Submitted:
26 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
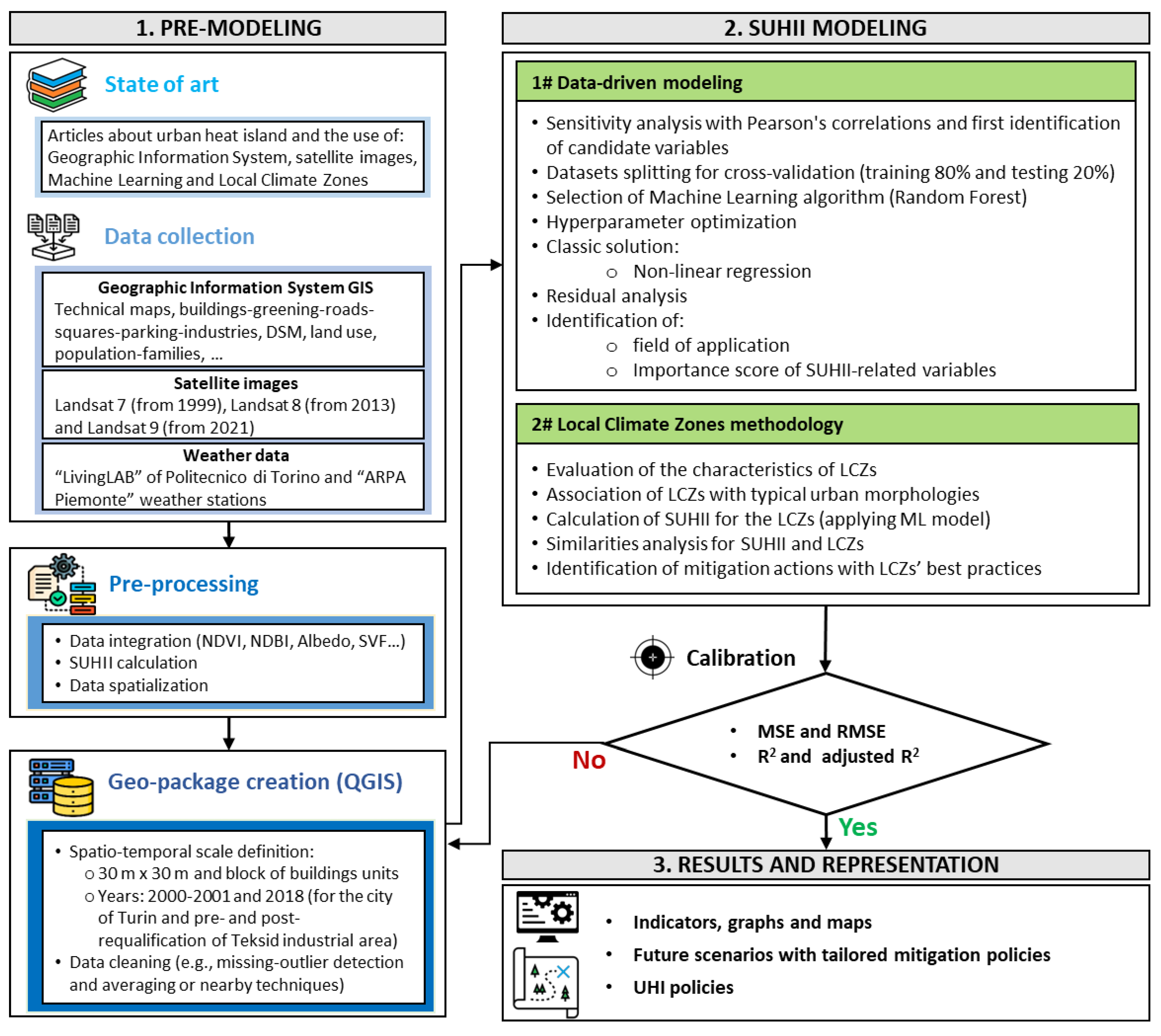
2. Material and Methods
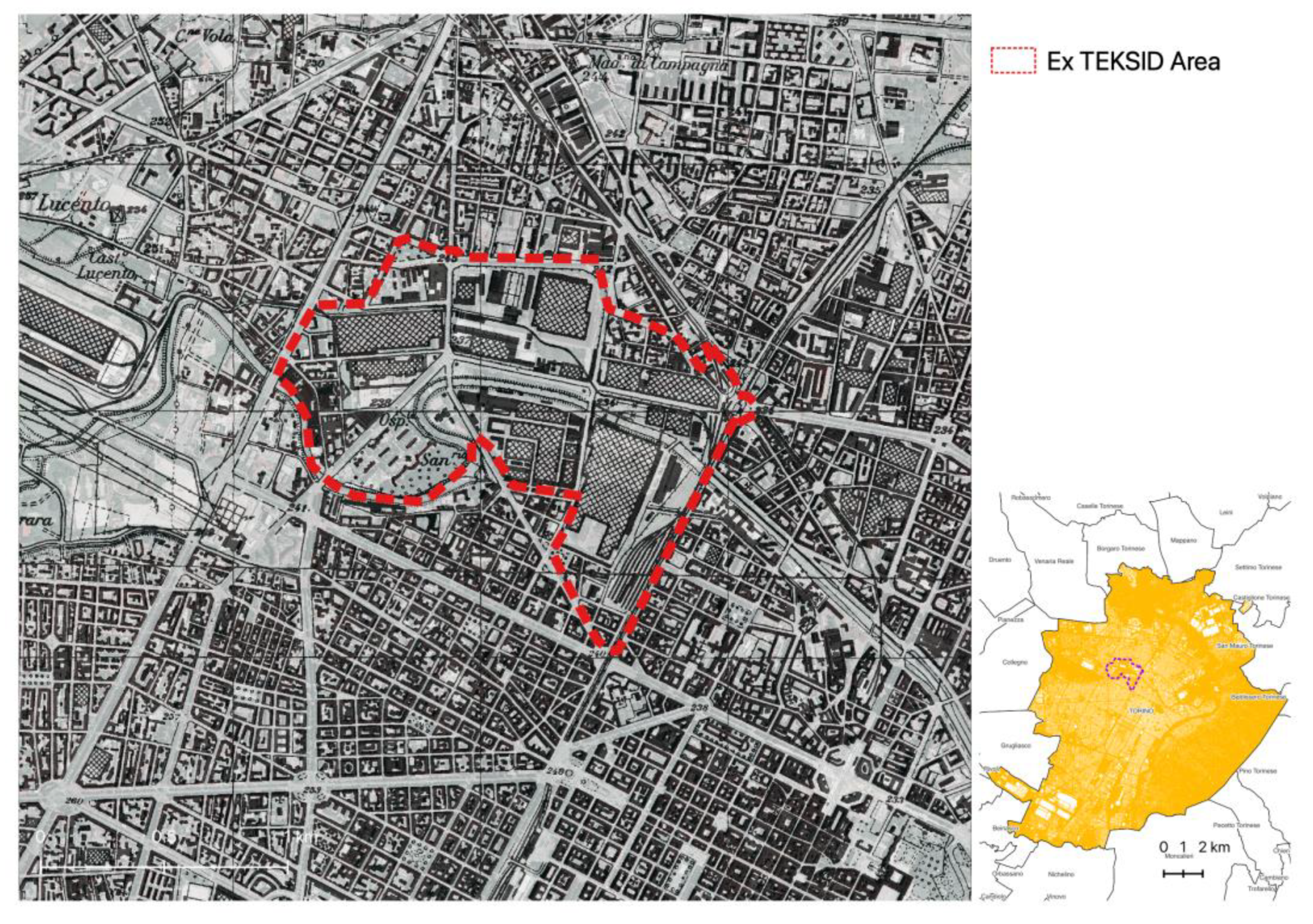
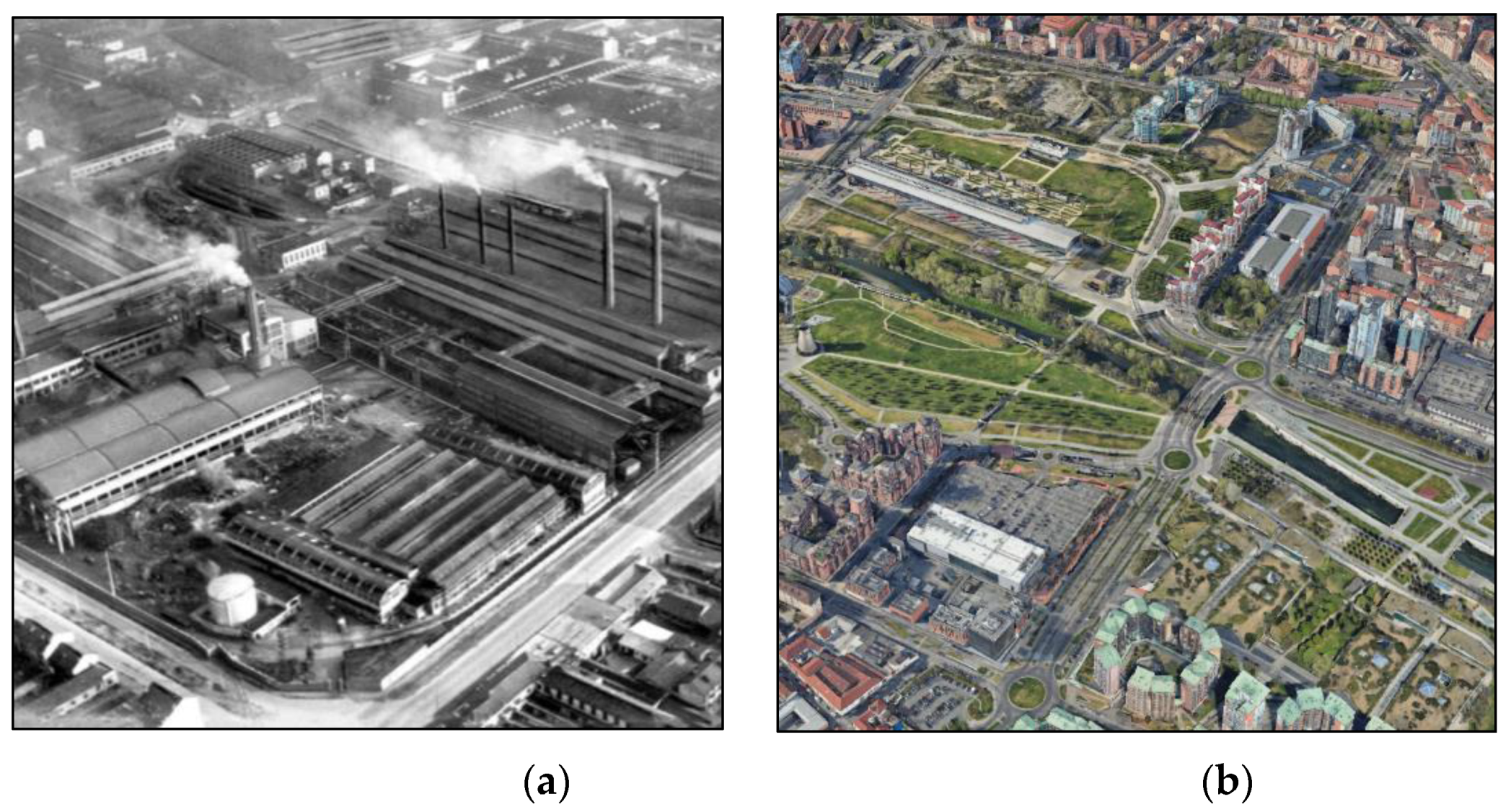
2.1. Investigation Area
2.2. Data Collection and Pre-Processing
- -
- buildings, rivers, parks, greenings, public spaces, squares, parking areas, roads, … : BDTRE (Banca Dati Territoriale di Riferimento degli Enti, in Italian) 2018 - https://www.geoportale.piemonte.it/geonetwork/srv/ita/catalog.search#/search?any=BDTRE and the municipal technical map of Torino CTC 1999 (Carta Tecnica Comunale, in Italian) http://geoportale.comune.torino.it/geocatalogocoto/?sezione=catalogo ;
- -
- land use: Corine land cover 2000 and 2018: https://land.copernicus.eu/en/products/corine-land-cover/cha-2000-2006; https://land.copernicus.eu/en/products/corine-land-cover/clc2018;
- -
- population and families in 2001, 2011 and 2021 from the National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT in Italian): https://www.istat.it/notizia/aggiornamento-basi-territoriali-2021-2/ ;
- -
- climate data: weather station of Politecnico di Torino collected by the LivingLAB: https://smartgreenbuilding.polito.it/; other weather stations in Turin: https://www.arpa.piemonte.it/rischi_naturali/snippets_arpa_graphs/map_meteoweb/?rete=stazione_meteorologica.
