Submitted:
27 September 2024
Posted:
29 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- -
- Lightweight because of stiffness and high specific strength
- -
- High degree of optimization capability, including directional strength and stiffness customization;
- -
- Ability to mold big complicated shapes in short cycle times, minimizing part count and assembly times
- -
- Good for construction with extensive curvature or thin walls
- -
- Able to retain dimensions and alignment stability in space
- -
- May have minimal dielectric loss in radar transparency
- -
- The potential for a low radar cross-section
- -
- There are certain intrinsic flaws in these composites as well.
- -
- Weakly interfaced laminated structure: inadequate resistance to tensile pressures applied out of plane
- -
- Absorption of moisture and ensuing deterioration of high temperature performance
- -
- High potential for impact damage and a high likelihood of interior damage remaining undetected
- -
- Variability in material properties and several manufacturing faults
- -
- To conduct an in-depth investigation of the mechanical properties of twelve polymers and sixteen natural fibers in terms of tensile strength, Young’s modulus, density, and elongation at a break from existing literature.
- -
- To examine and gather the chemical (micro-fibrillar angle, lignin, hemicellulose, cellulose, and moisture content) and physical (width of lumen, fiber length, thickness of single cell wall, and fiber diameter) characteristics of sixteen natural fibers
- -
- To determine the influence of data variation on the obtained mechanical properties on the performance score of each polymer.
- -
- To determine the influence of data variation on the obtained mechanical, physical, and chemical properties on the performance score of each natural fibre.
- -
- To assign weights to the criteria using the hierarchical strategy methodology to indicate the relative importance of the criteria.
- -
- To assess the performance scores of all the variants of the twelve polymers and sixteen natural fibers.
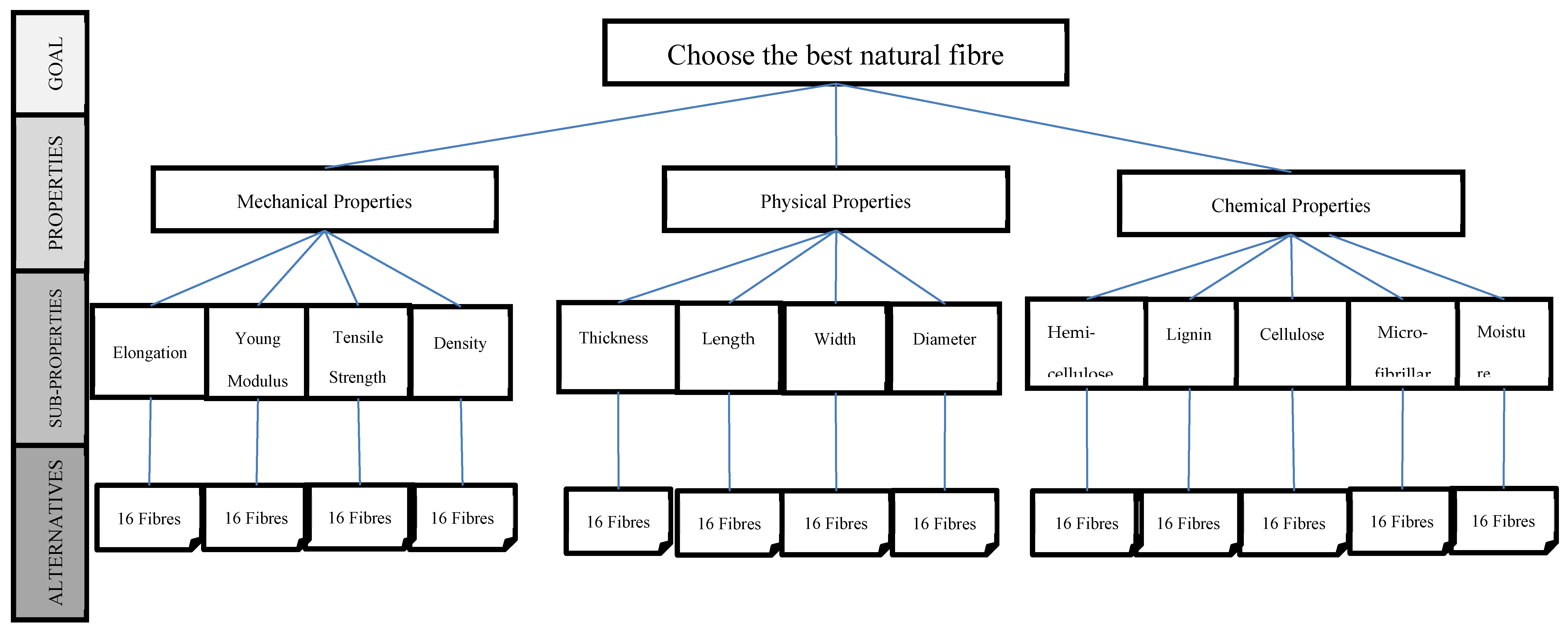
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data
3.1. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- M. Habibi, L. Laperri`ere, H.M. Hassanabadi, Replacing stitching and weaving in natural fiber reinforcement manufacturing, part 2: mechanical behavior of flax fiber composite laminates, J. Nat. Fibers 17 (3) (2020) 388–397. [CrossRef]
- M. Habibi, L. Laperri`ere, H. Mahi Hassanabadi, Replacing stitching and weaving in natural fiber reinforcement manufacturing, part 1: mechanical behavior of unidirectional flax fiber composites, J. Nat. Fibers 16 (7) (2019) 1064–1076.
- S. Selmi, M. Habibi, L. Laperri`ere, S. Kelouwani, Characterisation of natural flax fibers honeycomb: compression damage analysis using acoustic emission, J. Nat. Fibers 19 (3) (2022) 1084–1093.
- Drochytka R, Zach J, Korjenic A, Hroudova J. Improving the energy efficiency in buildings while reducing the waste using autoclaved aerated concrete made from power industry waste. Energy Build 2013;58:319–23.
- Wong NH, Cheong DKW, Yan H, Soh J, Ong CL, Sia A. The effects of rooftop garden on energy consumption of a commercial building in Singapore. Energy Build 2003;35:353–64.
- Stec WJ, Paassen AH, Maziarz A. Modelling the double skin facade with plants. Energy Build 2005;37:419–27.
- Ottele M, Perini K, Fraaij ALA, Haas EM, Raiteri R. Comparative life cycle analysis for green facades and living wall systems. Energy Build 2011;43:3419–29.
- Perez G, Rincon L, Vila A, Gonzales JM, Cabeza LF. Behaviour of green facades in Mediterranean Continental climate. Energy Convers Manag 2011;52:1861–7.
- Perez G, Rincon L, Vila A, Gonzales JM, Cabeza LF. Green vertical system for buildings as passive systems for energy savings. Appl Energy 2011;88:4854–9.
- Sheweka SM, Mohamed NM. Green facades as a new sustainable approach towards climate change. Energy Proc 2012;18:507–20.
- Suklje T, Medved S, Arkar C. An experimental study on a microclimatic layer of a bionic facade inspired by vertical greenery. J Bionic Eng 2013;10:177–85.
- Wong NH, Tang AYK, Tan PY, Wong NCh. Energy simulation of vertical greenery systems. Energy Build 2009;41:1401–8.
- Nadia S, Noureddine S, Hichem N, Djamila D. Experimental study of thermal performance and the contribution of plant-covered walls to the thermal behaviour of building. In: TerraGreen 13 international conference 2013 –advancements in renewable energy and clean environment. Energy Proc; 2013, 36. p. 995–1001.
- Ismail, MR. Quiet environment: acoustics of vertical green wall systems of the Islamic urban form. Front Archit Res 2013;2:162–77.
- Ray D, Sengupta S, Sengupta SP, Mohanty AK, Misra M. A study of the mechanical and fracture behaviour of jute–fabric–reinforced clay-modified thermoplastic starch-matrix composites. Macromol Mater Eng 2007;292:1075–84.
- Pietak A, Korte S, Tan E, Downard A, Staiger MP. A novel technique for characterizing the surface of natural fibres. Appl Surf Sci 2007;253:3627–35.
- Leduc S, Urena JRG, Gonzalez-Nunez R, Quirarte JR, Riedl B, Rodrigue D. LDPE/Agave fibre composites: effect of coupling agent and weld line on mechanical and morphological properties. Polym Polym Compos 2008;16:115–24. [CrossRef]
- Global Biomaterial Market (2009–2014), Markets and Markets, 2009.
- Shah, D. Developing plant fibre composites for structural applications by optimising composite parameters: a critical review. J Mat Sci 2013;48(18):6083–107.
- Velmurugan R, Manikandan V. Mechanical properties of palmyra/glass fibre hybrid composites. Compos Part A-Appl S 2007;38:2216–26.
- Bledzki AK, Zhang W, Chate A. Natural-fibre-reinforced polyurethane microfoams. Compos Sci Technol 2001;61:2405–11.
- Rashdi AAA, Sapuan SM, Ahmad MMHM, Khalina A. Combined effects of water absorbtion due to water immersion, soil buried and natural weather on mechanical properties of kenaf fibre unsaturated polyester composites (KFUPC). Int J Mech Manuf Eng 2010; 5:11–7.
