1. Introduction
Ultrasonic additive manufacturing (UAM) is a solid-state 3D printing process based on continuous ultrasonic metal welding. The system can typically draw up to around 9 kW for welding and is capable of welding a wide range of materials combinations: from soft metals like 3000 series aluminum [
1], higher strength materials such as 6000 series aluminum [
2], steel [
3,
4], and titanium [
5], and even embed temperature-sensitive materials such as PVDF due to the low formation temperatures in UAM [
6]. The welding or additive stage of the process works by bringing a tool piece called the welder, sonotrode, or horn into contact with a metallic foil under a controlled pressure. The sonotrode is actuated at a nominal resonance frequency of 20 kHz connected using a waveguide to piezoelectric transducers that work in a push-pull configuration [
7,
8]. The sonotrode scrubs the metallic foil against pre-deposited metal foils or a baseplate metal beneath. Parameters controlled during welding include normal force (weld force), amplitude setpoint of oscillation (weld amplitude), preheat temperature, and speed of rolling (weld speed). Bond formation in UAM occurs as follows: the applied pressure from the welder collapses the asperities of the two foils being welded; the applied ultrasonic vibrations and the resulting severe plastic deformation assist in plastic flow of the foil material as well as the dispersal of oxides and contaminants; this enables nascent metal contact and welding.
A detailed understanding of how the strength of UAM joints is affected by the different process parameters and operating conditions is not well understood. The different energies involved and their relative importance to the strength of the weld are also not well understood [
9]. The energy stored in the weld interface microstructure has been shown to quantified and the trends with process parameters such as weld amplitude and weld speed studied in [
10]. The energy of plastic deformation is also found to be an key driver for bond formation and an analytical expression for the relationship between weld strength and this energy was developed in [
11].
On the other hand, the energy required to collapse asperities and enable nascent metal contact has not been quantified in detail. In this work, an upper bound for this anergy is developed analytically. The contribution of this energy to weld strength can help understand if pre-weld surface treatments can improve the strength of welds in UAM. In other metal-metal joining processes such as adhesive bonding, resistance welding, and roll bonding, physical or chemical preparation such as wire brushing or chemical etching of the surface is crucial to obtain a good bond quality [
