Submitted:
29 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Hydrochloric Acid Leaching of Ilmenite
2.2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4/Fe2TiO5/TiO2 Based Nanocomposite
2.3. Adsorption Study
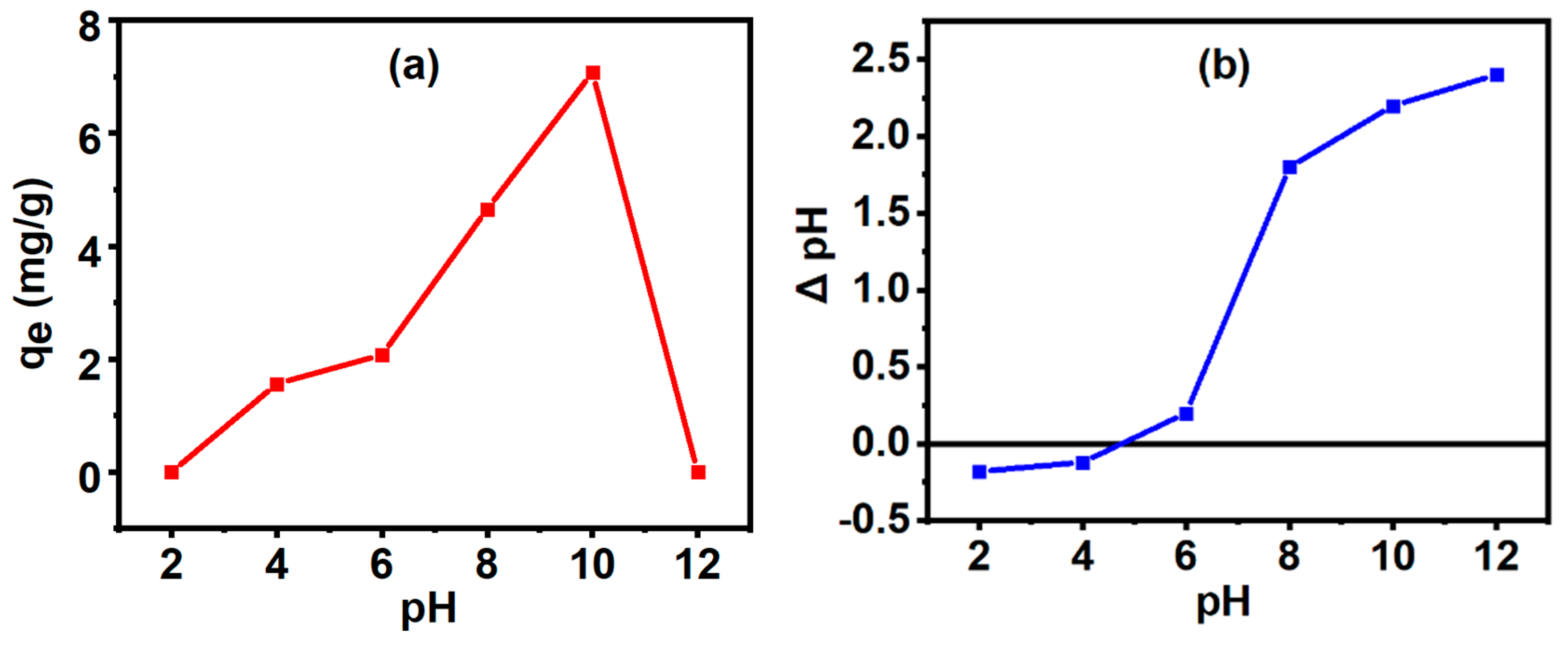
2.3.1. Finding the Point-of-Zero-Charge
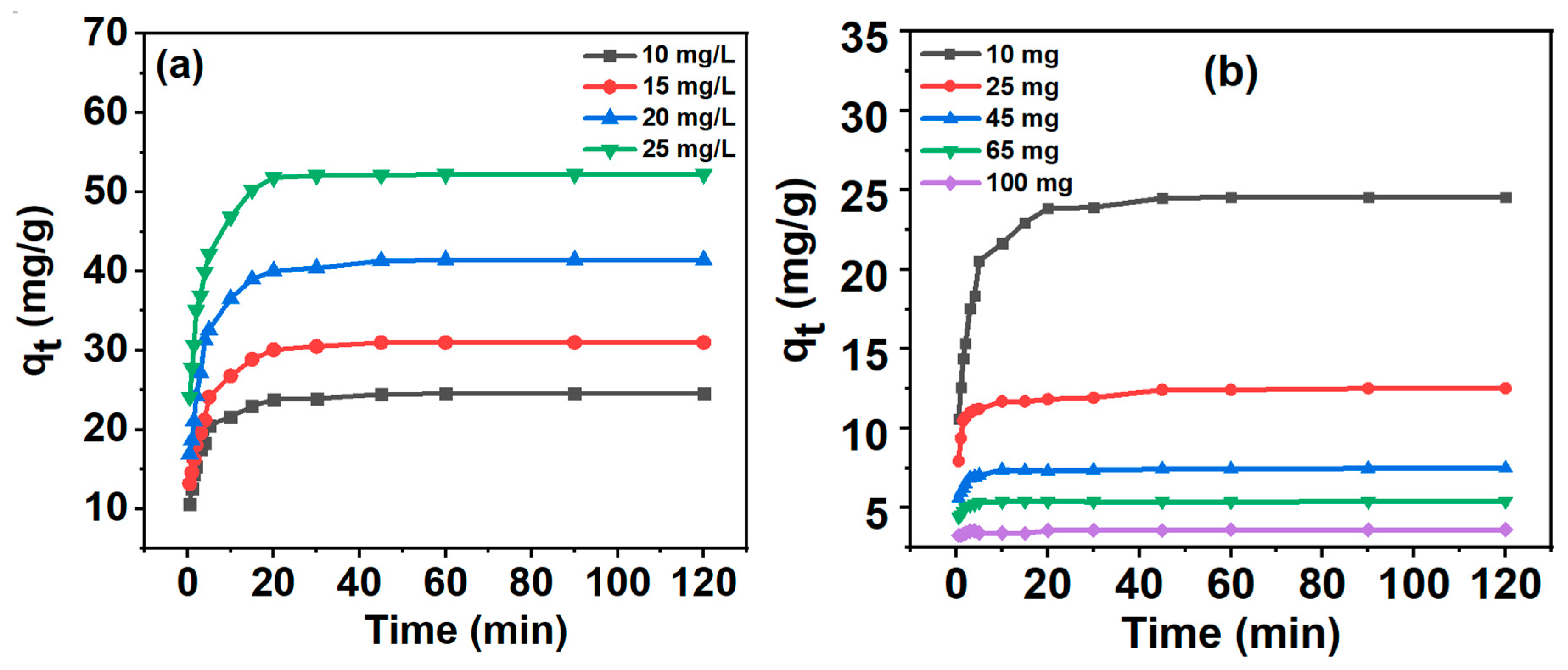
2.3.2. Effect of MB Concentration on Adsorption
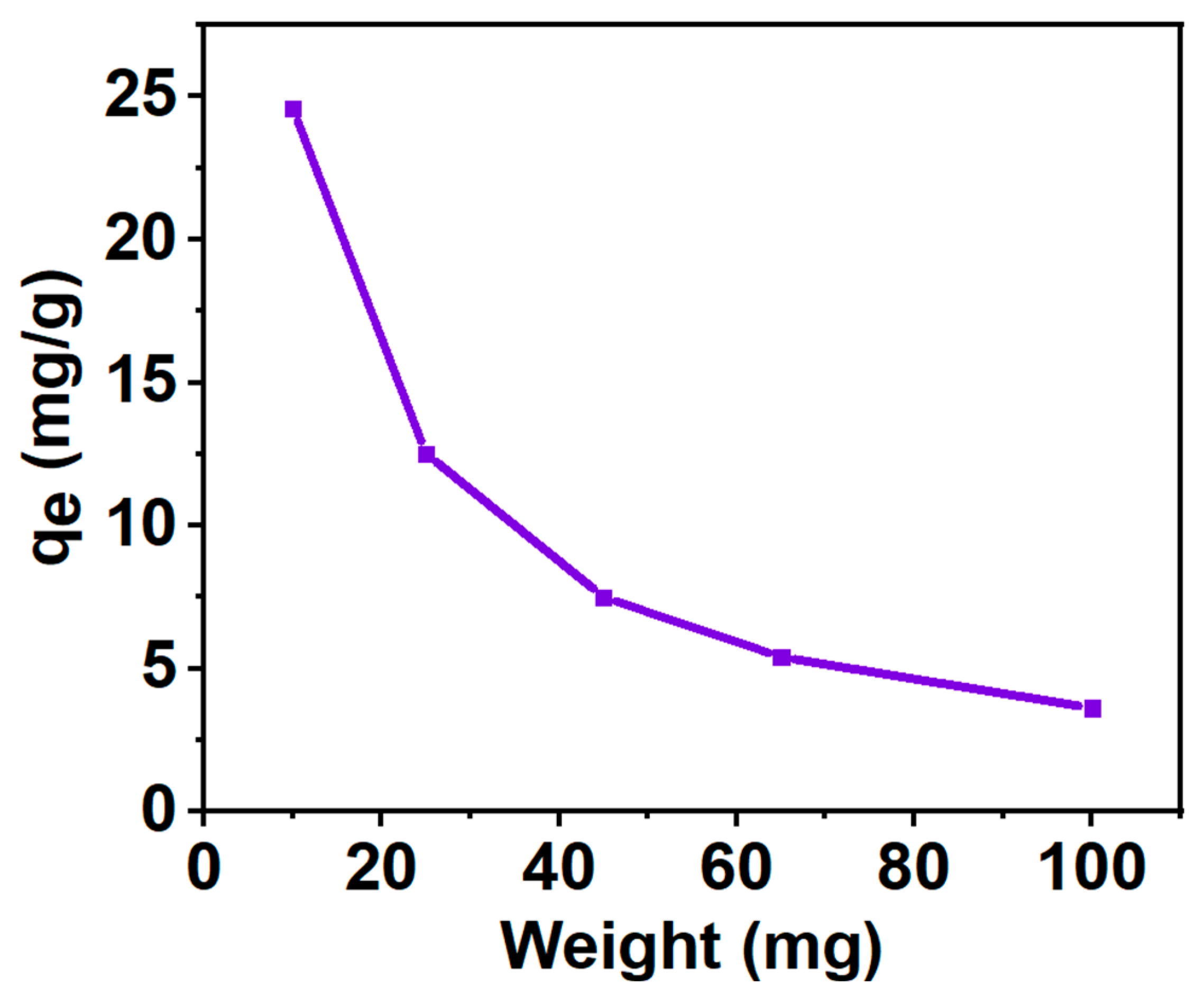
2.3.3. Effect of the Weight of the Adsorbent on Adsorption
2.3.4. Effect of Temperature on Adsorption
2.4. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRF Analysis
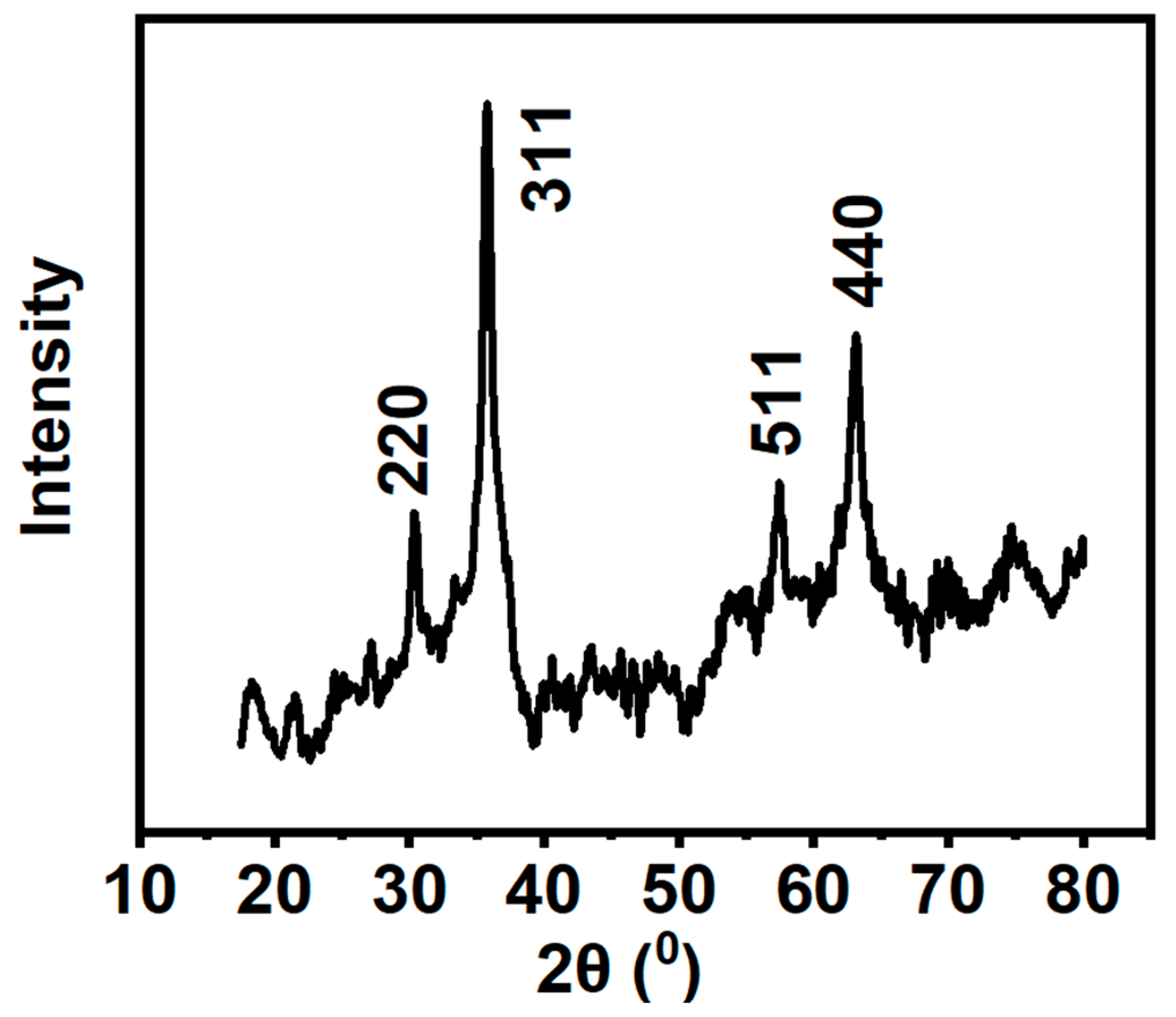
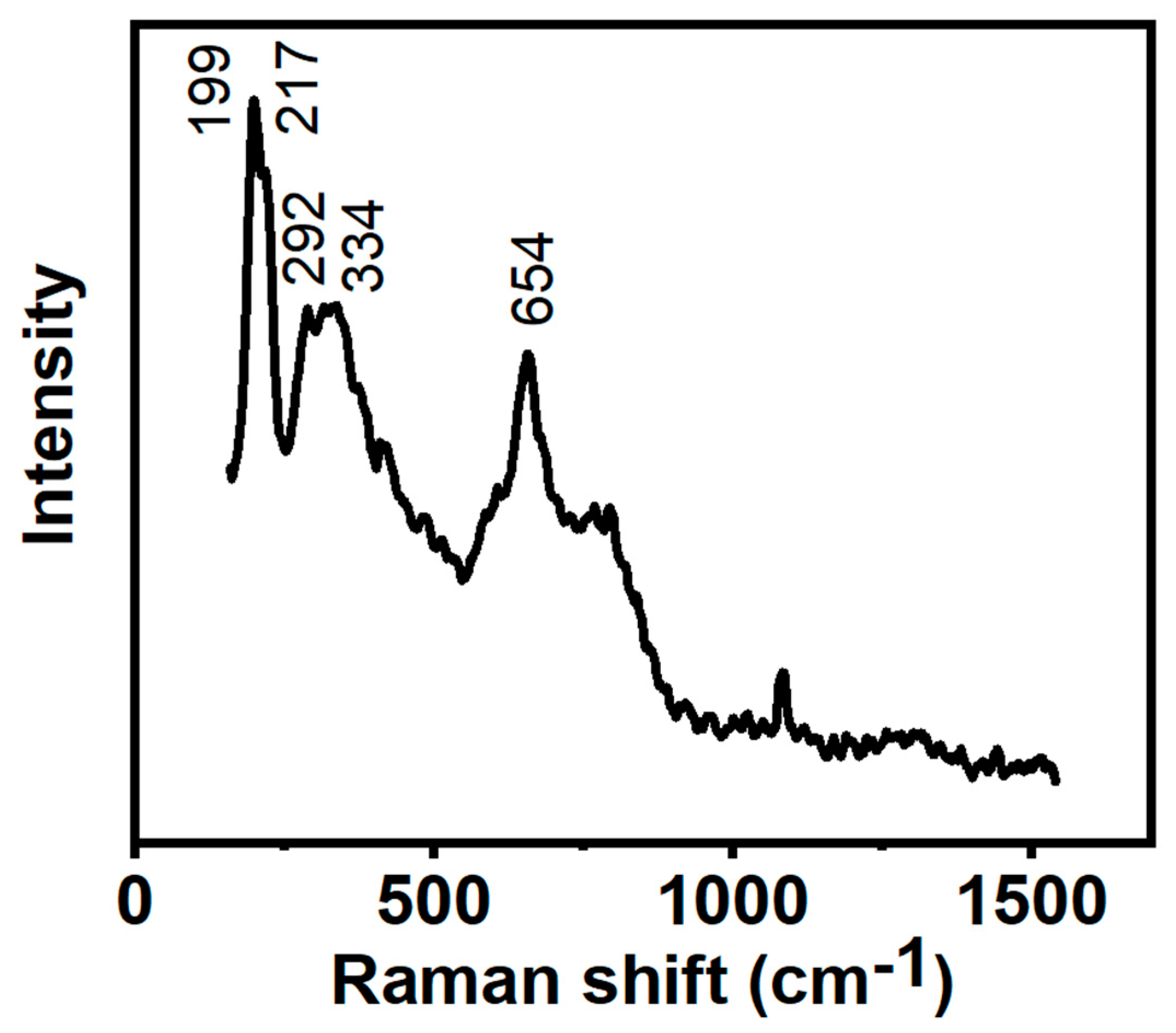
3.2. XRD and Raman Analysis
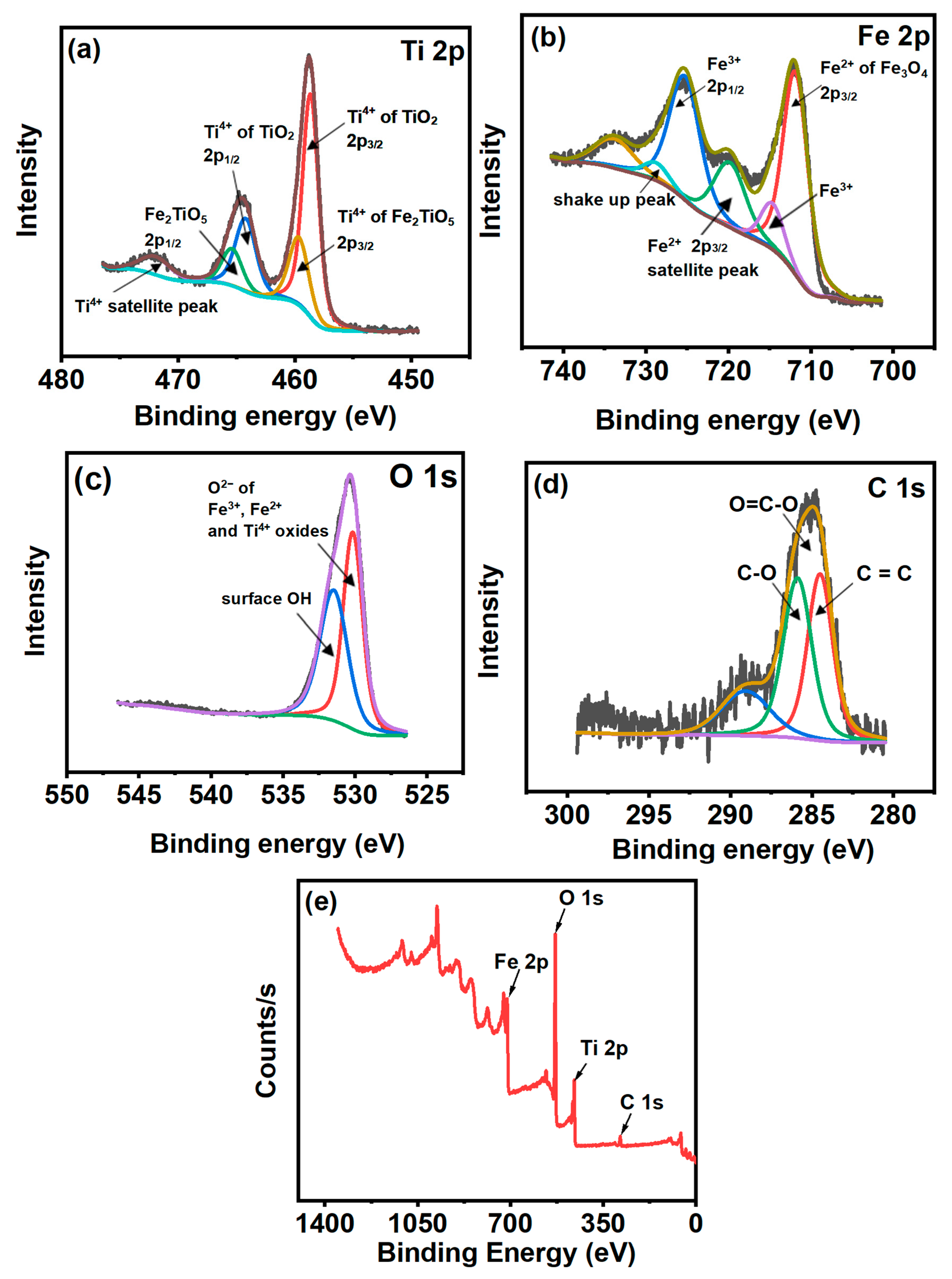
3.3. XPS Analysis
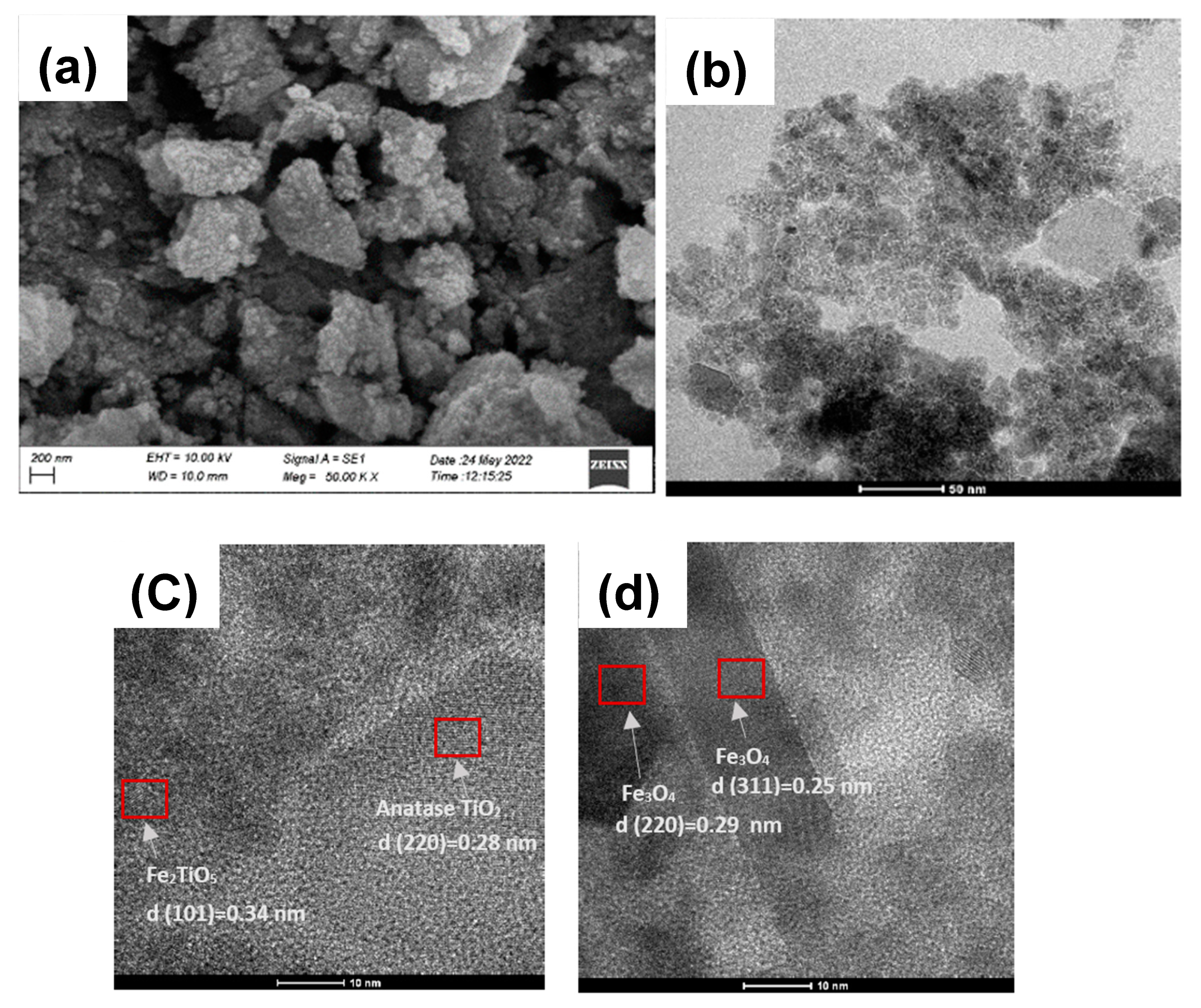
3.4. Morphological Analysis
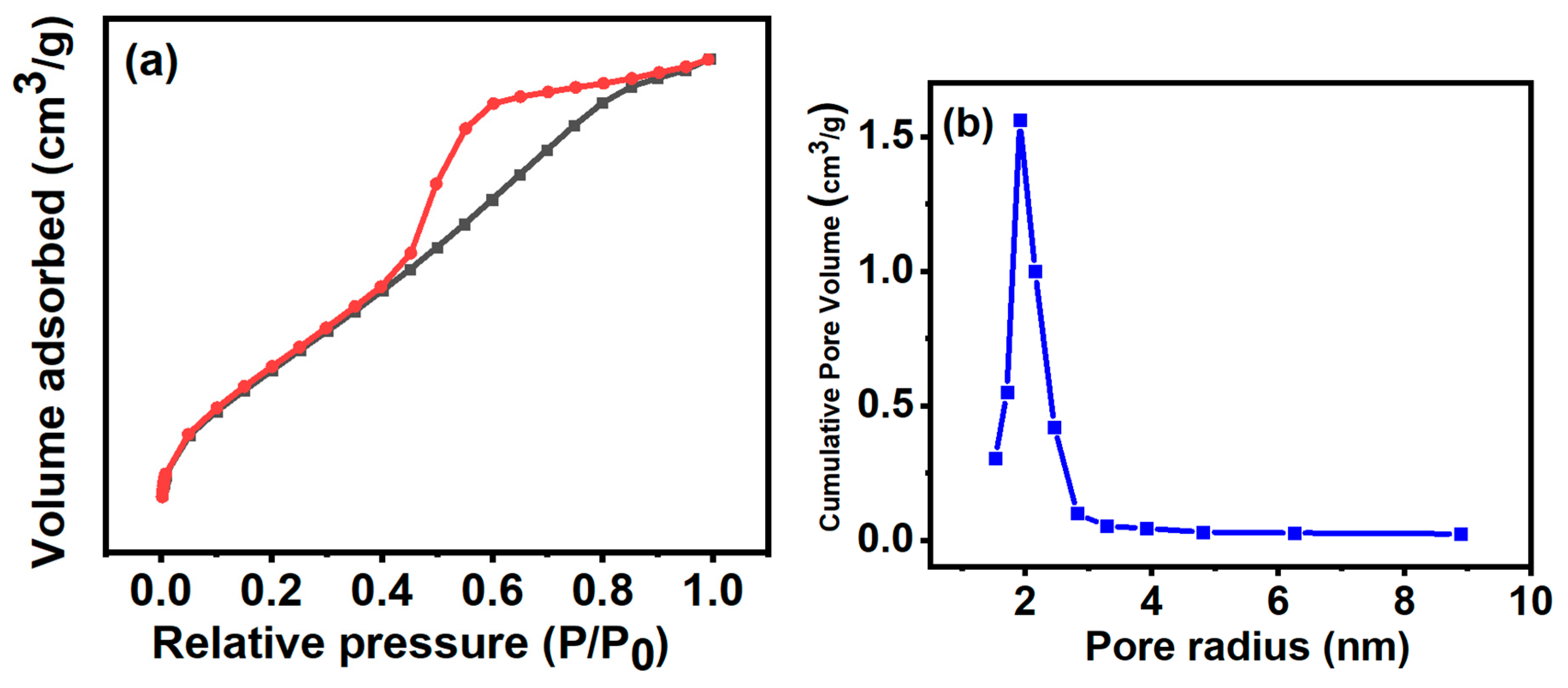
3.5. BET and BJH Analysis
3.6. Adsorption Study
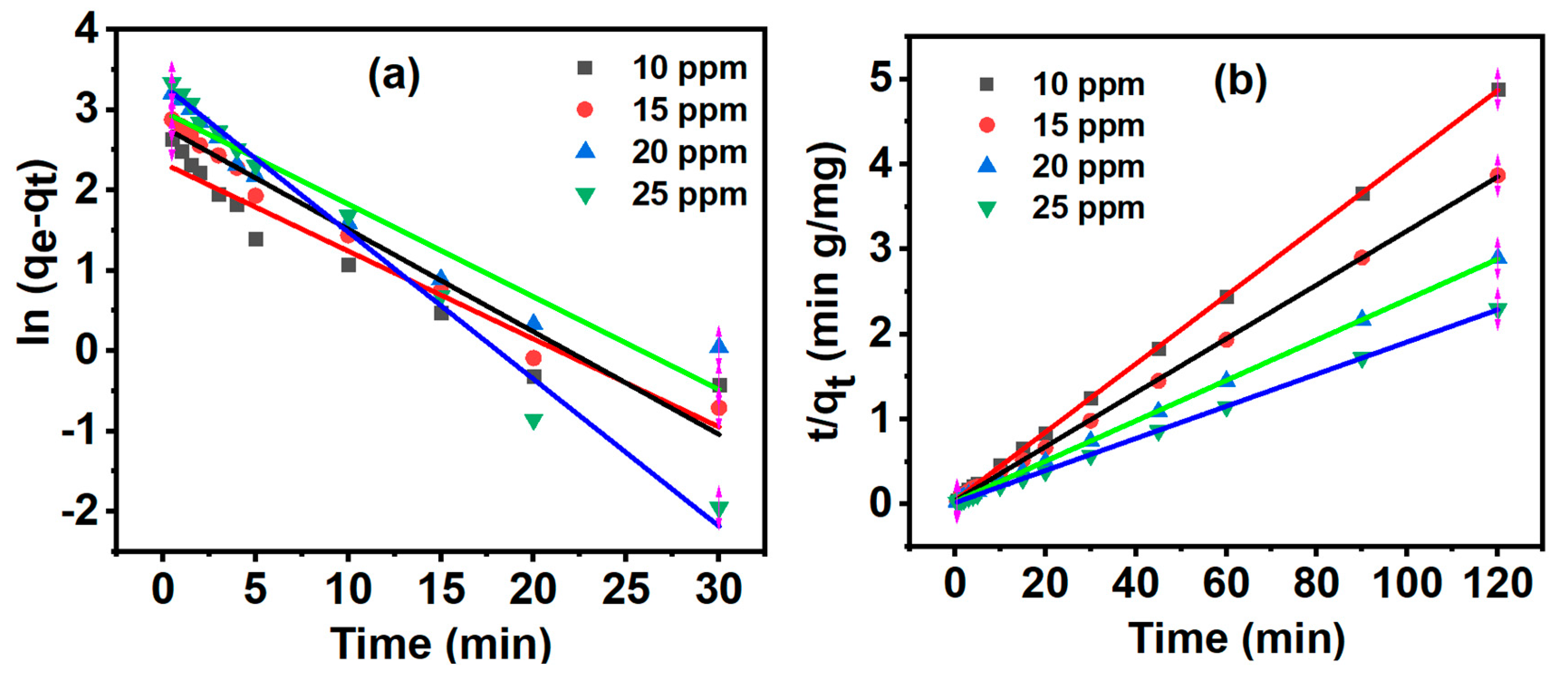
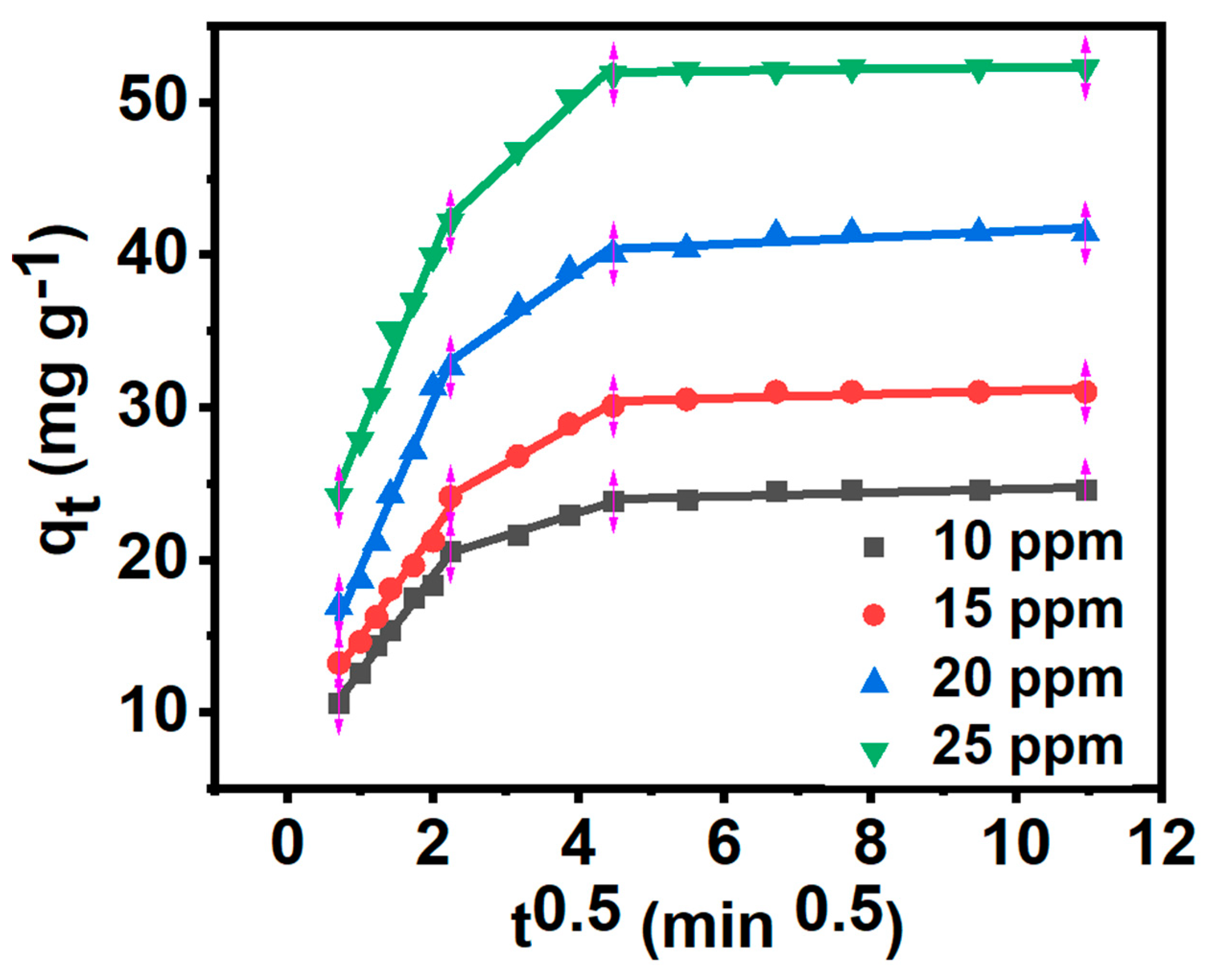
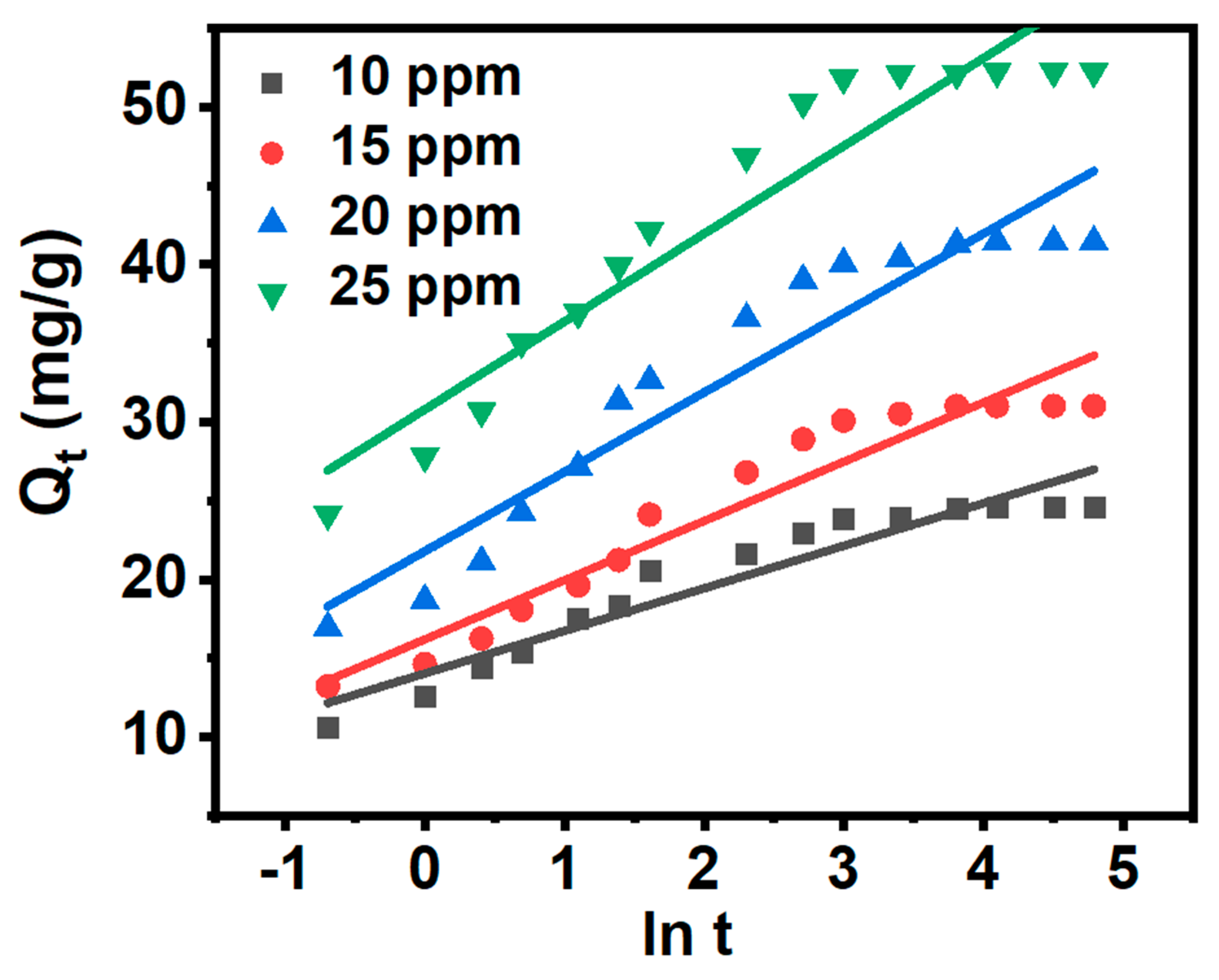
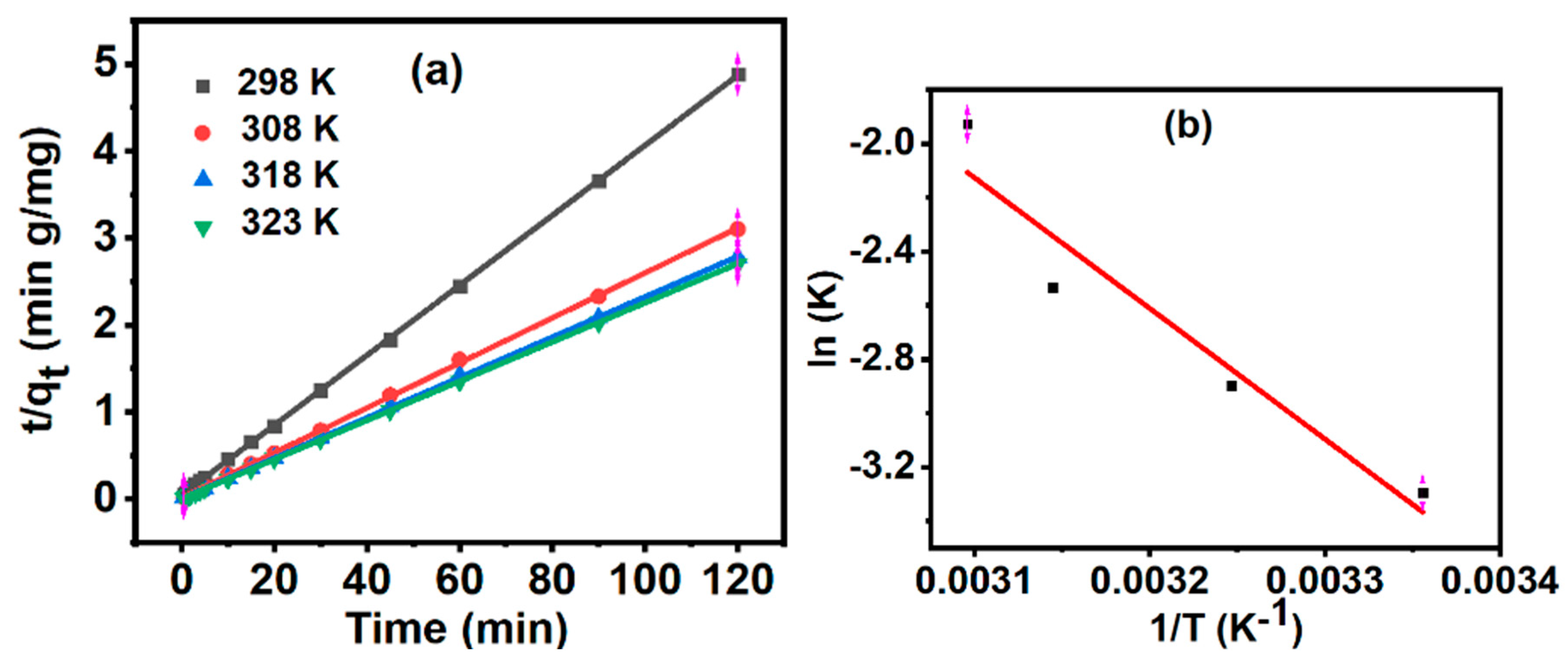
3.7. Adsorption Kinetics
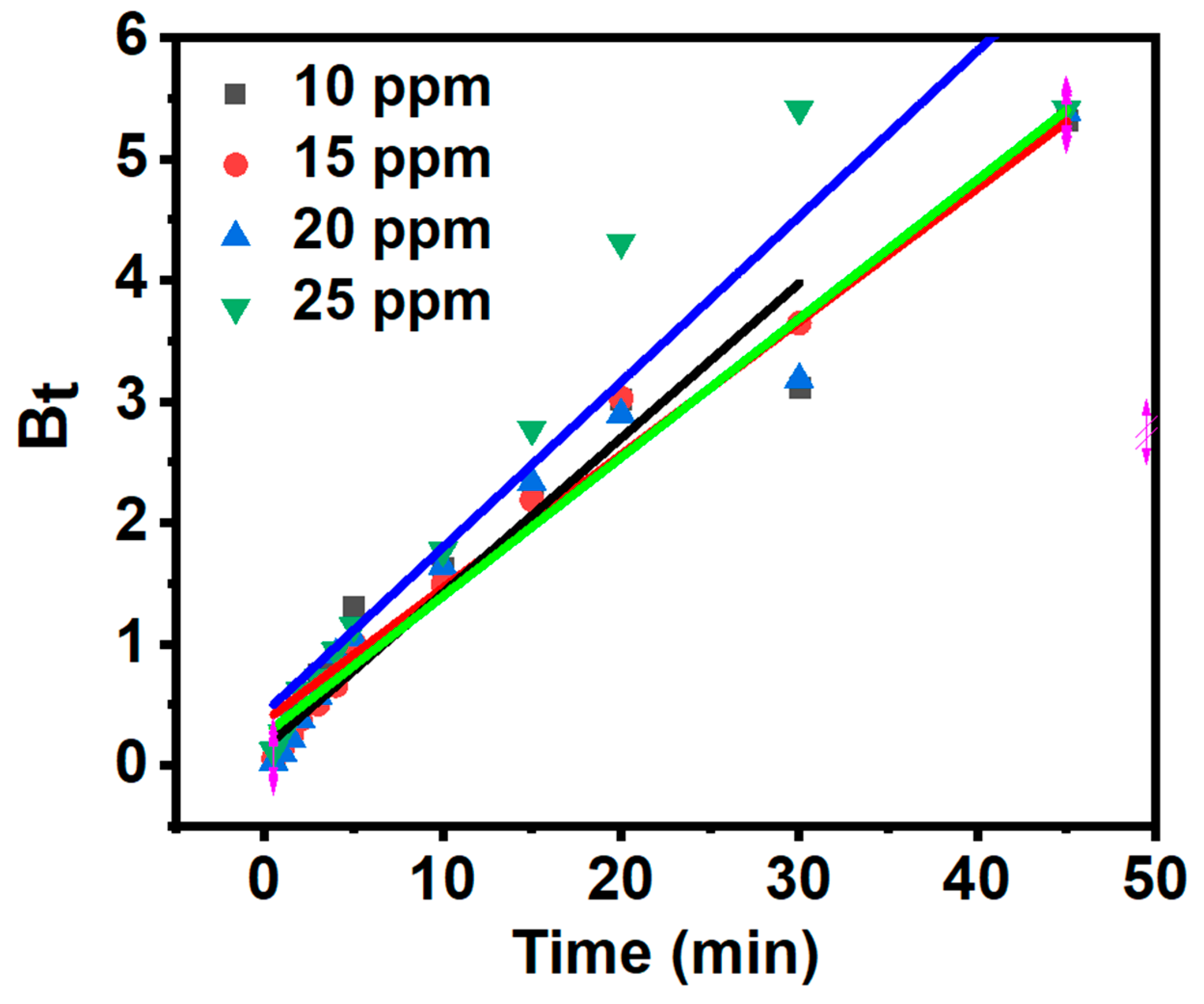
| MB concentration (mg/L) | α (mg/g min) | β (g/mg) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 487.621 | 0.370 | 0.917 |
| 15 | 278.440 | 0.265 | 0.930 |
| 20 | 379.398 | 0.198 | 0.914 |
| 25 | 1391.411 | 0.179 | 0.910 |
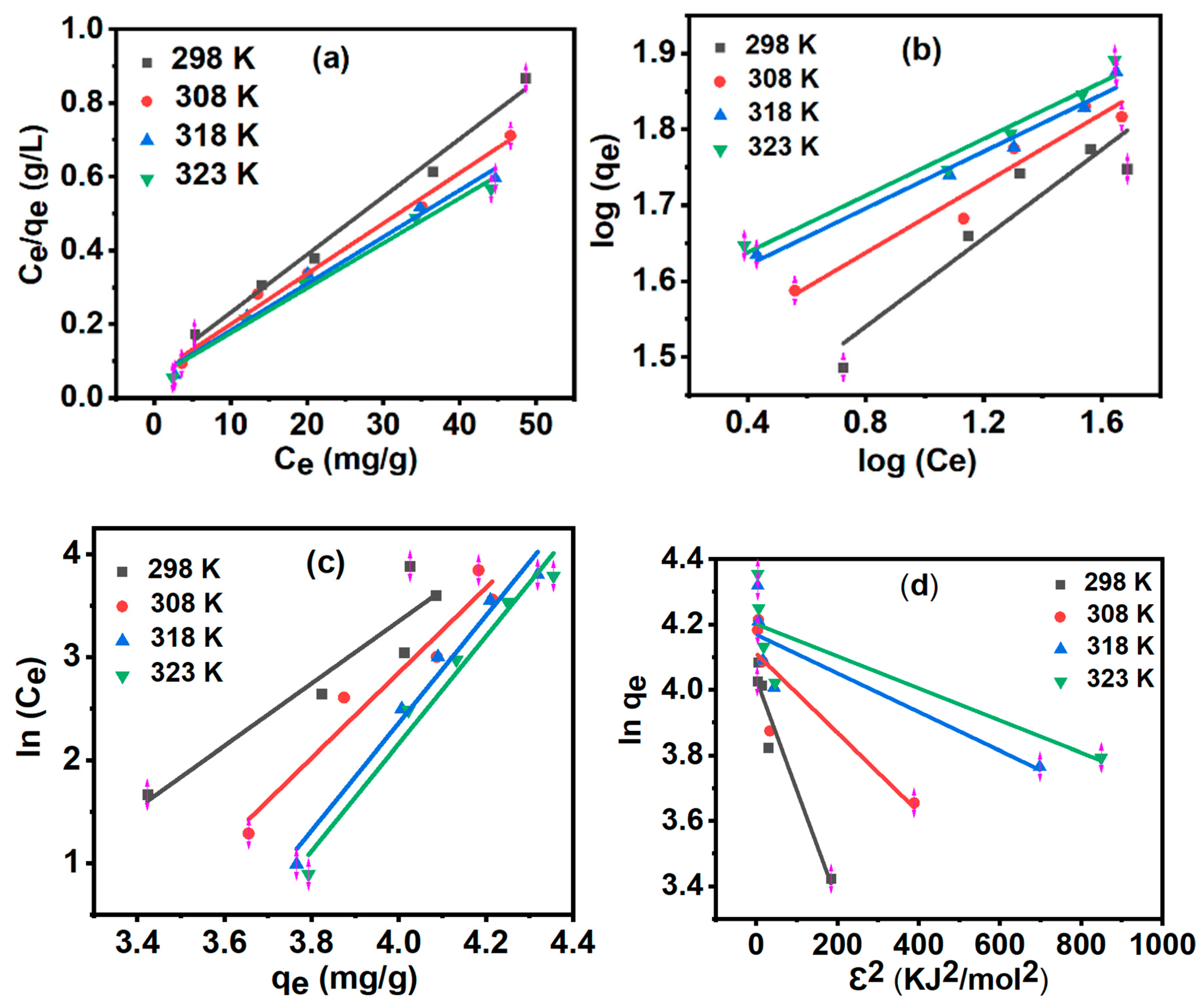
3.8. Adsorption Isotherms
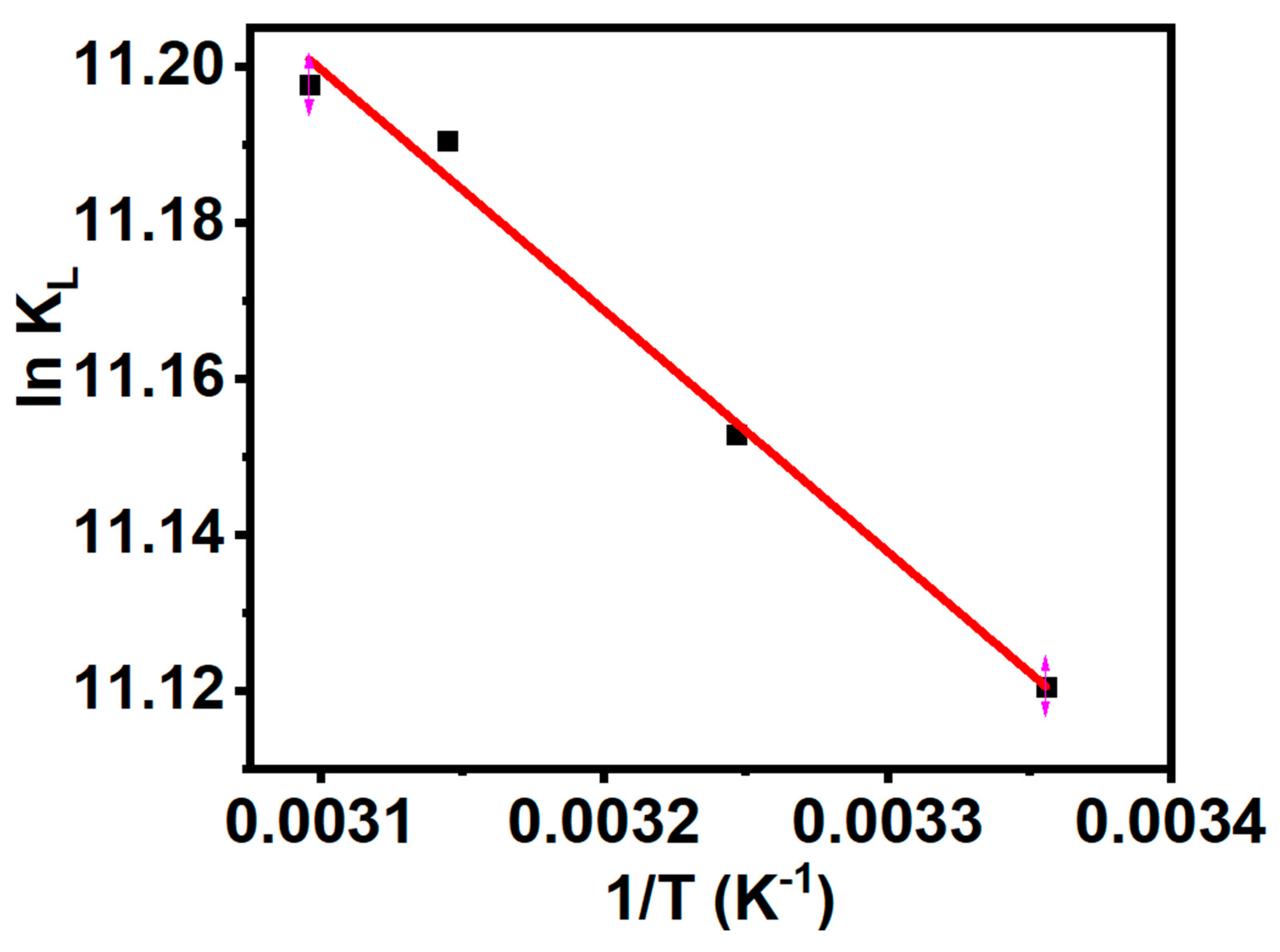
3.9. Adsorption Thermodynamics.
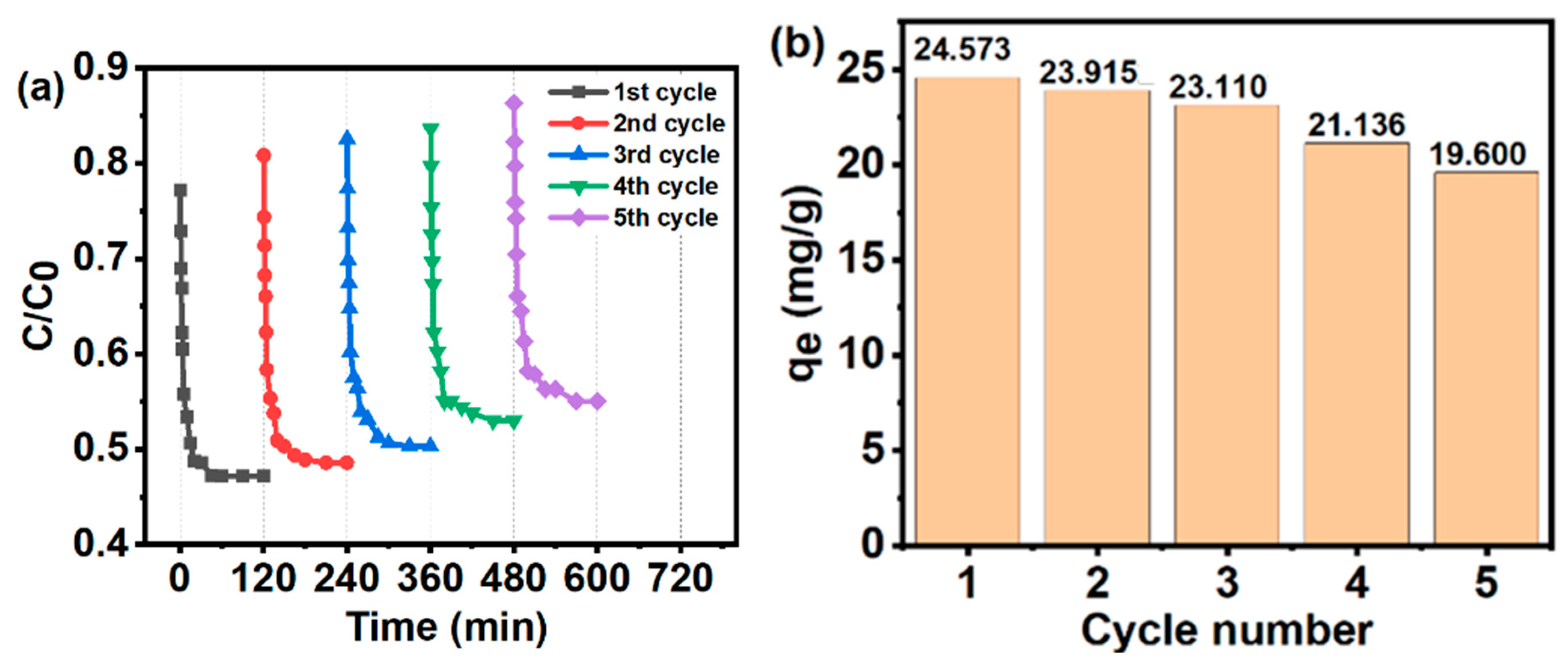
3.10. Reusability Studies
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- T. Charitha, U. Leshan, M. Shanitha, W. Ramanee, L. Buddi, and B. Martin, Efficient photodegradation activity of α-Fe2O3/Fe2TiO5/TiO2 and Fe2TiO5/TiO2 nanocomposites synthesized from natural ilmenite. Results in Materials, 2021; 12. [CrossRef]