2.3. Candidate Variables
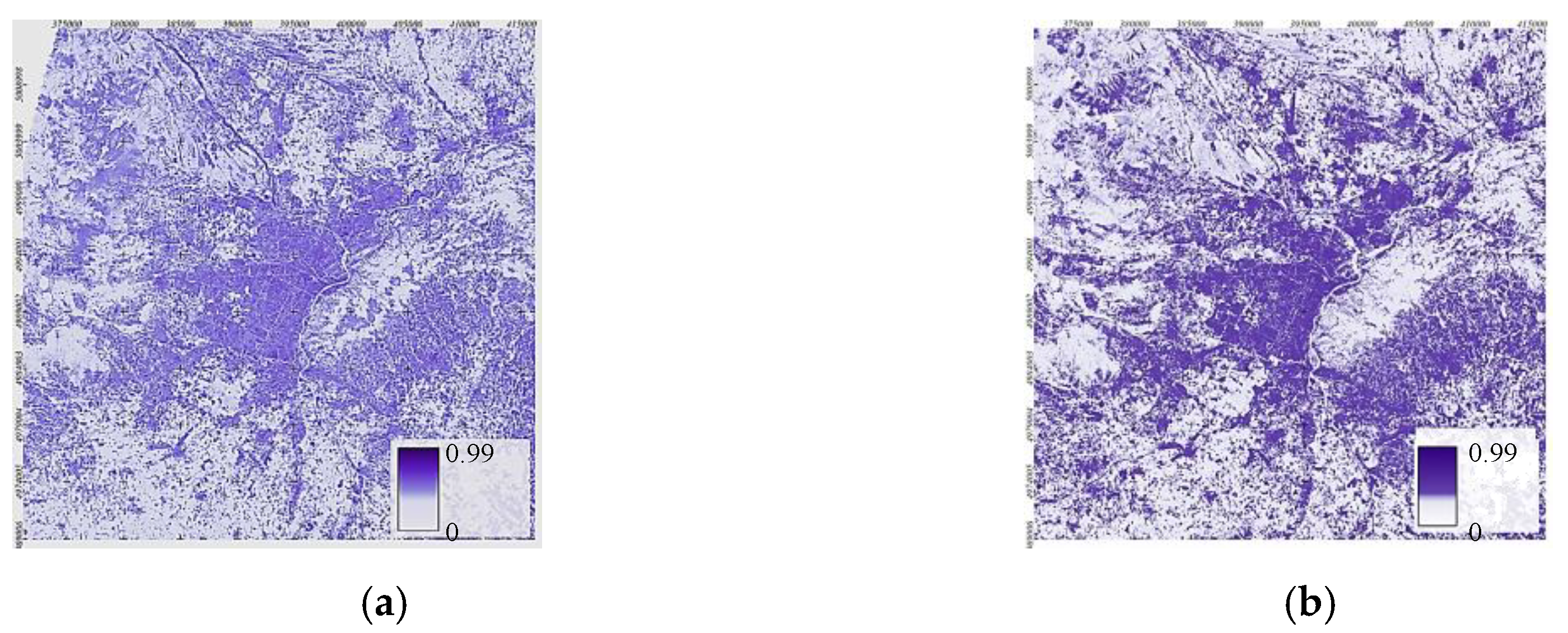
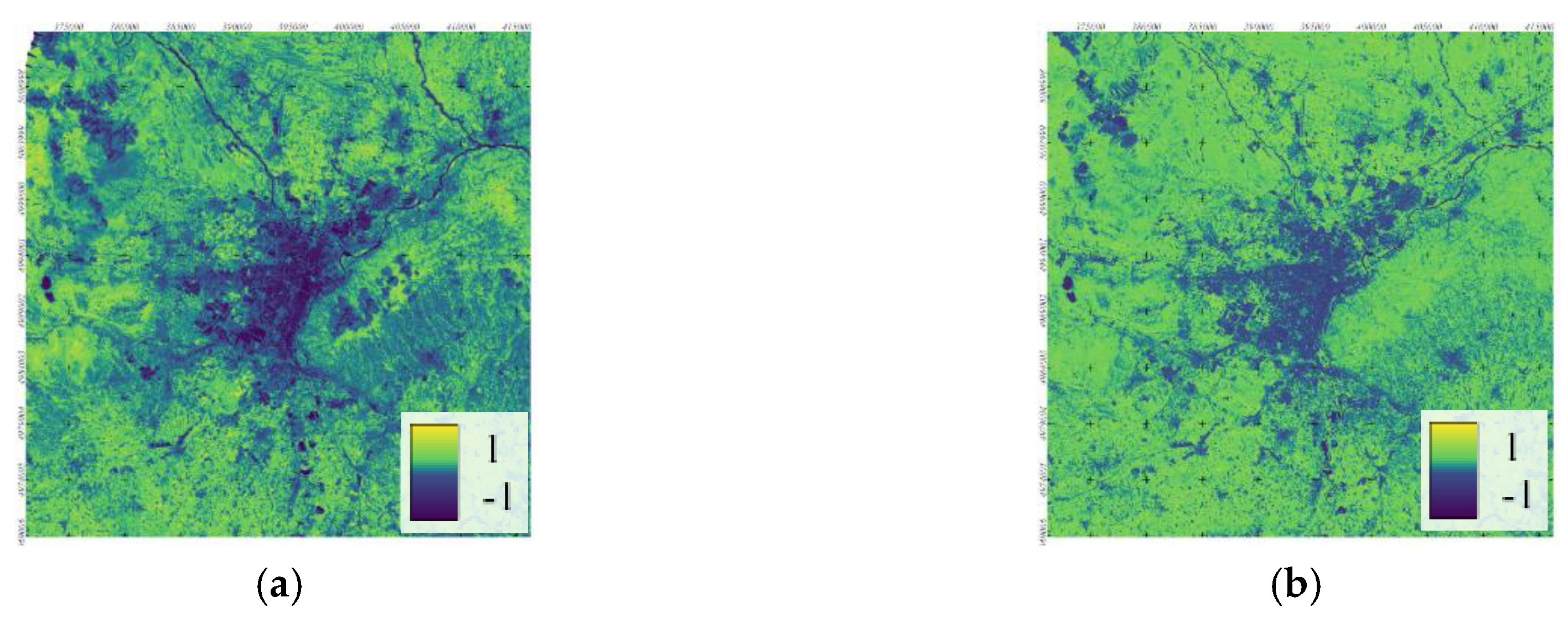
2.4. Evaluation of the Surface Urban Heat Island Intensity (SUHII)
2.5. Correlation Analysis with SUHII
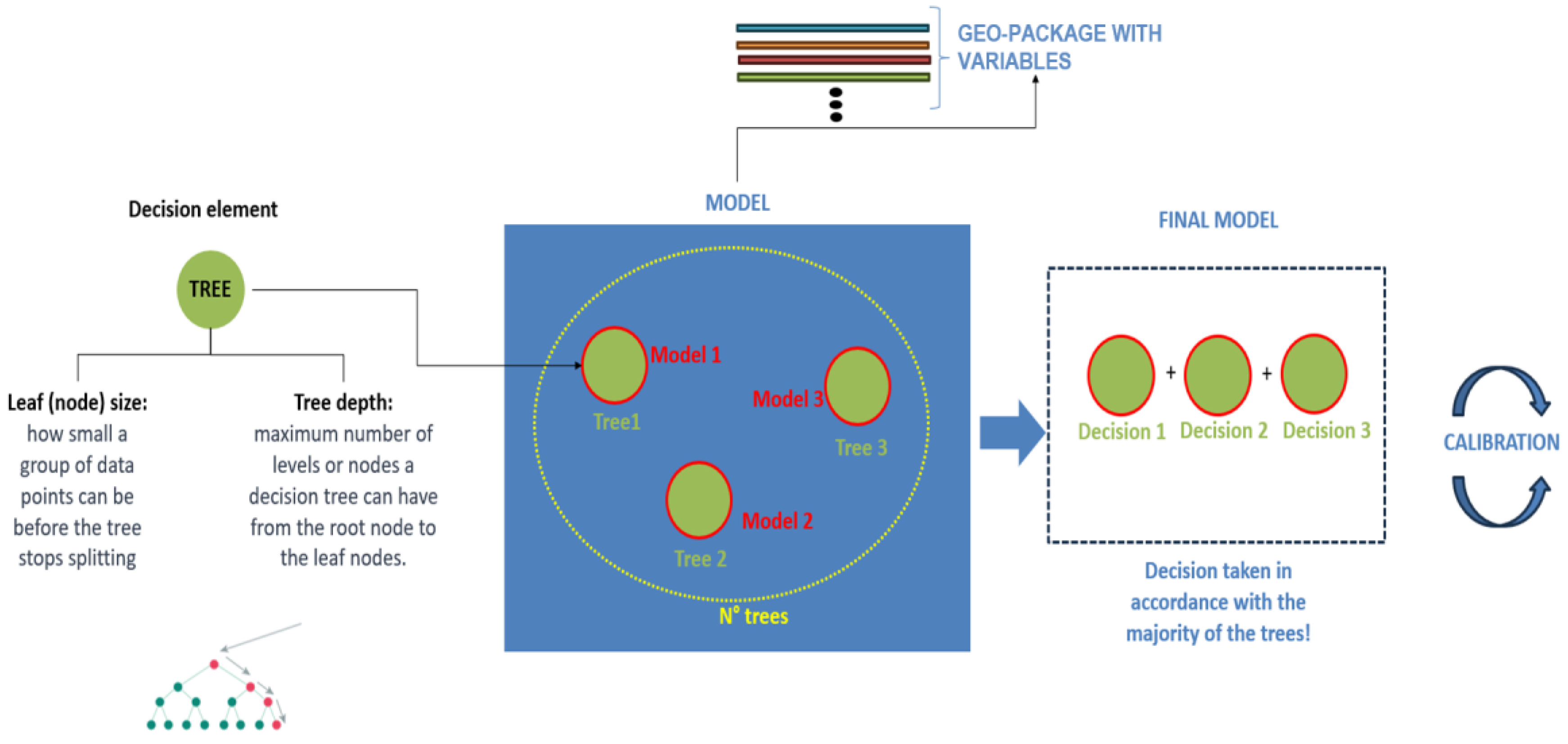
2.6. Machine Learning Modeling
- -
- the leaf (node) size that is defined by the minimum number of variables, when the tree stops splitting;
- -
- the tree depth that is the number of levels a decision tree can have.