- Baghaei B, Skrifvars M, Berglin L. Manufacture and characterization of thermoplastics composites made from PLA/hemp co-wrapped hybrid yarn prepregs. Compos Part A-Appl S 2013;50:93–101.
- A. Mitra, A. Majumdar, A. Ghosh, P.K. Majumdar, D. Bannerjee, Selection of hand- loom fabrics for summer clothing using multi-criteria decision making techniques, J. Nat. Fibres 12 (1) (Jan. 2015) 61–71.
- Reena antil, Amit Garvit Ritesh, Applications of composite materials in aerospace, International Journal of Science Technology and Management Vol: 4, Issue:11, November 2015.
- Al-oqla, F. M. , Salit, M. S., Ishak, M. R., and Aziz, N. A.. Selecting natural fibers for bio-based materials with conflicting criteria. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 12, 64–71.
- Al-oqla, F. M. , Sapuan, S., Ishak, M., and Nuraini, A.. Decision making model for optimal reinforcement condition of natural fiber composites. Fiber. Polym. 16, 153–163.
- Mansor, M. R., Sapuan, S., Zainudin, E. S., Nuraini, A., and Hambali, A. (2013). Hybrid natural and glass fibers reinforced polymer composites material selection using analytical hierarchy process for automotive brake lever design. Mater. Des. 51, 484–492.
- Da silva neves, A. J., and Camanho, R. (2015). The use of ahp for it Project priorization–a case study for oil & gas company. Proc. Comput. Sci. 55, 1097–1105.
- Chang, C.W., Wu, C.R., Lin, C.T., and Chen, H.C. (2007). An application of ahp and sensitivity analysis for selecting the best slicing machine. Comput. Ind. Eng. 52, 296–307.
- R.R. Kumar, S. Mishra, and C. Kumar, “A Novel Framework for Cloud Service Evaluation and Selection Using Hybrid MCDM Methods,” Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, Vol. 43, pp. 7015–7030, 2018.
- A. K. Babu, P. Venkataramaiah, and S. Yerrathota, S. “Material Selection for Preparation of Aluminium Hybrid Mmcs”, Materials Today: Proceedings, Vol. 5, pp. 12209–12222, 2018.
- X. Sun, “Incorporating multicriteria decision analysis techniques in aircraft conceptual design process,” Journal of Aircraft, Vol. 51 No.3 pp. 861–869, 2014.
- X. Sun, and V. Gollnick V., “Intelligent Multicriteria Decision Support System for Systems Design,” Journal of Aircraft, Vol. 51 No. 1, pp. 1–11, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Ogrodnik, K. Multi-criteria analysis of design solutions in architecture and engineering: Review of applications and a case study. Buildings 2019, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, D.; Lee, M.; Kim, M.; Kim, T. Analytic hierarchy process-based construction material selection for performance improvement of building construction: The case of a concrete system form. Materials 2020, 13, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, T.H.; Dinh, T.H.; Götze, U. Integration of sustainability criteria and life cycle sustainability assessment method into construction material selection in developing countries: The case of Vietnam. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plann. 2020, 15, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruslan, A.A.B.; Al-atesh, E.A.; Rahmawati, Y.; Utomo, C.; Zawawi, N.A.W.A.; Jahja, M.; lmansoury, A. A value-based decision making model for selecting sustainable materials for buildings. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2021, 6, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhoub, M.M.G.; El Sayad, Z.M.T.; Ali, A.A.M.; Ibrahim, M.G. Assessment of green building materials’ attributes to achieve sustainable building façades using AHP. Buildings 2021, 11, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowska-Renkas, E.; Jakiel, P.; Fabianowski, D.; Matyjaszczyk, D. Optimal selection of high-performance concrete for posttensioned girder bridge using advanced hybrid MCDA method. Materials 2021, 14, 6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Avikal, S.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, M.; Thakura, P. A fuzzy-AHP and M-TOPSIS based approach for selection of composite materials used in structural applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 3119–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Jia, H. Green decoration materials selection under interior environment characteristics: A grey-correlational based hybrid MCDM method. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akadiri, P.O.; Olomolaiye, P.O.; Chinyio, E.A. Multi-criteria evaluation model for the selection of sustainable materials for building projects. Autom. Constr. 2013, 30, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, K.; Pierrot, R.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Haddad, A. Sustainable material choice for construction projects: A life cycle sustainability assessment framework based on BIM and fuzzy-AHP. Build. Environ. 2021, 196, 107805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghzadeh, K. , & Salehi, M. B. (2011). Mathematical analysis of fuel cell strategic Technologies development solutions in the automotive industry by the TOPSIS multi-criteria decision making method. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 36, 13272–13280.
- Rahman, S. , Odeyinka, H., Perera, S., & Bi, Y. (2012). Product-cost modelling approach for the development of a decision support system for optimal roofing material selection. Expert Systems with Applications, 39, 6857–6871.
- Lee, K.-L. (2010). Two-phase fuzzy approach for evaluating service strategies in an airport’s international logistic system. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Industrial Engineers, 27, 209–225.
- Liu, H.-C. , Liu, L., & Wu, J. (2013). Material selection using an interval 2-tuple linguistic VIKOR method considering subjective and objective weights. Materials & Design, 52, 158–167.
- Jahan, A. , Mustapha, F., Ismail, M. Y., Sapuan, S., & Bahraminasab, M. (2011). A comprehensive VIKOR method for material selection. Materials & Design, 32, 1215–1221.
- Alptekin Ulutaş, Figen Balo, Ayşe Topal, Identifying the most efficient natural fibre for common commercial building insulation materials with an integrated PSI, MEREC, LOPCOW and MCRAT model, Polymers (MDPI), 15(6), 1500, pages:1-23, 2023.
- Alptekin Ulutaş, Figen Balo, Lutfu S. Sua, Darjan Karabasevic, Dragisa Stanujkic, Gabrijela Popovic, Selection of Insulation Materials with PSI-CRITIC based CoCoSo Method, Vol. 20 No. 2 (2021): Revista de la Construcción. Journal of Construction.
- Berrak Aksakal, Alptekin Ulutaş, Figen Balo and Darjan Karabasevic, A New Hybrid MCDM Model for Insulation Material Evaluation for Healthier Environment, Buildings (MDPI), 13.5.2022, 12(5), 655, 1-23.
- Figen Balo, Evaluation of Ecological Insulation Material Manufacturing with Analytical Hierarchy Process (Ekolojik yalıtım malzemesi üretiminin analitik hiyerarşi prosesi ile değerlendirilmesi), Journal of polytechnic (Politeknik Dergisi) 20(3): 733-742.
- Dweiri, F., Kumar, S., Khan, S. A., and Jain, V. (2016). Designing an integrated ahp based decision support system for supplier selection in automotive industry. Expert Syst. Appl. 62, 273–283.
- Tsita, K. G., and Pilavachi, P. A. (2012). Evaluation of alternative fuels for the greek road transport sector using the analytic hierarchy process. Ener. Policy 48, 677–686.
- Rashid, K., Razzaq, A., Ahmad, M., Rashid, T., and Tariq, S. (2017). Experimental and analytical selection of sustainable recycled concrete with ceramic waste aggregate. Constr. Build Mater. 154, 829–840.
- Mansor, M. R. , Sapuan, S., Zainudin, E. S., Nuraini, A., and Hambali, A. (2014). Conceptual design of kenaf fiber polymer composite automotive parking brake lever using integrated triz–morphological chart–analytic hierarchy process method. Mater.
- Hani, A. , Roslan, A., Mariatti, J., and Maziah, M. (2012). Body armor technology: a review of materials, construction techniques and enhancement of ballistic energy absorption. Adv. Mat. Res. 806–812.
- Dalalah, D., Al-oqla, F., and Hayajneh, M. (2010). Application of the analytic hierarchy process (ahp) in multi-criteria analysis of the selection of cranes. jordan, J. Mech. Indust. Eng. 4, 567–578.
- Figen Balo, Lutfu S.Sua, CRC press 2023 Book series on Handbook of Sustainable Materials: Modelling, Characterization, and Optimization, Chapter 1: Strategic Evaluation and Selection for Energy-Effective Natural Fibers as Alternative Sustainable Insulation Materials for Green Building Envelope, ISBN: 9781032286327, 2023, pages: 1-17.
- Figen Balo, Lutfu S.Sua, EMERALD Publishing 2023 Book Series on Pragmatic Engineering and Lifestyle - Responsible Engineering for a Sustainable Future, Chapter 2: Application of expert decision system at the optimal fiber selection for green building design components, ISBN: 978-1-80262-998-9, Emerald Publishing Limited, 217 pages, 21-38, 2023.
- Figen Balo, Lutfu Sua, Hierarchical Model for Optimizing Natural Fiber Selection Process for Eco-design of Buildings, Journal of Natural Fibers, 19(15), Page:10897-10909 ISSN: 1544-0478.
