Submitted:
01 October 2024
Posted:
02 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- -
- What are the spatial bibliometrics dimensions of funded and non-funded IoMT research in relation to country determinants?
- -
- What are the characteristics of funding patterns and its relation to country determinants?
- -
- Which are the most prolific themes of funded and non-funded IoMT research?
- -
- What is the impact of funded research on the Global Health Index?
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Bibliometric Dimensions of IoMT Research and Country Determinants
3.2. Thematic Analysis
3.3. IoMT Impact: Bloomberg Global Health Index in Relation to the Number of Funded Published Papers on IoMT
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heimburg, D.V.; Prilleltensky, I.; Ness, O.; Ytterhus, B. From Public Health to Public Good: Toward Universal Wellbeing. Scand J Public Health 2022, 50, 1062–1070. [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Trenfield, S.J.; Pollard, T.D.; Ong, J.J.; Elbadawi, M.; McCoubrey, L.E.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Connected Healthcare: Improving Patient Care Using Digital Health Technologies. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2021, 178, 113958. [CrossRef]
- Satam, H.; Joshi, K.; Mangrolia, U.; Waghoo, S.; Zaidi, G.; Rawool, S.; Thakare, R.P.; Banday, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Das, G.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Technology: Current Trends and Advancements. Biology 2023, 12, 997. [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P.; Blažun Vošner, H.; Kokol, M.; Završnik, J. Role of Agile in Digital Public Health Transformation. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 899874. [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P. Agile Software Development in Healthcare: A Synthetic Scoping Review. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 9462. [CrossRef]
- Khang, A.; Rana, G.; Tailor, R.K.; Abdullayev, V. Data-Centric AI Solutions and Emerging Technologies in the Healthcare Ecosystem; CRC Press, 2023; ISBN 978-1-00-092774-0.
- Šajnović, U.; Vošner, H.B.; Završnik, J.; Žlahtič, B.; Kokol, P. Internet of Things and Big Data Analytics in Preventive Healthcare: A Synthetic Review. Electronics 2024, 13, 3642. [CrossRef]
- El-Saleh, A.A.; Sheikh, A.M.; Albreem, M.A.M.; Honnurvali, M.S. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Opportunities and Challenges. Wireless Netw 2024. [CrossRef]
- Osama, M.; Ateya, A.A.; Sayed, M.S.; Hammad, M.; Pławiak, P.; Abd El-Latif, A.A.; Elsayed, R.A. Internet of Medical Things and Healthcare 4.0: Trends, Requirements, Challenges, and Research Directions. Sensors 2023, 23. [CrossRef]
- Razdan, S.; Sharma, S. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Overview, Emerging Technologies, and Case Studies. IETE Technical Review 2022, 39, 775–788. [CrossRef]
- Manickam, P.; Mariappan, S.A.; Murugesan, S.M.; Hansda, S.; Kaushik, A.; Shinde, R.; Thipperudraswamy, S.P. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Assisted Biomedical Systems for Intelligent Healthcare. Biosensors 2022, 12, 562. [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Khang, A. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Driving the Digital Transformation of the Healthcare Sector. In Data-Centric AI Solutions and Emerging Technologies in the Healthcare Ecosystem; CRC Press, 2023 ISBN 978-1-00-335618-9.
- Effects of Research Funding on the Academic Impact and Societal Visibility of Scientific Research - ScienceDirect Available online: https://www-sciencedirect-com.ezproxy.lib.ukm.si/science/article/pii/S1751157724001044?via%3Dihub (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Kokol, P. Discrepancies among Scopus and Web of Science, Coverage of Funding Information in Medical Journal Articles: A Follow-up Study. Journal of the Medical Library Association 2023, 111, 703–709. [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P.; Blažun Vošner, H. Discrepancies among Scopus, Web of Science, and PubMed Coverage of Funding Information in Medical Journal Articles. J Med Libr Assoc 2018, 106, 81–86. [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-Tool for Comprehensive Science Mapping Analysis. Journal of Informetrics 2017, 11, 959–975. [CrossRef]
- Scimago Journal & Country Rank Available online: https://www.scimagojr.com/ (accessed on 26 January 2023).
- Health and Health System Ranking of Countries Worldwide in 2023 Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1376359/health-and-health-system-ranking-of-countries-worldwide/ (accessed on 17 August 2024).
- World Development Indicators | DataBank Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators/Series/GB.XPD.RSDV.GD.ZS# (accessed on 17 August 2024).
