Submitted:
27 September 2024
Posted:
29 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Processing of LLDPE and LLDPE/Buriti Oil
2.2.2. Preparation of LLDPE and LLDPE/Buriti Oil Specimens
2.2.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.7. Mechanical Properties
2.2.8. Hydrophobicity (Contact Angle Measurement)
3. Results and Discussion
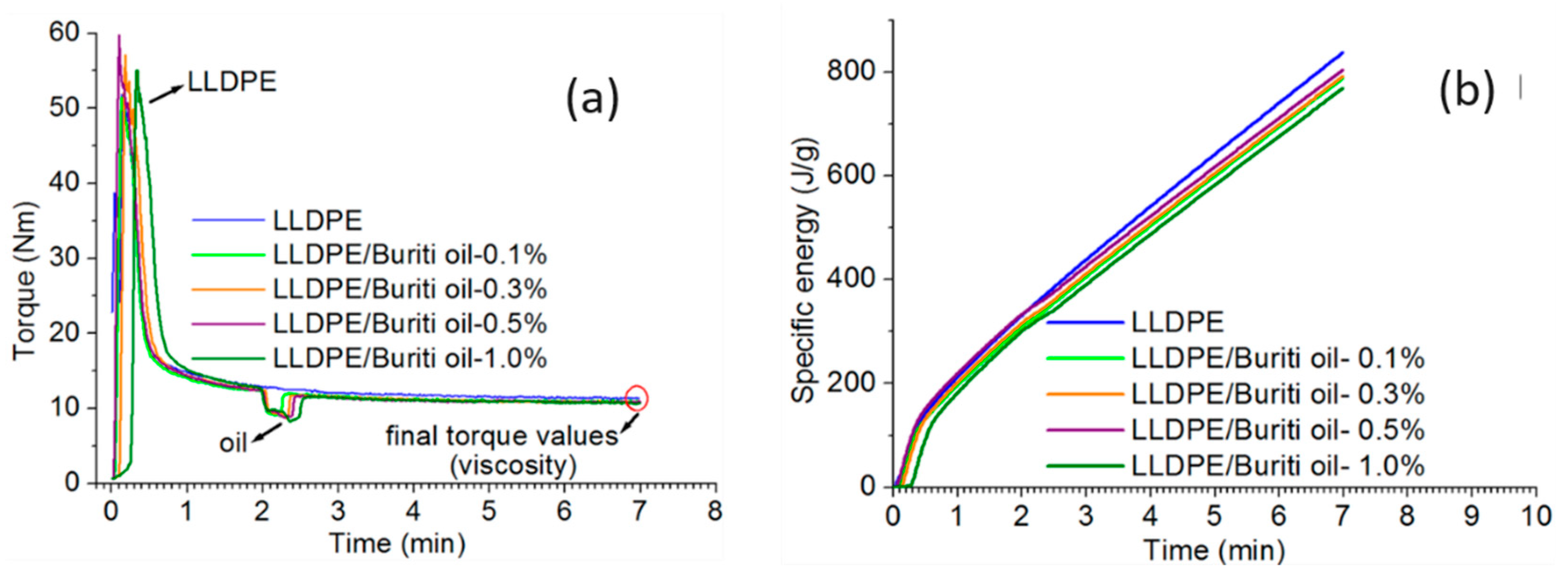
3.1. Torque-Specific Energy-Time Analysis
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