- Lütfü Şağbanşua, Figen Balo, Multi-Criteria Decision Making for 1.5 MW Wind Turbine Selection, Procedia Computer Science, Pages: 403-409, 111 (2017).
- Aynur Uçar, Figen Balo, “Investigation of wind energy potential in Kartalkaya -Bolu, Turkey”, International Journal of Green Energy, 6(4), 401-412, 2009.
- C. Fragassa , Lightening structures by metal replacement: from traditional gym equipment to an advanced fiber-reinforced composite exoskeleton, Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. (2021).
- K. Amarnath, K.J. Babu, M.V.S. Kumar, Selection of optimal flax fiber reinforced components for experimental investigation by using TOPSIS method, IOP Conf. Ser. 1057 (1) (2021) 12055. [CrossRef]
- H.N. Salwa, S.M. Sapuan, M.T. Mastura, M.Y.M. Zuhri, Analytic hierarchy process (AHP)-based materials selection system for natural fiber as reinforcement in biopoly- mer composites for food packaging, Bioresources 14 (4) (2019) 10014–10046.
- Rocchi, L.; Kadzinski, M.; Menconi, M.E.; Grohmann, D.; Miebs, G.; Paolotti, L.; Boggia, A. Sustainability evaluation of retrofitting solutions for rural buildings through life cycle approach and multi-criteria analysis. Energy Build. 2018, 173, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar D, Alam M, Zou PX, Sanjayan JG and Memon RA. Comparative analysis of building insulation material properties and performance. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2020 Oct 1; 131:110038.
- Ruzgys, A.; Volvaciovas, R.; Ignatavicius, C.; Turskis, Z. Integrated evaluation of external wall insulation in residential buildings using SWARA-TODIM MCDM method. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2014, 20, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameer H, Bringezu S. Life cycle input indicators of material resource use for enhancing sustainability assessment schemes of buildings. Journal of Building Engineering. 2019 Jan 1; 21: 230-42.
- Zagorskas, J.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z.; Burinskiene, M.; Blumberga, A.; Blumberga, D. Thermal insulation alternatives of historic brick buildingsin Baltic Sea Region. Energy Build. 2014, 78, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llantoy N, Chafer M, Cabeza LF. A comparative life cycle assessment (LCA) of different insulation materials for buildings in the continental Mediterranean climate. Energy and Buildings. 2020 Jul 23: 110323.
- P.K. Patnaik, P.T.R. Swain , S.K. Mishra , A. Purohit , S. Biswas , Composite material selection for structural applications based on AHP-MOORA approach, Mater. Today Proc. 33 (2020) 5659–5663.
- Civic, A.; Vucijak, B. Multi-criteria Optimization of Insulation Options forWarmth of Buildings to Increase Energy Efficiency. Procedia Eng. 2014, 69, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, R. Life Cycle Energy Consumption of Buildings; Embodied+ Operational. In Sustainable construction technologies 2019 Jan 1 (pp. 123-144). Butterworth-Heinemann.
- Robati M, Daly D, Kokogiannakis G. A method of uncertainty analysis for whole-life embodied carbon emissions (CO2-e) of building materials of a net-zero energy building in Australia. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2019 Jul 10; 225:541-53.
- Streimikiene, D.; Skulskis, V.; Balezentis, T.; Agnusdei, G.P. Uncertain multi-criteria sustainability assessment of green building insulation materials. Energy Build. 2020, 219, 110021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, Thomas L.; Peniwati, Kirti (2008). Group Decision Making: Drawing out and Reconciling Differences. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: RWS Publications. ISBN 978-1-888603-08-8.
- Saaty, Rozann, ed. (2009). "Participant Names and Papers". Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on the Analytic Hierarchy/Network Process. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: ISAHP.
- Saaty, Thomas L. (2008). Decision Making for Leaders: The Analytic Hierarchy Process for Decisions in a Complex World. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: RWS Publications. ISBN 978-0-9620317-8-6.
- Saaty, Thomas L. (2010). Principia Mathematica Decernendi: Mathematical Principles of Decision Making. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: RWS Publications. ISBN 978-1-888603-10-1.
- Saaty, Thomas L. (June 2008). "Relative Measurement and its Generalization in Decision Making: Why CiteSeerX 10.1.1.455.3274.
- Roman Hruška, Petr Průša, Darko Babić, The use of ahp method for selectıon of supplıer, Transport 2014 Volume 29(2): 195–203.
- Jabbarzadeh, A. (2018). Application of the AHP and TOPSIS in project management. Journal of Project Management, 3(2), 125-130.
- Kuo, R. J., Chi, S. C., & Kao, S. S. (1999). A decision support system for locating convenience store through fuzzy AHP. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 37(1-2), 323-326.
- Jalaliyoon, N. , Bakar, N. A., Taherdoost, H. (2012). Accomplishment of Critical Success Factor in Organization; Using Analytic Hierarchy Process. International Journal of Academic Research in Management, Helvetic Editions Ltd, 1(1); 1-9.
- Lee. M. C. (2007). A Method of Performance Evaluation by Using the Analytic Network Process and Balanced Score Card, International Conference on Convergence Information Technology.
- Ansah, R. H. , Sorooshian, S., and Mustafa, S, 2015, Analytic Hierarchy Process Decision Making Algorithm. Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. Vol. 11, No. 4, pp. 2393-2400.
- E. Aprianti, P. Shafigh, S. Bahri, Supplementary cementitious materials origin from agricultural wastes—a review, Construct. Build. Mater. 74 (2015) 176–187. [CrossRef]
- R. Arjmandi, A. Hassan, K. Majeed, Rice husk filled polymer composites, Int J Polym Sci (2015) 1–32.
- www.pig333.com.
- F. Asdrubali, et al., A review of unconventional sustainable building insulation materials, (2015).
- O. Faruk, A.K. Bledzki, S.H.-P. Fink, Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010, Prog. Polym. Sci. 37 (11) (2012) 1552–1596.
- M. N. M. A. L. Mohammed, G. Pua, M. Jawaid, and M. S. Islam, A Review on Natural Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composite and its Applications, International Journal of Polymer Science2015, (2015) 243947.
- K. Rohit, S. DiXit, November, A Review - Future Aspect of Natural Fiber Reinforced Composite, 2015.
- M.P.S.N. Tucker, Natural-fiber composites in structural applications, in: K. Pickering (Ed.), Properties and Performance of Naturalfibre Composites, Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, UK, 2008.
- S.K. Ramamoorthy, S. M, A. Persson, A review of natural fibers used in biocomposites: plant, animal and regenerated cellulose fibers, Polym. Rev. 55 (1) (2015) 107–162.
- S.D. K Rohit, A review-future aspect of natural fiber reinforced composite, Polym. Renew. Resour. 7 (2) (2016) 43–60.
- M. Thiruchitrambalam, A. Athijayamani, S. Sathiyamurthy, and A.A. Thaheer, "A Review on the Natural Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites for the Development of Roselle Fiber-Reinforced Polyester Composite" ed.
- S.B.K.N. Bharath, Applications of biocomposite materials based on natural fibers from renewable resources: a review, in: Materials Science, Science and Engineering of Composite Materials, 2015.
- V. Chauhan, T. Ka¨rki, J. Varis, Review of natural fiber-reinforced engineering plastic composites, their applications in the transportation sector and processing techniques, J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 35 (8) (2022) 1169–1209.
- H.R. T Sen, Various industrial applications of hemp, kenaf, flax and ramie natural fibres, Int J Innov Manage Technol 2 (3) (2011) 192–198.
- L.Y. Mwaikambo, Review of the history, properties and application of plant fibres, Afr. J. Sci. Technol. 7 (2) (2006) 120–133.
- J. Holbery, D. Houston, Natural-fiber-reinforced polymer composites in automotive applications, J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 58 (11) (2006) 80–86.
- S.H. Shuit, K.T. Tan, K.T. Lee, Oil palm biomass as a sustainable energy source: a Malaysian case study, Energy 34 (9) (2009) 1225–1235.
- S. Shinoj, R. Visvanathan, S. Panigrahi, Oil palm fiber (OPF) and its composites: a review, Ind. Crop. Prod. 33 (1) (2011) 7–22.
- S.S. D Verma, Green biocomposites: a prospective utilization in automobile industry, in: M. Jawaid, S. MS, O.Y. Alothman (Eds.), Green Biocomposites: Design and Applications, Springer, Cham, 2017, pp. 167–191.
- https://www.fao.org/3/cc9120en/cc9120en.pdf.
- A.K.B.J. Gassan, Composite reinforced with cellulose based fibers, Prog », Pol. Sci. 24 (1999) 221–274.
- Y. Li, Y.W. Mai, L. Ye, "Sisal fibre and its composites: a review of recent developments »," (in pt), Compos. Sci. Technol. 60 (11) (2000) 2037–2055.
- Y.Y. N Reddy, Biofibers from agricultural byproducts for industrial applications, Trends Biotechnol. 23 (1) (2005) 22–27.
- H.R. T Sen, Application of sisal, bamboo, coir and jute natural composites in structural upgradation, Int J Innov Manage Technol 2 (3) (2011) 186–191.
