Submitted:
29 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Patients
Demographic Clinical and Laboratory Data
Statistical Analysis
Results
Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
COVID-19 Vaccination and Infection
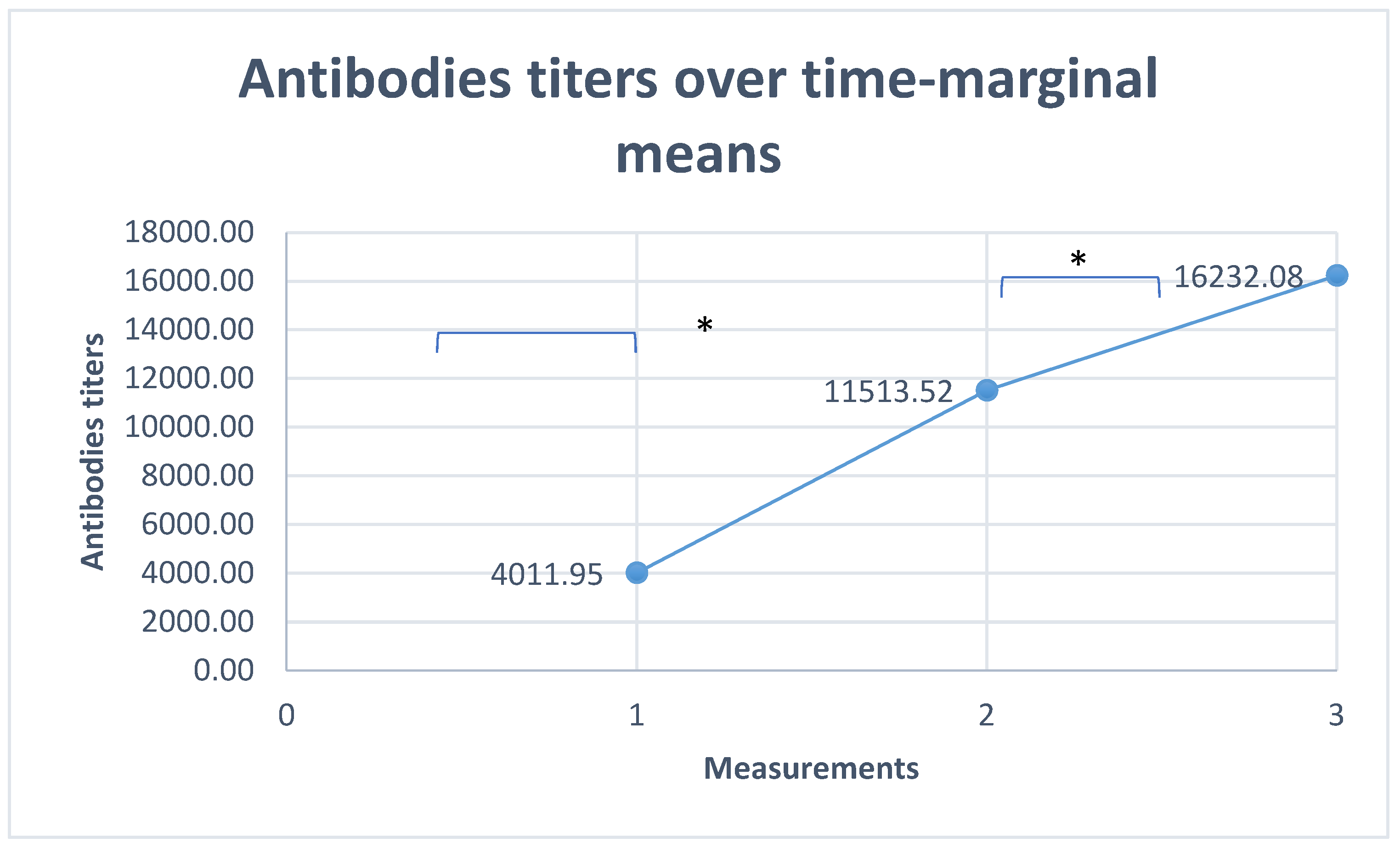
Antibodies Titer over Time
Multi Variant Analysis
Discussion
| First titer of COVID-19 antibodies (784 patients) | Second titer of COVID-19 antibodies (555 patients) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Std. Error | Wald (df=1) | Exp(B) | 95% Confidence Interval | B | Std. Error | Wald | Exp(B) | 95% Confidence Interval | |
| Age | 0.016 | 0.009 | 3.471 | 1.016 | 0.999-1.034 | 0.024 | 0.012 | 4.224* | 1.025 | 1.001-1.049 |
| Sex | 0.232 | 0.214 | 1.169 | 1.261 | 0.828-1.918 | 0.555 | 0.286 | 3.767 | 1.742 | 0.995-3.05 |
| COVID-19 infection | 0.214 | 0.244 | 0.769 | 1.238 | 0.768-1.996 | -0.220 | 0.318 | 0.479 | 0.803 | 0.431-1.496 |
| CD4 | -1.189 | 0.349 | 11.609* | 0.304 | 0.154-0.603 | -1.344 | 0.432 | 9.704** | 0.261 | 0.112-0.607 |
References
- Fernando P Polack 1, Stephen J Thomas 1, Nicholas Kitchin 1, Judith Absalon 1, Alejandra Gurtman 1, Stephen Lockhart et al. Clinical Trial Group. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N Engl J Med 2020 Dec 31;383(27):2603-2615. [CrossRef]
- Thompson MG, Burgess JL, Naleway AL, Tyner H, Yoon SK, Meece J et al. Prevention and Attenuation of Covid-19 with the BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 Vaccines. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jul 22;385(4):320-329. [CrossRef]
- Barbera LK, Kamis KF, Rowan SE, Davis AJ, Shehata S, Carlson JJ et al. HIV and COVID-19: review of clinical course and outcomes. HIV Res Clin Pract. 2021 Aug;22(4):102-118. [CrossRef]
- Lacey CJ. HPV vaccination in HIV infection. Papillomavirus Res. 2019 Dec;8:100174. [CrossRef]
- E. Irungu, N. Mugo, K. Ngure, R. Njuguna, C. Celum, C. Farquhar, et al. Immune response to hepatitis B virus vaccination among HIV-1 infected and uninfected adults in Kenya. J. Infect. Dis., 207 (2013), pp. 402-410. [CrossRef]
- R. Cubas, J. van Grevenynghe, S. Wills, L. Kardava, B.H. Santich, C.M. Buckner, et al. Reversible reprogramming of circulating memory T follicular helper cell function during chronic HIV infection. J. Immunol., 195 (2015), pp. 5625-5636. [CrossRef]
