Submitted:
01 October 2024
Posted:
02 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Adaptive Role of Metabolites Produced by Probiotic Bacteria
3. Overview of Probiotics Benefits in Child Health
4. Specific Probiotic Strains for Children’s Health
4.1. Lactobacillus rhamnosus
4.2. Bifidobacterium infantis
4.3. Streptococcus thermophilus
4.4. Lactobacillus acidophilus
4.5. Saccharomyces boulardii
5. Bioactive Metabolites Produced by Probiotics: Mechanisms of Action and Their Role in Enhancing Pediatric Health
5.1. Immunomodulatory Metabolites
5.2. Anti-Inflammatory Metabolites
5.3. Nutrient Absorption-Enhancing Metabolites
5.4. Gut Microbiota Balancing and Barrier-Enhancing Metabolites
6. Types and Mechanisms of Action of Probiotic Metabolites in Children
6.1. Vitamins
Vitamin B Complex
Vitamin K
6.2. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
7. Antimicrobial Peptides
8. Enzymes
9. Exopolysaccharides (EPSs)
10. Neurotransmitters
10.1. Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
10.2. Other Neurotransmitters Produced by Probiotics
11. Bioactive Postbiotic Fractions
12. Clinical Applications and Health Implications
Current Practice Guidelines
| Disorder | Probiotic Strain | Recommended Dose | Evidence Level ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute gastroenteritis [Reduced the risk of diarrhea lasting ≥ 48 h; reduced the mean duration of diarrhea [256]] | Probiotics as a general group | N/A | 1 |
| L. rhamnosus GG [257] | ≥1010 cfu/day, for 5–7 days | 1 | |
| S. boulardii * [258] | 250–750 mg/day, for 5–7 days | 1 | |
| L. reuteri DSM 17,938 [259] | 1 × 108 to 4 × 108 cfu/day, for 5 days | 1 | |
|
L. rhamnosus 19070-2 & L. reuteri DSM 12,246 [260] |
2 × 1010 cfu for each strain/day, for 5 days | 1 | |
| B. lactis B94 [261] | 5 × 1010 cfu once daily, for 5 days | 3 | |
| L. paracasei B21060 [262] | 2.5 × 109 cfu, twice daily, for 5 days | 3 | |
| L. rhamnosus strains 573L/1; 573L/2; 573L/3 [263] | 1.2 × 1010 cfu, twice daily, for 5 days | 3 | |
| L. delbrueckii var. bulgaricus, L. acidophilus, S thermophilus, B. bifidum (LMG- P17550, LMG-P 17549, LMG-P 17503, LMG-P 17500) [264]. | 109 cfu, 109 cfu, 109 cfu, 5 × 108 cfu/dose, for 5 days | 3 | |
| B. lactis Bi-07, L. rhamnosus HN001, and L. acidophilus NCFM [265] | Then 1 × 1010 cfu once a day, for the duration of diarrhea plus 7 days | 3 | |
| Prevention of AAD (Reduced risk of AAD [266]) | Probiotics as a general group | N/A | 1 |
| S. boulardii * [267] | ≥5 billion cfu per day, for the duration of antibiotic treatment | 1 | |
| L. rhamnosus GG [268] | ≥5 billion cfu per day, for the duration of antibiotic treatment | 1 | |
| Multispecies probiotic (Bifidobacterium bifidum W23, B. lactis W51, Lactobacillus acidophilus W37, Lactobacillus acidophilus W55, Lacticaseibacillus paracasei W20, Lactoplantibacillus plantarum W62, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus W71, and Ligilactobacillus salivarius W24] [269] | 10 billion cfu per day, for the duration of antibiotic treatment and for 7 days after | 3 | |
| L. rhamnosus (strains E/N, Oxy, and Pen) [270] | 2 × 1010 cfu, twice daily, for the duration of antibiotic treatment | 3 | |
| Prevention of C. difficile diarrhea | S. boulardii * [267] | 250–500 mg | 1 |
| Prevention of nosocomial diarrhea | L. rhamnosus GG [271,272] | At least 109 cfu/day, for the duration of the hospital stay | 1 |
| Prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis [273,274,275] | Systematic reviews and meta-analyses (> 10,000 neonates) of RCTs | 1 | |
| L. rhamnosus GG [276] | From 1 × 109 to 6 × 109 cfu | 1 | |
| B. infantis BB-02, B. lactis BB-12, and S. thermophilus TH-4 [276] | 3.0 to 3.5 × 108 cfu (of each strain) | 1 | |
| B. animalis subsp. lactis Bb-12 or B94 [276] | 5 × 109 cfu | 3 | |
|
L. reuteri ATCC 55730* or DSM 17938 *this strain is no longer available. [276,277] |
1 × 108 cfu (various regimens) | 1 | |
| B. longum subsp. infantis ATCC 15,697 + L. acidophilus ATCC 4356 [277,278] | 125 mg/kg/dose twice daily with breast milk until discharge | 3 | |
| B. longum subsp. longum 35,624 + L. rhamnosus GG [278] | 5 × 108 cfu and 5 × 108 cfu, respectively | 3 | |
|
Helicobacter pylori infection [279,280,281,282,283] |
Probiotics as a general group | 1 | |
| S. boulardii* [284,285] | 500 mg | 1 | |
| Infantile colic [286,287,288,289,290,291] | Probiotics as a general group | N/A | 1 |
| L. reuteri DSM 17,938 [292,293] | 108 cfu/day for at least 21 days | 1 | |
| B. lactis Bb12 [294,295] | 1 × 109 cfu/day, for 21–28 days | 2 | |
| L. rhamnosus 19070-2 and L. reuteri 12,246 [296] | 250 × 10⁶ cfu, respectively, for 28 days | 3 | |
| L. paracasei DSM 24733, L. plantarum DSM 24730, L. acidophilus DSM 24735, L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus DSM 24734), B. longum DSM 24736, B. breve DSM 24732, and B. infantis DSM 24737, and S. thermophilus DSM 24,731 [297] | 5 billion cfu, for 21 days | 3 | |
| Infantile colic—prevention | L. reuteri DSM 17,938 [298] | 108 cfu/day, to newborns each day for 90 days | 1 |
| Functional abdominal pain/IBS | L. reuteri DSM 17,938 [299,300] | 108 cfu to 2 × 108 cfu/day | 1 |
| L. rhamnosus GG [299,301] | 109 cfu to 3 × 109 cfu twice daily | 1 | |
| Ulcerative colitis [302] | Probiotics as a group | N/A | 1 |
| A mixture of 8 strains (L. paracasei DSM 24733, L. plantarum DSM 24730, L. acidophilus DSM 24735, L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus DSM 24734, B. longum DSM 24736, B. infantis DSM 24737, B. breve DSM 24732, and S. thermophilus DSM 247), as adjuvant therapy or in those intolerant to 5-ASA [303] | Daily dosages: 4–6 y (17–23 kg): 450 billion; 7–9 y (24–33 kg): 900 billion; 11–14 y (34–53 kg): 1350 billion; 15–17 y (54–66 kg): 1800 billion. |
3 | |
| Pouchitis | A mixture of 8 strains (L. paracasei DSM 24733, L. plantarum DSM 24730, L. acidophilus DSM 24735, L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus DSM 24734, B. longum DSM 24736, B. infantis DSM 24737, B. breve DSM 24732, and S. thermophilus DSM 247) [304,305] | Daily dosages: 4–6 y (17–23 kg): 450 billion; 7–9 y (24–33 kg): 900 billion; 11–14 y (34–53 kg): 1350 billion; 15–17 y (54–66 kg): 1800 billion. |
3 |
13. Challenges of Using Bioactive Molecules from Probiotics for Pediatric Diseases
14. Future Perspectives and Opportunities
14.1. Fostering of Clinical Research
14.2. Evidence-Based Clinical Guidelines
14.3. Strengthening Ethical Frameworks for Pediatric Research
14.4. Enhancing Professional Education and Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buonocore, G. Microbiota and gut immunity in infants and young children. Global Pediatrics 2024, 9, 100202. [CrossRef]
- Samara State Medical University; Sskvortsova, O.V.; Migacheva, N.B.; Samara State Medical University; Kaganova, T.I.; Samara State Medical University; Lyamin, A.V.; Samara State Medical University; Antipov, V.A.; Samara State Medical University Role of gut microbiota and selected metabolic products in the development of childhood obesity. bccm 2024, 17, 81–87. [CrossRef]
- Hoskinson, C.; Medeleanu, M.V.; Reyna, M.E.; Dai, D.L.Y.; Chowdhury, B.; Moraes, T.J.; Mandhane, P.J.; Simons, E.; Kozyrskyj, A.L.; Azad, M.B.; et al. Antibiotics taken within the first year of life are linked to infant gut microbiome disruption and elevated atopic dermatitis risk. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 154, 131–142. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, N. Probiotics for Children. In Probiotics: A comprehensive guide to enhance health and mitigate disease; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2024; pp. 95–128 ISBN 9781003452249.
- Bompalli, L.K. The Next-Gen Innovative Therapeutic Potential of Probiotics: Insights into Gut Microbiota Modulation and Health Promotion. Unpublished 2024. [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, J.; van Hemert, S.; Poveda, C.; Elmore, S.; Williams, C.; Lamport, D.; Walton, G. The effect of probiotic bacteria on composition and metabolite production of faecal microbiota using in vitro batch cultures. Nutrients 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Lee, N.-K.; Paik, H.-D. A narrative review on the advance of probiotics to metabiotics. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 487–494. [CrossRef]
- Alsharairi, N.A. Therapeutic Potential of Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolite Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Life (Basel) 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Golpour, F.; Abbasi-Alaei, M.; Babaei, F.; Mirzababaei, M.; Parvardeh, S.; Mohammadi, G.; Nassiri-Asl, M. Short chain fatty acids, a possible treatment option for autoimmune diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114763. [CrossRef]
- Calvo, L.N.; Greenberg, R.G.; Gray, K.D. Safety and Effectiveness of Probiotics in Preterm Infants with Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Neoreviews 2024, 25, e193–e206. [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.; Meader, N.; Oddie, S.J.; Rojas-Reyes, M.X.; McGuire, W. Probiotics to prevent necrotising enterocolitis in very preterm or very low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 7, CD005496. [CrossRef]
- Bartram, E.; Asai, M.; Gabant, P.; Wigneshweraraj, S. Enhancing the antibacterial function of probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle: when less is more. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0097523. [CrossRef]
- Thuy, T.T.D.; Lu, H.-F.; Bregente, C.J.B.; Huang, F.-C.A.; Tu, P.-C.; Kao, C.-Y. Characterization of the broad-spectrum antibacterial activity of bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance-producing probiotics isolated from fermented foods. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 85. [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Teng, Q.; Chen, J.; Peng, L.; Ren, Z.; Ma, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, B.; Wu, Z.; Wan, C. Probiotic potential of a novel exopolysaccharide produced by Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis SF. LWT 2024, 193, 115764. [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Laiño, J.E.; del Valle, M.J.; de Giori, G.S.; Sesma, F.; Taranto, M.P. B-Group Vitamins Production by Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria. In Biotechnology of lactic acid bacteria: novel applications; Mozzi, F., Raya, R.R., Vignolo, G.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2015; pp. 279–296 ISBN 9781118868386.
- Chowdhury, S.R. Psychobiotics and gut–brain axis—a new paradigm for improving mental health. In Probiotics: A comprehensive guide to enhance health and mitigate disease; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2024; pp. 146–158 ISBN 9781003452249.
