1. Introduction
Since the first monoclonal antibody (mAb) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1986, a variety of therapeutic antibodies and their derivatives have been developed together with advances in antibody engineering [
1,
2]. In mAb therapy for solid tumors, trastuzumab and pertuzumab were approved by the FDA for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-overexpressed breast cancer in 1998 and 2012, respectively [
3]. An anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mAb, cetuximab was approved by the FDA for metastatic colorectal cancer in 2004 and head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs) in 2006 [
4]. These mAbs exerted antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and have been used in monotherapy or combination therapy with chemotherapy [
5].
Although the number of naked mAb targets for solid tumors has not increased, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are one of the fastest-growing formats of mAb-based solid tumor therapy [
6]. ADCs possess covalently-bound cytotoxic agents (payloads) via synthetic linkers, which exhibit high stability and selectivity and favor pharmacokinetics [
7]. In solid tumor therapy, trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) was first approved by the FDA in 2013 [
8]. Since 2013, more than 60 ADCs entered clinical trials for a wide range of tumors. Enfortumab vedotin (target: Nectin-4) [
9], Sacituzumab govitecan (target: TROP2) [
10], Trastuzumab deruxtecan (target: HER2) [
11], Tisotumab vedotin (target: Tissue factor) [
12], and Mirvetuximab soravtansine (target: Folate receptor alpha) [
13] were approved by the FDA. However, toxicity remains an essential problem in the development. Among 97 ADCs that have entered clinical trials since 2000, 81 trials (84%) were terminated. Causes of termination were disclosed for 79. The reason for the discontinuation was a lack of efficacy (32 agents) and safety issues (32 agents) [
6]. On-target, off-tumor toxicity is a cause of adverse effects when the target antigen is expressed in normal cells. Therefore, a better understanding and management of the tumor specificity of mAbs will be essential for further optimization.
Podoplanin (PDPN)/T1α/gp36/Aggrus is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that contains three platelet aggregation-stimulating domains called PLAG1, PLAG2, and PLAG3 [
14]. Some PLAG-like domains (PLDs) also exist, one of which is called the PLAG4 [
14]. The PLAG3 and PLAG4 are modified with
O-glycosylation, which is essential to bind to C-type lectin-like receptor 2 (CLEC-2) and PDPN-induced platelet aggregation [
15,
16]. The PDPN-induced platelet aggregation plays critical roles in tumor cell survival in circulation and hematogenous metastasis through the evasion from antitumor immunity [
17] and promotion of embolization [
18,
19].
PDPN promotes tumor metastasis through the recruitment of the ezrin, radixin, and moesin (ERM) complex, which remodels actin cytoskeletons and regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) [
20]. The depletion of PDPN potently suppressed transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-induced EMT [
21], indicating the critical roles of PDPN in EMT and malignant progression of tumors. Moreover, PDPN-positive tumor cells exhibit the diverse pattern of invasion, such as ameboid invasion in melanoma [
22] and collective invasion in SCCs [
23]. Furthermore, PDPN binds to hyaluronan receptor CD44 [
24] and matrix metalloproteinases [
25]. The complexes mediate the formation of tumor invadopodia, which promotes extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation and invasiveness [
26]. In the clinic, high PDPN expression was associated with shortened overall survival in patients with various tumors, including HNSCCs, esophageal SCCs, gastric adenocarcinomas, gliomas, and mesotheliomas [
27,
28,
29,
30].
The elevated expression of PDPN is also observed in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), a main constituent of the tumor microenvironment (TME). Increased abundance of PDPN in CAFs is correlated with poor clinical outcomes in pancreatic [
31], breast [
32], and lung [
33,
34,
35] cancer patients. The PDPN-positive CAFs from lung tumors were reported to affect the therapeutic outcomes of EGFR inhibitors [
36]. The PDPN-positive CAFs are also involved in the formation of an immunosuppressive TME through the secretion of TGF-β, which reduces antitumor immune responses [
37]. Additionally, PDPN-positive CAFs were associated with low interleukin-2 activity and trastuzumab resistance in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer [
38]. Therefore, PDPN in tumors and CAFs has been recognized as a useful diagnostic marker and an attractive target for tumor therapy. Since PDPN plays an essential role in normal cells such as kidney podocytes, lymphatic endothelial cells, and lung alveolar epithelial type I cells, anti-PDPN mAbs that recognize tumor cell-expressed PDPN but not normal cell-expressed PDPN have been desired for tumor therapy.
Our group has developed cancer-specific mAbs (CasMabs) against PDPN, which were obtained by immunization of mice with PDPN-overexpressed glioblastoma LN229 cells. LpMab-2 [
39] and LpMab-23 [
40] were selected by the cancer-specific reactivity in flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry. Furthermore, they are converted and produced mouse IgG
2a type mAbs and showed the potent ADCC and antitumor effect in xenograft models of human tumors [
41,
42]. In this study, we established another CasMab against PDPN (PMab-117) by immunization of a rat with PDPN-overexpressed glioblastoma LN229 cells. We further evaluated the ADCC activity and antitumor effect against PDPN-positive tumor cells.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
LN229, HBEC3-KT, hTERT-HME1, and P3X63Ag8U.1 (P3U1) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA). 293FT was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (Thermo; Waltham, MA, USA). PODO/TERT256 and hTCEpi were purchased from EVERCYTE (Vienna, Austria). Human glioblastoma LN319 cells were purchased from Addexbio Technologies (San Diego, CA, USA). Human lung squamous cell carcinoma PC-10 cells were purchased from Immuno-Biological Laboratories Co., Ltd. (Gunma, Japan).
