1. Introduction
Hemodialysis (HD) is a critical treatment for patients with end-stage renal disease, but it is often accompanied by severe complications such as increased oxidative stress and inflammation, which can lead to cellular damage and increase the rates of morbidity and mortality in this population [
1]. Oxidative stress results from an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidant defenses, leading to damage to lipids, proteins, and DNA [
2]. Inflammation, commonly assessed by biomarkers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), is a prevalent issue among HD patients [
3]. For instance, increased levels of ROS and pro-inflammatory cytokines have been associated with cardiovascular complications and a poor prognosis in this population [
4]. Addressing these issues is crucial for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Physical exercise, particularly programs integrating both resistance and endurance training components during HD, known as concurrent training, has emerged as a promising strategy offering significant health benefits for HD patients [
5]. These exercise regimes have been associated with improvements in physical function, cardiovascular health, and overall quality of life [
6,
7]. However, despite these benefits, there remains a notable gap in research regarding the specific effects of intradialytic concurrent training (ICT) on oxidative stress and inflammation in this population. Evidence suggests that exercise can reduce oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in the general population, but the impact on HD patients remains underexplored [
8,
9]. Conducting exercise during dialysis sessions presents an opportunity to potentially alleviate some of the adverse effects associated with HD.
Melatonin (MEL), a hormone primarily known for regulating sleep-wake cycles, also possesses significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties [
10]. MEL supplementation could potentially amplify the benefits of exercise by further reducing OS and inflammation [
11,
12]. Despite the theoretical benefits, there has been limited research on the combined effects of ICT and MEL supplementation in HD patients [
5].
This study aims to explore, the synergistic effects of ICT training and MEL supplementation on oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular damage in HD patients. We hypothesized that this strategy would provide valuable insights into new therapeutic strategies to improve health outcomes for HD patients and potentially attenuate oxidative stress and inflammation in HD patients.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Size
The sample size for this study was calculated a priori using Beck's recommended methods [
13] and the G*Power program [
14] to determine the minimum required sample size. The alpha value (α) was set at 0.05, and the power (1-β error probability) was set at 0.95. Following discussions among the authors, the effect size was estimated to be 0.8. To achieve the desired power and minimize the risk of a type II statistical error, data from at least 21 participants is anticipated to be sufficient.
2.2. Participants
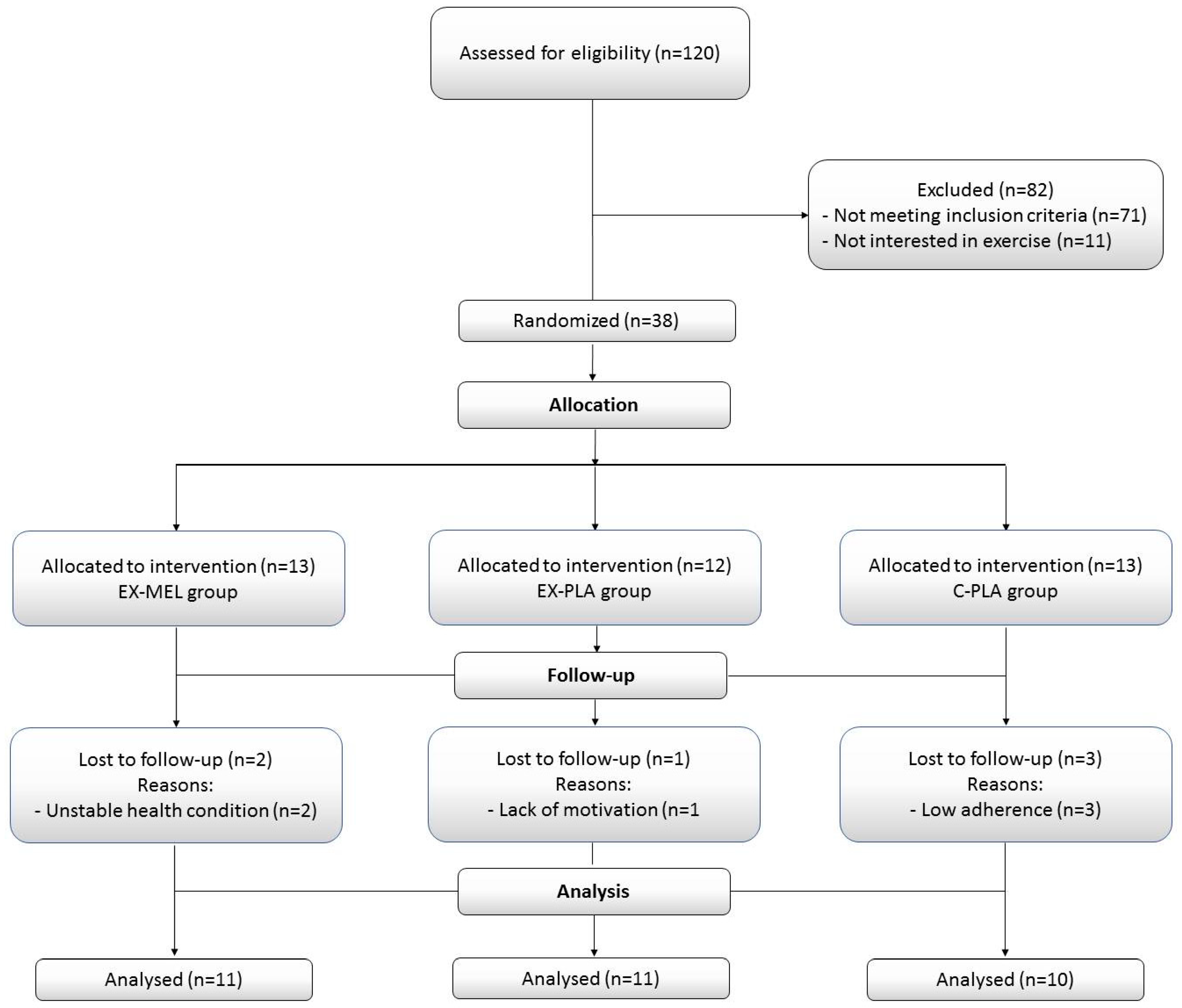
Thirty-two participants (average age 49.21 ± 10.56 years) undergoing HD (a four-hour session, three times per week) for at least six months were recruited from the HD unit of the local University Hospital, and all of them completed the study protocol.