- Lozano, J.; Fabius, S.; Fernández-Ciganda, S.; Urbanavicius, J.; Piccini, C.; Scorza, C.; Zunino, P. Beneficial effect of GABA-producing Lactiplantibacillus strain LPB145 isolated from cheese starters evaluated in anxiety- and depression-like behaviours in rats. Benef. Microbes 2024, 15, 465–479. [CrossRef]
- Ambat, J.; Antonio, J.; Bala, A.; Suntornsaratoon, P.; Flores, J.; Li, W.V.; Jones, A. Metabolomic and transcriptomic correlative analyses in germ free mice link probiotic-associated metabolites to host intestinal fatty acid metabolism and b-oxidation. Physiology (Bethesda) 2024, 39. [CrossRef]
- Indira, M.; Venkateswarulu, T.C.; Abraham Peele, K.; Nazneen Bobby, M.; Krupanidhi, S. Bioactive molecules of probiotic bacteria and their mechanism of action: a review. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 306. [CrossRef]
- Shealy, N.G.; Yoo, W.; Byndloss, M.X. Colonization resistance: metabolic warfare as a strategy against pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2021, 64, 82–90. [CrossRef]
- Roy D’Souza, S.; Singh, S.; Ravi, L. Secondary metabolites produced from symbiotic microbes. In Microbial Symbionts; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 803–830 ISBN 9780323993340.
- Kumar, M.K.; Morya, S. Probiotics: Role of bioactives in foods and dietary supplements. Pharma Innovation 2022, 11, 2592–2597. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Rashid, G.; Sharma, L. Probiotics. In Probiotics: A comprehensive guide to enhance health and mitigate disease; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2024; pp. 325–343 ISBN 9781003452249.
- Baldassare, M.A.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Coles, J.D.; Nelson, S.; McCollum, C.A.; Seekatz, A.M. Butyrate enhances Clostridioides difficile sporulation in vitro. J. Bacteriol. 2023, 205, e0013823. [CrossRef]
- Arbulu, S.; Kjos, M. Revisiting the multifaceted roles of bacteriocins : the multifaceted roles of bacteriocins. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 41. [CrossRef]
- Tarique, M.; Ali, A.H.; Kizhakkayil, J.; Liu, S.-Q.; Oz, F.; Dertli, E.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Ayyash, M. Exopolysaccharides from Enterococcus faecium and Streptococcus thermophilus: Bioactivities, gut microbiome effects, and fermented milk rheology. Food Chemistry: X 2024, 21, 101073. [CrossRef]
- Shenderov, B.A.; Sinitsa, A.V.; Zakharchenko, M.M.; Lang, C. Metabolic relationship between the host and its gut microbiota. In Metabiotics: present state, challenges and perspectives; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 15–21 ISBN 978-3-030-34166-4.
- Oleskin, A.V.; Shenderov, B.A. Neuromodulatory effects and targets of the SCFAs and gasotransmitters produced by the human symbiotic microbiota. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2016, 27, 30971. [CrossRef]
- Engevik, M.A.; Morra, C.N.; Röth, D.; Engevik, K.; Spinler, J.K.; Devaraj, S.; Crawford, S.E.; Estes, M.K.; Kalkum, M.; Versalovic, J. Microbial metabolic capacity for intestinal folate production and modulation of host folate receptors. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2305. [CrossRef]
- Chávarri, M.; Diez-Gutiérrez, L.; Marañón, I.; del Carmen Villarán, M.; Barrón, L.J.R. The role of probiotics in nutritional health: probiotics as nutribiotics. In Probiotics in the prevention and management of human diseases; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 397–415 ISBN 9780128237335.
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Chain, F.; Martín, R.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Courau, S.; Langella, P. Beneficial effects on host energy metabolism of short-chain fatty acids and vitamins produced by commensal and probiotic bacteria. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 79. [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Wang, L.; Huangfu, M.; Li, H. The impact of microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids on macrophage activities in disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic potentials. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115276. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.; Haider, R.; Aaqil, S.I.; Vohra, L.I.; Qamar, K.; Jawed, A.; Fatima, N.; Adnan, A.; Parikh, V.; Ochani, S.; et al. Probiotic formulations and gastro-intestinal diseases in the paediatric population: a narrative review. Ann Med Surg 2024, 86, 2836–2847. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Sant’Anna, A. Using probiotics in paediatric populations. Paediatr. Child Health 2022, 27, 482–491. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.P.; Raine, T.; Reddy, S.; Belteki, G. Probiotics for the prevention of necrotising enterocolitis in very low-birth-weight infants: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Paediatr. 2017, 106, 1729–1741. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Sun, C. Probiotics for Preventing Necrotizing Enterocolitis: A Meta-Analysis with Trial Sequential Analysis. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2023, 2023, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Isaeva, G.; Isaeva, R. Probiotics in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: reality and perspective. Minerva Gastroenterol (Torino) 2022, 68, 277–288. [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Agarwal, A.; Singh, K.; Jarouliya, U. Probiotics and immune response in disease prevention and treatment. In Immune-Boosting Nutraceuticals for Better Human Health: Novel Applications; Apple Academic Press: New York, 2023; pp. 99–129 ISBN 9781003371069.
- Thoda, C.; Touraki, M. Immunomodulatory properties of probiotics and their derived bioactive compounds. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4726. [CrossRef]
- Zambelli, R.A.; Mendonça, L.G. de Application of probiotics in food industry. In Probiotics: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhance Health and Mitigate Disease; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2024; pp. 282–304 ISBN 9781003452249.
- Kumar, H.; Dhalaria, R.; Guleria, S.; Cimler, R.; Choudhary, R.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Singh, R.; Kimta, N.; Dulta, K.; Pathera, A.K.; et al. To exploring the role of probiotics, plant-based fermented products, and paraprobiotics as anti-inflammatory agents in promoting human health. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research 2023, 14, 100896. [CrossRef]
- Kadia, B.M.; Allen, S.J. Effect of Pre-, Pro-, and Synbiotics on Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation in Children: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2024, 16. [CrossRef]
- Di Costanzo, M.; Vella, A.; Infantino, C.; Morini, R.; Bruni, S.; Esposito, S.; Biasucci, G. Probiotics in infancy and childhood for food allergy prevention and treatment. Nutrients 2024, 16. [CrossRef]
- Abavisani, M.; Ebadpour, N.; Khoshrou, A.; Sahebkar, A. Boosting vaccine effectiveness: The groundbreaking role of probiotics. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research 2024, 16, 101189. [CrossRef]
- Bradford, G.; Asgari, B.; Smit, B.; Hatje, E.; Kuballa, A.; Katouli, M. The Efficacy of Selected Probiotic Strains and Their Combination to Inhibit the Interaction of Adherent-Invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC) with a Co-Culture of Caco-2:HT29-MTX Cells. Microorganisms 2024, 12. [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Lv, R.; Jin, H.; Ma, T.; Zhao, Z.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Sun, Z. A large-scale comparative genomics study reveals niche-driven and within-sample intra-species functional diversification in Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus. Food Res. Int 2023, 173, 113446. [CrossRef]
- Ceapa, C.; Davids, M.; Ritari, J.; Lambert, J.; Wels, M.; Douillard, F.P.; Smokvina, T.; de Vos, W.M.; Knol, J.; Kleerebezem, M. The Variable Regions of Lactobacillus rhamnosus Genomes Reveal the Dynamic Evolution of Metabolic and Host-Adaptation Repertoires. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 1889–1905. [CrossRef]
- Cheong, Y.E.; Kim, J.; Jin, Y.-S.; Kim, K.H. Elucidation of the fucose metabolism of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG by metabolomic and flux balance analyses. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 360, 110–116. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Bu, X.; Cheng, S.; Duan, Z. Characterization of the anti-pathogenic, genomic and phenotypic properties of a Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus VHProbi M14 isolate. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285480. [CrossRef]
- Talbi, C.; Elmarrakchy, S.; Youssfi, M.; Bouzroud, S.; Belfquih, M.; Sifou, A.; Bouhaddou, N.; Badaoui, B.; Balahbib, A.; Bouyahya, A.; et al. Bacterial exopolysaccharides: from production to functional features. Prog Micobes Mol Biol 2023, 6. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Ahmad, A.A.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Shen, W.; Feng, M.; Shen, J.; Lan, X.; Ding, X. Lactobacillus rhamnosus CY12 Enhances Intestinal Barrier Function by Regulating Tight Junction Protein Expression, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation Response in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Caco-2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- Spaggiari, L.; Pedretti, N.; Ricchi, F.; Pinetti, D.; Campisciano, G.; De Seta, F.; Comar, M.; Kenno, S.; Ardizzoni, A.; Pericolini, E. An Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis of Lactobacillus (L.) rhamnosus, L. acidophilus, L. plantarum and L. reuteri Reveals an Upregulated Production of Inosine from L. rhamnosus. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Tso, L.; Bonham, K.S.; Fishbein, A.; Rowland, S.; Klepac-Ceraj, V. Targeted High-Resolution Taxonomic Identification of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis Using Human Milk Oligosaccharide Metabolizing Genes. Nutrients 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Román, L.; Melis-Arcos, F.; Pröschle, T.; Saa, P.A.; Garrido, D. Genome-scale metabolic modeling of the human milk oligosaccharide utilization by Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis. mSystems 2024, 9, e0071523. [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.B.; Huang, H.; Ning, Y.; Xiao, J. Probiotics in the New Era of Human Milk Oligosaccharides (HMOs): HMO Utilization and Beneficial Effects of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis M-63 on Infant Health. Microorganisms 2024, 12. [CrossRef]
- Reens, A.L.; Cosetta, C.M.; Saur, R.; Trofimuk, O.; Brooker, S.L.; Lee, M.L.; Sun, A.K.; McKenzie, G.J.; Button, J.E. Tunable control of B. infantis abundance and gut metabolites by co-administration of human milk oligosaccharides. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2304160. [CrossRef]
- Sela, D.A.; Chapman, J.; Adeuya, A.; Kim, J.H.; Chen, F.; Whitehead, T.R.; Lapidus, A.; Rokhsar, D.S.; Lebrilla, C.B.; German, J.B.; et al. The genome sequence of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis reveals adaptations for milk utilization within the infant microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008, 105, 18964–18969. [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, A.M.; Pacheco, A.R.; Henrick, B.M.; Taft, D.; Xu, G.; Huda, M.N.; Mishchuk, D.; Goodson, M.L.; Slupsky, C.; Barile, D.; et al. Indole-3-lactic acid associated with Bifidobacterium-dominated microbiota significantly decreases inflammation in intestinal epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 357. [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Pei, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Lu, W. Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis as widespread bacteriocin gene clusters carrier stands out among the Bifidobacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0097923. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Shen, J.; Chen, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, Z.; et al. Prophylactic supplementation with Bifidobacterium infantis or its metabolite inosine attenuates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury. iMeta 2024, 3, e220. [CrossRef]
- Kapse, N.; Pisu, V.; Dhakephalkar, T.; Margale, P.; Shetty, D.; Wagh, S.; Dagar, S.; Dhakephalkar, P.K. Unveiling the Probiotic Potential of Streptococcus thermophilus MCC0200: Insights from In Vitro Studies Corroborated with Genome Analysis. Microorganisms 2024, 12. [CrossRef]
- Rau, M.H.; Gaspar, P.; Jensen, M.L.; Geppel, A.; Neves, A.R.; Zeidan, A.A. Genome-Scale Metabolic Modeling Combined with Transcriptome Profiling Provides Mechanistic Understanding of Streptococcus thermophilus CH8 Metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0078022. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Hou, B.; Hung, W.; He, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Man, C. Streptococcus thermophilus JM905-Strain Carbon Source Utilization and Its Fermented Milk Metabolic Profile at Different Fermentation Stages. Foods 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Liu, G.; Leng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, X.; Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Feng, Z. Metabolic profiles of cysteine, methionine, glutamate, glutamine, arginine, aspartate, asparagine, alanine and glutathione in Streptococcus thermophilus during pH-controlled batch fermentations. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12441. [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Guo, M.; Yang, B.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Altered microbiome and metabolome features provide clues in understanding strain- specific regulation of Streptococcus thermophilus in the host. Res. Sq. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Vitetta, L.; Llewellyn, H.; Oldfield, D. Gut Dysbiosis and the Intestinal Microbiome: Streptococcus thermophilus a Key Probiotic for Reducing Uremia. Microorganisms 2019, 7. [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S. Co-production of parabiotic metabolites by Lactobacillus acidophilus LA5 and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB12 in dairy effluents. College & Research Libraries 2021.
- Rani, P.; Tiwari, S.K. Health benefits of bacteriocins produced by probiotic lactic acid bacteria. In Microbial Biomolecules; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 97–111 ISBN 9780323994767.
