1. Introduction
Additive Friction Stir Deposition (AFSD) is a novel solid-state metal additive manufacturing process that combines friction stir welding and material feeding to provide site-specific, solid-state deposition. In this method, a solid feed-rod material is given through a hollow rotating tool head, causing frictional heat at the feed-rod-substrate interface [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. This heat softens the feed material, which is subsequently deposited on the substrate via extreme plastic deformation and compression. The process requires high shear strain rates, which cause extra volumetric self-heating. The tool head's in-plane motion deposits a continuous track of material, which can be built up layer by layer to form a three-dimensional component [
6,
7,
8]. AFSD differs significantly from other solid-state additive manufacturing processes like friction stir welding (FSW) and traditional beam-based techniques such as powder bed fusion and directed energy deposition. In contrast to FSW, which mostly depends on a non-consumable pin's stirring action, AFSD employs a consumable feed rod that is continually fed into the deposition zone. This makes it possible to produce new material and deposit it onto the substrate. Whereas lateral material flow around a pin occurs in FSW, vertical interaction between the deposited material and substrate occurs in AFSD. The material flow properties and geometric configuration of AFSD are altered when a penetrating pin is not present. In contrast to FSW where the workpieces impose lateral limitations on the stir zone material, the deposited material in AFSD lays on top of the substrate without mechanical restraint in the lateral direction [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15]. AFSD produces high-quality interfaces with excellent mechanical properties in the as-deposited state. This contrasts with beam-based additive manufacturing technologies, which often result in anisotropic mechanical behavior due to weak interfacial bonding. AFSD can achieve isotropic mechanical properties, comparable tensile or compressive strength in both in-plane and out-of-plane directions, and high-quality interfaces that withstand significant bending without delamination.
Materials science and additive manufacturing (AM) could undergo a radical transformation because to generative AI's capacity to discover patterns, create original designs, and streamline intricate procedures. Vast design spaces can be explored by generative AI algorithms, which can then produce optimal structures that minimize material consumption and production time while meeting set performance standards. This could result in the creation of components with complex geometries that are lightweight, highly durable, and could not have been produced using conventional techniques. The development of novel materials with specific qualities can be sped up with the help of generative AI. AI algorithms may find viable candidates and forecast their performance under different conditions by analyzing massive databases of material compositions and properties [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21]. This greatly reduces the time and expense associated with traditional trial-and-error methods.
Building on the unique capabilities of Additive Friction Stir Deposition (AFSD), incorporating Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) into this process provides a significant technological advancement. The complexity and multidimensional nature of AFSD necessitates such an integration, as a diverse range of data types—including textual descriptions, high-resolution images, and audio signals—play critical roles in process optimization, monitoring, and quality assurance. Traditional data analysis tools are frequently limited in their ability to handle such heterogeneous data, resulting in inadequate process understanding and control. By using a multimodal RAG framework, it is feasible to smoothly integrate these many data modalities, improving the retrieval and creation of information pertinent to the AFSD process. The implementation of multimodal RAG in AFSD is critical for a variety of reasons. For first of all, it allows for more thorough and accurate data retrieval, combining information from numerous sources to create a more complete context for decision-making. Textual data on material qualities and deposition parameters, for example, can be coupled with visual data from in-situ imaging and acoustic signals generated during the deposition process. This holistic approach enables more precise identification of optimal process parameters, resulting in better material characteristics and component performance. Furthermore, integrating multimodal data aids in the detection and mitigation of potential errors in real time, considerably improving the AFSD process's reliability and efficiency.
The capacity to produce extensive, context-aware explanations and responses using multimodal RAG is extremely useful for both operators and researchers. It promotes knowledge sharing and innovation while also allowing for a better understanding of the intricate mechanisms at work in AFSD. For example, operators can obtain real-time insights and actionable recommendations based on the most recent research and historical data, shortening the learning curve and lowering the chance of errors. Researchers, on the other hand, can use the synthesized data to investigate new applications and improve existing procedures, resulting in additional progress in the field of solid-state additive manufacturing.
2. Problem Statement
The integration and successful use of multimodal data, especially text and images, is a significant problem in the field of Additive Friction Stir Deposition (AFSD). Current approaches frequently fall short of effectively evaluating and utilizing these different data sources, resulting in restricted process understanding and analysis capabilities. To improve understanding and potential applications of the AFSD process, a new framework capable of efficiently integrating and analysing multimodal data is required. The goal of this work is to create a Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system that is specifically designed for AFSD. The suggested system will retrieve and synthesize essential information from several data sources, resulting in greater insights and more thorough descriptions of process mechanisms. By utilizing advanced AI approaches, this system is intended to significantly increase our capacity to comprehend complicated AFSD data, provide thorough process descriptions, and detect critical properties of manufactured components. Finally, the adoption of this multimodal RAG system is expected to improve our understanding of AFSD, possibly leading to future advances in process control and material science applications.
