Submitted:
02 October 2024
Posted:
02 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goddard, M.A.; Dougill, A.J.; Benton, T.G. Scaling up from gardens: Biodiversity conservation in urban environments. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 2010, 25, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ye, W. Landscape design of garden plants based on green and low-carbon energy under the background of big data. Energy Reports 2022, 8, 13399–13408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basey, A.C.; Fant, J.B.; Kramer, A.T. Producing native plant materials for restoration: 10 rules to collect and maintain genetic diversity. Native Plants Journal 2015, 16, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruckeberg, A.R.; Chalker-Scott, L. Gardening with Native Plants of the Pacific Northwest, 3rd ed.; University of Washington Press, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mareri, L.; Parrotta, L.; Cai, G. Environmental Stress and Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Reynolds, M.; Xu, Y. Climate change challenges plant breeding. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2022, 70, 102308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Ranjan, R. Grasses as an Immense Source of Pharmacologically Active Medicinal Properties: An Overview. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy, 2020; pp. 1323–1329.
- Souza, F.H.D.d.; Gusmão, M.R.; Cavallari, M.M.; Barioni Jr, W. Characterization of the potential of native grasses for use as lawns. Ornamental Horticulture 2020, 26, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunster, K. Beyond Turf and Lawn: Poaceae in This Age of Climate Change. In Grasses-Benefits, Diversities and Functional Roles; Almusaed, A., Al-Samaraee, S.M.S., Eds.; IntechOpen, 2017; pp. 87–118. [Google Scholar]
- Aitken, K.S.; McNeil, M.D.; Berkman, P.J.; Hermann, S.; Kilian, A.; Bundock, P.C.; Li, J. Comparative mapping in the Poaceae family reveals translocations in the complex polyploid genome of sugarcane. BMC Plant Biology 2014, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Satya, P.; Sharma, L.; Roy, S.; Bera, A.; Santra, S.; Ghosh, S. Model Plants in Genomics. In Plant Genomics for Sustainable Agriculture; Singh, R.L., Mondal, S., Parihar, A., Singh, P.K., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022; pp. 241–264. [Google Scholar]
- Gaut, B.S. Evolutionary dynamics of grass genomes. New Phytologist 2002, 154, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, O.; Blatt, M.R.; Cammarano, A.; Zare-Behtash, H.; Busse, A. A new perspective on mechanical characterisation of Arabidopsis stems through vibration tests. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials 2020, 112, 104041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinke, D.W.; Cherry, J.M.; Dean, C.; Rounsley, S.D.; Koornneef, M. Arabidopsis thaliana: A Model Plant for Genome Analysis. Science 1998, 282, 662–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, E.A. Evolutionary History of the Grasses. Plant Physiology 2001, 125, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raissig, M.T.; Woods, D.P. Chapter Two - The wild grass Brachypodium distachyon as a developmental model system. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Goldstein, B., Srivastava, M., Eds.; Academic Press, 2022; Volume 147, pp. 33–71. [Google Scholar]
