1. Introduction
Shrimp farming is one of the fastest-growing industries worldwide, being the
Penaeus vannamei one of the most widely cultivated species [
1]. However, poor management practices and increasing stocking densities contribute to the incidence and prevalence of infectious diseases, such as Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND), which can cause high mortality during the first days of cultivation. This disease is characterized by the formation of biofilms on the cuticular surface of the shrimp’s stomach, where toxins are released and subsequently enter the hepatopancreas, causing necrosis that ultimately kills the shrimp [
2]. The global spread of multi-drug resistant pathogens is a major concern, particularly in aquaculture. The excessive use and improper prescription of antibiotics have contributed to the development of bacterial resistance, which now poses a serious threat to both shrimp farming and human health. While
Vibrio parahaemolyticus has not yet become a direct health risk for humans, shrimp farmers have historically relied on antibiotics without fully considering the environmental repercussions and the potential for bacterial resistance. Therefore, it is imperative to explore alternative solutions that reduce the use of antibiotics and prevent resistance from developing.
Several strategies have been implemented to limit the spread of AHPND, including the use of medicinal plant extracts and nanoparticles [
3,
4,
5].
Larrea tridentata, a plant from the Zygophyllaceae family, is endemic to Mexico but can also be found in southern North America [
6]. Among the bioactive compounds in this plant, lignans have demonstrated the most promising biological activity, with notable antimicrobial effects against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria [
3].
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are of particular interest due to their properties, including conductivity, antibacterial activity, and biological compatibility [
7]. Silver is known to be antagonistic to a broad range of microorganisms, and it’s most important applications currently lie in the industrial and healthcare sectors [
8]. In general, the functional groups in plant extracts serve as reducing agents, reacting with metal ions of the precursor salt to convert them into nanoparticles with varying shapes and sizes [
9].
Despite their potential, silver nanoparticles remain underutilized in aquaculture, largely due to a lack of scientific evidence regarding their ion-generating capacity and potential negative effects. Given their significance, this study aims to synthesize silver nanoparticles using L. tridentata (Gobernadora) and evaluate their impact on water quality, shrimp survival, and antibacterial activity against V. parahaemolyticus, as well as the expression of resistance genes associated with VpAHPND.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtaining Plant Material
Vegetative material from “gobernadora” (
L. tridentata) was collected outside Hermosillo, Sonora, located at 28°51'18.0"N 111°23'41.2"W. Subsequently, the leaves were dehydrated on blotting paper and a mash at 27 ± 2°C for 10 days. The dry samples of each plant were pulverized and sieved using an industrial blender (Thermo Fisher Scientific®) at 45˚C for 48h [
10]. After the leaves were dried, they were pulverized using a blender until they became a fine powder and stored in a dark container that was completely closed.
2.2. Plant Extraction
L. tridentata extracts were obtained by mixing 200 mL of distilled water with 40 g of powder sample (20 % w/v) and placed in a bottom flask under constant moving at 24 OC for 1 h. After this time, the solution was filtered through a Whatman No. 1 filter (180 µm thick) and filtered with a Buchner funnel attached to a filter- flask.
2.3. Green Synthesis
AgNPs were synthesized using the simplified protocol [
11], with silver nitrate (AgNO
3 > 99.8 %, Sigma-Aldrich®, USA) as precursor, aqueous extracts of
L. tridentata as a reducing and stabilizer agent, deionized water, and ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH) to adjust the pH. For the synthesis, at high dose (0.1 M) of AgNO
3 were placed at room temperature 140 mL of
L. tridentata aqueous extract in a bottom flask with 70 mL of AgNO
3, 35 mL of NH
4OH and finally 455 mL of distilled water. At low dose (0.01M) of AgNO
3 were employed 140 mL of
L. tridentata; 70 mL (0.01 M) of AgNO
3, the same volume of NH
4OH and of distilled water. Finally, at both doses the mixture with a final volume of 700 mL was stirred with a stir plate magnet for at least 4 h to promote nanoparticle synthesis. The samples were stored at room temperature for future use.
2.4. Characterization
Sample characterization was carried out with a spectrophotometer (UV-Vis) to analyze the surface plasmon resonance using diluted 1:4 nanoparticles solution with deionized water. The morphological characteristics of the samples were analyzed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
2.5. Experimental Animals
Pacific white shrimp (P. vannamei) postlarvae 8 ± 0.7 g were obtained at the “Acuícola 50” shrimp farm, located in El Sacrificio, Guasave, Sinaloa, Mexico (25° 27' 47.2"N 108° 42' 00.8"W). The specimens were carefully checked to rule out the presence of malformations or signs of disease and were immediately sent to the IPN-CIIDIR where the experiment was carried out. The organisms were placed in a container with seawater saturated with dissolved oxygen, at a salinity of 30 g/L and a temperature of 22 ºC for their transportation. Shrimp were maintained at 26 ± 1 °C and fed with a 35% (w/w) protein commercial diet. Once the acclimatization process was finished, 30 individuals were taken and placed in 200 L capacity tubs before starting the bioassay.
2.6. Experimental Diets
For the control diet (CN), 600 g of fine powder was obtained from the commercial feed; grinding was carried out at room temperature (18 ºC) with low light intensity, to which 360 mL of distilled water (60 %) was added. During the mixing process, 12 g (2% total weight) of Sodium alginate (C6H7NaO6) were added, as well as to the rest of the treatments. Subsequently, this mixture was passed to a meat grinder to make the pellets.