3. Methodology
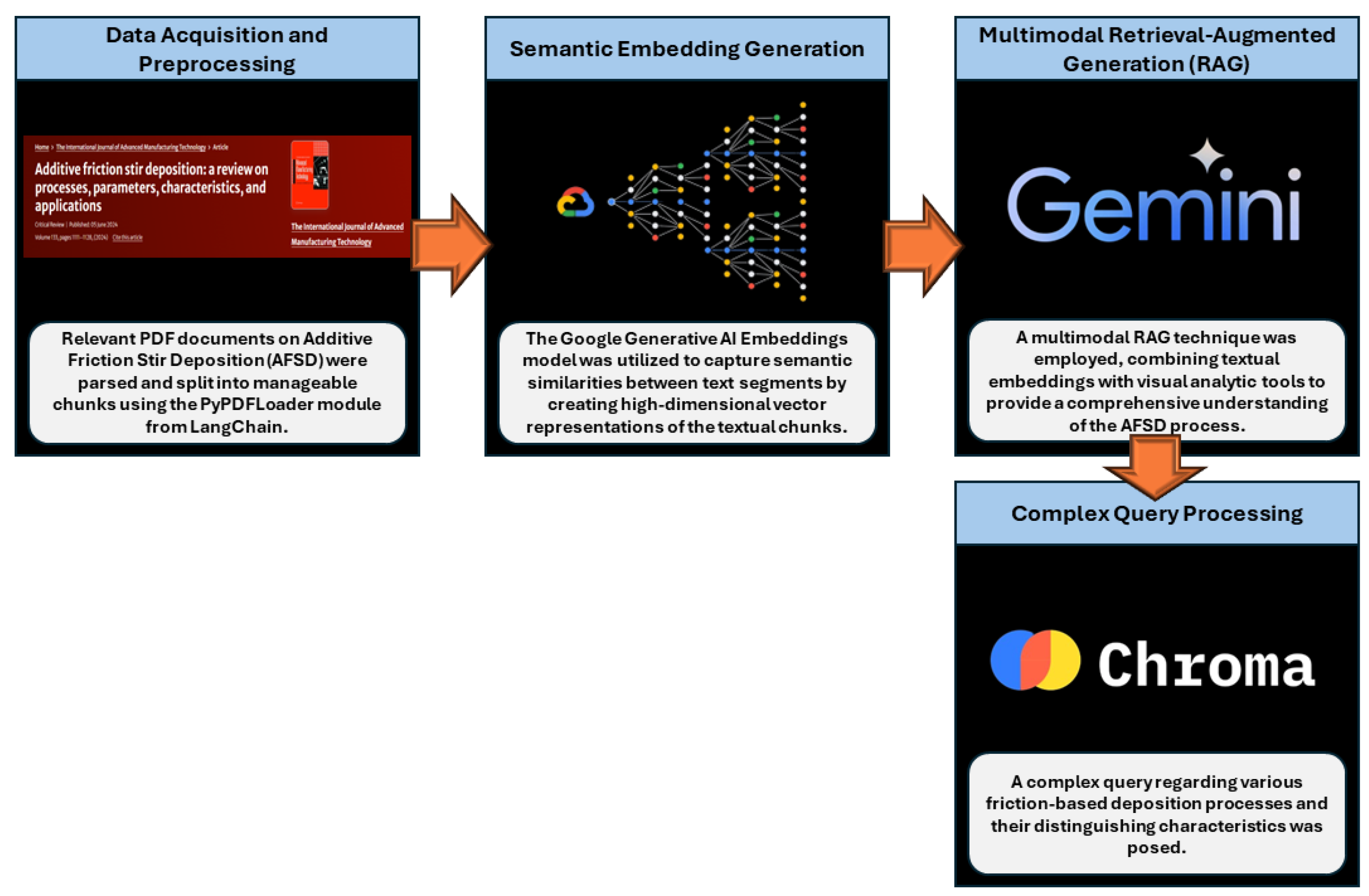
Figure 1 depicts the methodology employed in the present work. The initial phase of the methodology involved the acquisition and preprocessing of textual and image data pertinent to Additive Friction Stir Deposition (AFSD). Textual data was extracted from relevant PDF documents using the PyPDFLoader module from LangChain, which efficiently parsed and split the documents into manageable chunks. Each chunk was subjected to a recursive character text splitter, ensuring optimal size for subsequent processing by the language models. The extracted images were loaded and processed using the Python Imaging Library (PIL), facilitating the integration of visual data into the analysis pipeline.
The Google Generative AI Embeddings model was utilized to facilitate the efficient retrieval of pertinent information. This model captured semantic similarities between various text segments by creating high-dimensional vector representations of the textual chunks. The Chroma vector storage was then used to index the embeddings, making it possible to efficiently retrieve contextually relevant data. To make sure the system used the most relevant data available, the vector store was set up to return the top five most relevant chunks for any given query.
A multimodal RAG technique was used to produce complete responses to complicated queries. This method coupled textual embeddings with visual analytic tools to provide a comprehensive knowledge of the AFSD process. The system was built around Google's Gemini large language model (LLM), which was designed to accommodate both textual and visual inputs. The LLM was prompted with specific instructions to develop explanations and insights based on the acquired text chunks and supporting visuals.
