1. Introduction
In the past two years, a new generation of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) represented by ChatGPT, Sora, etc. has entered the public's attention. This kind of technology is driven by the full integration of big models, big data, and big computing power. With the characteristics of scale, emergence, and versatility, it has made a leap breakthrough in natural language processing, video generation, human-computer interaction, multi-modal integration, and so on, and is considered to be the "singularity" of strong artificial intelligence. When it comes to generative artificial intelligence, the first thing that comes to mind is the ability to generate cool things like conversations, text graphics, and Vincennes videos. Compared with the form of expression, the success of the technical route behind it and the new application ecology brought by it should attract our attention. It can be predicted that GAI will bring structural changes to all walks of life in the future.
As the civil aviation industry is highly informationized and immersed in big data, the technological revolution triggered by GAI undoubtedly provides a new opportunity to accelerate the digital transformation of the industry. This is mainly reflected in three aspects, one is the intelligent analysis of civil aviation professional knowledge, the second is the processing of multi-modal information, and the third is the deepening of human-computer interaction ability. In terms of the analysis of civil aviation professional knowledge, GAI has a strong generalization ability (for example, the core architecture of the GAI Transformer and Diffusion model has stronger data processing and knowledge generalization ability). Due to the outstanding characteristics of the civil aviation industry, such as a wide range of professionals, complicated rules and regulations, etc.
In the past, AI research and development of knowledge in the field of civil aviation faced significant training data gaps and cost-benefit problems. However, GAI can combine internal and external knowledge to carry out transfer learning between the general field and various subfields of civil aviation, to efficiently solve the knowledge learning problem in vertical fields, that is to say, AI can "understand" niche civil aviation professional knowledge. In terms of multimodal information processing, a significant technical trend of GAI is to compatibly combine multiple types or modes of data, such as text, images, video, audio, etc., to make more accurate judgments or predictions about more scenarios, situations, or problems. This capability can meet the common multi-form data association processing requirements in civil aviation services (such as operation control, safety management, etc.). For example, air traffic controllers often have to make comprehensive research and judgment decisions based on voice, image, message, etc.
The application of GAI will help air traffic controllers to comprehensively perceive and respond to unexpected scenarios, and have the ability of "Clearvision, wind ear, and wisdom brain". In terms of man-machine collaborative interaction, GAI's man-machine interaction ability is far more than traditional AI, traditional decision-making AI is more like doing "multiple choice", and GAI is good at doing "short answer". The characteristics of GAI "can prompt and guide" enable it to communicate, learn, and progress "human-machine" and "machine-machine" in a "human-like" way in multiple rounds of human-machine interaction, which can also provide more comprehensive and intelligent auxiliary decision-making for professionals.
It is foreseeable that in the future, with the ability of AI to be embedded in various application scenarios in the industry, civil aviation practitioners will have all kinds of "intelligent assistants" in their work (such as passenger service assistants, aircraft maintenance assistants, etc.), and people and AI will work together to "apply what they learn, promote learning, and learn to use each other". Collins Aerospace and SeeingMachines, a leader in eye tracking and driver safety technology, are working together to develop and implement revolutionary fatigue management technology solutions to improve safety across the aviation industry. These solutions will sense a pilot's fatigue and alertness from their eye movements to better understand the impact of the workload on their flight.
2. Related Work
2.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Modern Military Applications
In the realm of safety management, Generative AI (GAI) plays a crucial role, especially in aviation safety prediction. By "learning and understanding" vast amounts of aviation safety reports, GAI can develop a "Civil Aviation Complex System Safety Model," deducing and simulating aviation safety laws to achieve early warnings and predictions of unsafe events influenced by factors such as "human, aircraft, environment, and management." Additionally, GAI can accurately simulate and reproduce safety incidents that are challenging to observe and test in real scenarios, aiding in accident investigation and review analysis.
Table 1.
Application Data Example.
Table 1.
Application Data Example.
| Application Area |
Specific Function |
Practical Case |
| Safety Prediction |
Establish complex safety models, deduce safety laws |
GAI model successfully predicted potential safety hazards for a flight |
| Accident Simulation |
Reproduce difficult-to-observe safety incidents, assist investigations |
GAI simulated the entire process of an aviation accident, helping identify causes |
- 2.
Applications in Flight Operations
In-flight operations, GAI is expected to be deeply integrated with the cockpit, becoming an ideal flight assistant in real flights or training. On one hand, GAI can help pilots and crew quickly obtain the aircraft's status, provide critical route, weather, and other information, and assist in making timely and accurate decisions. Liu et al. (2024) present a study focused on predicting flight accidents using a Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN). Their research involves developing a predictive model that analyzes historical flight accident data to identify key factors contributing to accidents and predict potential risk scenarios.
The BPNN-based model is designed to learn from various input features, including flight parameters, operational conditions, and past incident records, to generate risk assessments and identify high-risk situations. This approach aims to enhance flight safety by providing actionable insights and early warnings based on predictive analytics. The study demonstrates the efficacy of neural network models in improving aviation safety management and highlights the potential for integrating advanced machine learning techniques into accident prediction and risk mitigation strategies. On the other hand, GAI's "generative" advantage can be utilized to create a rich and vivid flight training scene library in virtual reality, offering near-real or customized interactive scenes and feedback information to enhance training efficiency.
Table 2.
Application Data Example.
Table 2.
