Submitted:
01 October 2024
Posted:
02 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
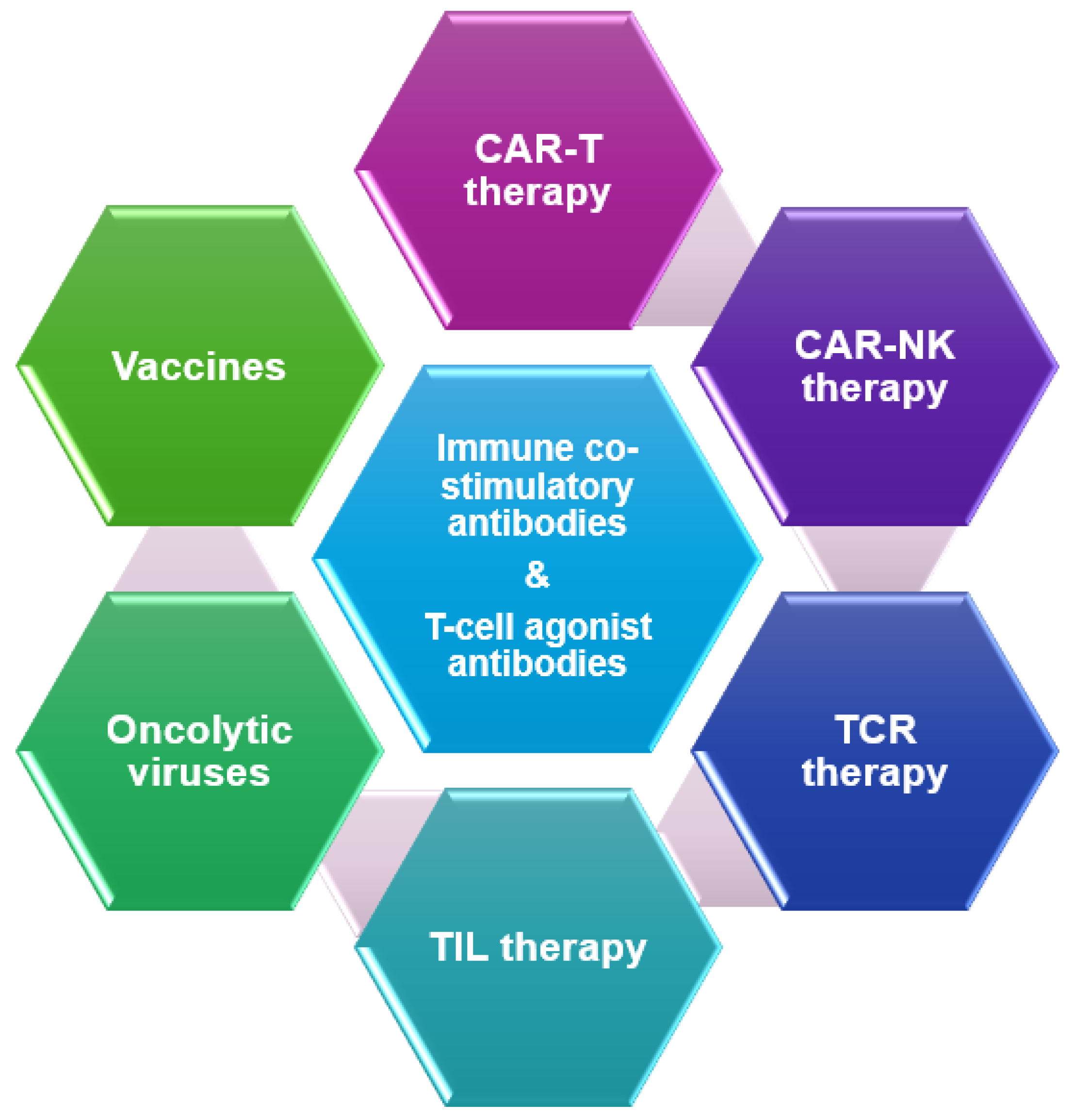
Introduction
Immune Co-Stimulatory Antibodies
T-Cell Agonist Antibodies
Vaccine Therapy
Oncolytic Viruses (OV)
Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs)
T-Cell Receptor (TCR) Therapy
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy
CAR NK Cell Therapy
| Therapy name | Mechanism of action | NCT number |
|---|---|---|
| Co-stimulatory antibodies | ||
| AZD2936 | PD-L1×TIGIT bispecific antibody | NCT04995523 (ARTEMIDE) |
| HB0036 | PD-L1×TIGIT bispecific antibody | NCT05417321 |
| HLX301 | PD-L1×TIGIT bispecific antibody | NCT05390528 |
| RO7247669 | PD-L1×LAG3 bispecific antibody | NCT04140500 |
| Cobolimab | Anti-TIM3 antibody | NCT02817633 (AMBER) |
| Cobolimab | Anti-TIM3 antibody | NCT04655976 (COSTAR Lung) |
| AZD7789 | PD-L1×TIM3 bispecific antibody | NCT04931654 |
| T- cell agonists | ||
| BGB-A445 | OX40 agonist mAB | NCT04215978 |
| INBRX-106 | OX40 agonist mAB | NCT04198766 |
| ES102 | OX40 agonist mAB | NCT04991506 |
| GEN1046 | PD-L1×4-1BB bispecific antibody | NCT05117242 |
| Vaccine therapy | ||
| OSE2101 | Vaccine targeting 5 TAA overexpressed in NSCLC | NCT06472245 (ARTEMIA) |
| KRAS vaccine | Pooled mutant-KRAS peptide vaccine | NCT05254184 |
| CIMAvax-EGF | Chemical conjugate between EGF and P64 | NCT02955290 |
| BNT116 | RNA-lipoplex vaccine with 6 RNAs each encoding TAA expressed in NSCLC | NCT05142189 (LuCa-MERIT-1) |
| BNT116 | NCT05557591 | |
| Oncolytic viruses | ||
| Aglatimagene besadenovec (Adv-Tk) | Adenovirus-based vector expressing thymidine kinase gene | NCT04495153 |
| MEM-288 | Conditionally replicative adenovirus vector encoding transgenes for human IFNβ & recombinant chimeric form of CD40-ligand | NCT05076760 |
| VSV-IFNβ-NIS | Oncolytic VSV expressing IFNβ and NIS | NCT03647163 |
| TIL therapy | ||
| LN-145 | Autologous TILs | NCT04614103 |
| CD-40L-augmented TIL | NCT05681780 | |
| TBio-4101 | Autologous TILs | NCT05576077 (STARLING) |
| OBX-115 | IL-15 expressing TIL | NCT06060613 |
| ATL001 | clonal neoantigen reactive TILs | NCT04032847 (CHIROS) |
| IOV-4001 | PD-1 inactivated TILs | NCT05361174 |
| LYL845 | Epigenetic reprogrammed TILs | NCT05573035 |
| TCR therapy | ||
| IMA203 | PRAME specific TCR | NCT03686124 (ACTengine) |
| AFNT-211 | HLA-A*11:01-restricted KRAS G12V TCR | NCT06105021 |
| FH-A11KRASG12V-TCR | KRAS G12V specific TCR | NCT06043713 |
| NT-112 | HLA-C*08:02-restricted KRAS G12D TCR | NCT06218914 |
| NT-175 | HLA-A*02:01-restricted TP53 R175H TCR | NCT05877599 |
| CAR-T | ||
| P-MUC1C-ALLO1 | Allogenic CAR-T targeting MUC1 expressing tumors | NCT05239143 |
| LY797 | ROR1 targeting CAR-T | NCT05274451 |
| CXCR5 modified EGFR targeted CAR-T | NCT05060796 | |
| A2B530 | Logic-gated CAR-T (CEA expression, but loss of HLA-A*A02 expression) | NCT05736731 (EVEREST-1) |
| A2B694 | Logic-gated CAR-T (MSLN expression, but loss of HLA-A*A02 expression) | NCT06051695 (EVEREST-2) |
| CAR-NK | ||
| anti-Trop2 CAR-NK | NCT06454890 | |
| MUC1 targeting CAR-NK | NCT02839954 | |
| COH06 | TRACK-NK | NCT05334329 |
References
- Kluger, H.M., et al., Defining tumor resistance to PD-1 pathway blockade: recommendations from the first meeting of the SITC Immunotherapy Resistance Taskforce. J Immunother Cancer, 2020. 8(1). [CrossRef]
- Uryvaev, A., et al., The role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) as a predictive biomarker of response to anti-PD1 therapy in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer or metastatic melanoma. Med Oncol, 2018. 35(3): p. 25. [CrossRef]