- Healthiest Countries 2024 Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/healthiest-countries (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Kokol, P.; Železnik, D.; Završnik, J.; Blažun Vošner, H. Nursing Research Literature Production in Terms of the Scope of Country and Health Determinants: A Bibliometric Study. Journal of Nursing Scholarship 2019, 51, 590–598. [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P. Synthetic Knowledge Synthesis in Hospital Libraries. Journal of Hospital Librarianship 2023, 0, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Health Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/topics/policy-areas/health.html (accessed on 17 August 2024).
- Zipf, G.K. The Psycho-Biology of Language; The psycho-biology of language; Houghton, Mifflin: Oxford, England, 1935;
- Scrugli, M.A.; Loi, D.; Raffo, L.; Meloni, P. An Adaptive Cognitive Sensor Node for ECG Monitoring in the Internet of Medical Things. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 1688–1705. [CrossRef]
- Ahila, A.; Dahan, F.; Alroobaea, R.; Alghamdi, W.Y.; Mustafa, K.M.; Hajjej, F.; Deema, mohammed alsekait; Raahemifar, K. A Smart IoMT Based Architecture for E-Healthcare Patient Monitoring System Using Artificial Intelligence Algorithms. Frontiers in Physiology 2023, 14. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, S.K. FEEL: FEderated LEarning Framework for ELderly Healthcare Using Edge-IoMT. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems 2023, 10, 1800–1809. [CrossRef]
- Haghi, M.; Benis, A.; Deserno, T.M. Accident & Emergency Informatics and One Digital Health. Yearbook of Medical Informatics 2022, 31, 40–46. [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Nehra, M.; Kumar, R.; Dilbaghi, N.; Hu, TonyY.; Kumar, S.; Kaushik, A.; Li, C. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)-Integrated Biosensors for Point-of-Care Testing of Infectious Diseases. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2021, 179, 113074. [CrossRef]
- Swayamsiddha, S.; Mohanty, C. Application of Cognitive Internet of Medical Things for COVID-19 Pandemic. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews 2020, 14, 911–915. [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, A.; Khodatars, M.; Jafari, M.; Ghassemi, N.; Sadeghi, D.; Moridian, P.; Khadem, A.; Alizadehsani, R.; Hussain, S.; Zare, A.; et al. Automated Detection and Forecasting of COVID-19 Using Deep Learning Techniques: A Review. Neurocomputing 2024, 577, 127317. [CrossRef]
- Samuel, O.; Omojo, A.B.; Onuja, A.M.; Sunday, Y.; Tiwari, P.; Gupta, D.; Hafeez, G.; Yahaya, A.S.; Fatoba, O.J.; Shamshirband, S. IoMT: A COVID-19 Healthcare System Driven by Federated Learning and Blockchain. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2023, 27, 823–834. [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.N.; Panneerselvam, V.; Koundal, D.; Ahmed, K.; Bui, F.M.; Ibrahim, S.M. Federated Machine Learning for Detection of Skin Diseases and Enhancement of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Security. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2023, 27, 835–841. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Pham, Q.-V.; Pathirana, P.N.; Ding, M.; Seneviratne, A.; Lin, Z.; Dobre, O.; Hwang, W.-J. Federated Learning for Smart Healthcare: A Survey. ACM Computing Surveys 2022, 55. [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Gao, M.; Jiang, Y.; Gu, X.; Ning, X.; Qian, P.; Ni, T. Hierarchical Domain Adaptation Projective Dictionary Pair Learning Model for EEG Classification in IoMT Systems. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems 2023, 10, 1559–1567. [CrossRef]
- Rahmadika, S.; Astillo, P.V.; Choudhary, G.; Duguma, D.G.; Sharma, V.; You, I. Blockchain-Based Privacy Preservation Scheme for Misbehavior Detection in Lightweight IoMT Devices. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2023, 27, 710–721. [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, M.M.; Nazir, M.; Yousafzai, A.; Khan, M.A.; Shaikh, A.A.; Algarni, A.D.; Elmannai, H. Modified Artificial Bee Colony Based Feature Optimized Federated Learning for Heart Disease Diagnosis in Healthcare. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 12080. [CrossRef]
- Lakhan, A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Nedoma, J.; Martinek, R.; Tiwari, P.; Vidyarthi, A.; Alkhayyat, A.; Wang, W. Federated-Learning Based Privacy Preservation and Fraud-Enabled Blockchain IoMT System for Healthcare. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2023, 27, 664–672. [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Naeem, F.; Tariq, M.; Kaddoum, G. Federated Learning for Privacy Preservation in Smart Healthcare Systems: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2023, 27, 778–789. [CrossRef]