Application Data Example.
| Application Area |
Specific Function |
Practical Case |
| Flight Assistance |
Provide aircraft status, assist in decision-making |
GAI helped pilots make quick decisions during simulated flights |
| Virtual Training |
Create interactive training scenes to improve efficiency |
GAI-based virtual training system significantly improved training outcomes |
- 3.
Applications in Aircraft Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO)
In MRO, GAI can act as both an "intelligent manual" and a "maintenance expert." Leveraging fleet big data, GAI can predict faults and provide corresponding maintenance measures, advancing the current maintenance concept from "preventive maintenance" to "predictive maintenance," thereby improving safety and efficiency. Leading predictive maintenance platforms like Lufthansa's Aviatar and Air France Engineering's PROGNOS are exploring GAI technology to further enhance their predictive capabilities and safety.
Table 3.
Application Data Example.
Table 3.
Application Data Example.
| Application Area |
Specific Function |
Practical Case |
| Fault Prediction |
Predict faults and provide maintenance advice |
GAI predicted and preemptively addressed potential faults in an aircraft |
| Maintenance Optimization |
Shift from preventive to predictive maintenance |
PROGNOS platform used GAI to significantly enhance maintenance efficiency |
- 4.
Applications in Production and Operations
In production and operations, GAI can enhance airline operational efficiency in various dimensions, such as improving crew scheduling efficiency and enhancing passenger service levels. Compared to flow-based operation planning software, GAI-based crew scheduling programs can intelligently analyze rules and operational manuals, achieving a better balance between airline operations, regulatory constraints, and human resource efficiency. Additionally, GAI helps passengers with ticket booking, simple boarding procedures, and more, reducing customer service resource investment for airlines.
Many large airlines both domestically and internationally have begun implementing relevant technologies.
Table 4.
Application Data Example.
Table 4.
Application Data Example.
| Application Area |
Specific Function |
Practical Case |
| Crew Scheduling |
Intelligent rule analysis for efficient scheduling |
GAI technology optimized crew scheduling processes for an airline |
| Customer Service |
Handle ticket booking and boarding, reduce service resource investment |
GAI improved customer service efficiency in large airlines |
The new generation of generative AI is set to profoundly enhance the level of intelligence in various fields of civil aviation, bringing new opportunities for its digital transformation. To fully leverage this new quality of productivity, especially in the civil aviation sector, attention should be given to three key issues: first, studying the algorithmic model mechanisms of GAI to improve model explainability and break through the "black box" of deep learning; second, addressing the balance between "artificial" and "intelligent" elements, building an ideal "human-machine interaction" paradigm to achieve the best balance between human intervention and assisted decision-making; and third, standardizing the development and application of GAI in terms of network security, data security, and ethical security, to build a reliable and controllable intelligent civil aviation system to ensure aviation safety.
2.2. AI-Assisted Fatigue Monitoring-Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)
The Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is an advanced sensor technology that tracks and records an athlete's movement in real time, including data such as acceleration, rotation, and direction. When this rich data is met with AI, it can reveal deep patterns and trends in the athlete's training process.
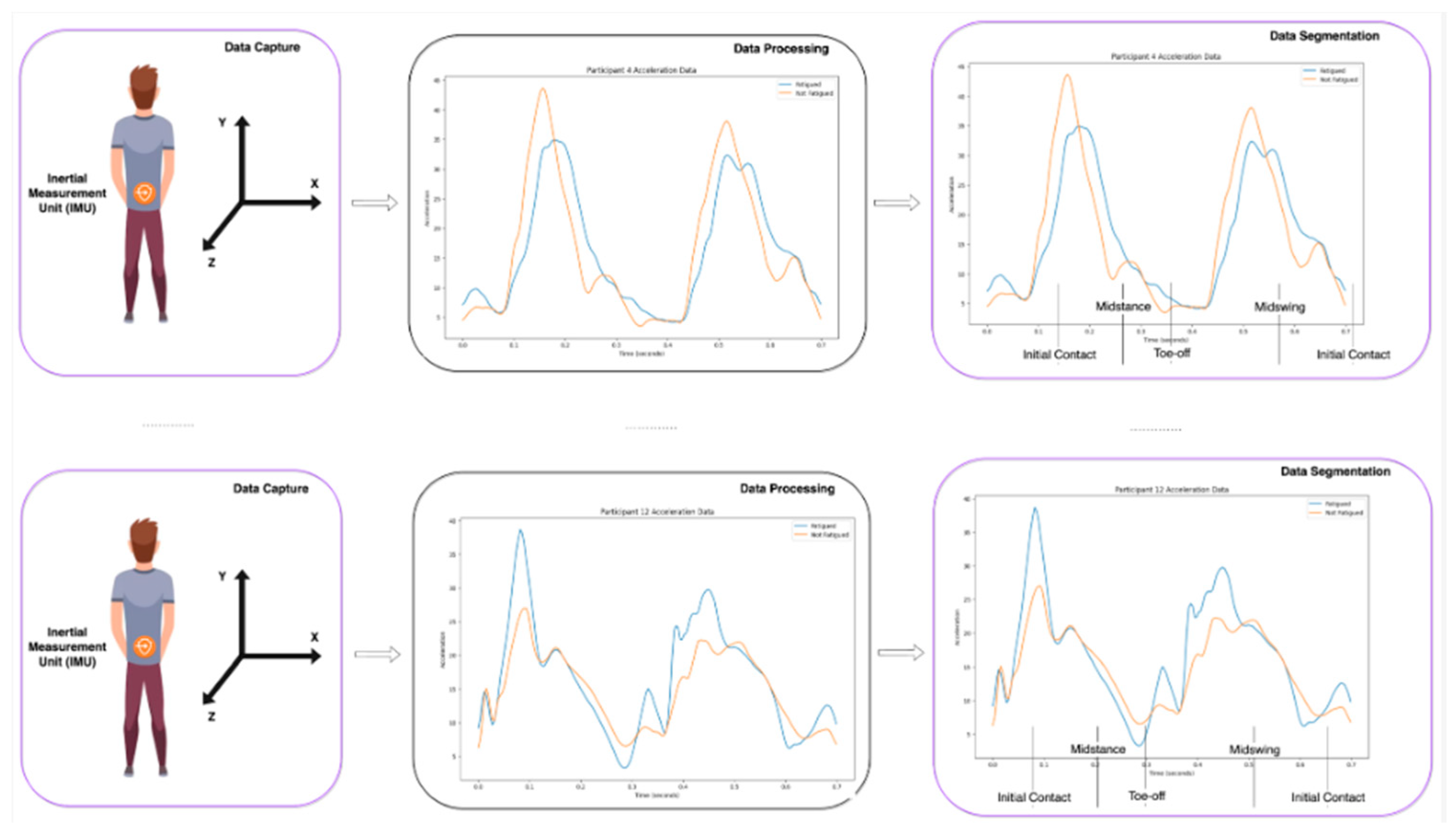
Figure 1.