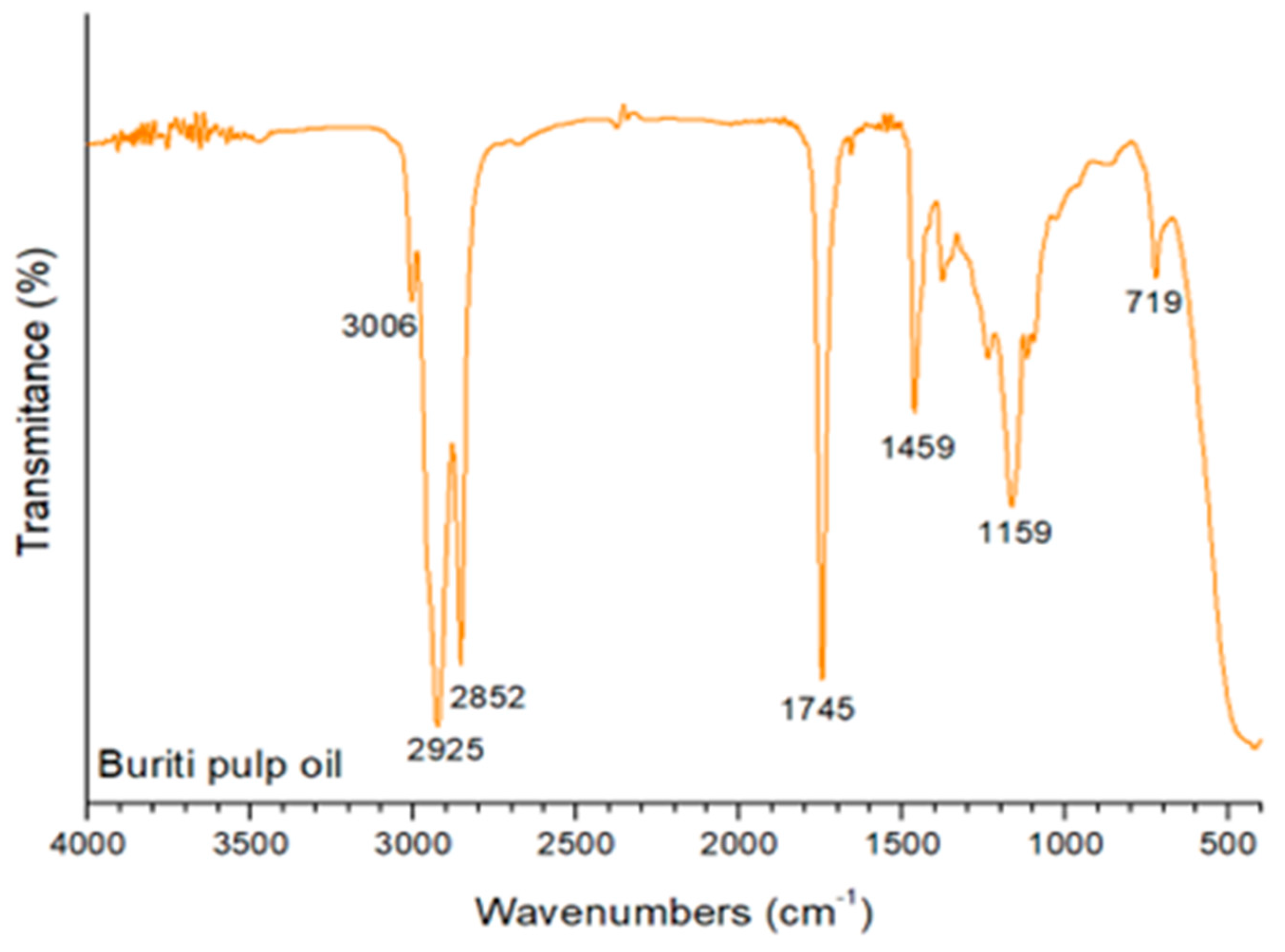
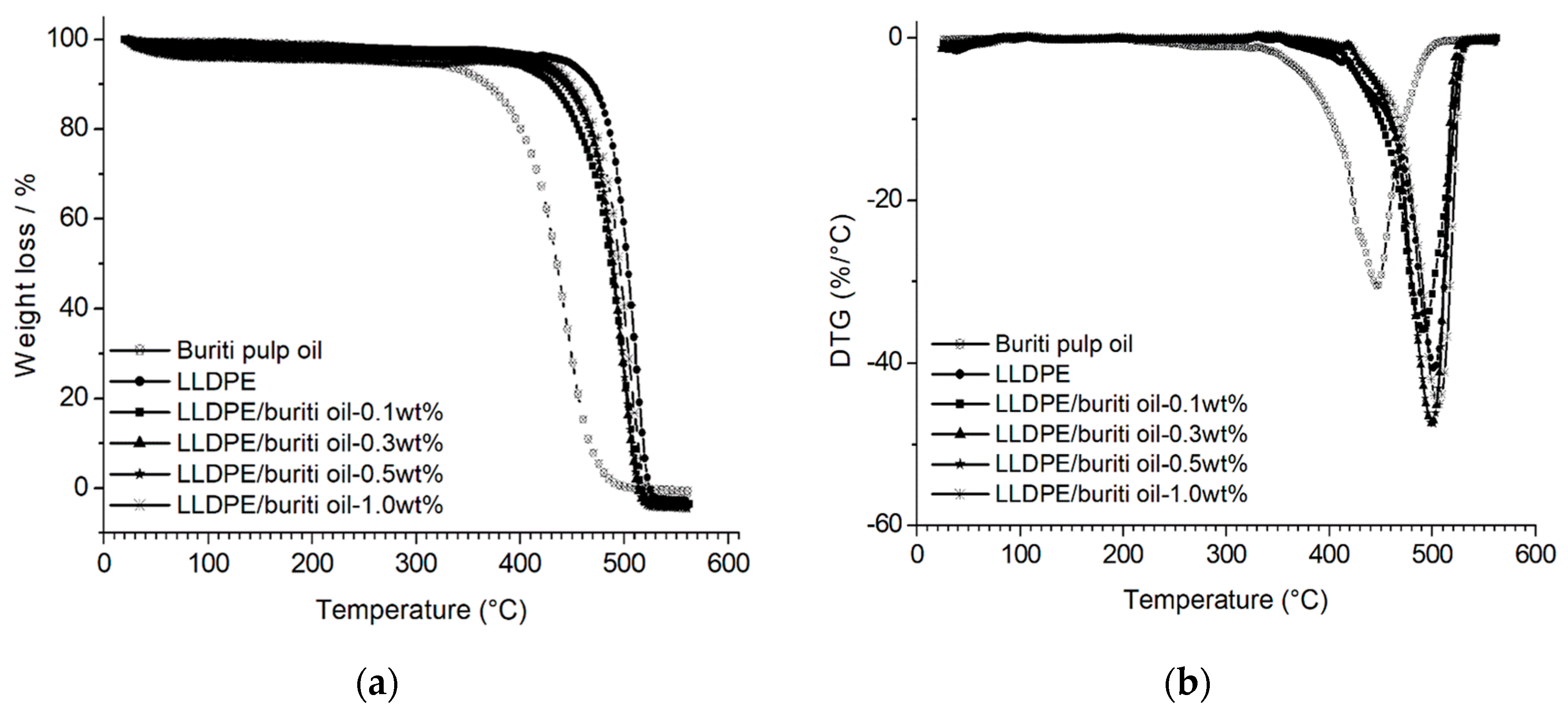
3.3. Thermogravimetry Analysis (TGA)
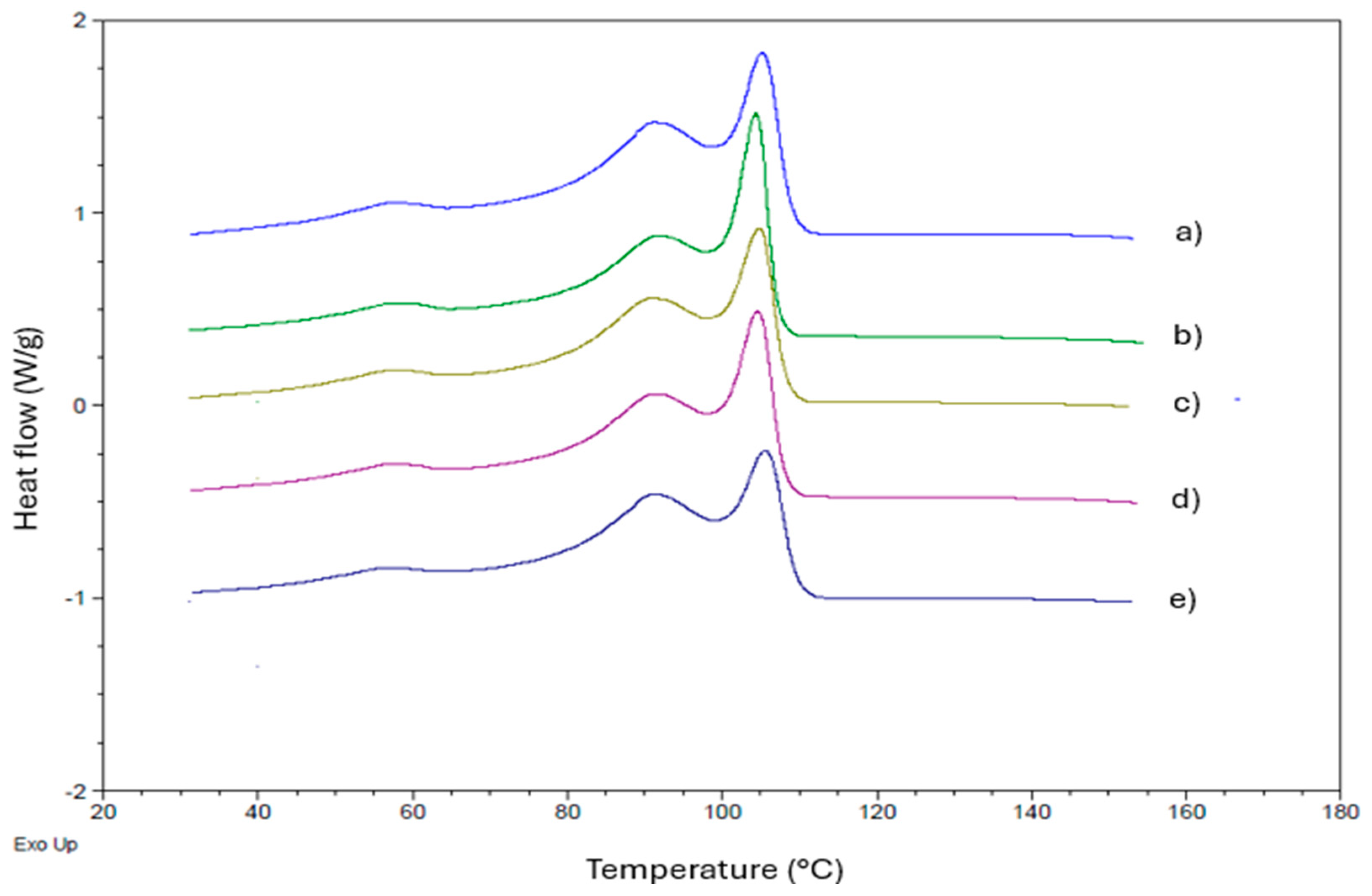
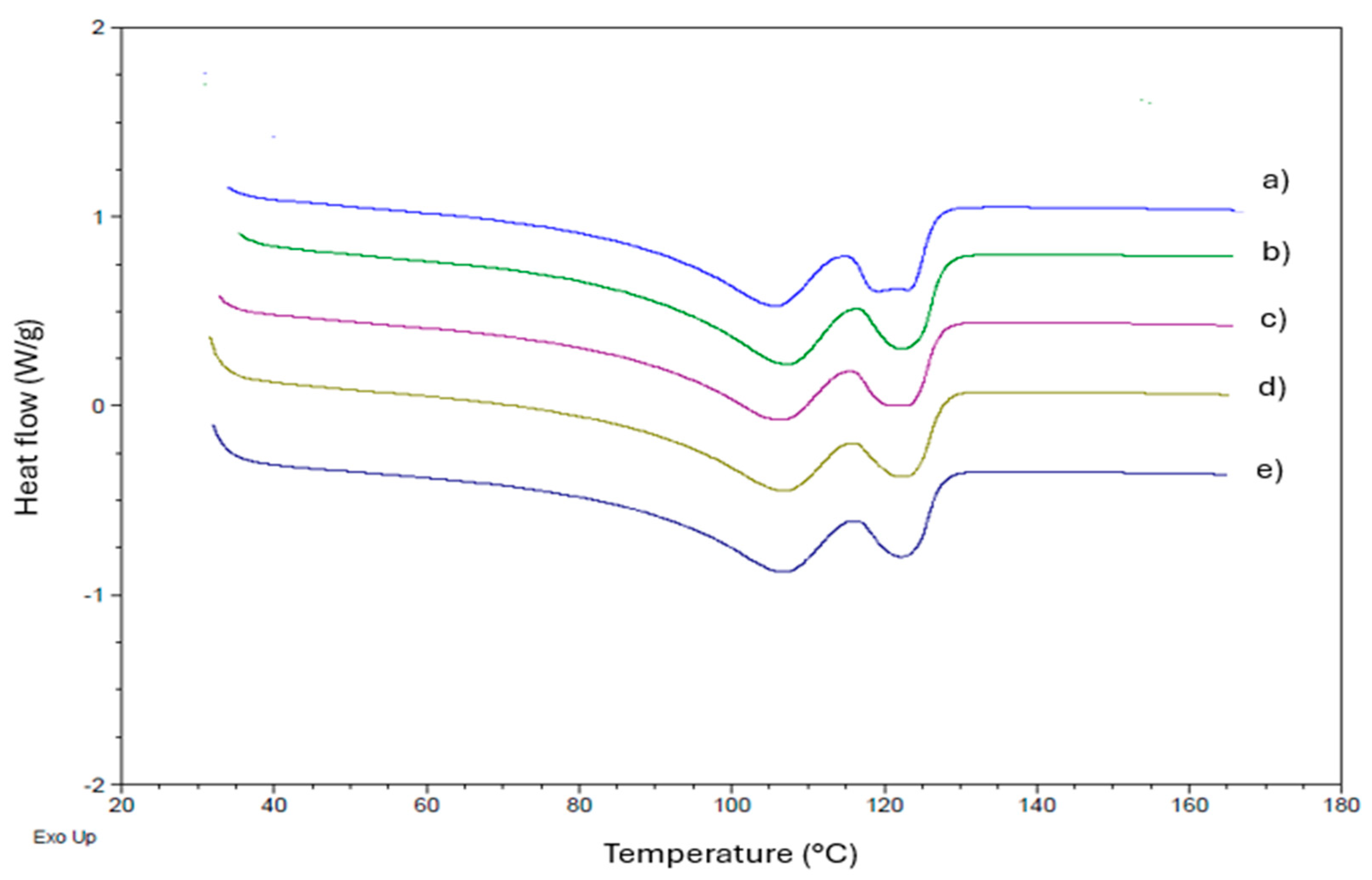
3.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
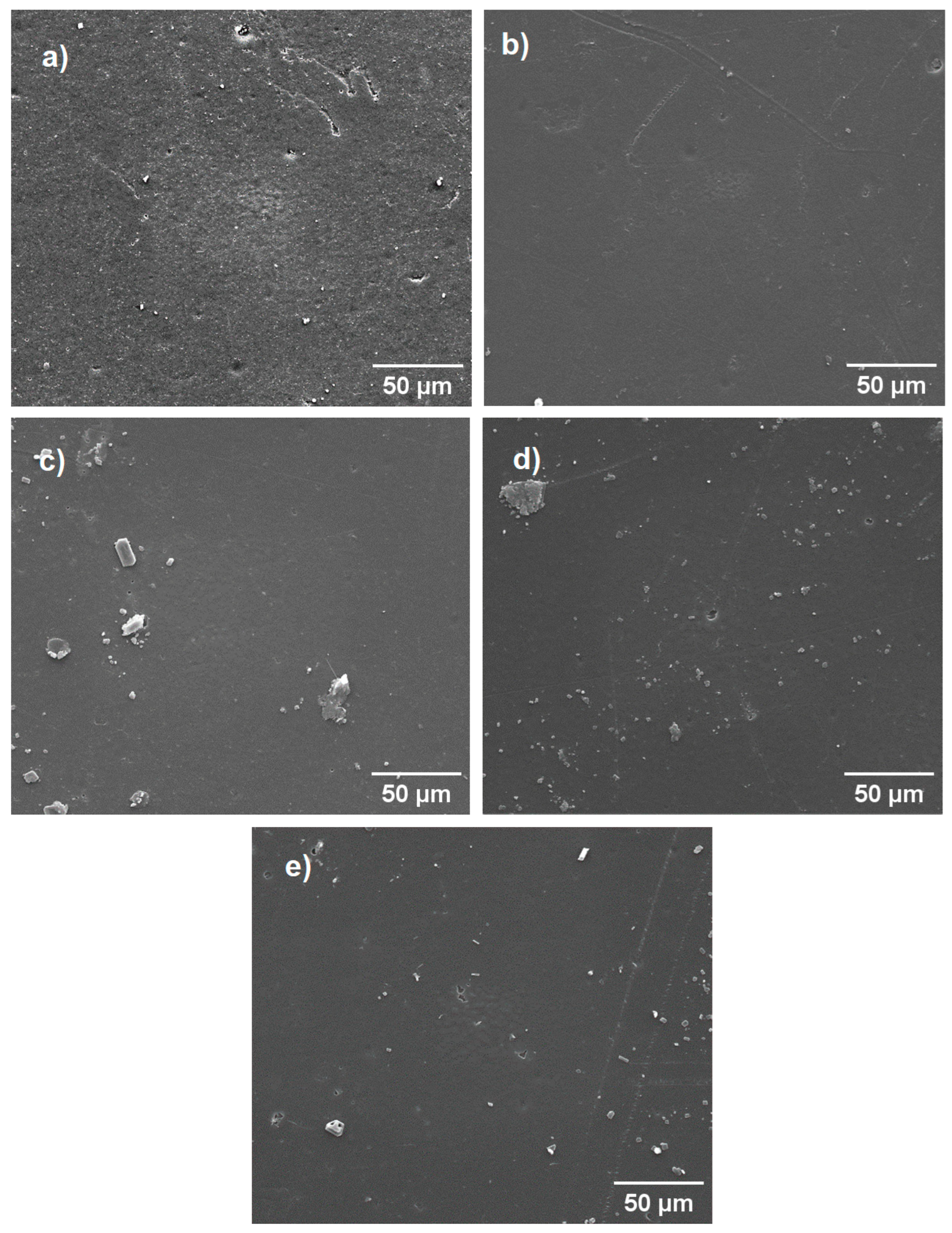
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.6. Contact Angle Analysis
| Sample | Contact Angle [°] | Image |
|---|---|---|
| PELBD Puro | 85,25 (2,01) | 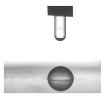 |