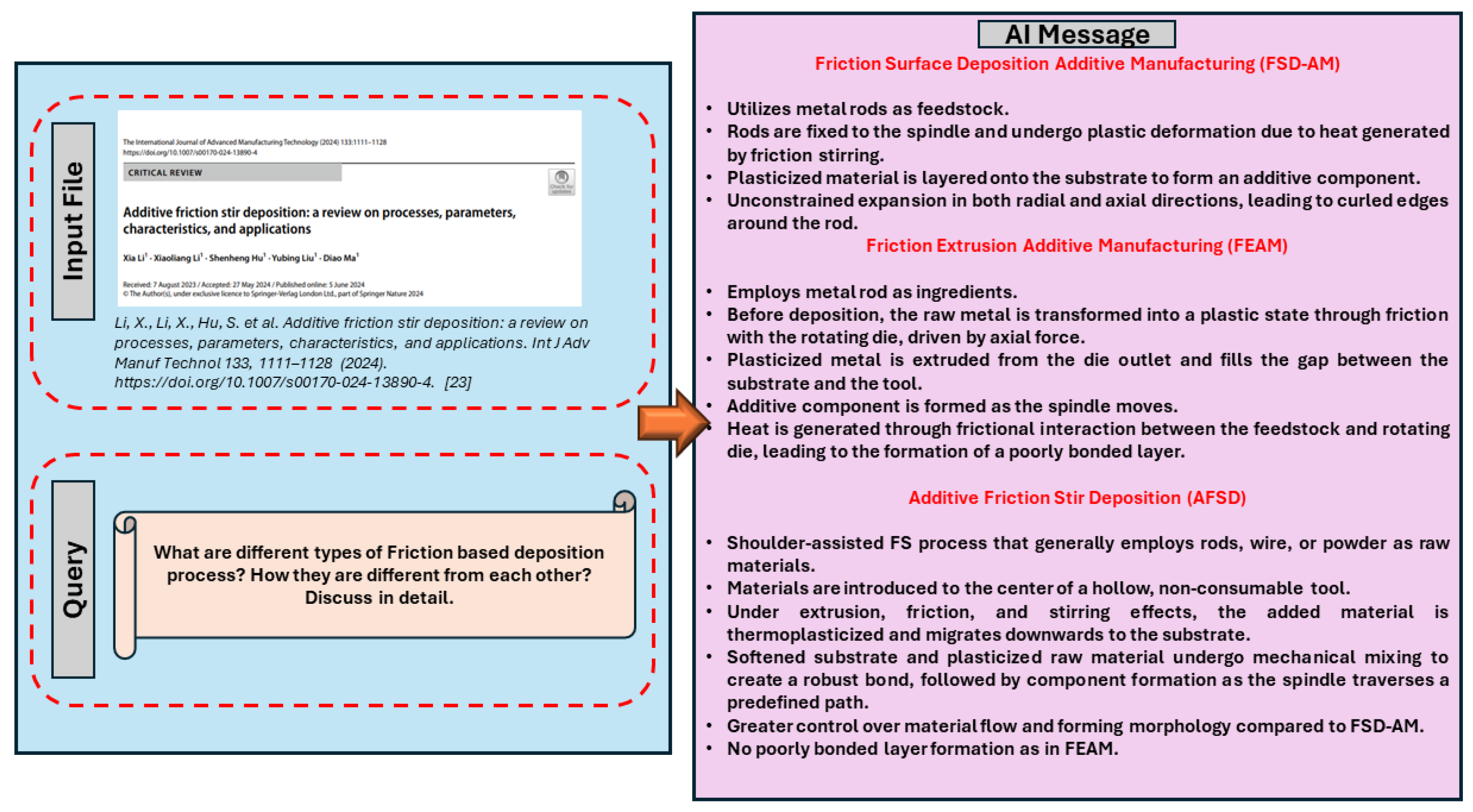
To demonstrate the system's capabilities, a complex query on the many forms of friction-based deposition processes and their differentiating properties was asked. This query was processed by the retrieval-augmented generation pipeline, which first extracted the most relevant textual chunks from the indexed vector storage. The Gemini LLM then synthesized this data, producing a detailed and coherent response that highlighted the differences between various friction-based deposition techniques, such as Friction Surface Deposition Additive Manufacturing (FSD-AM), Friction Extrusion Additive Manufacturing (FEAM), and Additive Friction Stir Deposition (AFSD).
4. Results and Discussion
Multimodal data is information that is gathered from various sources or modalities. These modalities may include text, graphics, audio, video, sensor readings, and so on. The combination of these many types of data enables richer and more thorough insights, which can be especially valuable in domains such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics. Multimodal data can be represented as a collection of data from various modalities. Suppose we have
different modalities, the data from each modality
can be represented as
. So, the entire multimodal dataset can be represented as shown in Equation (1).
where
could be text data represented by a matrix of word embeddings,
could be image data as a matrix of pixel values,
could be audio data in the form of a spectrogram.
The features are extracted from each modality in order to process the multimodal data. Let
be the feature matrix for the
modality as shown in Equation (2).
where
is the feature extraction function for modality
. These extracted features can then be used for further processing and analysis.