PDPN-overexpressed LN229 (LN229/PDPN) cells were established as previously described [
39]. LN229, LN229/PDPN, and LN319 cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) [Nacalai Tesque, Inc. (Nacalai), Kyoto, Japan]. PC-10 cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI)-1640 medium (Nacalai). These media were supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS; Thermo), 0.25 μg/mL amphotericin B, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 100 units/mL penicillin (Nacalai). ExpiCHO-S and Fut8-deficient ExpiCHO-S (BINDS-09) cells were cultured as described previously [
41].
Immortalized normal epithelial cell lines were maintained, as follows; PODO/TERT256, MCDB131 (Pan Biotech, Bayern, Germany) supplemented with GlutaMAXTM-I (Thermo), Bovine Brain Extract (9.6 μg/mL, Lonza, Basel, Switzerland), EGF [8 ng/ml, Sigma-Aldrich Corp. (Sigma), St. Louis, MO, USA], Hydrocortisone (20 ng/mL, Sigma), 20% FBS (Sigma), and G418 (100 μg/mL, InvivoGen, San Diego, CA); HBEC3-KT, Airway Epithelial Cell Basal Medium and Bronchial Epithelial Cell Growth Kit (ATCC); hTERT-HME1, Mammary Epithelial Cell Basal Medium BulletKitTM without GA-1000 (Lonza); hTCEpi, KGMTM-2 BulletKitTM (Lonza).
All cell lines were cultured at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 and 95% air.
2.2. Animals
The animal experiment for the establishment of anti-PDPN mAbs was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Tohoku University (approval no. 2016MdA-153). To investigate the ADCC and antitumor activity of PMab-117-mG2a, animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Committee for Experiments of the Institute of Microbial Chemistry (approval nos. 2024-062 [ADCC] and 2018-031 [antitumor activity]). Animals were maintained in a pathogen-free condition on 11 h light/13 h dark cycle with food and water supplied ad libitum. The health and weight were monitored every one or five days. We identified body weight loss exceeding 25% and maximum tumor size exceeding 3000 mm3 as humane endpoints.
2.3. Hybridoma Production
A five-week-old Sprague–Dawley rat (CLEA Japan, Tokyo, Japan) was immunized with LN229/PDPN (1 × 10
9 cells) together with Imject Alum (Thermo) via intraperitoneal injection. After three additional injections every week (1 × 10
9 cells/rat), a final booster injection (1 × 10
9 cells/rat) was performed two days before harvesting spleen cells. The hybridomas were produced, as described previously [
40]. Culture supernatants were screened using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for binding to PDPN ectodomain (PDPNec). The higher reactivity to cancer cell lines (PC-10 and LN319) than embryonic kidney 293FT cells using flow cytometry was critical for selecting CasMabs.
2.4. ELISA
PDPNec was immobilized on Nunc Maxisorp 96-well immunoplates (Thermo) at 1 μg/mL for 30 min. After blocking with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in 0.05% Tween 20-phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, Nacalai), the plates were incubated with culture supernatant followed by 1:20000 diluted peroxidase-conjugated anti-rat immunoglobulins (Sigma). The enzymatic reaction was produced with an ELISA POD Substrate TMB Kit (Nacalai). The optical density was measured at 655 nm using an iMark microplate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Berkeley, CA, USA).
2.5. Antibodies
For the generation of PMab-117-mG
2a, the complementarity determining region (CDR) of PMab-117 V
H, frame sequences of V
H in mouse IgG
2a, and C
H of mouse IgG
2a were cloned into the pCAG-Neo vector [FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation (Wako), Osaka, Japan]. The CDR of PMab-117 V
L, frame sequences of V
L in mouse Ig, and C
L of the mouse kappa chain were cloned into the pCAG-Ble vector (Wako). We transfected the PMab-117-mG
2a expression vectors into BINDS-09 cells using the ExpiCHO-S Expression System (Thermo). We purified PMab-117-mG
2a using Ab-Capcher (ProteNova Co., Ltd., Kagawa, Japan). NZ-1 (an anti-PDPN mAb) [
43] and PMab-231 (control mouse IgG
2a) [
44] were previously described. Mouse IgG (mIgG) was purchased from Wako.
2.6. Flow cytometry
Cells were collected using 0.25% trypsin and 1 mM ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA; Nacalai). The cells (1 × 105 cells/sample) were treated with NZ-1, PMab-117, PMab-117-mG2a, or blocking buffer (control) (0.1% BSA in PBS) for 30 min at 4 °C. Next, the cells were treated with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-rat or mouse IgG (1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA) for 30 min at 4 °C. The SA3800 Cell Analyzer (Sony Corp., Tokyo, Japan) was used to collect the fluorescence data, which were analyzed using FlowJo software (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA).
2.7. Determination of the Binding Affinity by Flow Cytometry
After being suspended in 100 μL of serially diluted PMab-117-mG2a or NZ-1, the cells were then incubated with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-mouse or rat IgG (1:200), respectively. The SA3800 Cell Analyzer was used to obtain the fluorescence data. To calculate the dissociation constant (KD), GraphPad PRISM 6 software (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA) was used.
2.8. ADCC
Effector splenocytes were obtained from the spleen of female BALB/c nude mice (Jackson Laboratory Japan, Inc., Kanagawa, Japan) as described previously [
45]. CHO/PDPN, PC-10, and LN319 cells were labeled with 10 µg/mL of Calcein AM (Thermo). Target cells (1 × 10
4 cells/well) were plated and mixed with the effector cells (effector-to-target ratio, 50: 1) and 100 μg/mL of control mouse IgG
2a (PMab-231) or PMab-117-mG
2a. The released calcein into the medium was measured after a 4.5 h incubation. Fluorescence intensity was determined using a microplate reader (Power Scan HT; BioTek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA) with excitation and emission wavelengths of 485 and 538 nm, respectively. After lysing all cells with a buffer containing 0.5% Triton X-100, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), and 10 mM EDTA, cytotoxicity (% lysis) was calculated as % lysis = (E − S)/(M − S) × 100, where E is the fluorescence of the combined target and effector cells, S is the spontaneous fluorescence of target cells only, and M is the maximum fluorescence measured.
