Submitted:
06 October 2024
Posted:
07 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Surveys
1.2. Method
1.3. Contributions
- 1)
- It provides a comprehensive review of advancements in AI and examines its role within the Metaverse’s layered architecture for smart cities. By exploring how AI as the core intelligence enables data analysis and decision-making, enhances user experiences through Computer Vision (CV) and Natural Language Processing (NLP), optimises connectivity with 6G and Edge AI, strengthens security through blockchain applications, and manages the creation of digital twins, the study explains the technical integration of AI into key Metaverse-enabling technologies to deepen the understanding of AI’s capabilities in improving user engagement, connectivity, efficiency, and services, laying the foundation for developing advanced Metaverse applications that address challenges in smart cities.
- 2)
- Building upon the technical insights, it reviews the integrated role of AI and key technologies in realising the Metaverse for sustainable smart cities. By presenting potential AI-enabled applications and use cases in smart environments, mobility, energy, health, governance, and the economy, it offers a practical roadmap for implementing sustainable solutions to enhance citizens’ quality of life, promote economic growth, and achieve sustainability.
- 3)
- It identifies and analyses the challenges and future research directions in integrating AI and key technologies within the Metaverse for sustainable smart cities by highlighting existing gaps, guiding future research and development efforts to overcome these challenges, and informing policymakers to facilitate the implementation of solutions that enhance the quality of life for citizens and promote economic growth and sustainability.
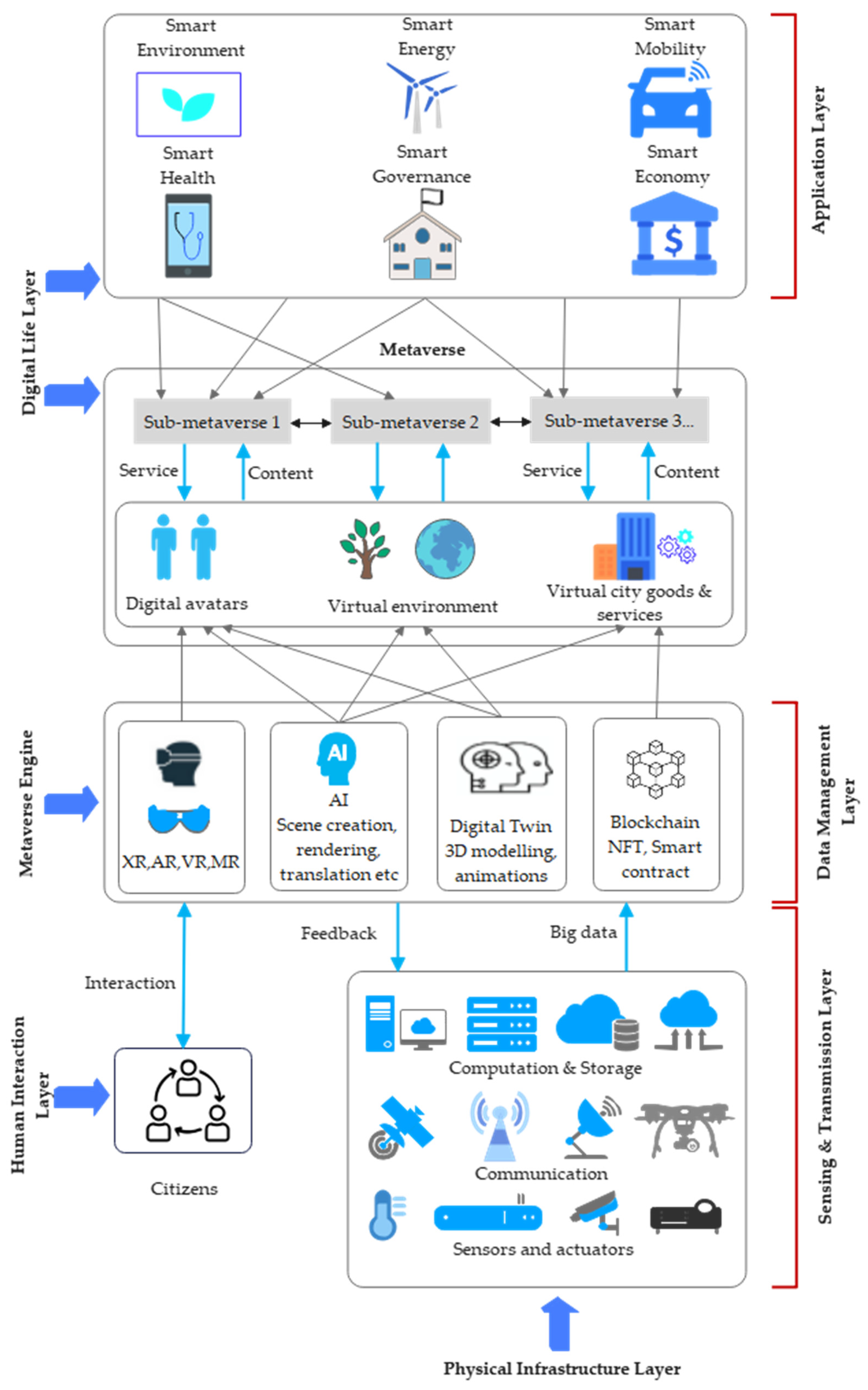
2. Background on Smart City and the Metaverse
2.1. Smart City
- 1)