60 mL of the aqueous extract of L. tridentata (200 mg/mL) were passed and mixed with 300 mL of distilled water to incorporate into the feed and pelletize the second treatment (Ext). To prepare treatment three (AgNps-Lt), the same process was carried out with the difference that it used 30 mL of AgNPs-Lt silver nanoparticle solution (0.10797 mg/mL Ag) and 330 mL of distilled water to be mixed and taken to the pelletizer. The last treatment (AgNPs+Lt) was carried out in the same way with the difference that 300 mL of AgNPs-Lt (0.7428 mg/mL Ag) and 60 mL of distilled water were used. The pellets were dried in the laboratory without lighting with a fan for at least 24 h. They were stored in opaque containers with hermetic closure in a freezer at -4 oC, within which the necessary food was taken in weekly rations in covered containers to avoid light exposure.
2.7. Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Strain
The VpAHPND-E9 strain was obtained from a previously isolated and characterized material, which is in storage at the CIIDIR Unidad Sinaloa facility. The bacterial inoculum was preserved in TSB with 2.5% NaCl and 15% glycerol cryopreserved at -70 °C in 2 at a concentration of 1 x 106 CFU/mL. A vial of 2 mL was taken to culture on TSB agar at room temperature for around 24 h. Colonies were then diluted in sterile saline solution and measure the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) to subsequently inoculate TCBS agar boxes using various dilutions and observe the number of colonies observed per dilution.
2.8. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
MIC is defined as the minimum concentration necessary, where bacteria growth is not detected. The MIC against a strain of VpAHPND-E9 (1 x 106 CFU/mL) was determined in a 96-well microplate reader. The culture medium used was TSB using fractional dilutions of silver nanoparticles in concentrations ranging from 297.12 to 0.57 μg/mL. 3 replicates per dilution were used and 10 µL of the bacteria were placed in each well. This was grown for 24h at 30 °C. To indicate the presence of bacteria, the presence of color and the absorbance measurement were indicative parameters of bacterial growth. The MIC was taken as the minimum concentration necessary to inhibit the growth of the bacteria.
2.9. Water Parameters
During the experiment, dissolved oxygen concentration (DO, mg/L), temperature (
oC), pH and salinity (g/L) were recorded twice a day (08:00 and 16:00 h). Weekly water samples were taken to determine the concentration of ammonium (NH
4, mg/mL), nitrites (NO
2, mg/mL), nitrates (NO
3, mg/mL) [
12,
13]. Also, weekly microbiological analyzes were carried out to determine the amount of
Vibrio spp and
Bacillus spp [
14].
2.10. Experimental Immunological Bioassay
Four treatments were established (n = 30 shrimp by replicate). Animals were fed with experimental diets for 35 consecutive days and mortality was daily recorded throughout the experiments. After the bioassay animals were sacrificed and gills samples were withdrawn to determine expression of immune-relevant genes.
2.11. Experimental Treatment with AgNPs after VpAHPND-E9 Infection
At the end of the culture, 10 organisms were taken from each treatment of the feeding bioassay. The challenges were carried out in 50 L aquariums with sterile seawater at 25 g/L salinity and with constant aeration at 30±1.0 °C. Infections were carried out by immersion, adding 260,000 CFU/mL of a V. parahaemolyticus strain to every experimental unit. After performing the challenge against VpAHPND-E9 and to evaluate resistance to the pathogen, survival was recorded at 0, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h post infection.
2.11.1. Immunological Analysis
Gene expression was calculated by the 2
ΔΔCq method [
15], using
β-actin as the reference gene. The stored samples were individually macerated with pistils to later add 500 µL of Trizol. This mixture was centrifuged at 10,000 G at 4 °C for 10 min, 500 µL were transferred to sterile vials containing 100 µL of chloroform to be centrifuged again at 12,000 G at 4 °C for 15 min to recover the transparent phase and place isopropanol at a 1:1 ratio of the volume obtained (250 µL). This was incubated again and centrifuged according to the mentioned conditions. They were suspended from the vial with 250 µL of 75% ethanol for washing after the last two centrifugations and decant to obtain a pellet, which was re-suspended in DPC water and placed in a freezer at -80 °C.
2.11.2. qPCR Analysis
Real-time PCR (qPCR) cDNA was used to quantify the expression of CTL-3, CTL-5, MNK, SR, ALF, β-actin and GILT genes. The gene name and reference are indicated in
Table 1 and are known to be significantly up-regulated by
V. parahaemolyticus infection. The qPCR was carried out using an Eva Green Bio-Rad®. The amplifications [
16] were performed in a reaction volume of 15 μL containing 7.5 μL of master PCR mixture, 10 μM of each specific primer (Forward/Reverse), and 5 μL of cDNA dilution. The following steps are included in the amplification program: 95 °C for 5 min followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 20 s, and 72 °C for 25 s.
