Submitted:
05 October 2024
Posted:
07 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
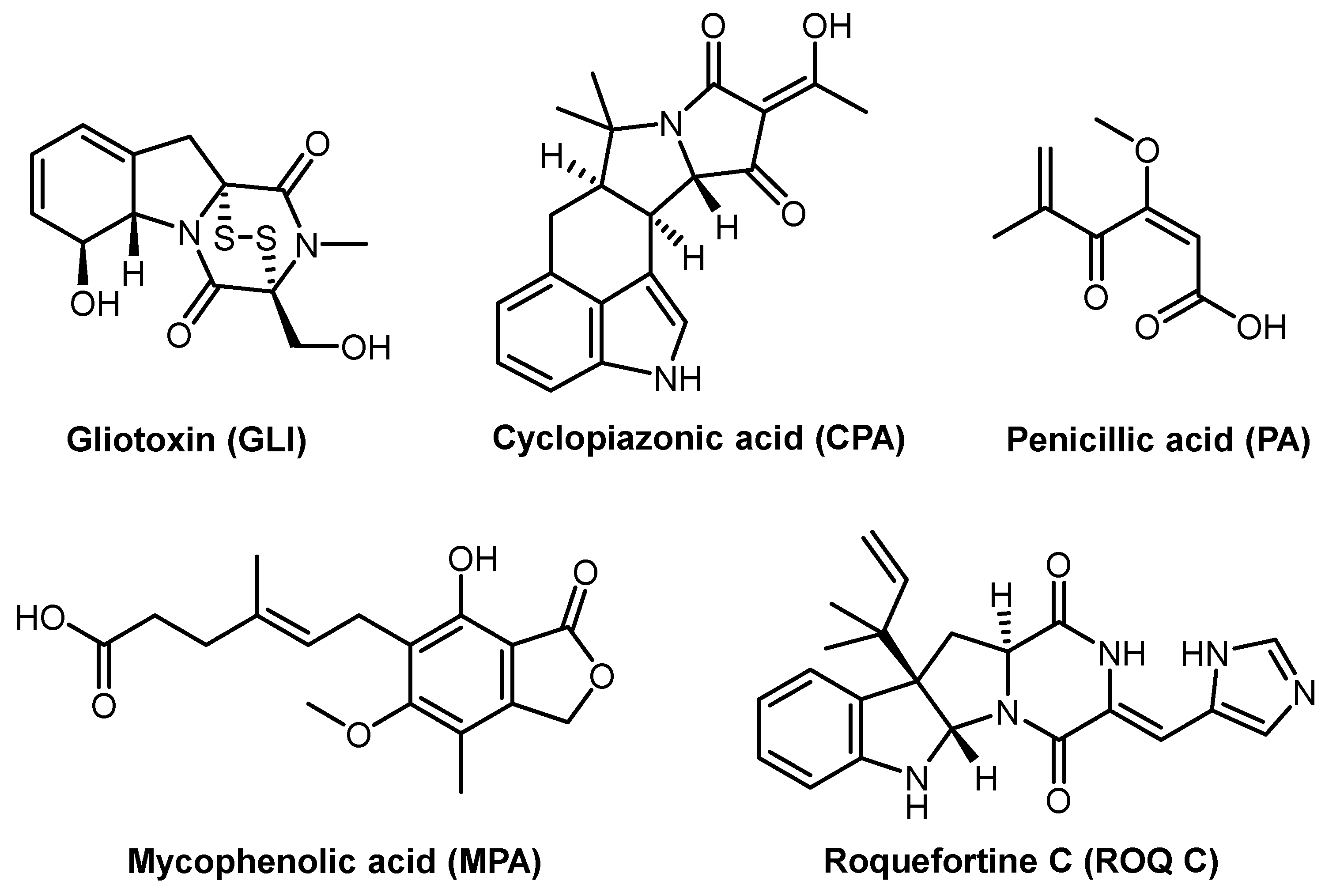
| Mycotoxins | Agricultural products | Species |
|---|---|---|
| Cyclopiazonic acid | Long-stored cereals, pasta, meat, and cheese | P. commune, P. camamberti, P. palitans, P. dipodomyicola, P. griseofulvum |
| Penicillic acid | Cereals, hay, onions, carrots, potatoes | P. aurantiogriseum, P. cyclopium, P. melaconidium, P. viridicatum, P. polonicum, P. radicicola |
| Roquefortine C | Farm silage, cheese, meat products, sugar beet pulp | P. roqueforti, P. carneum, P. chrysogenum, P. crustosum, P. expansum, P. paneum, P. albocoremium, P. allii, P. griseofulvum, P. hordei, P. melanoconidium, P. radicicola, P. sclerotigenum, plus other 13 Penicillium species |
| Mycophenolic acid | Cheese, sugar beet pulp | P. brevicompactum, P. roqueforti and P. carneum |
| Gliotoxin | Sugar beet pulp | A. fumigatus, Gliocladium fimbriatum |
2. Results
2.1. Co-Occurrence of five Mycotoxins in Maize and Wheat
| 2014 | |||||
| Parameter | Cyclopiazonic acid | Penicillium acid | Mycophenolic acid | Roquefortine C | Gliotoxin |
| Analyzed samples | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 |
| Positive samples | 4 | 0 | 10 | 2 | 0 |
| Incidence (%) | 12.9 | 0.0 | 32.3 | 6.5 | 0.0 |
| Min | 189.12 | 0.00 | 72.92 | 124.62 | 0.00 |
| Max | 868.89 | 0.00 | 3447.25 | 431.16 | 0.00 |
| Meana | 590.21 | 0.00 | 1063.89 | 277.89 | 0.00 |
| Mediana | 651.41 | 0.00 | 374.65 | 277.89 | 0.00 |
| Meanb | 76.16 | 0 | 343.19 | 17.93 | 0 |
| 2015 | |||||
| Analyzed samples | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 21 |
| Positive samples | 0 | 0 | 18.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Incidence (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 90.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Min | 0.00 | 0.00 | 25.46 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Max | 0.00 | 0.00 | 134.43 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Meana | 0.00 | 0.00 | 46.60 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Mediana | 0.00 | 0.00 | 37.30 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Meanb | 0.00 | 0.00 | 31.89 | 0.00 | 0 |