- Si-Ahmed, A.; Al-Garadi, M.A.; Boustia, N. Survey of Machine Learning Based Intrusion Detection Methods for Internet of Medical Things. Applied Soft Computing 2023, 140, 110227. [CrossRef]
- Aouedi, O.; Sacco, A.; Piamrat, K.; Marchetto, G. Handling Privacy-Sensitive Medical Data With Federated Learning: Challenges and Future Directions. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2023, 27, 790–803. [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Almaiah, M.A.; Hajjej, F.; Pasha, M.F.; Fang, O.H.; Khan, R.; Teo, J.; Zakarya, M. An Industrial IoT-Based Blockchain-Enabled Secure Searchable Encryption Approach for Healthcare Systems Using Neural Network. Sensors 2022, 22. [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Hajjej, F.; Ali, A.; Pasha, M.F.; Almomani, O. An AI-Enabled Hybrid Lightweight Authentication Model for Digital Healthcare Using Industrial Internet of Things Cyber-Physical Systems. Sensors 2022, 22. [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.A.; Moustafa, N.; Razzak, I.; Tanveer, M.; Pi, D.; Pan, Y.; Ali, B.S. XSRU-IoMT: Explainable Simple Recurrent Units for Threat Detection in Internet of Medical Things Networks. Future Generation Computer Systems 2022, 127, 181–193. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Khanna, V.; Ahmed Awan, H.T.; Singh, K.; Khalid, M.; Mishra, Y.K.; Bhansali, S.; Li, C.-Z.; Kaushik, A. Towards Hospital-on-Chip Supported by 2D MXenes-Based 5th Generation Intelligent Biosensors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2023, 220. [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Abbas, S.; Khan, M.A.; Ghazal, T.M.; Adnan, K.M.; Mosavi, A. A Secure Healthcare 5.0 System Based on Blockchain Technology Entangled with Federated Learning Technique. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 150, 106019. [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.A.; Razzak, I.; Pi, D.; Khan, N.; Hussain, Y.; Li, B.; Kousar, T. Fed-Inforce-Fusion: A Federated Reinforcement-Based Fusion Model for Security and Privacy Protection of IoMT Networks against Cyber-Attacks. Information Fusion 2024, 101, 102002. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Sharma, D.K.; Datta Gupta, K.; Kumar, A. A Tree Classifier Based Network Intrusion Detection Model for Internet of Medical Things. Computers and Electrical Engineering 2022, 102, 108158. [CrossRef]
- Firat Kilincer, I.; Ertam, F.; Sengur, A.; Tan, R.-S.; Rajendra Acharya, U. Automated Detection of Cybersecurity Attacks in Healthcare Systems with Recursive Feature Elimination and Multilayer Perceptron Optimization. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering 2023, 43, 30–41. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Ghazal, T.M.; Saeed, R.A.; Pandey, B.; Gohel, H.; Eshmawi, A.A.; Abdel-Khalek, S.; Alkhassawneh, H.M. A Review on Security Threats, Vulnerabilities, and Counter Measures of 5G Enabled Internet-of-Medical-Things. IET Communications 2022, 16, 421–432. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Alroobaea, R.; Krichen, M.; Rubaiee, S.; Vimal, S.; Almansour, F.M. Blockchain-Assisted Secured Data Management Framework for Health Information Analysis Based on Internet of Medical Things. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing 2024, 28, 59–72. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Singh, G. Internet of Medical Things Healthcare for Sustainable Smart Cities: Current Status and Future Prospects. Applied Sciences (Switzerland) 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Syed, L.; Jabeen, S.; S., M.; Alsaeedi, A. Smart Healthcare Framework for Ambient Assisted Living Using IoMT and Big Data Analytics Techniques. Future Generation Computer Systems 2019, 101, 136–151. [CrossRef]
- AlShorman, O.; AlShorman, B.; Al-khassaweneh, M.; Alkahtani, F. A Review of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) - Based Remote Health Monitoring through Wearable Sensors: A Case Study for Diabetic Patients. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 2020, 20, 414–422. [CrossRef]
- Khamisy-Farah, R.; Furstenau, L.B.; Kong, J.D.; Wu, J.; Bragazzi, N.L. Gynecology Meets Big Data in the Disruptive Innovation Medical Era: State-of-Art and Future Prospects. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, 5058. [CrossRef]
- Big Data-Based Smart Health Monitoring System: Using Deep Ensemble Learning | IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore Available online: https://ieeexplore-ieee-org.ezproxy.lib.ukm.si/document/10286815 (accessed on 17 September 2024).