- Scholthof, K.-B.G.; Irigoyen, S.; Catalan, P.; Mandadi, K.K. Brachypodium: A Monocot Grass Model Genus for Plant Biology. The Plant Cell 2018, 30, 1673–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brutnell, T.P.; Bennetzen, J.L.; Vogel, J.P. Brachypodium distachyon and Setaria viridis: Model Genetic Systems for the Grasses. Annual Review of Plant Biology 2015, 66, 465–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinwand, M.A.; Young, H.A.; Bragg, J.N.; Tobias, C.M.; Vogel, J.P. Brachypodium sylvaticum, a Model for Perennial Grasses: Transformation and Inbred Line Development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brutnell, T.P.; Wang, L.; Swartwood, K.; Goldschmidt, A.; Jackson, D.; Zhu, X.-G.; Kellogg, E.; Van Eck, J. Setaria viridis: A Model for C4 Photosynthesis. The Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.-w.; Inoue, M.; Yuyama, N.; Takahashi, W.; Hirata, M.; Sasaki, T. Isolation, characterization and mapping of simple sequence repeat markers in zoysiagrass (Zoysia spp.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics 2005, 112, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-J.; Song, I.-J.; Bae, T.-W.; Lee, H.-Y. Recent developments in biotechnological improvement of Zoysia japonica Steud. Journal of Plant Biotechnology 2010, 37, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Hirakawa, H.; Kosugi, S.; Nakayama, S.; Ono, A.; Watanabe, A.; Hashiguchi, M.; Gondo, T.; Ishigaki, G.; Muguerza, M. Sequencing and comparative analyses of the genomes of zoysiagrasses. DNA Research 2016, 23, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muguerza, M.B.; Gondo, T.; Ishigaki, G.; Shimamoto, Y.; Umami, N.; Nitthaisong, P.; Rahman, M.M.; Akashi, R. Tissue Culture and Somatic Embryogenesis in Warm-Season Grasses—Current Status and Its Applications: A Review. Plants 2022, 11, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-H.; Jeong, O.-C.; Sun, H.-J.; Kang, H.-G.; Lee, H.-Y. Genome analysis of Zoysia japonica ‘Yaji’ cultivar using PacBio long-read sequencing. Plant Biotechnology Reports 2023, 17, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baenziger, P.S. Plant breeding training in the US. HortScience 2006, 41, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaškin, J.; Tomaškinová, J.; Kizeková, M. Ornamental grasses as part of public green, their ecosystem services and use in vegetative arrangements in urban environment. Thaiszia. J Bot Košice 2015, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pamukcu-Albers, P.; Ugolini, F.; La Rosa, D.; Grădinaru, S.R.; Azevedo, J.C.; Wu, J. Building green infrastructure to enhance urban resilience to climate change and pandemics. Landscape Ecology 2021, 36, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfand, G.E.; Park, J.S.; Nassauer, J.I.; Kosek, S. The economics of native plants in residential landscape designs. Landscape and Urban Planning 2006, 78, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, A.J.; Swim, J.K. Adding native plants to home landscapes: The roles of attitudes, social norms, and situational strength. Journal of Environmental Psychology 2020, 72, 101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribaut, J.-M.; de Vicente, M.; Delannay, X. Molecular breeding in developing countries: Challenges and perspectives. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2010, 13, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersey, P.J. Plant genome sequences: Past, present, future. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2019, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, E.L.; Auger, H.; Jaszczyszyn, Y.; Thermes, C. Ten years of next-generation sequencing technology. Trends in Genetics 2014, 30, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.S.; Green, R.E. New Approaches for Genome Assembly and Scaffolding. Annual Review of Animal Biosciences 2019, 7, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y. Constraints in Using Wild Relatives in Breeding: Lack of Basic Knowledge on Crop Gene Pools. In International Crop Science I; 1993; pp. 437–443.