12] while this is usually not the case for UAM. The work in [
13] shows that for the UAM of Al 3003 to copper, changing the roughness of the copper foil from 0.17 to 1.17 μm does not produce a statistically significant increase in mechanical strength measured using a push-pin test and only a small increase in energy of failure for samples with higher roughness. This work expands on this study by quantifying the contribution of the energy required to collapse asperities and studying the impact of pre-weld foil surface roughness on weld strength.
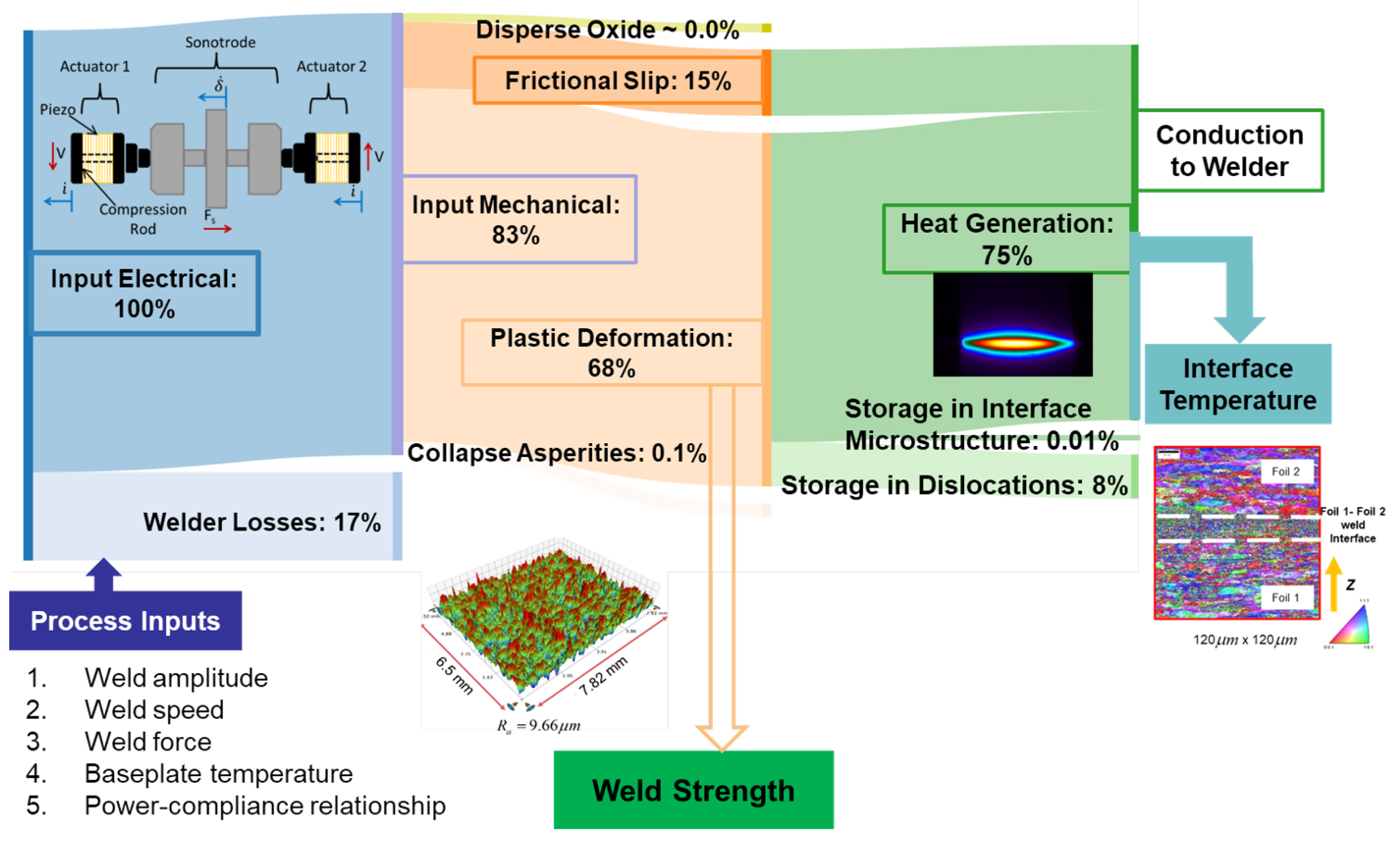
In summary, in this work, the different participating energies in UAM are quantified by developing an energy flow diagram, and their correlation to weld strength is investigated as well as their relationship to process inputs such as the vibration amplitude of the welder or weld amplitude, traversal speed of the rolling welder or weld speed, normal force applied or weld force, preheat applied to the baseplate, and the baseplate geometry. The effect of baseplate geometry on the input electrical and mechanical energies is detailed in [
14]. The correlations between the strength of welded joints in UAM to the different energies involved are also investigated to better understand the selection of process inputs to optimize weld strength and also optimize the UAM process by reducing the sources of lost energy such as losses in the welder and heat conduction to the welder.
2. Materials and Methods - Energy flow diagram
The relationship between the input energy and weld strength has been investigated in prior work by [
9] but detailed investigations of the participating energies and their effect on weld strength has not been studied to deduce the impact of changing different process inputs. The discussion in this manuscript applies to the welding of any metal combination using UAM but the data presented is for the commonly welded aluminum alloy Al 6061-H18. The composition of the alloy can be obtained from [
15]. The thickness of the 25.4 mm (1 inch) wide foil feedstock is 152 μm. The samples were welded using a 9 kW UAM welder onto an Al 6061-T6 baseplate, and the nominal UAM process conditions used were: 32 μm weld amplitude, 5000 N weld force, and 84.67 mm/s (200 in/min) weld speed. The participating energies in the UAM process listed in the energy flow diagram in
Figure 2 are listed below.