3. Discussion
3.1. Co-Occurrence with Fusarium, AFs, OTA, and Alternaria Toxins
3.2. Climate Conditions in Agricultural Districts of Albania
| Country | Commodity | Incidence of Positive Samples | Mean (μg/kg) |
Range (μg/kg) |
Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclopiazonic acid (CPA) | Indonesia | Feed | 1/1 | 6000 | 6000 | [32] |
| Feed | 21/26 | - | LOD-9000 | |||
| Indonesia/Australia | Poultry Feed | 19/26 | 2117 | 30-9220 | [33] | |
| USA | Feed | 33/38 | 390 | 120-1820 | [34] | |
| India | Feed | 10/26 | - | 400-12000 | [31] | |
| USA | Maize | 23/45 | - | LOD-2,771 | [29] | |
| Japan | Maize | 1/6 | 76 | 76 | [25] | |
| Mozambique | Feed | 1/13 | 606 | [35] | ||
| Penicillic acid (PA) | Bulgaria/South Africa | Feed | 23/25 | 904.9 | 30-9220 | [42] |
| USA | Maize | 7/20 | 59 | 5-231 | [43] | |
| Roquefortine C (ROQ C) | Czech Republic, Denmark, Hungary | Feed | 4/82 | 4.6 | 1.3-14 | [44] |
| USA | Maize silage | 30/60 | - | 20-1100 | [45] | |
| Germany | Maize silage | 12/12 | 17,000 | 700-36,000 | [46] | |
| Italy | Maize silage | 10/196 | 740 | Lod-32,000 | [47] | |
| Netherland | Maize silage | 778 | LOD-3160 | [48] | ||
| Mycophenolic acid (MPA) | USA | Maize silage | 16/60 | - | 80-600 | [45] |
| Germany | Maize silage | 38/135 | 690 | 20-23,000 | [49] | |
| Italy | Maize silage | 16/196 | 1760 | LOD-48,000 | [47] | |
| Netherland | Maize silage | 524 | LOD-2630 | [50] |
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Standards and Chemicals
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. LC-MS/MS Operation
| Mycotoxin | Abbrev. | Retention time (min) | Precursor ion (m/z) | Quantifier ion (m/z) | Qualifier ion (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roquefortine C | ROQ C | 2.92 | 390 | 215 | 200 |
| Gliotoxin | GLI | 3.61 | 325 | 261 | 243 |
| Penicillic acid | PA | 4.75 | 170 | 109.8 | 259 |
| Mycophenolic acid | MPA | 5.25 | 321 | 207 | 241 |
| Cyclopiazonic acid | CPA | 5.33 | 337 | 196 | 182 |
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bianchini, A.; Bullerman, L.B. Mycotoxins, Classification. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, Vol. 2. 2nd Ed, Batt, C. A.; Tortorello. M-L, Eds; Academic Press, Amsterdam, Netherland, 2014; pp. 854–861. [CrossRef]
