Submitted:
05 October 2024
Posted:
07 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Traditional Pap Smear and Liquid Cytology Image Acquisition
2.2. Cell Segmentation Algorithm
2.3. Malignant Cell Classification AI-Model Based in ResNet 50 Architecture
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Descriptive
2.4.2. Inferential
2.4.3. Diagnostic Performance Metrics
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CC | cervical cancer |
| ML | machine learning |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| DL | deep learning |
| CNN | convolutional neuronal network |
| LMICs | particularly in low- and middle-income countries |
| LBC | liquid-based cytology |
References
- Organization, W.H. *New WHO Recommendations on Screening and Treatment to Prevent Cervical Cancer among Women Living with HIV*; Wiley, 2023.
- Bustos Marisa, C.M. Especialistas alertan que cáncer de cuello uterino sigue en el Top 10 como causa de muerte en Chile 2023.
- Bogdanova, A.; Andrawos, C.; Constantinou, C. Cervical Cancer, Geographical Inequalities, Prevention and Barriers in Resource Depleted Countries (Review. *Oncol. Lett.* **2022**, *23*, 113. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Lee, B.; Cho, N.-H.; Park, J.H. Beyond the Microscope: A Technological Overture for Cervical Cancer Detection. *Diagnostics* **2023**, *13*, 3079. [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. *CA Cancer J. Clin.* **2018**, *68*, 394–424. [CrossRef]
- Almonte, M.; Murillo, R.; Sánchez, G.I.; González, P.; Ferrera, A.; Picconi, M.A.; Wiesner, C.; Cruz-Valdez, A.; Lazcano-Ponce, E.; Jerónimo, J.; et al. Multicentric Study of Cervical Cancer Screening with Human Papillomavirus Testing and Assessment of Triage Methods in Latin America: The ESTAMPA Screening Study Protocol. *BMJ Open* **2020**, *10*, e035796. [CrossRef]
- Rezende, L.F.M.; Murata, E.; Giannichi, B.; Tomita, L.Y.; Wagner, G.A.; Sanchez, Z.M.; Celis-Morales, C.; Ferrari, G. Cancer Cases and Deaths Attributable to Lifestyle Risk Factors in Chile. *BMC Cancer* **2020**, *20*, 693. [CrossRef]
- Saldivia, L.Z.; Silva, I.V.; Rojas, F.H.; Vidal, B.M. Distribución etaria e incidencia de lesiones preinvasoras y cáncer cérvico uterino, entre los años 2009-2019: revisión de tres zonas geográficas de Chile. *Rev. Conflu* **2022**, *5*, 56–59.
- Schiffman, M.; Castle, P.E.; Jeronimo, J.; Rodriguez, A.C.; Wacholder, S. Human Papillomavirus and Cervical Cancer. *Lancet* **2007**, *370*, 890–907.
- Fowler, M., Jr; Ev, D.; j., C. Cervical Cancer. In *StatPearls* [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2024.
- Núñez-Troconis, J. Papel del virus del papiloma humano en el desarrollo del cáncer del cuello uterino. *Investigación Clínica* **2023**, *64*, 233–254. [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, L.J.; Bryson, S.C.P. Human Papillomavirus—Lessons From History and Challenges for the Future. *J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can.* **2008**, *30*, 1025–1033,. [CrossRef]
- Contreras, R. Papanicolaou y Citología Líquida En Diagnóstico de Cáncer de Cérvix: Hospital Civil de Maracay. 2012. *Comunidad y Salud* **2015**, *13*, 12–22.
- Herrera Conza, E.M.; Salazar Torres, Z.K.; Espinosa Martín, L.; Aspiazu Hinostroza, K.A. Detección Oportuna de Cáncer Cérvico-Uterino. *Revista Vive* **2021**, *3*, 264–274. [CrossRef]
- Landy, R.; Pesola, F.; Castañón, A.; Sasieni, P. Impact of Cervical Screening on Cervical Cancer Mortality: Estimation Using Stage-Specific Results from a Nested Case-Control Study. *Br. J. Cancer* **2016**, *115*, 1140–1146. [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Bavikar, R.; Buch, A.; Kulkarni, M.; Dharwadkar, A.; Viswanathan, V.A. Comparison of Conventional Pap Smear and Liquid-Based Cytology for Cervical Cancer Screening. *Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther* **2023**, *18*;12(2):77-82.