2.9. Antitumor Activity of PMab-117-mG2a in Xenografts of LN229/PDPN, PC-10, and LN319
LN229/PDPN, PC-10, or LN319 was suspended in 0.3 mL of DMEM (1.33 × 108 cells/mL) and mixed with 0.5 mL of BD Matrigel Matrix Growth Factor Reduced (BD Biosciences). Then, BALB/c nude mice (Jackson Laboratory Japan, Kanagawa, Japan) were injected subcutaneously in the left flank with 100 μL of the suspension (5 × 106 cells). Following the inoculation of LN229/PDPN, PC-10, or LN319 (day 0), PMab-117-mG2a (n = 8) or control mIgG (n = 8) was intraperitoneally injected into the xenograft-bearing mice on days 1, 8, and 16 (LN229/PDPN and LN319) or days 1, 8, 14, and 22 (PC-10). The tumor volume was calculated using the following formula: volume = W2 × L/2, where W is the short diameter and L is the long diameter. All mice were euthanized by cervical dislocation 22~30 days after cell inoculation.
2.10. Statistical Analyses
All data are represented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Two-tailed unpaired t test was used for the statistical analyses of ADCC and tumor weight. Two-way ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparisons test was used for tumor volume and mouse weight. p < 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
4. Discussion
For the development of mAbs for tumor therapy, the identification and validation of adequate antigenic targets are important [
1]. To achieve an acceptable therapeutic index and avoid on-target toxicity, target antigens should ideally have high tumor expression levels and little or no expression in normal tissues. However, the limitation of the ideal target antigens is a severe problem. Some technologies, including bispecific antibodies, defucosylated antibodies, and ADCs, enhance the activity of antibodies, contributing to tumor therapy development. However, on-target toxicity due to recognizing antigens in normal cells has not been resolved. Therefore, selecting mAb that recognizes cancer-specific epitopes is essential to reduce the adverse effects. This study developed a novel CasMab against PDPN (PMab-117) by immunizing LN229/PDPN with a rat (
Figure 1). The mouse IgG
2a type PMab-117 (PMab-117-mG
2a) reacted with the PDPN-positive tumor cells but not with normal kidney podocytes and normal epithelial cells from lung bronchus, mammary gland, and corneal (
Figure 2). Furthermore, PMab-117-mG
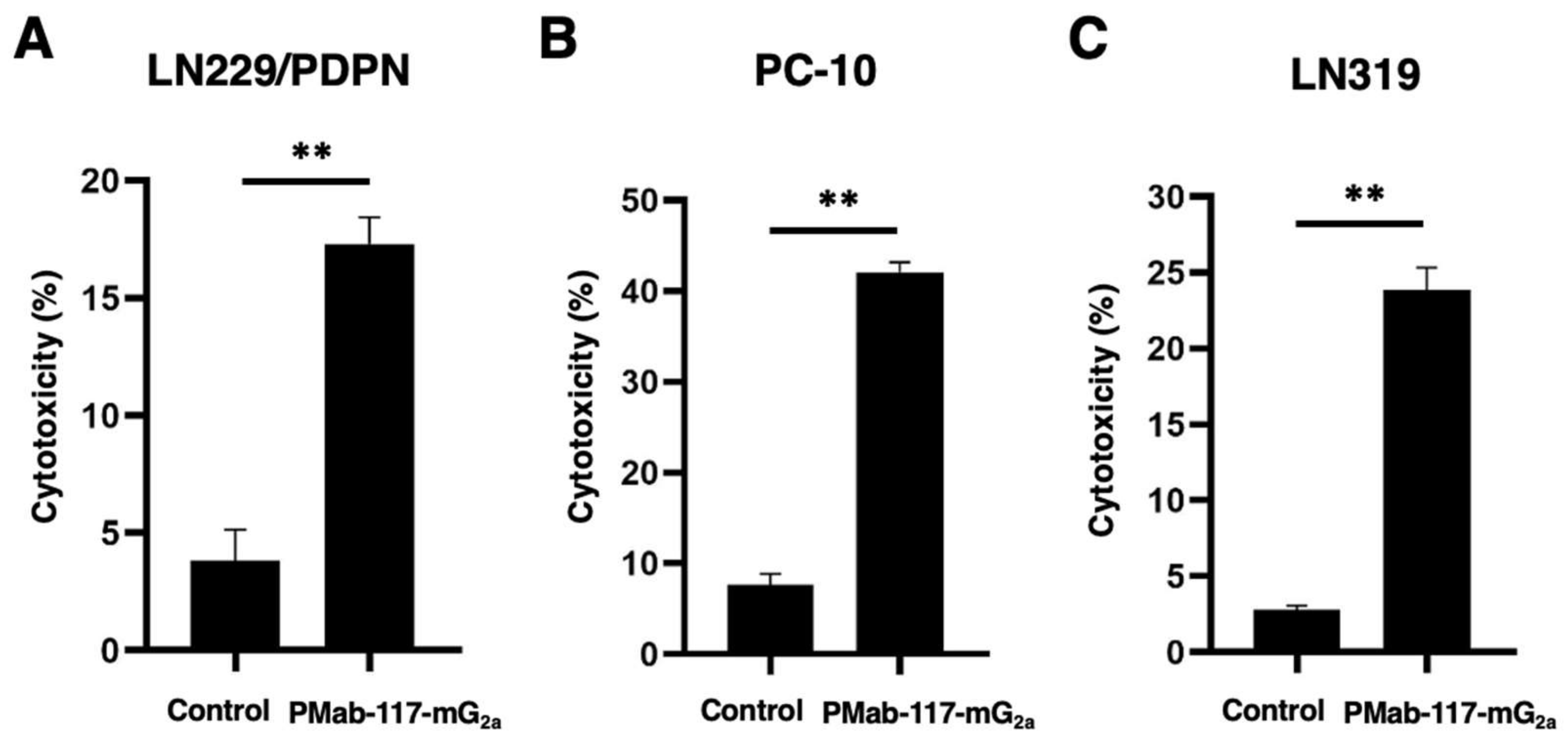
2a exerted a potent ADCC (
Figure 4) and antitumor effect in PC-10 and LN319 xenografts (
Figure 5).