- Lin, M.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, X.; Bian, Y.; Wu, R.S.; Park, G.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; et al. A Fully Integrated Wearable Ultrasound System to Monitor Deep Tissues in Moving Subjects. Nat Biotechnol 2024, 42, 448–457. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lai, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Vijayakumar, P.; Karuppiah, M. Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning for Internet of Medical Things Under Edge Computing. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2023, 27, 854–865. [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Wang, H.; Qiao, D.; Du, J. Application of Robust Zero-Watermarking Scheme Based on Federated Learning for Securing the Healthcare Data. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2023, 27, 804–813. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J. A Scalable and Transferable Federated Learning System for Classifying Healthcare Sensor Data. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2023, 27, 866–877. [CrossRef]
- Abidi, M.H.; Umer, U.; Mian, S.H.; Al-Ahmari, A. Big Data-Based Smart Health Monitoring System: Using Deep Ensemble Learning. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 114880–114903. [CrossRef]
- Raj, E.F.I. Data-Driven Modern Health Care Systems with the Internet of Medical Things Combined with Big Data and Machine Learning. In AI-Enabled IoT for Smart Health Care Systems; 2022; pp. 123–145.
- Chen, Z. Lung Tumor Diagnosis Technology Based on 6G Wireless Network Sensors and Big Data Analysis. Wireless Pers Commun 2024. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, R.; Ray, R.; Dash, S.R.; Jena, O.P. Conceptualizing Tomorrow’s Healthcare Through Digitization. In Computational Intelligence and Healthcare Informatics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2021; pp. 359–376 ISBN 978-1-119-81871-7.
