Introduction
Hypophosphatasia is a rare inherited disorder characterized by defective bone mineralization and a deficiency of tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) activity [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. The diagnosis of hypophosphatasia can be challenging due to its unspecific clinical presentation, with musculoskeletal pain being a common symptom in adult patients [
6,
7,
8,
9]. Low serum alkaline phosphatase activity is often the first indicator leading to a suspicion of hypophosphatasia [
10]. Adult patients with hypophosphatasia require comprehensive management that includes assessing bone and joint complications, chronic pain, and mood disorders [
11,
12]. Diagnostic delays are common in hypophosphatasia, emphasizing the need for increased awareness and timely identification of the condition [
13]. Atypical femoral fractures have been reported in adult patients with hypophosphatasia, highlighting the importance of considering this condition in cases of unusual fractures, especially during bisphosphonate exposure [
14,
15]. Furthermore, the use of asfotase alfa has shown success in treating adult patients with childhood-onset hypophosphatasia, indicating the potential for enzyme replacement therapy in managing this condition [
16,
17,
18]. In this paper, we present a retrospective analysis spanning fifteen years focusing on screening for hypophosphatasia in adult patients at a maximum care provider. By examining the clinical, biochemical, and genetic spectrum of hypophosphatasia in adults, we aim to contribute to the understanding and management of this rare metabolic disorder. In particular, efforts will be made to identify the challenges of laboratory diagnostic criteria using broad-available laboratory parameters.
Materials and Methods
Patients and Study Groups
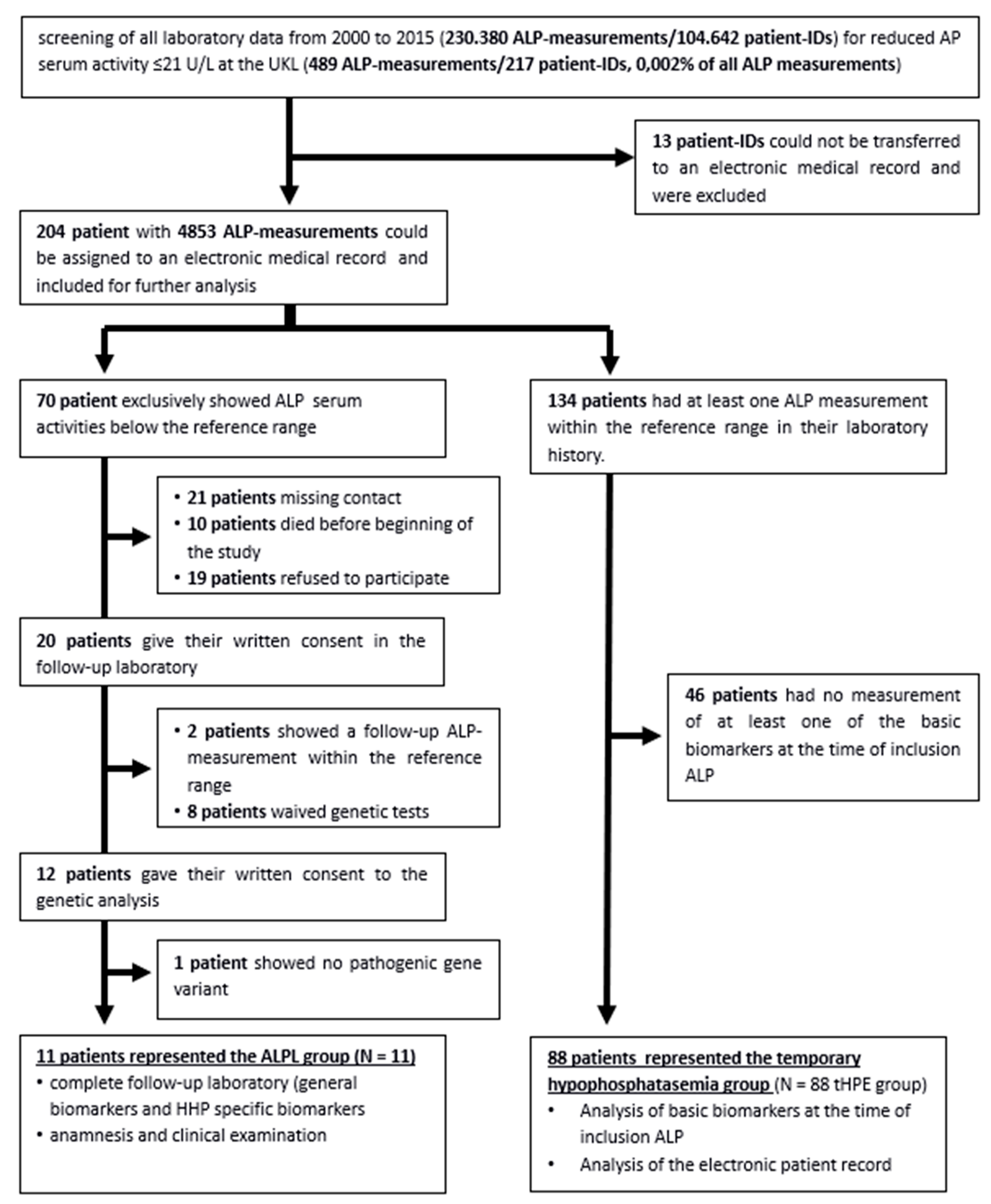
This retrospective study was approved by the local ethics committee (no. 508/16-ek). All laboratory data of adult patients (older than 18 years) of the University Hospital Leipzig (UHL) for the years 2000–2015 were retrospectively analysed to identify patients with ALP serum activity ≤ 21 U/L. The study cut-off of 21 U/L was based on reports from adult patients with confirmed clinical manifestations of severe HPP [