The reactivity of PMab-117-mG
2a in flow cytometry is low in PC-10 (
Figure 2B). In contrast, PMab-117-mG
2a exhibited high ADCC activity (
Figure 4) and antitumor effect (
Figure 5). Although the target cell-derived immunosuppressive factors such as PD-L1 or TGF-β would contribute to the responses, the reactivity of PMab-117-mG
2a in PC-10 is sufficient to exert ADCC and antitumor efficacy in vivo. In this condition, PMab-117-mG
2a did not react with normal kidney podocytes, lung bronchus epithelial cells, mammary gland epithelial cells, and corneal epithelial cells (
Figure 2C). We should investigate the in vivo side effects in the future. Human PDPN PLAG4 domain knock-in mice were generated [
46]. Since PMab-117-mG
2a possesses the epitope around the PLAG4 domain (see below), it is worthwhile to evaluate the side effect in vivo if PMab-117-mG
2a can recognize the human/mouse chimeric PDPN. Furthermore, evaluating the humanized PMab-117-mG
2a to apply clinical studies is essential. We should assess not only the antitumor efficacy but also toxicity to normal tissues using cynomolgus monkeys [
40].
We have reported CasMabs against PDPN (LpMab-2 [
39] and LpMab-23 [
40]), which were obtained by immunization of LN229/PDPN with mice. LpMab-2 recognizes a glycopeptide (Thr55-Leu64) structure of PDPN [
39]. LpMab-23 recognizes a naked peptide structure of PDPN (Gly54–Leu64), especially Gly54, Thr55, Ser56, Glu57, Asp58, Arg59, Tyr60, and Leu64 of PDPN is a critical epitope of LpMab-23 [
47]. PMab-117, obtained by immunization of LN229/PDPN with a rat, recognizes the glycopeptide structure of PDPN (Ile78-Thr85) around PLAG4 domain, which includes
O-glycosylated Thr85 [
14]. A mAb with the specificity and epitope of PMab-117 has never been obtained by immunization with mice. Therefore, the strategies for CasMab generation using mouse or rat immunization can contribute to developing novel CasMabs against various tumor antigens.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy against solid tumors has been evaluated in clinical trials [
48]. Our established anti-PDPN mAbs, NZ-1 and LpMab-2, were developed for CAR-T cell therapy and evaluated in pre-clinical studies. Systemic injection of an NZ-1-based CAR-T cells inhibited the intracranial glioma growth in immunodeficient mice [
49]. A LpMab-2-based CAR-T cell killed patient-derived glioma stem cells and also inhibited the growth of a glioma xenograft in immunodeficient mice [
50]. Therefore, CAR-T cell therapy that targets PDPN would be a promising immunotherapy for the treatment of GBM [
51]. We should investigate the cancer-specific reactivity of PMab-117 single-chain Fv and apply it to CAR-T cell therapy.
Our developed CasMabs against HER2 (clones H
2Mab-214 [
52] and H
2Mab-250 [
53]) were also screened by the reactivity to cancer and normal cells in flow cytometry. Both CasMabs exhibited the antitumor effect in mouse xenograft models using their recombinant mouse IgG
2a or human IgG
1 mAbs [
44,
54]. H
2Mab-250 has been developed as CAR-T-cell therapy. The phase I study has been conducted in the US (NCT06241456). Furthermore, the recognition mode of H
2Mab-214 was solved by X-ray crystallography. H
2Mab-214 recognizes a locally misfolded structure of HER2 extracellular domain 4, which usually forms a β-sheet [
52]. The structural analysis of the PMab-117-PDPN complex is also essential to reveal the mechanism of cancer-specific recognition.