Figure 1 presents a flowchart detailing the participants' progress through the study phases, while
Table 1 displays the participants' baseline characteristics.
All participants had an arteriovenous fistula for dialysis access. Participants were excluded from the study if they met any of the following criteria: (i) recent participation in an exercise program within the last six months; (ii) serious conditions necessitating hospitalization or hindering exercise, severe cardiovascular diseases, (iii) active infectious or inflammatory disease; (iv) orthopedic issues; (v) severe psychological or neurological disorders;(vi) use of antioxidant supplements (i.e., vitamin E, statins, or any other medication with antioxidant properties); (vii) and the use of psychoactive drugs. Participants were randomly assigned to one of three groups: Exercise (EX)-MEL (n=11), EX-Placebo (PLA) (n=11), and Control (C)-PLA (n=10). The dropout rate was set at 15-20% of the total training sessions. All participants received detailed information about the experimental procedures and provided written informed consent to participate. The study was approved by the South Institutional Human Research Ethics Committee in Sfax, Tunisia (N°0059/2017) and conducted in accordance with the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki (2013) [
15].
2.3. Experimental Design
This study was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Participants in the EX-MEL and EX-PLA groups participated in ICT sessions three times per week for 12 weeks. Each evening, 30 minutes before sleep, the EX-MEL group took 3 mg of MEL (Jamieson Laboratories, Toronto, Canada), while the EX-PLA and C-PLA groups received a placebo (Galpharma Laboratories, Sfax, Tunisia). The 3 mg MEL dose was chosen based on recommendations for HD patients by Koch et al. [
16] and Russcher et al. [
17], with no significant side effects reported at this dosage. Participants in the EX-MEL and EX-PLA groups were familiarized with the lower limb cycle ergometer, resistance exercises (including knee extension, hip abduction, and flexion), and the Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) scale to minimize learning effects. Additionally, the height and body weight of the participants were measured using a semi-analytical balance scale, and their body mass index (BMI) was calculated as BMI = weight (kg)/height (m)². Before and after the 12-week intervention period, blood samples were taken from all participants to assess lipid peroxidation [malondialdehyde (MDA)], antioxidant biomarkers [ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), reduced glutathione (GSH), total thiol (THIOL)], total bilirubin (TBIL), uric acid (UA), biomarkers of muscle and liver damage [aspartate aminotransferase (ASAT), alanine aminotransferase (ALAT), creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), Gamma-glutamyltransferase (Gamma-GT)], and CRP.
2.4. Concurrent Training Program
During the first 2 hours of HD, participants in the EX-MEL and EX-PLA performed an ICT program in the HD unit and under the supervision of physicians. Each ICT session involved endurance and resistance exercises. The endurance exercise began with a 5-minute warm-up, followed by 15 minutes of cycling on a lower-limb cycle ergometer (Everfit Welly-M, Italy) placed in front of each participant. The exercise duration was gradually increased, adding 5 minutes at the end of the first week and 10 minutes at the end of the second week to reach 30 minutes within the first two weeks. Subsequently, the exercise duration increased by 5-10% weekly, reaching 60 minutes by the end of the intervention. Exercise intensity was prescribed and monitored based on participants' heart rate (HR), targeting 50 to 60% of their maximum HR (HRmax = 207–0.7 × age) [
18]. Since many HD patients use beta-blockers, the modified Borg’s RPE scale [
19] was also employed to subjectively control the exercise intensity. The range of the modified RPE scale is 0 to 10, where 0 represents no exertion and 10 represents maximal effort. Participants were asked to cycle at a self-selected pace corresponding to an RPE of 3-4, corresponding to "mild" to "quite hard" effort.
For resistance training, the initial weights for knee extension, hip abduction, and flexion exercises were determined using a three-repetition maximum (3-RM) test [
5]. Participants performed 2-3 sets of 10 repetitions at approximately 60% of 3-RM using ankle weights. When participants could complete three sets with the correct technique, the weight was increased. Recovery periods were 1 minute between sets and 3 minutes between exercises. Throughout the training session, exercise intensity and vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation (SpO2)) were monitored every 5 minutes. After exercising, lower-limb stretching exercises were performed, targeting the hamstrings, hip adductors, hip abductors, tibialis anterior, gastrocnemius, and soleus muscles. The exercise regimen was discontinued if participants experienced any of the following indications or symptoms: (i) chest pain, (ii) arrhythmias, (iii) dyspnea, (iv) nausea, (v) muscle pain or cramps, (vi) episodes of hypotension or hypertension, or (vii) a high RPE score on the modified Borg’s scale. The C-PLA group continued their standard HD sessions without intradialytic exercise.