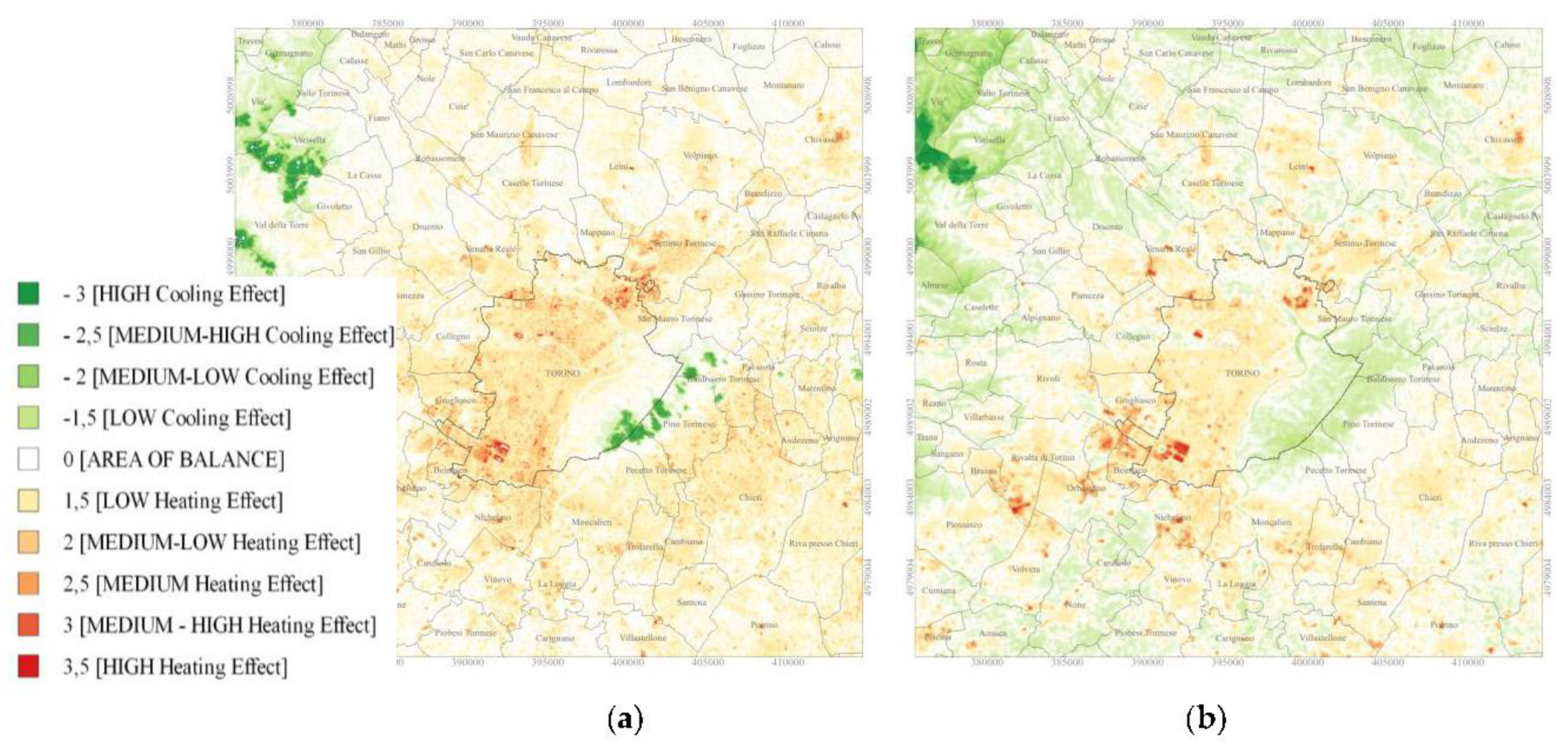
2.7. The Urban Heat Island Effects of Local Climate Zones and Settlement Morphologies
- -
- surface admittance, the surface's capacity to exchange heat that is influenced by material type, orientation, soil moisture, and wind velocity,
- -
- radiative properties, indicated by surface albedo, describe the ratio of reflected to incident solar radiation, which depends on surface colour, roughness, and moisture content and
- -
- metabolic properties, quantified as anthropogenic heat output, representing the annual average heat flux from human activities and fuel combustion.
3. Results
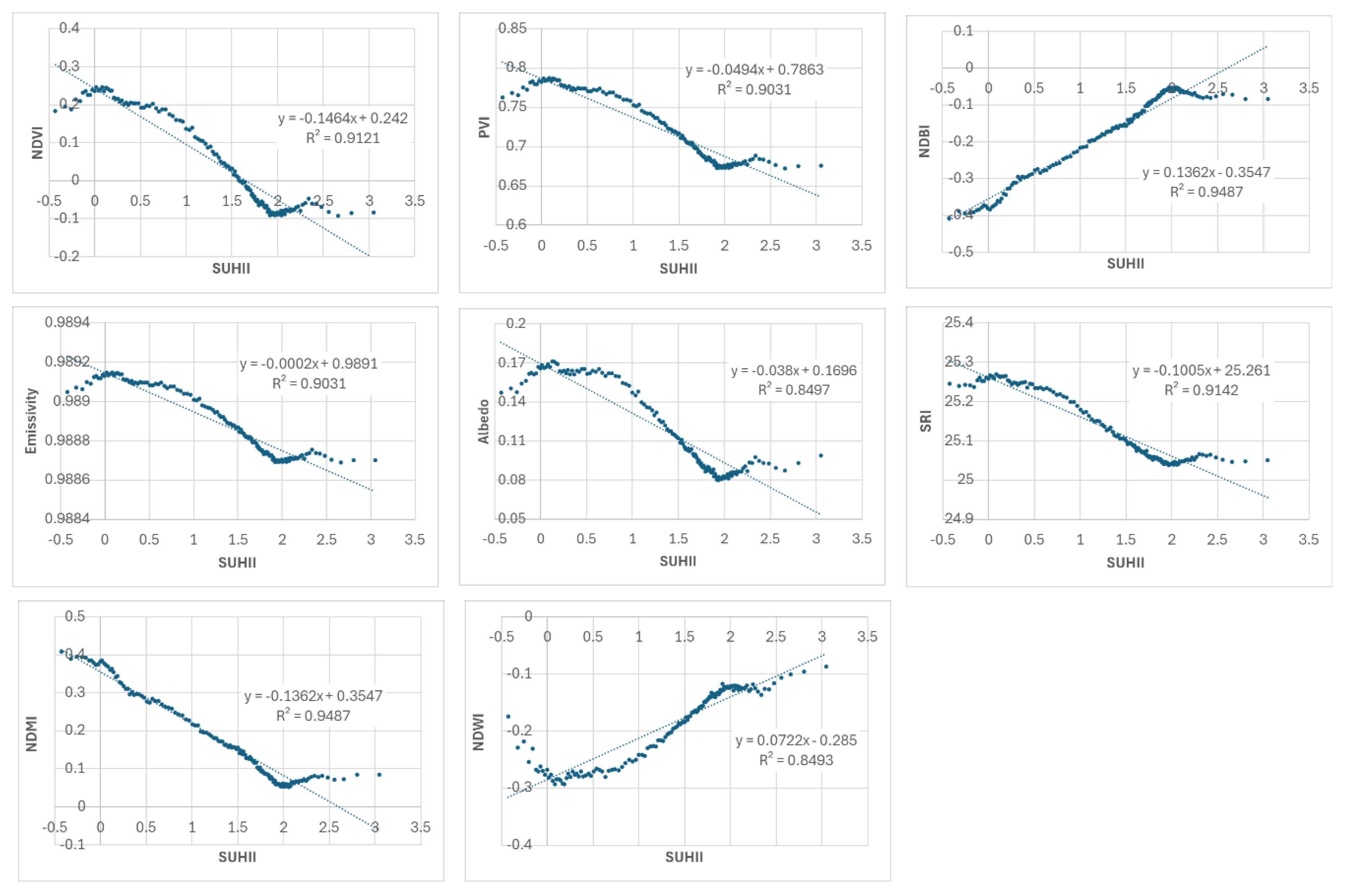
3.1. Linear Correlation Analysis between SUHII and Urban Variables
3.2. SUHII Modelling with Random Forest Algorithm
3.2. Assessing SUHII in the Ex-Industrial Area Teksid
3.3. The Evaluation of SUHII and Its Mitigation Interventions with Local Climate Zones
5. Conclusions
- A place-based approach that considers the so-called genius loci (spirit of the place) and therefore the multiple peculiarities of places in terms of geomorphology, climate, environment, social, economic, landscape, historical, architectural, and identity aspects, would allow containing or avoiding the construction of energy-intensive, polluting, and poorly resilient built environment, abandoning the universal style that continues to characterize and homogenize many cities despite very different contextual conditions.
- 2.
- An approach based on climate mainstreaming, i.e., the integration of climate issues within sectoral policies, would allow involving and activating multiple policy sectors. Not just construction, but also mobility, energy, air, water, environment, land use, biodiversity, etc.
- 3.
- An holistic approach aimed at creating a sense of co-responsibility for public and private actions, in which everyone, within their competencies and fields of action, is aware of acting in a transformative and global adaptation process to the changing climate conditions. Synergy, cooperation, and dissemination by the entire community (social organizations, businesses, various professions, citizens, schools, etc.) as an active part of the entire adaptation and mitigation process are necessary.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| BCR | Building Coverage Ratio |
| DTM | Digital Terrain Model |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| LCZ | Local Climate Zone |
| LST | Land Surface Temperature |
| m.i. | Settlements’ morphologies (“morfologie insediative”, in Italian) |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| NDBI | Normalized Difference Built-up Index |
| NDMI | Normalized Difference Moisture Index |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| NDWI | Normalized Difference Water Index |
| NIR | Near InfraRed |
| PVI | Proportion Vegetation Index |
| QGIS | Quantum GIS |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
| S/V | Surface-to-Volume ratio of buildings |
| SRI | Solar Reflectance Index |
| SUHII | Surface Urban Heat Island Intensity |
| SVF | Sky View Factor |
| SWIR | Short-wave Infrared |
| UHI | Urban Heat Island |
| UHII | Urban Heat Island Intensity |
| V | Buildings’ Volume |
| VIS | Visible |
Appendix A
| N° | Year | Place | Scale | Object | Factors | Methodology | Results | Keyword |
| 3 | 1833 | LDN | Urban | Analysis and characterization of the climate of London | Atmospheric conditions | Systematic observations of factors at regular intervals throughout the day to assess long-term climate trends in the city | Howard provided a comprehensive understanding of London's climate detailing factors | Investigation |
| 4 | 1976 | VAN | Urban | Causes of the UHI: canopy and boundary-layer | Surface properties, land use, and atmospheric conditions | Differentiate spatial heat island patterns within urban canopy and boundary layers | The study found a clear differentiation between canopy and boundary-layer UHI, influenced by factors | Investigation |
| 5 | 1982 | VAN | Urban | Investigating the physical processes driving UHI effect | Surface cover, Building materials, Anthropogenic heat, Weather conditions, Urban morphology | Comparing energy fluxes between urban and rural areas quantifies the UHI effect on temperature disparities. | Urban areas have higher night-time temperatures than rural areas, highlighting the importance of urban energy balance | Investigation |
| 9 | 2017 | BRA | Urban | Develop and validate a GIS-based extension model capable of accurately calculating UHII | Urban geometry and meteorological data | They collected urban geometry and meteorological data, applied a mathematical model to estimate UHII, validated it using empirical data in MATLAB | The outcome is a computational tool named THIS enabling simulation of hypothetical urban scenarios and assessing the impact of urban geometry | GIS |
| 10 | 2018 | SZ | Urban | Ventilation corridor planning to mitigate UHI | Built environment, wind patterns, land use distribution | GIS-based case study to analyse wind environments, mapping urban features, assessing wind patterns, and pinpointing suitable corridors for natural ventilation. | Recommendations for urban planning in Shenzhen to improve air quality and comfort through strategic development of natural ventilation corridors. | GIS |
| 11 | 2018 | HK | Local | The study mapped the spatial distribution of nocturnal UHIs using the Local Climate Zone framework | Climate data & Urban morphology data (total street length, pervious surface fraction, sky view factor) | GIS, GPS, and Landsat 8 images were used alongside Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) and Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR) to analyse the spatial distribution of nocturnal UHI. | Identification of UHI hotspots through the statistical models, with the statement that urban forms have significant influences on UHI development. | GIS |
| 12 | 2019 | HIJ | Urban | Develop and implement a GIS-based model for mitigating the UHI effect in Hiroshima | Urban Morphology, vegetation, density population, surface types | GIS to analyse with various urban parameters affecting heat absorption and retention. They collected data to create spatial models predicting heat distribution across the city. | The effectiveness of different mitigation strategies, such as green infrastructure and urban planning interventions, in reducing urban heat. | GIS |
| 13 | 2021 | TRN | Urban | Smart Rooftops | Roof suitability, context, codes, regulations. | Data analysis techniques (GIS), design strategies, and implementation frameworks to optimize the use of urban rooftops for sustainability. | A method to assess rooftop renovation opportunities, evaluating energy savings, thermal comfort, and environmental/economic benefits, was introduced. | GIS |
| 14 | 2022 | TRN | Urban | Outdoor thermal condition at urban scale | Urban Morphology, vegetation, outdoor thermal comfort, sky view factor, mean radiant temperature, urban surfaces | Utilized geospatial assessment QGIS [UMEP-SOLWEIG (QGIS)], DSM, and field measurements to evaluate outdoor thermal comfort on an urban scale. | SOLWEIG is a more suitable tool for assessment and analyses at the urban scale, while ENVI-met is more useful for feasibility studies with high spatial and temporal resolution or for the pre-design phase of little neighbourhoods | GIS |
| 15 | 2013 | XIA | Regional | Landsat 8 imagery for considering factors like climate, soil, vegetation, and acquisition timing | Pervious and impervious surface, LST | They conducted remote sensing analysis to grasp how impervious surface expansion affects local land surface temperature dynamics in the subtropical city. | Growing impervious surfaces increased land surface temperatures, showing urbanization's impact on subtropical city temperatures. | Remote sensing |
| 16 | 2019 | USA | Regional | UHI phenomenon in 54 US cities over 15 years, examining its correlation with temperature changes, weather conditions, and urban warming trends. | UHI, Temperature variation, Climate zones, Weather conditions, Urban Warming Trends | They analysed UHI intensity across cities using satellite data under different temperature conditions. Statistical methods evaluated changes in UHII concerning temperature variations. | In 38 of 54 US cities, UHI intensity decreases as temperatures rise, regardless of climate zones. This is propelled by rural area changes, particularly during moist weather, without a significant UHI effect increase in warming cities. | Remote sensing |
| 17 | 2021 | LX | Regional | Local weather types of data based on Copernicus Land Monitoring Service climate variables dataset | Thermal patterns (seasons); hourly air temperature, specific humidity, relative humidity and wind speed data |
Likely involved collecting and processing Lisbon's temperature and weather data, categorizing local weather types, and correlating them with UHI intensity variations across the metropolitan area. | UHI Intensity estimated in a R script using factors | Remote sensing |
| 18 | 2022 | CN | Urban | Ventilation corridor planning to mitigate UHI | LST, atmospheric data | A systematic approach combining data collection (satellite images), quantitative analysis, and validation to identify urban ventilation corridors effectively | Seven primary ventilation corridors primarily consisting of water bodies and green land areas, while four secondary ventilation corridors were mainly composed of roads. | Remote sensing |
| 19 | 2022 | SZ | Urban | Relationship between the morphological spatial pattern of green space and UHI intensity using machine learning methods. | Urban morphology, Land cover, morphological characteristics of green spaces, Population, Buildings | Employed machine learning methods to analyse the connection between the spatial arrangement of green spaces and the UHI effect. | The UHI intensity was negatively correlated with the cores, perforations, and loops of green space, but positively correlated with islets. | Machine Learning |
| 20 | 2021 | NAP | Urban | Predicting nocturnal (SUHI) during nigh, use of random forest approach to predict LST. | LCZ, Land cover, Air temperature, LST, short wave and long wave radiation, albedo, DEM | Random Forest in R, analysed Landsat-8 and MSG-SEVIRI data in QGIS, and used NASA Atmospheric calculator and GRASS-GIS to predict Naples heatwave nocturnal UHI. | Energy balance-based machine learning approach, to describe the daily cycle of the heat flux components and predict the nocturnal LST and SUHI, during an HW event. | Machine Learning |