- Cesarino, I.; Dello Ioio, R.; Kirschner, G.K.; Ogden, M.S.; Picard, K.L.; Rast-Somssich, M.I.; Somssich, M. Plant science’s next top models. Annals of Botany 2020, 126, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, J.; Mur, L.A.; Jenkins, G.; Ghosh-Biswas, G.C.; Bablak, P.; Hasterok, R.; Routledge, A.P. Brachypodium distachyon. A New Model System for Functional Genomics in Grasses. Plant Physiology 2001, 127, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osada, T. Nihon kika shokubutsu zukan: Illustrated Japanese alien plants; Hokuryukan: Japan, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, T.; Ohashi, H.; Murata, J.; Iwatsuki, K. Shin Makino Nihon shokubutsu zukan: New Makino’s Illustrated Flora of Japan; Hokuryukan: Japan, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, W.B.; Lee, M.B.; Kim, D.Y.; Hong, M.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, Y.W. Efficient Phosphinothricin Mediated Selection of Callus Derived from Brachypodium Mature Seed. Korean Journal of Breeding Science 2010, 42, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Seo, P.J.; Yang, M.-S.; Xiang, F.; Park, C.-M. Exploring valid reference genes for gene expression studies in Brachypodium distachyon by real-time PCR. BMC Plant Biology 2008, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, B.F.; Bertrand, A.; Charron, J.-B. Treatment Analogous to Seasonal Change Demonstrates the Integration of Cold Responses in Brachypodium distachyon. Plant Physiology 2020, 182, 1022–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, A.; Kodera, S.; Suzuki, K.; Nemoto, M.; Egawa, R.; Takizawa, H.; Hirata, A. Estimation of the number of heat illness patients in eight metropolitan prefectures of Japan: Correlation with ambient temperature and computed thermophysiological responses. Frontiers in Public Health 2023, 11, 1061135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lim, J.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; Won, M. Ground-Based NDVI Network: Early Validation Practice with Sentinel-2 in South Korea. Sensors 2024, 24, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.-K.; Shin, Y.; Baek, H.-J.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.-I.; Seok, M.; Oh, Y.; Park, D. Establishment potential across South Korea for two gecko species, Gekko japonicus and G. swinhonis, adapted to different climates. NeoBiota 2024, 93, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.T. Plant geographical study for the plant of Cheju. Korean Journal of Plant Taxonomy 1992, 22, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan, P.; López-Álvarez, D.; Díaz-Pérez, A.; Sancho, R.; López-Herránz, M.L. Phylogeny and Evolution of the Genus Brachypodium. Genetics and Genomics of Brachypodium 2016, 9–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felber, F.; Kozlowski, G.; Arrigo, N.; Guadagnuolo, R. Genetic and Ecological Consequences of Transgene Flow to the Wild Flora. In Green Gene Technology: Research in an Area of Social Conflict; Fiechter, A., Sautter, C., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2007; pp. 173–205. [Google Scholar]
- The_International_Brachypodium_Initiative. Genome sequencing and analysis of the model grass Brachypodium distachyon. Nature 2010, 463, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Gordon, S.P.; Liu, L.; Sade, N.; Lovell, J.T.; Rubio Wilhelmi, M.D.M.; Singan, V.; Sreedasyam, A.; Hestrin, R.; Phillips, J. The reference genome and abiotic stress responses of the model perennial grass Brachypodium sylvaticum. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics 2024, 14, jkad245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J. The Current State and Characteristics of Ornamental Grasses in South Korea. Journal of the Korean Institute of Landscape Architecture 2021, 49, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, L.E.; Hoveland, C.S. Cool-Season Grass Overview. In Cool-Season Forage Grasses; 1996; pp. 1–14.