- Perrone, G.; Susca, A. Penicillium Species and Their Associated Mycotoxins. In Mycotoxigenic Fungi. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1542; Moretti, A.; Susca, A. (eds) Humana Press, New York, USA. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Lopes, P.; Sobral, MM; Lopes, G. R.; Martins, Z.E.; Passos, C.P.; Petronilho, S.; Ferreira, I.M. Mycotoxins’ Prevalence in Food Industry By-Products: A Systematic Review. Toxins, 2023, 15, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisvad, J.; Samson, R.A. Polyphasic taxonomy of Penicillium subgenus Penicillium. A guide to the identification of food and air-borne terverticillate Penicillia and their mycotoxins. Stud. Mycol., 2004, 49, 1–174. [Google Scholar]
- Mostrom, M. Mycotoxins: Toxicology. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health, Caballero, B.; Finglas, P. M.; Toldrá, F. Eds.; Academic Press, Massachusetts, USA, 2016; pp. 29–34.
- Pitt, J.I. Penicillium toxins: Hazards and Diseases, In Encyclopedia of Food Safety, 2nd Ed.; Motarjemi, Y.; Moy, G.G.; Todd, E.C. Eds.; Elsevier Ltd., Academic Press, Netherland, 2014, pp. 283–288.
- Chang, P-K. ; Ehrlich, K.C.; Fujii, I. Cyclopiazonic Acid Biosynthesis of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus oryzae. Toxins, 2009, 1, 74–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryden, W.L.; Suksupath, S.; Taylor, D.J.; Prasongsidh, B.C. Cyclopiazonic Acid: Food Chain Contaminant? Poisonous Plants and Related Toxins. Acamovic, T.; Stewart, C.S.; & Pennycott, T.W. Eds. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, U.K., 2004; pp. 134–139.
- Ostry, V.; Toman, J.; Grosse, Y.; Malir, F. Cyclopiazonic acid: 50th anniversary of its discovery. World Mycotoxin J. 2018, 11, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.A.; Sebastio, L.S.; Fagundes, H.; Rosim, R.E.; Fernandes, A.M. Aflatoxins and cyclopiazonic acid in feed and milk from dairy farms in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Food Addit. Contam. 2008, 1, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidenbörner, M. Mycotoxins in Feedstuffs, 2nd Edition. Springer Science+Business Media, New York, USA. 2012; pp. 295.