- Tkaczyk, K. Mitrowska, and A. Posyniak, Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: A review. May 15, 2020, Elsevier B.V. [CrossRef]
- L. Usgodaarachchi, C. Thambiliyagodage, R. Wijesekera, and M. G. Bakker, Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles derived from rice husk and surface-controlled amine functionalization for efficient adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2021; 4. [CrossRef]
- R. Al-Tohamy et al., A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Feb. 01, 2022, Academic Press. [CrossRef]
- Y. Xu, Q. Wang, and Z. Ding, Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nano-Adsorbent Using an Energy-Saving and Pollution-Reducing Strategy for the Removal of Xylenol Orange Dye in Water. Energies (Basel) 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Q. Liu, Pollution and Treatment of Dye Waste-Water. in IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, IOP Publishing Ltd., Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Zafar, D. A. Bukhari, and A. Rehman, Azo dyes degradation by microorganisms – An efficient and sustainable approach. Dec. 01, 2022, Elsevier B.V. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, P. Zhang, F. Xu, B. Sun, G. Hong, and L. Bao, Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Azo Dye Wastewater by Molybdenum Disulfide Nanomaterials. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bożęcka, M. Orlof-Naturalna, and M. Kopeć, Methods of Dyes Removal from Aqueous Environment. Journal of Ecological Engineering 2021, 22, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Dutta, B. Gupta, S. K. Srivastava, and A. K. Gupta, Recent advances on the removal of dyes from wastewater using various adsorbents: A critical review. Royal Society of Chemistry, 2021; 21. [CrossRef]