| PELBD 0,1 | 87,08 (3,81) | 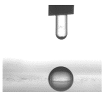 |
| PELBD 0,3 | 88,74 (1,69) | 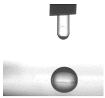 |
| PELBD 0,5 | 89,06 (1,58) | 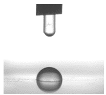 |
| PELBD 1,0 | 100,96 (3,44) | 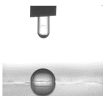 |
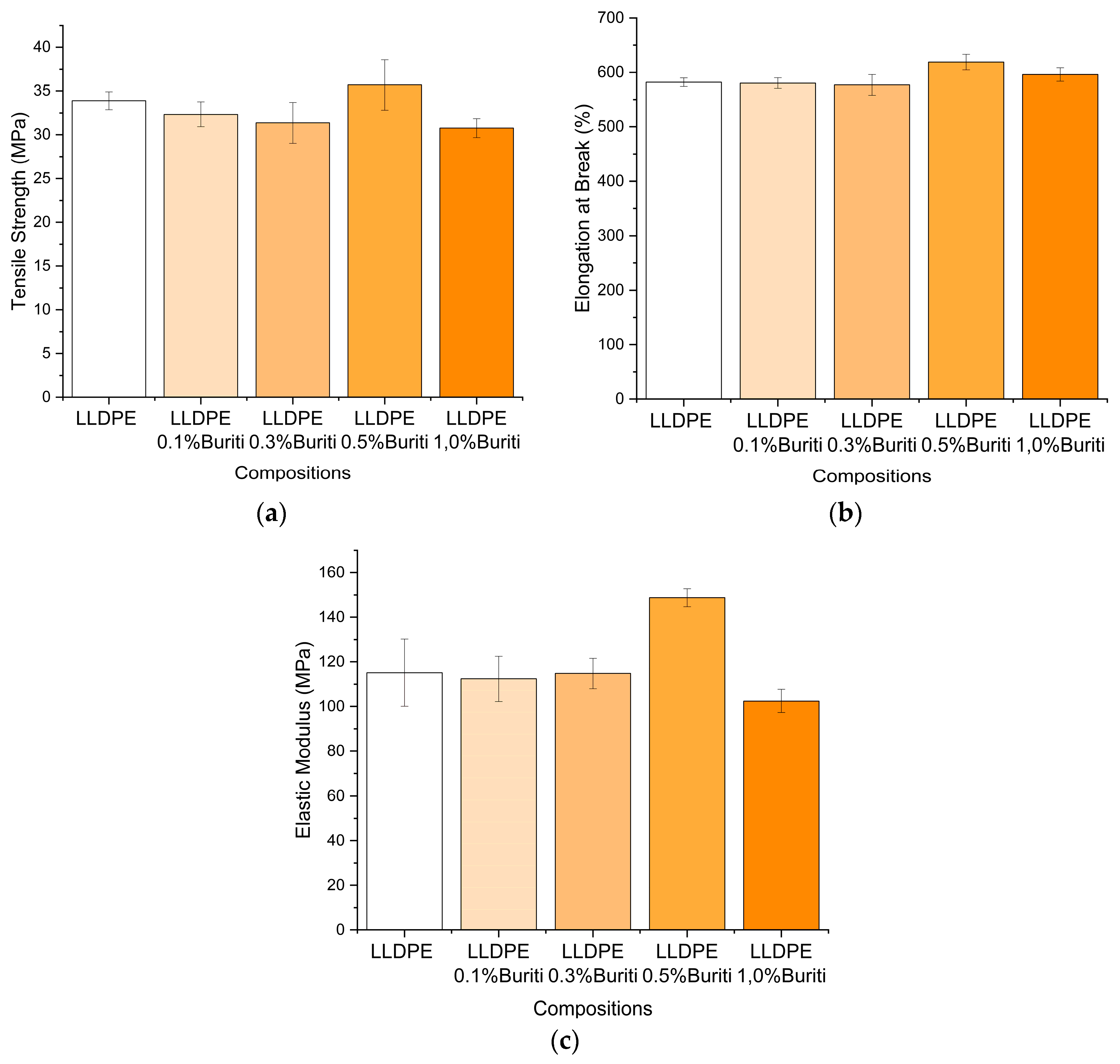
3.7. Mechanical Properties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vieira, M.G.A.; da Silva, M.A.; dos Santos, L.O.; Beppu, M.M. Natural-based plasticizers and biopolymer films: A review. European Polymer Journal 2011, 47, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Brazel, C.S. The plasticizer market: an assessment of traditional plasticizers and research trends to meet new challenges. Progress in Polymer Science 2004, 29, 1223–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marturano, V.; Marotta, A.; Salazar, S.A.; Ambrogi, V.; Cerruti, P. Recent advances in bio-based functional additives for polymers. Progress in Materials Science 2023, 139, 101186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.; Kim, B.S.J. A Trend and Market in Eco-friendly Plasticizers: Review and Prospective. Compos Res 2022, 35, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, X. Chapter 5 - Plasticization and Polymer Morphology. In Innovations in Food Packaging (Second Edition), Second Edition ed.; Han, J.H., Ed.; Food Science and Technology, Academic Press: San Diego, 2014; pp. 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Yu, S.; Liu, F. Synthesis of plasticizer ester using acid-functionalized ionic liquid as catalyst. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2008, 151, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvaéz Rincón, P.; Suárez Palacios, O. Plasticizers. In Polymers and Polymeric Composites: A Reference Series; Palsule, S., Ed.; Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2015. [CrossRef]
- S, C. Plasticizers and flexible PVC; The European Council for Plasticizers and Intermediates, Brussels, 2014.