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) sensor monitoring framework.
Figure 1.
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) sensor monitoring framework.
In the Biro team's study, they used IMUs to collect dynamic data on 19 athletes during multiple training sessions. Then, by applying machine learning algorithms - including random forests, gradient hoists, and Long short-term memory networks (LSTM) - they developed models capable of predicting an athlete's fatigue level and endurance. Researchers have cleverly used the advantages of IMU devices in data acquisition: high spatio-temporal resolution: millisecond high frequency sampling, which can accurately reflect instantaneous motion changes; Multi-structure: synchronously record a variety of data such as triaxial acceleration and triaxial angular velocity, presenting a complete motion picture; No constraint: small size, wireless, wearable, does not affect the natural movement of athletes.
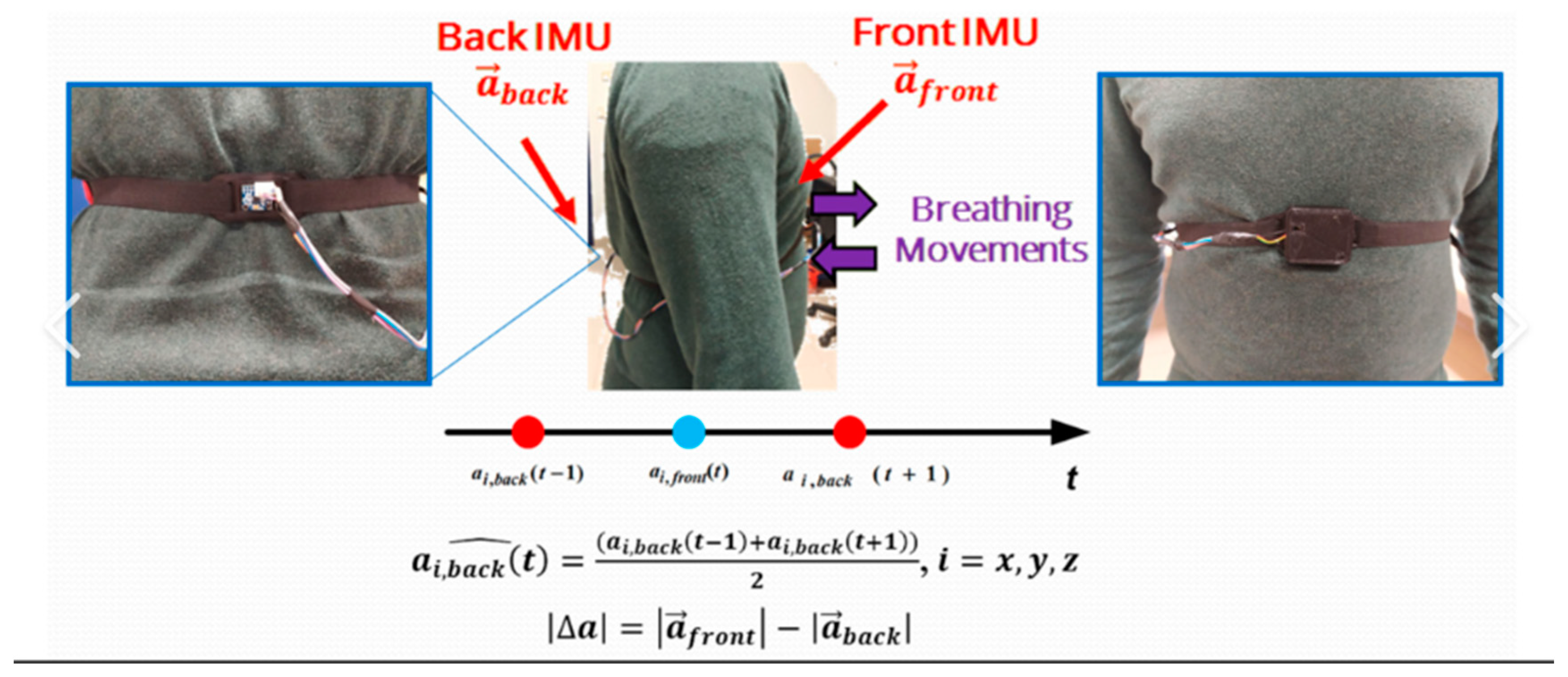
Figure 2.