- Levy I, Wieder-Finesod A, Litchevsky V, Biber A, Indenbaum V, Olmer L et al.. Immunogenicity and safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in people living with HIV-1. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Dec;27(12):1851-1855. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Han J, Li X, Chen D, Zhao X, Qiu Y et al. COVID-19 Vaccination in People Living with HIV (PLWH) in China: A Cross Sectional Study of Vaccine Hesitancy, Safety, and Immunogenicity. Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Dec 9;9(12):1458. [CrossRef]
- Noe S, Ochana N, Wiese C, Schabaz F, Von Krosigk A, Heldwein S et al. Humoral response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in people living with HIV. Infection 2022 Jun;50(3):617-623. [CrossRef]
- Tau L, Turner D, Adler A, Marom R, Ahsanov S, Matus N, Levi I et al. SARS-CoV-2 Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses of Patients With HIV After Vaccination With BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in the Tel-Aviv Medical Center. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022 Feb 23;9(4).
- Govere-Hwenje S, Jarolimova J, Yan J, Khumalo A, Zondi G, Ngcobo et al. Willingness to accept COVID-19 vaccination among people living with HIV in a high HIV prevalence community. BMC Public Health. 2022 Jun 22;22(1):1239. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rosenthal EM, Patterson W, Chicoine J, Dorabawila V, Adamashvili N, Rajulu DT, Rosenberg ES, Tesoriero JM. COVID-19 Vaccination and Hospitalization Among Persons Living With Diagnosed HIV in New York State. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2023 Jun 1;93(2):92-100. [CrossRef]
- Shkalim Zemer V, Grossman Z, Cohen HA, Hoshen M, Gerstein M, Yosef N et al. Acceptance Rates of COVID-19 Vaccine Highlight the Need for Targeted Public Health Interventions. Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jul 22;10(8):1167. [CrossRef]
- Israeli ministry of health. Corona virus in Israel - Data (in Hebrew). Available online: https://datadashboard.health.gov.il/portal/dashboard/health/%7Cdashboard.