- Jia, P.; Xia, H.; Tang, K.; Zhou, Y. Plasticizers Derived from Biomass Resources: A Short Review. Polymers 2018, 10, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Oßwald, K.; Langer, B.; Reincke, K. Influence of Plasticizers Basing on Renewable Sources on the Deformation and Fracture Behaviour of Elastomers. In Fatigue Crack Growth in Rubber Materials; Heinrich, G.; Kipscholl, R.; Stoček, R., Eds.; Springer, Cham, 2020; Vol. 286, Advances in Polymer Science. [CrossRef]
- Sanches, S.; Silva-Júnior, J.; Ribeiro-Costa, R. O uso dos óleos vegetais na prevenção do envelhecimento da pele. Research, Society and Development 2021, 10, e44010111941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemmer, D.; Sales, M.J.A.; Resck, I.S. Preparação, caracterização e degradação de blendas PS/TPS usando glicerol e óleo de buriti como plastificantes. Polímeros 2010, 20, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durães, J.; Drummond, A.; Pimentel, T.; et al. Thermal and structural behavior of Buriti oil/poly(methyl methacrylate) and Buriti oil/polystyrene materials. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 2008, 92, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de, F.; Silva, M.; Lopes, P.S.; da Silva, C.F.; Yoshida, C.M.P. Active packaging material based on buriti oil – Mauritia flexuosa L.f. (Arecaceae) incorporated into chitosan films. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2016, 133, 43210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bispo-Jr, A.G.; et al. Red-light-emitting polymer composite based on PVDF membranes and Europium phosphor using Buriti Oil as plasticizer. Materials Chemistry and Physics 2018, 217, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, M.A.D.; Waldman, W.R. Bio-based additives for thermoplastics. Polímeros 2019, 29, e2019030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Garrison, T.F.; Madbouly, S.A.; Kessler, M.R. Recent advances in vegetable oil-based polymers and their composites. Progress in Polymer Science 2017, 71, 91–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, B.; Onwona-Agyeman, B.; Nyankson, E.; et al. Effect of palm oil as plasticizer for compounding polar and non-polar rubber matrix reinforced carbon black composites. Journal of Polymer Research 2023, 30, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.; et al. Investigation of mechanical property, flame retardancy and thermal degradation of LLDPE–wood-fibre composites. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2023, 140, e54656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarnthong, M.; et al. Performance of Moringa Oil as an Effective Bioplasticizer on Static and Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber Vulcanizates. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2024, 12, 6440–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.; Othman, N.; Khimi, R.; Hayeemasae, N. Perspective on opportunities of bio-based processing oil to rubber industry: a short review. Iranian Polymer Journal 2023, 32, 10–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Poompiew, N.; Pongwisuthiruchte, A.; Potiyaraj, P. Application of Different Vegetable Oils as Processing Aids in Industrial Rubber Composites: A Sustainable Approach. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 31384–31389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarth, N.; Mahanwar, P. Modified Vegetable Oil Based Additives as a Future Polymeric Material—Review. Open Journal of Organic Polymer Materials 2015, 5, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarray, A.; Gerbaud, V.; Hemati, M. Polymer-plasticizer compatibility during coating formulation: A multi-scale investigation. Progress in Organic Coatings 2016, 101, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, T.; Goff, J. Plastics and Polymers. In Injection Molding of Thermoplastics Materials — 1; Springer, Boston, MA, 1990. [CrossRef]
- Borah, J.; Chaki, T. Thermogravimetric and dynamic mechanical analysis of LLDPE/EMA blends. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 2011, 105, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; He, J. Investigation of mechanical property, flame retardancy and thermal degradation of LLDPE–wood-fibre composites. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2004, 83, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.S.; Lee, D.H.; Park, E.S.; et al. Thermal and mechanical properties of ethylene/alpha-olefin copolymers produced over (2-MeInd)2ZrCl2/MAO system. Polymer 2000, 41, 4523–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gownder, M. Branching of LLDPE as Studied by Crystallization-Fractionation and its effect on Mechanical Properties of Films. Journal of Plastic Film & Sheeting 2001, 17, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizerovskii, L.N.; Afanas’eva, V.V.; Lytkina, N.I. Melting of binary mixtures of low-density polyethylene and alkylbenzenes. Fibre Chemistry 1996, 28, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpe, G.; Jarrin, J.; Dawans, F. Morphology-processing relationships in polyethylene-polyamide blends. Polymer Engineering & Science 1990, 30, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, C.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. A novel method for the determination of steady-state torque of polymer melts by HAAKE MiniLab. Polymer Testing 2014, 33, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, M.; Guedes, I.; Alcantara, P.; Moreira, S. Infrared absorption spectra of Buriti (Mauritia flexuosa L.) oil. Vibrational Spectroscopy 2003, 33, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira de Oliveira, J.; Almeida, O.P.; Campelo, P.H.; Carneiro, G.; de Oliveira Ferreira Rocha, L.; Santos, J.H.M.; Gomes da Costa, J.M. Tailoring the physicochemical properties of freeze-dried buriti oil microparticles by combining inulin and gum Arabic as encapsulation agents. LWT 2022, 161, 113372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, G.M.M. Nanoencapsulação de óleo de buriti (Mauritia flexuosa) em alginato e gelatina: caracterização e avaliação da solubilidade e potencial antimicrobiano. Dissertação de mestrado, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Natal, RN, Brasil, 2018. 78f. Dissertação (Mestrado em Nutrição) - Centro de Ciências da Saúde, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, 2018.