Sensor monitoring formula away.
Figure 2.
Sensor monitoring formula away.
The Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) sensor technology offers valuable contributions to pilot fatigue risk assessment by providing precise, real-time data on movement dynamics. By integrating IMUs with facial recognition and physiological signal analysis, the combined approach enhances the understanding of pilot fatigue. The IMU’s high spatio-temporal resolution allows for the detailed tracking of minute motion changes, which, when analyzed alongside facial expressions and physiological signals, can deliver a comprehensive picture of fatigue levels and movement patterns. This synergy aids in creating more accurate predictive models for fatigue, as it captures both the physiological and behavioral aspects of pilot performance. In study Liu et al. (2024) explore the application of machine learning techniques for predicting dangerous flight weather conditions.
The researchers propose a novel approach that leverages various machine learning algorithms to enhance the accuracy of weather forecasts critical for flight safety. Their model integrates historical weather data, real-time atmospheric measurements, and advanced learning algorithms to identify patterns and predict adverse weather events that could impact flight operations. This research highlights the potential of machine learning to improve flight safety by providing timely and precise weather predictions, thereby enabling better pre-flight planning and in-flight decision-making. The findings underscore the importance of incorporating cutting-edge technology into aviation safety protocols, offering a promising direction for future advancements in meteorological forecasting for aviation.
Additionally, the IMU’s ability to record multi-structural data, such as triaxial acceleration and angular velocity, complements facial recognition systems that monitor expressions and physiological signals indicating fatigue. The sensor’s small, wireless, and wearable design ensures that it does not interfere with natural movement, making it ideal for real-world applications where pilots' movements and conditions need to be continuously monitored without disrupting their duties. This integration allows for a more holistic and unobtrusive assessment of fatigue, leading to better preventive measures and improved flight safety.
2.3. The Role of Decision-Making Fatigue Monitoring
The effects of decision fatigue are profound, affecting not only our personal lives, but also our productivity at work. In a state of decision fatigue, we tend to make irrational decisions or choose the easiest, least thought-about option. At work, this may lead us to make wrong decisions and affect the effectiveness of our work. In life, it can cause us to be unable to handle our personal affairs well and even affect our health and happiness. Understanding the psychology of decision fatigue and its impact on our productivity in life and work is fundamental to how we use AI to optimize the decision-making process. In the next section, we'll detail how AI can be used to simplify decision-making and reduce decision fatigue. In today's era of information explosion, we need to make more and more decisions, and decision fatigue is becoming increasingly prominent. Fortunately, with the development of artificial intelligence, we have new tools to help us deal with this problem.
AI can simplify and optimize the decision-making process in a number of ways. First, AI can help us better understand problems and make more accurate decisions by analyzing vast amounts of data. For example, AI can help e-commerce companies recommend products that match the user's preferences by analyzing the user's shopping history, so that users do not need to compare a large number of products one by one, thus reducing the complexity of decision-making.
Secondly, AI can also help us save energy by automating some simple decision-making processes. For example, smart home systems can automatically adjust the temperature in the room, so we don't need to decide every day whether to turn on the air conditioner and at what degree. In addition, AI can also help us make decisions faster by learning our decision-making habits to provide personalized recommendations. For example, popular phone assistant AI such as Siri can remind us what to do or provide us with information we might need by learning our daily behavior.
The role of AI in simplifying decision-making can also be seen in some practical applications. For example, some companies are already using AI to aid hiring decisions. AI can simplify a recruiter's decision-making process by analyzing a candidate's resume and recommending the best fit. Another example is AI in the medical field, which can help doctors diagnose diseases and simplify the decision-making process of doctors by analyzing large amounts of case data. Overall, AI has tremendous potential to help us streamline and optimize the decision-making process and alleviate decision fatigue. As AI technology develops further, we expect to see more applications.
Ai has certainly played an important role in helping us streamline decision-making and alleviate decision fatigue. However, we must also recognize that AI also has some limitations and challenges in dealing with these issues.
First, AI recommendation systems could lead us into a "filter bubble." This is because they make recommendations based largely on our past behavior and preferences, which can cause us to miss out on new possibilities or content that doesn't fit our past behavior patterns. This limits our exposure to new information and ideas, which can lead to narrow perspectives and perceptions.
Second, over-reliance on AI to help in the decision-making process may lead to the degradation of our decision-making ability. This is because when our decision-making process is automated or outsourced to AI, we lose the opportunity to practice and improve our decision-making skills.
3. Methodology
3.1. Experimental Design
The study employed advanced Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) technology combined with AI to monitor and predict athletes' fatigue and endurance. The IMU sensors collected high-resolution, real-time data on the movement of 19 athletes during various training sessions. The collected data included triaxial acceleration, angular velocity, and magnetic field direction, which were crucial for analyzing the dynamic changes in athletes' movements. This rich dataset was then used to train and validate several machine learning models, including random forests, gradient boosting machines, and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks.
By integrating AI with IMU data, the study aimed to develop predictive models that could accurately gauge fatigue levels and endurance. The real-time data acquisition allowed for immediate adjustments to training regimens, optimizing performance and reducing the risk of overtraining. The models demonstrated high accuracy in fatigue prediction, showcasing the potential of data-driven approaches for personalized training adjustments and performance enhancement. The innovative use of IMU technology and AI in this study highlights its capability to provide detailed insights into athletes' physiological responses, contributing significantly to the advancement of sports training methodologies.