2.1. Welder Losses
The efficiency of the piezoelectric transducers that are part of the weld assembly are estimated to be around 80 and 85% in the work of [
16]. The energy
per unit of weld length is lost as heat in the transducer and wave guide components and quantifies the efficiency of the welder assembly in transferring the input energy per unit length,
, to the welded sample. This efficiency
e can be redefined from the expressions in [
16] in terms of
to be
where
is the traversal speed of the welder or weld speed,
is the welder vibration velocity,
is the shear force applied by the welder, and
is calculated as the ratio between the electrical power draw into the transducers and the weld speed. The welder efficiency
e defined in (2) is largely unaffected by the normal force applied by the welder and is found to decrease slightly with increasing weld amplitude in [
16].
2.2. Energy of Plastic Deformation
The energy of plastic deformation is a key driver of bond formation and bond strength in UAM. The work of [
11] details a simplified coupled thermal-mechanical model for UAM to estimate this energy per unit length of the weld,
, to be
where
is the weld speed, and the values for contact half-width
a, shear force
, welder vibration velocity
, shear stress
, and slip velocity of the foil
are estimated from the simplified analytical model of foil deformation.
This energy is used to deform the foil material, which results in energy
being stored in the foil microstructure as dislocations and remaining is dissipated as heat [
17]. It is also shown in [
18] that geometrically-necessary dislocations (GND) are the predominant type of dislocations in UAM and they determine the sub-grain diameter of the resulting microstructure. The fraction of the energy that is dissipated as heat is given by the Taylor−Quinney coefficient, is
and a typical value of 0.9 is chosen for aluminum [
19].
2.3. Frictional Energy Dissipation
The energy associated with frictional slip,
, is calculated in [
11] using the coefficient of friction
to be
where
is the normal stress in the foil material. This energy contributes to the temperature increase near the weld interface. Understanding this temperature rise is also critical to finding acceptable process parameter ranges to embed temperature-sensitive components using UAM, as detailed in [
11] where a thermal FE model was validated with in-situ infrared measurements of the process temperature.
2.4. Heat Generation
The heat generated Q in the UAM process is mainly from two sources - frictional slip and heat generation from plastic deformation. This heat generation contributes to the increase in temperature during the process. This increased temperature of the foil material can also affect the energy of plastic deformation by lowering the local yield strength.
2.5. Energy for Asperity Collapse
UAM requires the contact of nascent metal surfaces for solid-state bonding to occur successfully, which is enabled by asperity collapse and oxide layer removal [
20,
21]. The roughness of the surface needs to be studied to investigate the energy required for the collapse of asperities. The surface roughness profile of a surface can be characterized using different metrics [
22]. The most common statistical measures used are
and
[
23]. For a surface with profile
, these metrics are given by
The surface of the UAM welder is typically textured to increase the grip between the weld foil and the welder. The texture is produced using electric discharge machining (EDM) to create a roughened texture typically with an
value between 11 and 14 μm [
24]. This also imparts a rough texture on the deposited foil.
