammation and favors hippocampal newborn neuronal maturation in a rat model of Parkinsonism. Acta Neuropsychiatr 1-30 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Espadas I, Keifman E, Palomo-Garo C et al. Beneficial effects of the phytocannabinoid Delta(9)-THCV in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 141 104892 (2020).
- De Mattos BA, Bonato JM, Splendor MC, Del Bel E, Milani H, De Oliveira RMW. Cannabidiol improves non-motor symptoms, attenuates neuroinflammation, and favours hippocampal newborn neuronal maturation in a rat model of Parkinsonism. Acta Neuropsychiatr 1-13 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Burgaz S, Garcia C, Gomez-Canas M, Munoz E, Fernandez-Ruiz J. Development of An Oral Treatment with the PPAR-gamma-Acting Cannabinoid VCE-003.2 Against the Inflammation-Driven Neuronal Deterioration in Experimental Parkinson's Disease. Molecules 24(15), (2019).
- Burgaz S, Garcia C, Gomez-Canas M et al. Neuroprotection with the cannabigerol quinone derivative VCE-003.2 and its analogs CBGA-Q and CBGA-Q-Salt in Parkinson's disease using 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned mice. Mol Cell Neurosci 110 103583 (2021).
- Burgaz S, Garcia C, Gomez-Canas M, Rolland A, Munoz E, Fernandez-Ruiz J. Neuroprotection with the Cannabidiol Quinone Derivative VCE-004.8 (EHP-101) against 6-Hydroxydopamine in Cell and Murine Models of Parkinson's Disease. Molecules 26(11), (2021).
- Wang F, Jin T, Li H et al. Cannabidivarin alleviates alpha-synuclein aggregation via DAF-16 in Caenorhabditis elegans. FASEB J 37(2), e22735 (2023).
- Harrell ER, King JW, Stoeckel LE, Trevino M. National Institute on Aging's 50th anniversary: Advancing cognitive aging research and the cognitive health of older adults. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci (2024). [CrossRef]
- Ramirez BG, Blazquez C, Gomez Del Pulgar T, Guzman M, De Ceballos ML. Prevention of Alzheimer's disease pathology by cannabinoids: neuroprotection mediated by blockade of microglial activation. J Neurosci 25(8), 1904-1913 (2005).
- Solas M, Francis PT, Franco R, Ramirez MJ. CB2 receptor and amyloid pathology in frontal cortex of Alzheimer's disease patients. Neurobiol Aging 34(3), 805-808 (2013).
- Li S, Huang Y, Yu L, Ji X, Wu J. Impact of the Cannabinoid System in Alzheimer's Disease. Curr Neuropharmacol 21(3), 715-726 (2023).
- Khavandi M, Rao PPN, Beazely MA. Differential Effects of Endocannabinoids on Amyloid-Beta Aggregation and Toxicity. Int J Mol Sci 24(2), (2023).
- Rapaka D, Adiukwu PC, Challa SR, Bitra VR. Interplay Between Astroglial Endocannabinoid System and the Cognitive Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease. Physiol Res 72(5), 575-586 (2023).
- Iuvone T, Esposito G, Esposito R, Santamaria R, Di Rosa M, Izzo AA. Neuroprotective effect of cannabidiol, a non-psychoactive component from Cannabis sativa, on beta-amyloid-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 89(1), 134-141 (2004).
- Vallee A, Lecarpentier Y, Guillevin R, Vallee JN. Effects of cannabidiol interactions with Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and PPARgamma on oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 49(10), 853-866 (2017).
- Zhang N, Parr CJC, Birch AM, Goldfinger MH, Sastre M. The amyloid precursor protein binds to beta-catenin and modulates its cellular distribution. Neurosci Lett 685 190-195 (2018).
- Libro R, Diomede F, Scionti D et al. Cannabidiol Modulates the Expression of Alzheimer's Disease-Related Genes in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci 18(1), (2016).
- Li H, Liu Y, Tian D et al. Overview of cannabidiol (CBD) and its analogues: Structures, biological activities, and neuroprotective mechanisms in epilepsy and Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Med Chem 192 112163 (2020).
- Martin-Moreno AM, Reigada D, Ramirez BG et al. Cannabidiol and other cannabinoids reduce microglial activation in vitro and in vivo: relevance to Alzheimer's disease. Mol Pharmacol 79(6), 964-973 (2011).
- Cheng D, Low JK, Logge W, Garner B, Karl T. Chronic cannabidiol treatment improves social and object recognition in double transgenic APPswe/PS1∆E9 mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 231(15), 3009-3017 (2014).
- Cheng D, Spiro AS, Jenner AM, Garner B, Karl T. Long-term cannabidiol treatment prevents the development of social recognition memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice. J Alzheimers Dis 42(4), 1383-1396 (2014).