- C. Valli Nachiyar, A. D. Rakshi, S. Sandhya, N. Britlin Deva Jebasta, and J. Nellore, Developments in treatment technologies of dye-containing effluent: A review. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 2023; 7. [CrossRef]
- C. Thambiliyagodage, L. Usgodaarachchi, M. Jayanetti, C. Liyanaarachchi, M. Kandanapitiye, and S. Vigneswaran, Efficient Visible-Light Photocatalysis and Antibacterial Activity of TiO2-Fe3C-Fe-Fe3O4/Graphitic Carbon Composites Fabricated by Catalytic Graphitization of Sucrose Using Natural Ilmenite. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 25403–25421. [CrossRef]
- C. Osagie, A. Othmani, S. Ghosh, A. Malloum, Z. Kashitarash Esfahani, and S. Ahmadi, Dyes adsorption from aqueous media through the nanotechnology: A review. Sep. 01, 2021, Elsevier Editora Ltd.a. [CrossRef]
- S. Homaeigohar, The nanosized dye adsorbents for water treatment. Feb. 01, 2020, MDPI AG. [CrossRef]
- T. E. Oladimeji, B. O. Odunoye, F. B. Elehinafe, O. R. Obanla, and O. A. Odunlami, Production of activated carbon from sawdust and its efficiency in the treatment of sewage water. Heliyon, 2021; 7. [CrossRef]
- T. Sesuk, P. Tammawat, P. Jivaganont, K. Somton, P. Limthongkul, and W. Kobsiriphat, Activated carbon derived from coconut coir pith as high performance supercapacitor electrode material. J Energy Storage, 2019; 25. [CrossRef]
- M. N. Hossain, M. D. Islam, A. Rahaman, N. Khatun, and M. A. Matin, Production of cost-effective activated carbon from tea waste for tannery waste water treatment. Appl Water Sci, 2023; 13. [CrossRef]