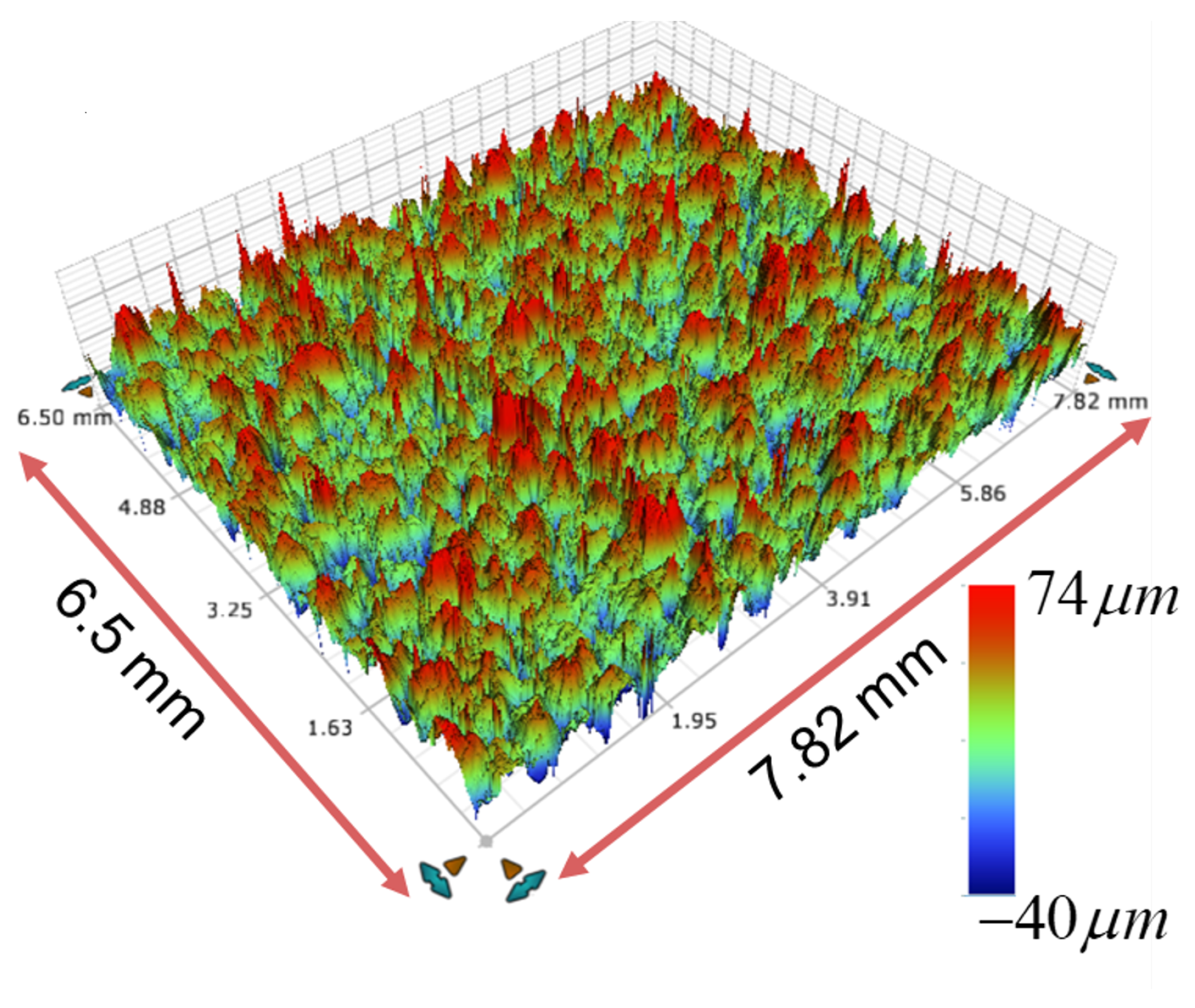
A sample textured surface of a rough weld foil is shown in
Figure 1. The data was collected using a Bruker Contour GT-K optical profilometer. To calculate the energy required to collapse the asperities, a simplified model of the asperities as cuboids is developed, with height
z and thus their total volume per unit length of weld foil can be estimated as the product of the width of the foil feedstock
w and its height
. In this case
w is 25.4 mm (1 inch). The upper bound for the energy required to collapse the asperity can be estimated using the failure energy of the bulk material and the volume of the asperities. An upper bound for the average energy required for asperity collapse,
can be estimated as follows:
where
is the shear stress at failure and
the shear strain at failure respectively for the foil feedstock material. The shear stress at failure is about 140 MPa from the work [
11], and for 6061 aluminum alloy, the shear strain at failure has a maximum value of 0.6 depending on the strain rate from the measurements in [
25]. These values are used to estimate the upper bound for the energy required to collapse the asperities.
The impact of the roughness of the foil surface on the shear strength of the resulting welded joint or weld strength was investigated in [
26]. The
values were varied from
m for a machined surface to
m for a roughened surface of the foil prepared using the welder in a process called pretexturing. The energy required to collapse the asperities for the 25.4 mm (1 inch) wide foil of Al 6061-H18 can be estimated for each case. The input energy in the different cases was observed to be unaffected by the roughness changes. An upper bound for the energy for asperity collapse can thus be estimated by (
7) to be 8 J/m for the samples with
of
m, which is about 0.06% of the input electrical energy, and
J/m for the machined sample with an
of
m. The corresponding strength of the welded joints in shear are plotted in
Figure 4.