- Singh, S.; Sharma, S.; Bhadula, S.; Mohan, S. Industry 4.0 Internet of Medical Things Enabled Cost Effective Secure Smart Patient Care Medicine Pouch. In New Horizons for Industry 4.0 in Modern Business; Nayyar, A., Naved, M., Rameshwar, R., Eds.; Contributions to Environmental Sciences & Innovative Business Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2023; pp. 149–170 ISBN 978-3-031-20442-5.
- Ajagbe, S.A.; Awotunde, J.B.; Adesina, A.O.; Achimugu, P.; Kumar, T.A. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Applications, Challenges, and Prospects in a Data-Driven Technology. In Intelligent Healthcare; Chakraborty, C., Khosravi, M.R., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022; pp. 299–319 ISBN 9789811681493.
- Robles, S.C. A Public Health Framework for Chronic Disease Prevention and Control. Food Nutr Bull 2004, 25, 194–199. [CrossRef]
- Abis, S.; Veldkamp, L. The Changing Economics of Knowledge Production. The Review of Financial Studies 2024, 37, 89–118. [CrossRef]
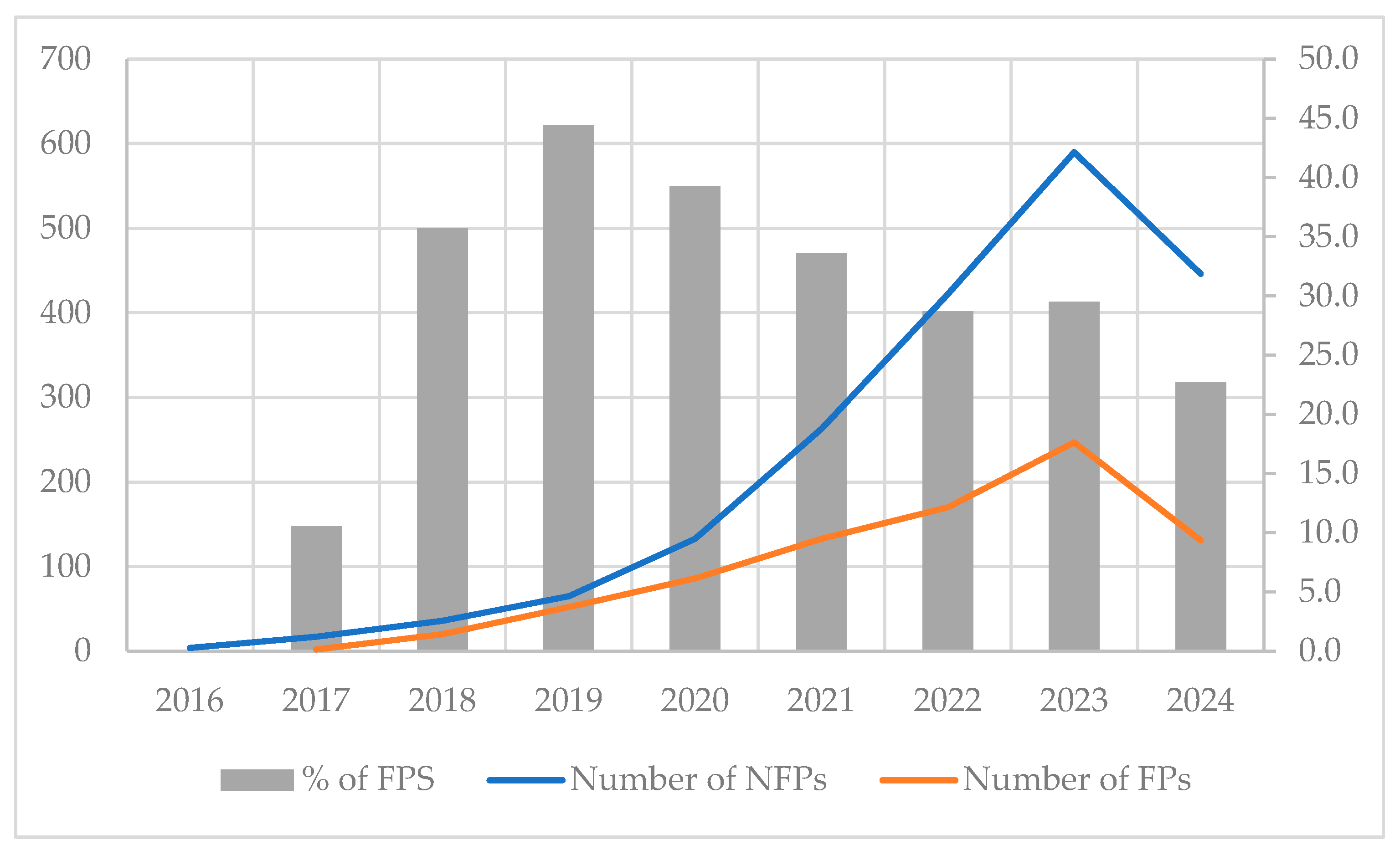
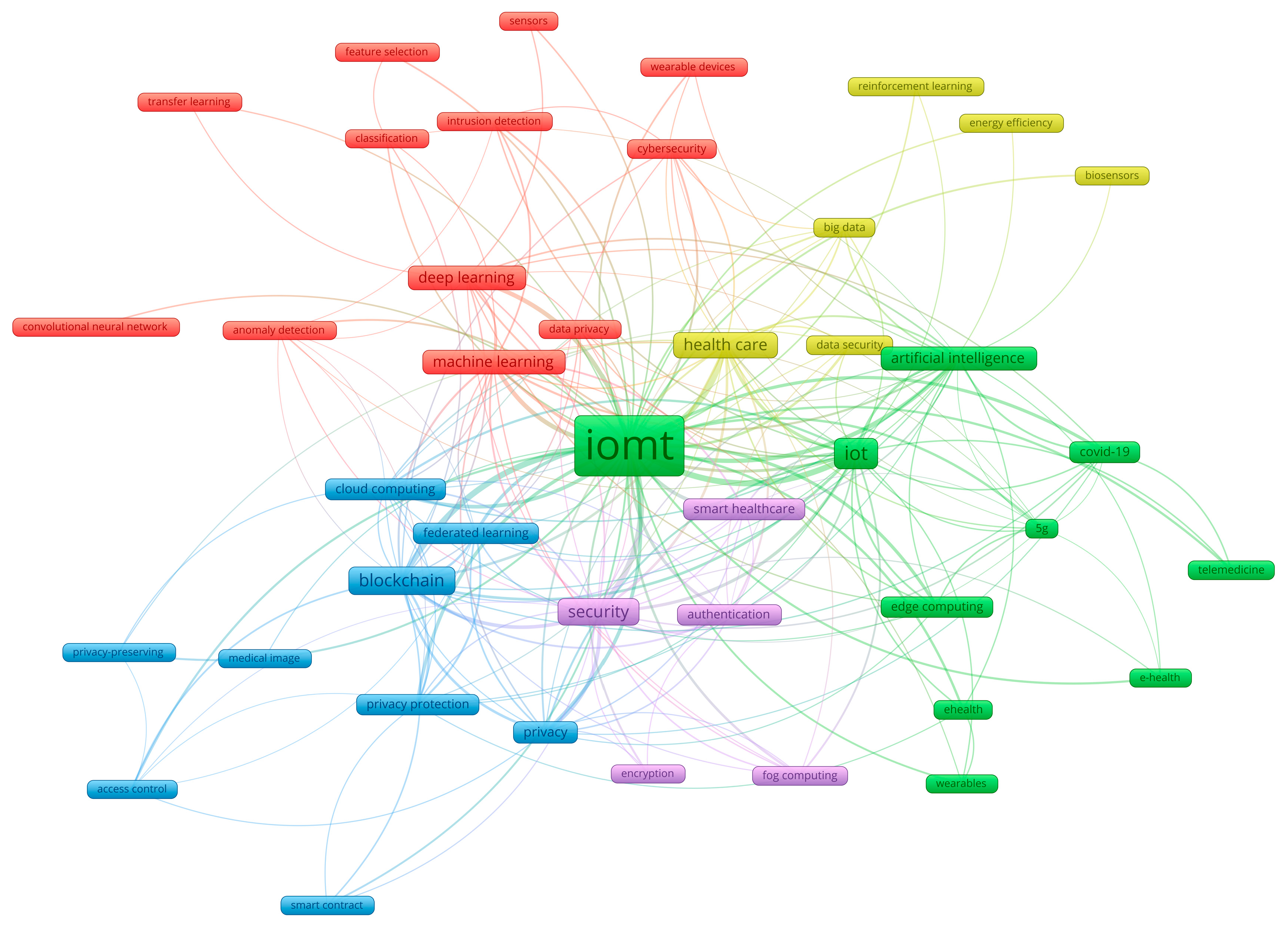
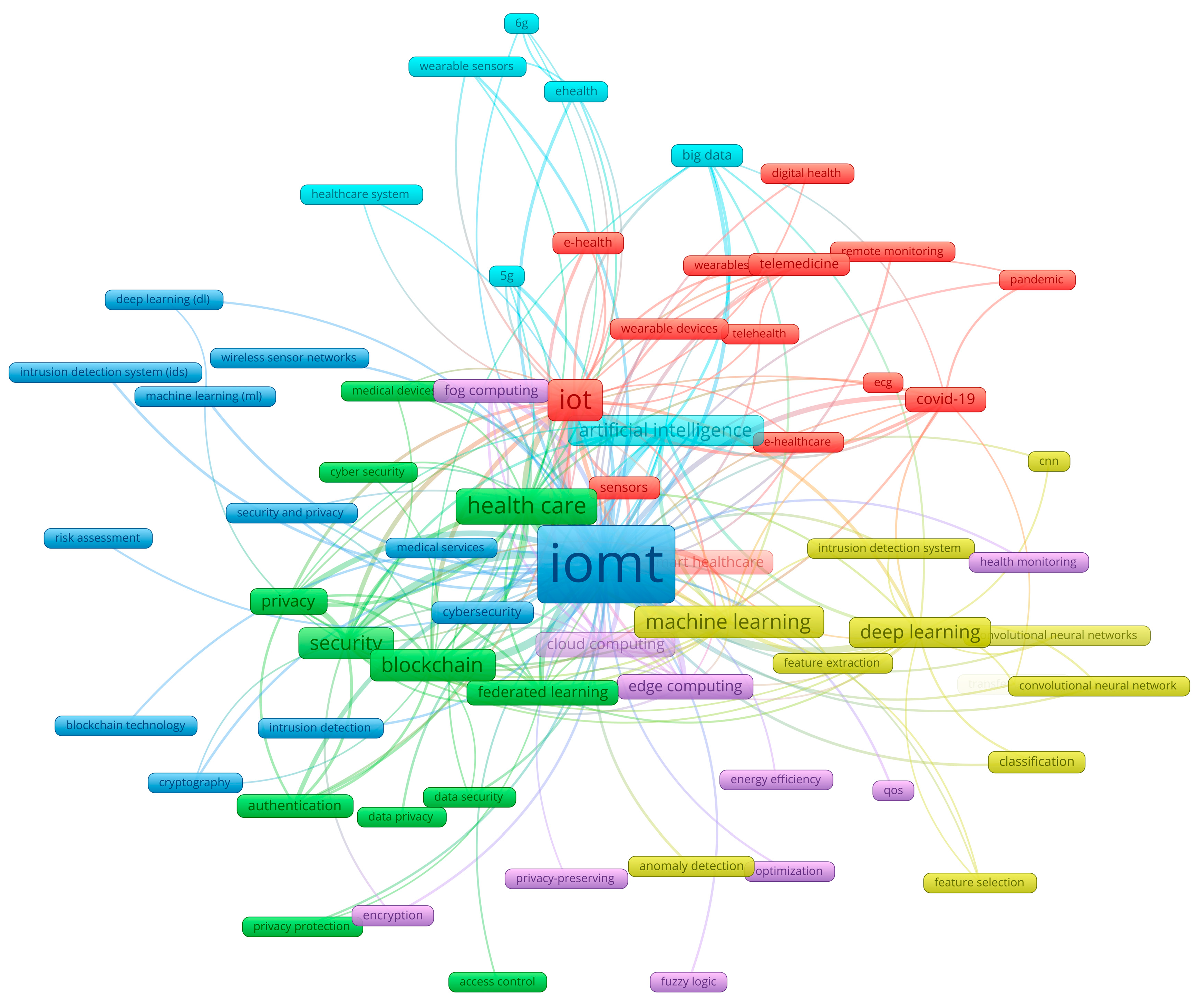

| Document Type | Number of NFPs | % of NFPs | Number of FPs | % of FPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Article | 910 | 46.0% | 602 | 71.5% |
| Conference Paper | 563 | 28.5% | 171 | 20.3% |
| Book Chapter | 300 | 15.2% | 9 | 1.1% |
| Review | 86 | 4.3% | 57 | 6.8% |
| Conference Review | 43 | 2.2% | 0 | 0.0% |
| Book | 33 | 1.7% | 0 | 0.0% |
| Editorial | 17 | 0.9% | 1 | 0.1% |
| Erratum | 11 | 0.6% | 0 | 0.0% |
| Retracted | 7 | 0.4% | 0 | 0.0% |
| Letter | 3 | 0.2% | 0 | 0.0% |
| Note | 3 | 0.2% | 1 | 0.1% |
| Short Survey | 2 | 0.1% | 1 | 0.1% |
| SOURCE TITLE | Number of FPs | SJR | Quarter | H-index | SOURCE TITLE | Number of NFPs | SJR | Quarter | H-index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEEE Access | 70 | 0.96 | 1 | 242 | IEEE Access | 59 | 0.96 | 1 | 242 |