| 21 | 2021 | WH | Urban | Machine learning to simulate and mitigate extreme UHI effects in a factory area. | Industrial morphology, type, production stage, scale, and internal structure. | Satellite data (Landsat-8) and ground measurements processed with ENVI and MATLAB to apply ML for simulating and mitigating extreme UHI effects in a factory area. | The results show that the scale of all types of factories affects LST | Machine Learning |
| 22 | 2022 | MAD | Urban | Modelling SHUI trough ArcGis plug-in, predict observed LST with high accuracy, using Random Forest Regression (RFR). | Building height, albedo, DTM, Land Cover map, LST | ArcUHI automates UHI modelling using GIS and machine learning, involving data preprocessing, feature selection, model training, validation, and mapping UHI patterns in urban areas. | Developing of an add-in (ArcUHI) for automated modelling the UHI effect. | Machine Learning |
| 23 | 2022 | AMD | Urban | Employed a machine learning algorithm to predict factors |
LULC maps, BI, NDVI, NDBI, NDMI, MNDWI |
Satellite imagery and ground-based measurements to train the algorithm, incorporating factors to characterize the surface UHI phenomena. | More than 70% area in summer and 40% in winter would likely face higher temperature zones than their respective present situation | Machine Learning |
| 24 | 2023 | AU | National | ML models to assess the link between health outcomes and heat and air quality exposure in diverse Australian urban areas. | Census, Health, Land use, Point of interest, Google earth engine, LST | Investigate the correlation between health metrics and exposure to heat and air quality in various urban areas across Australia | Social and built environmental factors are more influential to physical and mental health outcomes than heat and air pollution, especially in rural areas. | Machine Learning |
References
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). UN Launches Challenge for Cities to Harness Power of Nature for Cooling. Available online: https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/press-release/un-launches-challenge-cities-harness-power-nature-cooling (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) Handbook of Statistics 2023 https://unctad.org/publication/handbook-statistics-2023; https://www.un-ilibrary.org/content/periodicals/22253270. (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). Total and Urban Population. Available online: https://hbs.unctad.org/total-and-urban-population/ (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Howard, L. (1833). The Climate of London. London, UK: Harvey and Darton.
- Oke T.R. (1976) The distinction between canopy and boundary-layer urban heat islands, Atmosphere, 14:4, 268-277. [CrossRef]
- Voogt, J.A., Oke, T.R. (2003). Thermal remote sensing of urban climates, Remote Sensing of Environment 86 370–384. [CrossRef]
- Oke, T. R. (1982). The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 108(455), 1-24. [CrossRef]
- Oke, T. R. (1987). Boundary Layer Climates (2nd ed). Methuen.
- Stewart, I. D., & Oke, T. R. (2012). Local climate zones for urban temperature studies. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 93(12), 1879-1900. [CrossRef]
- Nakata-Osaki, C. M., Souza, L. C. L., & Rodrigues, D. S. (2017). Tool for Heat Island Simulation: A GIS extension model to calculate urban heat island intensity based on urban geometry. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 65, 104-117. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X., Huang, B., Li, R., Zhang, J., Gou, Q., Zhou, T., & Huang, Z. (2018). Wind environment assessment and planning of urban natural ventilation corridors using GIS: Shenzhen as a case study. Building and Environment, 129, 100-113. [CrossRef]
- Liao, K., Hong, Y., & Heo, J. (2018). The effect of spatial heterogeneity in urban morphology on surface urban heat islands. Environmental Research Letters, 13(6), 064014. [CrossRef]
- Mutani, G., Todeschi, V., & Matsuo, K. (2019). Urban Heat Island Mitigation: A GIS-based Model for Hiroshima. Sustainability, 11(8), 2369. [CrossRef]
- Todeschi, V., Mutani, G., Baima, L., Nigra, M., & Robiglio, M. (2021). Smart Solutions for Sustainable Cities—The Re-Coding Experience for Harnessing the Potential of Urban Rooftops. Sustainability, 13(16), 8954. [CrossRef]
- Mutani, G., & Beltramino, S. (2022). Geospatial assessment and modeling of outdoor thermal comfort at urban scale. Sustainable Cities and Society, 77, 103245. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H., Lin, D., & Tang, F. (2013). The Impact of Impervious Surface Development on Land Surface Temperature in a Subtropical City: Xiamen, China. International Journal of Climatology, 33, 1873–1883. [CrossRef]
- Scott, A. A., Waugh, D. W., & Zaitchik, B. F. (2019). Reduced urban heat island intensity under warmer conditions. Environmental Research Letters, 14(9), 094011. [CrossRef]
- Reis, C., Lopes, A., & Santos Nouri, A. (2021). Urban heat island data by local weather types in Lisbon metropolitan area based on Copernicus climate variables dataset for European cities. Sustainable Cities and Society, 65, 102618. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W., Wang, D., Chen, H., Wang, B., & Chen, X. (2022). Identifying urban ventilation corridors through quantitative analysis of ventilation potential and wind characteristics. Building and Environment, 208, 108759. [CrossRef]
- Lin, J., Qiu, S., Tan, X., & Zhuang, Y. (2022). Measuring the relationship between morphological spatial pattern of green space and urban heat island using machine learning methods. Sustainable Cities and Society, 95, 103877. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A., Lopes, A., Niza, S., & Soares, A. (2021). An urban energy balance-guided machine learning approach for synthetic nocturnal surface Urban Heat Island prediction: A heatwave event in Naples. Building and Environment, 195, 107749. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S., Zhang, J., Li, J., Li, Y., Zhang, J., & Wu, X. (2021). Simulating and mitigating extreme urban heat island effects in a factory area based on machine learning. Sustainable Cities and Society, 70, 102977. [CrossRef]
- Espino, D. J., Manchado, C., Valcarce, A. R., & Moscardò, V. (2022). ArcUHI: A GIS add-in for automated modelling of the Urban Heat Island effect through machine learning. Environmental Modelling & Software, 146, 105176. [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, P., Goswami, A., Chauhan, S., & Nayak, S. (2022). Machine learning algorithm-based prediction of land use land cover and land surface temperature changes to characterize the surface urban heat island phenomena over Ahmedabad city, India. Sustainable Cities and Society, 96, 103952. [CrossRef]
- Wang S., W. Cai, Y. Tao, Q. Chayn Sun, P. Pui Yun Wong, X.Huang, Y. Liu, (2023). Unpacking the inter- and intra-urban differences of the association between health and exposure to heat and air quality in Australia using global and local machine learning models. Science of The Total Environment. Volume 871. 162005, ISSN 0048-9697. [CrossRef]
- Martini, A.F.; Pirulli, N. (a cura di). "Torino: Storia di una città". Rivista TORINO. ISSN 2038-4068. Marzo 2011. MuseoTorino. Available online: http://www.museotorino.it/ (in Italian, accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Carlin, A.; Lo Verso, VRM; Invernizzi, S.; Polato, A. (2016). Optimised daylighting for comfort and energy saving for the factory of the future, International Journal of Mechanics and Control 18(1):15-29.
- Museo Torino. Scheda: Ex stabilimento Teksid, ex Ferriere Fiat Vitali. Available online: https://www.museotorino.it/view/s/2ddd80eae7ca4555b51692f187cf20cd (accessed on 02/09/2023).
- Museo Torino. Scheda: Ex Stabilimento Teksid, ex Ferriere Fiat Ingest. Available online: https://museotorino.it/view/s/a0886cd0a4924bde964799ca9952b297#:~:text=Lo%20stabilimento%2C%20collocato%20nell%27area%20compresa%20tra%20le%20vie,Urbana%20che%20ha%20trasformato%20l%E2%80%99area%20di%20Spina%203 (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- QGIS STAC API Browser (stac-utils.github.io).
- Congedo, Luca, (2021). Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin: A Python tool for the download and processing of remote sensing images in QGIS. Journal of Open-Source Software, 6(64), 3172. [CrossRef]
- Mancino, G.; Ferrara, A.; Padula, A.; Nolè, A. (2020). Cross-Comparison between Landsat 8 (OLI) and Landsat 7 (ETM+) Derived Vegetation Indices in a Mediterranean Environment. Remote Sensing, 12, 291. [CrossRef]
- Favretto A. (2018) Urban Heat Island analysis with Remote Sensing and GIS methods: an application in the Trieste area (North-East of Italy). Bollettino della Società Geografica Italiana serie 14, 1(1): 215-229. [CrossRef]
- Boehner, J., Antonic, O. (2009). Land-surface parameters specific to topo-climatology. In T. Hengl & H. Reuter (Eds.), Geomorphometry - Concepts, Software, Applications (pp. 195-226). Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.W.; Valente, D.S.M.; Queiroz, D.M.d.; Coelho, A.L.d.F.; Costa, M.M.; Grift, T. (2022). Smart-Map: An Open-Source QGIS Plugin for Digital Mapping Using Machine Learning Techniques and Ordinary Kriging. Agronomy, 12, 1350. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q., Su, Y., Hu, T. (2023). "LiDAR Data Filtering and Digital Elevation Model Generation." In: Guo, Q., Su, Y., Hu, T. (Eds), LiDAR Principles, Processing and Applications in Forest Ecology, Academic Press, 171-214. ISBN: 9780128238943. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.A., Roecker, S., Grunwald, S., & Owens, P.R. (2012). Digital Soil Mapping: Interactions with and Applications for Hydropedology. In H. Lin (Ed), Hydropedology (pp. 665-709). Academic Press. [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E., Justice, C., Claverie, M., & Franch, B. (2016). Preliminary Analysis of the Performance of the Landsat 8/OLI Land Surface Reflectance Product. Remote Sensing of Environment, 185, 46-56. [CrossRef]
- Masek, J.G., et al. (2006). A Landsat surface reflectance dataset for North America, 1990-2000. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 3(1), 68-72. [CrossRef]
- Kshetri, T. (2018). NDVI, NDBI & NDWI Calculation Using Landsat 7, 8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327971920_NDVI_NDBI_NDWI_Calculation_Using_Landsat_7_8.