3.2. Study and Its Implications
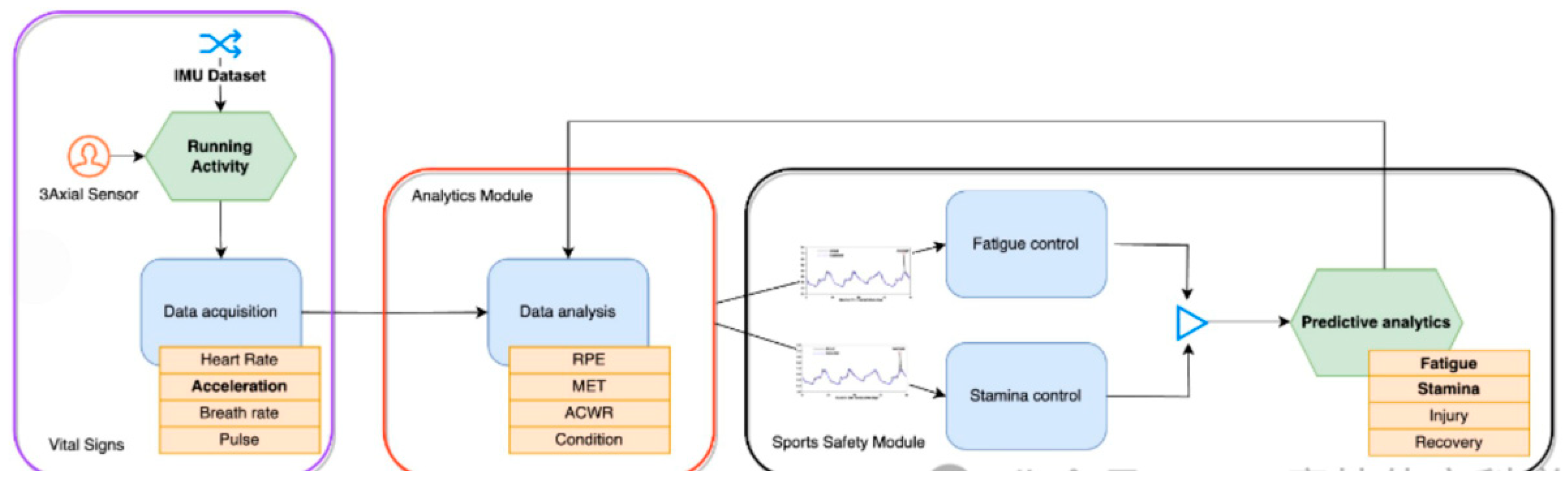
This study introduces a novel training method for athletes that leverages AI and IMU technology to monitor fatigue and endurance levels in real time and adjust training plans accordingly. By comparing various machine learning models, the researchers identified a highly accurate prediction method crucial for preventing overtraining and enhancing performance.
Figure 3.
Sports safety approach on specific use case.
Figure 3.
Sports safety approach on specific use case.
The research not only highlights the potential of AI in sports science but also outlines future technological advancements and underscores the need for ethical and privacy considerations in technology applications. This article opens new perspectives on AI’s role in sports training and offers profound insights into how technology can elevate human performance. We look forward to seeing how AI continues to transform the sports world!
3.3. Experimental Results Summary
Table 5 presents a comparison of various classifiers used in predicting pilot fatigue risk based on facial recognition and physiological signals. Among the classifiers, the (Extreme Trees Classifier) and (Random Forest Classifier) demonstrated moderate accuracy of around 50%, with the Extreme Trees Classifier slightly outperforming in precision. Both models show balanced trade-offs between precision and recall but have room for improvement in specificity and sensitivity. The(Quadratic Discriminant Analysis) classifier, with a lower accuracy of 48.98%, excelled in recall (70.72%), indicating its strength in identifying true positives, although its precision was lower.
3.4. Model Performance Insights
The K-Nearest Neighbor Classifier and Gradient Boosting Classifier showed lower overall performance with accuracies of 48.65% and 47.13%, respectively, highlighting potential issues in fitting the data complexity. Decision Tree Classifier performed competitively with an accuracy of 50.66% and an F1 score of 51.15%, suggesting robustness in this task but not necessarily the most effective for fatigue prediction. Logistic Regression and Linear Discriminant Analysis** both showed high recall (over 63%) but lower precision, reflecting their capability to identify true positives effectively, albeit at the cost of increased false positives.
The Support Vector Machine (Linear Kernel) achieved the highest F1 score of 54.39% due to its high recall of 77.91%, though with lower precision, indicating a preference for identifying true positives over minimizing false positives. The Naive Bayes classifier also performed well in terms of F1 score (52.09%), suggesting it is effective at detecting true positives but may generate more false positives. Notably, the Dummy Classifier showed an impressive F1 score of 67.78% due to its unrealistic perfect recall, which is not useful for practical predictions. These results underscore the need for careful model selection and tuning to balance precision, recall, and overall performance in fatigue risk assessment, ensuring accurate and actionable insights for pilot safety management.