- Marcelino, G.; Hiane, P.A.; Pott, A.; de Oliveira Filiú,W.F.; Caires, A.R.L.; Michels, F.S.; Júnior, M.R.M.; Santos, N.M.S.; Nunes, A.A.; Oliveira, L.C.S.; et al. Characterization of Buriti (Mauritia flexuosa) Pulp Oil and the Effect of Its Supplementation in an In Vivo Experimental Model. Nutrients 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Escalante, J.; Chen, W.H.; Tabatabaei, M.; Hoang, A.T.; Kwon, E.E.; Andrew Lin, K.Y.; Saravanakumar, A. Pyrolysis of lignocellulosic, algal, plastic, and other biomass wastes for biofuel production and circular bioeconomy: A review of thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) approach. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2022, 169, 112914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Niu, R.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Wen, X.; Mijowska, E.; Sun, Z.; Tang, T. Simultaneously improving the thermal stability, flame retardancy and mechanical properties of polyethylene by the combination of graphene with carbon black. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 33776–33784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Soberanis, C.R.; Collí-Pacheco, J.P.; Estrada-León, R.J.; Moo-Huchin, V.M.; Yee-Madeira, H.T.; Pérez-Pacheco, E. Biocomposites based on plasticized starch: thermal, mechanical and morphological characterization. Polymer Bulletin 2021, 78, 3687–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Berrío, Y.D.C.; Realpe Jiménez, Á.; De Ávila Montiel, G. Effect of glycerol, sunflower oil, and glucose on the physico-chemical and mechanical properties of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol-based films. Polymer Bulletin 2022, 79, 6389–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; He, L.; Yang, X. Effect of Crystallinity of Polyethylene with Different Densities on Breakdown Strength and Conductance Property. Materials 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubdub, I.; Al-Yaari, M. Pyrolysis of Low Density Polyethylene: Kinetic Study Using TGA Data and ANN Prediction. Polymers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Tan, Z.; Hong, R.; Ouyang, W.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, C. Automatically Predicting Material Properties with Microscopic Images: Polymer Miscibility as an Example. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 2023, 63, 5971–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Zhang, N.; Santos, R.M. Mineral Characterization Using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): A Review of the Fundamentals, Advancements, and Research Directions. Applied Sciences 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmakuri, A.; Janušas, G.; Siddabathula, M.; Palevicius, A. Wettability and Moisture Analysis on Natural Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Resin Hybrid Composites. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference Mechatronic Systems and Materials (MSM); 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.; Negi, Y.; Pradhan, S.; Dash, M.; Samal, S. 3 - Wettability and contact angle of polymeric biomaterials. In Characterization of Polymeric Biomaterials; Tanzi, M.C.; Farè, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing, 2017; pp. 57–81. [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.T.; Lambert, C.A.; Bliznyuk, M.; Kohl, J.G. Effect of a Tertiary Oil Phase on the Mechanical Properties of Natural Fiber-Reinforced Polyester Composites. Polymer-Plastics Technology and Engineering 2013, 52, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, D.G.; Pachekoski, W.M.; Dalmolin, C.; Agnelli, J.A.M. Natural additives for poly (hydroxybutyrate - CO - hydroxyvalerate) - PHBV: effect on mechanical properties and biodegradation. Materials Research 2014, 17, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | LLDPE | Buriti oil (%wt) |
|---|---|---|
| LLDPE | 100 | - |
| LLDPE/BO-0.1 | 100 | 0.1 |
| LLDPE/BO-0.3 | 100 | 0.3 |
| LLDPE/BO-0.5 | 100 | 0.5 |
| LLDPE/BO-1 | 100 | 1.0 |
| Samples | T (Nm) | e (J/g) |
|---|---|---|
| LLDPE | 11.4 | 838 |
| LLDPE/BO-0.1 | 10.9 | 788.1 |
| LLDPE/BO-0.3 | 10.8 | 791.8 |
| LLDPE/BO-0.5 | 10.8 | 804.9 |
| LLDPE/BO-1 | 10.7 | 768.4 |
| Samples | Tc1 (°C) | Tc2 (°C) | Tc3 (°C) | Tm1 (°C) | Tm2 (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLDPE | 105.3 | 91.2 | 57.7 | 107.6 | 122.1 | 114.2 | 39.0 |
| LLDPE/BO-0.1 | 104.4 | 91.7 | 57.1 | 105.1 | 121.9 | 103.8 | 35.4 |
| LLDPE/BO-0.3 | 104.8 | 90.9 | 57.7 | 107.8 | 122.5 | 106.2 | 36.6 |
| LLDPE/BO-0.5 | 104.6 | 91.2 | 57.4 | 106.7 | 123.4 | 104.1 | 35.5 |
| LLDPE/BO-1 | 105.5 | 91.2 | 56.9 | 107.7 | 122.2 | 103.8 | 35.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