- Deliorman Orhan, D. Bacteriocins produced by probiotic microorganisms. In Advances in Probiotics; Elsevier, 2021; pp. 277–291 ISBN 9780128229095.
- Wang, G.; Yu, Y.; Garcia-Gutierrez, E.; Jin, X.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Tian, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus JCM 1132 Strain and Its Mutant with Different Bacteriocin-Producing Behaviour Have Various in Situ Effects on the Gut Microbiota of Healthy Mice. Microorganisms 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.C.-H.; Zhang, X.; Ji, F.; Lin, Y.; Liang, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, D.; Fong, W.; Kang, X.; Liu, W.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus suppresses non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through producing valeric acid. EBioMedicine 2024, 100, 104952. [CrossRef]
- Prangli, A.-L.; Utt, M.; Talja, I.; Sepp, E.; Mikelsaar, M.; Rajasalu, T.; Uibo, O.; Tillmann, V.; Uibo, R. Antigenic proteins of Lactobacillus acidophilus that are recognised by serum IgG antibodies in children with type 1 diabetes and coeliac disease. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 21, e772-9. [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, B.; Bednarski, W.; Dziuba, B. Functional properties of Lactobacillus acidophilus metabolites. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 2467–2476. [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Heinemann, C.; Velraeds, M.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. [31] Biosurfactants produced by Lactobacillus. In Biofilms; Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier, 1999; Vol. 310, pp. 426–433 ISBN 9780121822118.
- Datta, S.; Timson, D.J.; Annapure, U.S. Antioxidant properties and global metabolite screening of the probiotic yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3039–3049. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; Alian Samakkhah, S.; Bahadori, A.; Jafari, S.M.; Ziaee, M.; Khodayari, M.T.; Pourjafar, H. Health-promoting properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii as a probiotic; characteristics, isolation, and applications in dairy products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 457–485. [CrossRef]
- Bai, A.; Weaver, M.; Bao, F.; Chan, E.D.; Bai, X. Saccharomyces boulardii Produces a Factor That Inhibits Mycobacterium intracellulare Burden in Human Macrophages. AIM 2016, 06, 965–974. [CrossRef]
- Buts, J.-P.; Dekeyser, N.; Stilmant, C.; Delem, E.; Smets, F.; Sokal, E. Saccharomyces boulardii produces in rat small intestine a novel protein phosphatase that inhibits Escherichia coli endotoxin by dephosphorylation. Pediatr. Res. 2006, 60, 24–29. [CrossRef]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Brunser, O.; Szajewska, H. Saccharomyces boulardii in childhood. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 168, 253–265. [CrossRef]
- Pais, P.; Almeida, V.; Yılmaz, M.; Teixeira, M.C. Saccharomyces boulardii: What Makes It Tick as Successful Probiotic? J Fungi (Basel) 2020, 6. [CrossRef]
- Offei, B.; Vandecruys, P.; De Graeve, S.; Foulquié-Moreno, M.R.; Thevelein, J.M. Unique genetic basis of the distinct antibiotic potency of high acetic acid production in the probiotic yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 1478–1494. [CrossRef]
- Im, E.; Pothoulakis, C. [Recent advances in Saccharomyces boulardii research]. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2010, 34 Suppl 1, S62-70. [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Freitas, A.; da Silva Fernandes, L.J.; Coelho-Rocha, N.D.; de Jesus, L.C.L.; de Rezende Rodovalho, V.; da Silva, T.F.; de Oliveira Carvalho, R.D.; Azevedo, V. Immunomodulatory and antiinflammatory mechanisms of probiotics. In Probiotics; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 321–341 ISBN 9780323851701.
- Tao, T.; Zhang, L.; Yu, T.; Ma, J.; Lu, S.; Ren, J.; Li, X.; Guo, X. Exopolysaccharide production by Lactobacillus plantarum T10 is responsible for the probiotic activity in enhancing intestinal barrier function in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 3583–3599. [CrossRef]
- Chia, T.-Y.; Zolp, A.; Miska, J. Polyamine immunometabolism: central regulators of inflammation, cancer and autoimmunity. Cells 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Filidou, E.; Kandilogiannakis, L.; Shrewsbury, A.; Kolios, G.; Kotzampassi, K. Probiotics: Shaping the gut immunological responses. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 2096–2108. [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, D. Immunometabolism and innate immunity in the context of immunological maturation and respiratory pathogens in young children. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 301–308. [CrossRef]
- Fong, F.L.Y.; Shah, N.P.; Kirjavainen, P.; El-Nezami, H. Mechanism of Action of Probiotic Bacteria on Intestinal and Systemic Immunities and Antigen-Presenting Cells. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 35, 179–188. [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, B.; Eslami, M.; Ghasemian, A.; Kokhaei, P.; Salek Farrokhi, A.; Darabi, N. Probiotics importance and their immunomodulatory properties. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8008–8018. [CrossRef]
- Kleniewska, P.; Pawliczak, R. Can probiotics be used in the prevention and treatment of bronchial asthma? Pharmacol. Rep. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Nova, E.; Wärnberg, J.; Gómez-Martínez, S.; Díaz, L.E.; Romeo, J.; Marcos, A. Immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in different stages of life. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98 Suppl 1, S90-5. [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, Y.; Kawata, Y.; Hara, H.; Terada, A.; Mitsuoka, T. Effect of a probiotic formula on intestinal immunoglobulin A production in healthy children. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 42, 39–44. [CrossRef]
- Fong, F.L.Y.; El-Nezami, H.; Mykkänen, O.; Kirjavainen, P.V. The effects of single strains and mixtures of probiotic bacteria on immune profile in liver, spleen, and peripheral blood. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 773298. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Guo, L.; Yu, D.; Du, X. New insights into immunomodulatory properties of lactic acid bacteria fermented herbal medicines. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1073922. [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, P.V.; Wong, S.-S.; Tang, M.L.; Karagiannis, T.C. Epigenome targeting by probiotic metabolites. Gut Pathog. 2010, 2, 24. [CrossRef]
- DeMuri, G.P.; Lehtoranta, L.M.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Wald, E.R. Ex vivo peripheral blood mononuclear cell response to R848 in children after supplementation with the probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM/Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07. Benef. Microbes 2021, 12, 85–93. [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Ning, L.; Zhang, X. A meta-analysis of the therapeutic effect of probiotic intervention in obese or overweight adolescents. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2024, 15, 1335810. [CrossRef]
- Atazadegan, M.A.; Heidari-Beni, M.; Entezari, M.H.; Sharifianjazi, F.; Kelishadi, R. Effects of synbiotic supplementation on anthropometric indices and body composition in overweight or obese children and adolescents: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. World J. Pediatr. 2023, 19, 356–365. [CrossRef]
- Karlsson Videhult, F.; Andersson, Y.; Öhlund, I.; Stenlund, H.; Hernell, O.; West, C.E. Impact of probiotics during weaning on the metabolic and inflammatory profile: follow-up at school age. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, 686–691. [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Guo, Y.; Ergun, A.; Lu, L.; Walker, W.A.; Ganguli, K. Secreted Metabolites of Bifidobacterium infantis and Lactobacillus acidophilus Protect Immature Human Enterocytes from IL-1β-Induced Inflammation: A Transcription Profiling Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124549. [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Benno, Y. Anti-inflammatory metabolite production in the gut from the consumption of probiotic yogurt containing Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis LKM512. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 1287–1292. [CrossRef]
- Ballini, A.; Gnoni, A.; De Vito, D.; Dipalma, G.; Cantore, S.; Gargiulo Isacco, C.; Saini, R.; Santacroce, L.; Topi, S.; Scarano, A.; et al. Effect of probiotics on the occurrence of nutrition absorption capacities in healthy children: a randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled pilot study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8645–8657. [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.-C.; Fang, T.-J.; Ho, H.-H.; Chen, J.-F.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Tsai, S.-Y.; Wu, S.-F.; Lin, H.-C.; Yeh, Y.-T. A multi-strain probiotic blend reshaped obesity-related gut dysbiosis and improved lipid metabolism in obese children. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Qin, L.; Wu, L. Effects of probiotic administration on overweight or obese children: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 525. [CrossRef]
- Toe, L.C.; Kerckhof, F.-M.; De Bodt, J.; Morel, F.B.; Ouedraogo, J.-B.; Kolsteren, P.; Van de Wiele, T. A prebiotic-enhanced lipid-based nutrient supplement (LNSp) increases Bifidobacterium relative abundance and enhances short-chain fatty acid production in simulated colonic microbiota from undernourished infants. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96. [CrossRef]
- Kambale, R.M.; Ntagazibwa, J.N.; Kasengi, J.B.; Zigashane, A.B.; Francisca, I.N.; Mashukano, B.N.; Amani Ngaboyeka, G.; Bahizire, E.; Zech, F.; Bindels, L.B.; et al. Probiotics for children with uncomplicated severe acute malnutrition (PruSAM study): A randomized controlled trial in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 976–984. [CrossRef]
- M., G.; A., G.; C, H.; M, R.; N, I.; Ts, M. The probiotic BIOHM improves nutrient absorption by disrupting gastrointestinal biofilms. J. Prob. Health 2019, 07. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [CrossRef]
- Bandsma, R.H.J.; Sadiq, K.; Bhutta, Z.A. Persistent diarrhoea: current knowledge and novel concepts. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2019, 39, 41–47. [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.I.; McPhail, G.; Lunn, P.G.; Elia, M.; Jeffries, D.J. Intestinal inflammation measured by fecal neopterin in Gambian children with enteropathy: association with growth failure, Giardia lamblia, and intestinal permeability. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 39, 153–157. [CrossRef]
- Sjögren, Y.M.; Jenmalm, M.C.; Böttcher, M.F.; Björkstén, B.; Sverremark-Ekström, E. Altered early infant gut microbiota in children developing allergy up to 5 years of age. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 518–526. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Pathak, K.; Das, J.; Bordoloi, S.; Pathak, M.P.; Barbhuiya, P.A.; Saikia, R. Therapeutic potential of gut microbiota in child health. AIA 2023, 21. [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Tapia, E.; Sebastiani, G.; Sailer, S.; Toledano, L.A.; Serra-Delgado, M.; García-Algar, Ó.; Andreu-Fernández, V. Probiotic supplementation during the perinatal and infant period: effects on gut dysbiosis and disease. Nutrients 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, J.; Bulotta, R.M.; Ruga, S.; Nucera, S.; Macrì, R.; Scarano, F.; Oppedisano, F.; Carresi, C.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; et al. The Postbiotic Properties of Butyrate in the Modulation of the Gut Microbiota: The Potential of Its Combination with Polyphenols and Dietary Fibers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25. [CrossRef]
- Dogra, S.K.; Dardinier, A.; Mainardi, F.; Siegwald, L.; Bartova, S.; Roy, C. le; Chou, C.J. Application of computational data modeling to a large-scale population cohort assists the discovery of specific nutrients that influence beneficial human gut bacteria Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. BioRxiv 2022. [CrossRef]
- Kadry, A.A.; El-Antrawy, M.A.; El-Ganiny, A.M. Impact of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) on antimicrobial activity of new β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations and on virulence of Escherichia coli isolates. J. Antibiot. 2023, 76, 225–235. [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhou, W.; Yang, C.; Mai, G.; Li, H.; Chen, Y. Gut microbiota-derived butyrate regulates gut mucus barrier repair by activating the macrophage/WNT/ERK signaling pathway. Clin. Sci. 2022, 136, 291–307. [CrossRef]
- Ornelas, A.; Welch, N.; Countess, J.A.; Zhou, L.; Wang, R.X.; Dowdell, A.S.; Colgan, S.P. Mimicry of microbially-derived butyrate reveals templates for potent intestinal epithelial HIF stabilizers. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2267706. [CrossRef]
- Recharla, N.; Geesala, R.; Shi, X.-Z. Gut microbial metabolite butyrate and its therapeutic role in inflammatory bowel disease: A literature review. Nutrients 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Conder, E.; Shay, H.C.; Vekaria, H.; Erinkitola, I.; Bhogoju, S.; Goretsky, T.; Sullivan, P.; Barrett, T.; Kapur, N. Butyrate-induced mitochondrial function improves barrier function in inflammatory bowel disease (ibd). Gastroenterology 2023, 164, S91. [CrossRef]
- Novella Nicese, M.; van den Berg, B.; Sol, W.; van Raalte, D.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Rotmans, J. MO618: influence of butyrate and acetate on behavior and metabolism of human glomerular microvascular endothelial cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 2022, 37. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.P.; Rubio, L.A.; Duncan, S.H.; Donachie, G.E.; Holtrop, G.; Lo, G.; Farquharson, F.M.; Wagner, J.; Parkhill, J.; Louis, P.; et al. Pivotal Roles for pH, Lactate, and Lactate-Utilizing Bacteria in the Stability of a Human Colonic Microbial Ecosystem. mSystems 2020, 5. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, W.; Guo, T.; Gu, R.; Kong, J. Potential Application and Bactericidal Mechanism of Lactic Acid-Hydrogen Peroxide Consortium. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 189, 822–833. [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Li, P. Biosynthesis of vitamins by probiotic bacteria. In Probiotics and prebiotics in human nutrition and health; Rao, V., Rao, L.G., Eds.; InTech, 2016 ISBN 978-953-51-2475-7.