- D. Bergna, T. Hu, H. Prokkola, H. Romar, and U. Lassi, Effect of Some Process Parameters on the Main Properties of Activated Carbon Produced from Peat in a Lab-Scale Process. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 2837–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. J. Thambiliyagodage, V. Y. Cooray, I. N. Perera, and R. D. Wijesekera, Eco-Friendly Porous Carbon Materials for Wastewater Treatment. in Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol. 44, Springer, 2020, pp. 252–260. [CrossRef]
- L. L. Schramm, E. N. Stasiuk, and D. G. Marangoni, Surfactants and their applications. 2003, Royal Society of Chemistry. [CrossRef]
- F. Damiri et al., Recent Advances in Adsorptive Nanocomposite Membranes for Heavy Metals Ion Removal from Contaminated Water: A Comprehensive Review. Aug. 01, 2022, MDPI. [CrossRef]
- S. Singh, K. C. Barick, and D. Bahadur, Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology Functional Oxide Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for the Removal of Heavy Metals and Dyes Invited Review Article. 2013. [Online]. Available online: www.intechopen.com.
- T. A. Dontsova, S. V. Nahirniak, and I. M. Astrelin, Metaloxide nanomaterials and nanocomposites of ecological purpose. 2019, Hindawi Limited. [CrossRef]
- Z. Alhalili, Metal Oxides Nanoparticles: General Structural Description, Chemical, Physical, and Biological Synthesis Methods, Role in Pesticides and Heavy Metal Removal through Wastewater Treatment. Apr. 01, 2023, MDPI. [CrossRef]
- L. Usgodaarachchi, M. Jayanetti, C. Thambiliyagodage, H. Liyanaarachchi, and S. Vigneswaran, Fabrication of r-GO/GO/α-Fe2O3/Fe2TiO5 Nanocomposite Using Natural Ilmenite and Graphite for Efficient Photocatalysis in Visible Light. Materials, 2023; 16. [CrossRef]