2.12. Statistical Analysis
Effects of the treatments related to physicochemical and biological parameters were analyzed using a multifactor ANOVA to evaluate the parameters of water quality, growth, and survival of the shrimp. When a significant difference was found, these differences were evaluated with a comparison of means using the Tukey test, with a significance of p ≤ 0.05. Gene expression results were analyzed directly using a one-way ANOVA. For these analyses, the SPSS program was used.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles
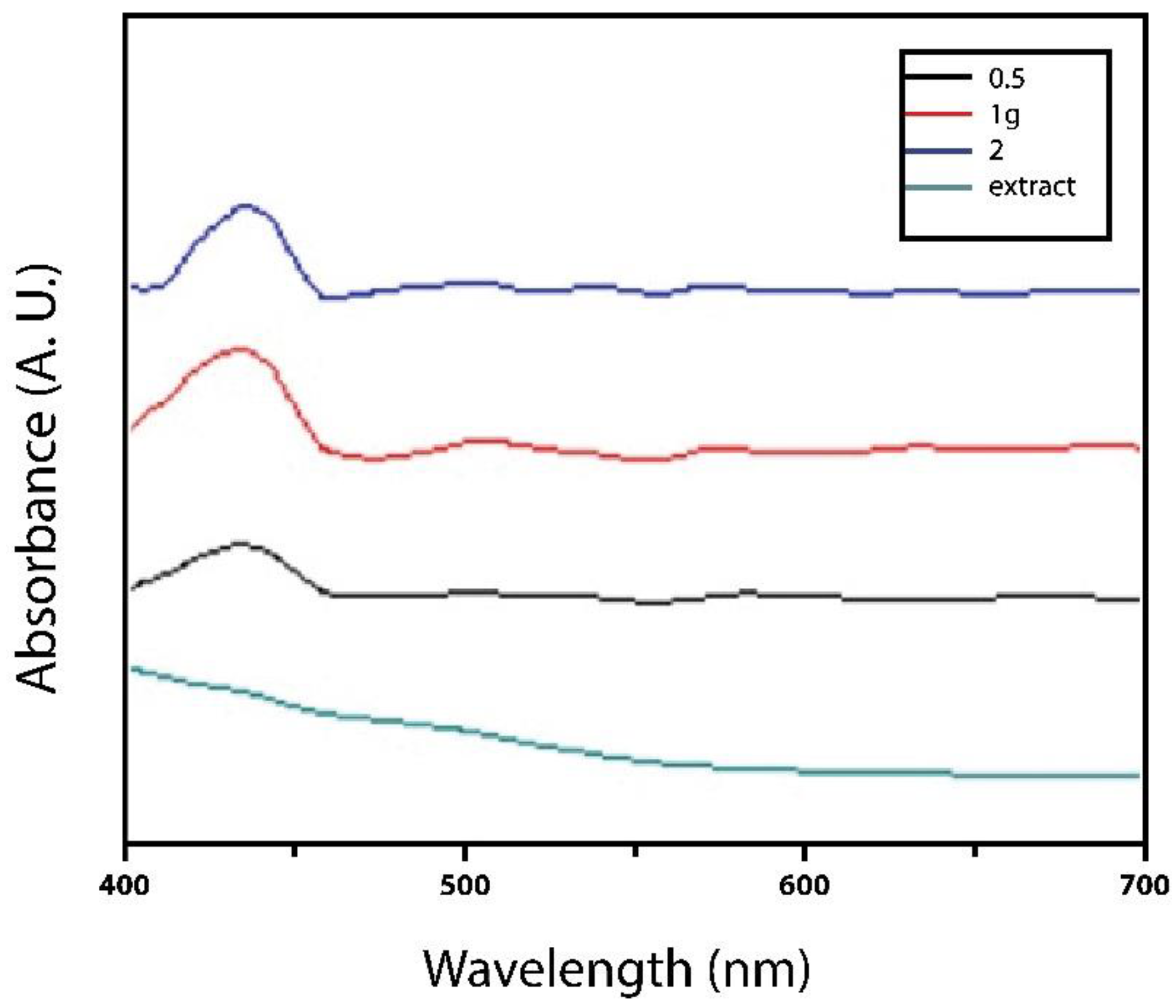
The UV-Vis spectra of AgNPs were measured at different concentrations 0.5-2 g/mL of extract as the reducing agent, as shown in
Figure 1. All the samples exhibited the peak for AgNPs at 330-450 nm, showing their surface plasmon resonance bands, characteristic of silver nanoparticles [
5] obtained nanoparticles of a similar size and shape since the metabolites present in the plant promote the synthesis of functional nanoparticles. These HR-TEM results indicate that both treatments worked as expected, showing that
L. tridentata serves as a reducing and stabilizing agent in the synthesis of Ag nanoparticles.
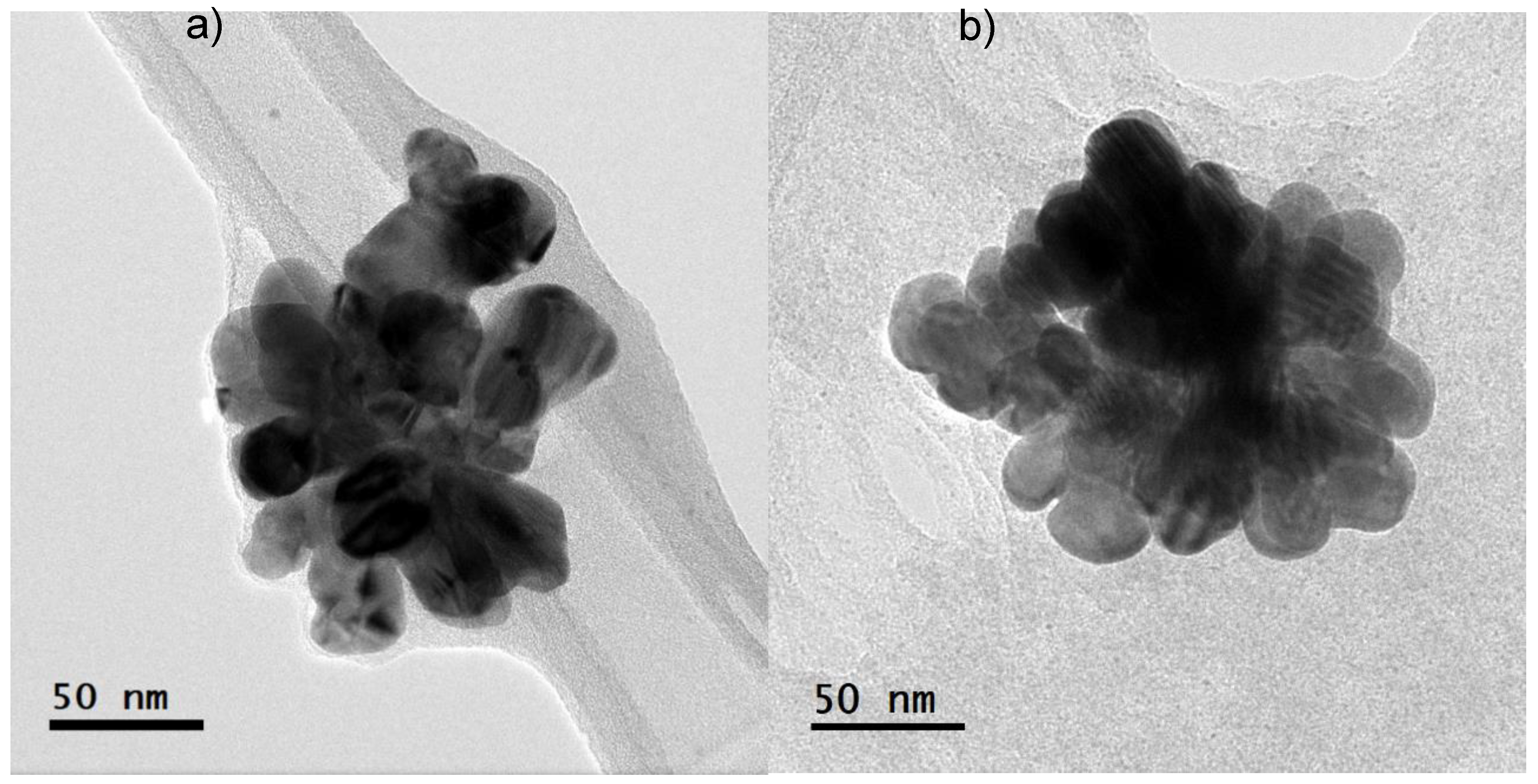
High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) analysis showed that the diameter of the nanoparticles ranged between 20-40 nm, with an almost spherical shape, apparently agglomerated (
Figure 2). The synthesized nanoparticles with the highest concentration of silver were agglomerated, maintaining the size. Several variables, such as particle size, surface charge and physicochemical features of water, are related to its effects and transport of the AgNPs and therefore, its bioavailability and stability [
17]. According to [
18], the changes in shape and agglomeration in nanoparticles are dependent on the surface charge, which determines their antibacterial capacity, and their resulting cytotoxicity. These nanoparticles have a diameter between 20-40 nm approximately and were suspended in a biological extract derived from
L. tridentata leaves. These characteristics may have contributed to the nanoparticle’s interaction with the cell walls of
V.
parahaemolyticus allowing their entry into the cytoplasm, which could result in cell death. Moreover, some studies have proposed that antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles can be incited by the adsorption of smaller nanoparticles (< 50 nm) on the cell surface, where ions would be released, and would interact with different types of macromolecules and functional groups present in the cells [
19]. The results obtained are similar with those described in the literature, however, using silver nanoparticles synthetized with
L. tridentata in shrimp farming had not been described up to now, promoting the synthesis of nanoparticles at a lower cost than traditional synthesis, with good antimicrobial capacity and capable of being incorporated to shrimp diets without altering their stability.
3.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
The concentration of AgNPs that shows a difference in absorbance (