- Odumosu, B.T.; Bamidele, T.A.; Ofem, D.W.; Agbozo, F.; Olasehinde, G.I. Screening, isolation and biotechnological potentials of foodborne Lactobacillus fermentum strains MT903311 and MT903312. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14959. [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Peng, X.; Yang, A.; Lin, M.; Ji, K.; Dai, X.; Huang, J.; Li, L.; Feng, L. Impact of oligosaccharides on probiotic properties and B vitamins production: a comprehensive assessment of probiotic strains. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 6044–6064. [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Uddin, S.; Deb, B.; Hussain, T.; Rafi, S.; Islam, A. The role of lactobacillus reuteri probiotic for preventing functional gastrointestinal disorders in toddlerhood. IJG 2024, 8, 14–21. [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.C.; Vannini, V.; Font, G.; Saavedra, L.; Taranto, M.P. Novel pathway for corrinoid compounds production in lactobacillus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2256. [CrossRef]
- Langa, S.; Peirotén, Á.; Rodríguez, S.; Calzada, J.; Prieto-Paredes, R.; Curiel, J.A.; Landete, J.M. Riboflavin bio-enrichment of soy beverage by selected roseoflavin-resistant and engineered lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 411, 110547. [CrossRef]
- Meucci, A.; Rossetti, L.; Zago, M.; Monti, L.; Giraffa, G.; Carminati, D.; Tidona, F. Folates biosynthesis by Streptococcus thermophilus during growth in milk. Food Microbiol. 2018, 69, 116–122. [CrossRef]
- Smajdor, J.; Jedlińska, K.; Porada, R.; Górska-Ratusznik, A.; Policht, A.; Śróttek, M.; Więcek, G.; Baś, B.; Strus, M. The impact of gut bacteria producing long chain homologs of vitamin K2 on colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 268. [CrossRef]
- Parama Iswara, R.; Yunus, K.; Pati, N. Vitamin K Deficiency. In Causes and management of nutritional deficiency disorders; Nayak, A., Misra, S., Eds.; Advances in medical diagnosis, treatment, and care; IGI Global, 2024; pp. 214–218 ISBN 9798369329474.
- A. Aljafary, M.; Alshwyeh, H.; Alahmadi, N.; Shehzad, A.; Tombuloglu, H.; Gaymalov, Z.; Homieda, A.; Al-Suhaimi, E. Physiological and cellular functions of vitamin K on cardiovascular function. In Vitamin K—Recent Topics on the Biology and Chemistry; Kagechika, H., Shirakawa, H., Eds.; Biochemistry; IntechOpen, 2022; Vol. 27 ISBN 978-1-83969-391-5.
- Ivanko, O.G.; Solianyk, O.V. Antibiotic-associated disorders of prothrombin synthesis and their probiotic correction with B. Clausii in breastfeed infants. ZMJ 2018, 0. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Good things come in small packages : delivery of vitamin K2 to human cells by extracellular vesicles from Lactococcus lactis. Doctoral dissertation, Wageningen University., 2022.
- Cooke, G.; Behan, J.; Costello, M. Newly identified vitamin K-producing bacteria isolated from the neonatal faecal flora. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2006, 18, 133–138. [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, D.; Kalsi, G. Dietary intervention of prebiotics and vitamins on gut health of children. Nutrition & Food Science 2022, 52, 1045–1054. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Choi, E.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoo, M.-S.; Heo, K.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, J.-L. Probiotic Potential of a Novel Vitamin B2-Overproducing Lactobacillus plantarum Strain, HY7715, Isolated from Kimchi. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5765. [CrossRef]
- Salvi, P.S.; Cowles, R.A. Butyrate and the intestinal epithelium: modulation of proliferation and inflammation in homeostasis and disease. Cells 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. Inducible Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell development by a commensal bacterium of the intestinal microbiota. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010, 107, 12204–12209. [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, M.; Nygaard, U.C.; Brodin, P.; Carlsen, K.C.L.; Fredheim, C.; Haugen, G.; Hedlin, G.; Jonassen, C.M.; Jonsmoen, U.L.A.; Lakshmikanth, T.; et al. Gut bacteria at 6 months of age are associated with immune cell status in 1-year-old children. Scand. J. Immunol. 2024, 99, e13346. [CrossRef]
- Treem, W.R.; Ahsan, N.; Shoup, M.; Hyams, J.S. Fecal short-chain fatty acids in children with inflammatory bowel disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1994, 18, 159–164. [CrossRef]
- Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Petito, V.; Gasbarrini, A. Commensal Clostridia: leading players in the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Gut Pathog. 2013, 5, 23. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Das, S.; Gazi, M.A.; Alam, M.A.; Haque, N.M.S.; Mahfuz, M.; Ahmed, T.; Damman, C.J. Association of faecal pH with childhood stunting: Results from a cross-sectional study. bmjpo 2019, 3, e000549. [CrossRef]
- van Limpt, C.; Crienen, A.; Vriesema, A.; Knol, J. 134 effect of colonic short chain fatty acids, lactate and PH on the growth of common gut pathogens. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 56, 487–487. [CrossRef]
- Hatayama, H.; Iwashita, J.; Kuwajima, A.; Abe, T. The short chain fatty acid, butyrate, stimulates MUC2 mucin production in the human colon cancer cell line, LS174T. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 356, 599–603. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. The SCFAs Production of Syntrophic Culture of L. johnsonii SZ-YL and A. Muciniphila in Different Macrobutrients. HSET 2023, 30, 24–33. [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Galla, R.; Mulè, S.; Rosso, G.; Brovero, A.; Macchi, V.; Ruga, S.; Uberti, F. The Role of Bifidobacterium bifidum novaBBF7, Bifidobacterium longum novaBLG2 and Lactobacillus paracasei TJB8 to Improve Mechanisms Linked to Neuronal Cells Protection against Oxidative Condition in a Gut-Brain Axis Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Ling, Z. Short-chain fatty acids-producing probiotics: A novel source of psychobiotics. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7929–7959. [CrossRef]
- Vital, M.; Karch, A.; Pieper, D.H. Colonic Butyrate-Producing Communities in Humans: an Overview Using Omics Data. mSystems 2017, 2. [CrossRef]
- Hojsak, I.; Benninga, M.A.; Hauser, B.; Kansu, A.; Kelly, V.B.; Stephen, A.M.; Morais Lopez, A.; Slavin, J.; Tuohy, K. Benefits of dietary fibre for children in health and disease. Arch. Dis. Child. 2022, 107, 973–979. [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.H.; Meneguetti, B.T.; Oliveira-Júnior, N.G.; Macedo, M.L.R.; Franco, O.L. Antimicrobial peptide production in response to gut microbiota imbalance. Peptides 2022, 157, 170865. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Kjos, M.; Nes, I.F.; Diep, D.B.; Lotfipour, F. Natural antimicrobial peptides from bacteria: characteristics and potential applications to fight against antibiotic resistance. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 723–736. [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Teng, K.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, T.; Ma, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, J. Bacteriocins: potential for human health. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5518825. [CrossRef]
- Spohn, R.; Daruka, L.; Lázár, V.; Martins, A.; Vidovics, F.; Grézal, G.; Méhi, O.; Kintses, B.; Számel, M.; Jangir, P.K.; et al. Integrated evolutionary analysis reveals antimicrobial peptides with limited resistance. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4538. [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D.; Kubicek-Sutherland, J.Z. Mechanisms and consequences of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial peptides. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 26, 43–57. [CrossRef]
- Yeaman, M.R.; Yount, N.Y. Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharmacol. Rev. 2003, 55, 27–55. [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.M.; Pati, B.R.; Chakraborty, R.; Franco, O.L. New insights into the bioactivity of peptides from probiotics. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 2016, 8, 450–459. [CrossRef]
- Heilbronner, S.; Krismer, B.; Brötz-Oesterhelt, H.; Peschel, A. The microbiome-shaping roles of bacteriocins. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 726–739. [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Gwak, J.W.; Kamarajan, P.; Fenno, J.C.; Rickard, A.H.; Kapila, Y.L. Biomedical applications of nisin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1449–1465. [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.; Petkova, A.; Hilpert, K. Cationic antimicrobial peptides as potential new therapeutic agents in neonates and children: a review. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 27, 258–267. [CrossRef]
- Arun, K.B.; Madhavan, A.; Emmanual, S.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A. Enzymes in probiotics and genetically modified foods. In Value-Addition in Food Products and Processing Through Enzyme Technology; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 13–23 ISBN 9780323899291.