- L. Usgodaarachchi, C. Thambiliyagodage, R. Wijesekera, S. Vigneswaran, and M. Kandanapitiye, Fabrication of TiO2Spheres and a Visible Light Active α-Fe2O3/TiO2-Rutile/TiO2-Anatase Heterogeneous Photocatalyst from Natural Ilmenite. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 27617–27637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. Usgodaarachchi and C. Thambiliyagodage, Photocatalytic activity of GO/Fe3O4 fabricated by Sri Lankan graphite under visible light irradiation. Journal of Science of the University of Kelaniya 2021, 14, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. Charitha, U. Leshan, M. Shanitha, W. Ramanee, L. Buddi, and B. Martin, Efficient photodegradation activity of α-Fe2O3/Fe2TiO5/TiO2 and Fe2TiO5/TiO2 nanocomposites synthesized from natural ilmenite. Results in Materials, 2021; 12. [CrossRef]
- C. Thambiliyagodage and L. Usgodaarachchi, Photocatalytic activity of N, Fe and Cu co-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under sunlight. Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2021; 4. [CrossRef]
- M. Humayun, F. Raziq, A. Khan, and W. Luo, Modification strategies of TiO2 for potential applications in photocatalysis: A critical review. Apr. 03, 2018, Taylor and Francis Ltd. [CrossRef]
- M. Serhan et al., Total iron measurement in human serum with a smartphone. in AIChE Annual Meeting, Conference Proceedings, American Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2019.
- M. Thommes et al., Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure and Applied Chemistry 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Mikšík, T. Miyazaki, and K. Thu, Adsorption isotherm modelling of water on nano-tailored mesoporous silica based on distribution function. Energies (Basel), 2020; 13. [CrossRef]