2.5. Blood Sampling and Assays
Patients were instructed to fast overnight for at least 8 hours and refrain from exercising for 24 hours before blood sample collection. Resting blood samples (~10 mL) were obtained from the antecubital vein both before (one day prior to the first training session) and after training (one day after the final training session). These samples were collected at the same time of day, between 07:00 and 07:30 AM, to minimize circadian fluctuations. Blood samples were divided into three tubes: one containing K2EDTA (3.5 ml), one containing lithium heparin (4 ml), and one without anticoagulant (2.5 ml). Samples were placed in an ice bath and immediately centrifuged at 2500 rpm and 4 °C for 10 minutes. Aliquots of the resulting plasma were stored at 80 °C until analysis. K2EDTA tubes were used to determine MDA, GSH, THIOL, and FRAP. Plasma levels of TBIL, UA, Gamma-GT, ASAT, ALAT, CK, LDH, and CRP were assessed using lithium heparin tubes. To reduce inter-assay variance, all samples were analyzed in the same assay run.
2.5.1. Determination of Lipid Peroxidation (MDA)
Following the method described by Wong et al. [
20], a 0.5 ml plasma sample was mixed with 0.1 ml of tris-HCL buffer (pH 7.2) and incubated at 95 °C in a water bath. After incubation, 0.5 ml of the mixture was combined with 9 ml of distilled water and 2 ml of 0.6% thiobarbituric acid and then heated for 30 minutes in a boiling water bath. After cooling, 5 ml of n-butanol was added, and the mixture was vigorously stirred. The n-butanol layer was then separated by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the malonic MDA content was quantified using a spectrophotometer at 532 nm (Libra S21, Biochrom).
2.5.2. Measurement of FRAP Levels
The determination of FRAP was conducted using the method of Benzie and Strain with a slight modification [
21].
Principle: This reaction involves the reduction of the ferric tripyridyltriazine complex (TPTZ-Fe3+) to the ferrous form (Fe2+) in an acidic medium by antioxidants present in the sample.
Required reagents include: Acetate buffer (pH 3.6), which is a mixture of two solutions: 46.3 ml of solution A and 3.7 ml of solution B. Solution A consists of 0.2 M acetic acid (11.55 ml in 1 L of distilled water), with a molar mass of 60.052 g/mol. Solution B consists of 0.2 M sodium acetate (16.4 g sodium acetate in 1 L of distilled water). The reactive mixture (1:1) comprises 20 mM ferric chloride [FeCl3•6H2O] and 10 mM tripyridyltriazine in 40 mM HCl. Ferric sulfate (FeSO4) was used to create the calibration curve [1-0.1 mmol/L]. The method was calibrated using a standard solution of hydrated ferrous sulfate FeSO4•5H2O with concentrations ranging from 0 to 1.5 mM. The reducing capacity of the sample was expressed in equivalents of ferrous ions in plasma (μmol Fe2+/L).
Calculation: The FRAP concentrations were calculated using the formula [FRAP] (μmol/L) = DO - b/a * 1000, where DO is the optical density, 'a' is the slope of the Fe2+SO4 calibration curve (mmol/L), 'b' is the y-intercept, and 1000 is the conversion factor from mmol to μmol.
2.5.3. Measurement of GSH Levels
Determination of GSH level is carried out using a colorimetric method with Ellman's reagent: 5,5'-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) [
22]. The principle involves the reaction of GSH with DTNB, releasing thionitrobenzoic acid (TNB), which has an absorbance at 412 nm. The necessary reagents include a 4% aqueous solution of sulfosalicylic acid, a Tris-EDTA buffer solution (0.25 M Tris base + 0.02 M EDTA) composed of two solutions: Tris base (0.5 M) prepared by weighing 3 g in 50 ml distilled water and EDTA (0.04 M) prepared by weighing 0.58 g in 50 ml distilled water. These solutions are mixed (V/V) to obtain the Tris-EDTA buffer, with the pH adjusted to 8.2. A freshly prepared 10 mM DTNB solution is made by dissolving DTNB in an adequate volume of methanol, and the bottle must be kept away from light by wrapping it in aluminum foil. Reduced glutathione (GSH) is used to create the calibration curve [1 - 0.03 mmol/L]. GSH levels were determined using Jollow et al.'s method [
23]. The calculation, based on a standard curve prepared with reduced glutathione, expresses the result in nanomoles per milliliter of plasma, then adjusted to protein levels (nmol GSH/mg protein).
The formula used is [GSH] (nmol/mg) = (DO - b/a * FD * 1000) / [proteins mg/ml], where 'DO' is the optical density, 'a' is the slope of the GSH calibration curve (μmol/ml), 'b' is the y-intercept, FD is the dilution factor, and 1000 is the conversion factor from μmol to nmol.
2.5.4. Determination of THIOL Levels
Following Hu's methodology [
24], THIOL levels were evaluated using a spectrophotometric technique. A mixture of 50 µl of plasma and 1000 µl of Tris-EDTA buffer (0.25 M, 20 mM, pH 8.2) was prepared, with the initial absorbance recorded at 412 nm. Subsequently, 20 µl of DTNB (10 mM) was added to the solution, which was then protected from light. After 10 minutes, the absorbance was measured again. The difference between the initial and final absorbance values was used to calculate the THIOL concentration, adjusting for the standard range coefficient and plasma protein concentration.