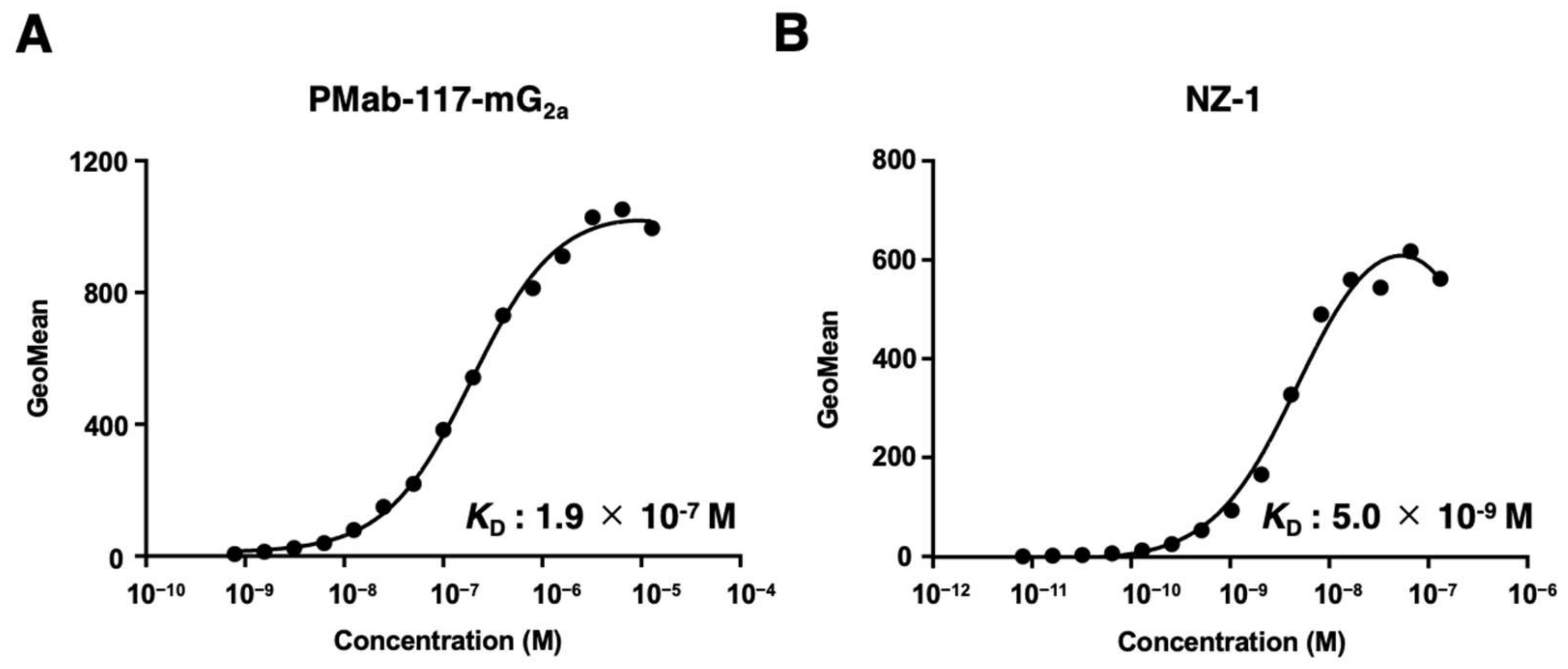
As shown in
Figure 3, PMab-117-mG
2a possesses ~ 40-fold lower affinity (
KD: 1.9 × 10
−7 M) than NZ-1 (
KD: 5.0 × 10
−9 M). The
KD values of other CasMabs against PDPN (LpMab-2 and LpMab-23) were previously determined as 5.7 × 10
−9 M and 1.2 × 10
−8 M, respectively [
39,
47]. These CasMabs have different binding affinity from 10
−7 M to 10
−9 M order. Recently, CAR's affinity to antigen determines CAR-T therapy's efficacy and persistence. Trogocytosis was first proposed as a mechanism of immune escape to CAR-T therapy against CD19 [
55]. When CD19-positive lymphoma cells are co-cultured with CAR-T cells with the high-affinity anti-CD19 FMC63-based CAR, the CAR-T cells remove CD19 from lymphoma cells and acquire it on the plasma membrane [
55]. The phenomenon is called “trogocytosis,” which generates antigen-negative target cells. Furthermore, the CAR-T cells that incorporated CD19 by trogocytosis can be attacked by the other CAR-T cells [
55]. To limit trogocytosis, the reduction of CAR affinity has been proposed. CD19-targeting CAR with ~ 40-fold lower affinity than the FMC63-based CAR showed higher efficacy and persistence than FMC63-based CAR-T in two clinical trials [
56,
57]. These results suggest that the reduction of CAR affinity limits trogocytosis and maintains antitumor activity as well as clinical efficacy. The property of anti-PDPN CasMabs could contribute to the future development of PDPN-targeting CAR-T cells by limiting trogocytosis and maintaining cancer specificity.
ADCs are one of the growing modalities for solid tumor therapy. However, safety issues are one of the reasons for the termination. Bivatuzumab
–mertansine, a humanized anti-CD44v6 ADC, was developed and evaluated in clinical trials [
58]. However, the clinical trials were terminated due to the severe skin toxicity. Since CD44v6 is expressed in the skin epidermis, the efficient accumulation of mertansine in the skin probably leads to skin disorders [
58,