- E. A. Al-Maliky, H. A. Gzar, and M. G. Al-Azawy, Determination of Point of Zero Charge (PZC) of Concrete Particles Adsorbents. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 2021, 1184, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Chang et al., Adsorption of methylene blue onto Fe3O4/activated montmorillonite nanocomposite. Appl Clay Sci 2016, 119, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Giraldo, I. Robles, L. A. Godínez, N. Acelas, and E. Flórez, Experimental and theoretical insights on methylene blue removal from wastewater using an adsorbent obtained from the residues of the orange industry. Molecules, 2021; 26. [CrossRef]
- E. D. Revellame, D. L. Fortela, W. Sharp, R. Hernandez, and M. E. Zappi, Adsorption kinetic modeling using pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws: A review. Dec. 01, 2020, Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- N. F. Al-Harby, E. F. Albahly, and N. A. Mohamed, Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies for efficient adsorption of congo red dye from aqueous solution onto novel cyanoguanidine-modified chitosan adsorbent. Polymers (Basel), 2021; 13. [CrossRef]
- J. Chang et al., Adsorption of methylene blue onto Fe3O4/activated montmorillonite nanocomposite. Appl Clay Sci 2016, 119, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N. Ebelegi, N. N. Ebelegi, N. Ayawei, and D. Wankasi, Interpretation of Adsorption Thermodynamics and Kinetics. Open J Phys Chem, 2020; 03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. O. Ojediran, A. O. Dada, S. O. Aniyi, R. O. David, and A. D. Adewumi, Mechanism and isotherm modeling of effective adsorption of malachite green as endocrine disruptive dye using Acid Functionalized Maize Cob (AFMC). Sci Rep, 2021; 11. [CrossRef]