2.6. Energy to Disperse Oxide Layer
The energy required to disperse the oxide layer was estimated in the work by [
26] using by imaging the oxide layer using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and the fracture energy of the oxide. It is shown in [
27] that cycles of mechanical deformation imparted by the welder under pressure can lead to the cracking of the the aluminum oxide layer, which can then be dispersed to enable nascent metal contact in the foil contact. The thickness of the oxide layer for Al 6061-H18 was measured using TEM to be less than 20 nm, and the energy required to disperse the oxide layer per unit length,
, is estimated to be about 4.7 mJ/m as the ratio of the power required for oxide dispersal, 0.4 mW, from [
26] and the weld speed value of 84.67 mm/s (200 in/min).
2.7. Energy Stored in the Microstructure
The energy stored in the grain boundaries is estimated in the work [
10] for samples prepared using different vibration amplitudes from 23 to 32 μm. Although it only represents a small part of the input energy from
Figure 2, it is important to understand how aspects of the weld interface microstructure such as degree of recrystallization and the volume of recrystallized grains around the weld interface are affected by process parameters. The energy stored in grain boundaries can be used as a metric to quantify these effects. Previous work on modifying the interface microstructure with heat treatments on as-welded Al 6061 showed in [
28] have shown improvements in fracture stress as a result which are a direct effect of microstructural changes such as grain growth.
Changes to the microstructure of the post-weld sample from the UAM process can be quantified using the process detailed in [
10], where EBSD images are processed using the MTEX toolbox in MATLAB to identify grain boundaries. The Read-Shockley relationship is then used to estimate the energy stored in the grain structure. The expression is given as
where
is the angle of misorientation between a boundary pixel and its neighboring pixels,
is the grain boundary energy density of aluminum (=0.324 J/m
2 [
29]), and
is the cross-section area.
3. Energy Mapping of UAM
The participating energies in the UAM process can be related using
Figure 2 with the following equation:
The interface temperature, which is a result of the different sources of heat generation, is coupled to the energy of plastic deformation through the reduction in yield strength of the foil material. The degree of coupling will depend on the type of foil used and its flow stress relationships. The effect of the different process inputs in
Figure 2 on the strength of the welded part can thus be studied from an energetic point of view using the framework developed.
4. Weld Strength Measurements in Shear
UAM samples have a thin laminated construction with subsequent layers usually welded on previous ones, and this provides a challenge for mechanical characterization. In previous work, characterization has been limited to push pin testing [
30] and peel testing [
1], which provided a means of comparing the interfacial strength of UAM builds, but they were not benchmarked against bulk properties. A fixture was developed in [
31] to characterize the absolute shear strength of a specific weld interface in a UAM build used, shown in
Figure 3(c). This method is used to quantify the bond strength of UAM welds in comparison to the strength of the bulk foil material. A full-size shear sample was constructed by welding 23 layers of Al 6061-H18 foil. The samples were fabricated by building up the 23-layer sample, cutting coupons, and then machining them to size as shown in
Figure 3(a) and
Figure 3(b).