2.5.5. Routine Biochemistry Parameters
The Cobas 6000 ® (module c501) automated biochemistry analyzer was used to measure TBIL, UA, ASAT, ALAT, CK, LDH, Gamma-GT, and CRP. TBIL was tested using the Diazo reaction [
25]. An enzymatic technique was employed to determine UA at 550 nm [
26]. The concentrations of ASAT, ALAT and CK levels were assessed using the N-acetyl-L-cysteine enzymatic technique [
27]. According to the IFCC, LDH concentration was measured using the UV test, and Gamma-GT was measured using the colorimetric enzymatic assay (L-γ-glutamyl carboxy-3-nitro-4-anilide as the substrate) [
28]. CRP was measured using the immunoturbidimetric technique [
29].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) in the tables and figures. The normality of the distribution was assessed and confirmed using the Shapiro–Wilk test prior to statistical analysis. Differences between group characteristics were examined using one-way ANOVA. Additionally, two-way repeated measures ANOVA [Groups (EX-MEL vs. EX-PLA vs. C-PLA) × Time (pre-training vs. post-training)] was used to analyze the data. Practical significance of the ANOVA was evaluated using partial eta-squared (ηp²). When necessary, the Bonferroni post-hoc test was used for pairwise comparisons. Effect sizes were calculated using Cohen’s d method and interpreted as small (<0.3), medium (<0.5), or large (>0.8) [
30]. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05. All statistical analyses were performed using Statistica 10 software (StatSoft, Maisons-Alfort, France).
3. Results