Table 2) was established as the MIC. Nanoparticles were able to inhibit the growth of VpAHPND-E9 with an MIC of 21.5 μg/mL Ag (0.01 M), while for the higher concentration of nanoparticles (AgNPs 0.1 M), the minimum dose was 73.8 µg/mL Ag, likely due to its possible agglomeration at high concentrations. In contrast to previous studies, we worked with concentrations of 21.5 μg/mL and 73.8 μg/mL during a period of 35 days with lower mortality than the control group.
V. parahaemolyticus was selected for use in this study because it has severely impacted the shrimp industry [
20] and can coexist in crustaceans colonizing the digestive tract, gills and cuticle, producing high mortalities within the first days of shrimp culture [
21]. It was found that nanoparticles with low concentrations can have a greater synergistic effect as they are coated with metabolites found in plant extracts, in agreement with what was mentioned by other authors, that leaves and branches of the plant should be used when making an extract to enhance its antibacterial effect. [
22] synthesized silver nanoparticles with
L. tridentata and found that the MIC corresponded to 50 mg/mL of nanoparticles to completely inhibit
Clavibacter michiganensis. The antimicrobial effect against Gram-positive bacteria is associated with the compounds found in
L. tridentata [
23]. However, it is known that the effect against Gram-negative bacteria may be less effective. This suggests that its use at low concentrations can inhibit bacteria without interfering with bacterial resistance. It is worth mentioning that, in the extracts in dilution 5 and 6, zero growth was observed (Figure DO). However, at the highest concentration there was constant atypical growth similar to that of the control group, even though it was done several times.
3.3. Water Quality
Dissolved oxygen (DO), temperature (
oC), and pH concentrations were similar between replicates and within appropriate ranges for shrimp farming (
Table 3). All conditions remained homogeneous throughout the first 30 days of the bioassay, except for the ammonium and nitrites (
Figure 3), which are more toxic to shrimp.
Water quality plays an important role in the stability of nanoparticles as well as environmental factors to which they are exposed [
24]. In aquatic environments its efficiency is determined by the phenomenon of aggregation, related to the collision of nanoparticles due to the difference in charges, and is closely related to the size, shape, and composition. It is well known that the higher the salinity, the greater the stability of nanoparticles [
25]. No evidence of any particle agglomeration or clinical signs associated with the release of silver ions was found in experimental units.
3.4. Effects of AgNPs on the Survival of Juvenile White Shrimps
No clinical signs associated with bioaccumulation by nanoparticles were found. In contrast, [
26] observed that low concentrations of nanoparticles induce histological damage in a period of 10 days, the mortality was 23% and 20% for the 5.3 and 7.9 μg of Ag/μL treatments, respectively.