- McFeeters, S. K. (1996). The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(7), 1425-1432. [CrossRef]
- Ozelkan, E. (2019). Water Body Detection Analysis Using NDWI Indices Derived from Landsat-8 OLI. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 29. [CrossRef]
- Shastri, S., Singh, Prof., Verma, P., Rai, P., & Singh, A. (2020). Land Cover Change Dynamics and their Impacts on Thermal Environment of Dadri Block, Gautam Budh Nagar, India. Journal of Landscape Ecology, 13, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Jumari, N.A.S.K., et al. (2023). Analysis of urban heat islands with Landsat satellite images and GIS in Kuala Lumpur Metropolitan City. Heliyon, 9(8), e18424. [CrossRef]
- Asdrubali, F., & Desideri, U. (2019). Building Envelope. In F. Asdrubali & U. Desideri (Eds), Handbook of Energy Efficiency in Buildings (pp. 295-439). Butterworth-Heinemann. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. N., Rony, M. R. H., Jannat, F. A., Chandra Pal, S., Islam, M. S., Alam, E., & Islam, A. R. M. T. (2022). Impact of Urbanization on Urban Heat Island Intensity in Major Districts of Bangladesh Using Remote Sensing and Geo-Spatial Tools. Climate, 10, 3. [CrossRef]
- Chunyang He, Peijun Shi, Dingyong Xie, & Yuanyuan Zhao. (2010). Improving the normalized difference built-up index to map urban built-up areas using a semi-automatic segmentation approach. Remote Sensing Letters, 1(4), 213-221. [CrossRef]
- Hantzschel, J., Goldberg, V., Bernhofer, C. (2005). GIS-based regionalisation of radiation, temperature and coupling measures in complex terrain for low mountain ranges. Meteorological Applications, 12(1), 33-42. [CrossRef]
- Cerba, Otakar & Charvat, Karel & Janecka, Karel & Jedlička, Karel & Ježek, Jan & Mildorf, Tomáš. (2012). The Overview of Spatial Data Harmonization Approaches and Tools.
- Grasso S. (2022-23), Isole di calore e Local Climate Zones. Verso un catalogo di azioni per la mitigazione e l'adattamento ai cambiamenti climatici (in Italian), Master di II Livello in “Metodi e Tecniche per il Governo di Territori Resilienti. Verso la gestione integrata dei rischi, Politecnico di Torino (in Italian).
- Latini A., Gatti L., Giagnacovo G., Muleo R., De Rossi P. (2021). "Albedo delle superfici vegetali e benefici dell’inverdimento urbano nella riduzione dell’isola di calore nelle città," in Gli ecosistemi vegetali per la rigenerazione ecologica delle città, RT/2021/13/ENEA. Available online: https://iris.enea.it/retrieve/dd11e37d-0561-5d97-e053-d805fe0a6f04/RT-2021-13-ENEA.pdf.
- Piano Paesaggistico Regionale della Regione Piemonte 2017 (in Italian). Available online: https://www.regione.piemonte.it/web/temi/ambiente-territorio/paesaggio/piano-paesaggistico-regionale-ppr (in Italian, accessed on 5 January 2024).
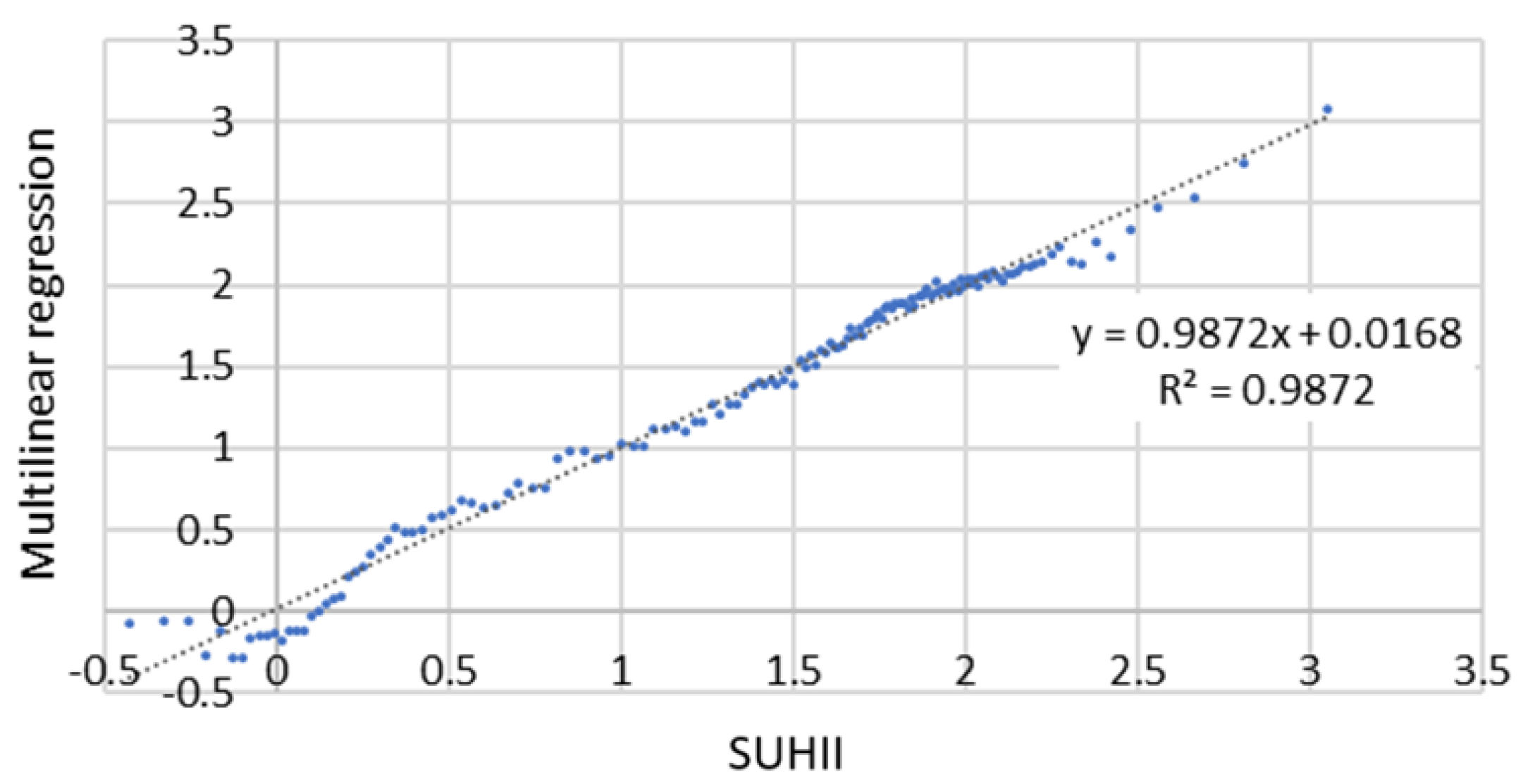
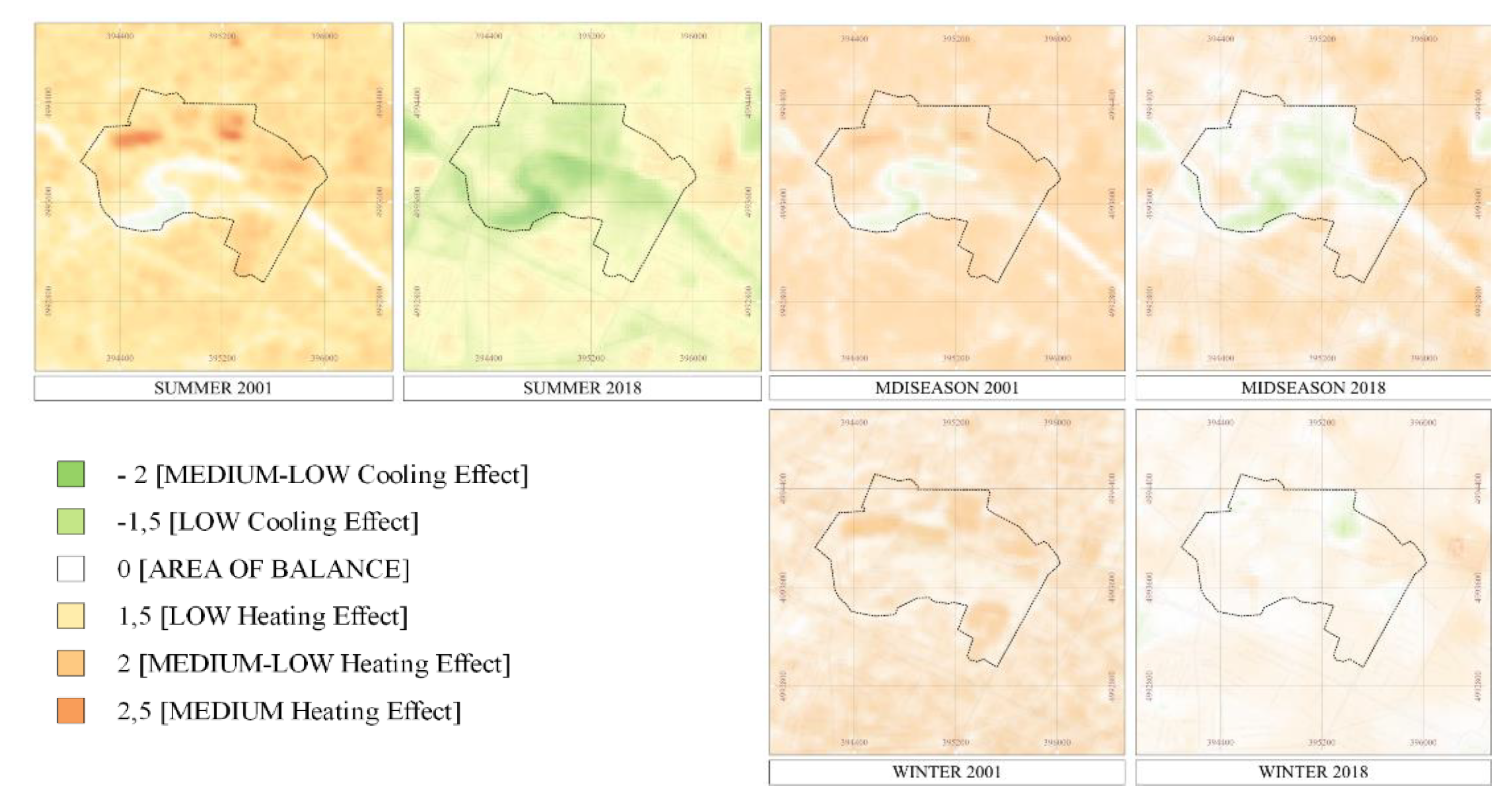
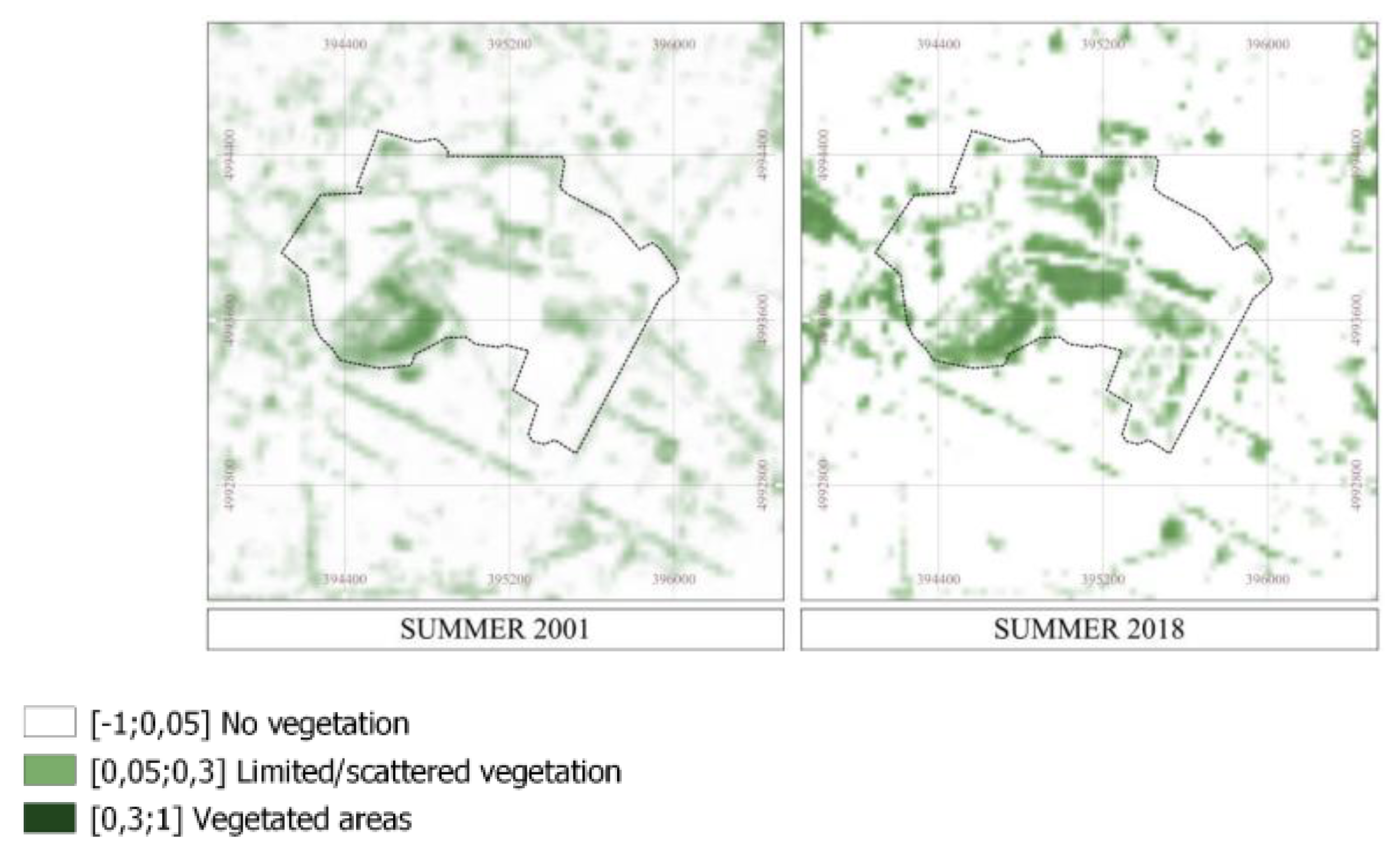
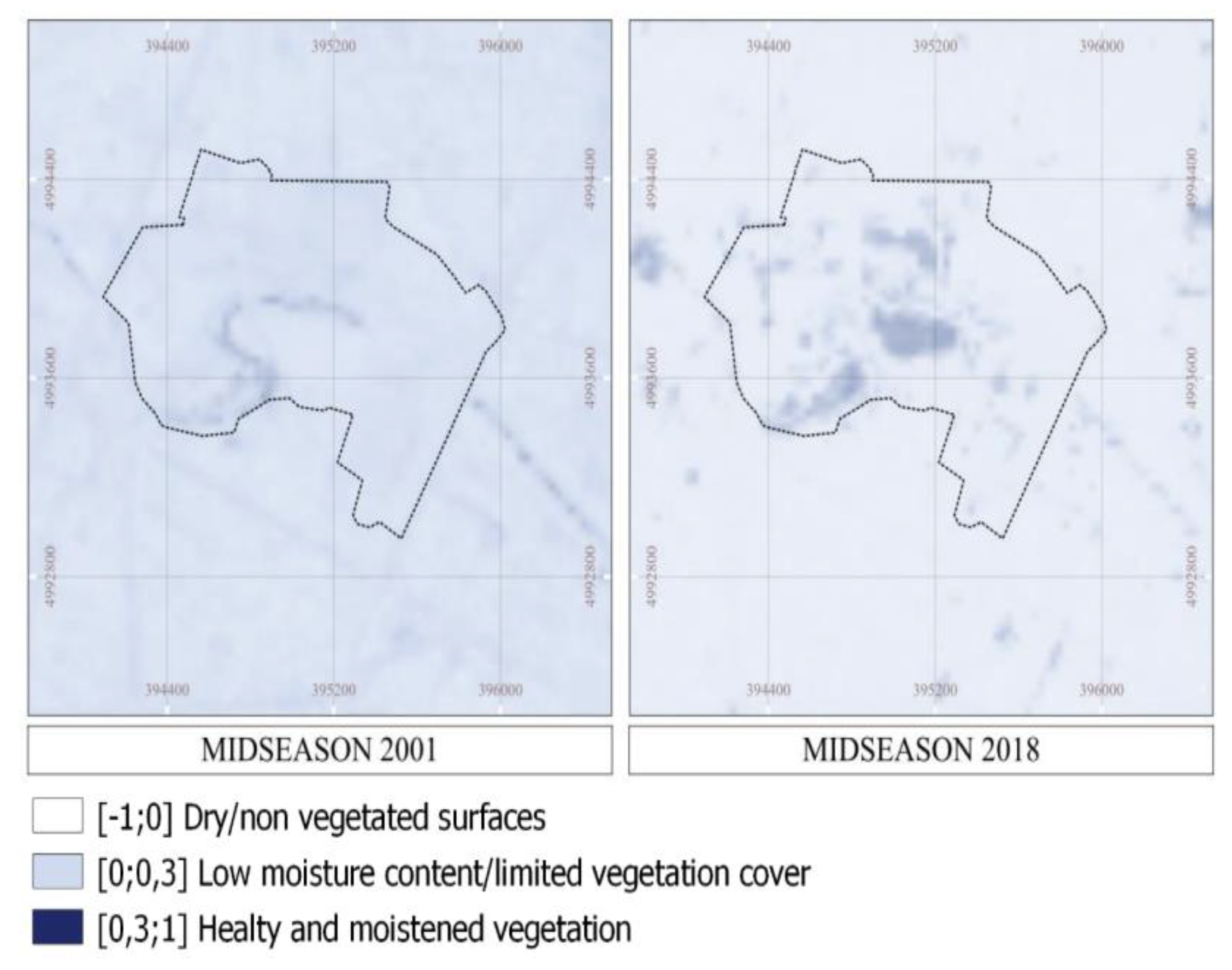
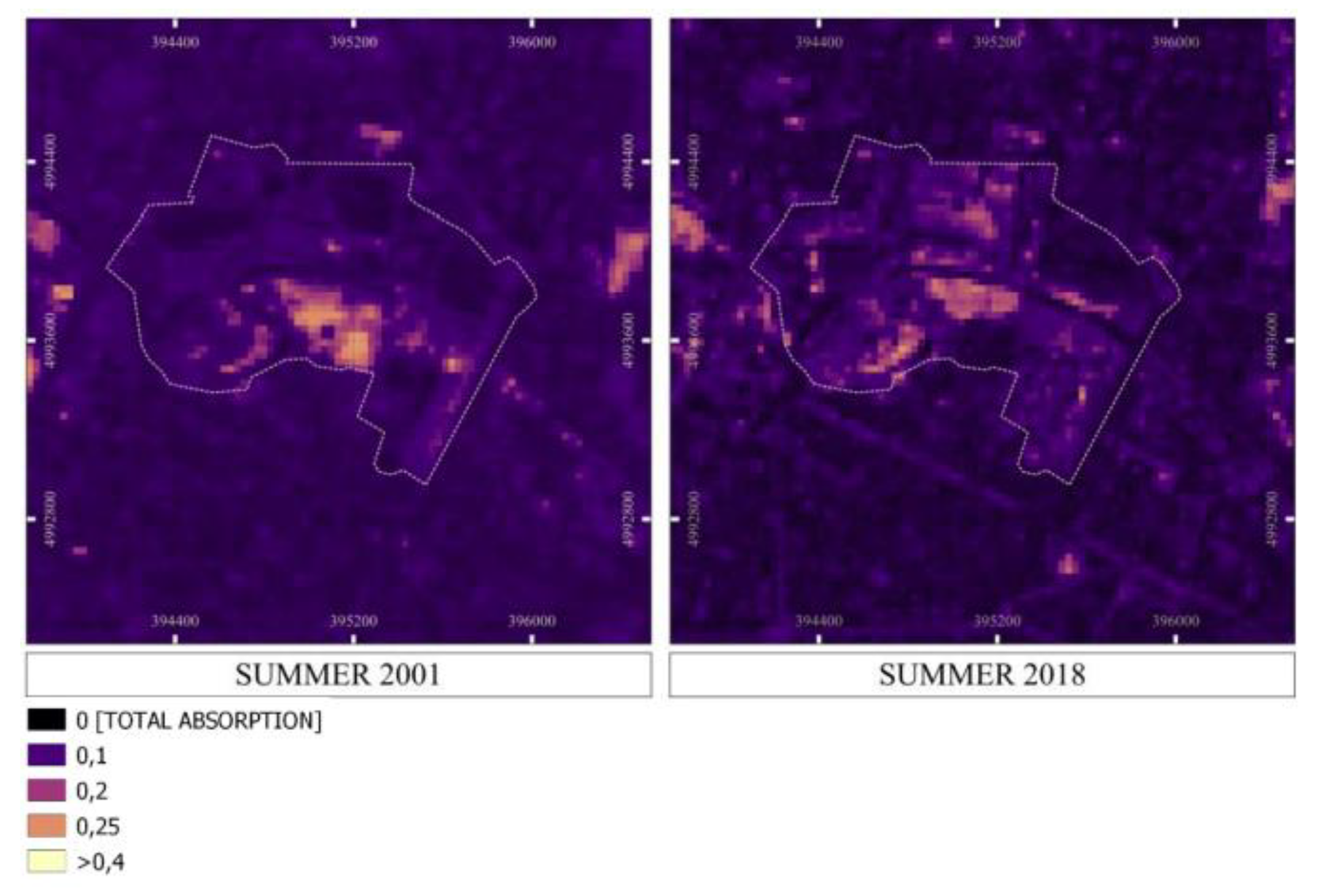
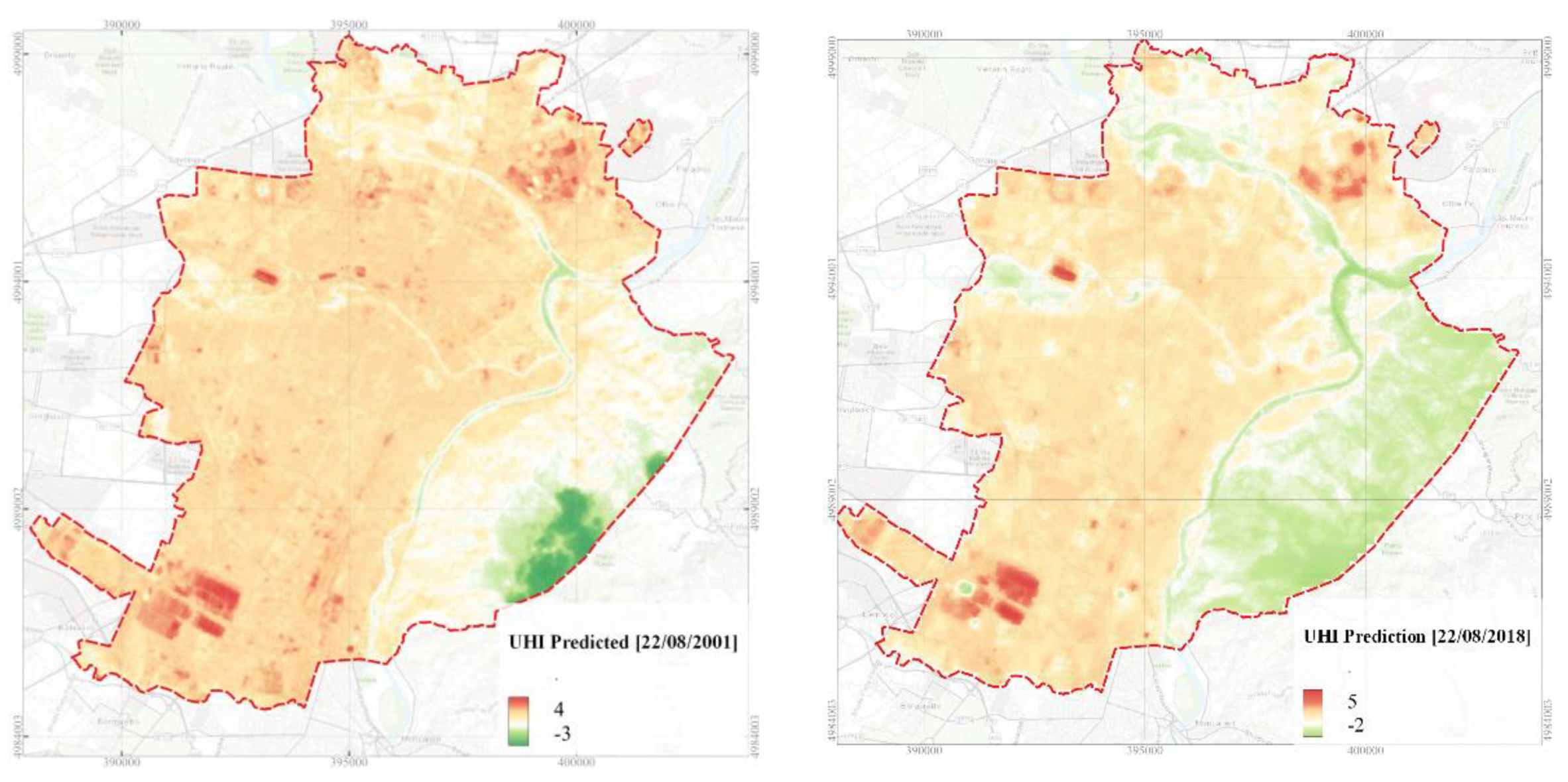
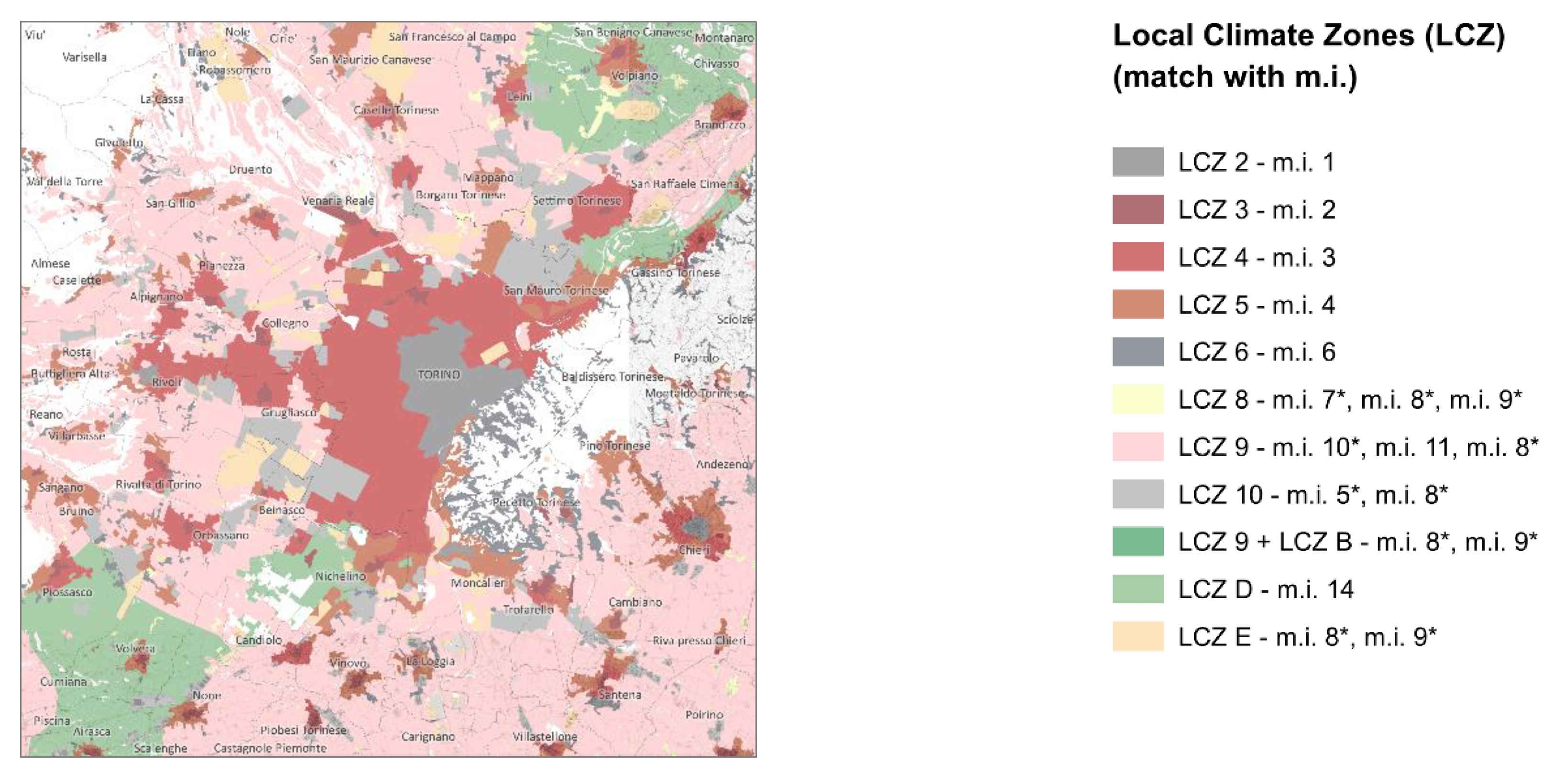
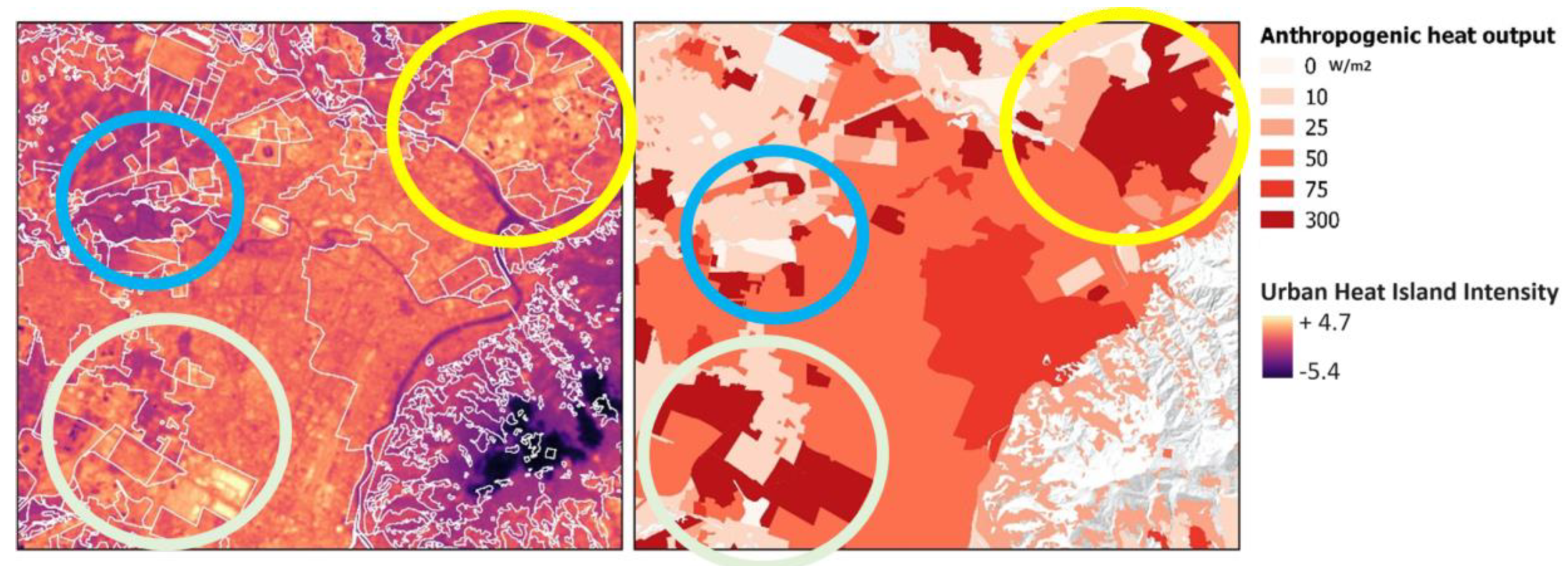
| Landsat product ID | Date | Time | Cloud Cover - |
Cell size m |
Season | Air Temp. °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC08_L2SP_195029_20180822_20200831_02_T1 | 2018-08-11 | 10:16 | 0.31 | 30 | Summer | 26.2 |
| LC08_L2SP_195029_20180211_20200902_02_T1 | 2018-02-22 | 10:17 | 0.23 | 30 | Winter | 3.8 |
| LC08_L2SP_195029_20180416_20200901_02_T1 | 2018-04-16 | 10:16 | 0.30 | 30 | Midseason | 17.9 |
| LE07_L1TP_194029_20010824_20200917_02_T1 | 2001-08-24 | 09:59 | 0.04 | 30 | Summer | 26.1 |