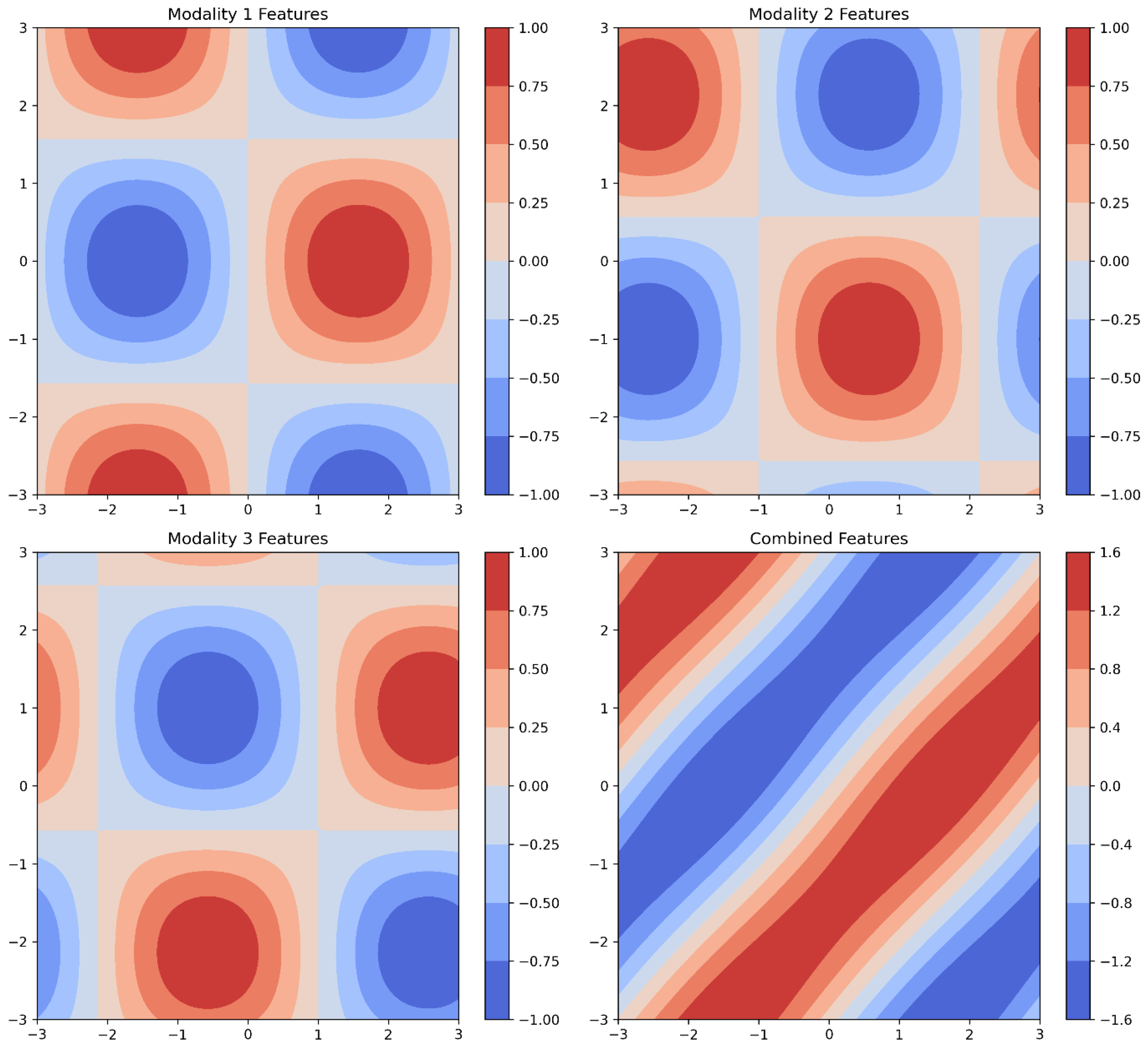
These extracted features from different modalities can be combined with the help of two common methods i.e. early fusion and late fusion. In early fusion method features from different modalities are concatenated into a single feature vector as shown in Equation (3).
where
represents the concatenated feature vector.
In late fusion method each modality is processed separately to produce modality-specific outputs, which are then combined to give the output from the modality
i.e.
shown in Equation (4).
where
is the processing function for modality
. The final output as shown in
Figure 2 is obtained by combining the outputs
shown in Equation (5).
where
is the function that combines the modality-specific outputs.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an effective approach for increasing the quality and relevance of generated content by exploiting multimodal data. RAG can provide richer and more contextually appropriate responses by using a variety of data modalities such as text, graphics, and audio. The combination of retrieval and production in RAG is especially effective when it can access and analyze multimodal data sources, allowing for a more comprehensive comprehension and exploitation of the available information.
The retrieval component of RAG is intended to search a huge corpus for relevant documents based on an input query as shown in
Figure 3. When broadened to multimodal data, the retriever can access more than simply text.
The retriever component of RAG can find relevant text documents
, images
, and audio clips
for a given query
. The probability of retrieving a document
for a given query
is denoted by Equation (6).
This scoring equation can be modified to handle multimodal data by taking into account the significance of various modalities, as illustrated in Equation (7).
where
are weights that balance the contribution of each modality's relevance score.
The generator component of the RAG synthesizes the information retrieved from the relevant multimodal documents to generate a coherent and contextually enriched response. The generator considers the input query
and the set of retrieved documents
. The likelihood of generating response
given the query
and the retrieved documents
can be denoted by using Equation (8) and in case of multimodal data this equation can be expanded to Equation (9).