- Singh, V.B.; Gupta, N.; Nijhawan, R.; Srinivasan, R.; Suri, V.; Rajwanshi, A. Liquid-Based Cytology versus Conventional Cytology for Evaluation of Cervical Pap Smears:Experience from the First 1000 Split Samples. *Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol.* **2015**, *58*, 17–21. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Yadav, R.; Sharda, A.; Kumar, D.; Sandeep, M.R. Comparative Evaluation of Conventional Cytology and a Low-Cost Liquid-Based Cytology Technique, EziPREPTM, for Cervicovaginal Smear Reporting:A Split Sample Study. *Cytojournal* **2019**, *16*. [CrossRef]
- Albarrán, M. Citología Líquida: un mejor diagnóstico en Cáncer De Cuello de Útero; Artemedica.Es, 2023.
- Krishna, C.; Chandraiah, S.; Krishna, C. Comparison of Conventional Papanicolaou Smear and Liquid-based Cytology: A Study of Cervical Cancer Screening at a Tertiary Care Center in Bengaluru. *International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology* **2021**, *10*. 3106, 10 18203 2320-1770 20212963.
- Zhao, L.; Li, K.; Wang, M.; Yin, J.; Zhu, E.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Zhu, C. Automatic Cytoplasm and Nuclei Segmentation for Color Cervical Smear Image Using an Efficient Gap-Search MRF. *Comput. Biol. Med.* **2016**, *71*, 46–56. 56. [CrossRef]
- Sompawong, N.; Mopan, J.; Pooprasert, P.; Himakhun, W.; Suwannarurk, K.; Ngamvirojcharoen, J.; Vachiramon, T.; Tantibundhit, C. Automated Pap Smear Cervical Cancer Screening Using Deep Learning. In *Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc*; 2019; pp. 7044–7049.
- Bao, H.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y. The Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Cytology Diagnostic System in Large-Scale Cervical Cancer Screening: A Population-Based Cohort Study of 0.7 Million Women. *Cancer Med.* **2020**, *9*, 6896–6906. [CrossRef]
- Shafi, S.; Parwani, A.V. Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostic Pathology. *Diagn. Pathol.* **2023**, *18*, 109. [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.E.C.D.; Santos, G.N.M.; Leite, A.F.; Mesquita, C.R.M.; Figueiredo, P.T.S.; Stefani, C.M.; Melo, N.S. The Use of Artificial Intelligence Tools in Cancer Detection Compared to the Traditional Diagnostic Imaging Methods: An Overview of the Systematic Reviews. *PLoS One* **2023**,. [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Shen, G.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Ma, X. Artificial Intelligence in Cervical Cancer Screening and Diagnosis. *Front. Oncol.* **2022**. [CrossRef]
- Kresnauli, P.; Zipora, Y.C. The Application of Artificial Intelligence In Cervical Cancer Screening With Colposcopy Imaging Device. Author content 2023.
- Razzak, M.A.; Islam, M.N.; Aadeeb, M.S.; Tasnim, T. Digital Health Interventions for Cervical Cancer Care: A Systematic Review and Future Research Opportunities. *PLoS One* **2023**, *18*, e0296015. [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. *arXiv* [cs.CV] **2015**.