14]. Hemoglobin (HB), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT), calcium, phosphate, thyrotropin (TSH), albumin, total protein and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were defined as general biomarkers and measured at baseline and at follow-up.
All ALP levels available at the UHL were analysed. The reference range was 35–105 U/L for healthy women and 40–130 U/L for healthy men [
19,
20]. 204 patients with at least one measured ALP serum activity < 21 U/L were selected [
18]. In cases of multiple ALP serum activities, the lowest was used as the inclusion value. After analysis of the medical history, 134 (66%) of the 204 patients had physiological ALP levels as defined by tHPE. 46 of them had no measurement of other common biomarkers and were therefore excluded. In 88 of them, at least one of the general biomarkers was measured simultaneously. They were included in the
temporary hypophosphatasemia group (N = 88,
tHPE group).
Twenty of the remaining 70 patients with only decreased ALP levels were contacted and agreed to participate in a follow-up examination, including a medical history and a follow-up laboratory test (flowchart). Eighteen of these showed a decrease in ALP at follow-up and have been further investigated. Two had ALP levels within reference ranges at follow-up and were excluded.
Methods
Blood samples were taken between 8:00 and 10:00 am after a 12-hour fast. Two S-Monovettes® 2.7 ml K3EDTA and one S-Monovette® 4.7 ml serum (Sarstedt AG & Co. KG, Postfach 1220, D-51588 Nümbrecht) were used. All biomarkers were measured at the Institute of Laboratory Medicine, Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics (ILM), UHL, using commercially certified biochemical assays. The determination of ALP activity in serum was performed using the “Alkaline Phosphatase according to IFCC Gen.2 ALP2” kit (Roche Diagnostics Deutschland GmbH) on a cobas® c501 instrument using the release of p-nitrophenol after cleavage of p-nitrophenyl phosphate by the enzyme. The product can be quantified by extinction.
PLP levels were measured using the Vitamin B6 in Serum/Plasma HPLC kit (Chromsystems Instruments & Chemical, Gräfelfing, Germany). After protein precipitation, vitamin B6 was derivatised and separated by HPLC. Quantitation was performed by fluorescence (415 nm).