| Sensors | 52 | 0.79 | 1 | 245 | Lecture Notes In Networks And Systems | 58 | 0.17 | 4 | 36 |
| IEEE Internet Of Things Journal | 43 | 3.38 | 1 | 179 | IEEE Internet Of Things Journal | 57 | 3.38 | 1 | 179 |
| Electronics Switzerland | 24 | 0.64 | 2 | 83 | IEEE Journal Of Biomedical And Health Informatics | 40 | 1.96 | 1 | 156 |
| IEEE Journal Of Biomedical And Health Informatics | 20 | 1.96 | 1 | 156 | Communications In Computer And Information Science | 27 | 0.2 | 4 | 69 |
| Future Generation Computer Systems | 19 | 1.95 | 1 | 164 | Internet Of Things | 24 | 1.64 | 1 | 52 |
| Computers Materials And Continua | 17 | 0.46 | 2 | 57 | Electronics Switzerland | 22 | 0.64 | 2 | 83 |
| Applied Sciences MDPI | 14 | 0.51 | 2 | 130 | IEEE Transactions On Industrial Informatics | 21 | 4.42 | 1 | 193 |
| Computer Communications | 13 | 1.40 | 1 | 128 | Lecture Notes In Electrical Engineering | 20 | 0.15 | 4 | 45 |
| Information Sciences | 12 | 2.24 | 1 | 227 | Sensors | 20 | 0.79 | 1 | 245 |
| Average | 1.43 | 1.3 | 161.1 | Average | 1.431 | 2 | 130 |
| Funded/Nonfunded publication | COUNTRY/TERRITORY | Number of NFPs | Scimago rank in subject Medicine | Scimago rank in sub-subject Computer networks and communications | Health systems ranking 2023 [18] | Current Health Expenditure as % of GDP - 2021/22 | Current R&D Expenditure as % of GDP - 2021/22 [19] | BGHI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NFP | India | 849 | 11 | 3 | 112 | 3.28 | 0.65 | 61.3 |
| NFP | United States | 213 | 1 | 2 | 69 | 16.57 | 3.45 | 79.5 |
| NFP | China | 192 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 5.38 | 2.43 | 46.3 |
| NFP | Saudi Arabia | 145 | 35 | 27 | 56 | 5.97 | 0.46 | 77.2 |
| NFP | Pakistan | 112 | 40 | 30 | 124 | 2.91 | 0.16 | 61.5 |
| NFP | United Kingdom | 93 | 3 | 6 | 34 | 11.34 | 2.91 | 88.8 |
| NFP | Australia | 73 | 9 | 13 | 21 | 10.54 | 3.25 | 90.9 |
| NFP | Iraq | 69 | 65 | 50 | 115 | 5.25 | 0.04 | 62.8 |