| LE07_L1TP_195029_20001218_20211122_02_T1 | 2000-12-18 | 10:07 | 0.05 | 30 | Winter | 2.1 |
| LE07_L1TP_195029_20010527_20200917_02_T1 | 2001-05-27 | 10:07 | 0.10 | 30 | Midseason | 23.2 |
| Category | Variables | Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land Cover | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | (NIR-VIS)/(NIR+VIS) | [38,39,40] |
| Proportion Vegetation Index (PVI) | (NDVI-NDVImin)/(NDVI-NDVImin) | [38,39,40] | |
| Normal Difference Water Index (NDWI) | (GREEN-NIR)/(GREEN+NIR) | [41,42] | |
| Normal Difference Moisture Index (NDMI) | (NIRshort - SWIR)/ (NIRshort + SWIR) | [38,39] | |
| Albedo | [43,44] | ||
| Emissivity | (0.004*PVI) + 0.986 | [43,44] | |
| Solar Reflectance Index (SRI) | [(SR-SRmin)/(SRmax-NDVImin)] .100 | [45] | |
| Land Surface Temperature (LST) | Tc= (K2/ (ln (K1/Lγ+1)))−273.15 * | [46] | |
| Urban Geomorphology | Buildings and human activities | Kernel Density Estimation QGIS tool | [33] |
| Normalized Difference Built-Up Index (NDBI) | (SWIR - NIR)/ (SWIR + NIR) | [47] | |
| Sky View Factor (SVF) | SAGA QGIS tool | [34,48] | |
| Building Coverage Ratio, Building Density | BCR, BD | [14] | |
| Building Volume and Surface-to-Volume ratio | V, S/V | [14] | |
| Weather Stations | Relative Humidity | Weather stations’ measurements (Kriging interpolation in Smart Map QGis tool) | [35,36,37] |
| Wind Speed and Direction | |||
| Solar Irradiation | |||
| Air Temperature |
| SUHII | NDVI | PVI | NDBI | EMISSIVITY | ALBEDO | SRI | NDMI | NDWI | SVF | BD | V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| minimum | -0.43 | -0.09 | 0.67 | -0.41 | 0.9887 | 0.08 | 25.04 | 0.05 | -0.29 | 0.62 | 0.03 | 2839.00 |
| average | 1.32 | 0.05 | 0.72 | -0.18 | 0.9889 | 0.12 | 25.13 | 0.18 | -0.19 | 0.74 | 0.19 | 3800.08 |
| median | 1.56 | 0.01 | 0.71 | -0.14 | 0.9888 | 0.11 | 25.09 | 0.14 | -0.17 | 0.73 | 0.20 | 3575.28 |
| maximum | 3.05 | 0.25 | 0.79 | -0.05 | 0.9891 | 0.17 | 25.27 | 0.41 | -0.09 | 0.94 | 0.30 | 8053.86 |
| Pearson’s Correlation r | -0.96 | -0.95 | 0.97 | -0.95 | -0.92 | -0.96 | -0.97 | 0.92 | -0.47 | 0.26 | 0.18 |
| Season | Number of Trees | Number of randomly sampled variables |
Leaf size | Tree depth range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer 2018 | 200 | 5 | 1 | 31 |
| Mid-season 2018 | 59 | 5 | 3 | 13 |
| Winter 2018 | 60 | 5 | 5 | 25 |
| Summer 2001 | 59 | 4 | 1 | 39-50 |
| Mid-season 2001 | 164 | 4 | 1 | 38-44 |
| Winter 2001 | 97 | 4 | 2 | 16 |
| Season | MSE | RMSE | R2 | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer 2018 | 0.023 | 0.152 | 0.997 | 0.001 |
| Winter 2018 | 0.021 | 0.145 | 0.991 | 0.002 |
| Mid-season 2018 | 0.080 | 0.283 | 0.948 | 0.001 |
| Summer 2001 | 0.045 | 0.212 | 0.994 | 0.001 |
| Winter 2000 | 0.011 | 0.105 | 0.853 | 0.002 |
| Mid-season 2001 | 0.017 | 0.130 | 0.990 | 0.001 |
| Season | Mean Residuals |
Standard deviation of residuals |
|---|---|---|
| Summer 2018 | -0.00041 | 0.0786 |
| Winter 2018 | -0.00020 | 0.0756 |
| Mid-season 2018 | -0.00004 | 0.2378 |
| Summer 2001 | -0.00082 | 0.1052 |
| Winter 2000 | -0.00013 | 0.0793 |
| Mid-season 2001 | -0.00026 | 0.0682 |
| 2001 | 2018 | |||||
| Rank | Variable | Score | Rank | Variable | Score | |
| 1 | DTM | 6102.32 | 1 | BCR | 18023.83 | |
| 2 | NDBI | 5555.31 | 2 | DTM | 12137.12 | |
| 3 | Solar Irradiation | 4327.89 | 3 | NDMI | 11733.99 | |
| 4 | NDMI | 4197.91 | 4 | Sky View Factor | 5901.33 | |
| 5 | Albedo | 3251.13 | 5 | NDVI | 4767.62 | |
| 6 | Air Temperature | 2824.21 | 6 | Emissivity | 4509.74 | |
| 7 | NDVI | 2696.72 | 7 | NDWI | 4488.35 | |
| 8 | Emissivity | 1950.37 | 8 | Wind speed | 4368.62 | |
| 9 | SRI | 1801.58 | 9 | S/V Ratio | 3173.45 | |