- Sensing Layer: This layer is at the bottom of the architecture and collects data from physical devices, such as sensors and IoT devices distributed throughout the city.
- 2)
- Transmission Layer: This layer facilitates communication between the sensing and upper layers, using various communication technologies to transmit collected data.
- 3)
- Data Management Layer: Once data is transmitted, it processes and stores valuable information, ensuring it is ready for analysis and service provision.
- 4)
- Application Layer: At the top, this layer provides various services and applications that utilise the processed data to deliver smart city functionalities, such as transportation, healthcare, and energy management.
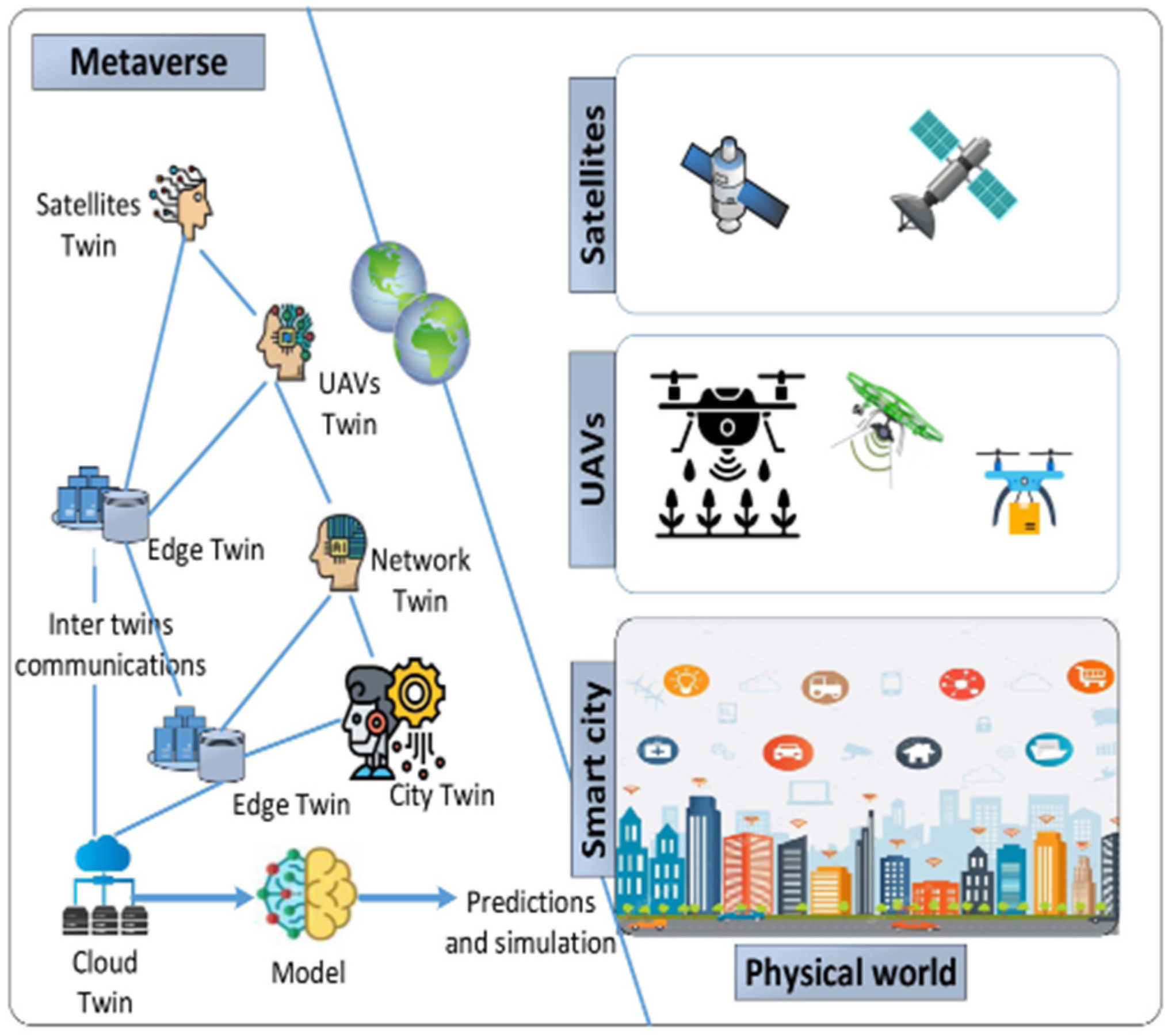
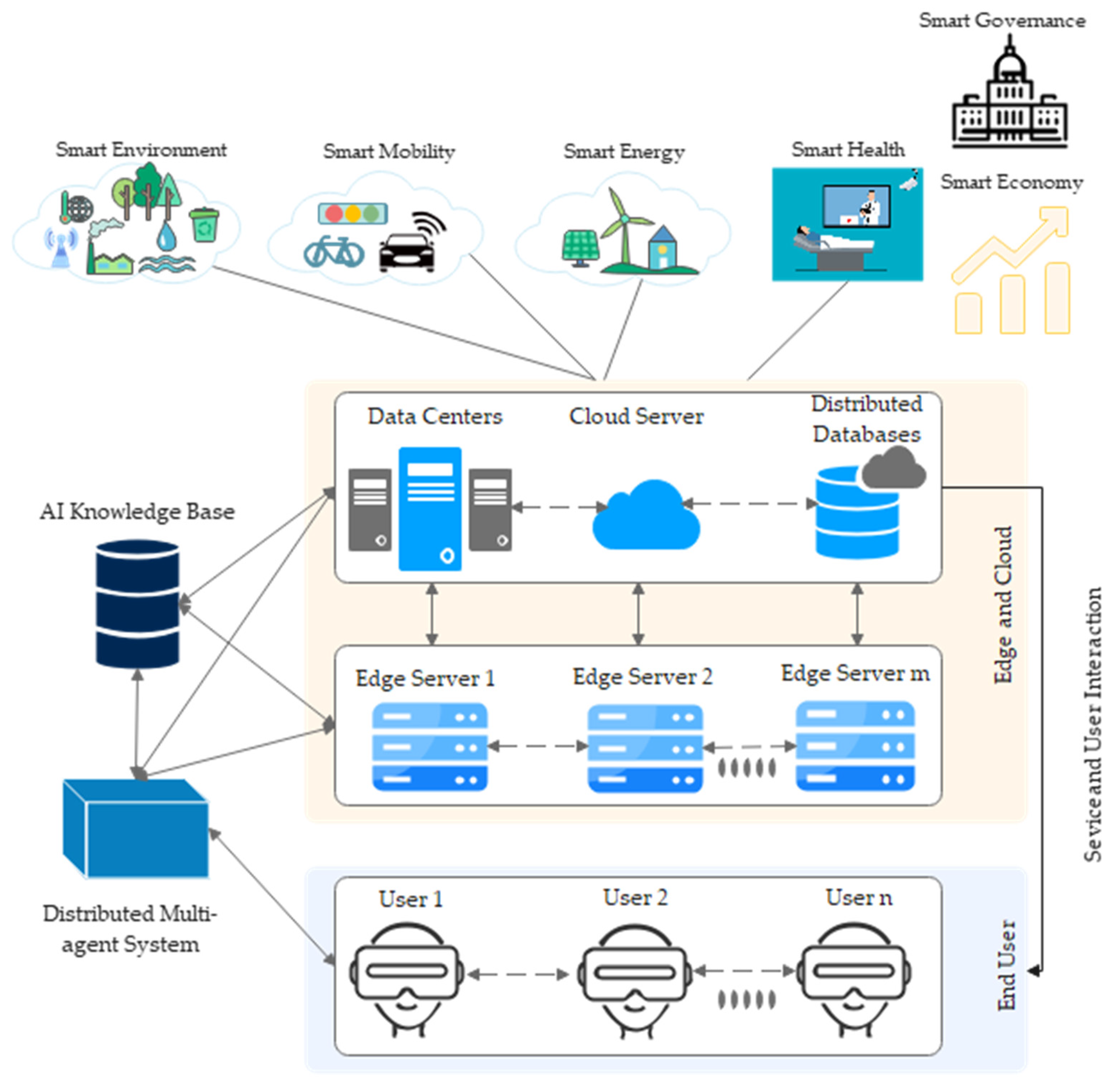
2.2. Metaverse Architecture for a Smart City
2.3. Challenges in Metaverse for Smart City
1. Data Acquisition, Management, Analysis and Processing Challenges
2. Lack of Trust in AI Systems
3. Privacy and Security Vulnerabilities in Smart City and Metaverse Integration
4. Technological Integration
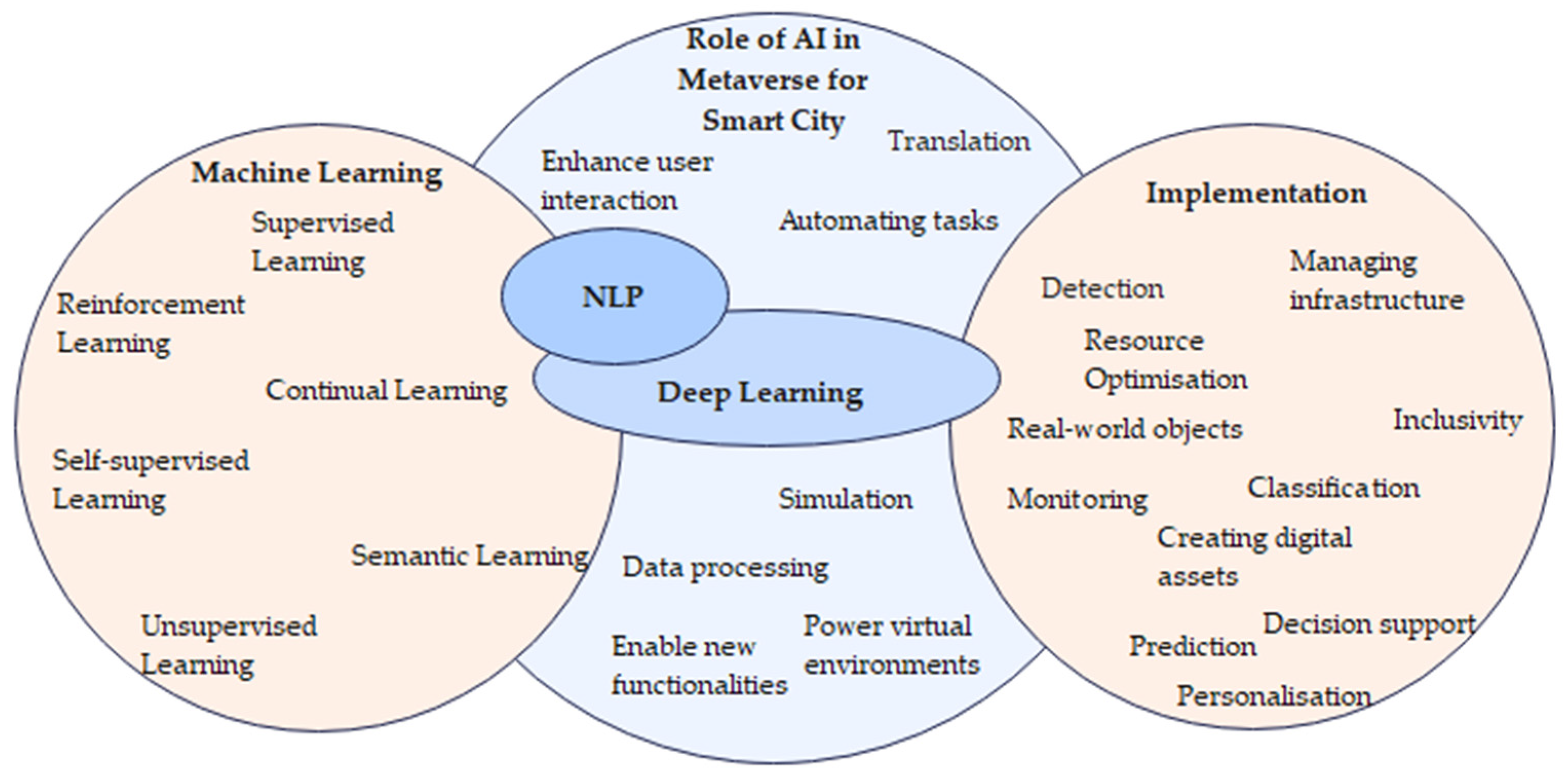
3. AI-enabled Metaverse for Smart City
3.1. Role of AI in the Metaverse for Smart City
3.2. AI Learning Techniques
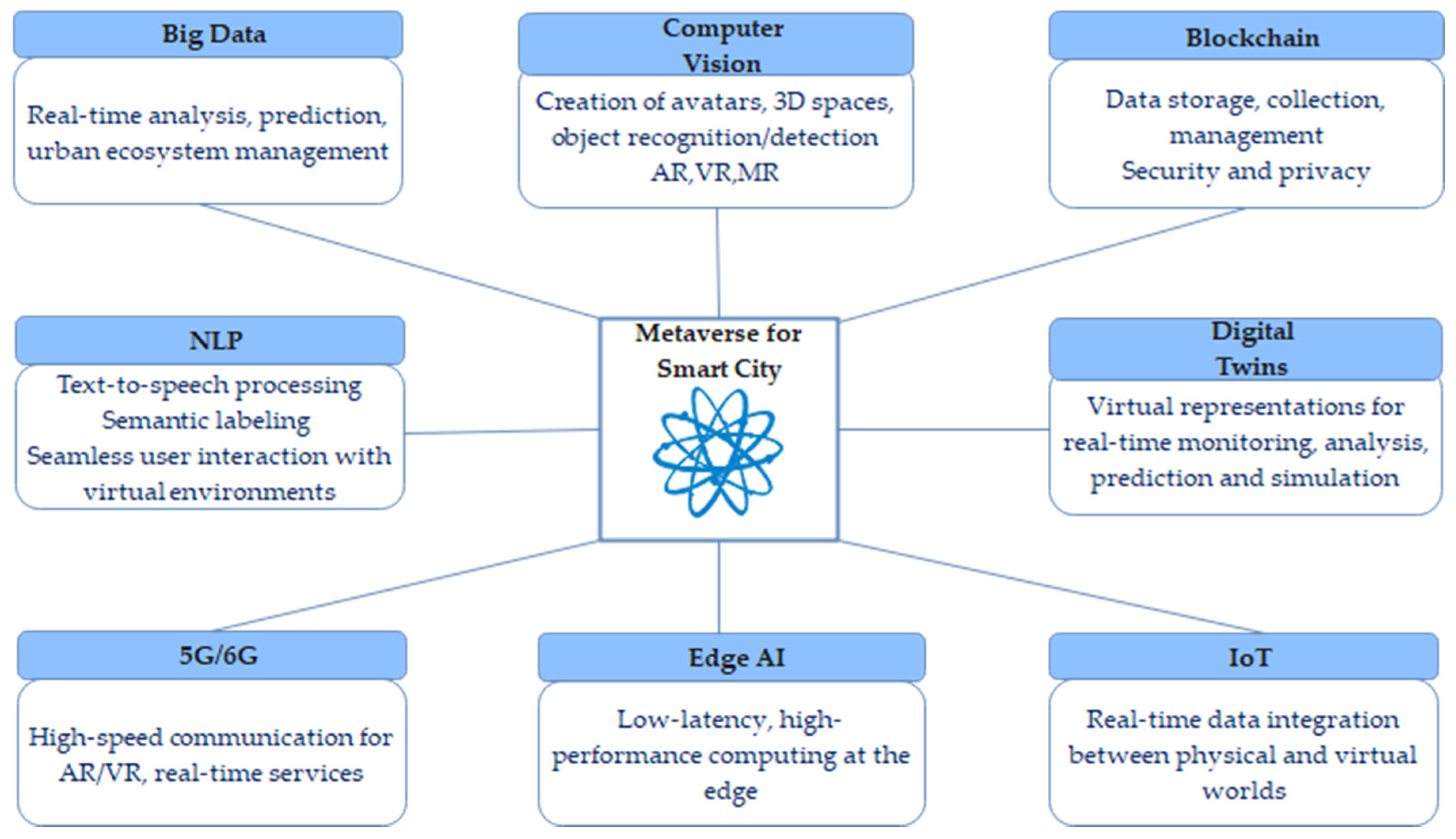
3.3. AI-Enabled Technologies for the Metaverse in Smart Cities
1). Big Data
2). Natural Language Processing
3). Computer Vision
4). Digital Twin
5). Blockchain
6). Internet of Things
7). Edge AI
8). 5G/6G Communication
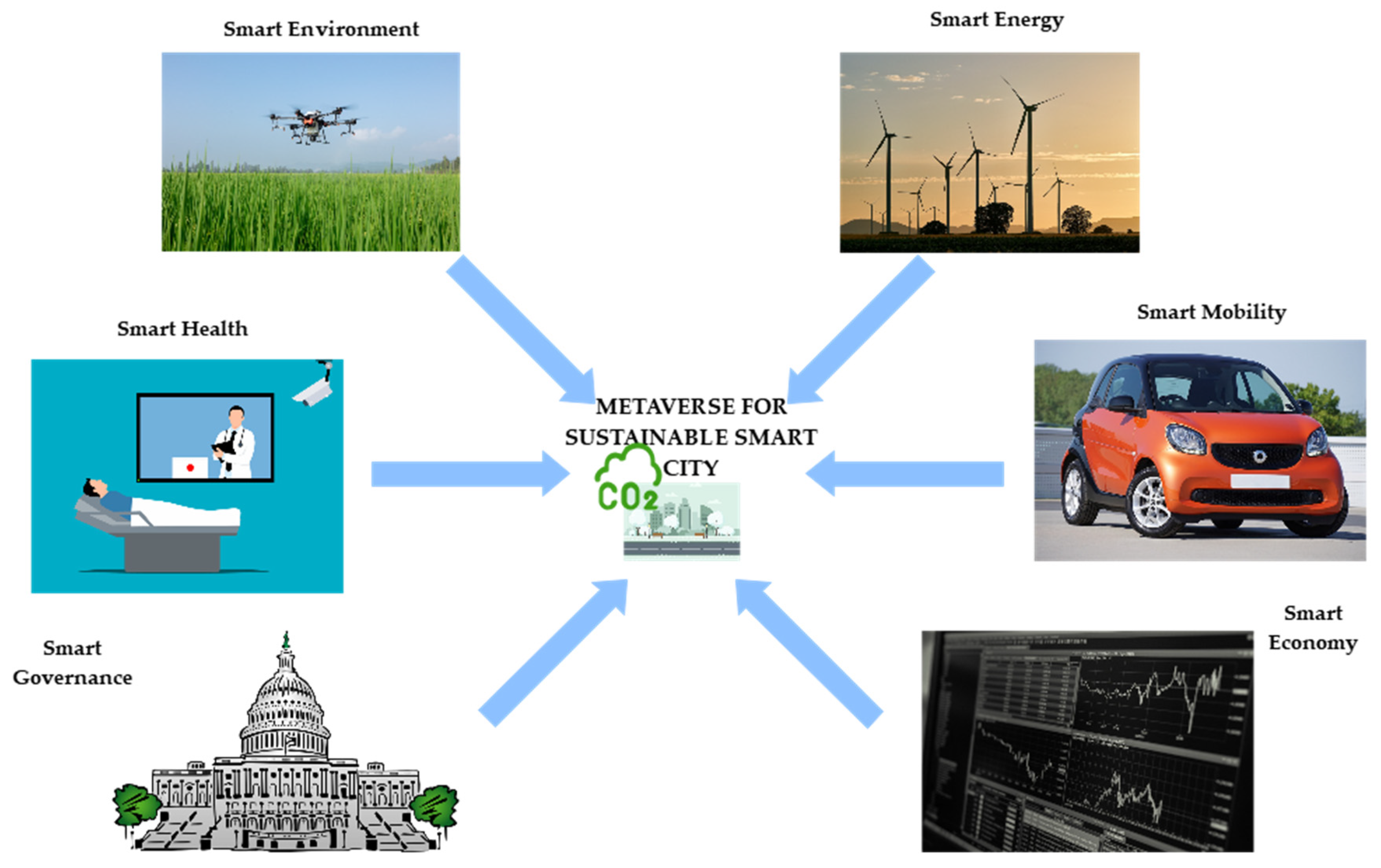
4. Sustainable Metaverse for Smart City
4.1. Applications and Use Cases
4.1.1. Smart Environment
| Domain | Sub Domain | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Environment | Air quality control | [32,180,181,182] |
| Environmental monitoring | [183,187] | |
| Disaster planning | [177,178,179] | |
| Water management | [188] | |
| Agriculture | [189,190,191,192,193,194,195] | |