Survival was similar to control (CN) and the AgNPs treatments, except for treatment two (commercial feed +
L. tridentata extract 20%). The growth of the organisms showed no significant differences between weight gain and final weight (
Table 4). There are studies that have evaluated survival and toxicological effects of nanomaterials in aquaculture, particularly metal and metal-oxide NPs [
27]. Author [
2] used chitosan nanoparticles to reinforce the immunity of
L. vannamei against
V. harvey, showing an increase in the specific growth rate, daily growth coefficient, and survival rate (
p < 0.05). [
28] had a higher survival than the negative control by using nanoparticle-based microalgae in shrimp feed. In this study, the addition of AgNPs in the diet improved non-specific immunity which led to improved survival of individuals exposed to
V. parahaemolyticus after AgNPs applications, in contrast to untreated animals that presented higher mortalities.
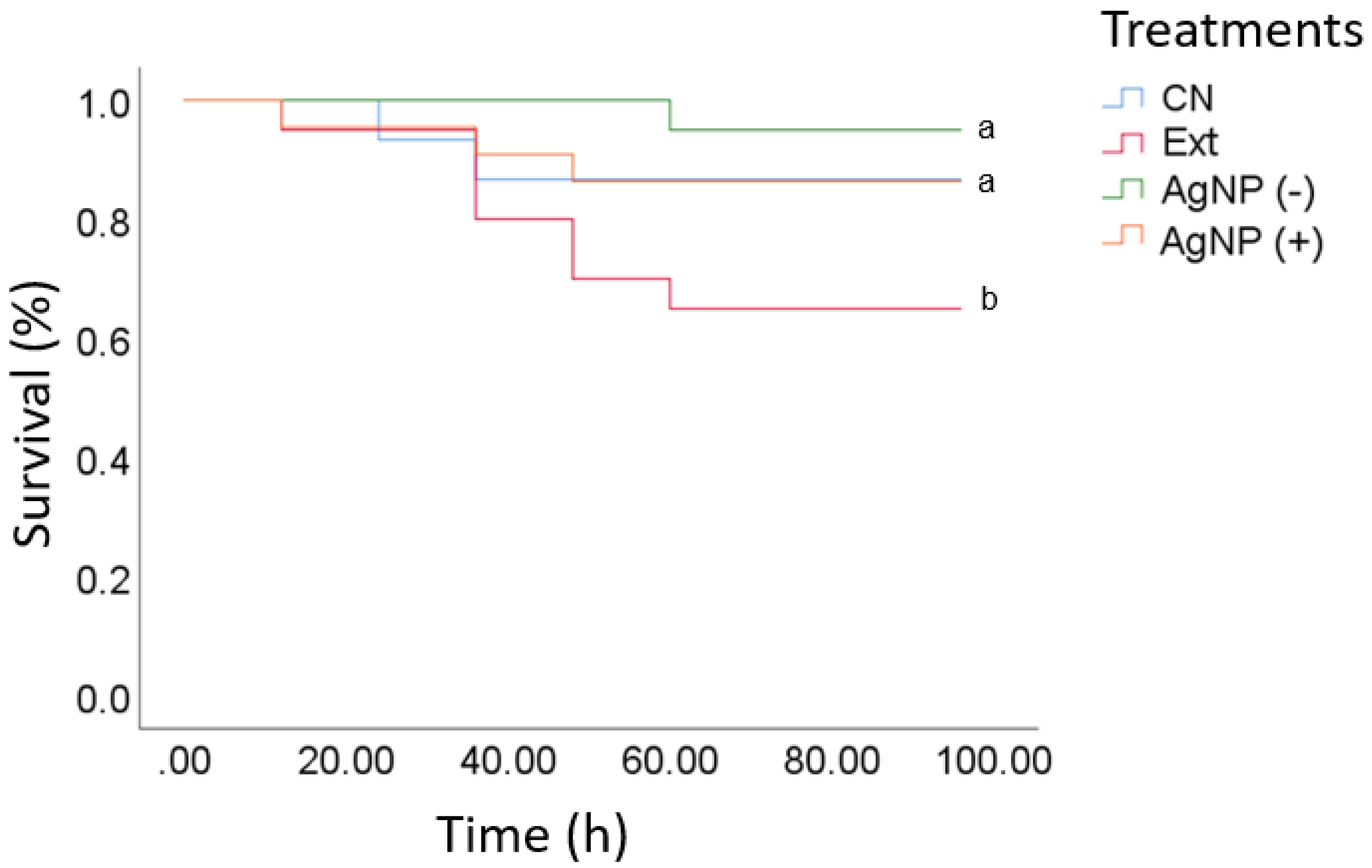
3.5. Treatment with AgNPs after VpAHPND-E9 Infection
A challenge bioassay was conducted on shrimp that had been previously infected, recording mortality every 4 h after the viral infection (hpi) until the last individual died of the positive control (CN), which was reached at 96 hpi. At 20 hpi, the shrimp did not display discomfort signs, but mortality started at 30 h of viral infection. Survival rates (95% and 85%) were not significantly different between the low and high AgNPs diet groups and the positive control (commercial diet) (
Figure 4). Organisms infected with VpAHPND-E9 showed survival >80% for the experimental treatment with
L.
tridentata extract. In AHPND-infected shrimp, mortality may reach 100% the first days of cultivation [
29]. Recently plant-derived compounds and functional feeds against AHPND have been published, but shrimp mortality was only delayed in time [
30,
31]. Therefore, it is not clear how shrimp will respond during the critical hours (hpi: 80–100 h). In this study, the application of AgNPs resulted in over 20% mortality during the first 100 hpi, a critical time for shrimp mortality in AHPND, compared to 5% in the positive control group. The most important finding, however, was that the survival curve reached a plateau after 60 hours, indicating the end of shrimp mortality. However, the persistence of these effects was not confirmed (
Figure 4).