- Arnanz MA, Ruiz De Martin Esteban S, Martinez Relimpio AM et al. Effects of Chronic, Low-Dose Cannabinoids, Cannabidiol, Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol and a Combination of Both, on Amyloid Pathology in the 5xFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res (2023). [CrossRef]
- Singh J, Neary JP. Neuroprotection Following Concussion: The Potential Role for Cannabidiol. Can J Neurol Sci 47(3), 289-300 (2020).
- Ma BQ, Jia JX, Wang H et al. Cannabidiol improves the cognitive function of SAMP8 AD model mice involving the microbiota-gut-brain axis. J Toxicol Environ Health A 87(11), 471-479 (2024).
- Velayudhan L, Dugonjic M, Pisani S et al. Cannabidiol for behavior symptoms in Alzheimer's disease (CANBiS-AD): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int Psychogeriatr 1-3 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Amini M, Abdolmaleki Z. The Effect of Cannabidiol Coated by Nano-Chitosan on Learning and Memory, Hippocampal CB1 and CB2 Levels, and Amyloid Plaques in an Alzheimer's Disease Rat Model. Neuropsychobiology 81(3), 171-183 (2022).
- Novotna A, Mares J, Ratcliffe S et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, enriched-design study of nabiximols* (Sativex((R)) ), as add-on therapy, in subjects with refractory spasticity caused by multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 18(9), 1122-1131 (2011).
- Broers B, Pata Z, Mina A, Wampfler J, De Saussure C, Pautex S. Prescription of a THC/CBD-Based Medication to Patients with Dementia: A Pilot Study in Geneva. Med Cannabis Cannabinoids 2(1), 56-59 (2019).
- Schubert D, Kepchia D, Liang Z, Dargusch R, Goldberg J, Maher P. Efficacy of Cannabinoids in a Pre-Clinical Drug-Screening Platform for Alzheimer's Disease. Mol Neurobiol 56(11), 7719-7730 (2019).
- Marsh DT, Sugiyama A, Imai Y, Kato R, Smid SD. The structurally diverse phytocannabinoids cannabichromene, cannabigerol and cannabinol significantly inhibit amyloid beta-evoked neurotoxicity and changes in cell morphology in PC12 cells. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 134(3), 293-309 (2024).
- Englund A, Atakan Z, Kralj A, Tunstall N, Murray R, Morrison P. The effect of five day dosing with THCV on THC-induced cognitive, psychological and physiological effects in healthy male human volunteers: A placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover pilot trial. J Psychopharmacol 30(2), 140-151 (2016).
- Puopolo T, Liu C, Ma H, Seeram NP. Inhibitory Effects of Cannabinoids on Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Enzyme Activities. Med Cannabis Cannabinoids 5(1), 85-94 (2022).
- Melnikova I. Therapies for Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6(5), 341-342 (2007).
- Mccolgan P, Tabrizi SJ. Huntington's disease: a clinical review. Eur J Neurol 25(1), 24-34 (2018).
- Denovan-Wright EM, Robertson HA. Cannabinoid receptor messenger RNA levels decrease in a subset of neurons of the lateral striatum, cortex and hippocampus of transgenic Huntington's disease mice. Neuroscience 98(4), 705-713 (2000).
- Glass M, Dragunow M, Faull RL. The pattern of neurodegeneration in Huntington's disease: a comparative study of cannabinoid, dopamine, adenosine and GABA(A) receptor alterations in the human basal ganglia in Huntington's disease. Neuroscience. 97 505-519 (2000).
- Van Laere K, Casteels C, Dhollander I et al. Widespread decrease of type 1 cannabinoid receptor availability in Huntington disease in vivo. J Nucl Med 51(9), 1413-1417 (2010).
- Laprairie RB, Kelly ME, Denovan-Wright EM. Cannabinoids increase type 1 cannabinoid receptor expression in a cell culture model of striatal neurons: implications for Huntington's disease. Neuropharmacology 72 47-57 (2013).
- Mccaw EA, Hu H, Gomez GT, Hebb AL, Kelly ME, Denovan-Wright EM. Structure, expression and regulation of the cannabinoid receptor gene (CB1) in Huntington's disease transgenic mice. Eur J Biochem 271(23-24), 4909-4920 (2004).
- Blazquez C, Chiarlone A, Sagredo O et al. Loss of striatal type 1 cannabinoid receptors is a key pathogenic factor in Huntington's disease. Brain 134(Pt 1), 119-136 (2011).
- Chiarlone A, Bellocchio L, Blazquez C et al. A restricted population of CB1 cannabinoid receptors with neuroprotective activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(22), 8257-8262 (2014).
- Consroe P, Laguna J, Allender J et al. Controlled clinical trial of cannabidiol in Huntington's disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40(3), 701-708 (1991).
- Valdeolivas S, Satta V, Pertwee RG, Fernandez-Ruiz J, Sagredo O. Sativex-like combination of phytocannabinoids is neuroprotective in malonate-lesioned rats, an inflammatory model of Huntington's disease: role of CB1 and CB2 receptors. ACS Chem Neurosci 3(5), 400-406 (2012).