The geometry of the samples was designed so that the samples would fail by shearing at the foil 1 − foil 2 interface as seen in
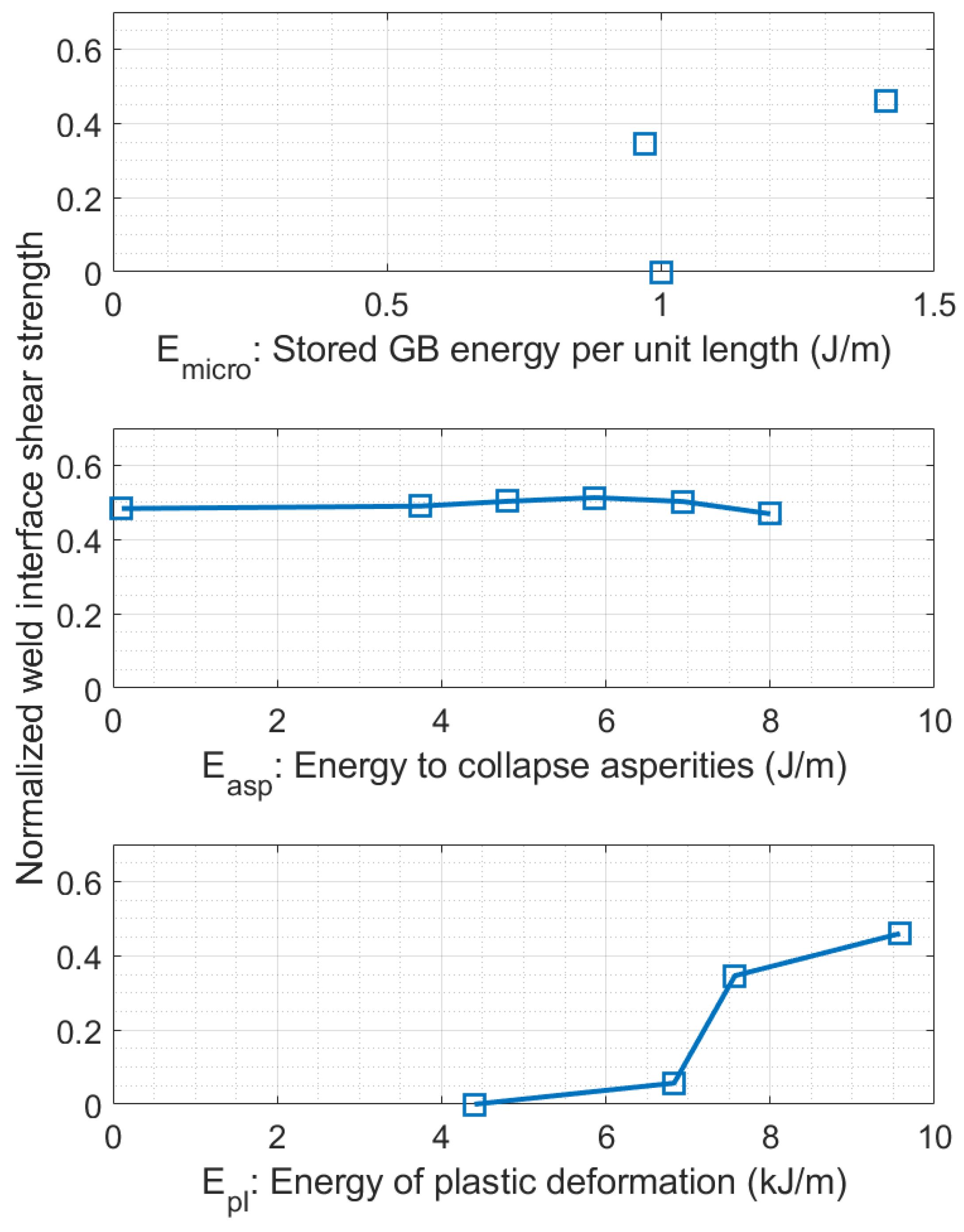
Figure 3(c). The shear area during testing is a square cross-section with side 0.195 mm. The shear stress was obtained by dividing the peak load by the shearing area of the sample. The strength value is normalized by the bulk shear strength of the foil material. Three different studies from the UAM of Al 6061-H18 using different process parameters are summarized in
Figure 4 to analyze the correlation between the weld strength and (a) energy stored in the microstructure, (b) energy required to collapse asperities, where the pre-weld surface roughness for foil-foil welding between the first and second layer is varied, and (c) energy of plastic deformation, where weld amplitude is varied.