- Tumeh, P.C., et al., PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature, 2014. 515(7528): p. 568-71. [CrossRef]
- Snyder, A., et al., Genetic basis for clinical response to CTLA-4 blockade in melanoma. N Engl J Med, 2014. 371(23): p. 2189-2199. [CrossRef]
- Ayers, M., et al., IFN-gamma-related mRNA profile predicts clinical response to PD-1 blockade. J Clin Invest, 2017. 127(8): p. 2930-2940. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M., et al., Immune checkpoint blockade and its combination therapy with small-molecule inhibitors for cancer treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2019. 1871(2): p. 199-224. [CrossRef]
- Bluthgen, M.V., N. Baste, and G. Recondo, Immunotherapy combinations for the treatment of patients with solid tumors. Future Oncol, 2020. 16(23): p. 1715-1736. [CrossRef]
- Li, T., et al., The enhanced antitumor activity of bispecific antibody targeting PD-1/PD-L1 signaling. Cell Commun Signal, 2024. 22(1): p. 179. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., et al., A multicenter, open-label phase Ib/II study of cadonilimab (anti PD-1 and CTLA-4 bispecific antibody) monotherapy in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (AK104-202 study). Lung Cancer, 2023. 184: p. 107355. [CrossRef]
- Yu, X., et al., The surface protein TIGIT suppresses T cell activation by promoting the generation of mature immunoregulatory dendritic cells. Nat Immunol, 2009. 10(1): p. 48-57. [CrossRef]
- Martin, C. and D. Enrico, Current and novel therapeutic strategies for optimizing immunotherapy outcomes in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol, 2022. 12: p. 962947. [CrossRef]
- Niu, J., et al., First-in-human phase 1 study of the anti-TIGIT antibody vibostolimab as monotherapy or with pembrolizumab for advanced solid tumors, including non-small-cell lung cancer(☆). Ann Oncol, 2022. 33(2): p. 169-180. [CrossRef]
- Rohrberg, K.S., et al., Safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics (PD) and preliminary efficacy of AZD2936, a bispecific antibody targeting PD-1 and TIGIT, in checkpoint inhibitor (CPI)-experienced advanced/metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): First report of ARTEMIDE-01. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2023. 41(16_suppl): p. 9050-9050. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y., et al., A phase I/II, open-label, multicenter study to evaluate the safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and efficacy of HB0036 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2024. 42(16_suppl): p. e14504-e14504. [CrossRef]
- Triebel, F., et al., LAG-3, a novel lymphocyte activation gene closely related to CD4. J Exp Med, 1990. 171(5): p. 1393-405. [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C., et al., Tiragolumab plus atezolizumab versus placebo plus atezolizumab as a first-line treatment for PD-L1-selected non-small-cell lung cancer (CITYSCAPE): primary and follow-up analyses of a randomised, double-blind, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol, 2022. 23(6): p. 781-792. [CrossRef]
- Majem, M., et al., 11MO Final data from a phase II study (TACTI-002) of eftilagimod alpha (soluble LAG-3) and pembrolizumab in 2nd-line metastatic NSCLC pts resistant to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 2023. 18(4, Supplement): p. S43-S44. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y., et al., 80P Safety, preliminary efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of HLX26 plus serplulimab in advanced solid tumours: An open-label, dose-escalation phase I study. Annals of Oncology, 2023. 34: p. S1497. [CrossRef]