- Xie, W.; Li, W.; Gao, F.; Li, T. In vitro digestion and fermentation of lacto- N -biose, a core building block of human milk oligosaccharides. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 4511–4518. [CrossRef]
- Florindo, R.N.; Souza, V.P.; Manzine, L.R.; Camilo, C.M.; Marana, S.R.; Polikarpov, I.; Nascimento, A.S. Structural and biochemical characterization of a GH3 β-glucosidase from the probiotic bacteria Bifidobacterium adolescentis. Biochimie 2018, 148, 107–115. [CrossRef]
- Ambrogi, V.; Bottacini, F.; O’Callaghan, J.; Casey, E.; van Breen, J.; Schoemaker, B.; Cao, L.; Kuipers, B.; O’Connell Motherway, M.; Schoterman, M.; et al. Infant-Associated Bifidobacterial β-Galactosidases and Their Ability to Synthesize Galacto-Oligosaccharides. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 662959. [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Guo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Kong, J. A new β-galactosidase extracted from the infant feces with high hydrolytic and transgalactosylation activity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8439–8448. [CrossRef]
- Enzymatic Production of Galactooligosaccharides by β-Galactosidase from Bifidobacterium longum BCRC 15708. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jf063126%2B (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Antonowicz, I.; Shwachman, H.; Sotoo, I. Beta-galactosidase and beta-glucuronidase activities in intestinal mucosa of infants and children. Pediatrics 1971, 47, 737–744. [CrossRef]
- Cuxart, I.; Coines, J.; Esquivias, O.; Faijes, M.; Planas, A.; Biarnés, X.; Rovira, C. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Human Milk Oligosaccharides. The Molecular Mechanism of Bifidobacterium Bifidum Lacto-N-biosidase. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 4737–4743. [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Katayama, T.; Hattie, M.; Sakurama, H.; Wada, J.; Suzuki, R.; Ashida, H.; Wakagi, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Stubbs, K.A.; et al. Crystal structures of a glycoside hydrolase family 20 lacto-N-biosidase from Bifidobacterium bifidum. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11795–11806. [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.I.M.; El-Borai, A.M.; Akl, S.H.; El-Aassar, S.A.; Abdel-Latif, M.S. Identification of Lactobacillus strains from human mother milk and cottage cheese revealed potential probiotic properties with enzymatic activity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22522. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ji, Q.; He, T.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y. Characterization of a recombinant bile salt hydrolase (BSH) from Bifidobacterium bifidum for its glycine-conjugated bile salts specificity. Biocatal. Biotransformation 2021, 39, 61–70. [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, M.; Kılıçsaymaz, Z.; Önal, C. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Bile Salt Hydrolase (BSH) from Lactobacillus plantarum B14 Confirms the Importance of the V58 and Y65 Amino Acids for Activity and Substrate Specificity. Food Biotechnol. 2023, 37, 74–88. [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Sánchez, M.A.; Herisson, F.M.; Keane, J.M.; García-González, N.; Rossini, V.; Pinhiero, J.; Daly, J.; Bustamante-Garrido, M.; Hueston, C.M.; Patel, S.; et al. Microbial bile salt hydrolase activity influences gene expression profiles and gastrointestinal maturation in infant mice. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2149023. [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Shen, X.; Shi, X.; Sakandar, H.A.; Quan, K.; Li, Y.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z. Targeting gut microbiota and metabolism as the major probiotic mechanism—An evidence-based review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 178–198. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Dey, P. Bacterial exopolysaccharides as emerging bioactive macromolecules: from fundamentals to applications. Res. Microbiol. 2023, 174, 104024. [CrossRef]
- Alessandri, G.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. The genus bifidobacterium: From genomics to functionality of an important component of the mammalian gut microbiota running title: Bifidobacterial adaptation to and interaction with the host. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1472–1487. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wan, X.; Deng, H.; Sun, W.; He, X.; Chen, K. Screening of exopolysaccharide-producing Enterobacter aerogenes NJ1023 and its cadaverine biosynthesis promotion. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1200123. [CrossRef]
- Salimi, F.; Farrokh, P. Recent advances in the biological activities of microbial exopolysaccharides. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 213. [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Bottacini, F.; Casey, E.; Turroni, F.; Mahony, J.; Belzer, C.; Delgado Palacio, S.; Arboleya Montes, S.; Mancabelli, L.; et al. The first microbial colonizers of the human gut: composition, activities, and health implications of the infant gut microbiota. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81. [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Haghshenas, B.; Nami, Y. Bifidobacterium exopolysaccharides: new insights into engineering strategies, physicochemical functions, and immunomodulatory effects on host health. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15. [CrossRef]
- Caggianiello, G.; Kleerebezem, M.; Spano, G. Exopolysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria: from health-promoting benefits to stress tolerance mechanisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 3877–3886. [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Liu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, L.; Li, B.; Huo, G. Exopolysaccharides of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis E4 on the immune and anti-inflammatory effects in vitro. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 107, 105699. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, C. The anti-cancer effects and mechanisms of lactic acid bacteria exopolysaccharides in vitro: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117308. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Chen, S.; Lv, H.; Peng, L.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Wan, C. Effect of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis SF on enhancing the tumor suppression of irinotecan by regulating the intestinal flora. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 184, 106406. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Tian, K.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Guo, C. Exopolysaccharide, Isolated From a Novel Strain Bifidobacterium breve lw01 Possess an Anticancer Effect on Head and Neck Cancer—Genetic and Biochemical Evidences. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1044. [CrossRef]
- Angelin, J.; Kavitha, M. Exopolysaccharides from probiotic bacteria and their health potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 853–865. [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, G.; Thanh, H.D.; Kim, J.-H.; Konkit, M.; Yoon, S.; Park, M.; Yang, S.; Park, E.; Kim, W. Exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus plantarum LRCC5310 offers protection against rotavirus-induced diarrhea and regulates inflammatory response. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 5702–5712. [CrossRef]
- Bhat, B.; Bajaj, B.K. Hypocholesterolemic potential and bioactivity spectrum of an exopolysaccharide from a probiotic isolate Lactobacillus paracasei M7. Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre 2019, 19, 100191. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ding, Q.; Xu, L. Isolated exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG alleviated adipogenesis mediated by TLR2 in mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36083. [CrossRef]
- Porges, E.C.; Woods, A.J.; Edden, R.A.E.; Puts, N.A.J.; Harris, A.D.; Chen, H.; Garcia, A.M.; Seider, T.R.; Lamb, D.G.; Williamson, J.B.; et al. Frontal Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Concentrations Are Associated With Cognitive Performance in Older Adults. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2017, 2, 38–44. [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.M.; Becker, M.; Qi, A.; Geiger, P.; Frank, U.I.; Rosedahl, L.A.; Malloni, W.M.; Sasaki, Y.; Greenlee, M.W.; Watanabe, T. Efficient learning in children with rapid GABA boosting during and after training. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 5022-5030.e7. [CrossRef]
- Yunes, R.A.; Poluektova, E.U.; Dyachkova, M.S.; Klimina, K.M.; Kovtun, A.S.; Averina, O.V.; Orlova, V.S.; Danilenko, V.N. GABA production and structure of gadB/gadC genes in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains from human microbiota. Anaerobe 2016, 42, 197–204. [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.J.; Sabir, S.; Sharma, S. GABA Receptor. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2024.
- Saleh, M.G.; Papantoni, A.; Mikkelsen, M.; Hui, S.C.N.; Oeltzschner, G.; Puts, N.A.; Edden, R.A.E.; Carnell, S. Effect of age on GABA+ and glutathione in a pediatric sample. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2020, 41, 1099–1104. [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo-Mera, A.; Fanti, V.; Rodriguez-Sobstel, C.; Gibson, G.; Wijeyesekera, A.; Karatzas, K.-A.; Chakrabarti, B. Gamma aminobutyric acid production by commercially available probiotic strains. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134. [CrossRef]
- Braga, J.D.; Thongngam, M.; Kumrungsee, T. Gamma-aminobutyric acid as a potential postbiotic mediator in the gut-brain axis. npj Sci. Food 2024, 8, 16. [CrossRef]
- Ueno, H. Enzymatic and structural aspects on glutamate decarboxylase. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic 2000, 10, 67–79. [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Lu, P.; Yan, C.; Fan, C.; Yin, P.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y. Structure and mechanism of a glutamate-GABA antiporter. Nature 2012, 483, 632–636. [CrossRef]
- Altaib, H.; Kozakai, T.; Badr, Y.; Nakao, H.; El-Nouby, M.A.M.; Yanase, E.; Nomura, I.; Suzuki, T. Cell factory for γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) production using Bifidobacterium adolescentis. Microb. Cell Fact. 2022, 21, 33. [CrossRef]
- Tamés, H.; Sabater, C.; Margolles, A.; Ruiz, L.; Ruas-Madiedo, P. Production of GABA in milk fermented by Bifidobacterium adolescentis strains selected on the bases of their technological and gastrointestinal performance. Food Res. Int 2023, 171, 113009. [CrossRef]
- Pokusaeva, K.; Johnson, C.; Luk, B.; Uribe, G.; Fu, Y.; Oezguen, N.; Matsunami, R.K.; Lugo, M.; Major, A.; Mori-Akiyama, Y.; et al. GABA-producing Bifidobacterium dentium modulates visceral sensitivity in the intestine. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29. [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-B.; Ji, G.-E.; Park, M.-S.; Oh, S.-H. Expression of rice glutamate decarboxylase in Bifidobacterium longum enhances gamma-aminobutyric acid production. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 1681–1684. [CrossRef]
- Cocean, A.-M.; Vodnar, D.C. Exploring the gut-brain Axis: Potential therapeutic impact of Psychobiotics on mental health. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2024, 134, 111073. [CrossRef]
- Annahazi, A.; Schemann, M. The enteric nervous system: “A little brain in the gut.” Neuroforum 2020, 26, 31–42. [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Sinniger, V.; Pellissier, S. The Vagus Nerve in the Neuro-Immune Axis: Implications in the Pathology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1452. [CrossRef]
- Barrio, C.; Arias-Sánchez, S.; Martín-Monzón, I. The gut microbiota-brain axis, psychobiotics and its influence on brain and behaviour: A systematic review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 137, 105640. [CrossRef]
- Sajdel-Sulkowska, E.M. The Impact of Maternal Gut Microbiota during Pregnancy on Fetal Gut-Brain Axis Development and Life-Long Health Outcomes. Microorganisms 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Duan, G.; Song, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Gut microbiota changes in patients with autism spectrum disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 129, 149–159. [CrossRef]
- Zuffa, S.; Schimmel, P.; Gonzalez-Santana, A.; Belzer, C.; Knol, J.; Bölte, S.; Falck-Ytter, T.; Forssberg, H.; Swann, J.; Diaz Heijtz, R. Early-life differences in the gut microbiota composition and functionality of infants at elevated likelihood of developing autism spectrum disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 257. [CrossRef]
- Cassidy-Bushrow, A.E.; Sitarik, A.R.; Johnson, C.C.; Johnson-Hooper, T.M.; Kassem, Z.; Levin, A.M.; Lynch, S.V.; Ownby, D.R.; Phillips, J.M.; Yong, G.J.M.; et al. Early-life gut microbiota and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in preadolescents. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 2051–2060. [CrossRef]
- Pärtty, A.; Kalliomäki, M.; Wacklin, P.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. A possible link between early probiotic intervention and the risk of neuropsychiatric disorders later in childhood: a randomized trial. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 823–828. [CrossRef]
- Braga, T.D.; da Silva, G.A.P.; de Lira, P.I.C.; de Carvalho Lima, M. Efficacy of Bifidobacterium breve and Lactobacillus casei oral supplementation on necrotizing enterocolitis in very-low-birth-weight preterm infants: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 81–86. [CrossRef]
- Dilli, D.; Aydin, B.; Fettah, N.D.; Özyazıcı, E.; Beken, S.; Zenciroğlu, A.; Okumuş, N.; Özyurt, B.M.; İpek, M.Ş.; Akdağ, A.; Turan, Ö.; Bozdağ, Ş. The propre-save study: effects of probiotics and prebiotics alone or combined on necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 545–51.e1. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Ross, R.P.; Ryan, C.A.; Dempsey, E.M.; Stanton, C. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics for the prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 667188. [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 32–48. [CrossRef]
- Wall, R.; Cryan, J.F.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C. Bacterial neuroactive compounds produced by psychobiotics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 221–239. [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Hiramoto, T.; Nishino, R.; Aiba, Y.; Kimura, T.; Yoshihara, K.; Koga, Y.; Sudo, N. Critical role of gut microbiota in the production of biologically active, free catecholamines in the gut lumen of mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G1288-95. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.M.; Versalovic, J. Probiotics-host communication: Modulation of signaling pathways in the intestine. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 148–163. [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.; Ross, R.P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. γ-Aminobutyric acid production by culturable bacteria from the human intestine. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 411–417. [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [CrossRef]
- Ozma, M.A.; Abbasi, A.; Akrami, S.; Lahouty, M.; Shahbazi, N.; Ganbarov, K.; Pagliano, P.; Sabahi, S.; Köse, Ş.; Yousefi, M.; Dao, S.; et al. Postbiotics as the key mediators of the gut microbiota-host interactions. Infez. Med. 2022, 30, 180–193. [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Garcia-Varela, R.; Garcia, H.S.; Mata-Haro, V.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; Hernández-Mendoza, A. Postbiotics: An evolving term within the functional foods field. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 105–114. [CrossRef]
- Konstantinov, S.R.; Kuipers, E.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Functional genomic analyses of the gut microbiota for CRC screening. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 741–745. [CrossRef]
- Sawada, H.; Furushiro, M.; Hirai, K.; Motoike, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yokokura, T. Purification and characterization of an antihypertensive compound from Lactobacillus casei. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1990, 54, 3211–3219.
- Nakamura, F.; Ishida, Y.; Sawada, D.; Ashida, N.; Sugawara, T.; Sakai, M.; Goto, T.; Kawada, T.; Fujiwara, S. Fragmented Lactic Acid Bacterial Cells Activate Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors and Ameliorate Dyslipidemia in Obese Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2549–2559. [CrossRef]
- Chaluvadi, S.; Hotchkiss, A.T.; Yam, K.L. Gut Microbiota. In Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics; Elsevier, 2016; pp. 515–523 ISBN 9780128021897.