- Frisvad, J.C.; Thrane, U.; Samson, R.A.; Pitt, J.I. Important mycotoxins and the fungi that produce them. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 2006, 571, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisvad, J.C. A critical review of producers of small lactone mycotoxins: patulin, penicillic acid, and moniliformin. World Mycotoxin J. 2018, 11, 73–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciegler, A.; Kurtzman, C. P. Penicillic Acid Production by Blue-Eye Fungi on Various Agricultural Commodities. Appl. Microbiol.; 1970, 20, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoev, S.D.; Vitanov, S.; Anguelov, G.; Petkova-Bocharova, T.; Creppy, E.E. Experimental mycotoxic nephropathy in pigs provoked by a diet containing ochratoxin A and penicillic acid, Vet. Res. Commun. 2001, 25, 205–223. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.; Dobson, A.D. Yeasts and Molds, Penicillium roqueforti. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences (2nd Ed), Fuquay, J.W. Ed.; Academic Press: Massachusetts, USA, 2011; pp. 772–775. [Google Scholar]
- Abramson, D. Mycotoxins, Toxicology. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, Robinson, R.K. Eds. Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 1999; pp. 1539–1547. [CrossRef]
- Tangni, E.K.; Pussemier, L.; Bastiaanse, H.; Haesaert, G.; Foucart, G. Van Hove F. Presence of Mycophenolic Acid, Roquefortine C, Citrinin, and Ochratoxin A in Maize and Grass Silages Supplied to Dairy Cattle in Belgium. J. Anim. Sci. Adv. 2013, 3, 598–612. [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick, A.D. 2,5-Diketopiperazines: Synthesis, Reactions, Medicinal Chemistry, and Bioactive Natural Products. Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112, 3641–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, R. Mycophenolic acid: a one-hundred-year odyssey from antibiotic to immunosuppressant. Chemical Review. 2000; 100, 3801–3825. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, N. J.; Marroquín-Cardona, A. G.; Romoser, A.; Phillips, T. D.; Hayes, A.W. Mycotoxins. Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences. Elsevier, Netherlands, 2014; [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, D.M.; Waring, P.; Howlett, B.J. The epipolythiodioxopiperazine (ETP) class of fungal toxins, distribution, mode of action, functions, and biosynthesis. Microbiology, 2005, 151, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.; McGinnis, M.R. Mycotoxins and their effects on humans. Clinical Mycology, 2009; 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhoft, A.; Keblys, M.; Morrison, E.; Jørgen, H.; Larsen, S.; Flaøyen, A. Combined effects of selected Penicillium mycotoxins on in vitro proliferation of porcine lymphocytes. Mycopathologia, 2004, 158, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Yoshizawa, T. Analysis of cyclopiazonic acid in corn and rice by a newly developed method. Food Chem. 2005, 93, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topi, D.; Babič, J.; Pavšič-Vrtač, K.; Tavčar-Kalcher, G.; Jakovac-Strajn, B. Incidence of Fusarium Mycotoxins in Wheat and Maize from Albania. Molecules, 2021; 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topi, D.; Babic, J.; Jakovac-Strajn, B.; Tavcar-Kalcher, G. Incidence of Aflatoxins and Ochratoxin A in Wheat and Corn from Albania. Toxins, 2023; 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, L.; Damani, Z.; Spahiu, J.; Halimi, E.; Seiti, B.; Topi, D. High Prevalence of Mycotoxigenic Fungi and Aflatoxin B1 Contamination in Corn and Wheat Grains Grown to Albania: Implications for Food Safety. Journal of Food Quality and Hazards Control, 2024, 11, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urano, T.; Trucksess, M.W.; Beaver, R.W.; Wilson, DM; Doenew, J. W.; Dowel, F.E. Co-occurrence of cyclopiazonic acid and aflatoxins in corn and peanut. Journal of AOAC International, 1992, 75, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finoli, C.; Vecchio, A.; Galli, A.; Franzetti, L. Production of cyclopiazonic acid by moulds isolated from taleggio cheese. J. Food Protection, 1999, 62, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, C.; Parthasarathy, K.R. Occurrence of cyclopiazonic acid in feeds and feedstuffs in Tamil Nadu, India. Mycopathologia, 1996, 133, 159–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoltz, D.R.; Widiastuti, R.; Maryam, R.; Akoso, B.T.; Amang, U.D. Suspected cyclopiazonic acid mycotoxicosis of quail in Indonesia. Toxicon, 1988, 26, 39–40. [Google Scholar]
- Widiastuti, R.; Maryam, R.; Blaney, B.J.; Salfina; Stoltz, D. R. Cyclopiazonic acid in combination with aflatoxins, zearalenone, and ochratoxin A in Indonesian corn. Mycopathologia, 1988, 104, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W. ; Yu, F-Y. ; Undersander, D.J.; Chu, F.S. Immunoassays of Selected Mycotoxins in Hay, Silage and Mixed Feed, Food and Agr. Immunol. 1999, 11, 307–319. [Google Scholar]
- Warth, B.; Parich, A.; Atehnkeng, J.; Bandyopadhayay, R.; Schumacher, R.; Sulyok, M.; et al. Quantitation of mycotoxins in food and feed from Burkina Faso and Mozambique using a modern LC-MS/MS multitoxin method. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2012, 60, 9352–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różewicz, M.; Wyzińska, M.; Grabiński, J. The Most Important Fungal Diseases of Cereals—Problems and Possible Solutions. Agronomy, 2021, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, M.A.; Jones, A.D.; Kuldau, G.A. Contamination of fresh and ensiled maize by multiple Penicillium mycotoxins. Phytopathology, 2008, 98, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidenborner, M. Mycotoxins in Foodstuffs, 2nd Edition. Springer, New York, USA, 2013; pp. 433; pp. 498-499.