59]. The strategy of CasMab selection may contribute to developing anti-CD44v6 CasMabs to reduce the adverse effects and overcome the depletion of target antigens for tumor therapy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K.K., and Y.K.; methodology, T.O.; formal analysis, T.T.; investigation, H.S., T.O., and T.T.; data curation, H.S. and Y.K.; writing—original draft preparation, H.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.K; project administration, Y.K.; funding acquisition, H.S., T.T., M.K.K., and Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
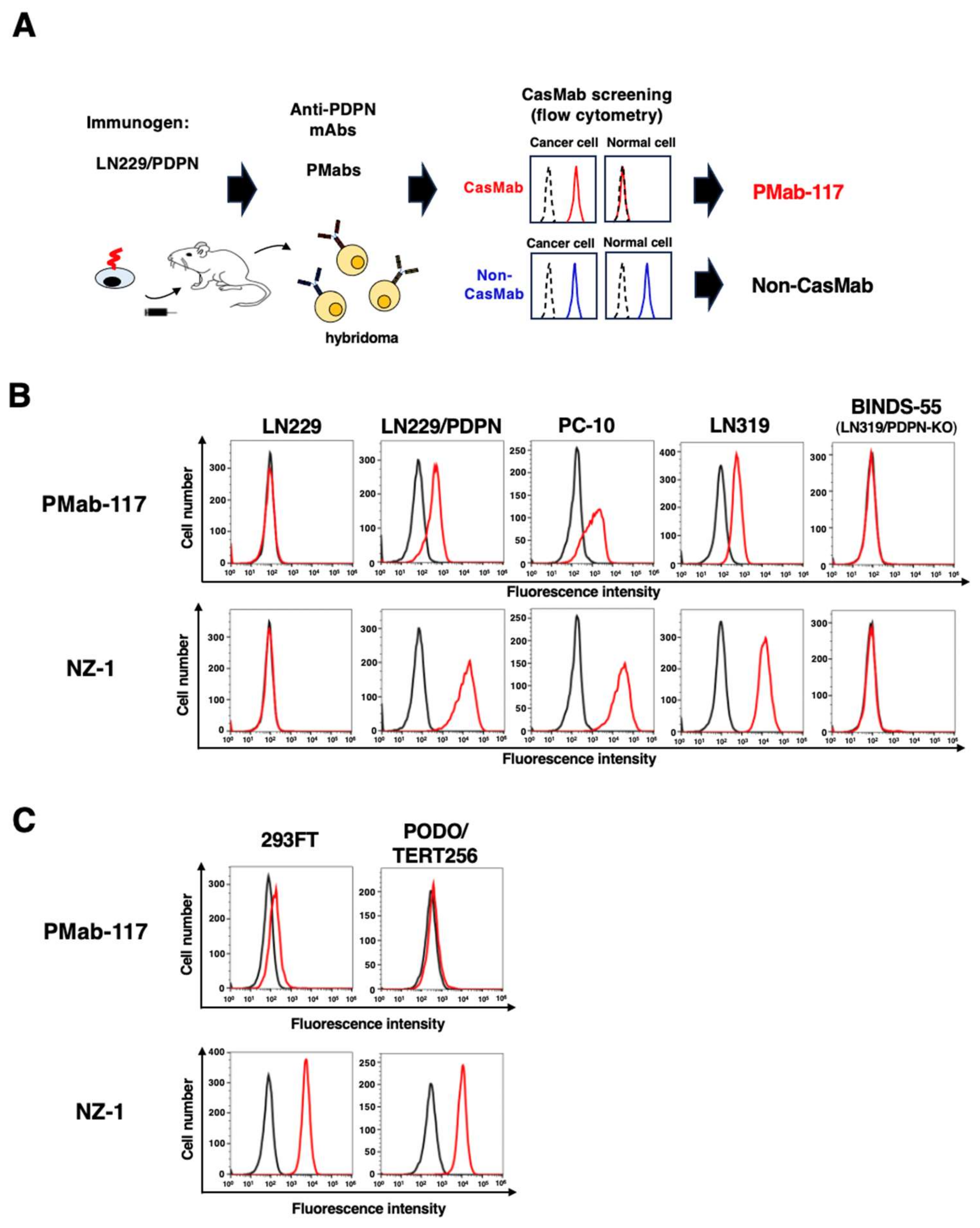
Figure 1.
Selection of anti-PDPN CasMab, PMab-117. (A) A scheme of CasMab selection from anti-PDPN mAb-producing hybridoma clones. (B) Flow cytometry using PMab-117 (10 μg/mL; Red line), NZ-1 (10 μg/mL; Red line) or buffer control (Black line) against LN229, LN229/PDPN, PC-10, LN319, and PDPN-knockout LN319 (BINDS-55). (C) Flow cytometry using PMab-117 (10 μg/mL; Red line), NZ-1 (10 μg/mL; Red line), or buffer control (Black line) against 293FT (human embryonic kidney) and PODO/TERT256 (TERT-expressed normal kidney podocyte).
Figure 1.
Selection of anti-PDPN CasMab, PMab-117. (A) A scheme of CasMab selection from anti-PDPN mAb-producing hybridoma clones. (B) Flow cytometry using PMab-117 (10 μg/mL; Red line), NZ-1 (10 μg/mL; Red line) or buffer control (Black line) against LN229, LN229/PDPN, PC-10, LN319, and PDPN-knockout LN319 (BINDS-55). (C) Flow cytometry using PMab-117 (10 μg/mL; Red line), NZ-1 (10 μg/mL; Red line), or buffer control (Black line) against 293FT (human embryonic kidney) and PODO/TERT256 (TERT-expressed normal kidney podocyte).
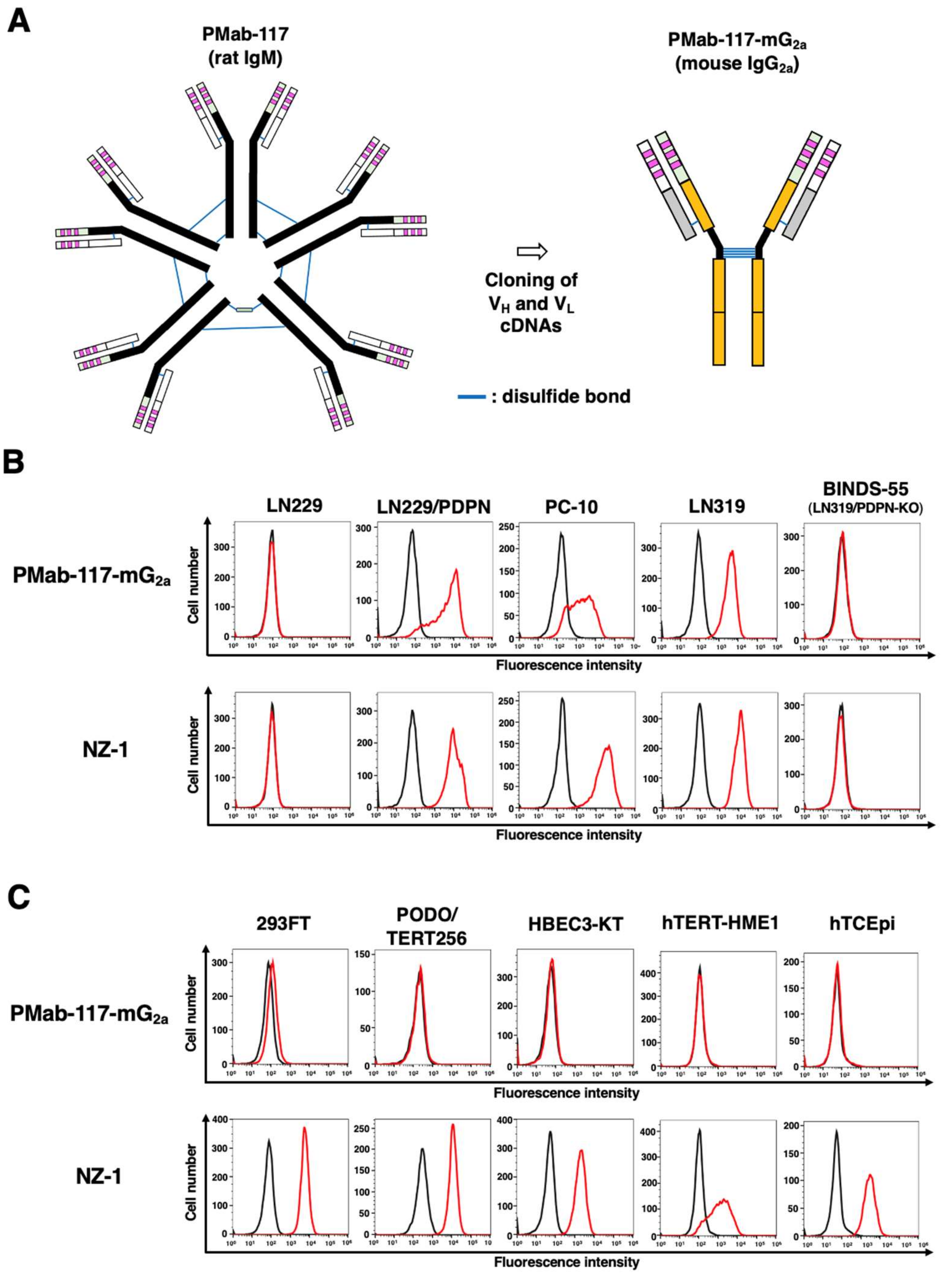
Figure 2.
Production of PMab-117-mG2a and the reactivity to cancer cells, normal kidney podocytes, and epithelial cells. (A) Class-switched mouse IgG2a mAb, PMab-117-mG2a, was generated from PMab-117 (rat IgM). (B) Flow cytometry using PMab-117-mG2a (1 μg/mL; Red line), NZ-1 (1 μg/mL; Red line) or buffer control (Black line) against LN229, LN229/PDPN, PC-10, LN319, and PDPN-knockout LN319 (BINDS-55). (C) Flow cytometry using PMab-117-mG2a (1 μg/mL; Red line), NZ-1 (1 μg/mL; Red line) or buffer control (Black line) against 293FT (human embryonic kidney), PODO/TERT256 (kidney podocyte), HBEC3-KT (lung bronchus epithelial cell), hTERT-HME1 (mammary gland epithelial cell), and hTCEpi (corneal epithelial cell).