- Venema, K. Beneficial microbes. Foreword. Benef. Microbes 2012, 3, 1–2. [CrossRef]
- Ozma, M.A.; Khodadadi, E.; Rezaee, M.A.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Aghazadeh, M.; Zeinalzadeh, E.; Ganbarov, K.; Kafil, H.S. Bacterial proteomics and its application in pathogenesis studies. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2022, 23, 1245–1256. [CrossRef]
- Shigwedha, N.; Sichel, L.; Jia, L.; Zhang, L. Probiotical cell fragments (pcfs) as “novel nutraceutical ingredients.” JBM 2014, 02, 43–55. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Lactobacillus casei Zhang modulate cytokine and toll-like receptor expression and beneficially regulate poly I:C-induced immune responses in RAW264.7 macrophages. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 54–62. [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, K.; He, F.; Kawase, M.; Kubota, A.; Yoda, K.; Hiramatsu, M. Enhancement of immunoregulatory effects of Lactobacillus gasseri TMC0356 by heat treatment and culture medium. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 53, 210–216. [CrossRef]
- Chuang, L.; Wu, K.-G.; Pai, C.; Hsieh, P.-S.; Tsai, J.-J.; Yen, J.-H.; Lin, M.-Y. Heat-killed cells of lactobacilli skew the immune response toward T helper 1 polarization in mouse splenocytes and dendritic cell-treated T cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 11080–11086. [CrossRef]
- Sokol, H.; Pigneur, B.; Watterlot, L.; Lakhdari, O.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Gratadoux, J.-J.; Blugeon, S.; Bridonneau, C.; Furet, J.-P.; Corthier, G.; et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008, 105, 16731–16736. [CrossRef]
- Tsilingiri, K.; Barbosa, T.; Penna, G.; Caprioli, F.; Sonzogni, A.; Viale, G.; Rescigno, M. Probiotic and postbiotic activity in health and disease: comparison on a novel polarised ex-vivo organ culture model. Gut 2012, 61, 1007–1015. [CrossRef]
- Haileselassie, Y.; Navis, M.; Vu, N.; Qazi, K.R.; Rethi, B.; Sverremark-Ekström, E. Postbiotic Modulation of Retinoic Acid Imprinted Mucosal-like Dendritic Cells by Probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri 17938 In Vitro. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 96. [CrossRef]
- Compare, D.; Rocco, A.; Coccoli, P.; Angrisani, D.; Sgamato, C.; Iovine, B.; Salvatore, U.; Nardone, G. Lactobacillus casei DG and its postbiotic reduce the inflammatory mucosal response: an ex-vivo organ culture model of post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 53. [CrossRef]
- Béghin, L.; Tims, S.; Roelofs, M.; Rougé, C.; Oozeer, R.; Rakza, T.; Chirico, G.; Roeselers, G.; Knol, J.; Rozé, J.C.; et al. Fermented infant formula (with Bifidobacterium breve C50 and Streptococcus thermophilus O65) with prebiotic oligosaccharides is safe and modulates the gut microbiota towards a microbiota closer to that of breastfed infants. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 778–787. [CrossRef]
- Thibault, H.; Aubert-Jacquin, C.; Goulet, O. Effects of long-term consumption of a fermented infant formula (with Bifidobacterium breve c50 and Streptococcus thermophilus 065) on acute diarrhea in healthy infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 39, 147–152. [CrossRef]
- Morisset, M.; Aubert-Jacquin, C.; Soulaines, P.; Moneret-Vautrin, D.A.; Dupont, C. A non-hydrolyzed, fermented milk formula reduces digestive and respiratory events in infants at high risk of allergy. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 175–183. [CrossRef]
- Nocerino, R.; Paparo, L.; Terrin, G.; Pezzella, V.; Amoroso, A.; Cosenza, L.; Cecere, G.; De Marco, G.; Micillo, M.; Albano, F.; et al. Cow’s milk and rice fermented with Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 prevent infectious diseases in children: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 118–125. [CrossRef]
- Corsello, G.; Carta, M.; Marinello, R.; Picca, M.; De Marco, G.; Micillo, M.; Ferrara, D.; Vigneri, P.; Cecere, G.; Ferri, P.; et al. Preventive Effect of Cow’s Milk Fermented with Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 on Common Infectious Diseases in Children: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2017, 9. [CrossRef]
- Lukovac, S.; Belzer, C.; Pellis, L.; Keijser, B.J.; de Vos, W.M.; Montijn, R.C.; Roeselers, G. Differential modulation by Akkermansia muciniphila and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii of host peripheral lipid metabolism and histone acetylation in mouse gut organoids. MBio 2014, 5. [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Santiago-López, L.; Peres, C.M.; Peres, C.; Garcia, H.S.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Hernández-Mendoza, A. Assessment of multifunctional activity of bioactive peptides derived from fermented milk by specific Lactobacillus plantarum strains. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 65–75. [CrossRef]
- Dronkers, T.M.G.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Rijkers, G.T. Global analysis of clinical trials with probiotics. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04467. [CrossRef]
- Critchfield, J.W.; van Hemert, S.; Ash, M.; Mulder, L.; Ashwood, P. The potential role of probiotics in the management of childhood autism spectrum disorders. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2011, 2011, 161358. [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, M.; Teng, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L. Prebiotics and probiotics for autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 71. [CrossRef]
- Depoorter, L.; Vandenplas, Y. Probiotics in pediatrics. A review and practical guide. Nutrients 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- van den Akker, C.H.P.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Shamir, R.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.D.; Hojsak, I.; Lapillonne, A.; Mihatsch, W.A.; Berni Canani, R.; Bronsky, J.; et al. Probiotics and preterm infants: A position paper by the european society for paediatric gastroenterology hepatology and nutrition committee on nutrition and the european society for paediatric gastroenterology hepatology and nutrition working group for probiotics and prebiotics. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 664–680. [CrossRef]
- Su, G.L.; Ko, C.W.; Bercik, P.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Sultan, S.; Weizman, A.V.; Morgan, R.L. AGA clinical practice guidelines on the role of probiotics in the management of gastrointestinal disorders. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 697–705. [CrossRef]
- Weizman, Z.; Vandenplas, Y. Why do clinical guidelines for probiotics differ? Benef. Microbes 2024, 15, 411–415. [CrossRef]
- Guarner, F.; Sanders, M.E.; Szajewska, H.; Cohen, H.; Eliakim, R.; Herrera-deGuise, C.; Karakan, T.; Merenstein, D.; Piscoya, A.; Ramakrishna, B.; et al. World gastroenterology organisation global guidelines: probiotics and prebiotics. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2024, 58, 533–553. [CrossRef]
- Collinson, S.; Deans, A.; Padua-Zamora, A.; Gregorio, G.V.; Li, C.; Dans, L.F.; Allen, S.J. Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 12, CD003048. [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Berni Canani, R.; Domellöf, M.; Guarino, A.; Hojsak, I.; Indrio, F.; Lo Vecchio, A.; Mihatsch, W.A.; Mosca, A.; Orel, R.; et al. ESPGHAN Special Interest Group on Gut Microbiota and Modifications Probiotics for the management of pediatric gastrointestinal disorders: position paper of the ESPGHAN special interest group on gut microbiota and modifications. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 76, 232–247. [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Kołodziej, M.; Zalewski, B.M. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Saccharomyces boulardii for treating acute gastroenteritis in children-a 2020 update. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 678–688. [CrossRef]