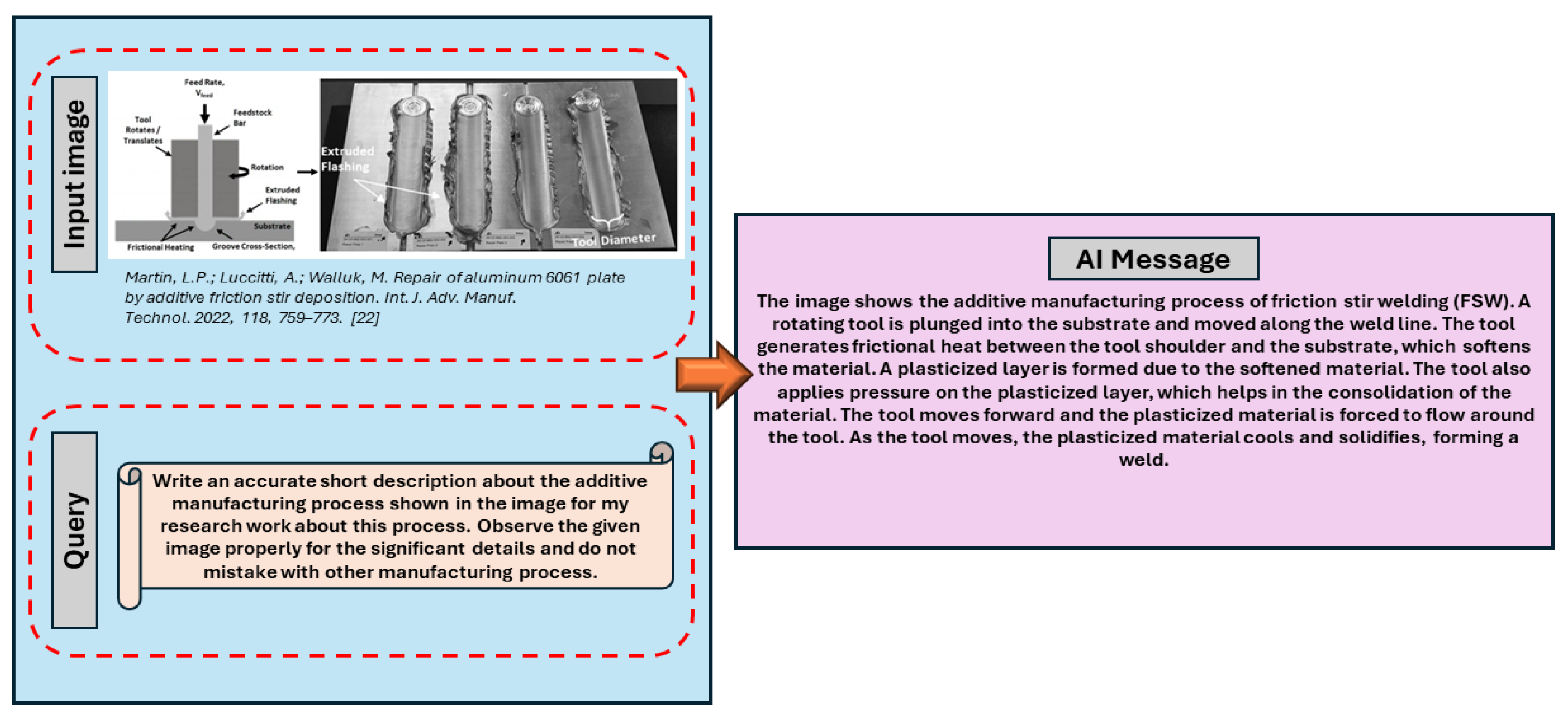
Figure 4 illustrates how features from an input image are extracted and compared to learnt patterns for different processes in order to determine which additive manufacturing technique was used to construct an object. The procedure with the greatest score is the most likely to be applied, according to the model, which determines similarity scores between the learned characteristics and the picture features for each step. This methodology showcases the potential of multimodal data analysis in enhancing and automating the identification of manufacturing processes.
As demonstrated in
Figure 5, the process of producing comprehensive explanations for various friction-based deposition processes include segmenting the input text, converting it into vector representations, and generating a vector index for effective retrieval. When the system receives a query, it searches the index for pertinent chunks and uses a language model to process them in order to provide a thorough response. This method ensures that the generated explanations are both contextually appropriate and instructive by combining the best aspects of retrieval and generative models.
The input image is represented as the matrix of pixel values denoted by
. The model extracts features from this image using a series of mathematical operations. For example, to detect edges (an important feature in distinguishing the tool and substrate), it may utilize a convolution operation with a kernel (filter) optimized to highlight edges as depicted in Equation (10).
where
is the resulting feature map highlighting edges, * denotes the convolution operation, and
is the edge detection kernel.
The extracted features are then compared to learned patterns for various additive manufacturing processes. This can be represented as a similarity score calculation shown in Equation (11).
where
is the similarity score between the image features
and the features learned for AFSD i.e.
. The model compares the similarity scores for different processes and chooses the one with the highest score.