- Tesoriero JM, Swain CE, Pierce JL, Zamboni L, Wu M, Holtgrave DR et al. COVID-19 Outcomes Among Persons Living With or Without Diagnosed HIV Infection in New York State. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Feb 1;4(2):e2037069. [CrossRef]
- Geretti AM, Stockdale AJ, Kelly SH, Cevik M, Collins S, Waters L, et al. Outcomes of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Related Hospitalization Among People With Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) in the ISARIC World Health Organization (WHO) Clinical Characterization Protocol (UK): A Prospective Observational Study. Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Oct 5;73(7):e2095-e2106. [CrossRef]
- Coburn SB, Humes E, Lang R, Stewart C, Hogan BC, Gebo KA, et al. Analysis of postvaccination breakthrough COVID-19 infections among adults with HIV in the United States. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:e2215934. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Q, Liu Y, Zeng F, Meng Y, Liu H, Deng G. Correlation between CD4 T-Cell Counts and Seroconversion among COVID-19 Vaccinated Patients with HIV: A Meta-Analysis. Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Apr 4;11(4):789. [CrossRef]
- Antinori A, Cicalini S, Meschi S, Bordoni V, Lorenzini P, Vergori A, et al. Humoral and Cellular Immune Response Elicited by mRNA Vaccination Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in People Living With Human Immunodeficiency Virus Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy Based on Current CD4 T-Lymphocyte Count. Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 24;75(1):e552-e563. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hassold N, Brichler S, Ouedraogo E, Leclerc D, Carroue S, Gater Y et al. Impaired antibody response to COVID-19 vaccination in advanced HIV infection. AIDS. 2022 Mar 15;36(4):F1-F5. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Olmedo, A.J., Schulz, A.R., Hochstätter, S. et al. Induction of robust cellular and humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2 after a third dose of BNT162b2 vaccine in previously unresponsive older adults. Nat Microbiol 7, 195–199 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Brumme ZL, Mwimanzi F, Lapointe HR, Cheung P, Sang Y, Duncan MC, et al. Humoral immune responses to COVID-19 vaccination in people living with HIV receiving suppressive antiretroviral therapy. Update in: NPJ Vaccines. 2022 Feb 28;7(1):28. [CrossRef]
| Demographic and clinical characteristics | Total number of PLVWH | PLVWH with CD4 <200 | PLVWH with 200<CD4 <500 | PLVWH with CD4≥500 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total number of PLWH (%) | 784 (100) | 77 (9.8) | 315 (40.2) | 392 (50) | |
| Females (%) | 348 (48.9) | 27 (35.1) | 127 (40.3) | 194 (49.4) | P=0.011 |
| Males (%) | 436 (55.6) | 50 (64.9) | 188 (59.7) | 198 (50.5) | |
| Mean age ±SD ( range), years | 50.2±12.2 (18-89) | 53.2±12.9 (22-89) | 51.7±13.1 (18-85) | 48.4±11.1 (20-89) | P=0.0001 |
| Years since HIV diagnosis | 16.5±7.8 | 17.4±8 | 16.2±7.7 | 16.6±7.8 | P=0.388 |
| Nadir of CD4 cells/µL | 187.8±170 | 79.4±100.6 | 136.8±98.1 | 249.9±199.7 | P=0.001 |
| Viral load suppression (%) | 736 (93.9) | 61 (79.2) | 293 (93) | 382 (97.4) | P=0.0001 |
| Clinical and laboratory data | Total number of PLVWH | PLVWH with CD4 <200 | PLVWH with 200<CD4 <500 | PLVWH with CD4≥500 | P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 vaccination (at least two doses) (%) | 708 (90.3) | 68 (88.3) | 281(89.2) | 359 (91.5) | ||||
| COVID-19 infection (%) | 217 (27.6) | 19 (24.6) | 88 (27.9) | 110 (28.1) | P=0.824 | |||
| Patients hospitalized for COVID-19 infection (%) | 6 (0.8) | 1 (1.3) | 5 (1.68) | 0 (0) | P=0.047 | |||
| Patients with first Antibodies titer for Covid-19 | Low titer | 784 | 166 (21.2) | 32 (41.6) | 62 (19.7) | 72 (18.3) | P=0.0001 | |
| Normal titer | 403 (51.4) | 29 (37.6) | 158 (50.2) | 216 (55.1) | ||||
| High titer | 215 (27.4) | 16 (20.7) | 95 (30.2) | 104 (26.5) | ||||
| Patients with second antibodies titer for Covid-19 | Low titer | 555 | 62 (11.2) | 11 (25.5) | 25 (10.9) | 26 (9.5) | P=0.041 | |
| Normal titer | 159 (28.6) | 18 (41.8) | 71 (31) | 70 (25.6) | ||||
| High titer | 334 (60.2) | 24 (55.8) | 133 (58.1) | 177 (64.8) | ||||
| Patients with third antibodies titer for Covid-19 | Low titer | 46 | 3 (6.5) | 2 (28.6) | 1 (5.2) | 0 (0) | P=0.038 | |
| Normal titer | 12 (26.1) | 3 ( 42.8) | 3 (15.7) | 6 (30) | ||||
| High titer | 31 (67.4) | 2 (28.6) | 15 (78.9) | 14 (70) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