- Shafiq, M.; Gu, Z. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition: A Survey. *Appl. Sci. (Basel)* **2022**, *12*, 8972. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Wen, Q.-M.; Zuo, Z.-Q.; Liu, J.-S.; Feng, J.; Pang, B.-C.; Xiao, D. CytoBrain: Cervical Cancer Screening System Based on Deep Learning Technology. *J. Comput. Sci. Technol.* **2021**, *36*, 347–360. [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.T.; Valls, J.; Baena, A.; Rojas, F.D.; Ramírez, K.; Álvarez, R.; Cristaldo, C.; Henríquez, O.; Moreno, A.; Reynaga, D.C.; et al. Performance of Cervical Cytology and HPV Testing for Primary Cervical Cancer Screening in Latin America: An Analysis within the ESTAMPA Study. *Lancet Reg Health Am* **2023**,. [CrossRef]
- Sachan, P.L.; Singh, M.; Patel, M.L.; Sachan, R. A Study on Cervical Cancer Screening Using Pap Smear Test and Clinical Correlation. *Asia-Pacific journal of oncology nursing* **2018**, *5*, 337–341. [CrossRef]
- Lozar, T.; Nagvekar, R.; Rohrer, C.; Dube Mandishora, R.S.; Ivanus, U.; Fitzpatrick, M.B. Cervical Cancer Screening Postpandemic: Self-Sampling Opportunities to Accelerate the Elimination of Cervical Cancer. *Int. J. Womens Health* **2021**, 841–859. [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S. The Efficiency of Cervical Pap and Comparison of Conventional Pap Smear and Liquid-Based Cytology. A Review. *Cureus* **2023**, *15*. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Norman, I.; Elfgren, K.; Gaberi, V.; Hagmar, B.; Hjerpe, A.; Andersson, S. A Comparison of Liquid-Based Cytology and Pap Smear as a Screening Method for Cervical Cancer. *Oncol. Rep.* **2007**, *18*, 157–160. [CrossRef]
- Sherman, M.E.; Mango, L.J.; Kelly, D.; Paull, G.; Ludin, V.; Copeland, C.; Schiffman, M.H. PAPNET Analysis of Reportedly Negative Smears Preceding the Diagnosis of a High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion or Carcinoma. *Mod. Pathol.* **1994**, *7*, 578–581.
- Kanavati, F.; Hirose, N.; Ishii, T.; Fukuda, A.; Ichihara, S.; Tsuneki, M. A Deep Learning Model for Cervical Cancer Screening on Liquid-Based Cytology Specimens in Whole Slide Images. *Cancers* **2022**, *14*, 1159. [CrossRef]
- Stoler, M.H.; Schiffman, M. Interobserver Reproducibility of Cervical Cytologic and Histologic Interpretations: Realistic Estimates from the ASCUS-LSIL Triage Study. *JAMA* **2001**, *285*, 1500–1505. [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, W.A.; Ismail, S.; Mokhtar, F.S.; Alquran, H.; Al-Issa, Y. Cervical Cancer Detection Techniques: A Chronological Review. *Diagnostics (Basel* **2023**, *17*;13(10):1763. [CrossRef]
- Mirbabaie, M.; Stieglitz, S.; Frick, N.R.J. Artificial Intelligence in Disease Diagnostics: A Critical Review and Classification on the Current State of Research Guiding Future Direction. *Health Technol. (Berl.)* **2021**, *11*, 693–731. [CrossRef]
- Alowais, S.A.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Alsuhebany, N.; Alqahtani, T.; Alshaya, A.I.; Almohareb, S.N.; Albekairy, A.M. Revolutionizing Healthcare: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Practice. *BMC Med. Educ.* **2023**, *23*, 689. [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.K.; Singh, K.; Kumar, A.; Kolambakar, S.B. HDFCN: A Robust Hybrid Deep Network Based on Feature Concatenation for Cervical Cancer Diagnosis on WSI Pap Smear Slides. *Biomed Res. Int.* **2023**, *2023*, 4214817. [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.; Ccopa, A.; Diaz, E.; Valcarcel, S.; Mauricio, D.; Villoslada, V. Deep Learning and Transfer Learning Methods to Effectively Diagnose Cervical Cancer from Liquid-Based Cytology Pap Smear Images. *Int. J. Online Biomed. Eng.* **2023**, *19*, 77–93. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shen, W.; Gao, L.; Li, X. Hybrid Loss-Constrained Lightweight Convolutional Neural Networks for Cervical Cell Classification. *Sensors (Basel)* **2022**, *22*, 3272. [CrossRef]
- Enciso Ortiz, S.E. Determinación de la mejor Arquitectura de Redes Neuronales Convolucionales: VGG16, ResNet50 ó MobileNet para detección de la Neumonía 2023 2024.
- Frangi, A.; Prince, J.; Sonka, M. *Medical Image Analysis*; Academic Press, 2023; ISBN 9780128136584.
- Masoodi, F.; Quasim, M.; Bukhari, S.; Dixit, S.; Alam, S. *Applications of Machine Learning and Deep Learning on Biological Data*; CRC Press, 2023; ISBN 9781000833768.