- Falchook, G.S., et al., Phase 1 trial of TIM-3 inhibitor cobolimab monotherapy and in combination with PD-1 inhibitors nivolumab or dostarlimab (AMBER). Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2022. 40(16_suppl): p. 2504-2504. [CrossRef]
- Hutloff, A., et al., ICOS is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally related to CD28. Nature, 1999. 397(6716): p. 263-6. [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.A., et al., First-in-Human Phase I/II ICONIC Trial of the ICOS Agonist Vopratelimab Alone and with Nivolumab: ICOS-High CD4 T-Cell Populations and Predictors of Response. Clin Cancer Res, 2022. 28(17): p. 3695-3708. [CrossRef]
- Desai, J., et al., A phase 1 study of the OX40 agonist, BGB-A445, with or without tislelizumab, an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2023. 41(16_suppl): p. 2574-2574. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C., et al., 742 Phase 1/2 study of the bispecific 4–1BB and PD-L1 antibody INBRX-105 alone and in combination with pembrolizumab in select solid tumors. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer, 2023. 11(Suppl 1): p. A836-A837. [CrossRef]
- Muik, A., et al., Preclinical Characterization and Phase I Trial Results of a Bispecific Antibody Targeting PD-L1 and 4-1BB (GEN1046) in Patients with Advanced Refractory Solid Tumors. Cancer Discov, 2022. 12(5): p. 1248-1265. [CrossRef]
- Tagliamonte, M., et al., Antigen-specific vaccines for cancer treatment. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2014. 10(11): p. 3332-46. [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, J. and J.M. Mehnert, Use of tumor cell lysate to develop peptide vaccine targeting cancer-testis antigens. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2021. 10(11): p. 4049-4052. [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M., et al., Personalized neoantigen vaccine NEO-PV-01 with chemotherapy and anti-PD-1 as first-line treatment for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell, 2022. 40(9): p. 1010-1026 e11. [CrossRef]
- Besse, B., et al., Randomized open-label controlled study of cancer vaccine OSE2101 versus chemotherapy in HLA-A2-positive patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with resistance to immunotherapy: ATALANTE-1. Ann Oncol, 2023. 34(10): p. 920-933. [CrossRef]
- Frascati, R., et al., Final results from a phase II trial of CIMAvax-EGF and nivolumab as second-line (2L) therapy after platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2023. 41(16_suppl): p. 9135-9135. [CrossRef]
- Deme, D., et al., 597 Preliminary results from LuCa-MERIT-1, a first-in-human Phase I trial evaluating the fixed antigen RNA vaccine BNT116 in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer, 2023. 11(Suppl 1): p. A679-A679. [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, H.L., F.J. Kohlhapp, and A. Zloza, Oncolytic viruses: a new class of immunotherapy drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2015. 14(9): p. 642-62. [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, J. and E.S. Kim, Oncolytic Viruses and Cancer Immunotherapy. Curr Oncol Rep, 2023. 25(1): p. 19-28. [CrossRef]