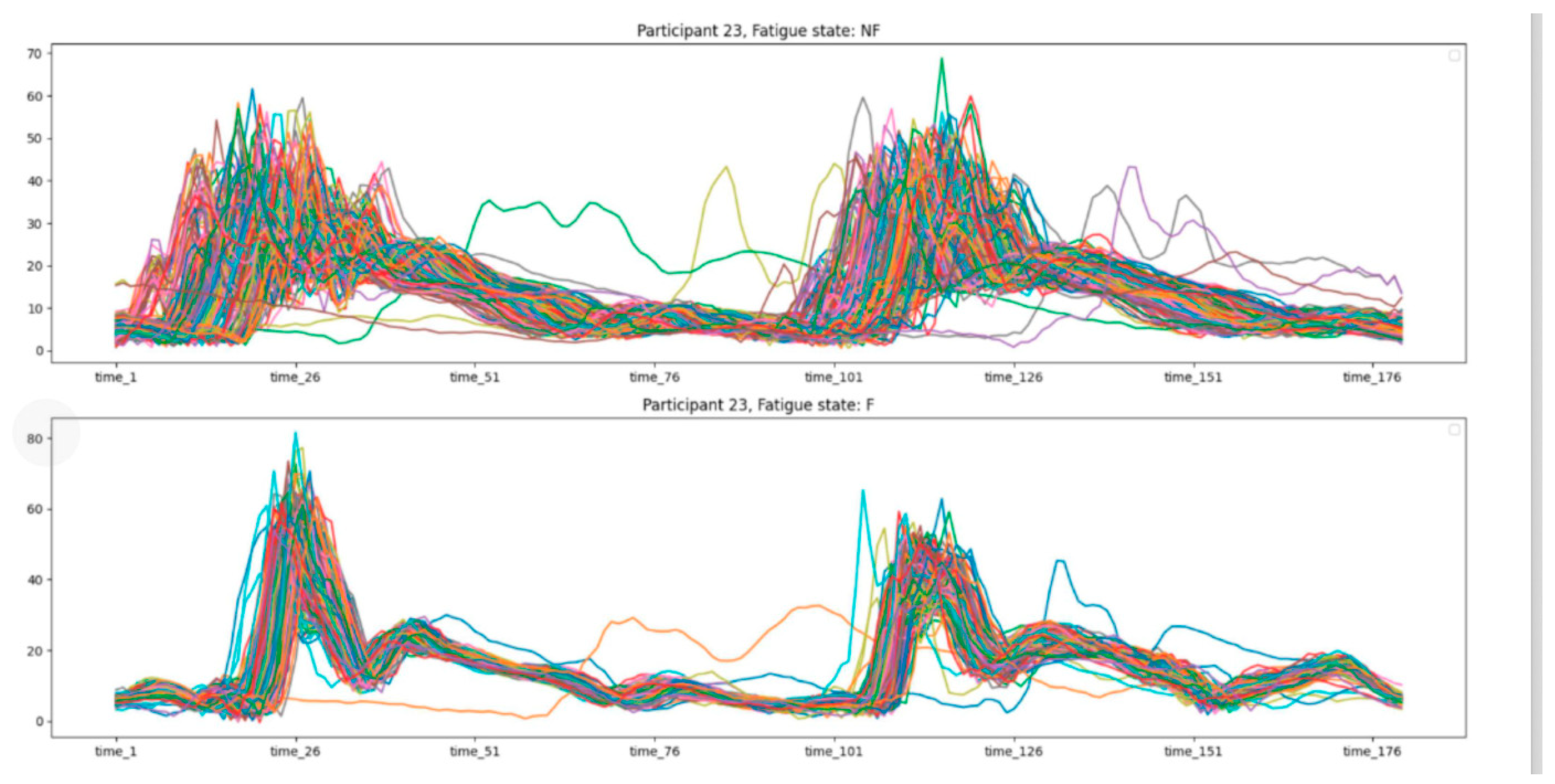
Figure 4.
Participant 23 non-fatigue (NF) and fatigiie (1y) states. Details of more participants: Séedata availability statement.
Figure 4.
Participant 23 non-fatigue (NF) and fatigiie (1y) states. Details of more participants: Séedata availability statement.
3.5. Experimental Discussion
Performance Analysis of Classifiers for AI-Assisted Pilot Fatigue Risk Assessment
The performance results of various classifiers using multivariate time series data generated by Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) for AI-assisted pilot fatigue and endurance control reveal key insights into their effectiveness and suitability for this specific application.
1. Tree-Based Methods:
- Extreme Random Trees** and Random Forest Classifiers demonstrated modest effectiveness with accuracy slightly above 50%. Both classifiers achieved balanced accuracy and recall rates, but their F1 scores around 50% indicate a need for improvement in specificity and sensitivity. While these models are competent, their performance suggests that they may not be the optimal choice for the nuanced task of fatigue risk assessment in pilots, where higher precision and recall are crucial.
2. Statistical Methods:
- The Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (QDA) Classifier showed lower accuracy but excelled in recall rates, suggesting its strength in identifying true positive cases. This model’s higher F1 score compared to other classifiers with less than 50% accuracy indicates its potential in scenarios where prioritizing high recall is important, such as in early detection of pilot fatigue where catching true positives is critical.
3. Instance-Based and Tree Models:
- K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) and Decision Tree Classifiers had lower performance metrics compared to tree-based methods. Their lower F1 scores and balanced accuracy-recall rates imply that these models may not be well-suited for the complexity of fatigue and endurance data or may require parameter optimization to improve performance.
4. Gradient Boosting and Linear Models:
- Gradient Boosting Classifier exhibited lower performance, suggesting potential underfitting issues, where the model may be too simplistic for the complex data patterns present in pilot fatigue assessment. Logistic Regression, Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), and Ridge Classifiers, being linear models, demonstrated higher recall rates but lower accuracy, indicating a tendency to identify positive cases effectively, albeit with a risk of increased false positives.