| Waste Management | [176,184,185,196] | |
| Infrastructure management | [151,186] | |
| Smart Mobility | Traffic flow prediction | [90,92,163,197,198] |
| Traffic monitoring | [199,200] | |
| Traffic condition analysis | [201,202,203,204] | |
| Autonomous vehicles & predictive maintenance | [121,205,206,207,208,209,210] | |
| Smart Energy | Energy management & forecasting | [211,212] |
| Energy optimisation | [186,213,214] | |
| Power grid management and monitoring | [215,216,217,218] | |
| Smart Health | Pandemic forecasting | [219,220] |
| Public health | [221] | |
| Medical care & management | [222,223,224,225,226] | |
| Medical training | [227,228] | |
| Smart Governance | Electronic voting | [229] |
| Decision-making and service delivery | [230,231,232,233] | |
| Smart Economy | Smart payment systems, e-business | [234] |
| Smart manufacturing | [235,236,237] | |
| Enhance customer experience | [238] |
4.1.2. Smart Mobility
4.1.3. Smart Energy
4.1.4. Smart Health
4.1.5. Smart Governance
4.1.6. Smart Economy
6. Analysis of the Findings
- 1)
- Integrating AI with key technologies such as XR, digital twins, blockchain, 5G/6G, and IoT is essential for building sustainable smart cities within the Metaverse. AI optimises resource management, enhances energy efficiency, and supports real-time decision-making across various domains, including agriculture, transportation, energy and health. XR and digital twins simulate environmental conditions and urban scenarios, enabling cities to reduce waste, improve infrastructure planning, and mitigate environmental impacts. Blockchain ensures secure data management, while edge AI and 5G/6G enhance the seamless transmission of massive amounts of data between the virtual and physical worlds, enabling real-time responses critical for sustainable city operations. These technologies foster a sustainable, energy-efficient, and data-driven urban ecosystem.