- Patro-Gołąb, B.; Szajewska, H. Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis: Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 for Treating Acute Gastroenteritis in Children. An Update. Nutrients 2019, 11. [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeldt, V.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Jakobsen, M.; Larsen, C.N.; Møller, P.L.; Tvede, M.; Weyrehter, H.; Valerius, N.H.; Paerregaard, A. Effect of probiotic Lactobacillus strains on acute diarrhea in a cohort of nonhospitalized children attending day-care centers. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2002, 21, 417–419. [CrossRef]
- İşlek, A.; Sayar, E.; Yılmaz, A.; Baysan, B.Ö.; Mutlu, D.; Artan, R. The role of Bifidobacterium lactis B94 plus inulin in the treatment of acute infectious diarrhea in children. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 25, 628–633. [CrossRef]
- Passariello, A.; Terrin, G.; Cecere, G.; Micillo, M.; De Marco, G.; Di Costanzo, M.; Cosenza, L.; Leone, L.; Nocerino, R.; Canani, R.B. Randomised clinical trial: efficacy of a new synbiotic formulation containing Lactobacillus paracasei B21060 plus arabinogalactan and xilooligosaccharides in children with acute diarrhoea. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 782–788. [CrossRef]
- Szymański, H.; Pejcz, J.; Jawień, M.; Chmielarczyk, A.; Strus, M.; Heczko, P.B. Treatment of acute infectious diarrhoea in infants and children with a mixture of three Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains--a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 23, 247–253. [CrossRef]
- Canani, R.B.; Cirillo, P.; Terrin, G.; Cesarano, L.; Spagnuolo, M.I.; De Vincenzo, A.; Albano, F.; Passariello, A.; De Marco, G.; Manguso, F.; et al. Probiotics for treatment of acute diarrhoea in children: randomised clinical trial of five different preparations. BMJ 2007, 335, 340. [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Xin, J.; Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Luo, L.; Yuan, S.; Bu, Y.; Yang, X.; Ge, Y.; Liu, C. A combination of three probiotic strains for treatment of acute diarrhoea in hospitalised children: an open label, randomised controlled trial. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 339–346. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Goldenberg, J.Z.; Humphrey, C.; El Dib, R.; Johnston, B.C. Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 4, CD004827. [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Canani, R.B.; Guarino, A.; Hojsak, I.; Indrio, F.; Kolacek, S.; Orel, R.; Shamir, R.; Vandenplas, Y.; van Goudoever, J.B.; et al. Probiotics for the Prevention of Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea in Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 62, 495–506. [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Kołodziej, M. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in children and adults. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 1149–1157. [CrossRef]
- Lukasik, J.; Dierikx, T.; Besseling-van der Vaart, I.; de Meij, T.; Szajewska, H.; Multispecies Probiotic in AAD Study Group Multispecies Probiotic for the Prevention of Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea in Children: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2022, 176, 860–866. [CrossRef]
- Ruszczyński, M.; Radzikowski, A.; Szajewska, H. Clinical trial: effectiveness of Lactobacillus rhamnosus (strains E/N, Oxy and Pen) in the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in children. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 28, 154–161. [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Wanke, M.; Patro, B. Meta-analysis: the effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG supplementation for the prevention of healthcare-associated diarrhoea in children. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 1079–1087. [CrossRef]
- Hojsak, I.; Szajewska, H.; Canani, R.B.; Guarino, A.; Indrio, F.; Kolacek, S.; Orel, R.; Shamir, R.; Vandenplas, Y.; van Goudoever, J.B.; et al. Probiotics for the prevention of nosocomial diarrhea in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 3–9. [CrossRef]
- Beghetti, I.; Panizza, D.; Lenzi, J.; Gori, D.; Martini, S.; Corvaglia, L.; Aceti, A. Probiotics for Preventing Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants: A Network Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Li, C.; Buys, N.; Wang, W.; Yin, C.; Sun, J. Effects of Probiotics in Preterm Infants: A Network Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2021, 147. [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, L.; Feng, W.; Yi, K. Effect and Safety of Saccharomyces boulardii for Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Pre-term Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2021, 67. [CrossRef]
- van den Akker, C.H.P.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Szajewska, H.; Embleton, N.D.; Hojsak, I.; Reid, D.; Shamir, R.; ESPGHAN Working Group for Probiotics, Prebiotics & Committee on Nutrition Probiotics for Preterm Infants: A Strain-Specific Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, 103–122. [CrossRef]
- Athalye-Jape, G.; Rao, S.; Patole, S. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 as a Probiotic for Preterm Neonates: A Strain-Specific Systematic Review. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2016, 40, 783–794. [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-C.; Su, B.-H.; Chen, A.-C.; Lin, T.-W.; Tsai, C.-H.; Yeh, T.-F.; Oh, W. Oral probiotics reduce the incidence and severity of necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2005, 115, 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.-R.; Wang, F.; Qiu, X.; McFarland, L.V.; Chen, P.-F.; Zhou, R.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J. Efficacy and safety of probiotic-supplemented triple therapy for eradication of Helicobacter pylori in children: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 73, 1199–1208. [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Peng, P.; Chen, P.; Zeng, L.; Pan, Q.; Wei, W.; He, J. Probiotics in 14-day triple therapy for Asian pediatric patients with Helicobacter pylori infection: a network meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 96409–96418. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.-G.; Chen, L.-X.; Li, B.; Wan, L.-Y.; Ai, Y.-W. Saccharomyces boulardii as an adjuvant therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12651. [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Horvath, A.; Kołodziej, M. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Saccharomyces boulardii supplementation and eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 41, 1237–1245. [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.-R.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Cheng, J.-Y.; Li, Z.-Y. Efficacy of Lactobacillus-supplemented triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection in children: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 7–16. [CrossRef]
- Hurduc, V.; Plesca, D.; Dragomir, D.; Sajin, M.; Vandenplas, Y. A randomized, open trial evaluating the effect of Saccharomyces boulardii on the eradication rate of Helicobacter pylori infection in children. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 127–131. [CrossRef]
- Bin, Z.; Ya-Zheng, X.; Zhao-Hui, D.; Bo, C.; Li-Rong, J.; Vandenplas, Y. The Efficacy of Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 in Addition to Standard Helicobacter pylori Eradication Treatment in Children. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2015, 18, 17–22. [CrossRef]
- Sung, V.; D’Amico, F.; Cabana, M.D.; Chau, K.; Koren, G.; Savino, F.; Szajewska, H.; Deshpande, G.; Dupont, C.; Indrio, F.; et al. Lactobacillus reuteri to Treat Infant Colic: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2018, 141. [CrossRef]
- Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Janda, K.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Marlicz, W.; Łoniewski, I.; Łoniewska, B. The Effect of Probiotics on Symptoms, Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Markers in Infantile Colic: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9. [CrossRef]