The Ostase® BAP EIA assay (Immunodiagnostic Systems Holdings, UK) was used to quantify BALP. BALP was purified by immunosorbent assay (EIA) using biotin-linked monoclonal antibodies and quantified using the same enzyme assay described for ALP.
The genetic analysis was performed at the Institute of Human Genetics at the UHL by targeted enrichment of the gene target regions of the human exome plus adjacent intronic regions (+/- 10 bp) using the TruSight®One enrichment kit (Illumina Inc., San Diego, California, USA). More than 95% of the target regions were covered at least twenty-fold. Sequencing was performed on a NextSeq550 sequencing instrument (Illumina Inc., San Diego, California, USA) using 150 base pair paired-end reads. Varvis software (Limbus Medical Technologies GmbH, Rostock, Germany) was used for bioinformatic analysis.
Statistics
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS (version 24, IBM) for Windows (Microsoft). Independent samples with normal distribution were calculated using the two-tailed t-test, and frequency differences were calculated using the chi-squared test.
Results
Comparison of tHPE-Group and ALPL-Group
Within and between the tHPE and ALPL groups, the sex and age distributions were statistically comparable (
Table 1; p > 0.05). The frequencies of pathological findings for the general biomarkers were equally distributed between the sexes in both the tHPE and ALPL groups (p > 0.05). Therefore, sex-specific analysis was not performed. Pathological values for HB, ALT, AST, creatine, calcium, albumin, total protein and CRP occurred significantly more frequent in the tHPE group than in the ALPL group (p ≤ 0.05;
Table 2). The mean levels of HB, ALP, AST, calcium, albumin and total protein were lower in the tHPE group than in the ALPL group (p < 0.05;
Table 2). However, analysis of serum concentrations of CRP showed significantly higher values in the tHPE group (p ≤ 0.05). No significant differences were found between the tHPE and ALPL groups for creatinine, GGT and TSH levels (p > 0.05;
Table 2).
In contrast to the ALPL group, all patients in the tHPE group had known additional diseases independent of HPP that are typical of tHPE, such as severe anaemia, sepsis, and gastrointestinal, haematological, and rheumatological diseases (
Table 1).
Patients of the ALPL-Group
All patients in the ALPL group (N = 11) exhibited a heterozygous pathological variant in the ALPL gene. Eight distinct pathological variants were identified, each associated with pathological values in the HPP-specific laboratory. Patient characteristics are detailed in
Table 3. Furthermore, all patients in the ALPL group exhibited clinical symptoms consistent with suspected HPP (100% recurrent musculoskeletal complaints, 27% premature caries, and a 9% prevalence of premature loss of primary teeth). At the start of the study, none of the patients in the ALPL group had a known history of HPP or permanent ALP reduction.
In the ALPL group, HB, ALT, calcium, albumin, total protein and CRP were within reference ranges in all follow-up laboratory data. Three patients (27%) had elevated GGT levels, two (18%) had elevated phosphate levels, one (9%) had decreased phosphate levels, one (9%) had elevated TSH or AST levels and one (9%) had elevated creatinine levels at follow-up. All patients in this group had decreased BALP levels and/or increased PLP levels.
Discussion
A persistent reduction in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity level is a hallmark feature of hypophosphatasia (HPP) [
12]. This is a crucial factor in differentiating HPP from other diseases, such as rickets [
19]. In clinical practice, it is essential to pay close attention to borderline or marginally reduced ALP values, as these may be indicative of hypophosphatasia and could otherwise be overlooked [
9].