- M. Jawaid, H. Khalil, Cellulosic/synthetic fibre reinforced polymer hybrid composites: a review, Carbohydr. Polym. 86 (1) (2011) 1–18.
- A.S. C Alves, L.G. Reis, M. Freitas, Ecodesign of automotive components making use of natural jute fiber composites, Journal of cleaner 18 (4) (2010) 313–327.
- Z. Chen, X. Y, S. Shivkumar, Microstructure and tensile properties of various varieties of rice husk, J. Sci. Food Agric. 98 (3) (2018) 1061–1070.
- Y.Y. N Reddy, Properties of high-quality long natural cellulose fibers from rice straw, J. Agric. Food Chem. 54 (21) (2006) 8077–8081.
- https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/coconut-production-by-country.
- A.S. Singha, V. Thakur, Mechanical properties of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites, Bull. Mater. Sci. 31 (2008) 791–799.
- W. Hoareau, W.G. Trindade, B. Siegmund, Sugar cane bagasse and curaua linens oXidized by chlorine di oXide and reacted with furfuryl alcohol: characterization and stability, Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 86 (2004) 567–657. [CrossRef]
- Bio-composite Materials: a Short Review of Recent Trends, Mechanical and Chemical Properties, and Applications," ed.
- C.M. Yeng, S. Husseinsyah, S.S. Ting, A comparative study of different crosslinking agent-modified chitosan/corn cob biocomposite films, Polym. Bull. 72 (4) (2015) 791–808.
- M.A. Fuqua, S. Huo, C.A. Ulven, Natural fiber rein-forced composites, Polym. Rev. 52 (3) (2012) 259–320.
- F. Ahmad, H.S. Choi, M.K. Park, A review: natural fiber composites selection in view of mechanical, light weight, and economic properties, Macromol. Mater. Eng. 300 (2015) 10–24.
- R.K.S.O.A. Sharma, Chemical Modifications of Natural Fiber for Composite Material, Pelagia Research Library, january, 2011.
- L.G. Angelini, M. Scalabrelli, S. Tavarini, P. Cinelli, I. Anguillesi, A. Lazzeri, Ramie fibers in a comparison between chemical and micro biological retting proposed for application in biocomposites, Ind. Crop. Prod. 75 (2015) 178–184.
- A.K. Mohanty, M. Misra, G. Hinrichsen, Biofibers, biodegradable polymers andbiocomposites, Macro, Mater. Eng. (Modena, Italy) 276 (277) (2000) 1–24.
- M. Ramesh, P. K, K.H. Reddy, Plant fibre based bio-composites: sustainable and renewable green materials, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 79 (2017) 558–584.
- H.M. Akil, M.F. Omar, A.A.M. Mazuki, Kenaf fiber reinforced composites: a review, Mater. Des. 32 (8) (2011) 4107–4121.
- X. Li, L.G. Tabil, S. Panigrahi, Chemical treatments of natural fiber for use in natural fiber-reinforced composites: a review, J. Polym. Environ. 15 (1) (2007) 25–33.
- A.S. Singha, V. Thakur, Mechanical properties of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites, Bull. Mater. Sci. 31 (2008) 791–799.
- L.R.S. Julinawati, Preparation of chitosan composite film reinforced with cellulose isolated from oil palm emp ty fruit bunch and application in cadmium ions removal from aque ous solutions, Carbohydr. Polym. 170 (2017) 226–233.
- N. Jauhari, M. R, H. Thakur, Natural fibre reinforced composite laminates—a review, Mater. Today Proc. 2 (4) (2015) 2868–2877.
- V.S. Srinivasan, S.R. Boopathy, D. Sangeetha, Evaluation of mechanical and thermal properties of banana–flax based natural fibre composite, Mater. Des. 60 (2014) 620–627.
- R.M. Rowell, A.R. Sanadi, D.F. Caulfield, R.E. Jacobsen, in: A.L. L, F.X. Carvalho, E. Frollini (Eds.), Utilization of Natural Fibers in Plastic Composite: Problems and Opportunities. Lignocellulosic-Plastic Composites, Brazil, USP and UNESP, 1997.
- T. Gurunathan, S. Mohanty, S.K. Nayak, A review of the recent developments in biocomposites based on natural fibres and their app lication perspectives, Composer Part Appl. Sci. Manufa cturing 77 (2015) 1–25.
- M.E. Boustani, G. Lebrun, F. Brouillette, A. Belfkira, Effect of a solvent-free acetylation treatment on reinforcements permeability and tensile behaviour of flax/epoXy and flax/wood fibre/epoXy composites, Can. J. Chem. Eng. 95 (6) (2017) 1082–1092. [CrossRef]
- R. Sun, M. Fang, G. J, Fractionation and characterization of polysaccharides from abaca fibre, M. L. A., J. B. J., and A, Car bohydrate Polym 37 (4) (1998) 351–359.
- J. Biagiotti, D. Puglia, J.M. Kenny, J. Nat. Fibers 1 (3) (2008).
- M.S. Huda, L.T. Drzal, A.K. Mohanty, M. Misra, Chopped glass and recycled newspaper as reinforcement fibers in injection molded poly(lactic acid) (PLA) composites: a comparative study, Sci. Technol. 66 (2006).
- S.B.R.D.S. Biswas, Physical and mechanical behavior of unidirectional banana/ jute fiber reinforced epoXy based hybrid compo sites, Polym. Compos. 38 (7) (2017) 1396–1403.
- J. Biagiotti, D. Puglia, J.M. Kenny, J. Nat. Fibers 1 (2) (2008).
- U.S. Bongarde, V. Shinde, Review on natural fiber reinforcement polymer composites, Int J Eng Sci Inn Tech 3 (2) (2014) 431–436.
- K. Senthilkumar, N. Saba, N. Rajini, Mechanical properties evaluation of sisal fiber reinforced polymer composites: a review, Construct. Build. Mater. 174 (2018) 713–729.
- S. Bouzouita, Optimisation des interfaces fibre/matrice de composites `a renfort naturel, in: Th`ese de doctorat, E´cole Centrale de Lyon. France, 2011, p. 179.
- G.R.T. Sundararajan, Studies on the durability of natural fibres and the effect of corroded fibres on the strength of mor tar, Cem. Concr. Compos. 27 (5) (2005) 575–582.
- S. Loiacono, G. Crini, B. Martel, G. Chanet, C. Cosentino, M. Raschetti, Simultaneous removal of Cd, Co, Cu, Mn, Ni, and Zn from synthetic solutions on a hemp-based felt. II, Chem. Modif. J. Appl. Polym. Sci 134 (32) (2017), 45138.
- R. Sun, M. Fang, G. J, Frac tionation and characterization of polysaccharides from abaca fibre, M. L. A., J. B. J., and A, Car bohydrate Polym 37 (4) (1998) 351–359.
- B.S. Santucci, J. Bras, M.N. Belgacem, A.A.S. Curvelo, M.T.B. Pimenta, Evaluation of the effects of chemical composition and refining treatments on the properties of nanofibrillated cellulose films from sugarcane bagasse, Ind. Crop. Prod. 91 (2016) 238–248.
- O. Faruk, A. K. Bledzki,H.-P.Fink, andM. Sain, “Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010,” Progress in Polymer Science, vol. 37, no. 11, pp. 1552–1596, 2012.
- K.S. Prado, M. Spinac´e, Characterization of fibers from pineapple’s crown, rice husks and cotton textile residues, Mater. Res. 18 (3) (2015) 530–537.
- R.M.V. K, Y.S. Negi, Recent development in natural fiber reinforced polypropylene composites, J. Reinforc. Plast. Compos. 28 (10) (2009) 1169–1189.
- R.V.A. Krishnamoorthy, Review on natural fiber reinforced composites, Mater. Today: Proc.16 (2019) 897–906.
- L.G.T. X Li, S. Panigrahi, W.J. Crerar, The Influence of Fiber Content on Properties of Injection Molded Flax Fiber-HDPE Biocomposites, American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, St. Joseph, Michigan, 2006.
- J.I.P. Wambua, I. Verpoest, Natural fibres: can they replace glass in fibre reinforced plastics? Compos. Sci. Technol. 63 (9) (2003) 1259–1264.
- F.A. O, International Year of Natural Fibers, International year of Natural Fibers Coordinating Unit, Trade and Markets Division, 2009.
- J.J. Dn Saheb, Natural Fiber Polymer Composites: a Review, Advance Polymer Technology, 1999.
- H.-y. M, F. DavidHui, Natural fibre-reinforced composites for bioengineering and environmental engineering applications, Compos. B Eng. 40 (7) (2009) 655–663. [CrossRef]
- M. N, N.H. M M, Treatments of Natural Fibre as Reinforcement in Polymer Composites-Short Review, researchgate, May 2021.
- J.K. Pandey, S.H. Ahn, C.S. Lee, “Recent advances in the application of natural fiber based composites”, Macromol. Mater. Eng. 295 (11) (2010) 975–989.
- S. Oztürk, “ Effect of fibre loading on the mechanical properties of kenaf and fiberfrax fibre-reinforced phenol-formaldehyde composites”, J. Compos. Mater. 44 (2010) 2265–2288.