- Phillips, A.R.; Seetharam, A.S.; Albert, P.S.; AuBuchon-Elder, T.; Birchler, J.A.; Buckler, E.S.; Gillespie, L.J.; Hufford, M.B.; Llaca, V.; Romay, M.C. A happy accident: A novel turfgrass reference genome. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics 2023, 13, jkad073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, D.; Veekman, E.; Grogg, D.; Stoffel-Studer, I.; Morishima, A.; Shimizu-Inatsugi, R.; Yates, S.; Shimizu, K.K.; Frey, J.E.; Studer, B.; et al. Ultralong Oxford Nanopore Reads Enable the Development of a Reference-Grade Perennial Ryegrass Genome Assembly. Genome Biology and Evolution 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Brutnell, T.P. Setaria viridis and Setaria italica, model genetic systems for the Panicoid grasses. Journal of Experimental Botany 2011, 62, 3031–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, S.; Healey, A.; Huang, P.; Grimwood, J.; Jenkins, J.; Barry, K.; Sreedasyam, A.; Shu, S.; Lovell, J.T.; Feldman, M. A genome resource for green millet Setaria viridis enables discovery of agronomically valuable loci. Nature Biotechnology 2020, 38, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielen, P.M.; Pendleton, A.L.; Player, R.A.; Bowden, K.V.; Lawton, T.J.; Wisecaver, J.H. Reference Genome for the Highly Transformable Setaria viridis ME034V. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics 2020, 10, 3467–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.K.; Nakayama, T.J.; Ribeiro, A.P.; da Cunha, B.A.D.B.; Nepomuceno, A.L.; Harmon, F.G.; Kobayashi, A.K.; Molinari, H.B.C. Setaria viridis floral-dip: A simple and rapid Agrobacterium-mediated transformation method. Biotechnology Reports 2015, 6, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, T.; Wang, C.; Kang, X.; Zhao, H.; Elena Gamo, M.; Starker, C.G.; Crisp, P.A.; Zhou, P.; Springer, N.M.; Voytas, D.F. Optimization of multiplexed CRISPR/Cas9 system for highly efficient genome editing in Setaria viridis. The Plant Journal 2020, 104, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.M.; Mattoon, E.M.; Zhang, N.; Becker, E.; McHargue, W.; Yang, J.; Patel, D.; Dautermann, O.; McAdam, S.A.; Tarin, T. High light and temperature reduce photosynthetic efficiency through different mechanisms in the C4 model Setaria viridis. Communications Biology 2021, 4, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danila, F.R.; Thakur, V.; Chatterjee, J.; Bala, S.; Coe, R.A.; Acebron, K.; Furbank, R.T.; von Caemmerer, S.; Quick, W.P. Bundle sheath suberisation is required for C4 photosynthesis in a Setaria viridis mutant. Communications Biology 2021, 4, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, I.K.; Yun, H.K.; Lee, S.M.; Jung, Y.B.; Lee, M.R. Composition and Utilization of Urban Garden Space Using the Planting System Design Process. Journal of People, Plants, and Environment 2020, 23, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, D.; Moretti, M. A comprehensive dataset on cultivated and spontaneously growing vascular plants in urban gardens. Data in Brief 2019, 25, 103982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Maximino, J.V.; Machado, M.A.S.; Mittelmann, A.; da Cunha Pinheiro, E.; da Silva Pires, E.; Longaray, M.B.; de Souza, F.H.D.; Stumpf, E.R.T. Potential of grass seed production for new lawns. Ornamental Horticulture 2017, 23, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Quan, Z.; Cheng, S.; Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Xie, M.; Zeng, P.; Yue, Z.; Wang, W. Genome sequence of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) provides insights into grass evolution and biofuel potential. Nature Biotechnology 2012, 30, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, A.; Miao, F.; Cong, L.; Song, H.; Yin, X. High-quality chromosome-scale de novo assembly of the Paspalum notatum ‘Flugge’ genome. BMC Genomics 2022, 23, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doust, A.N.; Kellogg, E.A.; Devos, K.M.; Bennetzen, J.L. Foxtail millet: A Sequence-Driven Grass Model System. Plant Physiology 2009, 149, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loch, D.S.; Ebina, M.; Choi, J.S.; Han, L. Ecological Implications of Zoysia Species, Distribution, and Adaptation for Management and Use of Zoysiagrasses. International Turfgrass Society Research Journal 2017, 13, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, S.-i.; Kobayashi, M.; Ebina, M. Zoysia. In Wild Crop Relatives: Genomic and Breeding Resources: Millets and Grasses, Kole, C., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011; pp. 297–309. [Google Scholar]
- Magni, S.; Pompeiano, A.; Gaetani, M.; Caturegli, L.; Grossi, N.; Minelli, A.; Volterrani, M. Zoysiagrass (Zoysia spp. Willd.) for European lawns: A review. Italian Journal of Agronomy 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavell, R. Role of Model Plant Species. In Plant Genomics: Methods and Protocols; Gustafson, J.P., Langridge, P., Somers, D.J., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2009; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Antonielli, M.; Pasqualini, S.; Batini, P.; Ederli, L.; Massacci, A.; Loreto, F. Physiological and anatomical characterisation of Phragmites australis leaves. Aquatic Botany 2002, 72, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, X.; Yu, D.; Liu, G.; Luo, L. Anatomical Characteristics of C4 and C3 Photosynthetic-pathway Poaceae Plants in Hainan. Chinese Bulletin of Botany 2011, 46, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Okamoto, K.; Hori, Y. Differences in Field Gas Exchange and Water Relations Between a C3 Dicot (Plantago Asiatica) and a C4 Monocot (Eleusine Indica). Photosynthetica 1999, 37, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo-Silva, A.E.; Soares, A.S.; Marques da Silva, J.; Bernardes da Silva, A.; Keys, A.J.; Arrabaça, M.C. Photosynthetic responses of three C4 grasses of different metabolic subtypes to water deficit. Functional Plant Biology 2007, 34, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, S.; Lewis, J. Occurrence of C3 and C4 Photosynthetic Pathways in North American Grasses. Journal of Range Management 1979, 32, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covshoff, S.; Szecowka, M.; Hughes, T.E.; Smith-Unna, R.; Kelly, S.; Bailey, K.J.; Sage, T.L.; Pachebat, J.A.; Leegood, R.; Hibberd, J.M. C4 Photosynthesis in the Rice Paddy: Insights from the Noxious Weed Echinochloa glabrescens. Plant Physiology 2015, 170, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barden, L.S. Invasion of Microstegium vimineum (Poaceae), An Exotic, Annual, Shade-Tolerant, C4 Grass, into a North Carolina Floodplain. The American Midland Naturalist 1987, 118, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, R.J.; Liddicoat, C.; Cando-Dumancela, C.; Fickling, N.W.; Peddle, S.D.; Ramesh, S.; Breed, M.F. Increasing aridity strengthens the core bacterial rhizosphere associations in the pan-palaeotropical C4 grass, Themeda triandra. Applied Soil Ecology 2024, 201, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, H.A.; Ryan, G.D.; Kovacs, H.M.; Newman, J.A. Effects of elevated CO2 on photosynthetic traits of native and invasive C3 and C4 grasses. BMC Ecology 2016, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianconi, M.E.; Hackel, J.; Vorontsova, M.S.; Alberti, A.; Arthan, W.; Burke, S.V.; Duvall, M.R.; Kellogg, E.A.; Lavergne, S.; McKain, M.R.; et al. Continued Adaptation of C4 Photosynthesis After an Initial Burst of Changes in the Andropogoneae Grasses. Systematic Biology 2019, 69, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.B. Origin, Biogeographical Migrations and Diversifications of Turfgrasses; Michigan State University Press: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast, H.D.V.; Hattersley, P.W.; Stone, N.E.; Lazarides, M. C4 acid decarboxylation type in Eragrostis (Poaceae) patterns of variation in chloroplast position, ultrastructure and geographical distribution. Plant, Cell & Environment 1986, 9, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvel, B.; Munier-Jolain, N.; Letouzé, A.; Grandgirard, D. Developmental patterns of leaves and tillers in a black-grass population (Alopecurus myosuroides Huds.). Agronomie 2000, 20, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamesch, P.; Berardini, T.Z.; Li, D.; Swarbreck, D.; Wilks, C.; Sasidharan, R.; Muller, R.; Dreher, K.; Alexander, D.L.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.; et al. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): Improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Research 2011, 40, D1202–D1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.-Y.; Krishnakumar, V.; Chan, A.P.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Schobel, S.; Town, C.D. Araport11: A complete reannotation of the Arabidopsis thaliana reference genome. The Plant Journal 2017, 89, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
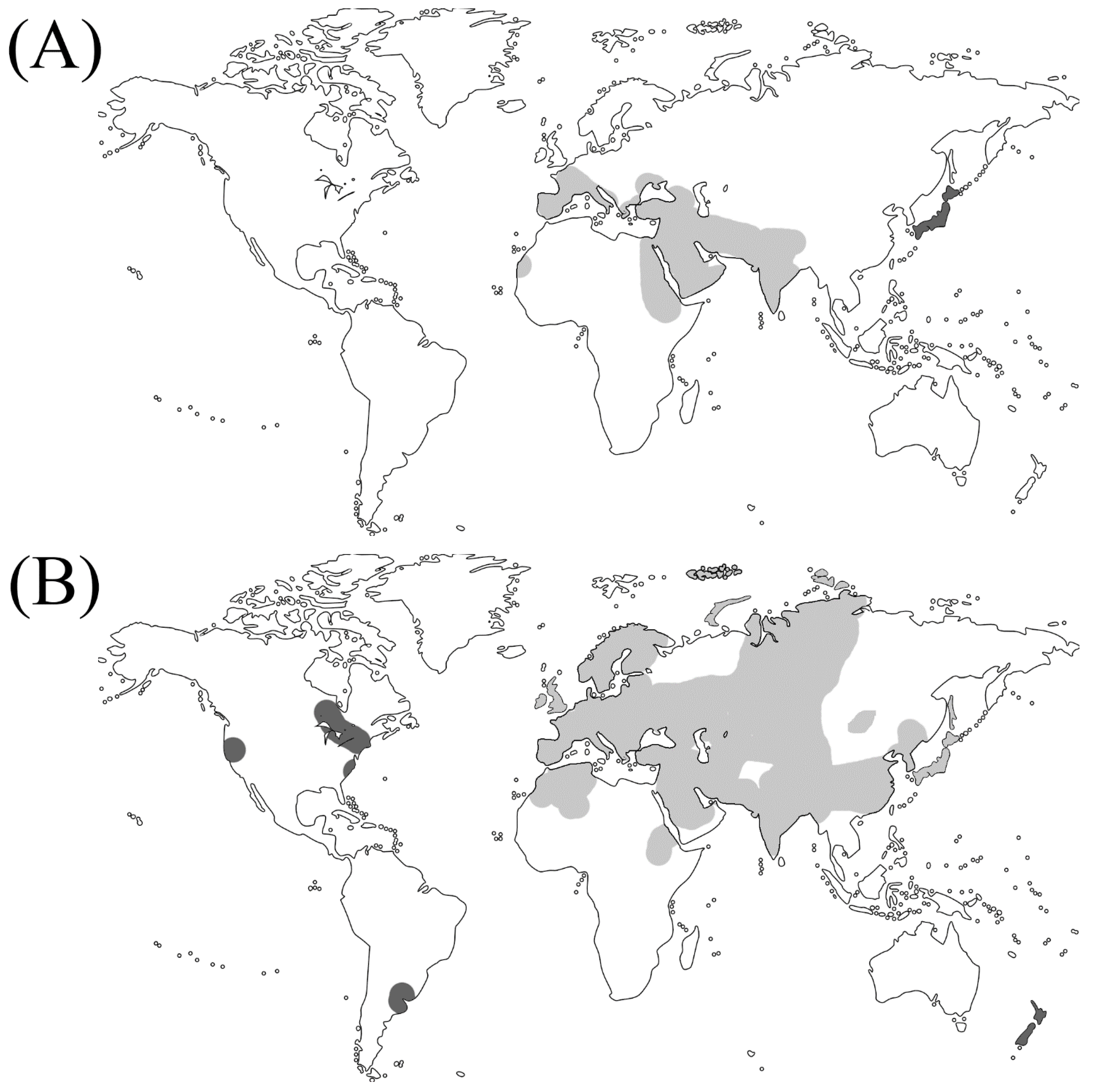
| Plant category | Subfamily | Scientific name | Genome size (Mbps) | Life cyclez | Photosynthetic Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native | Arundinoideae | Phragmites australis | 1,200 | P | C3 [72] |
| Native | Chloridoideae | Leptochloa chinensis | 460 | A | C4 [73] |
| Native | Chloridoideae | Eleusine indica | 590 | A | C4 [74] |
| Native | Chloridoideae | Cynodon dactylon | 1,020 | P | C4 [75] |
| Native | Chloridoideae | Zoysia japonica | 390 | P | C4 [75] |
| Native | Oryzoideae | Zizania latifolia | 1,800 | P | C3 [73] |
| Native | Panicoideae | Setaria viridis | 400 | A | C4 [76] |
| Native | Panicoideae | Echinochloa oryzoides | 1,000 | A | C4 [77] |
| Native | Panicoideae | Microstegium vimineum | 1,300 | A | C4 [78] |
| Native | Panicoideae | Echinochloa crus-galli | 1,400 | A | C4 [77] |
| Native | Panicoideae | Themeda triandra | 840 | P | C4 [79] |
| Native | Panicoideae | Miscanthus sinensis | 2,500 | P | C4 [73] |
| Native | Pooideae | Poa annua | 1,800 | A | C3 [76] |
| Native | Pooideae | Brachypodium sylvaticum | 360 | P | C3 [80] |
| Cultivated | Bambusoideae | Phyllostachys edulis | 2,080 | P | C3 [81] |
| Cultivated | Chloridoideae | Zoysia matrella | 380 | P | C4 [82] |
| Cultivated | Chloridoideae | Zoysia pacifica | 370 | P | C4 [82] |
| Cultivated | Oryzoideae | Oryza sativa | 430 | A | C3 [76] |
| Cultivated | Panicoideae | Panicum miliaceum | 920 | A | C4 [76] |
| Cultivated | Panicoideae | Sorghum bicolor | 820 | A | C4 [76] |
| Cultivated | Panicoideae | Coix lacryma-jobi | 1,560 | A | C4 [76] |
| Cultivated | Panicoideae | Zea mays | 2,300 | A | C4 [76] |
| Cultivated | Panicoideae | Setaria italica | 490 | A | C4 [76] |
| Cultivated | Pooideae | Avena sativa | 4,000 | A | C3 [76] |