| 10 | Wind direction | 1575.72 | 10 | Wind direction | 2875.59 | |
| 11 | NDWI | 1282.06 | 11 | Relative Humidity | 2757.80 | |
| 12 | Wind speed | 1090.55 | 12 | Air Temperature | 2680.04 | |
| 13 | Air Relative Humidity | 1035.66 | 13 | Solar Irradiation | 2603.21 | |
| 14 | - | - | 14 | SRI | 2572.03 | |
| 15 | - | - | 15 | Albedo | 2151.66 |
| Variable | Radius’ distance from intervention area [m] |
Summer | Spring | Winter | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UHII (ex-Teksid area) | 0 | -0.944 | -1.037 | -0.544 | -0.841 |
| UHII (district area) | 500 | -0.413 | -0.524 | -0.476 | -0.471 |
| UHII (Turin’s municipal area) |
within administrative borders | -0.500 | -0.849 | -0.492 | -0.614 |
| Variable | Scale | Summer | Spring | Winter | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | ex-Teksid | +19.46% | +21.79% | +8.23% | +16.49% |
| district | +6.41% | +16.61% | +7.61% | +10.21% | |
| Turin | +6.17% | +11.09% | +1.53% | +6.26% | |
| NDMI | ex-Teksid | +10.07% | -7.41% | +17.89% | +6.85% |
| district | +6.77% | -4.27% | +17.69% | +6.73% | |
| Turin | +8.44% | -12.43% | +17.39% | +4.47% | |
| ex-Teksid | +3.09% | +0.63% | +14.86% | +6.19% | |
| ALBEDO | district | +1.18% | +0.11% | +13.46% | +4.92% |
| Turin | +3.72% | +0.23% | +15.40% | +6.30% |
| Local Climate Zone | Surface admittance (J m-2 s-1/2 K-1) |
Average | Surface albedo (-) |
Average |
Anthropogenic heat output (W m-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCZ 1 compact high-rise | 1500 | 1800 | 0,10 | 0,20 | 50 | 300 | ||
| LCZ2 compact mid-rise | 1500 | 2000 | 1850 | 0,10 | 0,20 | 0,15 | >75 | |
| LCZ 3 compact low-rise | 1200 | 1800 | 1500 | 0,10 | 0,20 | 0,15 | >75 | |
| LCZ 4 open high-rise | 1400 | 1800 | 1600 | 0,12 | 0,25 | 0,185 | > 50 | |
| LCZ 5 open mid-rise | 1400 | 2000 | 1700 | 0,12 | 0,25 | 0,185 | >25 | |
| LCZ 6 open low-rise | 1200 | 1800 | 1500 | 0,12 | 0,25 | 0,185 | >25 | |
| LCZ 7 lightweight low-rise | 800 | 1500 | 0,15 | 0,35 | >35 | |||
| LCZ 8 large low-rise | 1200 | 1800 | 1500 | 0,15 | 0,25 | 0,20 | >50 | |
| LCZ 9 sparsely built | 1000 | 1800 | 1400 | 0,12 | 0,25 | 0,185 | >10 | |
| LCZ 10 heavy industry | 1000 | 2500 | 1750 | 0,12 | 0,20 | 0,16 | >300 | |
| LCZ A dense trees | unknown | 0,10 | 0,20 | 0 | ||||
| LCZ B scattered trees | 1000 | 1800 | 1400 | 0,15 | 0,25 | 0,20 | 0 | |
| LCZ C bush, scrub | 700 | 1500 | 0,15 | 0,30 | 0 | |||
| LCZ D low plants | 1200 | 1600 | 1400 | 0,15 | 0,25 | 0,20 | 0 | |
| LCZ E bare rock or paved | 1200 | 2500 | 1850 | 0,15 | 0,30 | 0,10*/ 0,225 | 0 | |
| LCZ F bare soil or sand | 600 | 1400 | 0,20 | 0,35 | 0 | |||
| LCZ G water | 1500 | 0,02 | 0,10 | 0 | ||||
| *Typical value for asphalt pavements in Italy | ||||||||
| Association of settlement morphologies with Local Climate Zones | |
|---|---|
| Settlements’ morphologies (“morfologie insediative m.i.” in Italian) | Local Climate Zone (LCZ) |
| (m.i. 1) - Consolidated urban areas of major centers | LCZ 2 - compact midrise |
| (m.i. 2) - Consolidated urban areas of minor centers | LCZ 3 - compact low rise |
| (m.i. 3) - Urban fabrics outside urban center | LCZ 4 - open high rise |
| (m.i. 4) - Discontinuous suburban fabrics | LCZ 5 - open midrise |
| (m.i. 5) - Organized specialized settlements | LCZ 10 - heavy industry |
| (m.i. 6) – Dispersed areas mainly residential | LC6 - open low rise |
| (m.i. 7) - Dispersed areas mainly specialized | LC8 - large low rise |
| (m.i. 8) - Specialized islands | LCZ E - bare rock or paved |
| (m.i. 9) - Infrastructural complexes | LCZ E - bare rock or paved |
| (m.i. 10) - Rural areas in plains or hills | LCZ 9 - sparsley built |
