Submitted:
04 October 2024
Posted:
04 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Descriptions
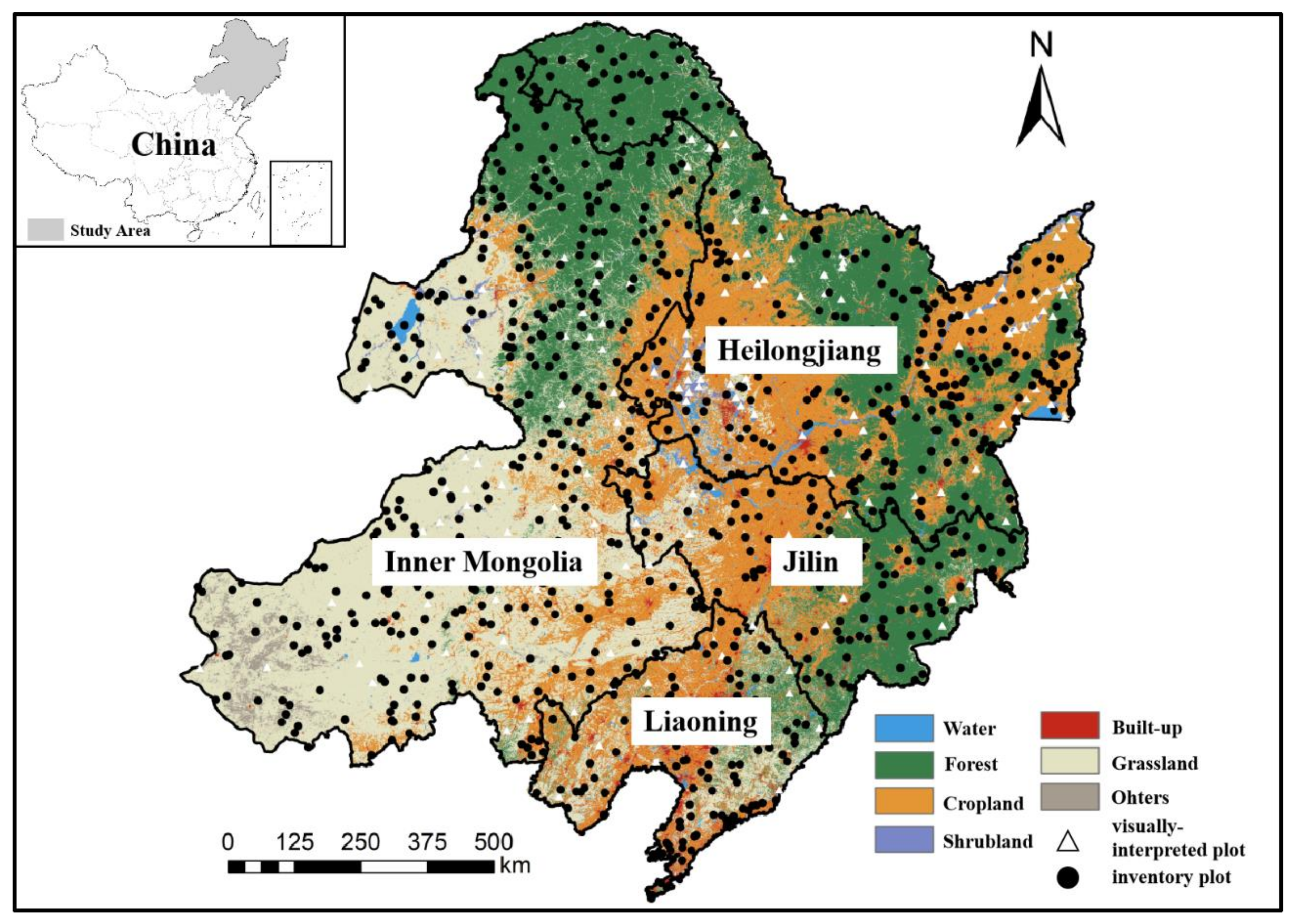
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Descriptions
2.2.1. Statistical Data
2.2.2. Geospatial Datasets
2.2.3. The Sampling Plot Datasets
3. Methods
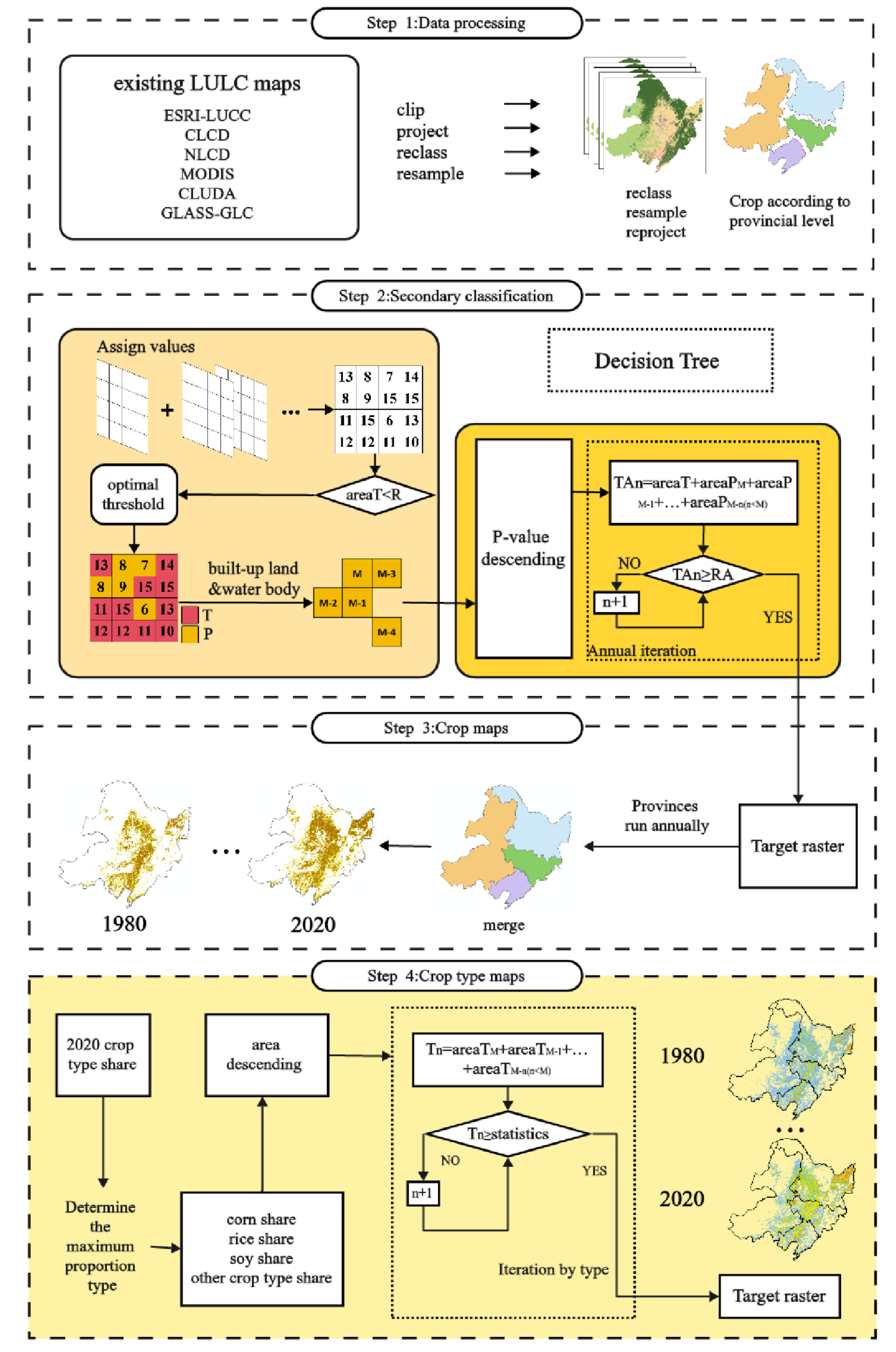
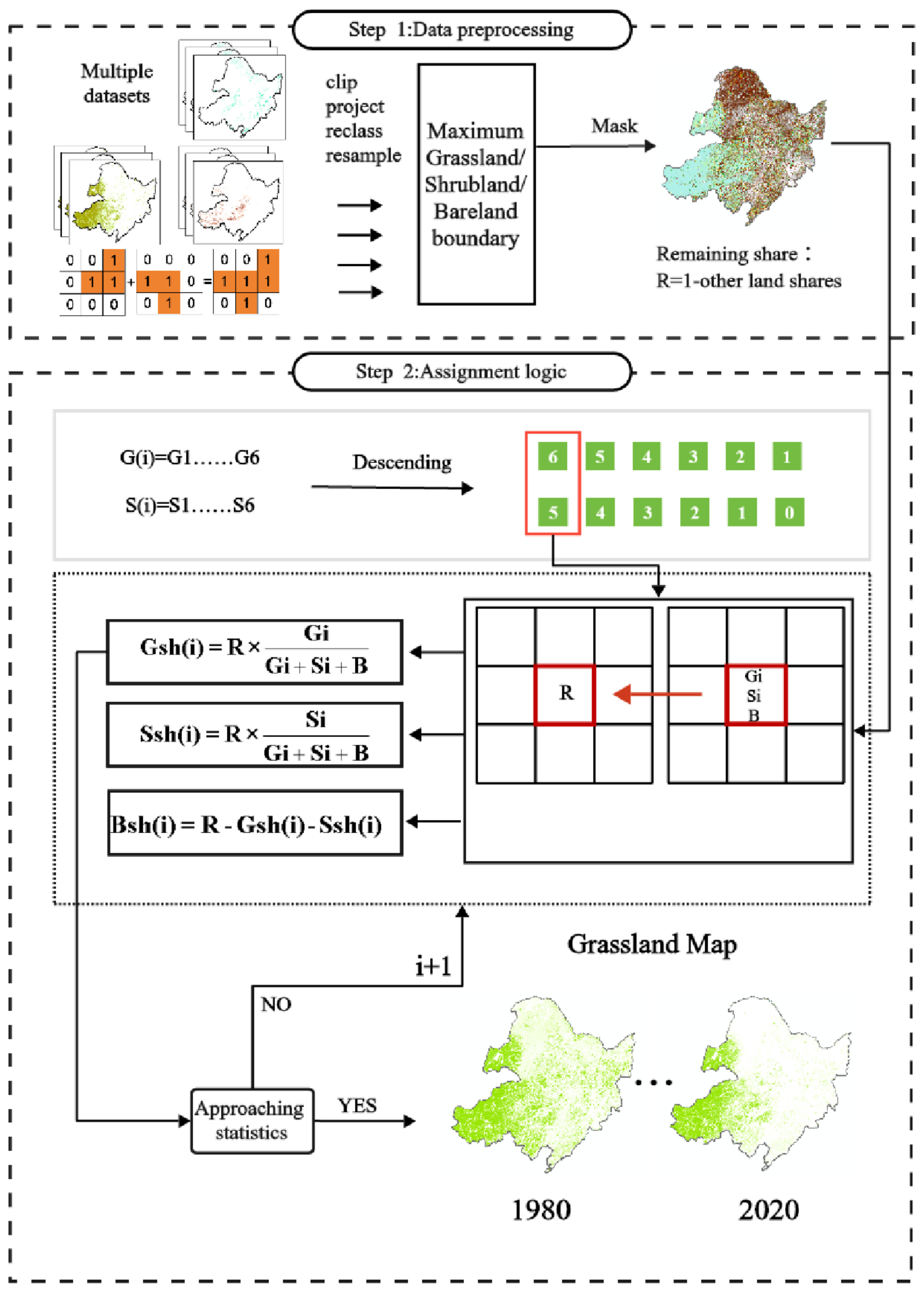
3.1. Hierarchical Assignment Method for Cropland Share Dataset
3.2. Built-Up Land and Water Body Share
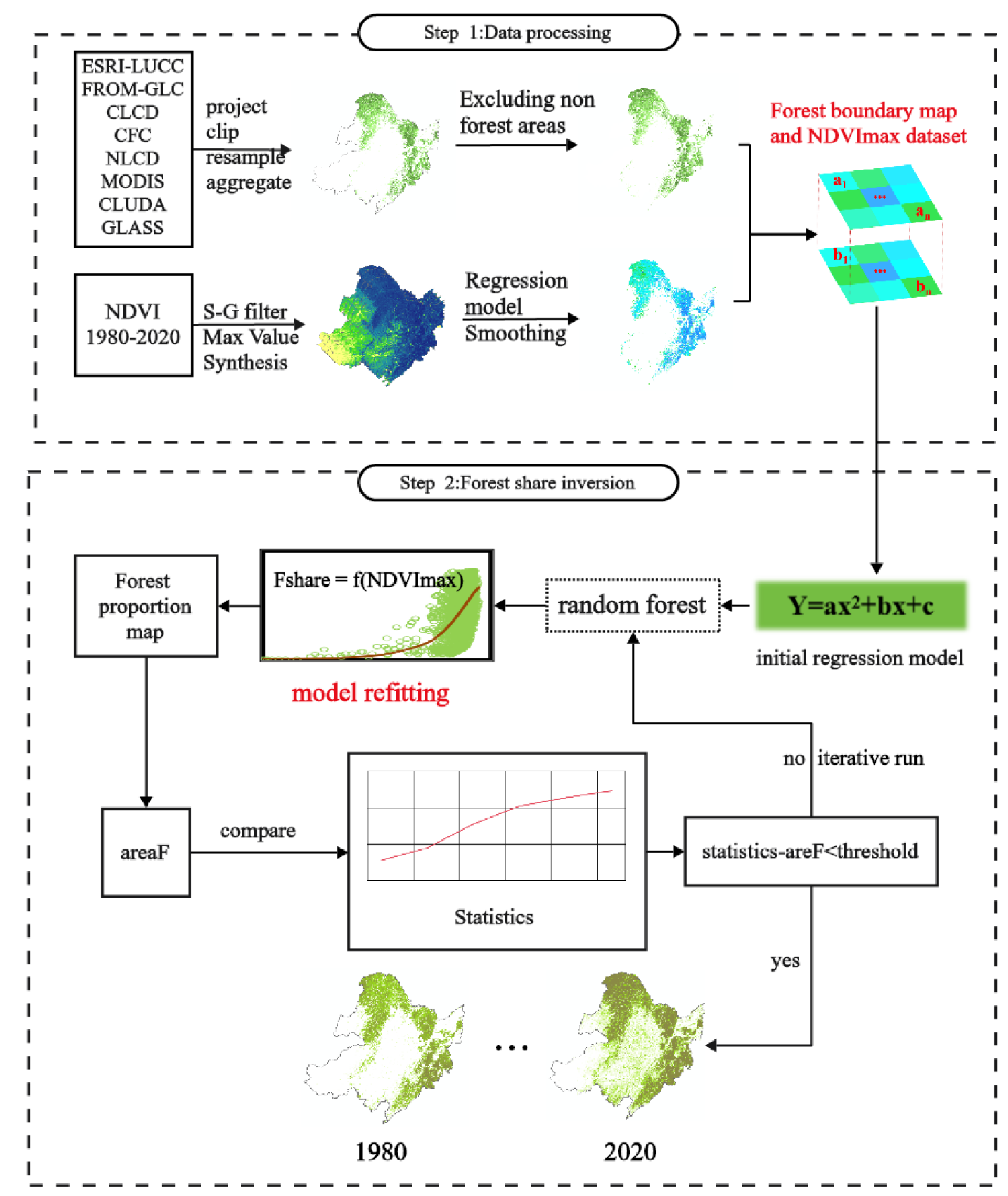
3.3. Forest Share Data Reconstruction Method
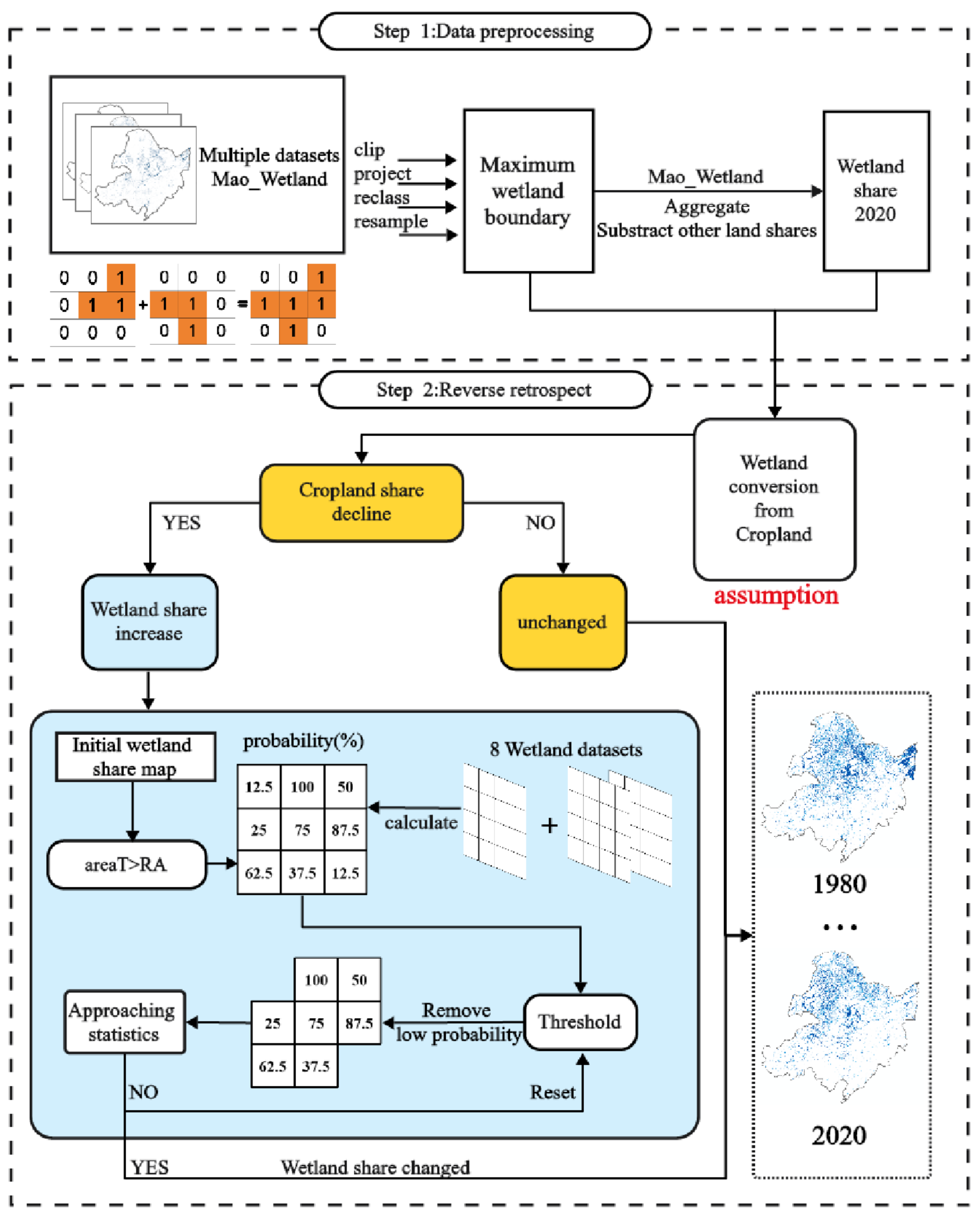
3.4. Wetland Share Dataset Development
3.5. Reconstruction of Grassland, Shrubland and Bareland Shares
3.6. Synthesis among All LUC Share Datasets
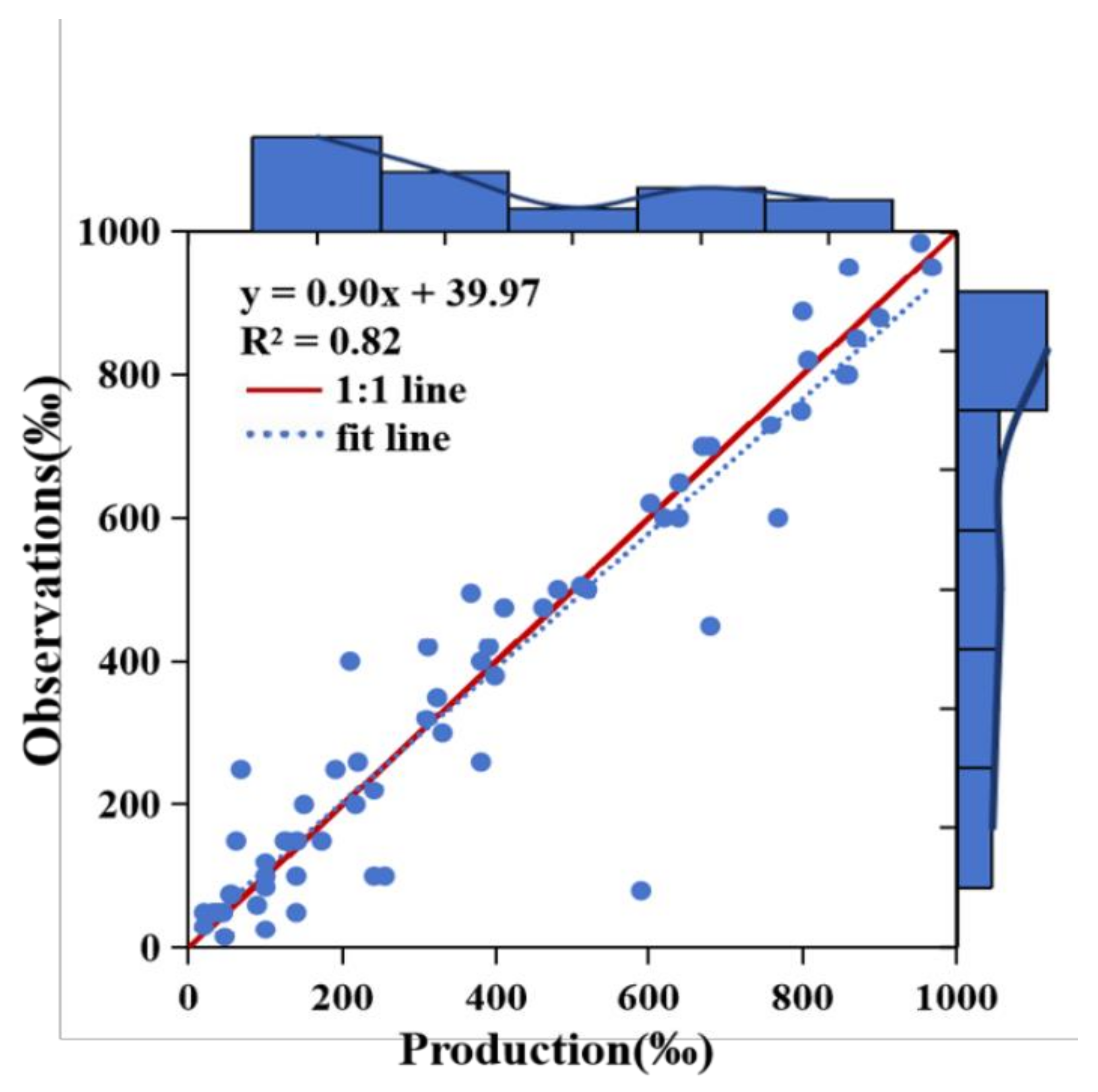
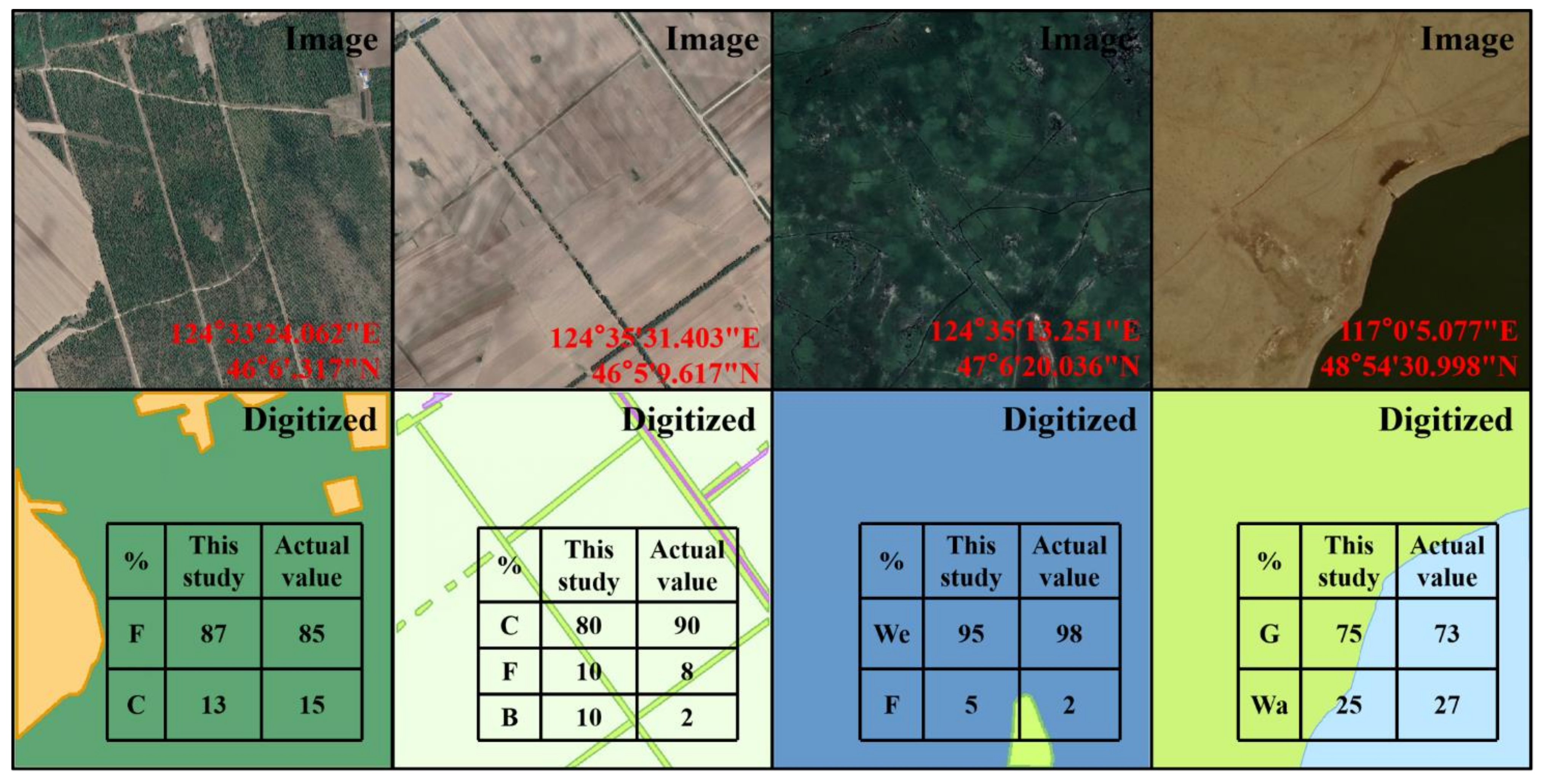
3.7. Accuracy Assessment and Intercomparisons
4. Results