Statistical analysis of MDA, FRAP, GSH, and THIOL showed significant effects of time (F(1,31) = 23.87, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.72; F(1,31) = 25.04, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.73; F(1,31) = 37.98, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.80; and F(1,31) = 26.04, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.74, respectively). Moreover, significant interactions (Time × Groups) were observed for THIOL and CRP (F(2,30) = 4.89, p < 0.05, ηp2 = 0.35 and F(2,30) = 6.70, p < 0.01, ηp2 = 0.42, respectively). However, no significant variations in TBIL, UA, CK, LDH, ASAT, ALAT, and Gamma-GT were observed pre- and post-training in all groups (
Table 2).
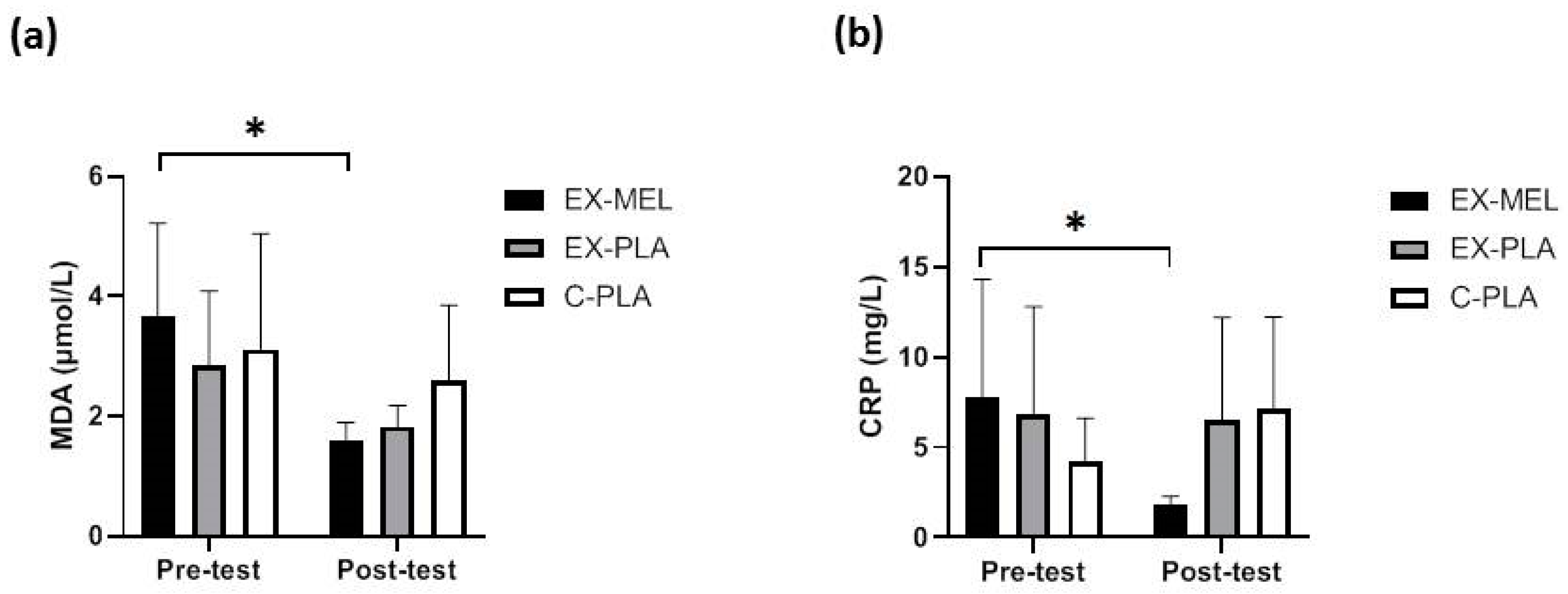
EX-MEL showed significant improvements in lipid peroxidation (MDA) (p < 0.05, d = 2.24) (
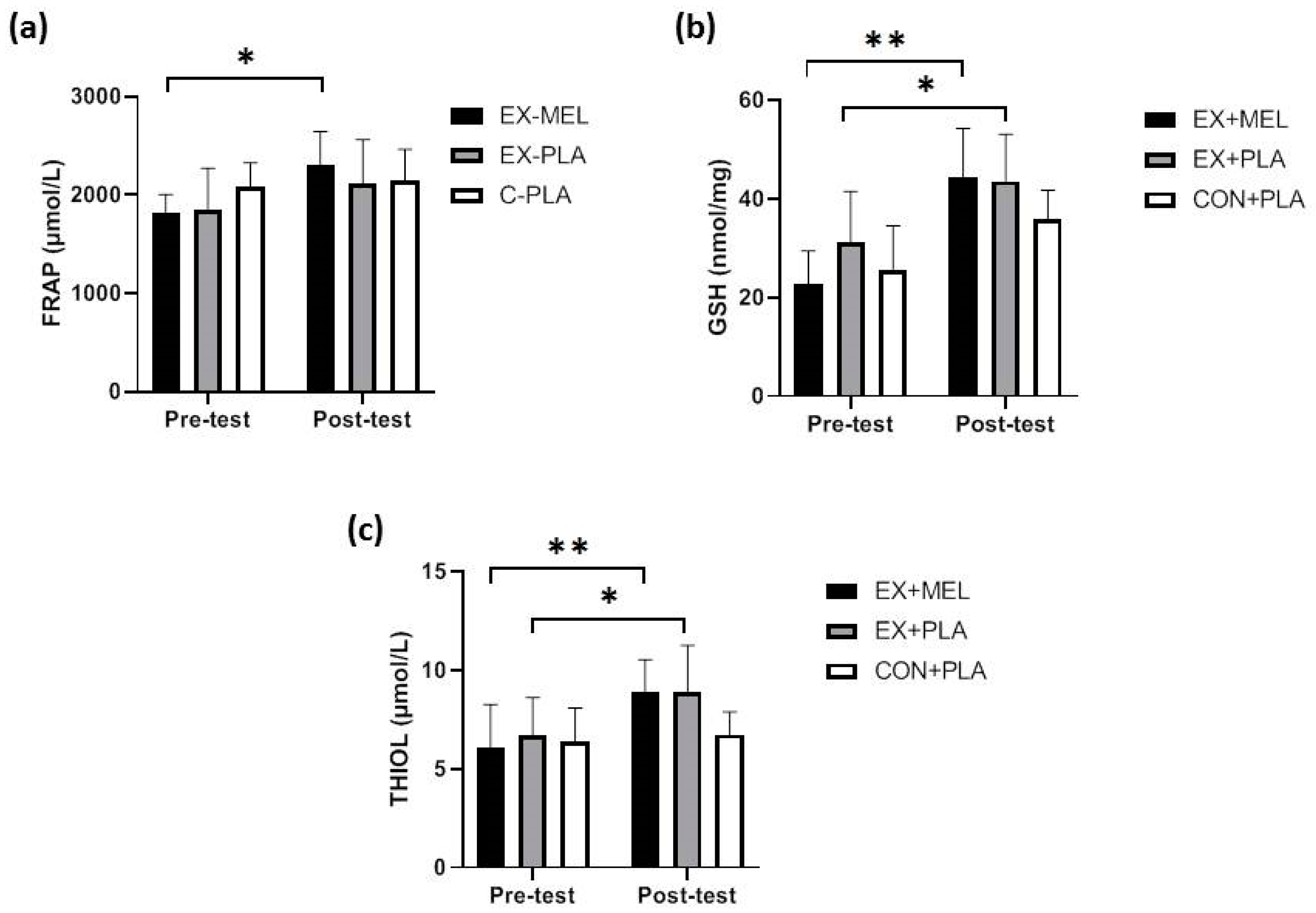
Figure 2a), total antioxidant capacity (FRAP) (p < 0.05, d = 1.83) (
Figure 3a), and CRP (p < 0.05, d = 1.70) (
Figure 2b) pre- and post-training.
EX-MEL and EX-PLA showed significant increases in GSH (p < 0.001, d = 2.57 and p < 0.05, d = 1.24, respectively) (
Figure 3b) and THIOL (p < 0.01, d = 1.46; p < 0.05, d = 1.01, respectively) (
Figure 3c) pre- and post-training. Nevertheless, no significant differences were noted between EX-MEL and EX-PLA.
4. Discussion
This study investigated the combined effects of ICT and MEL supplementation on oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular damage in HD patients. The results showed that both the EX-MEL and EX-PLA groups exhibited notable increases in GSH and THIOL levels, while the EX-MEL group showed significant improvements in MDA, FRAP, and CRP levels pre- and post-training. The potential benefits of this combined intervention highlight significant improvements in markers of oxidative stress and inflammation.