- Vinod, H. Pulikkalparambil, P. Jagadeesh, S. M. Rangappa, and S. Siengchin, Recent advancements in lignocellulose biomass-based carbon fiber: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Mar. 01, 2023, Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- D. A. Ali, H. Elsawy, D. A. Ali, F. M. Abdalla, D. A. Gamil, and H. A. Elsawy, Isotherm and Kinetics Studies for the Adsorption of Methylene Blue and Methyl Red Dyes from Aqueous Solutions Using Chitosan. vol. 16, no. 7, 2021, [Online]. Available online: www.arpnjournals.com.
- Inyinbor, A. A. Inyinbor, F. A. Adekola, and G. A. Olatunji, EDTA Modified Irvingia gabonensis: An Efficient Bioresource Material for the Removal of Rhodamine B. 2015. [Online]. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/289957652.
- S. Mohamed Nasser, M. Abbas, and M. Trari, Understanding the rate-limiting step adsorption kinetics onto biomaterials for mechanism adsorption control. Jan. 01, 2024, SAGE Publications Ltd. [CrossRef]
- N. Hasani et al., Theoretical, Equilibrium, Kinetics and Thermodynamic Investigations of Methylene Blue Adsorption onto Lignite Coal. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Smaranda, D. Bulgariu, and M. Gavrilescu, An investigation of the sorption of Acid Orange 7 from aqueous solution onto soil. in Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, Gheorghe Asachi Technical University of Iasi, Romania, 2009, pp. 1391–1402. [CrossRef]
- P. K. Singh, S. Banerjee, A. L. Srivastava, and Y. Chandra Sharma, Kinetic and equilibrium modeling for removal of nitrate from aqueous solutions and drinking water by a potential adsorbent, hydrous bismuth oxide.
- G. Muthuraman, Removal of Mn2+ REMOVAL OF MANGANESE FROM GROUND/ DRINKING WATER AT SOUTH MADRAS USING NATURAL ADSORBENTS”.