3.6. Immune System-Related Genes Expression by qRT-PCR Analysis
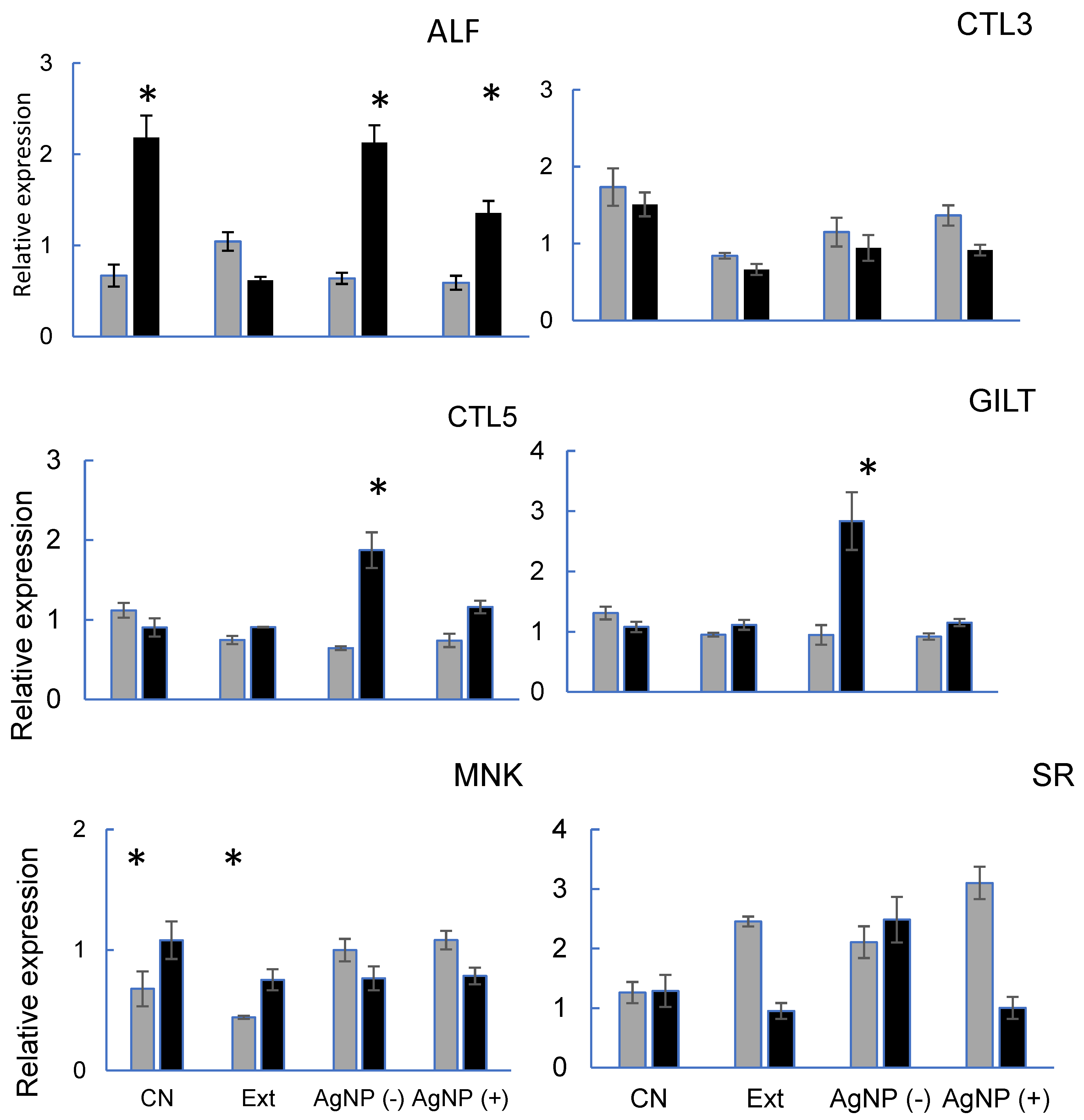
All the genes evaluated are related to the immune response against VpAHPND-E9 and different expressions were obtained according to the gene studied (
Figure 5). For ALF, treatment 3 (AgNPs-) obtained similar results to the control treatment (CN), on the other hand, treatment two (Ext) had a lower expression. Regarding the CTL-3, treatments with experimental diets showed lower expression than control, although following the same trend. Lectins play essential roles in many biological processes, such as molecular effectors, cell signaling, and pathogen recognition [
32]. In this study, feed-AgNPs did not affect the expression of CTL-3 before VpAHPND infection. In shrimp fed with daily AgNPs, the CTL-5 gene was up-regulated after infection. This is probably because that lectins have phagocytic capacity. ([
33] for the MNK there is no experimental treatment that obtains similar results to the control group. For CTL-5, treatment 3 (AgNPs -) is observed with greater expression when it has been infected with respect to the other treatments. For SR, basal and post-infection expression were higher in treatment 3 (AgNPs -). However, in treatments 2 (Ext) and 4 (AgNPs +), post-infection expression decreased significantly.
Throughout the bioassay, the addition of nanoparticles to the feed did not interfere with shrimp survival, which was greater than in the control, supporting the findings of [
34] that the use of nanoparticles in feed increases survival without causing bioaccumulation of silver in organisms. [
35] showed that the immune response genes expressed in
P. vannamei have preferences against VpAHPND. The results of this study show that some genes associated with VpAHPND-E9 have lower basal expression, while others, upon infection, exhibit significantly higher expression compared to the control, promoting a positive immune response in at least 4 of the 6 genes studied.