ICT showed positive effects on oxidative stress markers, consistent with prior studies on exercise benefits in HD patients [
31,
32]. In the present study, both the EX-MEL and EX-PLA groups demonstrated significant increases in GSH and THIOL levels, indicating enhanced antioxidant defenses. These findings support the idea that exercise during dialysis sessions improves the oxidant-antioxidant balance [
6,
33]. Regular exercise enhances antioxidant enzyme activity and reduces oxidative stress in various populations, involving those with chronic kidney disease (CKD) undergoing HD [
34]. The mechanisms by which ICT enhances antioxidant defenses include the upregulation of key antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which detoxify ROS [
35]. Exercise stimulates GSH synthesis, enhancing the cell's capacity to neutralize free radicals and regenerate other antioxidants [
36], and improves mitochondrial function, reducing electron leakage and ROS formation, thereby lowering oxidative stress [
37]. Additionally, exercise activates the Nrf2 pathway, promoting the expression of antioxidant and cytoprotective genes that maintain cellular redox homeostasis [
38] and decreasing the levels of pro-oxidant enzymes like NADPH oxidase and xanthine oxidase, reducing ROS production [
39]. MEL's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties are well-established, but its specific effects on HD patients have been less explored [
5,
12,
40]. The EX-MEL group's significant improvements in MDA, FRAP, and CRP levels highlight MEL's potential to enhance the benefits of exercise by further reducing oxidative stress and inflammation [
11,
12]. This synergy could be due to MEL's ability to scavenge ROS and upregulate antioxidant enzymes, thereby amplifying the exercise-induced protective effects [
41]. MEL directly neutralizes ROS such as hydroxyl radicals and superoxide anions, reducing oxidative stress [
42]. Moreover, MEL indirectly enhances the activities of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD and GPx [
42]. In HD patients, MEL supplementation reduces oxidative stress markers, including MDA and advanced oxidation protein products, while increasing biomarkers of the antioxidant system, such as CAT and total thiol. [
12].
MEL also inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β and suppresses NF-κB, a key transcription factor involved in inflammation [
43,
44]. Importantly, no side effects of MEL supplementation were observed in the present study, consistent with the findings of Marzougui et al. [
5] and Koch et al. [
16]. The improvements in MDA, FRAP, and CRP levels in the EX-MEL group underscore MEL's potential to enhance exercise-induced benefits, offering a promising adjunct therapy for HD patients [
5,
12].
TBIL and UA levels pre- and post-training did not change significantly across all groups. This outcome highlights the safety and metabolic stability of the combined intervention of ICT and MEL supplementation in HD patients. Bilirubin, a byproduct of hemoglobin breakdown processed in the liver, serves as a marker for liver function and hemolysis [
45]. Elevated levels can indicate liver dysfunction or hemolysis, while low levels may signal reduced red blood cell turnover [
46]. In this study, the unchanged TBIL levels post-intervention suggest that neither the exercise regimen nor MEL supplementation imposed additional stress on the liver, which is crucial for HD patients with compromised liver function due to CKD [
45].
Similarly, UA, a product of purine metabolism, is often elevated in CKD patients due to reduced renal clearance [
47]. High UA levels can contribute to gout and cardiovascular complications [
48,
49]. The absence of significant changes in UA levels post-intervention indicates that the interventions did not adversely impact purine metabolism. Additionally, it suggests that they did not exacerbate UA accumulation [
47,
48]. These findings underscore the metabolic stability of the combined exercise and MEL supplementation regimen in HD patients, supporting its safety and potential clinical benefits.
Interestingly, no significant changes in biomarkers of muscle and liver damage (CK, LDH, ASAT, ALAT, and Gamma-GT) were found across all groups pre- and post-intervention. This suggests that the concurrent training program, whether combined with MEL supplementation or not, did not exacerbate muscle or liver injuries in HD patients. This finding is crucial, as it indicates that the prescribed exercise regimen is safe and does not lead to additional cellular damage in these patients.
CK and LDH are commonly used biomarkers for muscle damage, while ASAT, ALAT, and Gamma-GT are indicators of liver damage [
50]. Elevated levels of these enzymes can signal tissue damage or stress [
51]. The lack of significant changes in these biomarkers suggests that the exercise intensity and duration were well-tolerated by the participants. This aligns with existing research showing that appropriately monitored exercise does not necessarily cause harm to HD patients and can be a safe part of their therapeutic regimen [
5,
12].
The outcomes of the current study have important clinical implications for the management of oxidative stress and inflammation in HD patients, which provides a strong rationale for integrating these interventions into routine HD care. It demonstrates that a combination of ICT and MEL supplementation can yield significant health benefits without causing muscle or liver damage. Future studies should explore the long-term effects of this combined approach and investigate the underlying mechanisms driving these benefits.
While the results are promising, the study has some limitations. The sample size, although calculated to ensure sufficient power, is relatively small, and the duration of the intervention was limited to 12 weeks. Larger sample size and longer-term studies are needed to confirm these findings and evaluate the sustainability of the observed benefits.
5. Conclusions
This study provides compelling evidence that combining ICT with MEL supplementation can significantly reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in HD patients without causing muscle or liver damage. These findings suggest a novel therapeutic strategy that could improve health outcomes and quality of life for individuals undergoing HD. Further research is warranted to validate these results and explore the broader implications of this combined intervention.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.M., O.H., M.B.-H., I.B.-D., R.M. and M.T.; methodology, H.M., O.H., S.T., K.K., M.B.-H and M.T.; formal analysis, H.M., I.M., S.T., M.N.-C ., F.A.; investigation, H.M., I.B.-D., R.M., M.N.-C, and S.T.; writing—original draft preparation, H.M., O.H., I.B.-D., and I.M.; writing—review and editing, H.M., M.B.-H., O.H., I.B.-D., K.K., I.M., and R.M.; supervision, O.H., M.T., M.B.-H., F.A., and K.K.; project administration, H.M., M.T., O.H., M.B.-H., and S.T.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the South Institutional Human Research Ethics Committee in Sfax, Tunisia (N°0059/2017) and conducted in accordance with the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki (2013).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the study.