- 2)
- Several use cases illustrate the role of AI and Metaverse technologies in advancing sustainable smart cities. For example, AI and IoT technologies in smart environments manage air quality, waste, and water pollution by leveraging real-time data for environmental monitoring and decision-making. XR and digital twins simulate environmental conditions and urban scenarios, enabling cities to reduce waste, improve infrastructure planning, and mitigate environmental impacts. In smart mobility, AI-driven predictive analytics optimise traffic flow and reduce congestion, contributing to lower emissions. Smart energy systems, supported by AI, digital twins, and IoT, allow efficient energy management and integration of renewable energy sources. Early detection of diseases and optimised emergency responses reduce strain on healthcare resources, contributing to social sustainability by improving public health outcomes. Similarly, AI-enabled decision support systems in smart governance help policymakers develop sustainable urban policies, while in the smart economy, AI and blockchain enable innovative business models, enhancing economic sustainability. A few case studies highlight the impact of AI and the Metaverse in creating sustainable smart cities. For instance, the RECLAIM Project initiative applies AI and robotics to decentralise waste management, enabling smart cities to address sustainability challenges effectively.
- 3)
- Integrating AI-enabled Metaverse technologies in smart cities presents significant benefits, highlighted above. However, challenges such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and the need for scalable infrastructure remain critical. Ensuring the interoperability of diverse systems and addressing the ethical implications of AI decisions are essential for achieving sustainability in the Metaverse for smart cities. Future research should focus on developing interoperable AI systems, explainable AI models, and enhanced privacy-preserving techniques to ensure that AI-driven smart city applications operate responsibly and equitably within the Metaverse. Further, federated learning, 6G networks, collaboration among stakeholders, and developing secure governance frameworks are essential for long-term sustainable growth.
- 4)
- While this study provides in-depth insights into current AI techniques and AI-enabled technologies and their applications within the Metaverse for smart cities, it has certain limitations. The rapid pace of technological advancement means that some of the technologies discussed may evolve, necessitating continuous updates to the findings presented. The study is also limited by its reliance on existing literature and technologies available at the time of writing. Furthermore, the paper primarily focuses on technological aspects, with less emphasis on socio-economic factors and user adoption challenges, which are critical for the successful implementation of AI in real-world scenarios essential for the Metaverse in smart cities. Recognising these limitations, future research should adopt a more holistic approach, incorporating technological advancements and addressing the human and societal dimensions of technology integration.
6. Future Directions
4.2. Scalability and Interoperability
4.3. Explainability and Responsible AI
4.4. Security and Privacy
4.5. Integrated Role of AI with Emerging Technologies
4.6. Governance and Ethics
4.7. Advanced NLP Capabilities
4.8. Virtual Collaboration
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 |
References
- “UN-Habitat - A Better Urban Future | UN-Habitat.”. Available online: https://unhabitat.org/ (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- M. E. E. Alahi et al., “Integration of IoT-Enabled Technologies and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Smart City Scenario: Recent Advancements and Future Trends,” Sensors 2023, Vol. 23, Page 5206, vol. 23, no. 11, p. 5206, 23. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- “World Urbanization Prospects - Population Division - United Nations.”. Available online: https://population.un.org/wup/Country-Profiles/ (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- S. Caird, “City approaches to smart city evaluation and reporting: case studies in the United Kingdom,” Urban Res Pract, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 159–179, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- P. Bagga, A. K. P. Bagga, A. K. Das, V. Chamola, and M. Guizani, “Blockchain-envisioned access control for internet of things applications: a comprehensive survey and future directions,” Telecommun Syst, vol. 81, no. 1, pp. 125–173, Sep. 2022. [CrossRef]
- U. Nations, “Rapid urbanisation: opportunities and challenges to improve the well-being of societies,” Human Development Reports, 2017.
- J. Yang, A. O. J. Yang, A. O. Purevjav, and S. Li, “The marginal cost of traffic congestion and road pricing: Evidence from a natural experiment in Beijing,” Am Econ J Econ Policy, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 418–453, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Flores-Albornoz, M. M. J. Flores-Albornoz, M. M. Nirmala, K. P. J. Mukthar, E. Asnate-Salazar, E. H. Ramirez, and V. Raju, “Unlocking Solution for Urban Transportation Woes: Addressing the Challenges of Modern City Living,” Studies in Systems, Decision and Control, vol. 440, pp. 3–10, 2024. [CrossRef]
- A.S. Alatawi, A. A. A.S. Alatawi, A. A. Youssef, M. Abaza, M. A. Uddin, and A. Mansour, “Effects of Atmospheric Turbulence on Optical Wireless Communication in NEOM Smart City,” Photonics 2022, Vol. 9, Page 262, vol. 9, no. 4, p. 262, Apr. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Deep, Y. S. Deep, Y. Tian, J. Lu, Y. Zhou, and X. Zheng, “Leveraging Multi-view Learning for Human Anomaly Detection in Industrial Internet of Things,” 2020 International Conferences on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData) and IEEE Congress on Cybermatics (Cybermatics), pp. 533–537, Nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- “Sustainable Cities - Introduction to the Special Theme.”. Available online: https://ercim-news.ercim.eu/en138/special/2849-sustainable-cities-introduction-to-the-special-theme (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- A. Akande, P. A. Akande, P. Cabral, P. Gomes, and S. Casteleyn, “The Lisbon ranking for smart sustainable cities in Europe,” Sustain Cities Soc, vol. 44, pp. 475–487, Jan. 2019. [CrossRef]
- C.A.R. Freire, F. A. F. C.A.R. Freire, F. A. F. Ferreira, E. G. Carayannis, and J. J. M. Ferreira, “Artificial Intelligence and Smart Cities: A DEMATEL Approach to Adaptation Challenges and Initiatives,” IEEE Trans Eng Manag, vol. 70, no. 5, pp. 1881–1899, 23. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- “Smart cities - European Commission.”. Available online: https://commission.europa.eu/eu-regional-and-urban-development/topics/cities-and-urban-development/city-initiatives/smart-cities_en (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- J. Yan, J. J. Yan, J. Liu, and F. M. Tseng, “An evaluation system based on the self-organizing system framework of smart cities: A case study of smart transportation systems in China,” Technol Forecast Soc Change, vol. 153, Apr. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. P. Mohanty, U. S. P. Mohanty, U. Choppali, and E. Kougianos, “Everything you wanted to know about smart cities,” IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 60–70, Jul. 2016. [CrossRef]
- N. Mohamed, J. N. Mohamed, J. Al-Jaroodi, I. Jawhar, S. Lazarova-Molnar, and S. Mahmoud, “SmartCityWare: A service-oriented middleware for cloud and fog enabled smart city services,” IEEE Access, vol. 5, pp. 17576–17588, Jul. 2017. [CrossRef]
- T. Alam, A. T. Alam, A. Poniszewska-Maranda, and W. Maranda, “Cloud-Based IoT Applications and Their Roles in Smart Cities,” Smart Cities 2021, Vol. 4, Pages 1196-1219, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 1196–1219, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Shafiq, Z. M. Shafiq, Z. Tian, Y. Sun, X. Du, and M. Guizani, “Selection of effective machine learning algorithm and Bot-IoT attacks traffic identification for internet of things in smart city,” Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 107, pp. 433–442, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- D. K. Y. Chiu, T. D. K. Y. Chiu, T. Xu, and I. Gondra, “Random Graph-based Multiple Instance Learning for Structured IoT Smart City Applications,” ACM Transactions on Internet Technology (TOIT), vol. 21, no. 3, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Sharma, E. A. Sharma, E. Podoplelova, G. Shapovalov, A. Tselykh, and A. Tselykh, “Sustainable Smart Cities: Convergence of Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain,” Sustainability 2021, Vol. 13, Page 13076, vol. 13, no. 23, p. 13076, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Arora, A. Jain, D. Yadav, V. Hassija, V. Chamola, and B. Sikdar, “Next Generation of Multi-Agent Driven Smart City Applications and Research Paradigms,” IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, vol. 4, pp. 2104–2121, 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. Mehta, A. D. Mehta, A. Mehta, P. Narang, V. Chamola, and S. Zeadally, “Deep Learning Enhanced UAV Imagery for Critical Infrastructure Protection,” IEEE Internet of Things Magazine, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 30–34, Jun. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang et al., “A Survey on Metaverse: Fundamentals, Security, and Privacy,” IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 319–352, 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. Milgram, H. P. Milgram, H. Takemura, A. Utsumi, and F. Kishino, “Augmented reality: a class of displays on the realityvirtuality continuum,” vol. 2351, pp. 282–292, Dec. 1995. [CrossRef]
- L.‐H. Lee et al., “All One Needs to Know about Metaverse: A Complete Survey on Technological Singularity, Virtual Ecosystem, and Research Agenda,” Oct 2021. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05352v3 (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- Z. Chen, W. Z. Chen, W. Gan, J. Wu, H. Lin, and C. M. Chen, “Metaverse for smart cities: A survey,” Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems, vol. 4, pp. 203–216, Jan. 2024. [CrossRef]
- T. Huynh-The, Q. V. T. Huynh-The, Q. V. Pham, X. Q. Pham, T. T. Nguyen, Z. Han, and D. S. Kim, “Artificial intelligence for the metaverse: A survey,” Eng Appl Artif Intell, vol. 117, p. 105581, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- N. P. Rana, S. N. P. Rana, S. Luthra, S. K. Mangla, R. Islam, S. Roderick, and Y. K. Dwivedi, “Barriers to the Development of Smart Cities in Indian Context,” Information Systems Frontiers 2018 21:3, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 503–525, Jul. 2018. [CrossRef]
- D. S. Sarwatt, Y. D. S. Sarwatt, Y. Lin, J. Ding, Y. Sun, and H. Ning, “Metaverse for Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS): A Comprehensive Review of Technologies, Applications, Implications, Challenges and Future Directions,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024. [CrossRef]
- T. H. Davenport, R. T. H. Davenport, R. Ronanki, J. Wheaton, and A. Nguyen, “FEATURE ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR THE REAL WORLD 108 HARVARD BUSINESS REVIEW”.