- Sompawong, N.; Mopan, J.; Pooprasert, P.; Himakhun, W.; Suwannarurk, K.; Ngamvirojcharoen, J.; Vachiramon, T.; Tantibundhit, C. Automated Pap Smear Cervical Cancer Screening Using Deep Learning. *Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc.* **2019**, *2019*, 7044–7048. [CrossRef]
- Alias, N.A.; Mustafa, W.A.; Jamlos, M.A.; Alquran, H.; Hanafi, H.F.; Ismail, S.; Rahman, K.S.A. Pap Smear Images Classification Using Machine Learning: A Literature Matrix. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gençtav, A.; Aksoy, S.; Önder, S. Unsupervised Segmentation and Classification of Cervical Cell Images. *Pattern Recognit.* **2012**, *45*, 4151–4168. [CrossRef]
- Azad, R.; Aghdam, E.K.; Rauland, A.; Jia, Y.; Avval, A.H.; Bozorgpour, A.; Karimijafarbigloo, S.; Cohen, J.P.; Adeli, E.; Merhof, D. Medical Image Segmentation Review: The Success of U-Net. *IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.* **2024**, PP, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Álvarez, A.M.; Salvador-Fernández, C.L.; Berruz-Alvarado, S.J.; Cañar-Lascano, G.G. Diagnóstico de cáncer cervicouterino: Comparación de la técnica de citología convencional y de base liquida. *RCS* **2023**, *6*, 18–33. [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Xue, Z.; Brown, G.; Long, R.; Antani, S. Deep Learning for Nuclei Segmentation and Cell Classification in Cervical Liquid Based Cytology. In *Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2020: Imaging Informatics for Healthcare, Research, and Applications*; SPIE, March 2 2020; Vol. 11318, pp. 268–278.
- Mosiichuk, V.; Viana, P.; Oliveira, T.; Rosado, L. Automated Adequacy Assessment of Cervical Cytology Samples Using Deep Learning. In *Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis*; Springer International Publishing, 2022; pp. 156–170.