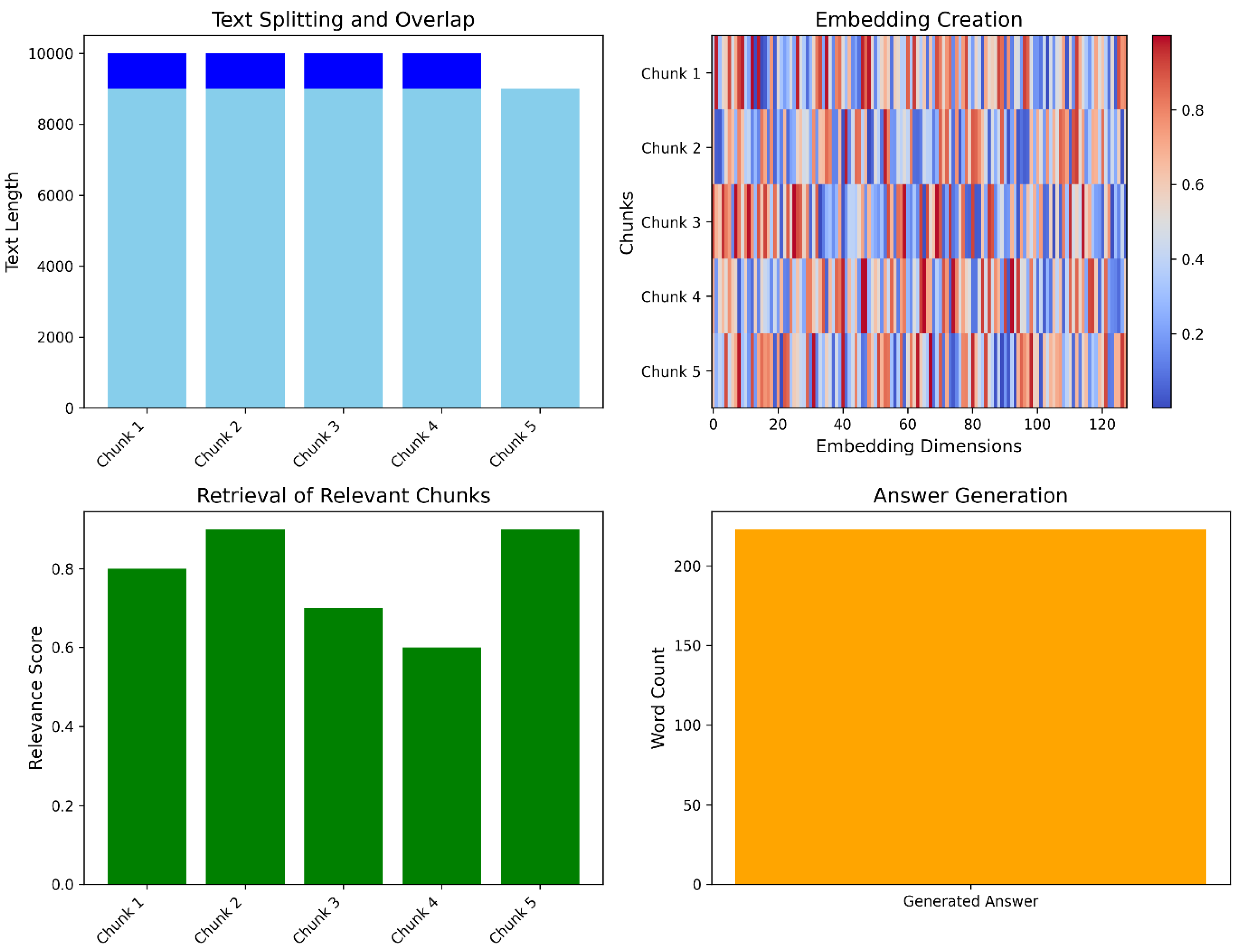
The mechanism for generating detailed explanations of different types of friction-based deposition processes involves several key steps. Initially, the input text is split into manageable chunks using a text splitting method that ensures some overlap between the chunks. This overlap prevents the loss of critical information at the boundaries. Each chunk is then transformed into a vector representation, known as an embedding, using a pre-trained Google Generative AI model. These embeddings are utilized to create a vector index, which facilitates the efficient retrieval of relevant text chunks based on a given query. When a query is submitted, the system retrieves the most relevant chunks from the vector index as shown In
Figure 6. This retrieval phase guarantees that only the most relevant information is evaluated when generating the response. The next step is to use a language model to process the retrieved text chunks and produce a thorough response to the query. The system's use of efficient retrieval and enhanced language creation allows it to deliver detailed and precise explanations, such as a comparison of several friction-based deposition processes, highlighting their distinct mechanisms and differences. This strategy assures that the generated responses are both informative and contextually relevant, by combining the strengths of retrieval and generative models.
Figure 7 illustrates how text and image analysis are used to assess the material microstructures created by additive manufacturing. While text analysis processes information on process parameters and material qualities, image analysis extracts features such grain size and shape. Through the integration of these collected features and data, a thorough assessment of the microstructure is produced, encompassing its attributes, flaws, and possible consequences for performance. This methodology exemplifies the ability of multimodal data analysis to offer a more profound comprehension of material qualities and how they relate to production procedures.
This is particularly evident in the system's capacity to generate thorough explanations of various friction-based deposition processes and identify production strategies using visual data. The use of multimodal analysis to material microstructure evaluation demonstrates the value of merging textual and visual data to gain deeper insights. This integrated approach not only improves process control and quality assurance, but it also provides new opportunities for innovation in solid-state additive manufacturing. The multimodal RAG system, as shown in the numerous figures and mathematical representations, provides a strong foundation for decision-making, defect identification, and process optimization in AFSD. This technology has the potential to accelerate advances in materials science and additive manufacturing, resulting in the discovery of innovative materials and more efficient manufacturing methods.