- S. Du, T. S. Du, T. Li, Y. Yang, and S. J. Horng, “Deep Air Quality Forecasting Using Hybrid Deep Learning Framework,” IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng, vol. 33, no. 6, pp. 2412–2424, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. A. Bhat and N. F. Huang, “Big Data and AI Revolution in Precision Agriculture: Survey and Challenges,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 110209–110222, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Z. Ullah, F. Z. Ullah, F. Al-Turjman, L. Mostarda, and R. Gagliardi, “Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning in smart cities,” Comput Commun, vol. 154, pp. 313–323, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- V. Kohli, U. V. Kohli, U. Tripathi, V. Chamola, B. K. Rout, and S. S. Kanhere, “A review on Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality use-cases of Brain Computer Interface based applications for smart cities,” Microprocess Microsyst, vol. 88, p. 104392, Feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Zawish et al., “AI and 6G Into the Metaverse: Fundamentals, Challenges and Future Research Trends,” IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, vol. 5, pp. 730–778, 2024. [CrossRef]
- K. Li et al., “When Internet of Things Meets Metaverse: Convergence of Physical and Cyber Worlds,” IEEE Internet Things J, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 4148–4173, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, J. X. Wang, J. Huang, Y. L. Tian, and F. Y. Wang, “AGI in Metaverse for Smart Cities and Societies: A Cyber Physical Social Approach,” 2024 Australian and New Zealand Control Conference, ANZCC 2024, pp. 61–66, 2024. [CrossRef]
- S. E. Bibri, “The Metaverse as a Virtual Model of Platform Urbanism: Its Converging AIoT, XReality, Neurotech, and Nanobiotech and Their Applications, Challenges, and Risks,” Smart Cities 2023, Vol. 6, Pages 1345-1384, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 1345–1384, 23. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- S. E. Bibri and S. K. Jagatheesaperumal, “Harnessing the Potential of the Metaverse and Artificial Intelligence for the Internet of City Things: Cost-Effective XReality and Synergistic AIoT Technologies,” Smart Cities 2023, Vol. 6, Pages 2397-2429, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 2397–2429, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Allam, A. Z. Allam, A. Sharifi, S. E. Bibri, D. S. Jones, and J. Krogstie, “The Metaverse as a Virtual Form of Smart Cities: Opportunities and Challenges for Environmental, Economic, and Social Sustainability in Urban Futures,” Smart Cities 2022, Vol. 5, Pages 771-801, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 771–801, Jul. 2022. [CrossRef]
- F. Maier and M. Weinberger, “Metaverse Meets Smart Cities—Applications, Benefits, and Challenges,” Future Internet 2024, Vol. 16, Page 126, vol. 16, no. 4, p. 126, Apr. 2024. [CrossRef]
- S. Rani et al., “Amalgamation of advanced technologies for sustainable development of smart city environment: A review,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 150060–150087, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Ali, F. M. Ali, F. Naeem, G. Kaddoum, and E. Hossain, “Metaverse Communications, Networking, Security, and Applications: Research Issues, State-of-the-Art, and Future Directions,” IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 1238–1278, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, K. Salah, R. Jayaraman, and M. Omar, “Metaverse applications in smart cities: Enabling technologies, opportunities, challenges, and future directions,” Internet of Things, vol. 23, p. 100884, Oct. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. E. E. Alahi et al., “Integration of IoT-Enabled Technologies and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Smart City Scenario: Recent Advancements and Future Trends,” Sensors 2023, Vol. 23, Page 5206, vol. 23, no. 11, p. 5206, 23. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- N. Silva, M. N. Silva, M. Khan, and K. Han, “Towards sustainable smart cities: A review of trends, architectures, components, and open challenges in smart cities,” Sustain Cities Soc, vol. 38, pp. 697–713, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Shahat Osman, A. A. A.M. Shahat Osman, A. A. Elragal, and A. Ståhlbröst, “Data-Driven Decisions in Smart Cities: A Digital Transformation Case Study,” Applied Sciences 2022, Vol. 12, Page 1732, vol. 12, no. 3, p. 1732, Feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Shahat Osman and A. Elragal, “Smart Cities and Big Data Analytics: A Data-Driven Decision-Making Use Case,” Smart Cities 2021, Vol. 4, Pages 286-313, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 286–313, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. Cheng, N. R. Cheng, N. Wu, S. Chen, and B. Han, “Will Metaverse Be NextG Internet? Vision, Hype, and Reality,” IEEE Netw, vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 197–204, Sep. 2022. [CrossRef]
- “Everything You Know About The Metaverse Is Wrong?”. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/everything-you-know-metaverse-wrong-william-burns-iii (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- H. Wang et al., “A Survey on the Metaverse: The State-of-the-Art, Technologies, Applications, and Challenges,” IEEE Internet Things J, vol. 10, no. 16, pp. 14671–14688, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- “Facebook Wants Us to Live in the Metaverse | The New Yorker.”. Available online: https://www.newyorker.com/culture/infinite-scroll/facebook-wants-us-to-live-in-the-metaverse (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- Han, J. Yun, J. Jang, and K. R. Park, “User-friendly home automation based on 3D virtual world,” IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, vol. 56, no. 3, pp. 1843–1847, Aug. 2010. [CrossRef]
- D. N. Dionisio, W. G. D. N. Dionisio, W. G. Burns, and R. Gilbert, “3D Virtual worlds and the metaverse,” ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), vol. 45, no. 3, Jul. 2013. [CrossRef]
- H. Duan, J. H. Duan, J. Li, S. Fan, Z. Lin, X. Wu, and W. Cai, “Metaverse for Social Good: A University Campus Prototype,” MM 2021 - Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 153–161, Oct. 2021. [CrossRef]
- T. Huynh-The et al., “Blockchain for the Metaverse: A Review,” Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 143, pp. 401–419, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- U. Khan, Z. U. Khan, Z. Han, D. Niyato, M. Guizani, and C. S. Hong, “Metaverse for Wireless Systems: Vision, Enablers, Architecture, and Future Directions,” IEEE Wirel Commun, 2024. [CrossRef]
- K. Polachan, J. K. Polachan, J. Pal, C. Singh, and T. V. Prabhakar, “Assessing Quality of Control in Tactile Cyber-Physical Systems,” IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 5348–5365, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Tariq, F. Naeem, and H. V. Poor, “Toward Experience-Driven Traffic Management and Orchestration in Digital-Twin-Enabled 6G Networks,” Jan. 2022. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.04259v1 (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- “The Metaverse Value-Chain. Trillions of dollars are pouring into… | by Jon Radoff | Building the Metaverse | Medium.”. Available online: https://medium.com/building-the-metaverse/the-metaverse-value-chain-afcf9e09e3a7 (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- A. Genay, A. A. Genay, A. Lecuyer, and M. Hachet, “Being an Avatar ‘for Real’: A Survey on Virtual Embodiment in Augmented Reality,” IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph, vol. 28, no. 12, pp. 5071–5090, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Genay, A. Lecuyer, and M. Hachet, “Being an Avatar ‘for Real’: A Survey on Virtual Embodiment in Augmented Reality,” IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph, vol. 28, no. 12, pp. 5071–5090, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Kai, H. Zhou, Y. Yi, and W. Huang, “Collaborative Cloud-Edge-End Task Offloading in Mobile-Edge Computing Networks with Limited Communication Capability,” IEEE Trans Cogn Commun Netw, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 624–634, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Kai, H. Zhou, Y. Yi, and W. Huang, “Collaborative Cloud-Edge-End Task Offloading in Mobile-Edge Computing Networks with Limited Communication Capability,” IEEE Trans Cogn Commun Netw, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 624–634, 2021. [CrossRef]
- “IEEE 2888 - Home.”. Available online: https://sagroups.ieee.org/2888/ (accessed on 8 September 2024).