- Pandha, H.S., et al., Keynote-200 phase 1b: A novel combination study of intravenously delivered coxsackievirus A21 and pembrolizumab in advanced cancer patients. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2017. 35(15_suppl): p. TPS3108-TPS3108. [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M., et al., Phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study on the safety, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary efficacy of intravenous Coxsackievirus A21 (V937), with or without pembrolizumab, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Immunother Cancer, 2023. 11(1). [CrossRef]
- Rajan, A., et al., Phase 1 trial of CV301 in combination with anti-PD-1 therapy in nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer, 2023. 152(3): p. 447-457. [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, C., et al., Stereotactic body radiation therapy and in situ oncolytic virus therapy followed by immunotherapy in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2021. 39(15_suppl): p. 9115-9115. [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C., et al., Phase I Study of Intrapleural Gene-Mediated Cytotoxic Immunotherapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion. Mol Ther, 2018. 26(5): p. 1198-1205. [CrossRef]
- Saltos, A.N., et al., A phase 1 first-in-human study of interferon beta (IFNβ) and membrane-stable CD40L expressing oncolytic virus (MEM-288) in solid tumors including non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2023. 41(16_suppl): p. 2569-2569. [CrossRef]
- Mountzios, G., et al., Beyond Chemoimmunotherapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: New Frontiers, New Challenges. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book, 2024. 44(3): p. e432526. [CrossRef]
- Poschke, I.C., et al., The Outcome of Ex Vivo TIL Expansion Is Highly Influenced by Spatial Heterogeneity of the Tumor T-Cell Repertoire and Differences in Intrinsic In Vitro Growth Capacity between T-Cell Clones. Clin Cancer Res, 2020. 26(16): p. 4289-4301. [CrossRef]
- Creelan, B.C., et al., Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte treatment for anti-PD-1-resistant metastatic lung cancer: a phase 1 trial. Nat Med, 2021. 27(8): p. 1410-1418. [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, A.J., et al., Lifileucel, an Autologous Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Monotherapy, in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Resistant to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancer Discov, 2024. 14(8): p. 1389-1402. [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J., M. Salm, and M. Dangl, Adoptive cell therapy with tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes: the emerging importance of clonal neoantigen targets for next-generation products in non-small cell lung cancer. Immunooncol Technol, 2019. 3: p. 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, V., J. Chesney, and G. Kloecker, Cellular Therapy for Lung Cancer: Focusing on Chimeric Antigen Receptor T (CAR T) Cells and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) Therapy. Cancers (Basel), 2023. 15(14). [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M., et al., T-cell receptor-based therapy: an innovative therapeutic approach for solid tumors. J Hematol Oncol, 2021. 14(1): p. 102. [CrossRef]
- D'Angelo, S.P., et al., Afamitresgene autoleucel for advanced synovial sarcoma and myxoid round cell liposarcoma (SPEARHEAD-1): an international, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet, 2024. 403(10435): p. 1460-1471. [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, M., et al., NY-ESO-1-specific redirected T cells with endogenous TCR knockdown mediate tumor response and cytokine release syndrome. J Immunother Cancer, 2022. 10(6). [CrossRef]