- Sagredo O, Pazos MR, Satta V, Ramos JA, Pertwee RG, Fernandez-Ruiz J. Neuroprotective effects of phytocannabinoid-based medicines in experimental models of Huntington's disease. J Neurosci Res 89(9), 1509-1518 (2011).
- Ruhaak LR, Felth J, Karlsson PC, Rafter JJ, Verpoorte R, Bohlin L. Evaluation of the cyclooxygenase inhibiting effects of six major cannabinoids isolated from Cannabis sativa. Biol Pharm Bull 34(5), 774-778 (2011).
- Valdeolivas S, Navarrete C, Cantarero I, Bellido ML, Munoz E, Sagredo O. Neuroprotective properties of cannabigerol in Huntington's disease: studies in R6/2 mice and 3-nitropropionate-lesioned mice. Neurotherapeutics 12(1), 185-199 (2015).
- Gugliandolo A, Silvestro S, Chiricosta L, Pollastro F, Bramanti P, Mazzon E. The Transcriptomic Analysis of NSC-34 Motor Neuron-Like Cells Reveals That Cannabigerol Influences Synaptic Pathways: A Comparative Study with Cannabidiol. Life (Basel) 10(10), (2020).
- De Lago E, Urbani P, Ramos JA, Di Marzo V, Fernandez-Ruiz J. Arvanil, a hybrid endocannabinoid and vanilloid compound, behaves as an antihyperkinetic agent in a rat model of Huntington's disease. Brain Res 1050(1-2), 210-216 (2005).
- Lastres-Becker I, Bizat N, Boyer F, Hantraye P, Brouillet E, Fernandez-Ruiz J. Effects of cannabinoids in the rat model of Huntington's disease generated by an intrastriatal injection of malonate. Neuroreport 14(6), 813-816 (2003).
- De Lago E, Fernandez-Ruiz J, Ortega-Gutierrez S et al. UCM707, an inhibitor of the anandamide uptake, behaves as a symptom control agent in models of Huntington's disease and multiple sclerosis, but fails to delay/arrest the progression of different motor-related disorders. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 16(1), 7-18 (2006).
- Lastres-Becker I, Fezza F, Cebeira M et al. Changes in endocannabinoid transmission in the basal ganglia in a rat model of Huntington's disease. Neuroreport 12(10), 2125-2129 (2001).
- Borrelli F, Fasolino I, Romano B et al. Beneficial effect of the non-psychotropic plant cannabinoid cannabigerol on experimental inflammatory bowel disease. Biochem Pharmacol 85(9), 1306-1316 (2013).
- Nachnani R, Raup-Konsavage WM, Vrana KE. The Pharmacological Case for Cannabigerol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 376(2), 204-212 (2021).
- Starkus J, Jansen C, Shimoda LMN, Stokes AJ, Small-Howard AL, Turner H. Diverse TRPV1 responses to cannabinoids. Channels (Austin) 13(1), 172-191 (2019).
- De Almeida DL, Devi LA. Diversity of molecular targets and signaling pathways for CBD. Pharmacol Res Perspect 8(6), e00682 (2020).
- Di Marzo V, Piscitelli F. The Endocannabinoid System and its Modulation by Phytocannabinoids. Neurotherapeutics 12(4), 692-698 (2015).
- Ramer R, Heinemann K, Merkord J et al. COX-2 and PPAR-gamma confer cannabidiol-induced apoptosis of human lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 12(1), 69-82 (2013).
- Deiana S, Watanabe A, Yamasaki Y et al. Plasma and brain pharmacokinetic profile of cannabidiol (CBD), cannabidivarine (CBDV), Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) and cannabigerol (CBG) in rats and mice following oral and intraperitoneal administration and CBD action on obsessive-compulsive behaviour. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 219(3), 859-873 (2012).
- Glass M, Dragunow M, Faull RL. Cannabinoid receptors in the human brain: a detailed anatomical and quantitative autoradiographic study in the fetal, neonatal and adult human brain. Neuroscience 77(2), 299-318 (1997).
- Basavarajappa BS, Joshi V, Shivakumar M, Subbanna S. Distinct Functions of Endogenous Cannabinoid System in Alcohol Abuse Disorders. Br J Pharmacol (2019). [CrossRef]
- Parsons LH, Hurd YL. Endocannabinoid signalling in reward and addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(10), 579-594 (2015).
- Stern CaJ, De Carvalho CR, Bertoglio LJ, Takahashi RN. Effects of Cannabinoid Drugs on Aversive or Rewarding Drug-Associated Memory Extinction and Reconsolidation. Neuroscience 370 62-80 (2018).
- Sabia S, Fayosse A, Dumurgier J et al. Alcohol consumption and risk of dementia: 23 year follow-up of Whitehall II cohort study. BMJ 362 k2927 (2018).
- Stampfer MJ, Kang JH, Chen J, Cherry R, Grodstein F. Effects of moderate alcohol consumption on cognitive function in women. N Engl J Med 352(3), 245-253 (2005).