- L. Chang et al., “6G-Enabled Edge AI for Metaverse: Challenges, Methods, and Future Research Directions,” Journal of Communications and Information Networks, vol. 7, no. 2, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. K. Dwivedi et al., “Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy,” Int J Inf Manage, vol. 57, p. 101994, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Yang, Z. L. Yang, Z. Luo, S. Zhang, F. Teng, and T. Li, “Continual Learning for Smart City: A Survey,” Apr. 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. M. L. Alcaraz and N. Strodthoff, “Diffusion-based Time Series Imputation and Forecasting with Structured State Space Models,” Aug. 2022. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.09399v3 (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- R. Madhavan, J. A. R. Madhavan, J. A. Kerr, A. R. Corcos, and B. P. Isaacoff, “Toward Trustworthy and Responsible Artificial Intelligence Policy Development,” IEEE Intell Syst, vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 103–108, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Rymarczyk, J. Van De Weijer, B. Z. Zieli´nski, and B. Twardowski, “ICICLE: Interpretable Class Incremental Continual Learning,” 2023.
- J. Han et al., “ParaDefender: A Scenario-Driven Parallel System for Defending Metaverses,” IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 2118–2127, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Allam and Z. A. Dhunny, “On big data, artificial intelligence and smart cities,” Cities, vol. 89, pp. 80–91, Jun. 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. G.-Chem. Eng. Prog and undefined 2018, “Introduction to deep learning: Part 1,” aiche.org, 2018. Available online: https://www.aiche.org/sites/default/files/cep/20180622.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- T. Park, M.-Y. Liu, T.-C. Wang, and J.-Y. Zhu, “Semantic Image Synthesis With Spatially-Adaptive Normalization,” 2019.
- A. Ramesh et al., “Zero-Shot Text-to-Image Generation,” Jul. 01, 2021, PMLR. Available online: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/ramesh21a.html (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- A. Radford et al., “Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision,” Jul 01, 2021, PMLR. Available online: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/radford21a.html (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- R. Nishant, M. R. Nishant, M. Kennedy, and J. Corbett, “Artificial intelligence for sustainability: Challenges, opportunities, and a research agenda,” Int J Inf Manage, vol. 53, p. 102104, Aug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Joshi, S. S. Joshi, S. Saxena, T. Godbole, and Shreya, “Developing Smart Cities: An Integrated Framework,” Procedia Comput Sci, vol. 93, pp. 902–909, Jan. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Angelidou, “Smart cities: A conjuncture of four forces,” Cities, vol. 47, pp. 95–106, Sep. 2015. [CrossRef]
- S. P. Mohanty, U. S. P. Mohanty, U. Choppali, and E. Kougianos, “Everything you wanted to know about smart cities,” IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 60–70, Jul. 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. Nilssen, “To the smart city and beyond? Developing a typology of smart urban innovation,” Technol Forecast Soc Change, vol. 142, pp. 98–104, 19. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- R. Foresti, S. R. Foresti, S. Rossi, M. Magnani, C. Guarino Lo Bianco, and N. Delmonte, “Smart Society and Artificial Intelligence: Big Data Scheduling and the Global Standard Method Applied to Smart Maintenance,” Engineering, vol. 6, no. 7, pp. 835–846, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- W. van Winden and D. van den Buuse, “Smart City Pilot Projects: Exploring the Dimensions and Conditions of Scaling Up,” Journal of Urban Technology, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 51–72, Oct. 2017. [CrossRef]
- K. Li, B. P. L. K. Li, B. P. L. Lau, X. Yuan, W. Ni, M. Guizani, and C. Yuen, “Toward Ubiquitous Semantic Metaverse: Challenges, Approaches, and Opportunities,” IEEE Internet Things J, vol. 10, no. 24, pp. 21855–21872, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Baevski, W. N. Hsu, Q. Xu, A. Babu, J. Gu, and M. Auli, “data2vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language,” Proc Mach Learn Res, vol. 162, pp. 1298–1312, Feb. 2022, Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555v3 (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- Z. Li et al., “Steering the Future: Redefining Intelligent Transportation Systems with Foundation Models,” CHAIN, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 46–53, Jul. 2024. [CrossRef]
- X. Meng et al., “Spatial data intelligence and city metaverse: A review,” Fundamental Research, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- W. Chen et al., “A novel fuzzy deep-learning approach to traffic flow prediction with uncertain spatial–temporal data features,” Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 89, pp. 78–88, Dec. 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. Guo et al., “Optimized Graph Convolution Recurrent Neural Network for Traffic Prediction,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 1138–1149, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Rui, Y. Y. Rui, Y. Gong, Y. Zhao, K. Luo, and W. Lu, “Predicting Traffic Flow Parameters for Sustainable Highway Management: An Attention-Based EMD–BiLSTM Approach,” Sustainability 2024, Vol. 16, Page 190, vol. 16, no. 1, p. 190, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Guo, and H. Zhang, “Spatial temporal data visualization in emergency management : A view from data-driven decision,” Proceedings of the 3rd ACM SIGSPATIAL International Workshop on the Use of GIS in Emergency Management, EM-GIS 2017, Nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. K. Prasad et al., “Parallel Processing over Spatial-Temporal Datasets from Geo, Bio, Climate and Social Science Communities: A Research Roadmap,” Proceedings - 2017 IEEE 6th International Congress on Big Data, BigData Congress 2017, pp. 232–250, Sep. 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Chakareski, “Aerial UAV-IoT sensing for ubiquitous immersive communication and virtual human teleportation,” 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, INFOCOM WKSHPS 2017, pp. 718–723, Nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- T. Jung, M. C. T. Jung, M. C. tom Dieck, H. Lee, and N. Chung, “Tracking Tourist Spatial-Temporal Behavior in Urban Places, A Methodological Overview and GPS Case Study,” pp. 481–494, 2016. [CrossRef]
- K. Li, B. P. L. K. Li, B. P. L. Lau, X. Yuan, W. Ni, M. Guizani, and C. Yuen, “Toward Ubiquitous Semantic Metaverse: Challenges, Approaches, and Opportunities,” IEEE Internet Things J, vol. 10, no. 24, pp. 21855–21872, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Beněs, M. K. K. Beněs, M. K. Baskar, and L. Burget, “Residual memory networks in language modeling: Improving the reputation of feed-forward networks,” Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, INTERSPEECH, vol. 2017-August, pp. 284–288, 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, L. C. J. Wang, L. C. Yu, K. R. Lai, and X. Zhang, “Tree-Structured Regional CNN-LSTM Model for Dimensional Sentiment Analysis,” IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process, vol. 28, pp. 581–591, 2020. [CrossRef]
- T. Han, Q. T. Han, Q. Yang, Z. Shi, S. He, and Z. Zhang, “Semantic-Preserved Communication System for Highly Efficient Speech Transmission,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 245–259, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Xie, Z. H. Xie, Z. Qin, and G. Y. Li, “Task-Oriented Multi-User Semantic Communications for VQA,” IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 553–557, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Z. Weng, Z. Z. Weng, Z. Qin, X. Tao, C. Pan, G. Liu, and G. Y. Li, “Deep Learning Enabled Semantic Communications With Speech Recognition and Synthesis,” IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, vol. 22, no. 9, pp. 6227–6240, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- X. Mu and Y. Liu, “Semantic Communications in Multi-user Wireless Networks,” Nov. 2022. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08932v1 (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- C. Luong et al., “Edge Computing for Semantic Communication Enabled Metaverse: An Incentive Mechanism Design,” Dec. 2022, Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.06463v1 (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- W. Yang et al., “Semantic Communication Meets Edge Intelligence,” IEEE Wirel Commun, vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 28–35, Oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- X. Peng et al., “A Robust Deep Learning Enabled Semantic Communication System for Text,” Proceedings - IEEE Global Communications Conference, GLOBECOM, pp. 2704–2709, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Ramalingam et al., “A Comprehensive Analysis of Blockchain Applications for Securing Computer Vision Systems,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 107309–107330, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Chowdhary, M. L. Chowdhary, M. Alazab, A. Chaudhary, S. Hakak, and T. R. Gadekallu, “Computer Vision and Recognition Systems Using Machine and Deep Learning Approaches: Fundamentals, technologies and applications,” Computer Vision and Recognition Systems Using Machine and Deep Learning Approaches: Fundamentals, technologies and applications, pp. 1–483, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. S. Fangbemi, Y. F. Lu, M. Y. Xu, X. W. Luo, A. Rolland, and C. Raissi, “ZooBuilder: 2D and 3D Pose Estimation for Quadrupeds Using Synthetic Data,” 19th ACM SIGGRAPH / Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation 2020, SCA 2020 - Showcases, pp. 1–2, Sep. 2020, Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.05389v1 (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- T. Karras, S. Laine, M. Aittala, J. Hellsten, J. Lehtinen, and T. Aila, “Analyzing and Improving the Image Quality of StyleGAN,” 2020. Available online: https://github.com/NVlabs/stylegan2 (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- R. Gal, O. R. Gal, O. Patashnik, H. Maron, A. H. Bermano, G. Chechik, and D. Cohen-Or, “StyleGAN-NADA: CLIP-Guided Domain Adaptation of Image Generators,” ACM Trans Graph, vol. 41, no. 4, Jul. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Saharia et al., “Photorealistic Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Deep Language Understanding,” Adv Neural Inf Process Syst, vol. 35, pp. 36479–36494, Dec. 2022.