Figure 2.
Production of PMab-117-mG2a and the reactivity to cancer cells, normal kidney podocytes, and epithelial cells. (A) Class-switched mouse IgG2a mAb, PMab-117-mG2a, was generated from PMab-117 (rat IgM). (B) Flow cytometry using PMab-117-mG2a (1 μg/mL; Red line), NZ-1 (1 μg/mL; Red line) or buffer control (Black line) against LN229, LN229/PDPN, PC-10, LN319, and PDPN-knockout LN319 (BINDS-55). (C) Flow cytometry using PMab-117-mG2a (1 μg/mL; Red line), NZ-1 (1 μg/mL; Red line) or buffer control (Black line) against 293FT (human embryonic kidney), PODO/TERT256 (kidney podocyte), HBEC3-KT (lung bronchus epithelial cell), hTERT-HME1 (mammary gland epithelial cell), and hTCEpi (corneal epithelial cell).
Figure 3.
Determination of the binding affinity of PMab-117-mG2a and NZ-1 using flow cytometry. LN319 cells were suspended in PMab-117-mG2a or NZ-1 at indicated concentrations, followed by treatment with anti-mouse or rat IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488. The SA3800 Cell Analyzer was used to analyze fluorescence data. The dissociation constant (KD) values were determined using GraphPad Prism 6.
Figure 3.
Determination of the binding affinity of PMab-117-mG2a and NZ-1 using flow cytometry. LN319 cells were suspended in PMab-117-mG2a or NZ-1 at indicated concentrations, followed by treatment with anti-mouse or rat IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488. The SA3800 Cell Analyzer was used to analyze fluorescence data. The dissociation constant (KD) values were determined using GraphPad Prism 6.
Figure 4.
The ADCC activity by PMab-117-mG2a in PDPN-positive cells. The ADCC induced by PMab-117-mG2a or control mouse IgG2a (PMab-231) against LN229/PDPN (A), PC-10 (B), and LN319 (C) cells. Values are shown as the mean ± SEM. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (** p < 0.01; two-tailed unpaired t-test).
Figure 4.
The ADCC activity by PMab-117-mG2a in PDPN-positive cells. The ADCC induced by PMab-117-mG2a or control mouse IgG2a (PMab-231) against LN229/PDPN (A), PC-10 (B), and LN319 (C) cells. Values are shown as the mean ± SEM. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (** p < 0.01; two-tailed unpaired t-test).