Authors [
35] show that the expression of these genes reveals forms of immune response and structural alteration against
V. parahaemolyticus, demonstrating that the ability of
P. vannamei to significantly reduce bacterial elimination is reduced when the transcriptional response is not adequate, hence, addition of silver nanoparticles in commercial feed could be used in non-continuous periods to promote immunostimulant without causing bioaccumulation problems and avoid gene overexpression in
P. vannamei shrimp. The optimal efficiency of AgNPs against
Vibrio parahaemolyticus can be achieved by optimizing the dose and searching for organic vehicle options for aquaculture pond application.
4. Conclusions
The green synthesis of spherical AgNPs nanoparticles with L. tridentata, may be effective as a prophylactic method in shrimp aquaculture. The inclusion of AgNPs in food to enhance survival and prophylaxis against bacteria in infectious challenges did not show any efficacy when compared to the negative control. At low concentrations, Ag-NPs, demonstrated minimal efficacy in preventing VpAHPND. In order to achieve optimal effectiveness, the concentration must be at least 21.5 µg/mL. This study suggests that to reduce the negative effects of VpAHPND, treatment with commercial feed mixed with Larrea tridentata extracts was not practical in Penaeus vannamei shrimp culture. Silver nanoparticles promote immune stimulation in shrimp genes (CTL-5, MNK, SR and GILT), when incorporated into diets or used as an alternative treatment for disease prevention. The frequency of administration to Penaues vannamei shrimp must be in non-continuous periods to avoid gene overexpression problems. More complex in vivo studies are needed to imply this effectively, in order to determine the best efficiency of AgNPs.
Author Contributions
GLV: Formal analysis, Investigation. WVQ: Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Funding acquisition Writing—Original Draft. PAR and MMM: Investigation, Visualization, Project administration and edition of the writing. CASR, ENP and GLC: Supervision, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—Review & Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The shrimp for all the experimental work were used following the protocols of the Official Mexican Standard (NOM-062-ZOO-1999).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by a grant from the Instituto Politécnico Nacional (PAR: SIP20210242, SIP20220606 and MMM: SIP20210237, SIP20220601). GLV had the fellowship grant of CONACYT (1032851) and BEIFI-IPN (SIP20201514). The authors appreciate financial support from the Comisión de Operación y Fomento de Actividades Académicas (COFAA-IPN; Commission for the Advancement of Academic Activities) and Estímulo al Desempeño de los Investigadores (EDI-IPN; Performance Incentives) of the Instituto Politécnico Nacional (IPN; National Polytechnic Institute). Thanks to Language Editing Services by language help. Thanks to special contribution by the realization of the research of Esparza-Leal H.M.†.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- FAO. FAO Yearbook-Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics Summary Tables. Rome, Italy. 2016 Pp. 108.
- Bhoopathy, S.; Inbakandan, D.; Rajendran, T.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Prabha S, B.; Reddy, B. A.; Dharani, G. Dietary supplementation of curcumin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles stimulates immune response in the white leg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei challenged with Vibrio harveyi. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2021, 117, 188–191. [CrossRef]
- Itza-Ortiz M.; Carrera Chavez J. M.; Aguilar Urquizo E.; Parra Suescun J. E. Actividad fitobiótica de Larrea tridentate, origanum vulgare y plectranthus amboinicus en bacterias gram positivas y gram negativas. Interciencia: Revista de ciencia y tecnología de América, 2019, 44(5), 298-302.
- Promthale, P.; Pongtippatee, P.; Withyachumnarnkul, B.; Wongprasert, K. Bioflocs substituted fishmeal feed stimulates immune response and protects shrimp from Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Fish and Shellfish Immunology 2019, 93(6): 1067–1075. [CrossRef]
- Córdova-Cisneros, K.; Sáenz-Galindo, A.; Ascacio-Valdés, J.; Narro-Cespedes, R. & Castañeda-Facio, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the aqueous extract of Larrea tridentata and Eucalyptus. Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química 2020, 20(1), 13-24. [CrossRef]
- Villicana, C.; Amarillas L.; Soto, L.; Gomez, B.; Lizarraga, M. L.; & Leon, J. Occurrence and Abundance of Pathogenic Vibrio Species in Raw Oysters at Retail Seafood Markets in Northwestern Mexico. Journal of Food Protection 2019, 82(12), 2094–2099. [CrossRef]
- Allafchian, A.; Jalali, S.A.H.; Bahramian, H.; Ahmadvand, H. Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity of NiFe2O4/PAMA/Ag–TiO2 nanocomposite. J. Magn. Mater. 2016, 404, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, M. M.; Mirtajani, S.; Karimzadeh. B.; Mirtajani, K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Trapa natans extract and their anticancer activity against A431 human skin cancer cells. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2018, 47, 375-379. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D. and Gupta, R. Nanotechnology and potential of microorganisms. Critical Reviews Biotechnology 2005, 25, 199-204. [CrossRef]
- Armenta-López, A. R.; Nava-Pérez, E.; Lugo-García, G. A.; Sánchez-Soto, B. H.; Romero-Felix, C. S.; & Gaxiola-Félix, J. Extractos vegetales para el manejo del gorgojo del frijol. Southwestern Entomologist 2023, 47(4), 903-914. [CrossRef]
- Girón-Vázquez, N. G.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, C. M.; Soto-Robles, C. A.; Nava, O.; Lugo-Medina, E.; Castrejón-Sánchez, V. H.; Luque, P. A. Study of the effect of Persea americana seed in the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial properties. Results in Physics 2019, 13, 102142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; & Parsons, T.R. A Practical Hand Book of Seawater Analysis. Fisheries Research Board of Canada Bulletin 1972, 157, 2nd Edition, 310 p.
- APHA (American Public Health Association). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 18th edition. American Public Health Association, Washington, 1998. DC, USA. [CrossRef]
- Gámez, E. P. & De la Lanza, E. G. Análisis del estado de la camaronicultura en México, hasta el año de 1991. 1era. Edición. México, D.F. 1992, 48 pp.