- T. Müller, A. T. Müller, A. Evans, C. Schied, and A. Keller, “Instant neural graphics primitives with a multiresolution hash encoding,” ACM Trans Graph, vol. 41, no. 4, Jul. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. C. Lo and H. H. Tsai, “Design of 3D Virtual Reality in the Metaverse for Environmental Conservation Education Based on Cognitive Theory,” Sensors 2022, Vol. 22, Page 8329, vol. 22, no. 21, p. 8329, Oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Gao and Y. Yang, “The Design of Virtual Reality Systems for Metaverse Scenarios,” Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies, vol. 173, pp. 11–20, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhao et al., “Metaverse: Perspectives from graphics, interactions and visualization,” Visual Informatics, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 56–67, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang, K. L. Y. Wang, K. L. Siau, and L. Wang, “Metaverse and Human-Computer Interaction: A Technology Framework for 3D Virtual Worlds,” Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), vol. 13518 LNCS, pp. 213–221, 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Kuru, “MetaOmniCity: Toward Immersive Urban Metaverse Cyberspaces Using Smart City Digital Twins,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 43844–43868, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Q. Qu, “The Microverse: A Task-Oriented Edge-Scale Metaverse,” Future Internet 2024, Vol. 16, Page 60, vol. 16, no. 2, p. 60, Feb. 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, Y. J. Wang, Y. Chen, X. Ji, Z. Dong, M. Gao, and C. S. Lai, “Metaverse Meets Intelligent Transportation System: An Efficient and Instructional Visual Perception Framework,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024. [CrossRef]
- M. Xu et al., “Generative AI-Empowered Simulation for Autonomous Driving in Vehicular Mixed Reality Metaverses,” IEEE Journal on Selected Topics in Signal Processing, vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 1064–1079, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Xie et al., “A Survey of Blockchain Technology Applied to Smart Cities: Research Issues and Challenges,” IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 2794–2830, Jul. 2019. [CrossRef]
- K. Biswas and V. Muthukkumarasamy, “Securing smart cities using blockchain technology,” Proceedings - 18th IEEE International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications, 14th IEEE International Conference on Smart City and 2nd IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Systems, HPCC/SmartCity/DSS 2016, pp. 1392–1393, Jan. 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Xie et al., “A Survey of Blockchain Technology Applied to Smart Cities: Research Issues and Challenges,” IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 2794–2830, Jul. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Zhao, H. Huang, Z. Xiong, J. Kang, and Z. Zheng, “Fusing Blockchain and AI With Metaverse: A Survey,” IEEE Open Journal of the Computer Society, vol. 3, pp. 122–136, 2022. [CrossRef]
- N. Lambert, “Beyond NFTs: A Possible Future for Digital Art,” ITNOW, vol. 63, no. 3, pp. 8–10, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Dr.Liew Voon Kiong, Metaverse Made Easy: A Beginner’s Guide to the Metaverse: Everything you need to know about Metaverse, NFT and GameFi. 2022.
- T. A. Oliveira, M. T. A. Oliveira, M. Oliver, and H. Ramalhinho, “Challenges for Connecting Citizens and Smart Cities: ICT, E-Governance and Blockchain,” Sustainability 2020, Vol. 12, Page 2926, vol. 12, no. 7, p. 2926, Apr. 2020. [CrossRef]
- “Blockchain: Rebalancing & Amplifying the Power of AI and Machine Learning (ML) | by Jorden Woods | JustStable | Medium.”. Available online: https://medium.com/crypto-oracle/blockchain-rebalancing-amplifying-the-power-of-ai-and-machine-learning-ml-af95616e9ad9 (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Y. Liu et al., “BlockSC: A Blockchain Empowered Spatial Crowdsourcing Service in Metaverse while Preserving User Location Privacy,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 880–892, Apr. 2024. [CrossRef]
- L. U. Khan, I. L. U. Khan, I. Yaqoob, N. H. Tran, S. M. A. Kazmi, T. N. Dang, and C. S. Hong, “Edge-Computing-Enabled Smart Cities: A Comprehensive Survey,” IEEE Internet Things J, vol. 7, no. 10, pp. 10200–10232, Oct. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Z. Lv, L. Z. Lv, L. Qiao, Y. Li, Y. Yuan, and F. Y. Wang, “BlockNet: Beyond reliable spatial Digital Twins to Parallel Metaverse,” Patterns, vol. 3, no. 5, p. 100468, 22. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- Cliff and M. Rollins, “Methods Matter: A Trading Agent with No Intelligence Routinely Outperforms AI-Based Traders,” Nov. 2020. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.14346v1 (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- T. Kanter, “The Metaverse and eXtended Reality with Distributed IoT,” IEEE IoT Newsletter, vol. 2021, no. November, 2021. Available online: https://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:su:diva-200630 (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Lu, J. Miller, N. Pereira, and A. Rowe, “FlasH: Video-embeddable AR anchors for live events,” Proceedings - 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, ISMAR 2021, pp. 489–497, 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Xie and Z. Qin, “A Lite Distributed Semantic Communication System for Internet of Things,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 142–153, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Xiao, Y. Li, and X. Xie, “From Semantic Communication to Semantic-Aware Networking: Model, Architecture, and Open Problems,” IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 59, no. 8, pp. 44–50, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. N. S. Rubí and P. R. de Lira Gondim, “IoT-based platform for environment data sharing in smart cities,” International Journal of Communication Systems, vol. 34, no. 2, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Solmaz et al., “Toward Understanding Crowd Mobility in Smart Cities through the Internet of Things”. [CrossRef]
- “Digital Twin: Manufacturing Excellence through Virtual Factory Replication”.
- Boje, A. Guerriero, S. Kubicki, and Y. Rezgui, “Towards a semantic Construction Digital Twin: Directions for future research,” Autom Constr, vol. 114, p. 103179, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Listl, D. G. Listl, D. Dittler, G. Hildebrandt, V. Stegmaier, N. Jazdi, and M. Weyrich, “Knowledge Graphs in the Digital Twin-A Systematic Literature Review About the Combination of Semantic Technologies and Simulation in Industrial Automation”.