The causes of low ALP are numerous and vary according to the temporality of hypophosphatasaemia (tHPE) [
3,
8]. The prevalence of hypophosphatasaemia of any cause is reported to be 1.18% to 8.46% [
8,
20]. In the authors opinion, first, it is essential that the assessment of a reduced ALP level takes into account other serum parameters that could represent differential diagnoses. This study shows that HB, AST, calcium, albumin, total protein and CRP were significantly more often in the physiological range in patients carrying a heterozygous ALPL pathogenic variant than in patients with tHPE. Thus, if the serum activity of ALP is decreased and these other values are within the reference range, a pathogenic variant in the ALPL gene is highly suspected in these cases, which may be a sign of possible HPP. On the other hand, if serum ALP activity is decreased and the other values are in the pathological range, a differential diagnosis other than HPP should be considered. The results presented here are consistent with the laboratory and clinical findings reported by Larid et al. and represent a valuable contribution to this existing body of knowledge [
8,
12].
To our knowledge, this is the first study to present general biomarkers that can be used for the first-line assessment of reduced ALP activity in relation to possible HPP-causing ALPL gene pathogenic variants in adults.
Differential Diagnosis of HPE
The results of the present study align with those of previous research, which suggests that a single reduction in ALP activity does not necessarily indicate the presence of hypophosphatemia (HPP). The proportion of patients with transient hypophosphatasaemia (tHPE) was shown to be between 66.7% and 72.4% which is consistent with the demonstrated 66% [
8,
21,
22]. There are numerous reasons for the transient HPE study conducted by Lum et al. (1995) revealed that in 47% of patients with tHPE, other medical conditions accounted for the observed decline in ALP values [
8,
23]. These included cardiac surgery and cardiopulmonary bypass (26.5%), malnutrition (12.0%), magnesium deficiency (4.8%), hypothyroidism (2.4%) and severe anemia (1.2%). A total of 53% of cases exhibited no identifiable cause for tHPE In contrast to the present study, no patients in the study by Lum et al. exhibited clinically overt HPP [
23]. McKiernan et al. (2014) identified numerous conditions that may potentially cause tHPE, including anaemia, major surgery, multisystem failure, tumours, sepsis, disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, gastrointestinal bleeding, severe caloric restriction, and blood transfusion [
3]. It is important to note that these non-physiological conditions are usually reflected by the biomarkers investigated in the present study, as detailed in
Table 2. Therefore, it is essential to consider these factors when assessing reduced ALP levels [
3].
Furthermore, McKiernan et al. (2014) showed that tHPE is associated with a more severe reduction in ALP to 10 U/L and increased mortality compared to patients with HPP [
3]. According to recent literature, mean ALP levels in adult patients with confirmed HPP ranged from 27.8 U/L to 28.5 U/L, which is comparable to the mean ALP level of 22 U/L in the ALPL group studied [
12]. However, it should be noted that a massively reduced ALP may also indicate a homozygous form of HPP or a childhood form diagnosed in adulthood [
7]. It has also been suggested that ALP reduction may occur in up to 43% of patients receiving bisphosphonate therapy [
24]. Therefore, the significantly lower ALP levels in the tHPE group are consistent with literature data and do not automatically imply HPP.