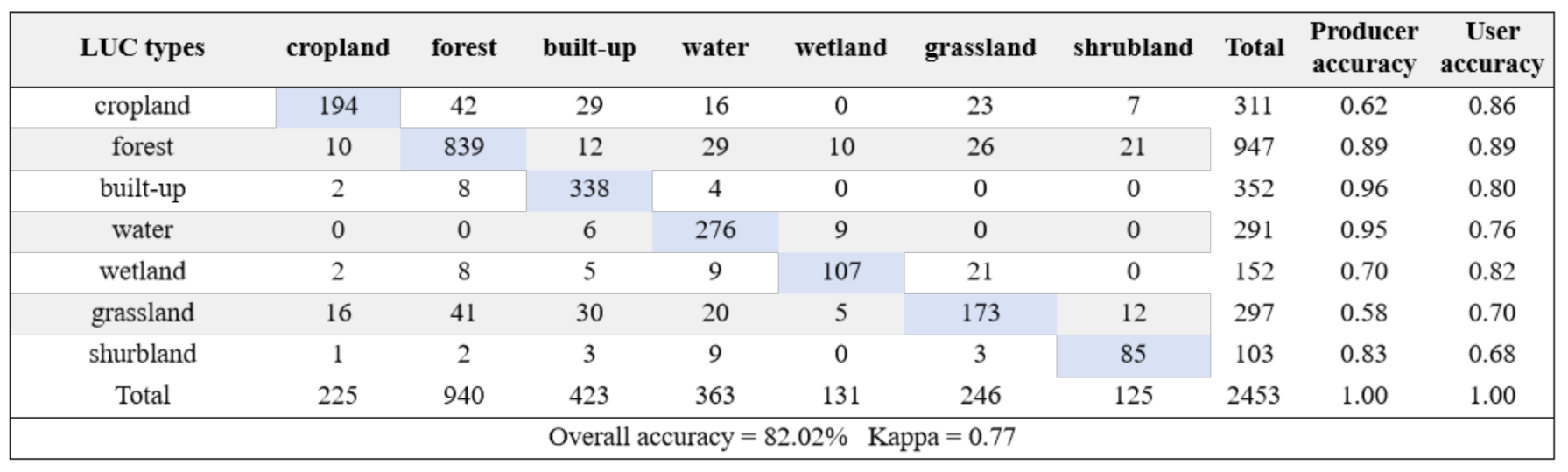
4.1. Accuracy Assessment
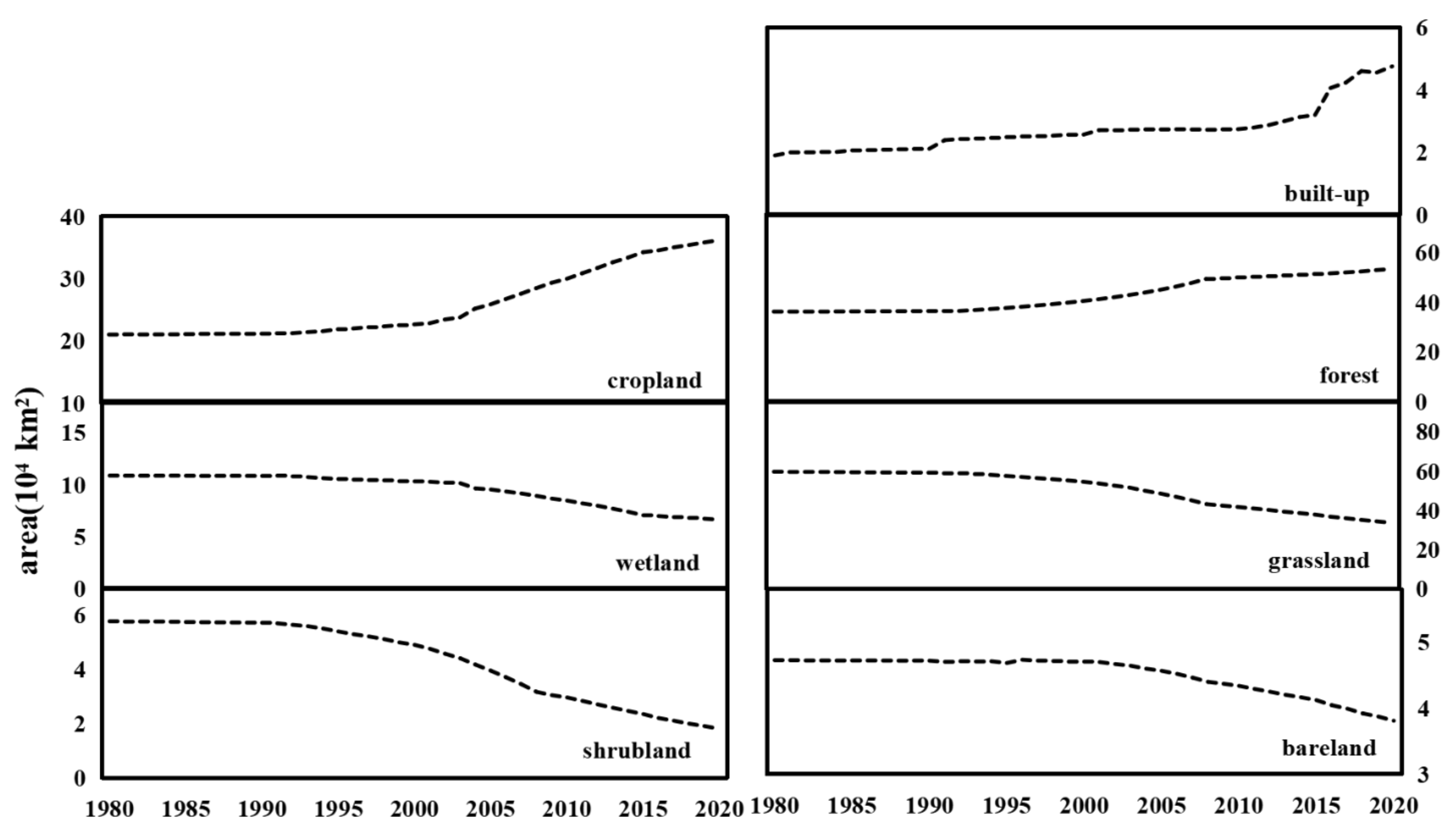
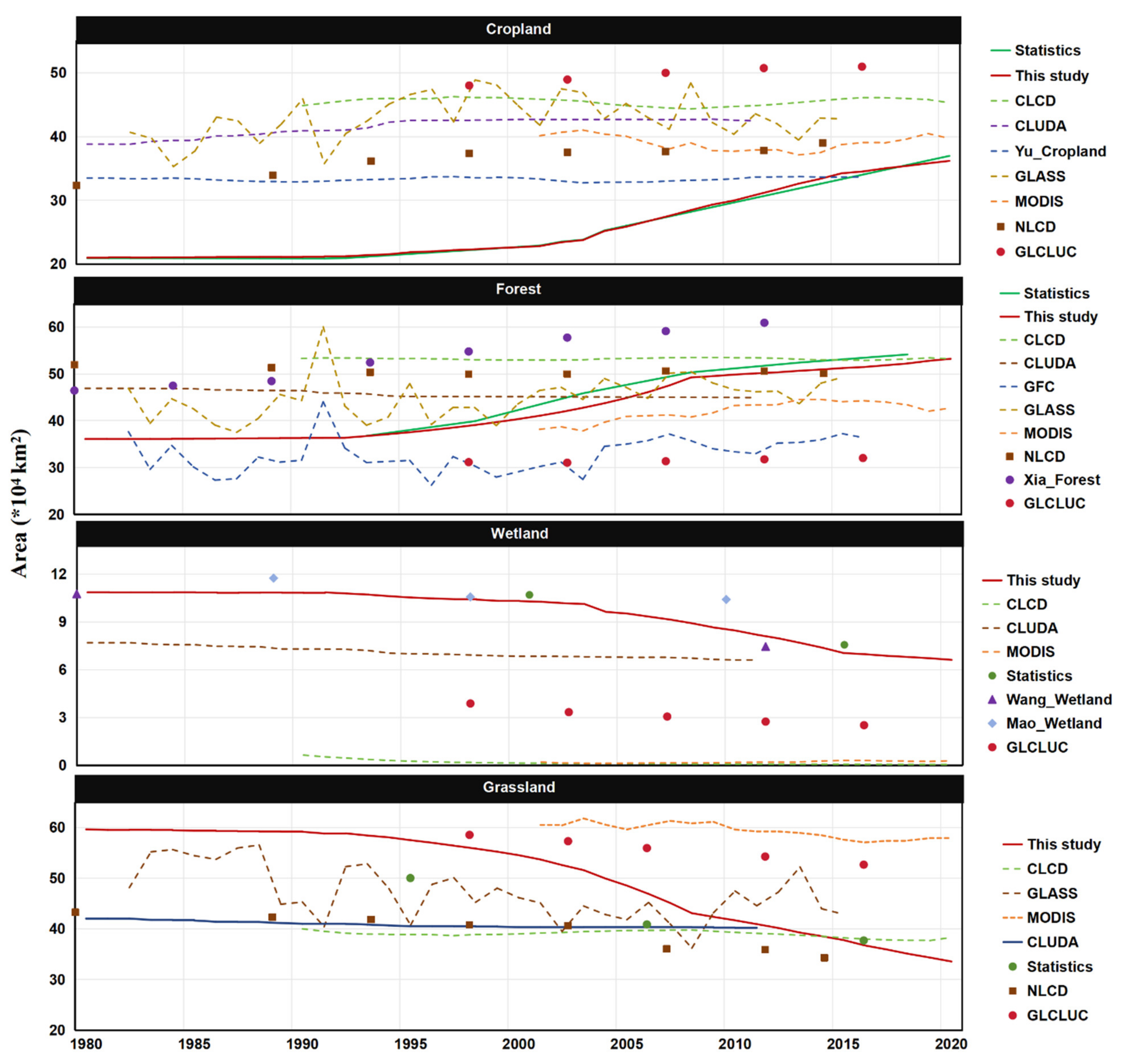
4.2. Temporal change patterns of different land use and cover types
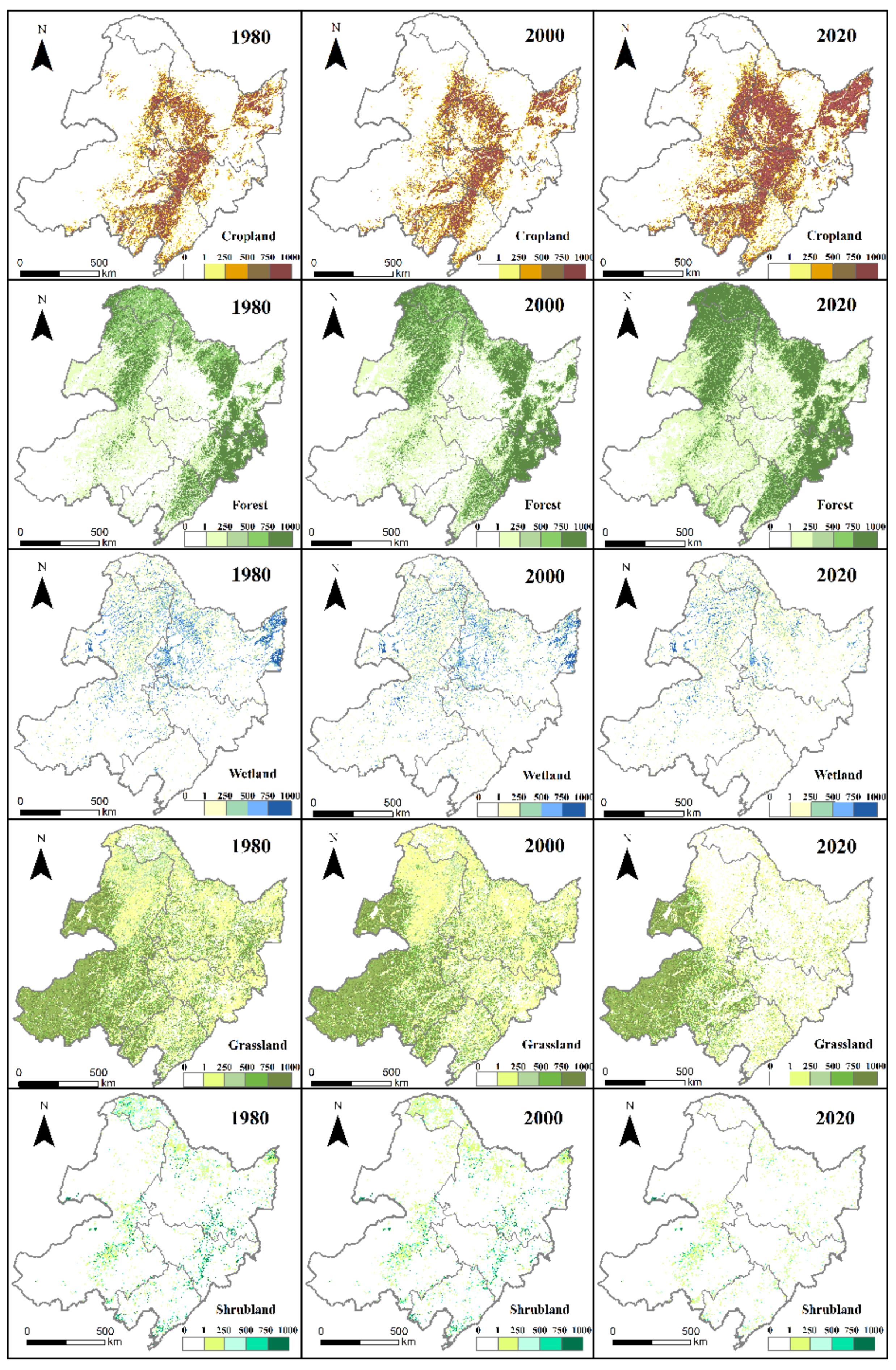
4.3. Spatial Change Patterns in Land Use and Cover Types
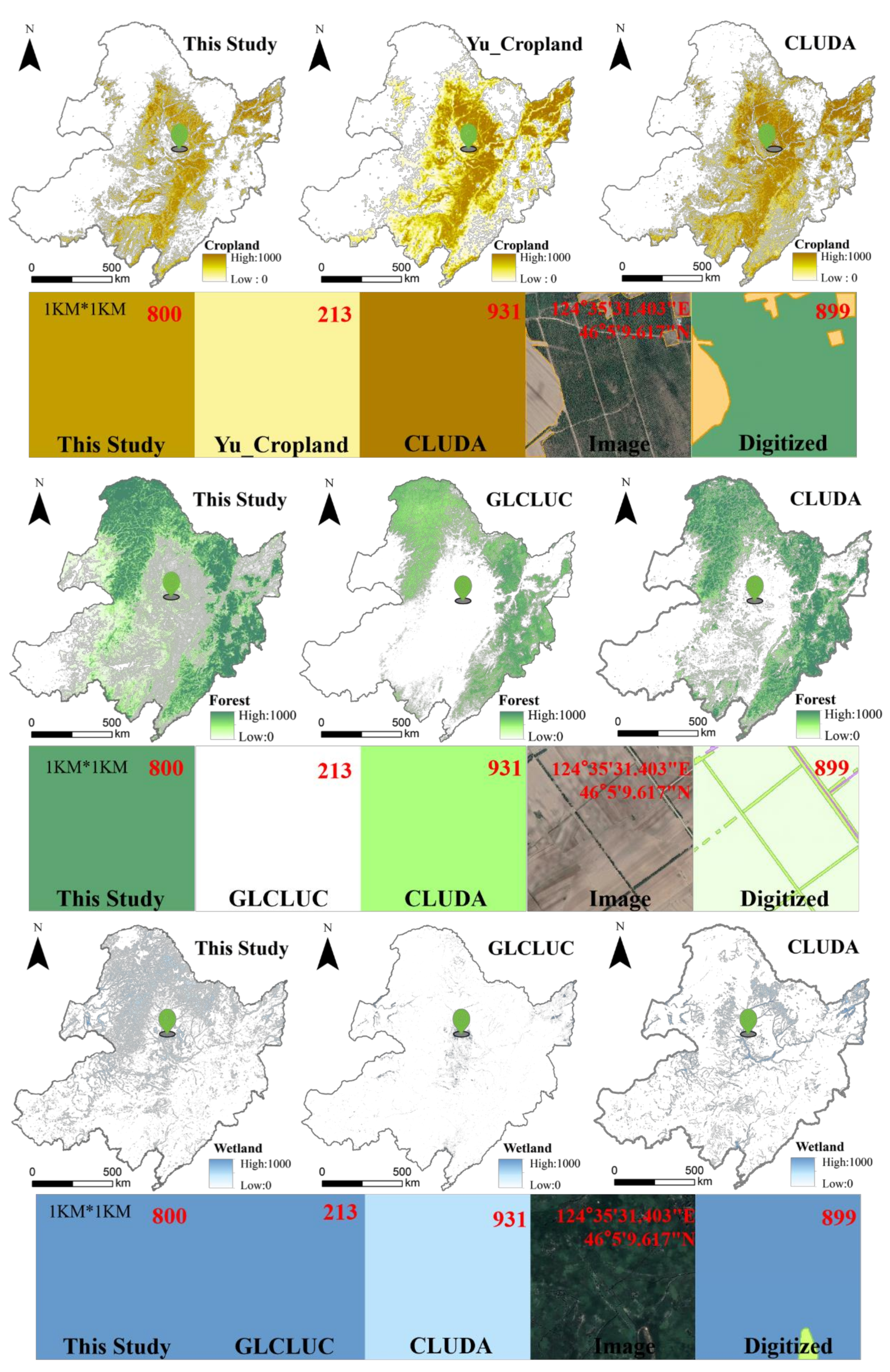
4.4. The Comparisons with Existing LUCC Products
5. Discussion
5.1. The Effectiveness of Our Approach in Reflecting Spatiotemporal LUCC Patterns
5.2. The Reliability and Mechanisms of Our Approach
5.3. Uncertainties and Outlooks
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Findell, K.L.; Berg, A.; Gentine, P.; Krasting, J.P.; Lintner, B.R.; Malyshev, S.; Santanello Jr, J.A.; Shevliakova, E. The impact of anthropogenic land use and land cover change on regional climate extremes. Nature Communications 2017, 8, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbard, S.; Caldeira, K.; Bala, G.; Phillips, T.J.; Wickett, M. Climate effects of global land cover change. Geophys Res Lett 2005, 32, 024550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, Y.; Heuvelink, G.B.; An, R.; Chen, Y. Object-based superresolution land-cover mapping from remotely sensed imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2017, 56, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihlar, J. Land cover mapping of large areas from satellites: Status and research priorities. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2000, 21, 1093–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveland, T.R.; Reed, B.C.; Brown, J.F.; Ohlen, D.O.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, L.; Merchant, J.W. Development of a global land cover characteristics database and IGBP discover from 1 km avhrr data. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2000, 21, 1303–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholome, E.; Belward, A.S. GLC2000: A new approach to global land cover mapping from earth observation data. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2005, 26, 1959–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Tan, B.; Schneider, A.; Ramankutty, N.; Sibley, A.; Huang, X. MODIS collection 5 global land cover: Algorithm refinements and characterization of new datasets. Remote Sensing of Environment 2010, 114, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M. Global land cover mapping at 30 m resolution: A pok-based operational approach. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Yuan, C.; Suen, H.P.; Guo, J.; Xu, N.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J. Stable classification with limited sample: Transferring a 30-m resolution sample set collected in 2015 to mapping 10-m resolution global land cover in 2017. Science Bulletin 2019, 64, 370–373. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Mi, J. GLC_FCS30: Global land-cover product with fine classification system at 30 m using time-series landsat imagery. Earth System Science Data 2021, 13, 2753–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, K.L.; Lamarche, C.; Hartley, A.; Peylin, P.; Ottlé, C.; Bastrikov, V.; Martín, D.S.; Bohnenstengel, S.I. A 29-year time series of annual 300 m resolution plant-functional-type maps for climate models. Earth Syst Sci Data 2023, 15, 1465–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karra, K.; Kontgis, C.; Statman-Weil, Z.; Mazzariello, J.C.; Mathis, M.; Brumby, S.P. In Global land use/land cover with sentinel 2 and deep learning, 2021 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium IGARSS, 2021; IEEE: pp 4704-4707.
- Ning, J.; Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yan, C.; Li, R.; Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Du, G. Spatiotemporal patterns and characteristics of land-use change in china during 2010–2015. Journal of Geographical Sciences 2018, 28, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in china since the late 1980s. Journal of Geographical sciences 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, L.; Peng, D.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Meng, R.; Xu, X.; Gong, P. Annual 30-m land use/land cover maps of china for 1980–2015 from the integration of AVHRR, modis and landsat data using the BFAST algorithm. Science China Earth Sciences 2020, 63, 1390–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst Sci Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xia, X.; Chen, X.; Fan, L.; Liu, S.; Qin, Y.; Qin, Z.; Xiao, X.; Xu, W.; Yue, C., et al. Reconstructing long-term forest cover in China by fusing national forest inventory and 20 land use and land cover data sets. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 2023, 128, e2022JG007101.
- Qin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Shimada, M.; Liu, J. Forest cover maps of China in 2010 from multiple approaches and data sources: PALSAR, Landsat, MODIS, FRA, and NFI. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2015, 109, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Jin, X.; Miao, L.; Yang, X. A historical reconstruction of cropland in China from 1900 to 2016. Earth Syst Sci Data 2021, 13, 3203–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Yao, W.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, H.; Li, N.; Huang, H.; Li, C., et al. Mapping wetland changes in china between 1978 and 2008. China Science Bulletin 2012, 57, 2813–2823.