5. Conclusions
This study highlighted the tremendous potential for incorporating Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) into the Additive Friction Stir Deposition (AFSD) process. We have generated a more comprehensive and complex understanding of AFSD by combining many data modalities, such as text, and images. The multimodal approach has proven particularly effective in generating detailed explanations of various friction-based deposition processes and in identifying specific manufacturing techniques from visual data. This capability not only enhances process control and quality assurance but also provides valuable insights for researchers and operators in the field of solid-state additive manufacturing. Implementing the multimodal RAG system for real-time monitoring and adjustment of AFSD parameters could significantly improve process consistency and output quality. Incorporating additional data types, such as thermal imaging or acoustic emissions, could provide even richer insights into the AFSD process.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yu, H.Z. and Mishra, R.S., 2021. Additive friction stir deposition: a deformation processing route to metal additive manufacturing. Materials Research Letters, 9(2), pp.71-83. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.S., Patil, S.M., Mazumder, S., Sharma, S., Riley, D.A., Dowden, S., Banerjee, R. and Dahotre, N.B., 2022. Additive friction stir deposition of AZ31B magnesium alloy. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 10(9), pp.2404-2420. [CrossRef]
- Stubblefield, G.G., Fraser, K.A., Robinson, T.W., Zhu, N., Kinser, R.P., Tew, J.Z., Cordle, B.T., Jordon, J.B. and Allison, P.G., 2023. A computational and experimental approach to understanding material flow behavior during additive friction stir deposition (AFSD). Computational Particle Mechanics, 10(6), pp.1629-1643. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y., Wang, T., Liu, T., Yang, T., Dowden, S., Neogi, A. and Dahotre, N.B., 2024. Gradient process parameter optimization in additive friction stir deposition of aluminum alloys. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 195, p.104113. [CrossRef]
- Gumaste, A., Dhal, A., Agrawal, P. et al. A Novel Approach for Enhanced Mechanical Properties in Solid-State Additive Manufacturing by Additive Friction Stir Deposition Using Thermally Stable Al-Ce-Mg Alloy. JOM 75, 4185–4198 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-06044-6. [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P., Haridas, R.S., Agrawal, P. and Mishra, R.S., 2022. Deformation based additive manufacturing of a metastable high entropy alloy via Additive friction stir deposition. Additive Manufacturing, 60, p.103282. [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P., Haridas, R.S., Yadav, S., Thapliyal, S., Gaddam, S., Verma, R. and Mishra, R.S., 2021. Processing-structure-property correlation in additive friction stir deposited Ti-6Al-4V alloy from recycled metal chips. Additive Manufacturing, 47, p.102259. [CrossRef]
- Hang, Z.Y., Jones, M.E., Brady, G.W., Griffiths, R.J., Garcia, D., Rauch, H.A., Cox, C.D. and Hardwick, N., 2018. Non-beam-based metal additive manufacturing enabled by additive friction stir deposition. Scripta Materialia, 153, pp.122-130. [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.J., Avery, D.Z., Liu, T., Rodriguez, O.L., Mason, C.J.T., Jordon, J.B., Brewer, L.N. and Allison, P.G., 2019. Microstructure-deformation relationship of additive friction stir-deposition Al–Mg–Si. Materialia, 7, p.100387. [CrossRef]