- R.D. Anandjiwala, S. Blouw, Composites from bast fibres—prospects and potential in the changing market environment, J. Nat. Fibers 4 (2) (2007 2007) 91–901.
- M.R. Sanjay, A. Gr, B. Yogesha, Study on mechanical properties of natural—glass fibre reinforced polymer hybrid composites: a review, Mater. Today Proc. 2 (4) (2015) 2959–2967.
- K.N.B.S. Basavarajappa, Applications of biocomposite materials based on natural fibers from renewable resources: a review, Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 23 (2) (May 2015).
- M.R. Hss Shekar, Green composites: a review, Mater. Today Proc. 5 (1) (2018) 2518–2526.
- S. S. Kamatha, D. Sampathkumarb, and B. Bennehallia, "A Review on Natural Areca Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composite Materials," ed.
- Natural fibre-reinforced polymer composites and nanocomposites for automotive applications », in: J. Njuguna, P. Wambua, K. Pielichowski, S. Kalia, K. BS, I. Kaur (Eds.), Cellulose Fibers: Bio- and Nano-Polymer Composites: Green Chemistry and Technology, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 2011, pp. 661–700.
- N.K. T Mukherjee, PLA based biopolymer reinforced with natural fibre: a review, J. Polym. Environ. 19 (3) (2011) 714–725.
- L. Mohammed, M.N.M. Ansari, G. Pua, M. Jawaid, M.S. Islam, A review on natural fiber reinforced polymer composite and its applications, International Journal of Polymer Science 2015 (2015), 243947.
- S. Jayavani, H. Deka, T.O. Varghese, Recent development and future trends in coir fiber reinforced green polymer composites: review and evaluation, Polym. Compos. 37 (11) (2016) 3296–3309.
- M.F. D Dai, Wood fibres as reinforcements in natural fibre composites: structure, properties, processing and applications, in: H.A. S R (Ed.), Natural Fibre Composites, Woodhead, Cambridge, 2014, pp. 3–65.
- M.J. John, B. Francis, K.T. Varughese, Effect of chemical modification on properties of hybrid fiber biocomposites, Composer A 39 (2) (2008) 352–363.
- C. Baley,, AM, Fibres naturelles de renfort pour mat´eriauX composites ». Techniques de l’Inge´nieur, 5 130, 2005, pp. 1–12.
- F.M.A. L, O.M. Omari, Sustainable Biocomposites: Challenges, Potential and Barriers for Development, vol. 11, Chapter Green Energy Technol. , 2017.
- Material profiles », in: M.F. Ashby, M.F. Ashby (Eds.), Materials and the Environment, second ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, 2013, pp. 459–595.
- Azom, "Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)—Properties and Applications—Supplier Data by Goodfellow," ed.
- H. Ku, H. Wang, N. Pattarachaiyakoop, M. Trada, A review on the tensile properties of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites, Composer Part B 42 (2011 2011) 856–873.Author 1, A.; Author 2, B. Title of the chapter. In Book Title, 2nd ed.; Editor 1, A., Editor 2, B., Eds.; Publisher: Publisher Location, Country, 2007; Volume 3, pp. 154–196.
| Samples | Implementation |
|---|---|
| Storage silos, biogas containers, fuel containers, post boxes, etc. | Storage devices |
| Snowboards, frames, bicycle, ball, tennis racket, | leisure and sport goods |
| Laptops cases mobile cases, | Electronics appliances |
| Carpet, mats, sacking, hessians, bags, ropes, pipes, covers, units, bath, shower, helmets, paperweights, helmets, suitcases, lampshades, partitions, food trays, Profiles of door-frame, interior paneling, door panels, Fencing elements, chairs, and tables |
Utility and household products |
| Panel for false and partition ceiling, door and window frames, floor, wall, partition boards, roof tiles, bridge, railing, transportable buildings that are resilient to natural disasters. | Construction and building sector |
| Architectural moldings, interior paneling, boats, railway and automobile coach interior, spare-wheel pan, spare tyre covers, parcel shelves, decking, trunk liners, pallets, car door, dash boards, headliners, seat backs, door panels | Aviation, transportation and automobile sector |
| Applicability | Requirement | Effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Overall programs for aerospace | *Less weightage | * Use of low density materials * Stiffened structures or thin-walled box * Semi-monocoque construction * Composites * Al-alloys * Wood * High weight strain and weight/stiffness |
||
| *Every space program | • Elevated dependability | * Certification: evidence of design * Ensure accurate data Tight quality control * Extensive testing to |
||
| * Vehicles for passengers | * Safety of passengers | * Comprehensive testing: Reliability * Using materials that are fire retardant |
||
| Reusable Spacecraft Aircraft | *Durability: Corrosion and fatigue Vacuum Radiation Thermal Degradation |
* High-integrity thin materials * Thorough testing in the necessary setting * Damage and safe-life, life extension issues * Issues with damage, safe life, and life extension * There is no fatigue limit for al-alloys. * Thorough fatigue testing and analysis |
||
| Spaceships Reusable aircraft |
Performance in aerodynamics |
*Machinability: N/C Milling and Molding *Intricately curved shapes *Dynamics *Extremely intricate loading *Deformed shape-aeroelasticity *Control surfaces and flexible, thin, wings |
||
| *Every Aerospace initiative |
*Multiple functions or roles |
*Application: composites with useful characteristics *Effective design |
||
| Airplanes, primarily fighters but some passenger |