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to all the participants and the medical staff at the Nephrology Department of Hedi Chaker Hospital and the Chaabouni Dialysis Clinic for their invaluable support and assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Daugirdas, J.T.; Depner, T.A.; Inrig, J.; Mehrotra, R.; Rocco, M.V.; Suri, R.S.; Weiner, D.E.; Greer, N.; Ishani, A.; MacDonald, R. KDOQI clinical practice guideline for hemodialysis adequacy: 2015 update. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2015, 66, 884–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M. Free radicals in biology and medicine; Oxford university press, USA: 2015.
- Stenvinkel, P.; Heimbürger, O.; Paultre, F.; Diczfalusy, U.; Wang, T.; Berglund, L.; Jogestrand, T. Strong association between malnutrition, inflammation, and atherosclerosis in chronic renal failure. Kidney international 1999, 55, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daenen, K.; Andries, A.; Mekahli, D.; Van Schepdael, A.; Jouret, F.; Bammens, B. Oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Pediatric nephrology 2019, 34, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzougui, H.; Maaloul, R.; Ben Dhia, I.; Toumi, S.; Kammoun, K.; Ben Hmida, M.; Ayadi, F.; Turki, M.; Elleuch, M.H.; Ghroubi, S. Effects of intradialytic exercise in combination with melatonin supplementation on functional capacity, postural balance, and quality of life in hemodialysis patients. Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis 2023, 27, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, B.S.B.; Fiatarone Singh, M.A. Exercise training in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis: a systematic review of clinical trials. American journal of nephrology 2005, 25, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, N.A.; Williams, A.D.; Levinger, I.; Selig, S.; Howden, E.; Coombes, J.S.; Fassett, R.G. Exercise & Sports Science Australia (ESSA) position statement on exercise and chronic kidney disease. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 2013, 16, 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Wilund, K.R.; Tomayko, E.J.; Wu, P.-T.; Ryong Chung, H.; Vallurupalli, S.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; Fernhall, B. Intradialytic exercise training reduces oxidative stress and epicardial fat: a pilot study. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2010, 25, 2695–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.L.; Toffelmire, E.B.; King-VanVlack, C.E. Exercise training during hemodialysis improves dialysis efficacy and physical performance. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation 2006, 87, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J., et al., Peripheral reproductive organ health and melatonin: ready for prime time. International journal of molecular sciences, 2013. 14(4): p. 7231-7272.
- Marzougui, H., et al., Melatonin ingestion before intradialytic exercise improves immune responses in hemodialysis patients. International Urology and Nephrology, 2021. 53: p. 553-562.
- Marzougui, H. , et al., Melatonin intake before intradialytic exercise reverses oxidative stress and improves antioxidant status in hemodialysis patients. The International Journal of Artificial Organs, 2023. 46(5): p. 264-273.
- Beck, T.W. The importance of a priori sample size estimation in strength and conditioning research. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research 2013, 27, 2323–2337. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G* Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior research methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, W.M. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 2001, 79, 373. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, B.C.; Nagtegaal, J.E.; Hagen, E.C.; Van Der Westerlaken, M.M.; Boringa, J.B.; Kerkhof, G.A.; Ter Wee, P.M. The effects of melatonin on sleep–wake rhythm of daytime haemodialysis patients: a randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over study (EMSCAP study). British journal of clinical pharmacology 2009, 67, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russcher, M.; Koch, B.C.; Nagtegaal, J.E.; van Ittersum, F.J.; Pasker-de Jong, P.C.; Hagen, E.C.; van Dorp, W.T.; Gabreëls, B.; Wildbergh, T.X.; van der Westerlaken, M.M. Long-term effects of melatonin on quality of life and sleep in haemodialysis patients (M elody study): a randomized controlled trial. British journal of clinical pharmacology 2013, 76, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellish, R.L.; Goslin, B.R.; Olson, R.E.; McDONALD, A.; Russi, G.D.; Moudgil, V.K. Longitudinal modeling of the relationship between age and maximal heart rate. Medicine and science in sports and exercise 2007, 39, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G.A. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Medicine and science in sports and exercise 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Knight, J.A.; Hopfer, S.; Zaharia, O.; Leach Jr, C.N.; Sunderman Jr, F.W. Lipoperoxides in plasma as measured by liquid-chromatographic separation of malondialdehyde-thiobarbituric acid adduct. Clinical chemistry 1987, 33, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płonka-Półtorak, E.; Zagrodzki, P.; Chłopicka, J.; Bartoń, H.; Westermarck, T.; Kaipainen, P.; Kaski, M.; Atroshi, F. Valproic acid modulates superoxide dismutase, uric acid-independent FRAP and zinc in blood of adult epileptic patients. Biological trace element research 2011, 143, 1424–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsu, S.; Bolu, A.; Aydemir, E.; Zincir, S.B.; Kurt, Y.G.; Zincir, S.; Erdem, M.; Uzun, Ö. The relationship between the number of manic episodes and oxidative stress indicators in bipolar disorder. Psychiatry investigation 2018, 15, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jollow, D.; Mitchell, J.; Zampaglione, N.a.; Gillette, J. Bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3, 4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 1974, 11, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-L. [41] Measurement of protein thiol groups and glutathione in plasma. In Methods in enzymology, Elsevier: 1994; Vol. 233, pp. 380-385.