5. Conclusions
A detailed energy flow diagram was developed for UAM to map the participating energies involved from the input electrical energy from the transducers to the energy stored in recrystallized grains in the resulting weld microstructure. Simplified analytical models were developed to estimate the energy used to collapse asperities and to disperse the oxide layer. The energies of plastic deformation and heat generation are estimated using previously developed techniques in [
11] with a simplified coupled thermo-mechanical model of the process using analytical and FE modeling. The energy stored in the microstructure is also quantified from EBSD analysis of the welded samples.
A shear testing rig was used to measure the strength of the weld interface for different process parameters. The corresponding participating energies were estimated and correlated with the weld strength in
Figure 4. The energy of plastic deformation is found to have the strongest impact on the weld strength. The UAM of a material is observed to have a threshold energy of plastic deformation below which bonding fails, and higher energies result in an up to 50% bulk strength for the weld in Al 6061-H18. The energy stored in the microstructure is also found to strongly increase with higher weld amplitude which is caused by the increase in the degree and volume of recrystallized grains in the foil material. Increasing in the energy required to collapse asperities of the foil material was not found to affect the weld strength significantly for the UAM of Al 6061-H18. This is expected to be due to asperities collapsing when a sufficiently high normal force is applied and thus not significantly reducing the energy available for bond formation.
The energy-based framework developed can be used to reduce the lost energies such as the heat lost to the welder by lowering the conductivity of the welder and the welder losses at the transducer by increasing the efficiency of the transducer assembly. This energy-based paradigm can also be used to optimize the process and maximize the portion of input energy from the welder used for bond formation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.V., L.H., and M.D.; methodology, G.V., L.H., and M.D.; software, G.V.; formal analysis, G.V. and L.H.; resources, M.D.; data curation, G.V.; writing - original draft preparation, G.V.; writing - review and editing, G.V., L.H., and M.D.; visualization, G.V.; supervision, M.D.; project administration, M.D.; funding acquisition, M.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation, Grant IIP 1738723 and the member organizations of the Smart Vehicle Concepts Center (
http://www.SmartVehicleCenter.org), a National Science Foundation Industry/University Cooperative Research Center. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Kong, C.Y.; Soar, R.C.; Dickens, P.M. Characterisation of aluminium alloy 6061 for the ultrasonic consolidation process. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2003, 363, 99–106. [CrossRef]
- Wolcott, P.J.; Hehr, A.; Dapino, M.J. Optimized welding parameters for Al 6061 ultrasonic additive manufactured structures. Journal of Materials Research 2014, 29, 2055–2065. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.; Stucker, B.E. Experimental determination of optimum parameters for stainless steel 316L annealed ultrasonic consolidation. Rapid Prototyping Journal 2012, 18, 180–182. [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Kuo, C.H.; Sridharan, N.; Headings, L.M.; Babu, S.S.; Dapino, M.J. Effect of preheat temperature and post-process treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of stainless steel 410 made via ultrasonic additive manufacturing. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2020, 769, 138457. [CrossRef]
- Pagan, M.; Zhao, N.; Headings, L.; Dapino, M.J.; Rossy, A.M.; Emery, R.; Rack, P.D.; Massey, C.; Zinkle, S.J.; Babu, S. Improvements in bonding through ultrasonic additive manufacturing of titanium by stabilizing displacive phase transformations. Materialia 2024, 33, 101979. [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, A.K.; Gingerich, M.B.; Headings, L.M.; Dapino, M.J. Metal structures embedded with piezoelectric PVDF sensors using ultrasonic additive manufacturing. Manufacturing Letters 2022, 31, 96–100. [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lin, S. Study on a large-scale three-dimensional ultrasonic plastic welding vibration system based on a quasi-periodic phononic crystal structure. Crystals 2020, 10, 21. [CrossRef]
- Graff, K.; Short, M.; Norfolk, M. Very high power ultrasonic additive manufacturing (VHP UAM). International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, 2011.