- M. Abodif et al., Mechanisms and Models of Adsorption: TiO2-Supported Biochar for Removal of 3,4-Dimethylaniline. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13630–13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L. Taofeek Popoola, Characterization and adsorptive behaviour of snail shell-rice husk (SS-RH) calcined particles (CPs) towards cationic dye. Heliyon 2019, 5, 1153. [Google Scholar]
- S. Raghav and D. Kumar, Adsorption Equilibrium, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Studies of Fluoride Adsorbed by Tetrametallic Oxide Adsorbent. J Chem Eng Data 2018, 63, 1682–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Kalam, S. A. Abu-Khamsin, M. S. Kamal, and S. Patil, Surfactant Adsorption Isotherms: A Review. Dec. 07, 2021, American Chemical Society. [CrossRef]
- H. Liyanaarachchi, C. Thambiliyagodage, H. Lokuge, and S. Vigneswaran, Kinetics and Thermodynamics Study of Methylene Blue Adsorption to Sucrose- and Urea-Derived Nitrogen-Enriched, Hierarchically Porous Carbon Activated by KOH and H3PO4. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 16158–16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. Adane, K. Siraj, and N. Meka, Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study of 2-chlorophenol adsorption onto Ricinus communis pericarp activated carbon from aqueous solutions. Oct. 02, 2015, Taylor and Francis Ltd. [CrossRef]
- B. Meroufel, O. Benali, M. Benyahia, Y. Benmoussa, and M. A. Zenasni, Adsorptive removal of anionic dye from aqueous solutions by Algerian kaolin: Characteristics, isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Mater. Environ. Sci 2013, 4, 482–491. [Google Scholar]
- E. Ajenifuja, J. A. Ajao, and E. O. B. Ajayi, Equilibrium adsorption isotherm studies of Cu (II) and Co (II) in high concentration aqueous solutions on Ag-TiO2-modified kaolinite ceramic adsorbents. Appl Water Sci 2017, 7, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. Y. George, L. Ma, W. Zhang, and G. Yao, Parametric modelling and analysis to optimize adsorption of Atrazine by MgO/Fe3O4-synthesized porous carbons in water environment. Environ Sci Eur 2023, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. S. Piccin, G. L. Dotto, and L. A. A. Pinto, ADSORPTION ISOTHERMS AND THERMOCHEMICAL DATA OF FD&C RED N° 40 BINDING BY CHITOSAN. vol. 28, no. 02, pp. 295–304, [Online]. Available: www.abeq.org.
- V. J. Inglezakis, Solubility-normalized Dubinin–Astakhov adsorption isotherm for ion-exchange systems. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 2007, 103, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pholosi, E. B. Naidoo, and A. E. Ofomaja, Intraparticle diffusion of Cr(VI) through biomass and magnetite coated biomass: A comparative kinetic and diffusion study. S Afr J Chem Eng 2020, 32, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E. Sterenzon, V. K. Vadivel, Y. Gerchman, T. Luxbacher, R. Narayanan, and H. Mamane, Effective Removal of Acid Dye in Synthetic and Silk Dyeing Effluent: Isotherm and Kinetic Studies. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M. A. Zulfikar and H. Setiyanto, Study Of The Adsorption Kinetics And Thermodynamic For The Removal Of Congo Red From Aqueous Solution Using Powdered Eggshell. 2013. [Online]. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236263530.
- T. N. Dharmapriya, D. Y. Li, Y. C. Chung, and P. J. Huang, Green Synthesis of Reusable Adsorbents for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 30478–30487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- J. M. Jabar, Y. A. Odusote, K. A. Alabi, and I. B. Ahmed, Kinetics and mechanisms of congo-red dye removal from aqueous solution using activated Moringa oleifera seed coat as adsorbent. Appl Water Sci, 2020; 10. [CrossRef]
- S. Z. Razali, M. Y. Aziz, H. A. Edinur, and A. Razali Ishak, Adsorption of Methylene Blue onto Iron Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Sugarcane Bagasse. in IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, IOP Publishing Ltd., Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Bavi, M. S. Jafari, M. Heydari, F. Ebrahimi, and A. Sadeghizadeh, Batch and continuous mode adsorption of methylene blue cationic dye onto synthesized titanium dioxide/polyurethane nanocomposite modified by sodium dodecyl sulfate. Colloids and Surfaces C: Environmental Aspects 2023, 1, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V. Cao, P. A. Cao, D. L. Han, M. T. Ngo, T. X. Vuong, and H. N. Manh, The Suitability of Fe3O4/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue and Congo Red. Nature Environment and Pollution Technology 2024, 23, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. Ai, C. Zhang, and Z. Chen, Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by a solvothermal-synthesized graphene/magnetite composite. J Hazard Mater 2011, 192, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. V. Tran, L. T. Bui, T. T. Dinh, D. H. Le, C. D. Huynh, and A. X. Trinh, Graphene oxide/Fe3O4/chitosan nanocomposite: A recoverable and recyclable adsorbent for organic dyes removal. Application to methylene blue. Mater Res Express, 2017; 4. [CrossRef]
| Material | Al2O3 (%) | SiO2 (%) |
CaO (%) |
TiO2 (%) |
Cr2O3 (%) | MnO2 (%) | FeO (%) |
ZnO (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4/Fe2TiO5/TiO2 nanocomposite | 0.92 | 2.81 | 0.30 | 26.05 | 0.11 | 1.45 | 68.30 | 0.19 |
| Component | Peak position | Crystalline plane | Full width at half maximum (FWHM) | Integrated peak area | Crystalline size (nm) | Interplanar distance (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Octahedral Fe3O4 |
30.39 | 220 | 0.674 | 30.524 | 12.2 | 0.293 |
| 35.79 | 311 | 1.412 | 206.007 | 5.91 | 0.250 | |
| 57.55 | 511 | 5.062 | 156.543 | 1.78 | 0.160 | |
| 63.17 | 440 | 2.777 | 205.933 | 3.35 | 0.147 |
| Surface area SBET (m² g-1) | Average pore size (nm) | Pore Volume, Vpore (cm3g-1 ) | C value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 292.182 | 153 | 0.202 | 94.309 |
| Pseudo first order model | Pseudo second order model | |||||||
| MB concentration (mg/L) | qe, exp (mg g-1) | qe, exp (mg g-1) | k1 (min-1) | qe, exp (mg g-1) | k2 (g mg-1 min-1) | |||
| 10 | 24.573 | 10.361 | 0.109 | 0.919 | 24.863 | 0.037 | 0.999 | |
| 15 | 31.012 | 16.300 | 0.127 | 0.977 | 31.476 | 0.024 | 0.999 | |
| 20 | 41.443 | 19.700 | 0.115 | 0.933 | 42.016 | 0.019 | 0.999 | |
| 25 | 52.259 | 27.400 | 0.183 | 0.986 | 52.826 | 0.020 | 0.999 | |
|
MB concentration (mg/L) |
intraparticle diffusion model | ||||||||
| ki,1 (mg g−1 min−1/2) | C1 (mg g−1) | ki,2 (mg g−1 min−1/2) | C2 (mg g−1) | ki,3 (mg g−1 min−1/2) | C3 (mg g−1) | ||||
| 10 | 6.269 | 6.391 | 0.991 | 1.498 | 17.102 | 0.991 | 0.119 | 23.435 | 0.691 |
| 15 | 6.925 | 7.959 | 0.985 | 2.717 | 18.140 | 0.994 | 0.124 | 29.843 | 0.622 |
| 20 | 11.026 | 8.346 | 0.987 | 3.385 | 25.427 | 0.975 | 0.213 | 39.424 | 0.691 |
| 25 | 11.838 | 16.375 | 0.981 | 4.412 | 32.626 | 0.986 | 0.056 | 51.722 | 0.679 |
| Curve | 298 K | 308 K | 318 K | 323 K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | ||||
| qm (mg/g) | 63.694 | 73.046 | 78.802 | 81.900 |
| KL (L/mg) | 0.211 | 0.218 | 0.226 | 0.228 |
| R2 | 0.990 | 0.990 | 0.985 | 0.985 |
| Freundlich | ||||
| KF (mg/g) | 3.658 | 3.533 | 3.366 | 3.648 |
| 1/n | 0.291 | 0.228 | 0.187 | 0.186 |
| n | 3.433 | 4.378 | 5.341 | 5.358 |
| R2 | 0.938 | 0.971 | 0.987 | 0.985 |
| Temkin | ||||
| KT (L/g) | 0.055 | 0.036 | 0.028 | 0.027 |
| B (J/mol) | 857.626 | 944.870 | 978.052 | 994.678 |
| R2 | 0.880 | 0.943 | 0.976 | 0.971 |
| Dubinin−Radushkevich | ||||
| qm (mg/g) | 56.355 | 60.972 | 64.630 | 66.741 |
| K (mol2 /KJ-2) | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Em (KJ/mol) | 17.175 | 28.748 | 41.130 | 45.128 |
| R2 | 0.939 | 0.744 | 0.728 | 0.708 |
| Van’t Hoff Plot | |
| ∆G (KJ/mol) | -27.552 (298 K) |
| -28.562 (308 K) | |
| -29.573 (318 K) | |
| -30.079 (323 K) | |
| ∆H (KJ/mol) | 2.571 |
| ∆S (J/mol/K) | 101.086 |
| Activation energy (KJmol-1) | 40.306 |
| Pre-exponential factor (A) | 401989 |
| Temperature (K) | Pseudo second order rate constant, K2 (g mg-1 min-1) | Qe (mg g−1) |
| 298 | 0.037 | 24.573 |
| 308 | 0.055 | 38.677 |
| 318 | 0.079 | 43.178 |
| 323 | 0.145 | 44.373 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorption Dosage (mg) |
Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Sugarcane Bagasse | 600 | 37.45 | [66] |
| titanium dioxide/polyurethane nanocomposite modified by sodium dodecyl sulfate | 200 | 20.12 | [67] |
| Fe3O4/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite | 50 | 135.10 | [68] |
| Graphene nanosheet/Fe3O4 | 10 | 44 | [69] |
| Graphene oxide/Fe3O4/chitosan nanocomposite | 10 | 30 | [70] |
| Fe3O4/Fe2TiO5/TiO2 nanocomposite | 10 | 23.573 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