- Watson, D. Analytic methods for bilirubin in blood plasma. Clinical Chemistry 1961, 7, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SUzUKI, M.; TAKAYANAGI, M.; YASHIRO, T. Use of the o-phenylenediamine fluorescence system in the enzymatic assay of serum uric acid. Chemical and pharmaceutical bulletin 1991, 39, 2745–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nealon, D.; Henderson, A. N-Acetyl-L-cysteine as a reactivator of creatine kinase. Clinical chemistry 1977, 23, 618–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siekmann, L.; Bonora, R.; Burtis, C.A.; Ceriotti, F.; Clerc-Renaud, P.; Férard, G.; Ferrero, C.A.; Forest, J.-C.; Franck, P.F.; Gella, F.-J. IFCC primary reference procedures for the measurement of catalytic activity concentrations of enzymes at 37 C. Part 7. Certification of four reference materials for the determination of enzymatic activity of γ-glutamyltransferase, lactate dehydrogenase, alanine aminotransferase and creatine kinase according to IFCC reference procedures at 37 C. 2002.
- Dupuy, A.M.; Badiou, S.; Descomps, B.; Cristol, J.P. Immunoturbidimetric determination of C-reactive protein (CRP) and high-sensitivity CRP on heparin plasma. Comparison with serum determination. Walter de Gruyter: 2003.
- Cohen, J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences; routledge: 2013.
- Storer, T.W.; Casaburi, R.; Sawelson, S.; Kopple, J.D. Endurance exercise training during haemodialysis improves strength, power, fatigability and physical performance in maintenance haemodialysis patients. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2005, 20, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koufaki, P.; Mercer, T.H.; Naish, P.F. Effects of exercise training on aerobic and functional capacity of end-stage renal disease patients. Clinical physiology and functional imaging 2002, 22, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustata, S.; Groeneveld, S.; Davidson, W.; Ford, G.; Kiland, K.; Manns, B. Effects of exercise training on physical impairment, arterial stiffness and health-related quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease: a pilot study. International urology and nephrology 2011, 43, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, K.L.; Painter, P.L.; Sakkas, G.K.; Gordon, P.; Doyle, J.; Shubert, T. Effects of resistance exercise training and nandrolone decanoate on body composition and muscle function among patients who receive hemodialysis: a randomized, controlled trial. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006, 17, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, E.C.; Silva, A.N.; Oliveira, M.R.d. Oxidants, antioxidants, and the beneficial roles of exercise-induced production of reactive species. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2012, 2012, 756132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Jackson, M.J. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiological reviews 2008, 88, 1243–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Duarte, J.; Kavazis, A.N.; Talbert, E.E. Reactive oxygen species are signalling molecules for skeletal muscle adaptation. Experimental physiology 2010, 95, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Done, A.J.; Traustadóttir, T. Nrf2 mediates redox adaptations to exercise. Redox biology 2016, 10, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.I.; Griendling, K.K. Regulation of signal transduction by reactive oxygen species in the cardiovascular system. Circulation research 2015, 116, 531–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzougui, H.; Hammouda, O.; Dhia, I.B.; Maaloul, R.; Agrebi, I.; Chaker, H.; Kammoun, K.; Hmida, M.B.; Ayadi, F.; Kallel, C. Melatonin ingestion before intradialytic exercise improves immune responses in hemodialysis patients. International Urology and Nephrology 2021, 53, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.-x.; Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; Leon, J.; Czarnocki, Z. Melatonin as an antioxidant: biochemical mechanisms and pathophysiological implications in humans. Acta Biochimica Polonica 2003, 50, 1129–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Srinivasan, V.; Maestroni, G.; Cardinali, D.P.; Poeggeler, B.; Hardeland, R. Melatonin: Nature's most versatile biological signal? The FEBS journal 2006, 273, 2813–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R. Atioxidative protection by melatonin: Multiplicity of mechanisms from radical detoxification to radical avoidance. Endocrine 2005, 27, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Vico, A.; Lardone, P.J.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Guerrero, J.M. Melatonin: buffering the immune system. International journal of molecular sciences 2013, 14, 8638–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; McDonagh, A.F.; Glazer, A.N.; Ames, B.N. Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance. Science 1987, 235, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitek, L.; Ostrow, J.D. Bilirubin chemistry and metabolism; harmful and protective aspects. Current pharmaceutical design 2009, 15, 2869–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.J.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Gaucher, E.A. Uric acid: a danger signal from the RNA world that may have a role in the epidemic of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiorenal disease: evolutionary considerations. In Proceedings of Seminars in nephrology; pp. 394-399.
- Feig, D.I.; Johnson, R.J. Hyperuricemia in childhood primary hypertension. hypertension 2003, 42, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Yoon, Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Hien, T.T.; Kang, K.W.; Kim, K.C.; Lee, J.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Kang, D.H. Uric acid induces endothelial dysfunction by vascular insulin resistance associated with the impairment of nitric oxide synthesis. The FASEB Journal 2014, 28, 3197–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler Jr, W.; Gardner, G.; Kazerunian, H.; Lauvstad, W. The effect of exercise on serum enzymes. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation 1968, 49, 554–565. [Google Scholar]
- Nathwani, R.A.; Pais, S.; Reynolds, T.B.; Kaplowitz, N. Serum alanine aminotransferase in skeletal muscle diseases. Hepatology 2005, 41, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).