5. Boosting and SVM:
- The AdaBoost Classifier showed balanced but modest performance, with accuracy, recall, and F1 scores all around 49%, reflecting its generally adequate performance across metrics. The Light Gradient Boosting Machine exhibited reasonable accuracy but struggled with recall, highlighting its effectiveness in identifying true negatives but needing improvement in detecting true positives.
6. Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Naive Bayes:
- The Support Vector Machine with Linear Kernel achieved the highest F1 score and demonstrated a high recall rate, indicating a strong preference for identifying true positives, albeit with some compromise in accuracy. Similarly, the Naive Bayes Classifier, with its probabilistic approach, prioritized recall, reflected in its relatively high F1 score despite moderate accuracy.
7. Virtual Classifier:
- The **Dummy Classifier** showed high accuracy and F1 scores but its results are misleading because it classifies all instances as positive. This highlights the importance of context when interpreting performance metrics, especially in practical applications like pilot fatigue assessment where real predictive capability is crucial.
In summary, the performance of various classifiers in the context of pilot fatigue risk assessment underscores the need for models that balance precision and recall, and are capable of handling complex data patterns effectively. The insights gained from this analysis can guide the selection and refinement of models to improve the accuracy and reliability of fatigue predictions in aviation settings.
4. Conclusions
In the future, the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in pilot fatigue monitoring is very broad. First, advances in AI technology will facilitate the fusion of multimodal data, making the combination of facial recognition and physiological signal analysis more closely. By integrating data from different sensors, AI is able to provide a more comprehensive, real-time assessment of fatigue. This combination can not only improve the accuracy of detection, but also help adjust the pilot's work and rest schedule in real time, reducing operational errors due to fatigue. In addition, AI will be able to recognize more subtle signs of fatigue and give timely warnings, further improving flight safety.
Secondly, with the development of technology, AI systems will have stronger adaptive capabilities and personalized service capabilities. Future AI models will be able to process more complex behavioral patterns and physiological data, monitor pilots' state changes in real time, and adjust monitoring strategies based on individual differences. This high level of personalized management not only improves the accuracy of monitoring, but also provides pilots with tailor-made fatigue management solutions. In addition, the application of AI in fatigue monitoring will also involve in-depth study of ethical and privacy issues to ensure the security and compliance of data use. Overall, AI will play an increasingly important role in pilot fatigue monitoring, promoting aviation safety management into a new era of intelligence.
References
- Chen, Y., Yan, S., Liu, S., Li, Y., & Xiao, Y. (2024, August). EmotionQueen: A Benchmark for Evaluating Empathy of Large Language Models. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics ACL 2024 (pp. 2149-2176).
- Chen, Z., Ge, J., Zhan, H., Huang, S., & Wang, D. (2021). Pareto self-supervised training for few-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 13663-13672).
- Feng, Z., Ge, M., & Meng, Q. (2024). Enhancing Energy Efficiency in Green Buildings Through Artificial Intelligence. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z., Ge, M., Meng, Q., & Chen, Y. (2024). Research on Old Building Renovation Strategies by using Green Building Technologies. [CrossRef]
- Ge, M., Feng, Z., & Meng, Q. (2024). Urban Planning and Green Building Technologies Based on Artificial Intelligence: Principles, Applications, and Global Case Study Analysis. [CrossRef]
- Huang, D., Liu, Z., & Li, Y. (2024). Research on Tumors Segmentation based on Image Enhancement Method. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.05170. [CrossRef]
- Huang, D., Xu, L., Tao, W., & Li, Y. (2024). Research on Genome Data Recognition and Analysis based on Louvain Algorithm. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G., Zhao, S., Yang, H., & Zhang, K. (2024). Research on Finance Risk Management based on Combination Optimization and Reinforcement Learning. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y., Shimizu, S., Li, Y., Yao, Y., Liu, X., Si, H., ... & Xiao, W. (2023). Proton therapy (PT) combined with concurrent chemotherapy for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer with negative driver genes. Radiation Oncology, 18(1), 189. [CrossRef]
- Kumada, H., Li, Y., Yasuoka, K., Naito, F., Kurihara, T., Sugimura, T., ... & Sakae, T. (2022). Current development status of iBNCT001, demonstrator of a LINAC-based neutron source for BNCT. Journal of Neutron Research, 24(3-4), 347-358. [CrossRef]
- Lai, S., Feng, N., Sui, H., Ma, Z., Wang, H., Song, Z., ... & Yue, Y. (2024). FTS: A Framework to Find a Faithful TimeSieve. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.19647. [CrossRef]
- Li, B., Jiang, G., Li, N., & Song, C. (2024). Research on Large-scale Structured and Unstructured Data Processing based on Large Language Model. [CrossRef]
- Li, B., Zhang, K., Sun, Y., & Zou, J. (2024). Research on Travel Route Planning Optimization based on Large Language Model. [CrossRef]
- Li, B., Zhang, X., Wang, X. A., Yong, S., Zhang, J., & Huang, J. (2019, April). A Feature Extraction Method for Daily-periodic Time Series Based on AETA Electromagnetic Disturbance Data. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence (pp. 215-219).