| Cultivated | Pooideae | Triticum aestivum | 17,000 | A | C3 [76] |
| Cultivated | Pooideae | Hordeum vulgare | 5,100 | A | C3 [76] |
| Exotic | Chloridoideae | Eragrostis curvula | 660 | P | C4 [83] |
| Exotic | Panicoideae | Saccharum spontaneum | 3,360 | P | C4 [76] |
| Exotic | Panicoideae | Paspalum notatum | 550 | P | C4 [76] |
| Exotic | Panicoideae | Eremochloa ophiuroides | 800 | P | C4 [76] |
| Exotic | Panicoideae | Panicum virgatum | 1,200 | P | C4 [76] |
| Exotic | Pooideae | Lolium rigidum | 2,400 | A | C3 [76] |
| Exotic | Pooideae | Poa pratensis | 3,500 | P | C3 [76] |
| Exotic | Pooideae | Alopecurus myosuroides | 3,500 | A | C3 [84] |
| Exotic | Pooideae | Lolium multiflorum | 600 | A | C3 [76] |
| Exotic | Pooideae | Poa trivialis | 1,350 | P | C3 [76] |
| Exotic | Pooideae | Bromus tectorum | 2,500 | A | C3 [76] |
| Exotic | Pooideae | Lolium perenne | 2,000 | P | C3 [76] |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | Brachypodium distachyon | Brachypodium sylvaticum |
Setaria viridis |
Zoysia japonica | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common name | mouseear cress |
purple false brome | slender false brome | green bristlegrass | Korean lawngrass |
| Cotyledon | Eudicots | Monocots | Monocots | Monocots | Monocots |
| Order | Brassicales | Poales | Poales | Poales | Poales |
| Family | Brassicaceae | Poaceae | Poaceae | Poaceae | Poaceae |
| Tribe | Camelineae | Brachypodieae | Brachypodieae | Paniceae | Zoysieae |
| Genus | Arabidopsis | Brachypodium | Brachypodium | Setaria | Zoysia |
| Life cycle | Annual | Annual | Perennial | Annual | Perennial |
| Photosynthetic type | C3 | C3 | C3 | C4 | C4 |
| Chromosome number | 2n = 2x = 10 | 2n = 2x = 10 | 2n = 2x = 18 | 2n = 2x = 18 | 2n = 4x = 40 |
| Native in Korea | Y | N | Y | Y | Y |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | Brachypodium distachyon | Brachypodium sylvaticum | Setaria viridis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genomeversion | TAIR10 | Araport11 | v2.1 | v3.2 | v1.1 | v2.1 | v2.1 | v4.1 |
| Source | TAIR | TAIR | JGI | JGI | JGI | JGI | JGI | JGI |
| Accession | Col-0 | Col-0 | Bd21 | Bd21 | Ain-1 | Ain-1 | A10.1 | A10 |
| Assembled genome size | 119,667,750 | 119,667,750 | 271,997,306 | 271,163,419 | 358,283,154 | 360,731,464 | 395,731,502 | 397,277,387 |
| No. ofcontigs | 169 | 169 | 485 | 34 | 1,117 | 14 | 75 | 39 |
| Protein-codingtranscripts | 35,386 | 48,456 | 42,868 | 56,847 | 50,263 | 54,423 | 52,459 | 50,526 |
| Protein-codinggenes | 27,416 | 27,655 | 31,694 | 32,439 | 36,927 | 31,643 | 38,334 | 29,807 |
| Reference publication | Lamesch et al. [85] | Cheng et al. [86] | Lei et al. [50] | Mamidi et al. [56] | ||||
| Zoysia japonica | Zoysia matrella | Zoysia pacifica | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession | Yaji | Nagirizaki | Wakaba | Zanpa |
| Estimated genome size | 421 Mbps | 390 Mbps | 380 Mbps | 370 Mbps |
| Genome version | unknown | ZJN_r1.1 | ZMW_r1.0 | ZPZ_r1.0 |
| Source | unreleased | Zoysia Genome Database | Zoysia Genome Database | Zoysia Genome Database |
| Number of sequences | 1,350 | 11,786 | 13,609 | 11,428 |
| Total length | 373,429,196 | 334,384,427 | 563,438,595 | 397,009,957 |
| Average length | 276,614 | 28,371 | 41,402 | 34,740 |
| Max. length | 17,601,860 | 8,501,895 | 1,041,506 | 1,506,652 |
| Min. length | unknown | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| N50 length | 3,962,554 | 2,370,062 | 108,897 | 111,449 |
| Number of predicted genes | 50,140 | 59,271 | 95,079 | 65,252 |
| Reference publication | Yang et al. [25] | Tanaka et al. [23] | Tanaka et al. [23] | Tanaka et al. [23] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