- Topi, D. , Tavčar-Kalcher G., Pavšič-Vrtač K., Babič J., Jakovac-Strajn B. (2019). Alternaria mycotoxins in grains from Albania: alternariol, alternariol monomethyl ether, tenuazonic acid, and tentoxin. World Mycotoxin Journal. 12: 89-99. [CrossRef]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, Ch.; Rudolf, B.; Rube, F. World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Geosciences, (2020). Monthly climate bulletin. https://www.geo.edu.al/newweb/. ISSN 2521-831X. (Accessed on September 15, 2024).
- Stoev, S.D.; Dutton, M.F.; Njobeh, P.B.; Mosonik, J.S.; Steenkamp, P.A. Mycotoxic nephropathy in Bulgarian pigs and chickens: complex etiology and similarity to Balkan endemic nephropathy. Food Addit. Contam. Part A, Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2010, 27, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, C.W.; & Johnson, R.L.; & Johnson, R. L. Analysis of penicillic acid by gas-liquid chromatography. Journal of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 1974, 57, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monbaliu, S.; Van Poucke, C.; Detavernier, C.; Dumoulin, F.; Van De Velde, M.; Schoeters, E.; et al. . Occurrence of mycotoxins in feed as analyzed by a multi-mycotoxin LC-MS/MS method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, M.A.; Archibald, D.D.; Jones, A.D.; Kuldau, G.A. Relationship of sphinganine analogue mycotoxin contamination in maize silage to seasonal weather conditions and agronomic and ensiling practices. Phytopathology, 2007, 97, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, H.; Oldenburg, E.; Weissbach, F. Incidence of Penicillium roqueforti and roquefortine C in silages. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1998, 76, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Giuberti, G.; Frisvad, J.C.; Bertuzzi, T.; Nielsen, K.F. Review on Mycotoxin Issues in Ruminants: Occurrence in Forages, Effects of Mycotoxin Ingestion on Health Status and Animal Performance and Practical Strategies to Counteract Their Negative Effects. Toxins, 2015, 7, 3057–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driehuis, F.; Spanjer, M.C.; Scholten, J.M.; Te Giffel, M.C. Occurrence of mycotoxins in maize, grass, and wheat silage for dairy cattle in the Netherlands. Food Addit. Contam. Part B., 2008, 1, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneweis, I.; Meyer, K.; Hörmansdorfer, S.; Bauer, J. ; Mycophenolic acid in silage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol, 2000, 66, 3639–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driehuis, F.; Spanjer, M.C.; Scholten, J.M.; Te Giffel, M.C. Occurrence of mycotoxins in feedstuffs of dairy cows and estimation of total dietary intakes. J. Dairy Science, 2008, 91, 4261–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandicke, J.; De Visschere, K.; Ameye, M.; Croubels, S.; De Saeger, S.; Audenaert, K.; Haesaert, G. Multi-Mycotoxin Contamination of Maize Silages in Flanders, Belgium: Monitoring Mycotoxin Levels from Seed to Feed. Toxins, 2021, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, L.; Damani, Z.; Osmanaj, A.; & Topi, D.; & Topi, D. Nutritional value and quality aspects of wheat produced and consumed in Albania. 3rd International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies (I-CRAFT-2023). BIO Web of Conferences 2024, 85, 01059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, R.R.; Storm, I.M.; Rasmussen, P.H.; Smedsgaard, J.; Nielsen, K.F. Multi-mycotoxin analysis of maize silage by LC-MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