Offered Diagnostic Approach for a Suspected ALPL Gene Mutation
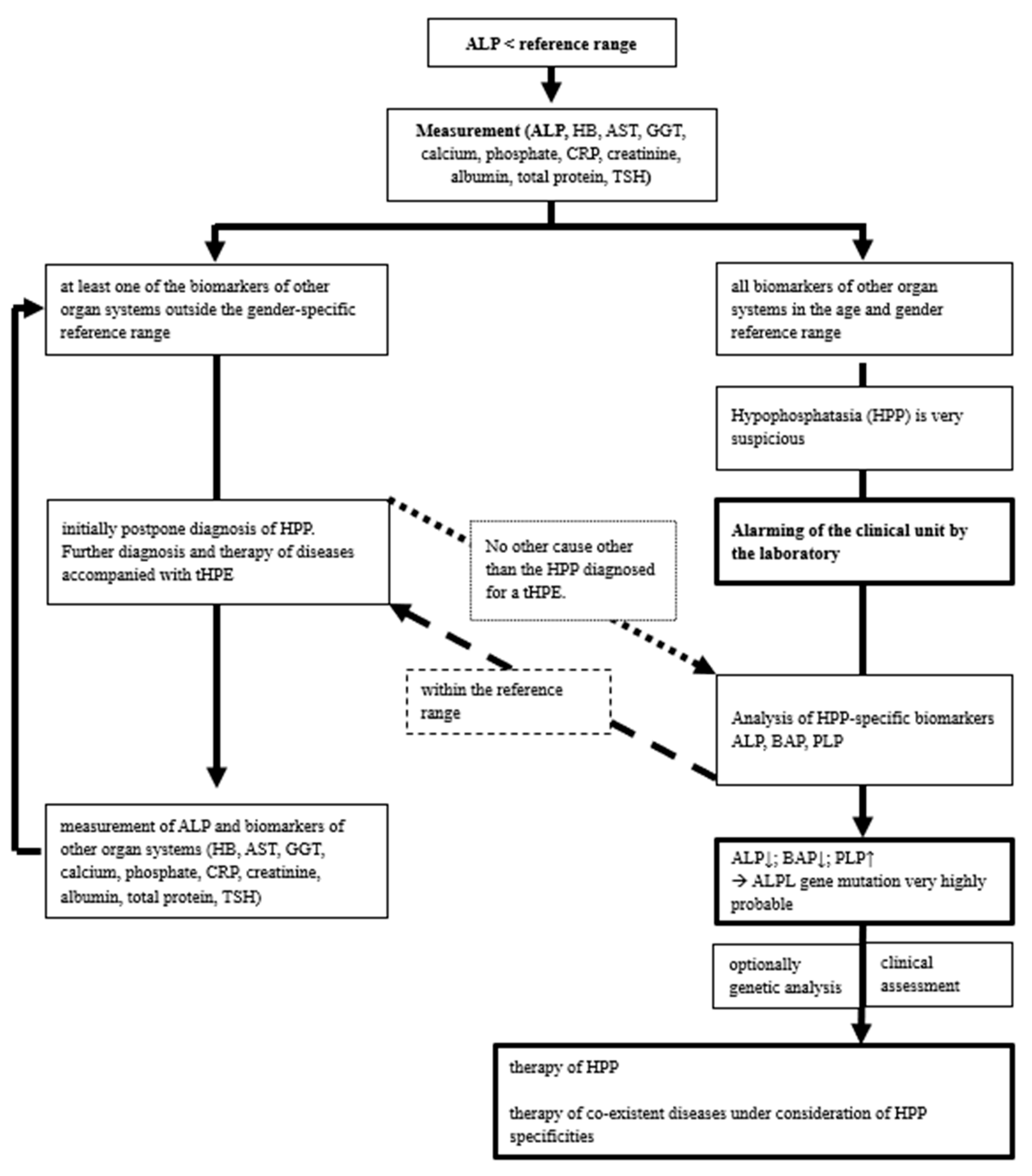
In the case of persistently low ALP values, HPP-specific diagnostics with BALP, PLP and PEA are usually recommended [
18]. In summary, HPP-specific diagnostics are expensive, time-consuming, and not available universally. Considering the presented results, it can be argued that the reduction in alkaline phosphatase activity should be assessed in conjunction with a number of additional biomarkers. Of particular interest here are biomarkers that enable a differential diagnosis to be made. These include the levels of haemoglobin, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), calcium, albumin and total serum protein, as well as the levels of C-reactive protein (CRP).