| (m.i. 11) - Systems of rural nuclei in plains, hills, and low mountains | LCZ 9 - sparsley built |
| (m.i. 12) - Mountain villages | LCZ B - Scattered trees + LCZ 9 - sparsley built |
| (m.i. 13) - Rural areas in mountains or hills with scattered & dispersed buildings | LCZ B - Scattered trees + LCZ 9 - sparsley built |
| (m.i. 14) - Rural areas in plains | LCZ D – Low plants |
| (m.i. 15) - Mountain pasturelands and high-altitude rural settlements | LCZ D – Low plants + LCZ 9 - sparsley built |
| Note | Association of LCZ and m.i. |
Surface admittance |
Surface albedo |
Anthropogenic heat output | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (J m-2 s-1/2 K-1) | (-) | (W m-2) | |||
| m.i. 1 | LCZ 2 | 1850 | 0,15 | 75 | |
| m.i. 2 | LCZ 3 | 1500 | 0,15 | 75 | |
| m.i. 3 | LCZ 4 | 1600 | 0,185 | 50 | |
| m.i. 4 | LCZ 5 | 1700 | 0,185 | 25 | |
| *With: Refineries (ex m.i. 8) | m.i. 5* | LCZ 10 | 1750 | 0,16 | 300 |
| m.i. 6 | LCZ 6 | 1500 | 0,185 | 25 | |
| * With large commercial structures, purification plants, hospitals, military and prison areas (ex m.i 8), warehouses, rail junction, logistics hubs, and nodes (ex m.i. 9) | m.i. 7* | LCZ 8 | 1500 | 0,20 | 50 |
| * Contains only: mining areas/extraction plants | m.i. 8* | LCZ E | 1850 | 0,225 | 0 |
| * Contains: runways (albedo value variation*) | m.i. 8* | LCZ E* | 1850 | 0,10* | 0 |
| * with energy production systems (e.g., photovoltaic systems) | m.i. 9* | LCZ E | 1850 | 0,225 | 0 |
| * with motorway infrastructures (change in albedo value*) | m.i. 9* | LCZ E* | 1850 | 0,10* | 0 |
| * with theme parks, campsites, sports facilities, golf clubs, cemeteries (ex m.i. 8) | m.i. 10* | LCZ 9 | 1400 | 0,185 | 10 |
| m.i. 11 | LCZ 9 | 1400 | 0,185 | 10 | |
| m.i. 12 | LCZ B + LCZ 9 | 1400 | 0,1925 | 10 | |
| m.i. 13 | LCZ B + LCZ 9 | 1400 | 0,1925 | 10 | |
| m.i. 14 | LCZ D | 1400 | 0,20 | 0 | |
| m.i. 15 | LCZ D + LCZ9 | 1400 | 0,1925 | 10 | |
| *for some specific categories of m.i. the associations with LCZs were re-defined as indicate in the column Note | |||||
| Priority order | Thermal properties | Radiative properties | Metabolic properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Consolidated urban areas of major centers (m.i. 1) |
Specialized islands (m.i. 8) * | Organized specialized settlements (m.i. 5) |
| 2 | Specialized islands (m.i. 8) * | Infrastructural complexes (m.i. 9) * | Consolidated urban areas of major and minor centers (m.i. 1, m.i. 2) |
| 3 | Infrastructural complexes (m.i. 9) * | Consolidated urban areas of major and minor centers (m.i. 1, m.i. 2) |
Urban fabrics outside centers (m.i. 3) |
| 4 | Organized specialized settlements (m.i. 5) * | Organized specialized settlements (m.i. 5) * | Dispersed areas mainly specialized (m.i. 7) |
| 5 | Discontinuous suburban fabrics (m.i. 4) |
| Properties (to improve) |
Settlement morphologies | Types of interventions |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal properties | Consolidated urban areas of major centers (m.i.1) Specialized islands (m.i. 8) * Infrastructural complexes (m.i. 9) * Organized specialized settlements (m.i.5) * Discontinuous suburban fabrics (m.i. 4) |
|
| Radiative properties | Specialized islands (m.i. 8) * Infrastructural complexes (m.i.9) * Consolidated urban areas of major and minor centres (mm.ii. 1, 2) Organized specialized settlements (m.i. 5) * |
|
| Metabolic properties | Organized specialized settlements (m.i. 5) Consolidated urban areas of major and minor centres (m.i. 1, m.i. 2) Urban fabrics outside of centres (m.i. 3) Areas of predominantly specialized dispersion (m.i. 7) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