- Liu SJ, Fang ZY, Yang Y, Deng HM, Wang JZ. Alzheimer-like phosphorylation of tau and neurofilament induced by cocaine in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin 24(6), 512-518 (2003).
- Shukla M, Vincent B. The multi-faceted impact of methamphetamine on Alzheimer's disease: From a triggering role to a possible therapeutic use. Ageing Res Rev 60 101062 (2020).
- Morgan CJ, Das RK, Joye A, Curran HV, Kamboj SK. Cannabidiol reduces cigarette consumption in tobacco smokers: preliminary findings. Addict Behav 38(9), 2433-2436 (2013).
- Hindocha C, Freeman TP, Grabski M et al. Cannabidiol reverses attentional bias to cigarette cues in a human experimental model of tobacco withdrawal. Addiction 113(9), 1696-1705 (2018).
- Hindocha C, Freeman TP, Grabski M et al. The effects of cannabidiol on impulsivity and memory during abstinence in cigarette dependent smokers. Sci Rep 8(1), 7568 (2018).
- Gournay LR, Petry J, Bilsky S et al. Cannabidiol Reduces Nicotine Withdrawal Severity and State Anxiety During an Acute E-cigarette Abstinence Period: A Novel, Open-Label Study. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res (2023). [CrossRef]
- Cheeks SN, Buzzi B, Valdez A, Mogul AS, Damaj MI, Fowler CD. Cannabidiol as a potential cessation therapeutic: Effects on intravenous nicotine self-administration and withdrawal symptoms in mice. Neuropharmacology 246 109833 (2024).
- Smith LC, Tieu L, Suhandynata RT et al. Cannabidiol reduces withdrawal symptoms in nicotine-dependent rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 238(8), 2201-2211 (2021).
- Black N, Stockings E, Campbell G et al. Cannabinoids for the treatment of mental disorders and symptoms of mental disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 6(12), 995-1010 (2019).
- Hindocha C, Freeman TP, Schafer G et al. Acute effects of cannabinoids on addiction endophenotypes are moderated by genes encoding the CB1 receptor and FAAH enzyme. Addict Biol 25(3), e12762 (2020).
- Broyd SJ, Van Hell HH, Beale C, Yucel M, Solowij N. Acute and Chronic Effects of Cannabinoids on Human Cognition-A Systematic Review. Biol Psychiatry 79(7), 557-567 (2016).
- Freeman AM, Petrilli K, Lees R et al. How does cannabidiol (CBD) influence the acute effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in humans? A systematic review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 107 696-712 (2019).
- Pokorski I, Clement N, Phung N, Weltman M, Fu S, J. C. Cannabidiol in the management of inpatient cannabis withdrawal: clinical case series. Future Neurol. 12(3), 133–140. (2017).
- Crippa JA, Hallak JE, Machado-De-Sousa JP et al. Cannabidiol for the treatment of cannabis withdrawal syndrome: a case report. J Clin Pharm Ther 38(2), 162-164 (2013).
- Shannon S, Opila-Lehman J. Cannabidiol Oil for Decreasing Addictive Use of Marijuana: A Case Report. Integr Med (Encinitas) 14(6), 31-35 (2015).
- Cleirec G, Desmier E, Lacatus C et al. Efficiency of Inhaled Cannabidiol in Cannabis Use Disorder: The Pilot Study Cannavap. Front Psychiatry 13 899221 (2022).
- Solowij N, Broyd SJ, Beale C et al. Therapeutic Effects of Prolonged Cannabidiol Treatment on Psychological Symptoms and Cognitive Function in Regular Cannabis Users: A Pragmatic Open-Label Clinical Trial. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res 3(1), 21-34 (2018).
- Lorenzetti V, Mctavish E, Broyd S et al. Daily Cannabidiol Administration for 10 Weeks Modulates Hippocampal and Amygdalar Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Cannabis Users: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Open-Label Clinical Trial. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res (2023). [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho CR, Takahashi RN. Cannabidiol disrupts the reconsolidation of contextual drug-associated memories in Wistar rats. Addict Biol 22(3), 742-751 (2017).
- Ren Y, Whittard J, Higuera-Matas A, Morris CV, Hurd YL. Cannabidiol, a nonpsychotropic component of cannabis, inhibits cue-induced heroin seeking and normalizes discrete mesolimbic neuronal disturbances. J Neurosci 29(47), 14764-14769 (2009).
- Navarrete F, Gasparyan A, Manzanares J. CBD-mediated regulation of heroin withdrawal-induced behavioural and molecular changes in mice. Addict Biol 27(2), e13150 (2022).
- Scicluna RL, Wilson BB, Thelaus SH, Arnold JC, Mcgregor IS, Bowen MT. Cannabidiol Reduced the Severity of Gastrointestinal Symptoms of Opioid Withdrawal in Male and Female Mice. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res 9(2), 547-560 (2024).