| NFP | Italy | 63 | 6 | 8 | 17 | 9.00 | 1.45 | 91.5 |
| NFP | Malaysia | 62 | 42 | 16 | 42 | 4.38 | 0.59 | 84.2 |
| AVERAGE | 21.4 | 15.6 | 59.5 | 7.462 | 1.539 | 74.4 | ||
| FP | China | 280 (57.1%) | 2 | 1 | 5 | 5.38 | 2.43 | 46.3 |
| FP | Saudi Arabia | 176 (52.1) | 35 | 27 | 56 | 5.97 | 0.46 | 77.2 |
| FP | India | 171 (20.0%) | 11 | 3 | 112 | 3.28 | 0.65 | 61.3 |
| FP | United States | 127 (36.3%) | 1 | 2 | 69 | 16.57 | 3.45 | 79.5 |
| FP | South Korea | 88 (69.3%) | 14 | 9 | 3 | 9.72 | 4.93 | 94.3 |
| FP | Pakistan | 75 (38.9%) | 40 | 30 | 124 | 2.91 | 0.16 | 61.5 |
| FP | United Kingdom | 66 (40.2%) | 3 | 6 | 34 | 11.34 | 2.91 | 88.8 |
| FP | Italy | 49 (42.2%) | 6 | 8 | 17 | 9 | 1.45 | 91.5 |
| FP | Egypt | 44 (48.4%) | 33 | 36 | 107 | 4.61 | 1.02 | 64.6 |
| FP | Malaysia | 42 (37.5%) | 42 | 16 | 42 | 4.38 | 0.59 | 84.2 |
| AVERAGE | 14 | 10.75 | 52.5 | 8.02125 | 2.055 | 74.9 |
| FPs Themes | Representative topics identified in prominent publications | NFPs themes | Representative topics identified in prominent publications |
|---|---|---|---|
| IoMT and AI use in e-health and telemedicine | ECG monitoring [25], e-health patient monitoring [26], elderly healthcare [27], Accident and emergency detection in One digital health [28] | Role of IoMT in pandemic management | Point of care testing of infectious diseases [29], Cognitive IoMT for pandemic management [30], Pandemic forecasting [31], Covid-19 management by federated learning [32] |
| Privacy in federated learning | Skin diseases [33], Smart healthcare [34], ECG classification [35], Misbehaviour detection [36], Heart disease diagnosing [37] | Privacy and security within federated learning | Privacy preservation with fraud enabled blockchain [38]. Privacy preservation in smart healthcare [39], Intrusion detection [40], Privacy sensitive federated learning [41] |