- Ong, T.G.; Gordon, M.; Banks, S.S.; Thomas, M.R.; Akobeng, A.K. Probiotics to prevent infantile colic. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 3, CD012473. [CrossRef]
- Dryl, R.; Szajewska, H. Probiotics for management of infantile colic: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 1137–1143. [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Castrellón, P.; Indrio, F.; Bolio-Galvis, A.; Jiménez-Gutiérrez, C.; Jimenez-Escobar, I.; López-Velázquez, G. Efficacy of Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 for infantile colic: Systematic review with network meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017, 96, e9375. [CrossRef]
- Schreck Bird, A.; Gregory, P.J.; Jalloh, M.A.; Risoldi Cochrane, Z.; Hein, D.J. Probiotics for the treatment of infantile colic: A systematic review. J. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 30, 366–374. [CrossRef]
- Harb, T.; Matsuyama, M.; David, M.; Hill, R.J. Infant Colic-What works: A Systematic Review of Interventions for Breast-fed Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 62, 668–686. [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Gyrczuk, E.; Horvath, A. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 for the management of infantile colic in breastfed infants: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 257–262. [CrossRef]
- Nocerino, R.; De Filippis, F.; Cecere, G.; Marino, A.; Micillo, M.; Di Scala, C.; de Caro, C.; Calignano, A.; Bruno, C.; Paparo, L.; et al. The therapeutic efficacy of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12® in infant colic: A randomised, double blind, placebo-controlled trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 110–120. [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; You, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, C.; Xu, S.; Melsaether, C.; Yuan, S. Efficacy of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis, BB-12® on infant colic—a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. Benef. Microbes 2021, 12, 531–540. [CrossRef]
- Gerasimov, S.; Gantzel, J.; Dementieva, N.; Schevchenko, O.; Tsitsura, O.; Guta, N.; Bobyk, V.; Kaprus, V. Role of Lactobacillus rhamnosus (FloraActiveTM) 19070-2 and Lactobacillus reuteri (FloraActiveTM) 12246 in Infant Colic: A Randomized Dietary Study. Nutrients 2018, 10. [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, M.E.; Di Mauro, A.; Tafuri, S.; Rizzo, V.; Gallone, M.S.; Mastromarino, P.; Capobianco, D.; Laghi, L.; Zhu, C.; Capozza, M.; et al Effectiveness and Safety of a Probiotic-Mixture for the Treatment of Infantile Colic: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial with Fecal Real-Time PCR and NMR-Based Metabolomics Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10. [CrossRef]
- Indrio, F.; Di Mauro, A.; Riezzo, G.; Civardi, E.; Intini, C.; Corvaglia, L.; Ballardini, E.; Bisceglia, M.; Cinquetti, M.; Brazzoduro, E.; et al. Prophylactic use of a probiotic in the prevention of colic, regurgitation, and functional constipation: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 228–233. [CrossRef]
- Trivić, I.; Niseteo, T.; Jadrešin, O.; Hojsak, I. Use of probiotics in the treatment of functional abdominal pain in children-systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 339–351. [CrossRef]
- Weizman, Z.; Abu-Abed, J.; Binsztok, M. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 for the Management of Functional Abdominal Pain in Childhood: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Pediatr. 2016, 174, 160-164.e1. [CrossRef]
- Gawrońska, A.; Dziechciarz, P.; Horvath, A.; Szajewska, H. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of Lactobacillus GG for abdominal pain disorders in children. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 177–184. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Gordon, M.; Baines, P.A.; Iheozor-Ejiofor, Z.; Sinopoulou, V.; Akobeng, A.K. Probiotics for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 3, CD005573. [CrossRef]
- Miele, E.; Pascarella, F.; Giannetti, E.; Quaglietta, L.; Baldassano, R.N.; Staiano, A. Effect of a probiotic preparation (VSL#3) on induction and maintenance of remission in children with ulcerative colitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 437–443. [CrossRef]
- Mimura, T.; Rizzello, F.; Helwig, U.; Poggioli, G.; Schreiber, S.; Talbot, I.C.; Nicholls, R.J.; Gionchetti, P.; Campieri, M.; Kamm, M.A. Once daily high dose probiotic therapy (VSL#3) for maintaining remission in recurrent or refractory pouchitis. Gut 2004, 53, 108–114.
- Gionchetti, P.; Rizzello, F.; Venturi, A.; Brigidi, P.; Matteuzzi, D.; Bazzocchi, G.; Poggioli, G.; Miglioli, M.; Campieri, M. Oral bacteriotherapy as maintenance treatment in patients with chronic pouchitis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 305–309. [CrossRef]
- Blanchetière, A.; Dolladille, C.; Goyer, I.; Join-Lambert, O.; Fazilleau, L. State of the Art of Probiotic Use in Neonatal Intensive Care Units in French-Speaking European Countries. Children 2023, 10. [CrossRef]
- Hempel, S.; Newberry, S.; Ruelaz, A.; Wang, Z.; Miles, J.N.V.; Suttorp, M.J.; Johnsen, B.; Shanman, R.; Slusser, W.; Fu, N.; et al. Safety of probiotics used to reduce risk and prevent or treat disease. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep) 2011, 1–645.
- Zhao, F.; Bai, X.; Zhang, J.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Shen, L.; Jin, H.; Sun, T.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Gut Bifidobacterium responses to probiotic Lactobacillus casei Zhang administration vary between subjects from different geographic regions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 2665–2675. [CrossRef]
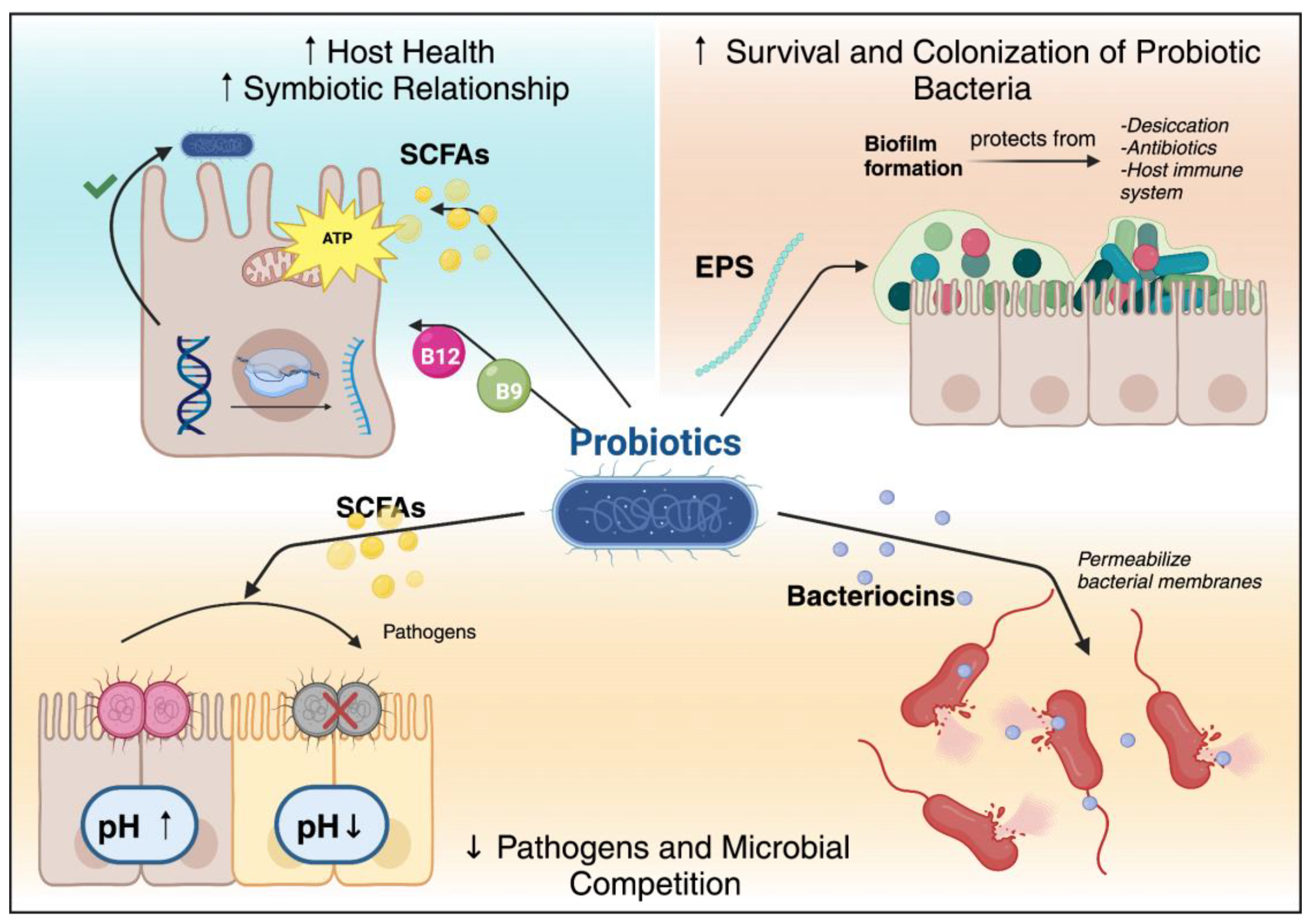
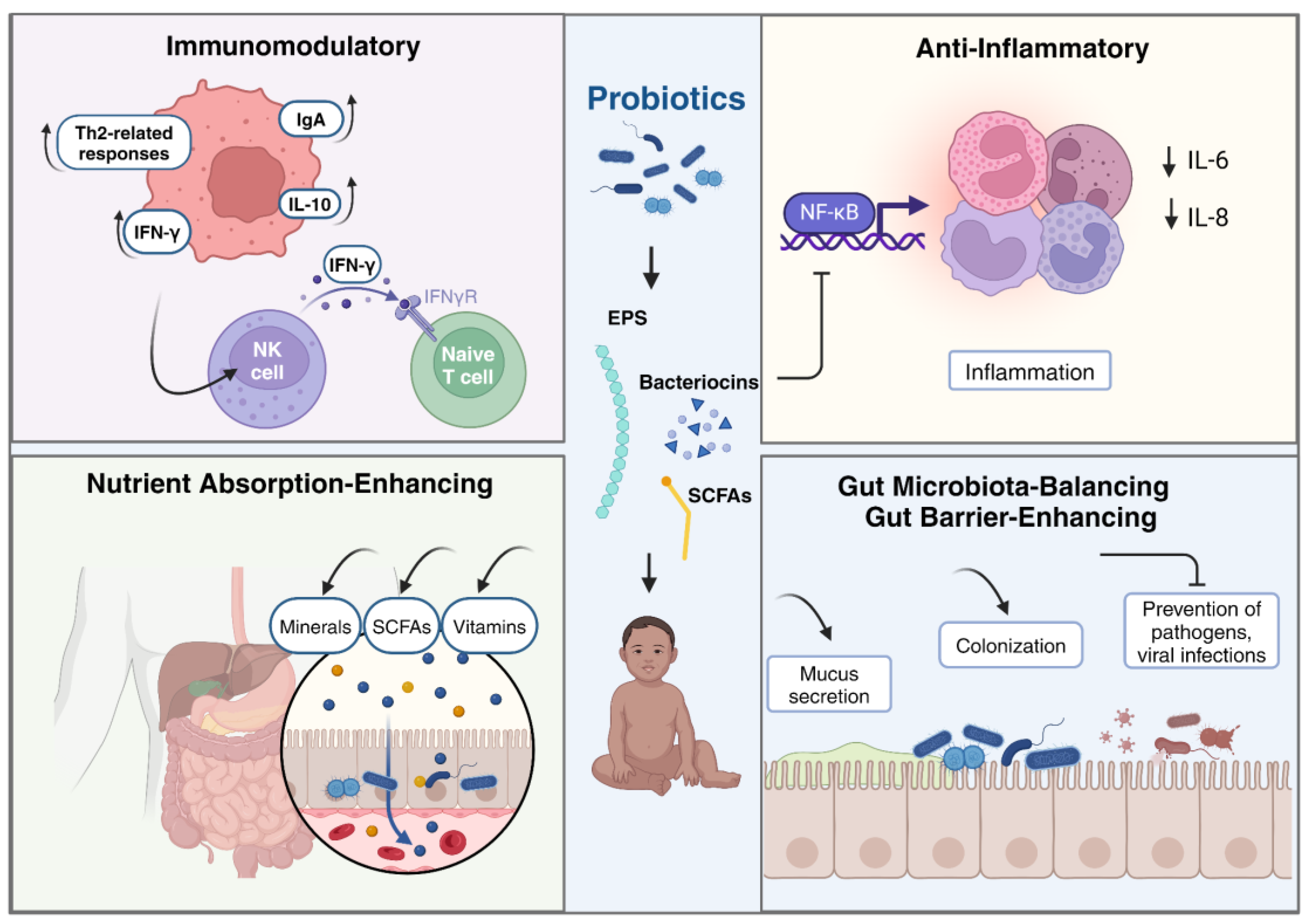
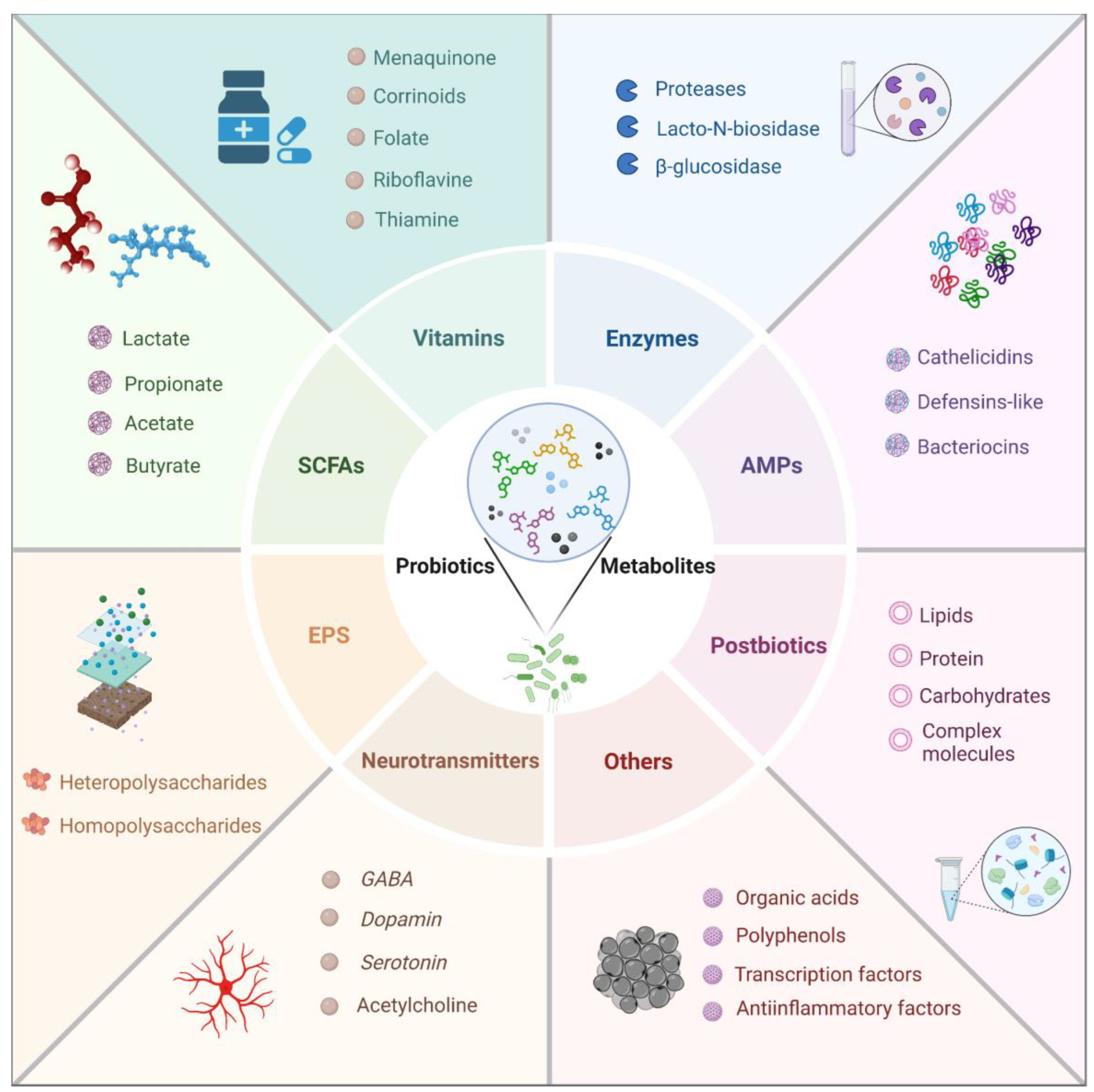
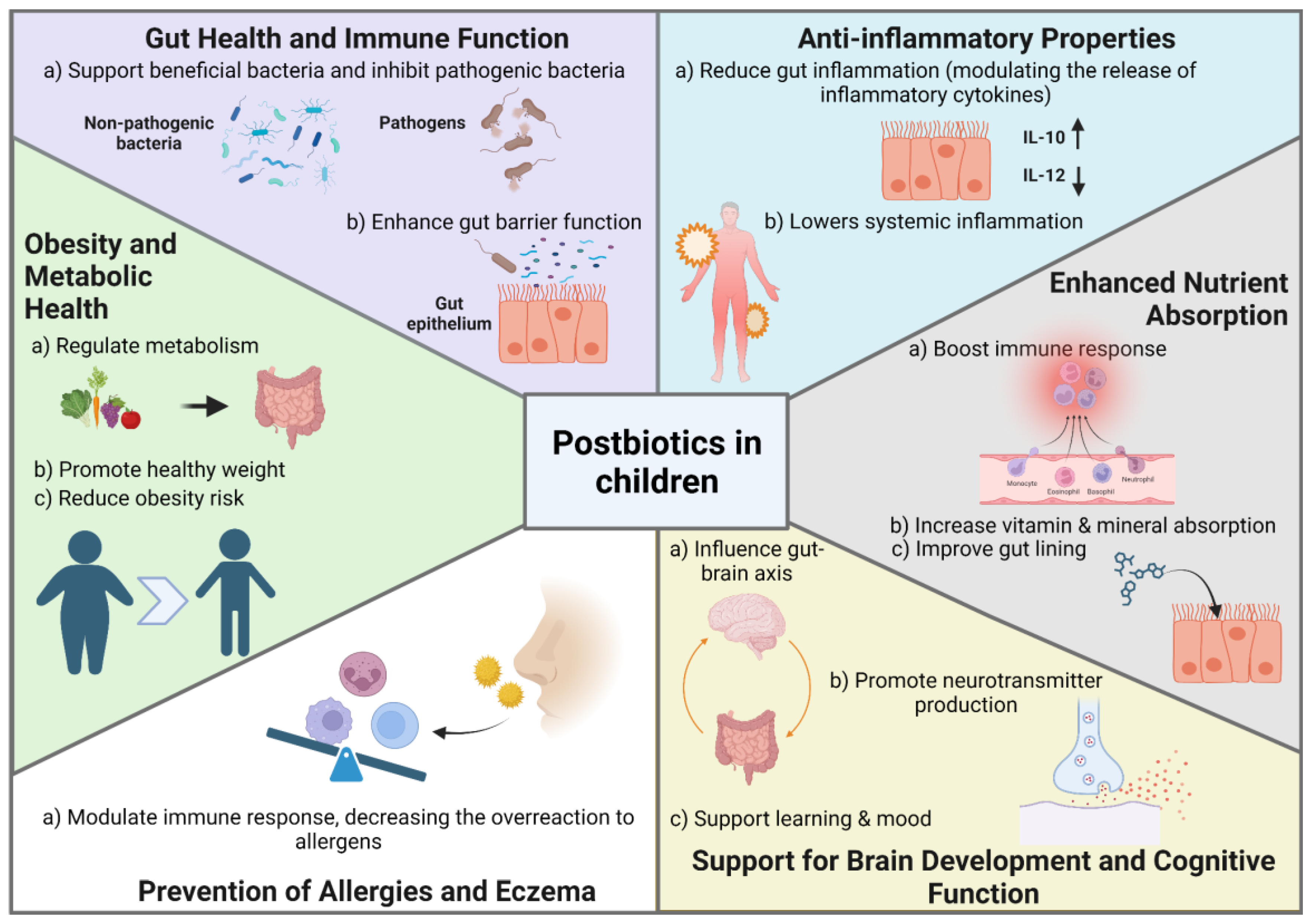
| Probiotic Strain | Vitamin Produced | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus fermentum [126] | Folate (B9), Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Synthesis of folate and B12 |
| Lactobacillus reuteri (DCM 20016, JCM1112, CRL1324, CRL1327) [31] | Corrinoids (related to Vitamin B12) | Production of corrinoids. |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus (ATCC314, FTDC 8833) [125] | Riboflavin (B2) | Enhance riboflavin production |
| Streptococcus thermophilus (ABM5097) [15] | 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) (Folate) | Increase folate production. |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG [31] | Folate (B9), Riboflavin (B2), Thiamine (B1) | Production and releases folate and riboflavin efficiently; low production of intracellular thiamine. |
| Bacillus clausii [135] | Vitamin K2 (Menaquinone) | Production of vitamin K2 |
| Lactococcus lactis [136] | Vitamin K2 (Menaquinone) | Production of vitamin K2 |
| Enterobacter agglomerans, Serratia marcescens, Enterococcus faecium [137] | Menaquinones (Vitamin K2) | Contribute to vitamin K production in the neonatal gut. |
| Various strains (Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium) [127] | B Vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12), Vitamin K | Utilize oligosaccharides to enhance hydrophobicity, auto-aggregation, and biofilm formation, improving B vitamin production. |
| Lactobacillus gasseri (FTDC 8131) [139] | Riboflavin (B2) | Interacts with riboflavin; context suggests strain-dependent variability in production or consumption of the vitamin. |
| Bifidobacterium strains (B. longum, B. bifidum) [31] | Thiamine (B1) | Low but significant production of intracellular thiamine without extracellular synthesis; do not produce folates or riboflavin. |
| Children consuming probiotics [102] | Vitamin D, Vitamin A | Probiotics enhance absorption and serum concentrations of vitamins. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