- Gong, P.; Niu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, D.; Guo, J.; Liang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, D. China’s wetland change (1990-2000) determined by remote sensing. Science China Earth Sciences 2010, 53, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xia, J.; Chen, X.; Fan, L.; Liu, S.; Qin, Y.; Qin, Z.; Xiao, X.; Xu, W.; Yue, C. Reconstructing long-term forest cover in China by fusing national forest inventory and 20 land use and land cover data sets. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 2023, 128, 007101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Du, B.; Li, L.; Tian, Y.; Jia, M.; Zeng, Y.; Song, K.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y. National wetland mapping in china: A new product resulting from object-based and hierarchical classification of landsat 8 oli images. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2020, 164, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lu, C. Historical cropland expansion and abandonment in the continental US during 1850 to 2016. Global Ecology and Biogeography 2018, 27, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.c.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.q.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W. Annual maps of global artificial impervious area (gaia) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sensing of Environment 2020, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Dai, J.; Wu, C.; Xia, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y., et al. Divergent shifts in peak photosynthesis timing of temperate and alpine grasslands in China. Remote Sensing of Environment 2019, 233, 111395. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, J.; Yuan, Z.; Bai, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y. A daily gap-free normalized difference vegetation index dataset from 1981 to 2023 in China. Scientific Data 2024, 11, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. A 10m year-by-year ndvi maximum dataset for China. Resource and environmental science data registration and publication system 2022. Available online: http://www.resdc.cn/. [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, H. Diverse policies leading to contrasting impacts on land cover and ecosystem services in northeast China. Journal of Cleaner Production 2019, 240, 117961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Biging, G.S.; Yuan, C.; Hu, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, X., et al. The first all-season sample set for mapping global land cover with Landsat-8 data. Science Bulletin 2017, 62, 508–515. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Clinton, N.; Bai, Y.; Liang, S. Annual dynamics of global land cover and its long-term changes from 1982 to 2015. Earth Syst Sci Data 2020, 12, 1217–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Lü, X. Change characteristics of landscape pattern and climate in marsh areas of northeast China during 1980–2015. Earth and Environment 2020, 48, 348–357. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Ren, C.; Jia, M. Monitoring the evolution of wetland ecosystem pattern in northeast China from 1990 to 2013 based on remote sensing. Journal of Natural Resources 2016, 31, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Fang, X.Q. Spatial pattern of land cover changes across northeast China over the past 300 year. Journal of Historical Geography 2011, 37, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, L.; Peng, D.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Meng, R.; Xu, X.; Gong, P. Annual 30-m land use/land cover maps of China for 1980–2015 from the integration of AVHRR, MODIS and Landsat data using the BFAST algorithm. Science China Earth Sciences 2020, 63, 1390–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Yu, L.; Li, X.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; Hao, P.; Gong, P. A 1 km global cropland dataset from 10000 bce to 2100 ce. Earth Syst Sci Data 2021, 13, 5403–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, P.; Hansen, M.C.; Pickens, A.; Hernandez-Serna, A.; Tyukavina, A.; Turubanova, S.; Zalles, V.; Li, X.; Khan, A.; Stolle, F., et al. The global 2000-2020 land cover and land use change dataset derived from the Landsat archive: First results. Frontiers in Remote Sensing 2022, 3, 856903. [CrossRef]
- Song, X.P.; Hansen, M.C.; Stehman, S.V.; Potapov, P.V.; Tyukavina, A.; Vermote, E.F.; Townshend, J.R. Global land change from 1982 to 2016. Nature 2018, 560, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, N.; Dong, J.; Huang, J.; Du, G.; Zhang, G.; He, Y.; Yang, T.; Di, Y.; Xiao, X. The 10-m crop type maps in northeast China during 2017–2019. Scientific Data 2021, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, J.; Ge, Q. Mapping 20 years of irrigated croplands in China using modis and statistics and existing irrigation products. Scientific Data 2022, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Luo, L.; Wang, Z.; Wilson, M.C.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. Conversions between natural wetlands and farmland in China: A multiscale geospatial analysis. Science of the Total Environment 2018, 634, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Y. Space-time change of marsh wetland in Liaohe Delta area and its ecological effect. Journal of Northeast Normal University 2003, 35, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Asselen, S.; Verburg, P.H.; Vermaat, J.E.; Janse, J.H. Drivers of wetland con-version: A global meta-analysis. PloS one 2013, 8, 381292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S. Selecting and interpreting measures of thematic classification accuracy. Remote Sensing of Environment 1997, 62, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.J. Estimation of shelter forest area in three-north shelter forest program region based on multi-sensor remote sensing data. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 2013, 24, 2257–2264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.J.; Zheng, X. The prospects of development of the three-north afforestation program(TNAP) : On the basis of the results of the 40-year construction general assessment of the TNAP. Chinese Journal of Ecology 2019, 38, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, W.J.; Ballantyne, A.; He, H.S.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Ciais, P.; Wimberly, M.C.; Piao, S.; Yu, K., et al. Forest disturbance decreased in China from 1986 to 2020 despite regional variations. Communications Earth and Environment 2023, 4, 15. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Park, T.; Wang, X.; Piao, S.; Xu, B.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Fuchs, R.; Brovkin, V.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R., et al. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nature sustainability 2019, 2, 122–129.
- Zhu, Z.C.; Piao, S.L.; Myneni, R.B.; Huang, M.T.; Zeng, Z.Z.; Canadell, J.G.; Ciais, P.; Sitch, S.; Friedlingstein, P.; Arneth, A., et al. Greening of the earth and its drivers. Nat Clim Change 2016, 6, 791–795.
- Zhang, C.; Dong, J.; Ge, Q. Mapping 20 years of irrigated croplands in China using MODIS and statistics and existing irrigation products. Scientific Data 2022, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, J. A multi-source data fusion method for land cover production: A case study of the east European plain. International Journal of Digital Earth 2024, 17, 2339360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Ciais, P.; Piao, S.; Houghton, R.A.; Lu, C.; Tian, H. Forest expansion dominates China’s land carbon sink since 1980. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Xing, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Gong, W. Effects of land use and cover change (LUCC) on terrestrial carbon stocks in China between 2000 and 2018. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 2022, 182, 106333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, X.; Chuai, X.; Xie, F.; Yang, F.; Gao, R.; Ji, X. Reexamine China’s terrestrial ecosystem carbon balance under land use-type and climate change. Land Use Policy 2021, 102, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Datasets | Resolution | Time period | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| ESRI-LUCC | 10 m | 2017-2023 | https://livingatlas.arcgis.com/landcover/ |
| FROM-GLC | 10 m | 2017 | [10] |
| NLCD | 30 m | 1980, 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, 2020 | http://www.nesdc.org.cn/ |
| MODIS | 500 m | 2000-2020 | https://modis-land.gsfc.nasa.gov/landcover.html |
| CLUDA | 1 km | 1980-2015 | [36] |
| CLCD | 30 m | 1990-2020 | [17] |
| GLASS-GLC | 0.05° | 1982-2015 | [32] |
| GLC | 1 km | 1980-2100 | [37] |
| Yu_cropland | 5 km | 1900-2016 | [20] |
| Xia_forest (CFCD) | 1 km | 1980-2015 | [18] |
| GLCLUC | 30 m | 2000-2020 | [38] |
| GFC | 0.05° | 1982-2016 | [39] |
| You_croptype | 10 m | 2017-2019 | [40] |
| Mao_wetland | 30 m | 2015 | [24,34] |
| NDVI | 30 m | 1986-2020 | [29] |
| NDVI | 0.05° | 1981-2023 | [28] |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