First, in patients where a reduced alkaline phosphatase (ALP) has been identified alongside other general parameters within the reference range, a specific hypophosphatasia (HPP) diagnosis can be recommended. Second, in patients with one or more general parameters in the pathological range in addition to reduced ALP, further investigation of the treatable differential diagnoses (
Table 1) is strongly recommended. Following the targeted treatment of the differential diagnoses, a re-measurement of the biomarkers is recommended. iin the event, that the general biomarkers normalize concurrently with persistently low ALP levels, a pathogenic variant of the ALPL gene remains a probable explanation. In both situations, it is recommended that an extended HPP-specific diagnostic work-up be performed, including BALP and PLP levels [
25]. A diagnosis of HPP can be made in the presence of additional clinical symptoms that are characteristic of the HPP. In rare cases, a pathogenic variant of the ALPL gene can coexist with pathological values of the general biomarkers presented. In such cases, genetic analysis is recommended according to the literature. However, if the patient presents with clinical and laboratory findings consistent with a diagnosis of HPP, it is not recommended that genetic analysis be conducted as a routine procedure [
5,
26,
27].
Limitations of the Study
It should be noted that this study is not without limitations. Primarily, the retrospective design of the study may have introduced discrepancies in the number of observations for the various parameters, potentially affecting the validity of our conclusions. The precise number of patients who had their alkaline phosphatase levels measured at the UHL during the specified period could not be ascertained. During the inclusion period, software modifications were implemented, creating challenges in accessing historical data. The present study identified 10,464 cases in which at least one ALP determination was performed. Of these, 217 exhibited an ALP serum activity level of ≤ 21 U/L (0.2%). This information would have been interesting to estimate the frequency of low levels and how often they were ignored. Another drawback, despite the significant differences, was the number of patients who agreed to be followed up. While this was still relatively high in the tHPT group (88), only 11 patients in the ALPL group were available for complete data collection. Furthermore, the selected screening cut-off of 21 U/L has the potential to result in an underdiagnosis of patients exhibiting milder reductions in ALP activity due to a pathogenic variant of the ALPL gene. The results suggest that the prevalence of moderate forms of genetic HPP in adults is likely to be higher than previously assumed, highlighting the necessity for greater attention to be paid to the value of ALP [
8].
It should be noted that the presented algorithm cannot be applied unreservedly to forms of HPP resulting from homozygous or compound heterozygous ALPL variants. The patients presented with an oligosymptomatic mild form of HPP in the presence of a heterozygous mutation, a finding that is consistent with data in the literature [
26,
28,
29]. Given the genetic heterogeneity of the disease, a genetically based nosology of HPP, as suggested by Mornet et al., may be a useful approach [
26]. Nevertheless, the clinical relevance of such an entity also remains to be seen in the context of patient-specific, individualized therapy, which should be the subject of further investigation. The validity of the presented algorithm for this purpose must be corroborated by prospective studies, ideally including a comprehensive genetic diagnosis for tHPE.
Conclusion
The results of this unicentric retrospective study indicate that oligosymptomatic HPP remains undiagnosed in adults. A heterozygous pathogenic ALPL gene variant is associated with persistently low ALP activity and mostly reference-value routine biomarkers (HB, AST, calcium, albumin, total protein and CRP). Persistently low ALP activity, particularly in the context of unexplained musculoskeletal pain, should raise suspicion of hypophosphatasia and prompt further diagnostic investigations.
Figure 1.
Overview of our recommended laboratory algorithm for the evaluation of a single low serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity (hypophosphatasemia, HPE) in the setting of a pathogenic variant of the ALPL gene and possible differential diagnosis of temporary hypophosphatasemia (tHPE).
Figure 1.
Overview of our recommended laboratory algorithm for the evaluation of a single low serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity (hypophosphatasemia, HPE) in the setting of a pathogenic variant of the ALPL gene and possible differential diagnosis of temporary hypophosphatasemia (tHPE).
Flowchart: Flow chart of the assessment of the patients and the resulting study groups, UHL = University Hospital of Leipzig.
Conflicts of Interests
Hennings R and Roth A have received research grants from Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc. in New Haven, CT, USA. Neither author has received any honoraria or travel support for lectures or consultancy from Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc. Lemke JR, Le Duc D, Kratzsch J, Tönjes A and Thiery J declare no conflicts of interest.