- Hayduk SA, Hughes AC, Winter RL, Milton MD, Ward SJ. Single and Combined Effects of Cannabigerol (CBG) and Cannabidiol (CBD) in Mouse Models of Oxaliplatin-Associated Mechanical Sensitivity, Opioid Antinociception, and Naloxone-Precipitated Opioid Withdrawal. Biomedicines 12(6), (2024).
- Socha J, Grochecki P, Marszalek-Grabska M et al. Cannabidiol Protects against the Reinstatement of Oxycodone-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Adolescent Male but Not Female Rats: The Role of MOR and CB1R. Int J Mol Sci 25(12), (2024).
- Li H, Ward SJ. Paclitaxel-Associated Mechanical Sensitivity and Neuroinflammation Are Sex-, Time-, and Site-Specific and Prevented through Cannabigerol Administration in C57Bl/6 Mice. Int J Mol Sci 25(8), (2024).
- Lorenzetti V, Mctavish E, Broyd S et al. Daily Cannabidiol Administration for 10 Weeks Modulates Hippocampal and Amygdalar Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Cannabis Users: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Open-Label Clinical Trial. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res 9(4), e1108-e1121 (2024).
- Guimaraes FS, Chiaretti TM, Graeff FG, Zuardi AW. Antianxiety effect of cannabidiol in the elevated plus-maze. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 100(4), 558-559 (1990).
- Almeida V, Levin R, Peres FF et al. Cannabidiol exhibits anxiolytic but not antipsychotic property evaluated in the social interaction test. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 41 30-35 (2013).
- Arnone M, Maruani J, Chaperon F et al. Selective inhibition of sucrose and ethanol intake by SR 141716, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology. 132 104-106 (1997).
- Basavarajappa BS. Endocannabinoid system in the development of tolerance to alcohol. . Klinik and Forschung (Journal of Clinical Research). 11 16-19 (2005).
- Colombo G, Agabio R, Fa M et al. Reduction of voluntary ethanol intake in ethanol-preferring sP rats by the cannabinoid antagonist SR-141716. Alcohol and alcoholism 33 126-130 (1998).
- Hungund BL, Szakall I, Adam A, Basavarajappa BS, Vadasz C. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice exhibit markedly reduced voluntary alcohol consumption and lack alcohol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 84(4), 698-704 (2003).
- Hamelink C, Hampson A, Wink DA, Eiden LE, Eskay RL. Comparison of cannabidiol, antioxidants, and diuretics in reversing binge ethanol-induced neurotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 314(2), 780-788 (2005).
- Liput DJ, Hammell DC, Stinchcomb AL, Nixon K. Transdermal delivery of cannabidiol attenuates binge alcohol-induced neurodegeneration in a rodent model of an alcohol use disorder. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 111 120-127 (2013).
- Brenneman DE, Petkanas D, Kinney WA. Pharmacological Comparisons Between Cannabidiol and KLS-13019. J Mol Neurosci 66(1), 121-134 (2018).
- Oberlin BG, Grahame NJ. High-alcohol preferring mice are more impulsive than low-alcohol preferring mice as measured in the delay discounting task. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33(7), 1294-1303 (2009).
- Wilhelm CJ, Mitchell SH. Strain differences in delay discounting using inbred rats. Genes Brain Behav 8(4), 426-434 (2009).
- Amlung M, Vedelago L, Acker J, Balodis I, Mackillop J. Steep delay discounting and addictive behavior: a meta-analysis of continuous associations. Addiction 112(1), 51-62 (2017).
- Mackillop J, Amlung MT, Few LR, Ray LA, Sweet LH, Munafo MR. Delayed reward discounting and addictive behavior: a meta-analysis. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 216(3), 305-321 (2011).
- Viudez-Martinez A, Garcia-Gutierrez MS, Navarron CM et al. Cannabidiol reduces ethanol consumption, motivation and relapse in mice. Addict Biol 23(1), 154-164 (2018).
- Karoly HC, Drennan ML, Prince MA, Zulic L, Dooley G. Consuming oral cannabidiol prior to a standard alcohol dose has minimal effect on breath alcohol level and subjective effects of alcohol. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 240(5), 1119-1129 (2023).
- Maccioni P, Bratzu J, Carai MaM, Colombo G, Gessa GL. Reducing Effect of Cannabidiol on Alcohol Self-Administration in Sardinian Alcohol-Preferring Rats. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res 7(2), 161-169 (2022).
- Gasparyan A, Navarrete F, Navarro D, Manzanares J. Cannabidiol regulates behavioral and brain alterations induced by spontaneous alcohol withdrawal. Neuropharmacology 233 109549 (2023).
- Tringali G, Lavanco G, Castelli V et al. Cannabidiol tempers alcohol intake and neuroendocrine and behavioural correlates in alcohol binge drinking adolescent rats. Focus on calcitonin gene-related peptide's brain levels. Phytother Res 37(11), 4870-4884 (2023).
- Brancato A, Castelli V, Lavanco G et al. Social stress under binge-like alcohol withdrawal in adolescence: evidence of cannabidiol effect on maladaptive plasticity in rats. Psychol Med 53(12), 5538-5550 (2023).