*Fly-by-wire | *EMI protection *Prolonged usage of devices and computers *Elevator-servo-elevator *Arrangement-Control Relationships |
||
| *Particular use in military aerospace | *Stealth | *Stealth coatin *Aircraft shape and Specific surface |
||
| *Aircraft | *Weather-Related Operations | *Erosion resistance, lightning protection | ||
| Thermosets | Thermo-plastics | |||
| Creates cross-linked networks during heating-curing polimerization | No alteration in composition | |||
| Polyimides | Polyester | Phenolics | Epoxies | PPS, PEEK |
| * Brittle *Complicated to handle *3000C high temperature application |
* Recommended for general use at room temperature * Simple to employ *Low cost |
* Difficult to obtain composites of high quality * Reduced viscosity *High temperature consumption * Simple to operate *Less expensive |
*Comparatively expensive *Moderately high temperature* Most often used (80% of all composites) | *Process is challenging since a high temperature of 400–3000C is needed. *High resilience to damage |
| High shrinkage (about 7.5 percent) | Volatiles released while curing More shrinkage |
*No volatiles are released when curing *Less shrinkage |
||
|
*Low Temperature *Brittle *Broad spectrum of propetiles, albeit less so than epoxies *Natural stability in the face of oxidation * Strong resilience to chemicals |
*More brittle than epoxy *Good resistance to fire and naming *Natural stability in the face of Oxidations |
May be polymerized in a number of ways, yielding a wide range of structures, morphologies, and characteristics. | ||
| Challenging to prepare | *Less stable storage and challenging preparation | Sufficient storage stability for preparing | Endless existence in storage. But challenging to prepare | |
| Less moisture-sensitive than epoxy | • Absorbs moisture, but molasses has no discernible impact on its operational range. | Long-term ultra violet degradation. Complete wetness (5–6%), which causes temperature pastries to expand and degrade | Absence of moisture absorption | |
| Fibers | Global Production (×103 t) |
Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | 16000000 | China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Bangladesh | [90,91] |
| Corn | 122080 | USA, China, brazil, Argentina, India, | [92] |
| Cotton | 21400000 | Asia, USA | [93] |
| Ramie | 10000 | India, China, Brazil, Philippines | [94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104] |
| Kenaf | 97000 | India, Bangladesh, United States | [94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,105] |
| Bamboo | 3000 | India, China, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines | [94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102] |
| Oil palm | 4000 | Malaysia, Indonesia | [94,95,98,99,106,107] |
| Flax | 83000 | Canada, France, Belgium | [94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103] |
| Abaca | 7000 | Philippines, Ecuador, Costa Rica | [94,95,96,97,98,99,108] |
| Banana | 1920 | Latin America and the Caribbean Asia Africa | [109] |
| Jute | 230000 | India, China, Bangladesh | [94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,110] |
| Pineapple | 7400 | Philippines, Thailand, Indonesia | [94,95,98,99,100,101,102,104] |
| Sisal | 37800 | Tanzania, Brazil, Kenya | [94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,104,108,110,111] |
| Coir | 10000 | India, Sri Lanka, Philippines, Malaysia | [94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,112,113,114,115,116,117] |
| Coconut | 7700 | Indonesia, Philippines, India, Sri Lanka | [118] |
| Sugar can bagasse | 7500000 | India, Brazil, China | [94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102] |
| Fibre Code | Fibres | Micro-fibrillar angle [◦] | Lignin (wt%) | Hemicellulose (wt%) | Cellulose (wt%) | Moisture content (%) | Reference |
| NF 1 | Rice | 20 | 19–28 | 35–45 | 7,9 | [94,95,96,98,99,100,101,102,108,119,120] | |
| NF 2 | Corn | - | 7,4 | 46 | 41,7 | 8,5 | [121,122] |
| NF 3 | Cotton | 82,7–92 | 9,8 | [121,123] | |||
| NF 4 | Ramie | 61,85–85 | 3–7,58 | 0,5–9,06 | 69–83 | 9 | [94,95,96,100,101,119,120,121,124,125,126] |
| NF 5 | Kenaf | 2 2–6,2 | 9 8–21 | 20–33 | 31–72 | 9,2 | [94,95,96,98,99,100,101,102,108,114,119,120,121,124,125,127,129,130] |
| NF 6 | Bamboo | - | 21–31 | 17,2–43,8 | 22,8–56,7 | 8,9 | [94,95,96,100,101,102,119,120,121,130] |
| NF 7 | Oil palm | 24,45–29 | 19,06 | 47,91–65 | 11 | [94,95,96,119,120,121,138] | |
| NF 8 | Flax | 5–10 | 2–5 | 10,37–20,6 | 64,1–75 | 7 | [94,95,96,98,99,100,101,102,108,114,121,122,124,127,128,129,133,134,135,136,137] |
| NF 9 | Abaca | 20–25 | 7–12,4 | 20–25 | 56–63 | 15 | [94,95,96,98,99,100,101,102,108,119,120,121,123,124,128,129,138,139] |
| NF 10 | Banana | 11–12 | 5–10 | 10–24 | 60–65 | 12,1 | [100,101,121,124,140,141] |
| NF 11 | Jute | 8 | 5–13 | 13–20,4 | 61–71 | 12 | [94,95,96,98,99,100,101,102,108,114,119,120,121,124,127,128,129,133,136,142,143] |
| NF 12 | Pineapple | 5-12,7 | 18 | 70–82 | 13 | [94,95,96,101,102,112,119,120,121] | |
| NF 13 | Sisal | 10–25 | 8–14 | 10–38,2 | 60–78 | 11 | [94,95,96,98,99,100,101,102,108,114,119,120,121,127,128,129,133,143,144,145,146] |
| NF 14 | Coir | 30,45 | 40–45 | 0,15–0,25 | 32–43 | 10 | [94,95,96,98,99,100,101,102,108,114,119,120,121,124,125,127,128,129,143,147] |
| NF 15 | Coconut | 8–13,1 | 4–20 | 70–77,6 | 8,2 | [121,123,148] | |
| NF 16 | Sugar can bagasse | 22,3–25,3 | 16,8–31,8 | 41,1–55,2 | 8,8 | [94,95,96,119,120,121,149,150] |