- Wermke, M., et al., Abstract PR018: IMA203 TCR-T targeting PRAME demonstrates potent anti-tumor activity in patients with different types of metastatic solid tumors. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 2023. 22(12_Supplement): p. PR018-PR018. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S., et al., AFNT-211: A phase 1 study of autologous CD4+ and CD8+ T cells engineered to express a high avidity HLA-A*11:01-restricted, KRAS G12V-specific, transgenic TCR, a CD8α/β coreceptor, and a FAS41BB switch receptor in patients with advanced/metastatic solid tumors. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2024. 42(16_suppl): p. TPS8650-TPS8650. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J., B. Abila, and Y. Mostafa Kamel, CAR-T: What Is Next? Cancers (Basel), 2023. 15(3). [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.Y., et al., Advances in CAR T Cell Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Curr Issues Mol Biol, 2023. 45(11): p. 9019-9038. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y., et al., 35O - Phase I clinical trial of PD-1 knockout anti-MUC1 CAR-T cells in the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Annals of Oncology, 2019. 30: p. xi12. [CrossRef]
- Adusumilli, P.S., et al., A Phase I Trial of Regional Mesothelin-Targeted CAR T-cell Therapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Disease, in Combination with the Anti-PD-1 Agent Pembrolizumab. Cancer Discov, 2021. 11(11): p. 2748-2763. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., et al., Phase I clinical trial of EGFR-specific CAR-T cells generated by the piggyBac transposon system in advanced relapsed/refractory non-small cell lung cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2021. 147(12): p. 3725-3734. [CrossRef]
- Chocarro, L., et al., CAR-T Cells for the Treatment of Lung Cancer. Life (Basel), 2022. 12(4). [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y., Increasing T Cell Versatility with SUPRA CARs. Cell, 2018. 173(6): p. 1316-1317. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F., et al., Advances in CAR-NK cell therapy for lung cancer: is it a better choice in the future? Front Oncol, 2024. 14: p. 1390006. [CrossRef]
- Lu, C., et al., A novel chimeric PD1-NKG2D-41BB receptor enhances antitumor activity of NK92 cells against human lung cancer H1299 cells by triggering pyroptosis. Mol Immunol, 2020. 122: p. 200-206. [CrossRef]
- Villalona-Calero, M.A., et al., A phase 1 trial of umbilical cord blood–derived tumor-reactive PD-L1+ natural killer cells engineered to express soluble IL-15 (TRACK-NK) in patients with non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) refractory to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2023. 41(16_suppl): p. TPS2665-TPS2665. [CrossRef]
- Yang, S., et al., Targeting B7-H3 Immune Checkpoint With Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Engineered Natural Killer Cells Exhibits Potent Cytotoxicity Against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Pharmacol, 2020. 11: p. 1089. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y., et al., Engineering c-Met-CAR NK-92 cells as a promising therapeutic candidate for lung adenocarcinoma. Pharmacol Res, 2023. 188: p. 106656. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