- Szulc M, Kujawski R, Pacholak A et al. Cannabidiol as a Modulator of the Development of Alcohol Tolerance in Rats. Nutrients 15(7), (2023).
- Melkumyan M, Annaswamy VM, Evans AM et al. Effects of cannabidiol, with and without ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol, on anxiety-like behavior following alcohol withdrawal in mice. Front Neurosci 18 1375440 (2024).
- Filev R, Engelke DS, Da Silveira DX, Mello LE, Santos-Junior JG. THC inhibits the expression of ethanol-induced locomotor sensitization in mice. Alcohol 65 31-35 (2017).
- Moore CF, Zamarripa CA, Weerts EM. Oral Cannabidiol does not alter Alcohol Seeking and Self-Administration in Baboons. Drug Alcohol Depend 245 109829 (2023).
- Garcia-Baos A, Puig-Reyne X, Garcia-Algar O, Valverde O. Cannabidiol attenuates cognitive deficits and neuroinflammation induced by early alcohol exposure in a mice model. Biomed Pharmacother 141 111813 (2021).
- Koren G, Cohen R, Sachs O. Use of Cannabis in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res 6(1), 74-76 (2021).
- Gasparyan A, Navarro D, Navarrete F et al. Cannabidiol repairs behavioral and brain disturbances in a model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Pharmacol Res 188 106655 (2023).
- Arnone M, Maruani J, Chaperon F et al. Selective inhibition of sucrose and ethanol intake by SR 141716, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 132(1), 104-106 (1997).
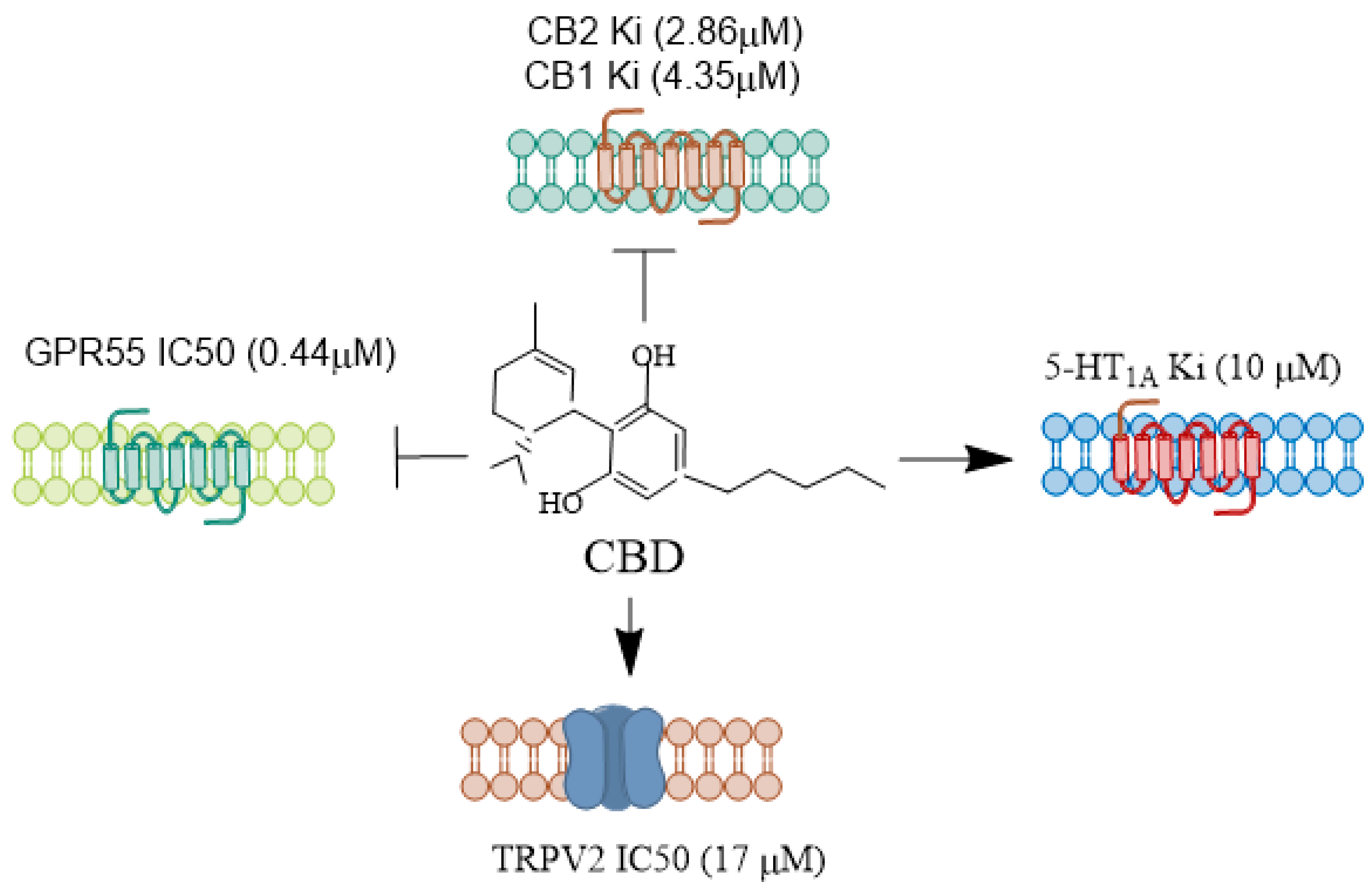
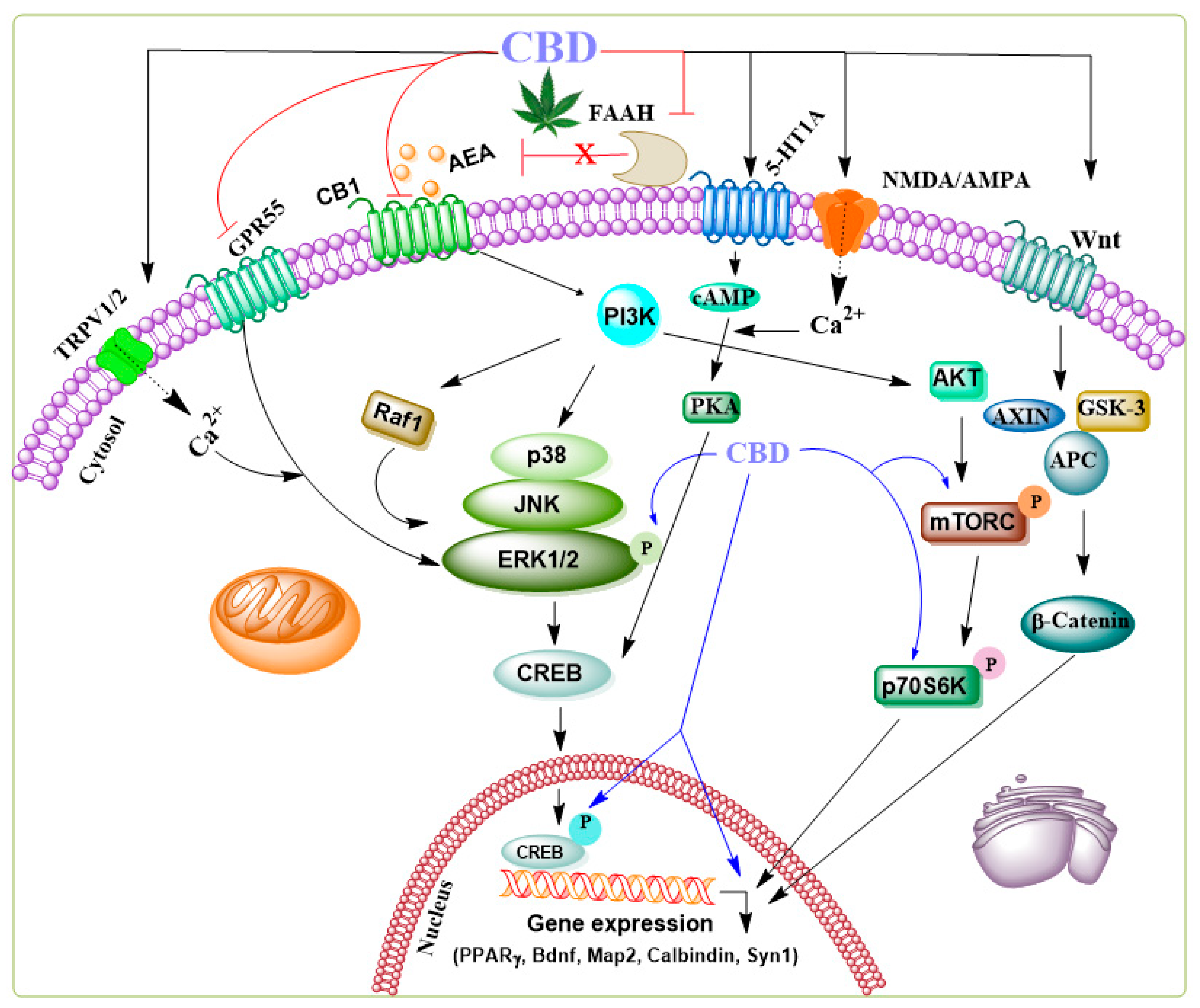
 , antagonist.
, antagonist.
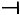 , antagonist.
, antagonist.
 , antagonist.
, antagonist.
 , antagonist.
, antagonist.
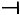 , antagonist.
, antagonist.
 , antagonist.