| Fibre Code | Fiber source | Elongation at break (%) | Young’s modulus (GPa) | Tensile strength | Density (g/cm3) |
References |
| NF 1 | Rice | 2,2 | 0,3–2,6 | 19–135 | 1,4 | [100,101,102,116,151] |
| NF 2 | Corn | 3–4,7 | 10,1–16,3 | 355–580 | 1,2–1,4 | [95,96,105,115,121,152,153,154,155,156,157,158] |
| NF 3 | Cotton | 3–10 | 5,5–12,6 | 45,5–1000 | 1,5–1,6 | [95,96,105,114,121,152,153,154,155,156,157] |
| NF 4 | Ramie | 1,2–8 | 24,5–128 | 348–938 | 1,45–1,5 | [94,96,105,114,121,152,153,154,155,156,157,158] |
| NF 5 | Kenaf | 1,6–6,9 | 2,86–60 | 215,4–1191 | 0,6–1,5 | [94,95,96,98,99,100,101,102,103,114,121,128,129,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,165,166] |
| NF 6 | Bamboo | 1,5-11 | 11–17 | 140–230 | 0,6–11 | [121,159] |
| NF 7 | Oil palm | 8–25 | 1–9 | 92-1200 | 0,7–1,55 | [121] |
| NF 8 | Flax | 1,2–10 | 24–80 | 88–1600 | 0,6–1,5 | [94,95,96,105,110,114,128,129,134,143,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164,166,167,168] |
| NF 9 | Abaca | 3–10 | 3–12 | 220–980 | 1,5 | [96,99,105,107,112,113,114,121,152,153,154,155,156,157,160,169,170] |
| NF 10 | Banana | 3–53 | 12–33,8 | 350–980 | 1,35 | [96,105,114,121,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,169] |
| NF 11 | Jute | 1,16–8 | 10–55 | 385–850 | 1,3–1,5 | [96,105,114,121,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,169] |
| NF 12 | Pineapple | 1–14,5 | 60–82 | 170–1672 | 0,8–1,6 | [95,96,105,114,121,152,153,154,155,156,157,158] |
| NF 13 | Sisal | 2–25 | 9–38 | 80–840 | 1,3–1,5 | [94,95,96,99,100,101,102,105,110,114,115,121,127,128,129,143,144,152,166,167,168,171,172] |
| NF 14 | Coir | 14,21–59,9 | 1,27–6 | 106–593 | 1,1–1,6 | [94,96,105,110,114,115,121,127,128,129,143,144,152,166,167,168,172] |
| NF 15 | Coconut | 10-23 | 21,1 | 150 | 0,43 | |
| NF 16 | Sugar can bagasse | 1,1 | 17–27,1 | 20–290 | 1,2–1,5 | [95,96,105,114,121,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159] |
| Fibre Code | Fibers | Width of lumen (micron) |
Thickness of single cell wall (micron) |
Fiber diameter (mm) |
Fiber length (mm) |
| NF 1 | Rice | 8,7 | 1,2 | 15,5 | 8,7 |
| NF 2 | Corn | 20,1 | 1,4 | 26,7 | 20,1 |
| NF 3 | Cotton | 16,4 | 56,0 | 45,0 | 16,4 |
| NF 4 | Ramie | 13,0 | 60,4 | 80,0 | 13,0 |
| NF 5 | Kenaf (core) | 22,7 | 1,1 | 37,0 | 22,7 |
| NF 6 | Bamboo | 8,6 | 9,0 | 17,8 | 3,0 |
| NF 7 | Oil palm | 9,8 | 11 | 25,0 | 1,4 |
| NF 8 | Flax | 6,42 | 20,0 | 38,0 | 65,0 |
| NF 9 | Areca | 18,1 | 1,2 | 476 | 60 |
| NF 10 | Banana | 22,4 | 1,5 | 30,0 | 4,2 |
| NF 11 | Jute | 7,6 | 11,3 | 30,0 | 6,0 |
| NF 12 | Pineapple | 3 | 18,3 | 80,0 | 9,0 |
| NF 13 | Sisal | 12,0 | 25,0 | 47,0 | 8,0 |
| NF 14 | Coir | 21 | 0,06 | 12,0 | 0,3 |
| NF 15 | Coconut | 3,2 | 8,0 | 14,0 | 1,0 |
| NF 16 | Sugar can bagasse | 19,1 | 9,4 | 40,0 | 2,8 |
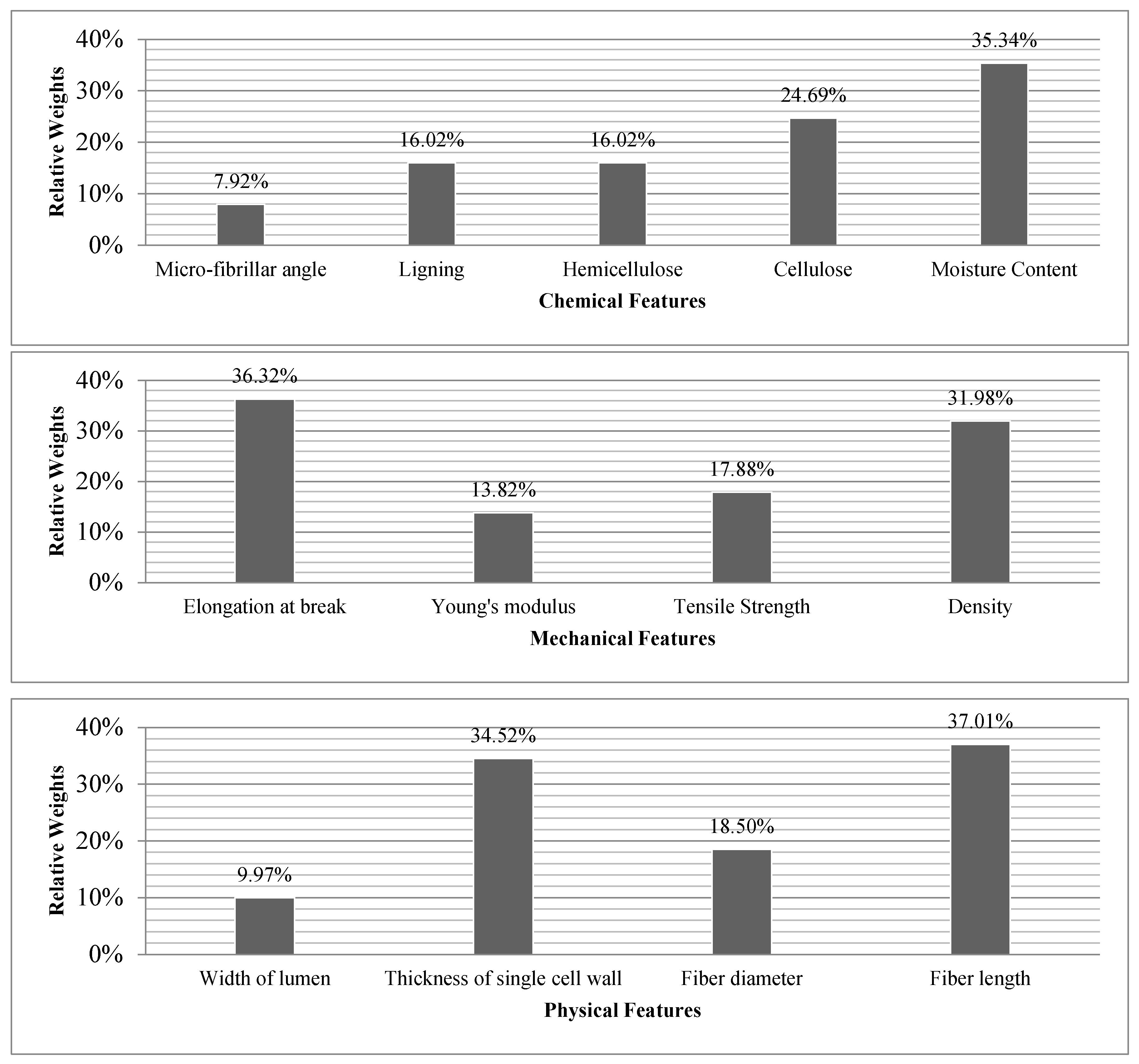
| Criteria | % |
| Physical | 16,98 |
| Mechanical | 44,29 |
| Chemical | 38,73 |
| Micro-fibrillar angle | Lignin | Hemicellulose | Cellulose | Moisture content | Normalized Principal Eigenvector | |||
| Chemical Features | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Micro-fibrillar angle | 1 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/4 | 1/2 | 7,92% | ||
| Lignin | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 16,02% | ||
| Hemicellulose | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 16,02% | ||
| Cellulose | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1/3 | 24,69% | ||
| Moisture content | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 35,34% | ||
| Mechanical Features | Elongation at break | Young's modulus | Tensile strength | Density | Normalized Principal Eigenvector | |||
| Elongation at break | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 36,32% | |||
| Young's modulus | 1/2 | 1 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 13,82% | |||
| Tensile strength | 1/3 | 2 | 1 | 1/2 | 17,88% | |||
| Density | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 31,98% | |||
| Physical Features | Width of lumen | Thickness of single cell wall | Fiber diameter | Fiber length | Normalized Principal Eigenvector | |||
| Width of lumen | 1 | 1/3 | 1/2 | 1/4 | 9,97% | |||
| Thickness of single cell wall | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 34,52% | |||
| Fiber diameter | 2 | 1/2 | 1 | 1/2 | 18,50% | |||
| Fiber length | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 37,01% | |||
| Normalized | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro-fibrillar angle | 0,062 | 0,062 | 0,062 | 0,224 | 0,013 | 0,062 | 0,062 | 0,023 | 0,069 | 0,035 | 0,025 | 0,027 | 0,054 | 0,093 | 0,062 | 0,062 |
| Ligning | 0,081 | 0,030 | 0,062 | 0,021 | 0,060 | 0,105 | 0,107 | 0,014 | 0,039 | 0,030 | 0,036 | 0,062 | 0,044 | 0,171 | 0,042 | 0,094 |
| Hemicel. | 0,073 | 0,144 | 0,062 | 0,016 | 0,083 | 0,094 | 0,060 | 0,047 | 0,070 | 0,053 | 0,052 | 0,056 | 0,075 | 0,001 | 0,038 | 0,076 |
| Cellulose | 0,042 | 0,044 | 0,091 | 0,080 | 0,054 | 0,041 | 0,059 | 0,073 | 0,062 | 0,066 | 0,069 | 0,080 | 0,072 | 0,039 | 0,077 | 0,050 |
| Moisture Content | 0,049 | 0,053 | 0,061 | 0,056 | 0,057 | 0,055 | 0,068 | 0,043 | 0,093 | 0,075 | 0,074 | 0,081 | 0,068 | 0,062 | 0,051 | 0,055 |
| Elong. | 0,013 | 0,023 | 0,039 | 0,027 | 0,025 | 0,037 | 0,098 | 0,033 | 0,039 | 0,166 | 0,053 | 0,046 | 0,080 | 0,218 | 0,098 | 0,007 |
| Young's modulus | 0,004 | 0,033 | 0,022 | 0,188 | 0,076 | 0,036 | 0,012 | 0,128 | 0,018 | 0,055 | 0,080 | 0,175 | 0,058 | 0,009 | 0,052 | 0,054 |