- Mitra, S.; Das, N.; Dey, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Nasipuri, M.; Naskar, M.K. Cytology Image Analysis Techniques toward Automation. *ACM Comput. Surv.* **2022**, *54*, 1–41. [CrossRef]
- McManus, D.T. Miscellaneous Specimens and Ancillary Techniques. In *Histopathology Specimens*; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2017; pp. 519–531 ISBN 9783319573595.
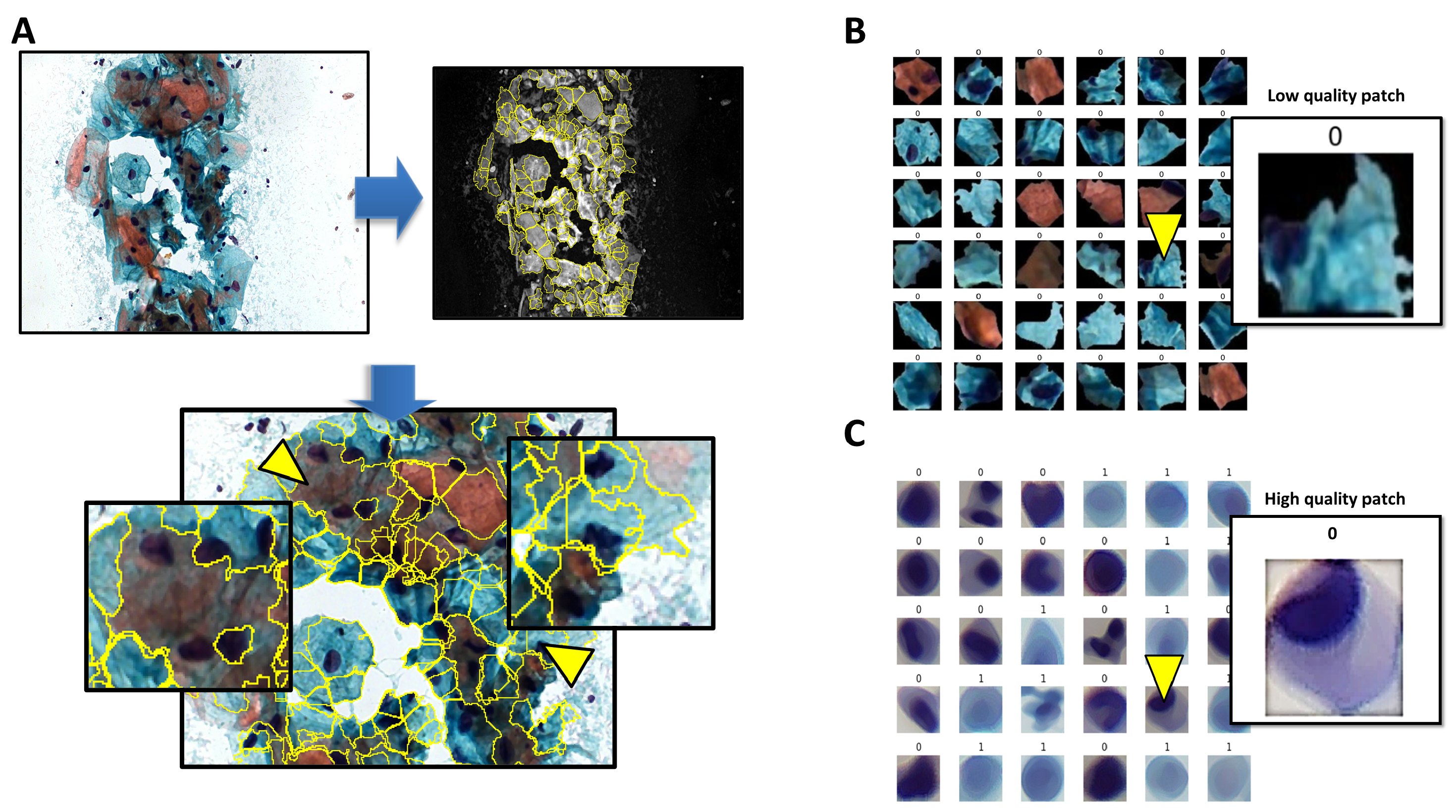
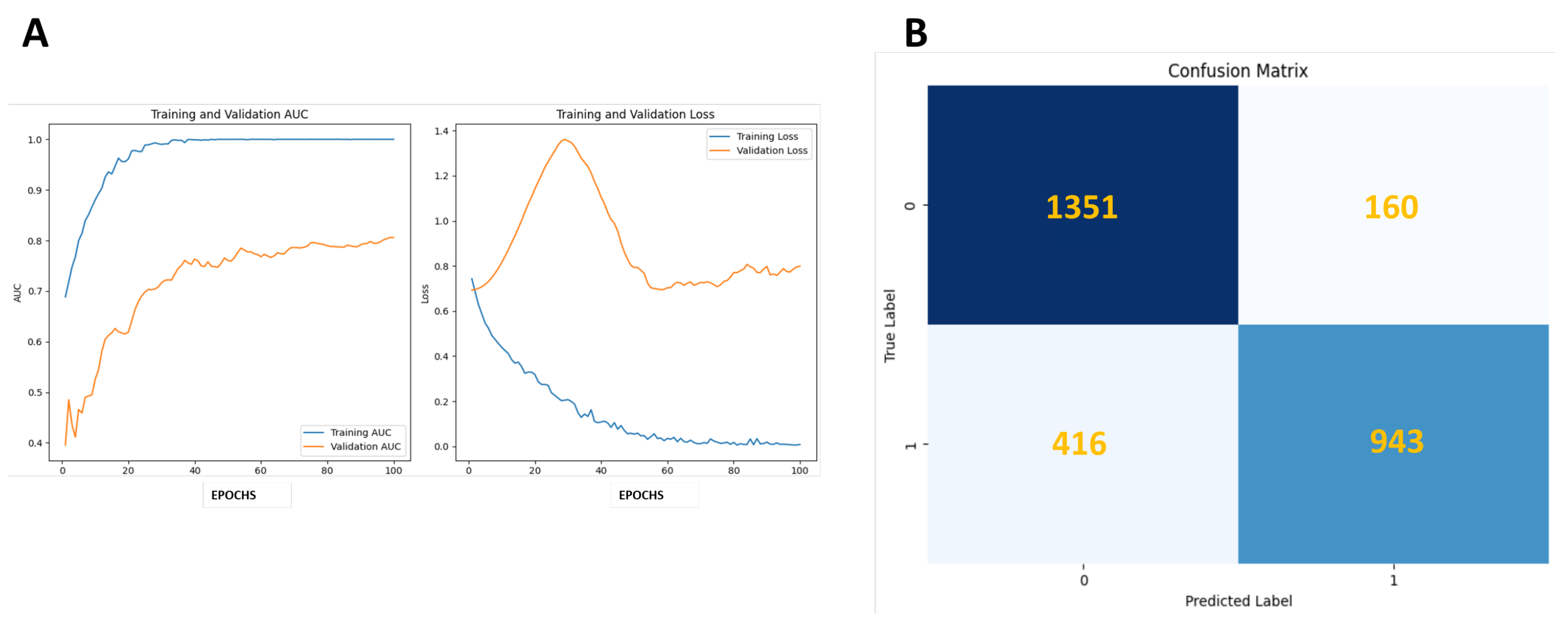
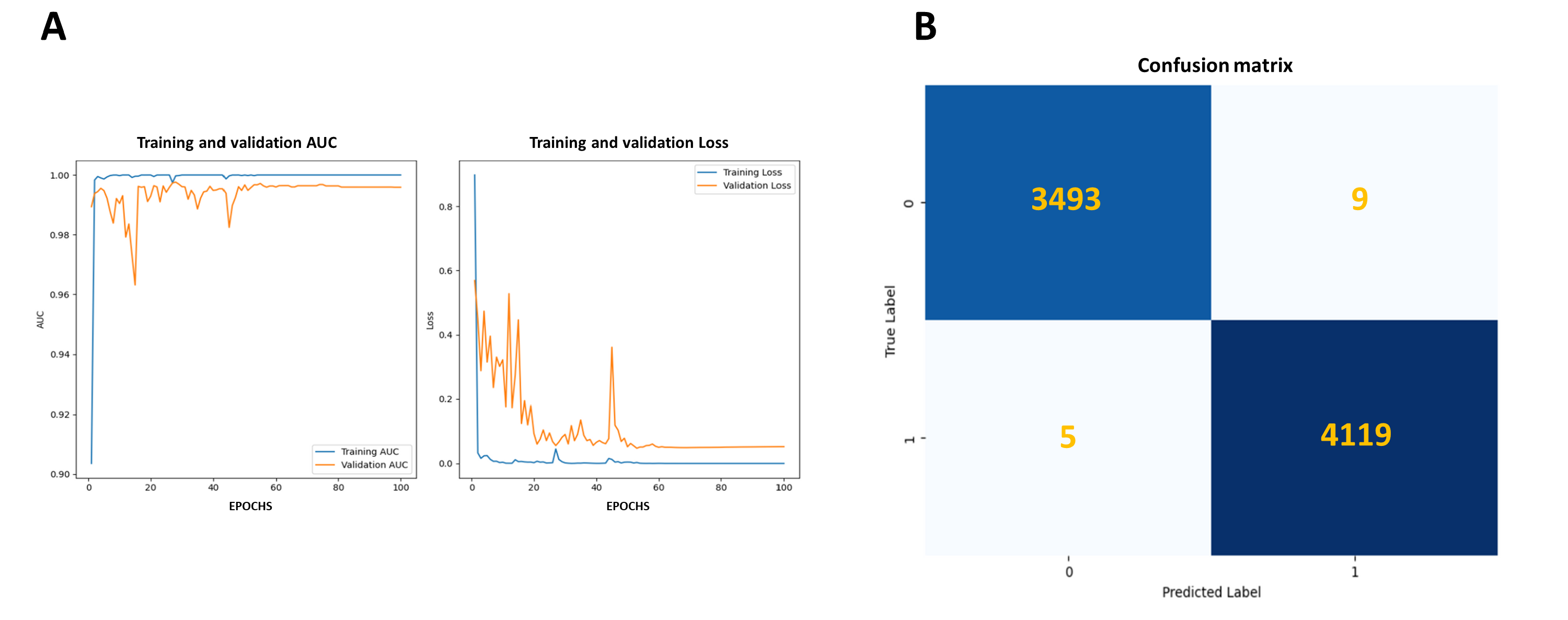
| Metrics | ResNet50-PAP |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.8341 |
| Sensitivity | 0.6939 |
| Precision | 0.8549 |
| Specificity | 0.8386 |
| F-Score | 0.8042 |
| Metrics | ResNet50-LCyt | R-CNN LCyt Sompawong *et al*. | VGG-LCyt Chen *et al*. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.998 | NR | NR |
| Sensitivity | 0.999 | 0.917 | 0.928 |
| Precision | 0.998 | 0.917 | 0.822 |
| Specificity | 0.997 | 0.917 | 0.911 |
| F-Score | 0.998 | NR | NR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