- Li, S., & Tajbakhsh, N. (2023). Scigraphqa: A large-scale synthetic multi-turn question-answering dataset for scientific graphs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.03349. [CrossRef]
- Li, S., Lin, R., & Pei, S. (2024). Multi-modal preference alignment remedies regression of visual instruction tuning on language model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.10884. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Matsumoto, Y., Chen, L., Sugawara, Y., Oe, E., Fujisawa, N., ... & Sakurai, H. (2023). Smart Nanofiber Mesh with Locally Sustained Drug Release Enabled Synergistic Combination Therapy for Glioblastoma. Nanomaterials, 13(3), 414. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Mizumoto, M., Oshiro, Y., Nitta, H., Saito, T., Iizumi, T., ... & Sakurai, H. (2023). A retrospective study of renal growth changes after proton beam therapy for Pediatric malignant tumor. Current Oncology, 30(2), 1560-1570. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H., Shen, F., Qin, H., & Gao, F. (2024). Research on Flight Accidents Prediction based Back Propagation Neural Network. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.13954. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H., Xie, R., Qin, H., & Li, Y. (2024). Research on Dangerous Flight Weather Prediction based on Machine Learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.12298.
- Luo, H., Li, Y., Song, H., Zhao, K., Li, W., Hong, H., ... & Zhang, Y. (2024). Role of EZH2-mediated epigenetic modification on vascular smooth muscle in cardiovascular diseases: A mini-review. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 15, 1416992. [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q., Ge, M., & Feng, Z. (2024). The Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Architectural Visualization Enhances Augmented Realism and Interactivity. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M., Mizumoto, M., Saito, T., Shimizu, S., Li, Y., Oshiro, Y., ... & Sakurai, H. (2024). A systematic review and meta-analysis of radiotherapy and particle beam therapy for skull base chondrosarcoma: TRP-chondrosarcoma 2024. Frontiers in Oncology, 14, 1380716. [CrossRef]
- Nitta, H., Mizumoto, M., Li, Y., Oshiro, Y., Fukushima, H., Suzuki, R., ... & Sakurai, H. (2024). An analysis of muscle growth after proton beam therapy for pediatric cancer. Journal of Radiation Research, 65(2), 251-255. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z. H. A. N. G., Bin-MeiZi, Z. H. A. N. G., Jian-Ke, Z. O. U., & Xiang-Beng, L. I. U. (2018). The Methods, Effects and Mechanism of Priming Attachment Security towards Social Behaviors. Journal of Psychological Science, (3), 615.
- Qu, M. (2024). High Precision Measurement Technology of Geometric Parameters Based on Binocular Stereo Vision Application and Development Prospect of The System in Metrology and Detection. Journal of Computer Technology and Applied Mathematics, 1(3), 23-29.
- Restrepo, D., Wu, C., Cajas, S. A., Nakayama, L. F., Celi, L. A. G., & Lopez, D. M. (2024). Multimodal Deep Learning for Low-Resource Settings: A Vector Embedding Alignment Approach for Healthcare Applications. medRxiv, 2024-06. [CrossRef]
- Shimin, L. E. I., Ke, X. U., Huang, Y., & Xinye, S. H. A. (2020). An Xgboost based system for financial fraud detection. In E3S Web of Conferences (Vol. 214, p. 02042). EDP Sciences.
- Shimizu, S., Mizumoto, M., Okumura, T., Li, Y., Baba, K., Murakami, M., ... & Sakurai, H. (2021). Proton beam therapy for a giant hepatic hemangioma: A case report and literature review. Clinical and Translational Radiation Oncology, 27, 152-156. [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S., Nakai, K., Li, Y., Mizumoto, M., Kumada, H., Ishikawa, E., ... & Sakurai, H. (2023). Boron neutron capture therapy for recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: imaging evaluation of a case with long-term local control and survival. Cureus, 15(1). [CrossRef]
- Shui, H., Sha, X., Chen, B., & Wu, J. (2024, May). Stock weighted average price prediction based on feature engineering and Lightgbm model. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Digital Society and Artificial Intelligence (pp. 336-340).
- Wang, C., Chen, J., Xie, Z., & Zou, J. (2024). Research on Education Big Data for Students Academic Performance Analysis based on Machine Learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.16907. arXiv:2407.16907. [CrossRef]
Table 5.
Contrasting the challenges in sports health with the solutions provided by classic methodsand those provided by AI-assisted approaches.
Table 5.
Contrasting the challenges in sports health with the solutions provided by classic methodsand those provided by AI-assisted approaches.
| hallenges/Issues |
Existing Solutions [7,8] |
Novelties of the AI-Assisted Approach |
| Fatigue Detection |
Reliant on subjective measures, such as athlete self-reports and coach observations. |
AI models predict fatigue objectively before physical symptoms manifest, using physiological data. |
| Personalization |
Generic training programs, one-size-fits-all approach with limited personalization. |
Tailored training regimens adapted to individual physiological responses and recovery profiles. |
| Real-time Feedback |
Delayed feedback after training sessions, based on manual data review. |
Instantaneous feedback during training via wearable tech integration, enabling immediate adjustments. |
| Injury Prevention |
Reactive approaches that respond to injuries post-occurrence. |
Proactive injury risk assessments and preventative suggestions based on predictive analytics. |
| Training Load Optimization |
Empirical methods for deciding on training loads often leading to over- or under-training. |
Data-driven load optimization that continuously adapts to an athlete's current state and needs. |
| Long-term Monitoring |
Fragmented data collection with sporadic athlete longitudinal performance testing, lacking continuity. |
Continuous monitoring and tracking, with detailed historical data analysis. |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).