| Tensile Strength | 0,010 | 0,061 | 0,010 | 0,085 | 0,081 | 0,024 | 0,085 | 0,111 | 0,096 | 0,087 | 0,083 | 0,121 | 0,060 | 0,046 | 0,020 | 0,020 |
| Density | 0,057 | 0,053 | 0,063 | 0,060 | 0,042 | 0,235 | 0,045 | 0,042 | 0,061 | 0,055 | 0,057 | 0,049 | 0,057 | 0,055 | 0,017 | 0,055 |
| Width of lumen | 0,041 | 0,095 | 0,077 | 0,061 | 0,107 | 0,041 | 0,046 | 0,030 | 0,085 | 0,106 | 0,036 | 0,014 | 0,057 | 0,099 | 0,015 | 0,090 |
| Thicknes | 0,005 | 0,006 | 0,238 | 0,257 | 0,005 | 0,038 | 0,047 | 0,085 | 0,005 | 0,006 | 0,048 | 0,078 | 0,106 | 0,000 | 0,034 | 0,040 |
| Fiber D. | 0,015 | 0,026 | 0,044 | 0,079 | 0,036 | 0,018 | 0,025 | 0,037 | 0,469 | 0,030 | 0,030 | 0,079 | 0,046 | 0,012 | 0,014 | 0,039 |
| Fiber length | 0,036 | 0,083 | 0,068 | 0,054 | 0,094 | 0,012 | 0,006 | 0,269 | 0,248 | 0,017 | 0,025 | 0,037 | 0,033 | 0,001 | 0,004 | 0,012 |
| Priorities | ||||||||||||||||
| Micro-fibrillar angle | 0,005 | 0,005 | 0,005 | 0,018 | 0,001 | 0,005 | 0,005 | 0,002 | 0,005 | 0,003 | 0,002 | 0,002 | 0,004 | 0,007 | 0,005 | 0,005 |
| Ligning | 0,013 | 0,005 | 0,010 | 0,003 | 0,010 | 0,017 | 0,017 | 0,002 | 0,006 | 0,005 | 0,006 | 0,010 | 0,007 | 0,027 | 0,007 | 0,015 |
| Hemicel. | 0,012 | 0,023 | 0,010 | 0,003 | 0,013 | 0,015 | 0,010 | 0,008 | 0,011 | 0,009 | 0,008 | 0,009 | 0,012 | 0,000 | 0,006 | 0,012 |
| Cellulose | 0,010 | 0,011 | 0,023 | 0,020 | 0,013 | 0,010 | 0,015 | 0,018 | 0,015 | 0,016 | 0,017 | 0,020 | 0,018 | 0,010 | 0,019 | 0,012 |
| Moisture Content | 0,017 | 0,019 | 0,021 | 0,020 | 0,020 | 0,019 | 0,024 | 0,015 | 0,033 | 0,026 | 0,026 | 0,028 | 0,024 | 0,022 | 0,018 | 0,019 |
| Elong. | 0,005 | 0,008 | 0,014 | 0,010 | 0,009 | 0,013 | 0,036 | 0,012 | 0,014 | 0,060 | 0,019 | 0,017 | 0,029 | 0,079 | 0,036 | 0,002 |
| Young's modulus | 0,000 | 0,005 | 0,003 | 0,026 | 0,011 | 0,005 | 0,002 | 0,018 | 0,003 | 0,008 | 0,011 | 0,024 | 0,008 | 0,001 | 0,007 | 0,007 |
| Tensile Strength | 0,002 | 0,011 | 0,002 | 0,015 | 0,014 | 0,004 | 0,015 | 0,020 | 0,017 | 0,016 | 0,015 | 0,022 | 0,011 | 0,008 | 0,004 | 0,004 |
| Density | 0,018 | 0,017 | 0,020 | 0,019 | 0,014 | 0,075 | 0,014 | 0,014 | 0,019 | 0,017 | 0,018 | 0,016 | 0,018 | 0,017 | 0,006 | 0,017 |
| Width of lumen | 0,004 | 0,009 | 0,008 | 0,006 | 0,011 | 0,004 | 0,005 | 0,003 | 0,009 | 0,011 | 0,004 | 0,001 | 0,006 | 0,010 | 0,002 | 0,009 |
| Thicknes | 0,002 | 0,002 | 0,082 | 0,089 | 0,002 | 0,013 | 0,016 | 0,029 | 0,002 | 0,002 | 0,017 | 0,027 | 0,037 | 0,000 | 0,012 | 0,014 |
| Fiber D. | 0,003 | 0,005 | 0,008 | 0,015 | 0,007 | 0,003 | 0,005 | 0,007 | 0,087 | 0,005 | 0,005 | 0,015 | 0,009 | 0,002 | 0,003 | 0,007 |
| Fiber length | 0,013 | 0,031 | 0,025 | 0,020 | 0,035 | 0,005 | 0,002 | 0,100 | 0,092 | 0,006 | 0,009 | 0,014 | 0,012 | 0,000 | 0,002 | 0,004 |
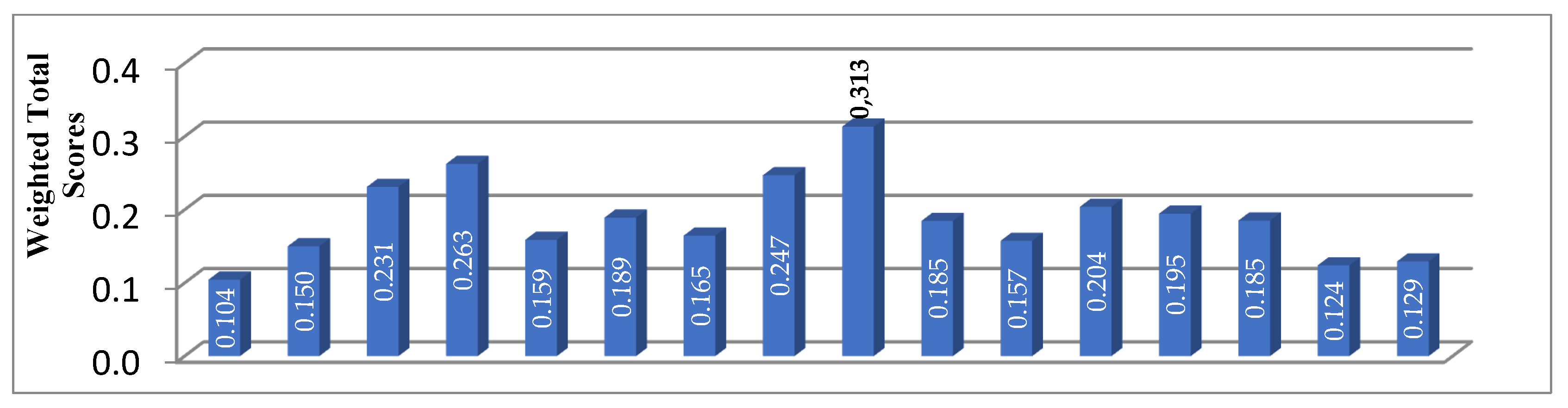
| Weighted Score | 0,104 | 0,150 | 0,231 | 0,263 | 0,159 | 0,189 | 0,165 | 0,247 | 0,313 | 0,185 | 0,157 | 0,204 | 0,195 | 0,185 | 0,124 | 0,129 |
| Polymer code | Polymer material |
Elongation at break (%) |
Modulus of elasticity(GPa) | Tensile strength (MPa) | Density (g/cm3) | References |
| P 1 | Vinyl ester resin | 2 | 2–4,5 | 40–90 | 1,2–1,5 | [175,176,177] |
| P 2 | Polystyrene | 1–3,6 | 1,2–2,6 | 35,9–56,6 | 1,04–1,06 | [100,101,102,142] |
| P 3 | Epoxy | 1–6 | 3–6 | 35–100 | 1,1–1,4 | [175,176,177] |
| P 4 | Polybutylene terephthalate | 250 | 1,93–3 | 50–60 | 1,30–1,38 | [139] |
| P 5 | Polyethylene terephthalate | 30–300 | 2,76–4,14 | 48,3–72,4 | 1,29–1,40 | [100,101,102,142] |
| P 6 | Polycarbonate | 70–150 | 2–2,44 | 60–72,4 | 1,14–1,21 | [100,101,102,142] |
| P 7 | Nylon 6 | 20–150 | 2,9 | 43–79 | 1,12–1,14 | [175,176,177] |
| P 8 | Polyamide | 30–100 | 1,2–3,2 | 90–165 | 1,12–1,14 | [100,101,102,142] |
| P 9 | High density polyethylene (HDPE) | 2,0–130 | 0,4–1,5 | 14,5–38 | 0,94–0,96 | [175,176,177] |
| P 10 | Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) | 90–800 | 0,055–0,38 | 40–78 | 0,910–0,925 | [175,176,177] |
| P 11 | Acrylonitrile b utadiene styrene | 1,5–100 | 1,1–2,9 | 27,6–55,2 | 1–1,2 | [100,101,102,142] |
| P 12 | PP | 15–700 | 0,95–1,77 | 26–41,4 | 0,899–0,920 | [175,176,177] |
| Normalized | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elongation at break | 0,001 | 0,001 | 0,002 | 0,143 | 0,094 | 0,063 | 0,049 | 0,094 | 0,066 | 0,254 | 0,029 | 0,204 | |
| Young's modulus | 0,115 | 0,067 | 0,159 | 0,088 | 0,123 | 0,078 | 0,102 | 0,078 | 0,032 | 0,007 | 0,067 | 0,085 | |
| Tensile Strength | 0,092 | 0,064 | 0,092 | 0,078 | 0,085 | 0,094 | 0,087 | 0,181 | 0,038 | 0,084 | 0,058 | 0,048 | |
| Density | 0,099 | 0,077 | 0,092 | 0,096 | 0,099 | 0,086 | 0,083 | 0,083 | 0,070 | 0,067 | 0,081 | 0,066 | |
| Priorities | |||||||||||||
| Elongation at break | 0,000 | 0,000 | 0,001 | 0,052 | 0,034 | 0,023 | 0,018 | 0,034 | 0,024 | 0,092 | 0,010 | 0,074 | |
| Young's modulus | 0,016 | 0,009 | 0,022 | 0,012 | 0,017 | 0,011 | 0,014 | 0,011 | 0,004 | 0,001 | 0,009 | 0,012 | |
| Tensile Strength | 0,016 | 0,011 | 0,016 | 0,014 | 0,015 | 0,017 | 0,015 | 0,032 | 0,007 | 0,015 | 0,010 | 0,009 | |
| Density | 0,032 | 0,025 | 0,029 | 0,031 | 0,032 | 0,028 | 0,027 | 0,027 | 0,022 | 0,021 | 0,026 | 0,021 | |
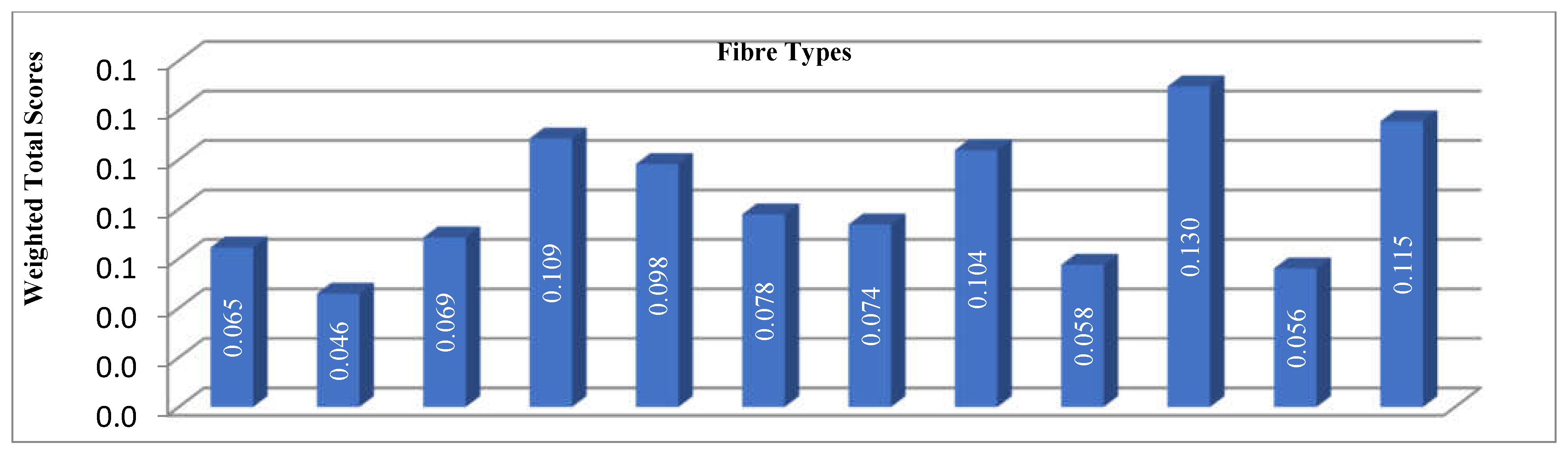
| Total Weighted Score | 0,065 | 0,046 | 0,069 | 0,109 | 0,098 | 0,078 | 0,074 | 0,104 | 0,058 | 0,130 | 0,056 | 0,115 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