| Security in smart health care | Blockchain industrial secure encryption in healthcare [42], Hybrid authentication for digital healthcare [43], Threat detection in IoMT networks [44], Secure intelligent biosensors [45] | Machine learning detection of cybersecurity treads on IoMT applications | Cybersecurity of healthcare 5.0 systems using federated learning [46,47]. Tree classifier based intrusion detection in IoMT [48]. Multilayer perceptron optimisation for cybersecurity [49] |
| Secure big data analysis in healthcare | security threats, vulnerabilities, and counter measures [50], Blockchain, Blockchain assisted big data management [51], Healthcare in Smart Cities [52] | Big data analysis of data from wearable sensors for eHealth | Ambient assisted living [53], edge-stream computing for real time analysis of wearable data [54], big and wearable data in gynaecology [55], Big data based Smart Health Monitoring [56] |
| Advanced machine learning and data security in accessing data from wearables and sensors | Secure wearable ultrasound system [57], Privacy preserving federated learning [58], Robust zero watermarking for federated learning [59], Scalable transferable federated learning in classification of healthcare IoMT data [60] | Advanced machine learning | Remote patient monitoring [61,62]. Lung tumour diagnosing [63], Digitalization [64] |
| National Natural Science Foundation of China, China | 167 |
| National Science Foundation, USA | 45 |
| National Research Foundation of Korea,” Korea | 40 |
| National Key Research and Development Program of China, China | 36 |
| King Saud University, Saudi Arabia | 35 |
| Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, China | 33 |
| Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia | 32 |
| European Commission, EU | 29 |
| Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, South Korea | 25 |
| Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China | 24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