- Gopan, V., Wins, K.L.D. and Surendran, A., 2021. Innovative potential of additive friction stir deposition among current laser based metal additive manufacturing processes: A review. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, 32, pp.228-248. [CrossRef]
- Elfishawy, E., Ahmed, M.M.Z. and El-Sayed Seleman, M.M., 2020. Additive manufacturing of aluminum using friction stir deposition. In TMS 2020 149th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings (pp. 227-238). Springer International Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhshi, F. and Gerlich, A.P., 2018. Potentials and strategies of solid-state additive friction-stir manufacturing technology: A critical review. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 36, pp.77-92. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S., Haridas, R.S. and Agrawal, P., 2022. Friction stir-based additive manufacturing. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 27(3), pp.141-165. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M., Rathee, S., Maheshwari, S., Noor Siddiquee, A. and Kundra, T.K., 2019. A review on recent progress in solid state friction based metal additive manufacturing: friction stir additive techniques. Critical Reviews in Solid State and Materials Sciences, 44(5), pp.345-377. [CrossRef]
- Maurya, M., Maurya, A. and Kumar, S., 2024. Variants of friction stir based processes: review on process fundamentals, material attributes and mechanical properties. Materials Testing, 66(2), pp.271-287. [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I. and Buehler, M., 2024. Molecular analysis and design using multimodal generative artificial intelligence via multi-agent modeling. [CrossRef]
- Luu, R.K., Arevalo, S., Lu, W., Ni, B., Yang, Z., Shen, S.C., Berkovich, J., Hsu, Y.C., Zan, S. and Buehler, M.J., 2024. Learning from Nature to Achieve Material Sustainability: Generative AI for Rigorous Bio-inspired Materials Design. [CrossRef]
- Fuhr, A.S. and Sumpter, B.G., 2022. Deep generative models for materials discovery and machine learning-accelerated innovation. Frontiers in Materials, 9, p.865270. [CrossRef]
- Dhamdar, T.S., Sandhya, K.V. and Basavaraj, B.V., 2024. Advancing Innovation through Biomimicry and AI: Inspiration to Implementation. BIONATURE, 44(1), pp.16-27. [CrossRef]
- Menon, D. and Ranganathan, R., 2022. A generative approach to materials discovery, design, and optimization. ACS omega, 7(30), pp.25958-25973. [CrossRef]
- Luu, R.K. and Buehler, M.J., 2024. BioinspiredLLM: Conversational Large Language Model for the Mechanics of Biological and Bio-Inspired Materials. Advanced Science, 11(10), p.2306724. [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.P.; Luccitti, A.; Walluk, M. Repair of aluminum 6061 plate by additive friction stir deposition. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 118, 759–773. [CrossRef]
- Li, X., Li, X., Hu, S. et al. Additive friction stir deposition: a review on processes, parameters, characteristics, and applications. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 133, 1111–1128 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13890-4. [CrossRef]
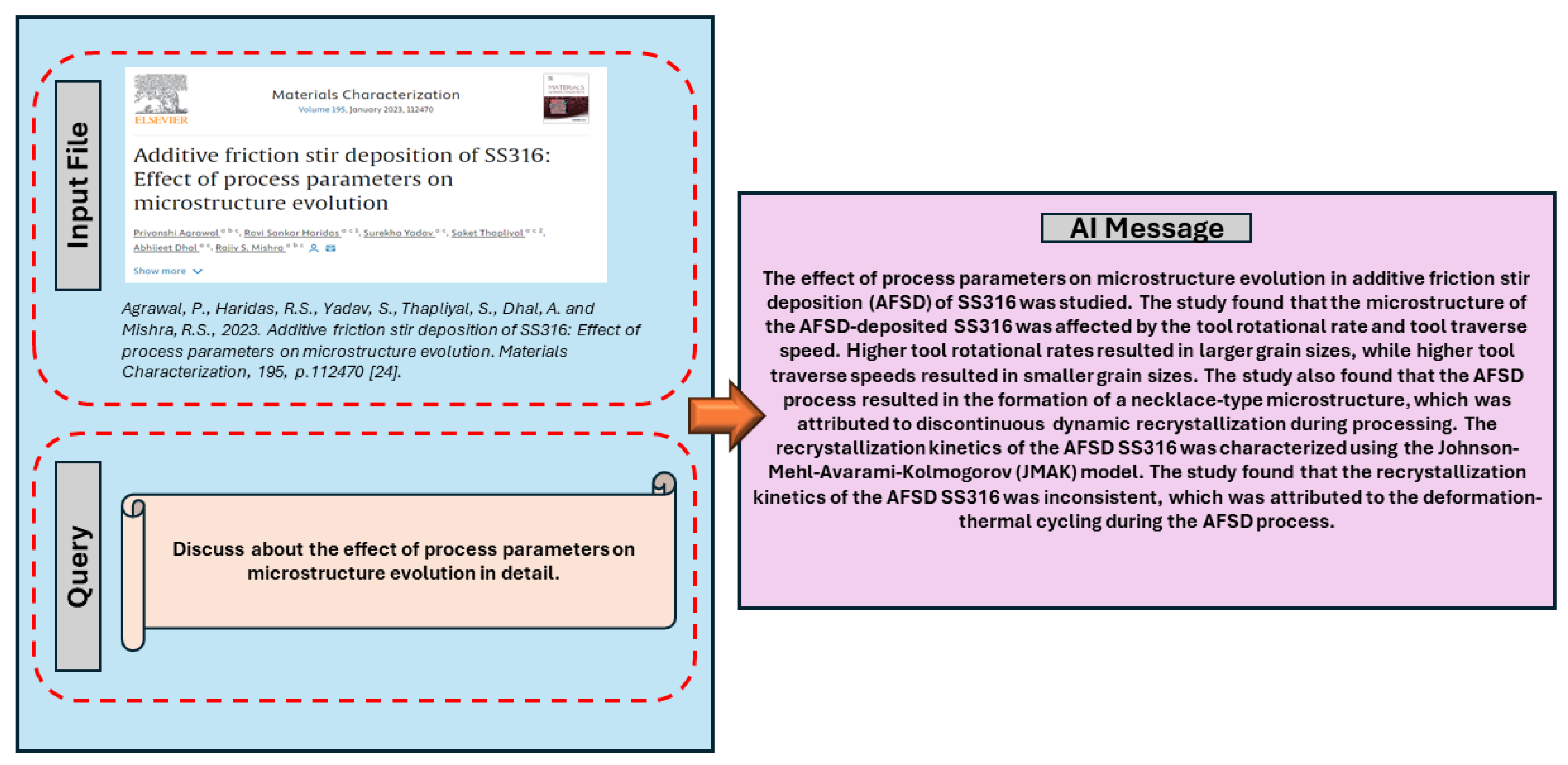
- Agrawal, P., Haridas, R.S., Yadav, S., Thapliyal, S., Dhal, A. and Mishra, R.S., 2023. Additive friction stir deposition of SS316: Effect of process parameters on microstructure evolution. Materials Characterization, 195, p.112470. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).