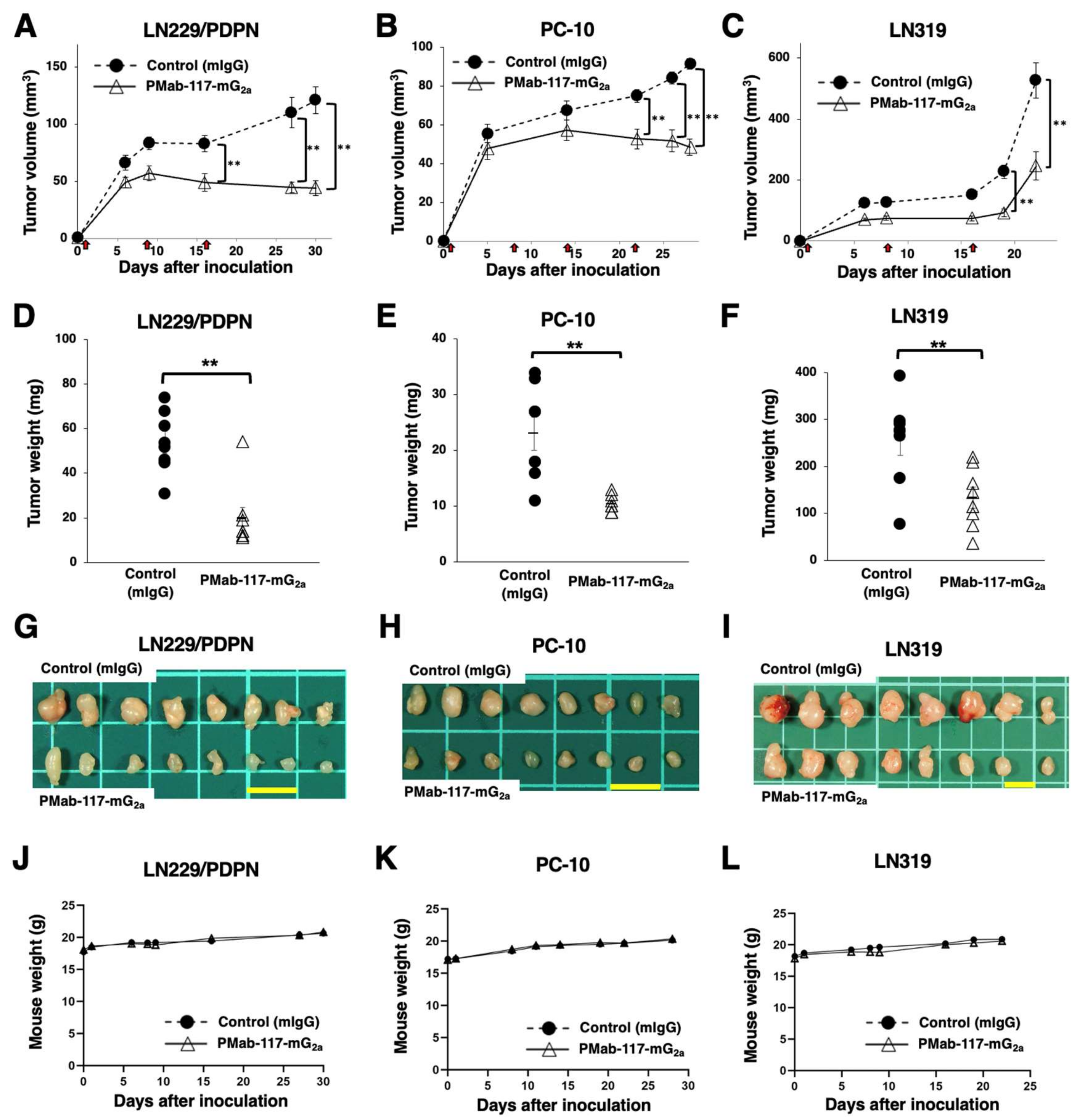
Figure 5.
Antitumor activity of PMab-117-mG2a against human tumor xenografts. (A–C) LN229/PDPN (A), PC-10 (B), and LN319 (C) cells were subcutaneously injected into BALB/c nude mice (day 0). PMab-117-mG2a (100 μg) or control mouse IgG (mIgG, 100 μg) were intraperitoneally injected into each mouse on days 1, 8, and 16 (LN229/PDPN and LN319, arrows) or days 1, 8, 14, and 22 (PC-10, arrows). The tumor volume is represented as the mean ± SEM. ** p < 0.01 (two-way ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). (D–F) The mice were euthanized on day 30 (LN229/PDPN), day 28 (PC-10), or day 22 (LN319) after cell inoculation. The tumor weights of LN229/PDPN (D), PC-10 (E), and LN319 (F) xenografts were measured. Values are presented as the mean ± SEM. ** p < 0.01, (two-tailed unpaired t-test). (G–I) LN229/PDPN (G), PC-10 (H), and LN319 (I) xenograft tumors (scale bar, 1 cm). (J–L) Body weights of LN229/PDPN (J), PC-10 (K), and LN319 (L) xenograft-bearing mice treated with control mIgG or PMab-117-mG2a.
Figure 5.
Antitumor activity of PMab-117-mG2a against human tumor xenografts. (A–C) LN229/PDPN (A), PC-10 (B), and LN319 (C) cells were subcutaneously injected into BALB/c nude mice (day 0). PMab-117-mG2a (100 μg) or control mouse IgG (mIgG, 100 μg) were intraperitoneally injected into each mouse on days 1, 8, and 16 (LN229/PDPN and LN319, arrows) or days 1, 8, 14, and 22 (PC-10, arrows). The tumor volume is represented as the mean ± SEM. ** p < 0.01 (two-way ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). (D–F) The mice were euthanized on day 30 (LN229/PDPN), day 28 (PC-10), or day 22 (LN319) after cell inoculation. The tumor weights of LN229/PDPN (D), PC-10 (E), and LN319 (F) xenografts were measured. Values are presented as the mean ± SEM. ** p < 0.01, (two-tailed unpaired t-test). (G–I) LN229/PDPN (G), PC-10 (H), and LN319 (I) xenograft tumors (scale bar, 1 cm). (J–L) Body weights of LN229/PDPN (J), PC-10 (K), and LN319 (L) xenograft-bearing mice treated with control mIgG or PMab-117-mG2a.