, antagonist.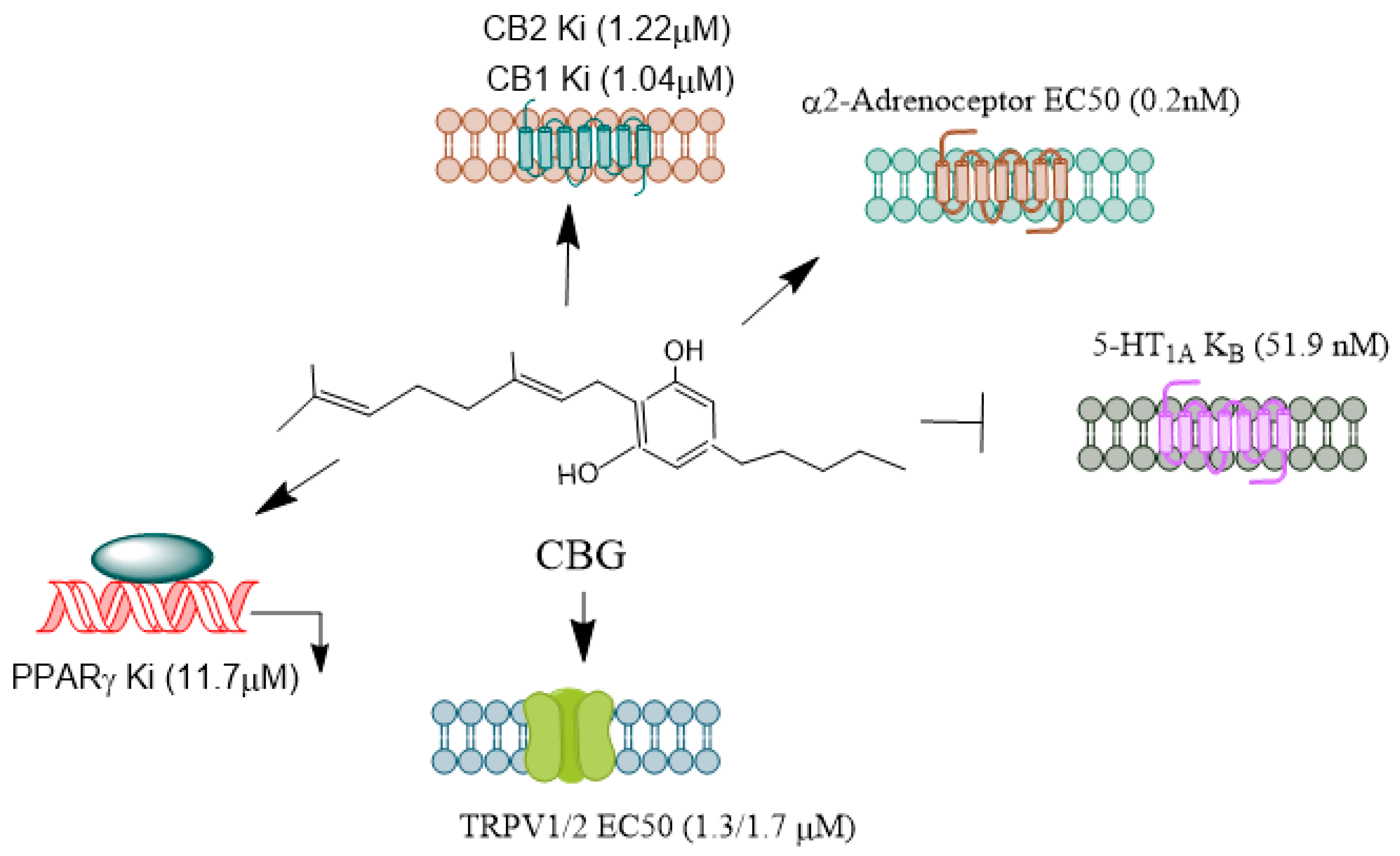
| Model | NMPs | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pilocarpine-epilepticus rat | CBD | Convulasent ↓Neurodegenration ↓ | [49] |
| PTZ seizures | CBD and CBG | Nav current in cells ↓ | [104] |
| Epilepsy-spontaneous LFPs in Cells | CBDV | Amplitude and duration of LFPs ↓Mg2+ free induced LFPs frequency ↑ | [93] |
| Epilepsy in transfected cells (TRPV1, TRPV2, and TRPA1. | CBDV +CBD | Convulasent ↓Phosphorylation of TRPV1 at the S800 site ↑ | [108] |
| Electrophysiology (epileptiform bursting) (In vitro) | Δ9-THCV | Epileptiform burst ↓ | [81] |
| PTZ seizures | CBDV | Seizure severity ↓Latency to first signs of seizure ↑ | [93,97,98] |
| PTZ seizures | Δ9-THCV | Median seizure severity, duration, progression, or latency was unaffected | [81] |
| 6-hydroxytryptamine or LPS in rats and mice | Δ9-THCV | Neuronal loss, microglial activation, ↓TH positive neurons and Motor activity↑ | [109] |
| Rat model | CBD | Convulasent ↓Seizure severity ↓ | [61] |
| Rats (GEPR-3) strain | CBD | Seizure ↓ | [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