Author Contributions
Robert Hennings, MD contributed significantly to the idea, planning and data collection of this paper. Furthermore, he contributed significantly to the preparation of the manuscript, literature research, analysis and interpretation of the data. Johannes (Lemke JR) Lemke and Diana-Gabriela (Le Duc D) Le Duc made a significant contribution to the genetic analysis of the present work. Joachim (Thiery J) Thiery and Anke (Tönjes A) Tönjes contributed to the realisation and final proof of the manuscript. Jürgen (Kratzsch J) Kratzsch *; Prof. Dr. rer. nat. contributed significantly to the idea, planning and data collection of this paper. Furthermore, he contributed significantly to the preparation of the manuscript and final proof of the manuscript. Andreas (Roth A) Roth*; Prof. Dr. med. contributed significantly to the idea and planning of this study. Furthermore, he contributed significantly to the preparation of the manuscript, analysis and interpretation of the data as well as final proof of the manuscript. * Both authors contributed equally to this work and should be considered equal senior authors in sense of shared senior authorship.
Acknowledgment
We thank all the patients who participated in this study. We would also like to thank our colleagues at the Institute of Laboratory Medicine, Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics at the University of Leipzig, especially Dr Anja Willenberg, for their support in data analysis.
References
- Maman E, Borderie D, Roux C, Briot K. Absence of recognition of low alkaline phosphatase level in a tertiary care hospital. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27:1251–4. [CrossRef]
- González-Cejudo T, Villa-Suárez JM, Ferrer-Millán M, Andújar-Vera F, Contreras-Bolívar V, Andreo-López MC, et al. Mild hypophosphatasia may be twice as prevalent as previously estimated: an effective clinical algorithm to detect undiagnosed cases. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM) [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 Sep 30];0. Available from:. [CrossRef]
- McKiernan FE, Shrestha LK, Berg RL, Fuehrer J. Acute hypophosphatasemia. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25:519–23. [CrossRef]
- Lia-Baldini A, Muller F, Taillandier A, Gibrat J, Mouchard M, Robin B, et al. A molecular approach to dominance in hypophosphatasia. Hum Genet. 2001;109:99–108. [CrossRef]
- Whyte, MP. Hypophosphatasia and the Role of Alkaline Phosphatase in Skeletal Mineralization*. Endocrine Reviews. 1994;15:439–61.
- Berkseth KE, Tebben PJ, Drake MT, Hefferan TE, Jewison DE, Wermers RA. Clinical spectrum of hypophosphatasia diagnosed in adults. Bone. 2013;54:21–7. [CrossRef]
- Weber TJ, Sawyer EK, Moseley S, Odrljin T, Kishnani PS. Burden of disease in adult patients with hypophosphatasia: Results from two patient-reported surveys. Metabolism. 2016;65:1522–30. [CrossRef]
- Larid G, Vix J, Preuss P, Robin F, Tison A, Delaveau C, et al. Detection of hypophosphatasia in hospitalised adults in rheumatology and internal medicine departments: a multicentre study over 10 years. RMD Open. 2024;10:e004316. [CrossRef]
- Feurstein J, Behanova M, Haschka J, Roetzer K, Uyanik G, Hadzimuratovic B, et al. Identifying adult hypophosphatasia in the rheumatology unit. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022;17:435. [CrossRef]
- Riancho-Zarrabeitia L, García-Unzueta M, Tenorio JA, Gómez-Gerique JA, Ruiz Pérez VL, Heath KE, et al. Clinical, biochemical and genetic spectrum of low alkaline phosphatase levels in adults. European Journal of Internal Medicine. 2016;29:40–5. [CrossRef]
- Galeano-Valle F, Vengoechea J, Galindo RJ. A rare mutation in hypophosphatasia: a case report of adult form and review of the literature. Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2019;63:89–93. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt T, Mussawy H, Rolvien T, Hawellek T, Hubert J, Rüther W, et al. Clinical, radiographic and biochemical characteristics of adult hypophosphatasia. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28:2653–62. [CrossRef]
- Högler W, Langman C, Gomes Da Silva H, Fang S, Linglart A, Ozono K, et al. Diagnostic delay is common among patients with hypophosphatasia: initial findings from a longitudinal, prospective, global registry. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20:80. [CrossRef]
- Sutton RA, Mumm S, Coburn SP, Ericson KL, Whyte MP. “Atypical femoral fractures” during bisphosphonate exposure in adult hypophosphatasia. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27:987–94.