- Livak, K.J. and Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method, Methods 2001, 25, 402–408.
- Tello-Olea, M., Rosales-Mendoza, S., Campa-Córdova, A. I., Palestino, G., Luna-González, A., Reyes-Becerril, M., Velazquez, E., Hernandez-Adame, L., & Angulo, C.. Gold nanoparticles (AuNP) exert immunostimulatory and protective effects in shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2019, 84, 756–767. [CrossRef]
- Grün, A.-L., Manz, W., Kohl, Y. L., Meier, F., Straskraba, S., Jost, C., Drexel, R., & Emmerling, C. Impact of silver nanoparticles (AgNP) on soil microbial community depending on functionalization, concentration, exposure time, and soil texture. Environ Sci Eur 2019, 31-15. [CrossRef]
- Mulenos, M. R.; Lujan, H.; Pitts, L. R.; & Sayes, C. M. Silver Nanoparticles Agglomerate Intracellularly Depending on the Stabilizing Agent: Implications for Nanomedicine Efficacy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10(10), 1953. [CrossRef]
- Gomathi M, Rajkumar PV, Prakasam A. Study of dislocation density (defects such as Ag vacancies and interstitials) of silver nanoparticles, green-synthesized using Barleria cristata leaf extract and the impact of defects on the antibacterial activity. Results Phys. 2018, 10:858–64.
- Comisión Nacional de Acuacultura y Pesca. CONAPESCA (2019). Available online: https://www.gob.mx/conapesca/articulos/produjo-mexico-47-mil-664-toneladas-de-camaron-en-la-temporada-de-captura-2019-2020-agricultura.
- Morales, M.S. Enfermedades bacterianas. En: Morales, V., & Cuéllar, J., Guía técnica - patología e inmunología de camarones penaeidos. Programa CYTED Red II-D Vannamei, Panamá, Rep. de Panamá. 2008. 117-134.
- Vargas, G. Biosíntesis y caracterización de nanopartículas de plata obtenidas mediante extractos de Larrea tridentata y su efecto potencial como antagonistas de fitopatógenos y promotor de crecimiento en plantas. [Tesis para obtener el título de INGENIERO AGRÍCOLA Y AMBIENTAL, Universidad Autonoma Agraria Antonio Narro] 2018.
- Saldívar, R.H. Estado Actual del Conocimiento sobre las Propiedades Biocidas de la Gobernadora [Larrea tridentata (D.C.) Coville]. Revista Mexicana de Fitopatología 2003, 21(2):214-222.
- Virkutyte, J.; & Varma, R. S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles: Biodegradable polymers and enzymes in stabilization and surface functionalization. Chemical Science 2011, 2(5), 837-846. [CrossRef]
- Salari J.; Hamid K.; Mohammad R.; YuIl J.; Lee, J.; Johari, Seyed A. Bioaccumulation of silver nanoparticles in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Influence of concentration and salinity. Aquatic toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands). 2013. 398-406. [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Sánchez, MC.; Abad-Rosales, S.; Lozano-Olvera, R. Silver nanoparticles induce histopathological alterations in juvenile Penaeus vannamei. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020, 28, 8224–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, T.; Tyler, C.; Galloway, T. Impacts of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on marine organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 257e271. [CrossRef]
- Sharawy, Z.; Mohamed, A.; Labena, A.; Ahmed, S.; Abdallah, T.; Eman, M. Effects of dietary Arthrospira platensis nanoparticles on growth performance, feed utilization, and growth-related gene expression of Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, Aquaculture 2022, 551, 737905. [CrossRef]
- Aranguren-Caro F.L.; A., Mai, H. N., Noble, B., & Dhar, A. K. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease ( VP AHPND ), a chronic disease in shrimp ( Penaeus vannamei ) population raised in Latin America. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2020. 174, 107424. [CrossRef]
- Quiroz-Guzmán E., Cabrera-, G. M., Mendoza-, F., Encinas-, C. T., Gómez-, B., Peña-, G. A., Sánchez-, A., & Barajas-, D. Effect of functional diets on intestinal microbiota and resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus causing acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) of Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). J Appl Microbiol. 2022, 2649–2660. [CrossRef]
- Hoa TTT, Tran Thi Tuyet, et al. Growth Performance and Disease Resistance against Vibrio parahaemolyticus of Whiteleg Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Fed Essential Oil Blend (Phyto AquaBiotic). Animals, 2023, vol. 13, no 21, p. 3320. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.H.; Wan, D.H.; Gu, Z.H.; Deng, X.X.; Weng, S.P.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J.G. Litopenaeus vannamei tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) responds to Vibrio alginolyticus and white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) infection and activates antimicrobial peptide genes. Dev Comp Immunol. 2011, 35:105-114.
- Chen D.D.; Meng X.L.; Xu J.P.; Yu J.Y.; Meng M.X.; Wanga J. PcLT a novel C-type lectin from Procambarus clarkii, is involved in the innate defense against Vibrio alginolyticus and WSSV. Developmental and Comparative Immunology 2013, 39:255-264.
- Juarez-Moreno, K.; Mejía-Ruiz, C.H.; Díaz, F.; Reyna-Verdugo, H.; Denisse, A.; Vazquez- Felix, E.F.; Bogdanchikova, N. Effect of silver nanoparticles on the metabolic rate, hematological response, and survival of juvenile white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Chemosphere 2017, 169: 716–724. [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Babu, V. S.; Wan, Q.; Zhou, M.; Liang, R.; Muhammad, A.; Lin, L. Transcriptome analysis of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei ) challenged by Vibrio parahaemolyticus reveals unique immune-related genes. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2018, 77: 164–174.Res. 00, 1–9. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).