- Kelly, G.S.; Just Jr, M.S.; Advani, S.G.; Gillespie Jr, J.W. Energy and bond strength development during ultrasonic consolidation. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2014, 214, 1665–1672. [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, G.; Headings, L.M.; Dapino, M.J. Effect of process parameters on the microstructure of aluminum alloys made via ultrasonic additive manufacturing. Crystals 2022, 12, 1696. [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, G.; Shah, U.; Liu, X.; Dapino, M.J. In-situ IR imaging for modeling energy transfer and its relationship to shear strength of the weld interface in ultrasonic additive manufacturing. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology 2023, 43, 181–192. [CrossRef]
- Critchlow, G.W.; Brewis, D.M. Review of surface pretreatments for aluminium alloys. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives 1996, 16, 255–275. [CrossRef]
- Truog, A.G. Bond improvement of Al/Cu joints created by very high power ultrasonic additive manufacturing. PhD thesis, The Ohio State University, 2012.
- Venkatraman, G.; Hehr, A.; Headings, L.M.; Dapino, M.J. Effect of system compliance on weld power in ultrasonic additive manufacturing. Rapid Prototyping Journal 2021. [CrossRef]
- Wolcott, P.J.; Hehr, A.; Dapino, M.J. Optimized welding parameters for Al 6061 ultrasonic additive manufactured structures. Journal of Materials Research 2014, 29, 2055–2065. [CrossRef]
- Hehr, A.; Dapino, M.J. Dynamics of ultrasonic additive manufacturing. Ultrasonics 2017, 73, 49–66. [CrossRef]
- Koehler, J. On the dislocation theory of plastic deformation. Physical Review 1941, 60, 397. [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Stucker, B. A study of subgrain formation in Al 3003 H-18 foils undergoing ultrasonic additive manufacturing using a dislocation density based crystal plasticity finite element framework. Journal of applied physics 2013, 113, 203517. [CrossRef]
- Sriraman, M.R.; Gonser, M.; Fujii, H.T.; Babu, S.S.; Bloss, M. Thermal transients during processing of materials by very high power ultrasonic additive manufacturing. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2011, 211, 1650–1657. [CrossRef]
- Pagan, M.; Petrie, C.; Leonard, D.; Sridharan, N.; Zinkle, S.; Babu, S.S. Interdiffusion of Elements During Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 2021, 52, 1142–1157. [CrossRef]
- Wolcott, P.J.; Dapino, M.J. Ultrasonic additive manufacturing. In Additive Manufacturing Handbook; CRC Press, 2017; pp. 275–298.
- Le, H.R.; Sutcliffe, M.P.F. Analysis of surface roughness of cold-rolled aluminium foil. Wear 2000, 244, 71–78. [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Introduction to tribology; John Wiley & Sons, 2013.
- Johnson, K. Interlaminar subgrain refinement in ultrasonic consolidation. PhD thesis, Loughborough University, 2008.
- Zhu, H.; Qi, F. Mechanical properties and fracture behaviors on 6061 aluminum alloy under shear stress state. Rare Metals 2011, 30, 550–554. [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, G. Process Modeling of Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing. PhD thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2022.
- Fujii, H.T.; Shimizu, S.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. High-strain-rate deformation in ultrasonic additive manufacturing. Scripta Materialia 2017, 135, 125–129. [CrossRef]
- Gussev, M.; Sridharan, N.; Norfolk, M.; Terrani, K.; Babu, S. Effect of post weld heat treatment on the 6061 aluminum alloy produced by ultrasonic additive manufacturing. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2017, 684, 606–616. [CrossRef]
- Beucia, B.; Queyreau, S.; Kahloun, C.; Chaubet, D.; Franciosi, P.; Bacroix, B. Plastic strain-induced grain boundary migration (SIBM) in pure aluminum: SEM in-situ and AFM examinations. International Journal of Plasticity 2019, 115, 29–55. [CrossRef]
- Hehr, A.; Wolcott, P.J.; Dapino, M.J. Effect of weld power and build compliance on ultrasonic consolidation. Rapid Prototyping Journal 2016, 22, 377–386. [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Headings, L.M.; Hahnlen, R.; Dapino, M.J. Effect of process parameters on interfacial temperature and shear strength of ultrasonic additive manufacturing of carbon steel 4130. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering 2022, 144, 084501. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).