- Whyte MP, Wenkert D, McAlister WH, Mughal MZ, Freemont AJ, Whitehouse R, et al. Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis Mimicked in Childhood Hypophosphatasia. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2009;24:1493–505. [CrossRef]
- Remde H, Cooper MS, Quinkler M. Successful Asfotase Alfa Treatment in an Adult Dialysis Patient With Childhood-Onset Hypophosphatasia. Journal of the Endocrine Society. 2017;1:1188–93. [CrossRef]
- Orimo, H. Pathophysiology of hypophosphatasia and the potential role of asfotase alfa. TCRM. 2016;777. [CrossRef]
- Whyte, MP. Hypophosphatasia: Enzyme Replacement Therapy Brings New Opportunities and New Challenges: ENZYME REPLACEMENT THERAPY FOR HYPOPHOSPHATASIA. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32:667–75.
- Chen H, Han Y, Li X, Liu X, Feng W, Xu W. Hypophosphatasia. Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42:317–8.
- Schmidt T, Schmidt C, Amling M, Kramer J, Barvencik F. Prevalence of low alkaline phosphatase activity in laboratory assessment: Is hypophosphatasia an underdiagnosed disease? Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021;16:452.
- McKiernan FE, Berg RL, Fuehrer J. Clinical and Radiographic Findings in Adults With Persistent Hypophosphatasemia: HYPOPHOSPHATASEMIA; CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29:1651–60.
- Vieira LHR, Peixoto KC, Flósi CL, Farias MLFD, Madeira M. Active search of adult patients with persistently low serum alkaline phosphatase levels for the diagnosis of hypophosphatasia. Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2024 Aug 2]; Available from: https://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2359-39972021005005203&lng=en&nrm=iso.
- Lum, G. Significance of low serum alkaline phosphatase activity in a predominantly adult male population. Clinical Chemistry. 1995;41:515–8. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya T, Jha S, Wang H, Kastner DL, Remmers EF. Hypophosphatasia and the risk of atypical femur fractures: a case–control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:332. [CrossRef]
- Beck C, Morbach H, Stenzel M, Schneider P, Collmann H, Girschick G, et al. Hypophosphatasie. Klin Padiatr. 2009;221:219–26.
- Mornet E, Taillandier A, Domingues C, Dufour A, Benaloun E, Lavaud N, et al. Hypophosphatasia: a genetic-based nosology and new insights in genotype-phenotype correlation. Eur J Hum Genet. 2021;29:289–99. [CrossRef]
- Deeb A, Elfatih A. Could Alerting Physicians for Low Alkaline Phosphatase Levels Be Helpful in Early Diagnosis of Hypophosphatasia? Jcrpe. 2018;10:19–24.
- Taillandier A, Domingues C, De Cazanove C, Porquet-Bordes V, Monnot S, Kiffer-Moreira T, et al. Molecular diagnosis of hypophosphatasia and differential diagnosis by targeted Next Generation Sequencing. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 2015;116:215–20. [CrossRef]
- Taillandier A, Domingues C, Dufour A, Debiais F, Guggenbuhl P, Roux C, et al. Genetic analysis of adults heterozygous for ALPL mutations. J Bone Miner Metab. 2018;36:723–33. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).