- J. Akroyd, S. J. Akroyd, S. Mosbach, A. Bhave, and M. Kraft, “Universal Digital Twin - A Dynamic Knowledge Graph,” Data-Centric Engineering, vol. 2, no. 4, p. e14, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. Sahlab, S. N. Sahlab, S. Kamm, T. Muller, N. Jazdi, and M. Weyrich, “Knowledge graphs as enhancers of intelligent digital twins,” Proceedings - 2021 4th IEEE International Conference on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems, ICPS 2021, pp. 19–24, 21. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhao, H. L. Zhao, H. Zhang, Q. Wang, and H. Wang, “Digital-Twin-Based Evaluation of Nearly Zero-Energy Building for Existing Buildings Based on Scan-to-BIM,” Advances in Civil Engineering, vol. 2021, no. 1, p. 6638897, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Lydon, S. P. Lydon, S. Caranovic, I. Hischier, and A. Schlueter, “Coupled simulation of thermally active building systems to support a digital twin,” Energy Build, vol. 202, p. 109298, Nov. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. E. Sepasgozar, “Differentiating Digital Twin from Digital Shadow: Elucidating a Paradigm Shift to Expedite a Smart, Sustainable Built Environment,” Buildings 2021, Vol. 11, Page 151, vol. 11, no. 4, p. 151, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Austin, P. M. Austin, P. Delgoshaei, M. Coelho, and M. Heidarinejad, “Architecting Smart City Digital Twins: Combined Semantic Model and Machine Learning Approach,” Journal of Management in Engineering, vol. 36, no. 4, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Sahal, S. H. Alsamhi, K. N. Brown, D. O’shea, C. McCarthy, and M. Guizani, “Blockchain-Empowered Digital Twins Collaboration: Smart Transportation Use Case,” Machines 2021, Vol. 9, Page 193, vol. 9, no. 9, p. 193, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- X. Hu, Y. X. Hu, Y. Zhou, and Q. Shi, “Method for 2D-3D Registration under Inverse Depth and Structural Semantic Constraints for Digital Twin City,” Applied Sciences 2022, Vol. 12, Page 8543, vol. 12, no. 17, p. 8543, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Jiang, J. L. Jiang, J. Shi, C. Wang, and Z. Pan, “Intelligent control of building fire protection system using digital twins and semantic web technologies,” Autom Constr, vol. 147, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. Eneyew, M. A. M. D. Eneyew, M. A. M. Capretz, and G. T. Bitsuamlak, “Toward Smart-Building Digital Twins: BIM and IoT Data Integration,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 130487–130506, 2022. [CrossRef]
- X. Li, L. X. Li, L. Wang, C. Zhu, and Z. Liu, “Framework for manufacturing-tasks semantic modelling and manufacturing-resource recommendation for digital twin shop-floor,” J Manuf Syst, vol. 58, pp. 281–292, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- W. Y. B. Lim et al., “Realizing the Metaverse with Edge Intelligence: A Match Made in Heaven,” IEEE Wirel Commun, vol. 30, no. 4, pp. 64–71, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Dev, S. A. K. Dev, S. A. Khowaja, P. K. Sharma, B. S. Chowdhry, S. Tanwar, and G. Fortino, “DDI: A Novel Architecture for Joint Active User Detection and IoT Device Identification in Grant-Free NOMA Systems for 6G and beyond Networks,” IEEE Internet Things J, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 2906–2917, Feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. She et al., “Deep Learning for Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communications in 6G Networks,” IEEE Netw, vol. 34, no. 5, pp. 219–225, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Alsenwi, N. H. M. Alsenwi, N. H. Tran, M. Bennis, S. R. Pandey, A. K. Bairagi, and C. S. Hong, “Intelligent Resource Slicing for eMBB and URLLC Coexistence in 5G and Beyond: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Approach,” IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, vol. 20, no. 7, pp. 4585–4600, Jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Gu, X. Zhang, Z. Lin, and M. Alazab, “Deep Multiagent Reinforcement-Learning-Based Resource Allocation for Internet of Controllable Things,” IEEE Internet Things J, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 3066–3074, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. Cheng et al., “Space/Aerial-Assisted Computing Offloading for IoT Applications: A Learning-Based Approach,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 1117–1129, 19. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- B. Tunze, T. B. Tunze, T. Huynh-The, J. M. Lee, and D. S. Kim, “Sparsely Connected CNN for Efficient Automatic Modulation Recognition,” IEEE Trans Veh Technol, vol. 69, no. 12, pp. 15557–15568, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Huynh-The, C. H. Hua, Q. V. Pham, and D. S. Kim, “MCNet: An Efficient CNN Architecture for Robust Automatic Modulation Classification,” IEEE Communications Letters, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 811–815, Apr. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Luo, J. Ji, Q. Wang, X. Chen, and P. Li, “Channel State Information Prediction for 5G Wireless Communications: A Deep Learning Approach,” IEEE Trans Netw Sci Eng, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 227–236, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Guo, Y. S. Guo, Y. Lin, S. Li, Z. Chen, and H. Wan, “Deep Spatialoral 3D Convolutional Neural Networks for Traffic Data Forecasting,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 20, no. 10, pp. 3913–3926, Oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Van Huynh, S. R. Khosravirad, A. Masaracchia, O. A. Dobre, and T. Q. Duong, “Edge Intelligence-Based Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communications for Digital Twin-Enabled Metaverse,” IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 1733–1737, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z. Zhang, S. Mao, and D. Liu, “A view synthesis-based 360° VR caching system over MEC-Enabled C-RAN,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 30, no. 10, pp. 3843–3855, Oct. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Z. Gu, H. Z. Gu, H. Lu, P. Hong, and Y. Zhang, “Reliability Enhancement for VR Delivery in Mobile-Edge Empowered Dual-Connectivity Sub-6 GHz and mmWave HetNets,” IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 2210–2226, Apr. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu, J. Y. Liu, J. Liu, A. Argyriou, and S. Ci, “MEC-Assisted panoramic VR video streaming over millimeter wave mobile networks,” IEEE Trans Multimedia, vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 1302–1316, 19. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Wang, D. Chen, Q. Liu, H. Ke, and K. K. T. Han, “Metamobility: Connecting Future Mobility with the Metaverse,” IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 69–79, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. M. Aslam, R. A. M. Aslam, R. Chaudhary, A. Bhardwaj, I. Budhiraja, N. Kumar, and S. Zeadally, “Metaverse for 6G and Beyond: The Next Revolution and Deployment Challenges,” IEEE Internet of Things Magazine, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 32–39, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Giordani, M. M. Giordani, M. Polese, M. Mezzavilla, S. Rangan, and M. Zorzi, “Toward 6G Networks: Use Cases and Technologies,” IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 58, no. 3, pp. 55–61, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- P. Moya Osorio et al., “Towards 6G-Enabled Internet of Vehicles: Security and Privacy,” IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, vol. 3, pp. 82–105, 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Lovén et al., “EdgeAI: A Vision for Distributed, Edge-native Artificial Intelligence in Future 6G Networks". Available online: http://5gtn.fi (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- J. Kang et al., “Blockchain-based Federated Learning for Industrial Metaverses: Incentive Scheme with Optimal AoI,” Proceedings - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain, Blockchain 2022, pp. 71–78, 2022. [CrossRef]
- “ESA - Working towards a Digital Twin of Earth.”. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/Working_towards_a_Digital_Twin_of_Earth (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- S. L. Ullo and G. R. Sinha, “Advances in Smart Environment Monitoring Systems Using IoT and Sensors,” Sensors 2020, Vol. 20, Page 3113, vol. 20, no. 11, p. 3113, 20. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- M. Saad, M. M. Saad, M. Bin Ahmad, M. Asif, M. K. Khan, T. Mahmood, and M. T. Mahmood, “Blockchain-Enabled VANET for Smart Solid Waste Management,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 5679–5700, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Jiang, “An Integrated Situational Awareness Platform for Disaster Planning and Emergency Response,” 2020 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference, ISC2 2020, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yu, Y. Y. Yu, Y. Chen, R. Wei, X. Zhang, K. Li, and D. Wan, “A Deep Learning-Based Multi-model Ensemble Method for Hydrological Forecasting,” Proceedings - 2022 IEEE SmartWorld, Ubiquitous Intelligence and Computing, Autonomous and Trusted Vehicles, Scalable Computing and Communications, Digital Twin, Privacy Computing, Metaverse, SmartWorld/UIC/ATC/ScalCom/DigitalTwin/PriComp/Metaverse 2022, pp. 1245–1251, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Gu, J. Wang, X. Guo, G. Liu, S. Qin, and Z. Bi, “A Metaverse-Based Teaching Building Evacuation Training System With Deep Reinforcement Learning,” IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 2209–2219, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. Zhou, P. N. Tan, X. Liu, and L. Luo, “Spatiooral Multi-Task Learning via Tensor Decomposition,” IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng, vol. 33, no. 6, pp. 2764–2775, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- W. Mao, W. W. Mao, W. Wang, L. Jiao, S. Zhao, and A. Liu, “Modeling air quality prediction using a deep learning approach: Method optimization and evaluation,” Sustain Cities Soc, vol. 65, p. 102567, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Nunez-Cacho, J. M. P. Nunez-Cacho, J. M. Maqueira-Marin, B. M. Rata, and V. Molina-Moreno, “Building a model for the predictive improvement of air quality in Circular Smart cities,” ISC2 2022 - 8th IEEE International Smart Cities Conference, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Anul Haq and, C. Author, “SMOTEDNN: A Novel Model for Air Pollution Forecasting and AQI Classification”. [CrossRef]
- W. L. Mao, W. C. W. L. Mao, W. C. Chen, C. T. Wang, and Y. H. Lin, “Recycling waste classification using optimized convolutional neural network,” Resour Conserv Recycl, vol. 164, p. 105132, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Han, X. H. Han, X. Fan, and F. Li, “Prototype Enhancement-Based Incremental Evolution Learning for Urban Garbage Classification,” IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 398–411, Jan. 2024. [CrossRef]
- D. D. Eneyew, M. A. M. D. D. Eneyew, M. A. M. Capretz, and G. T. Bitsuamlak, “Toward Smart-Building Digital Twins: BIM and IoT Data Integration,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 130487–130506, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Das, M. Pratama, and S. K. Ghosh, “SARDINE,” ACM Transactions on Spatial Algorithms and Systems (TSAS), vol. 6, no. 3, Apr. 2020. [CrossRef]
- E. Kim et al., “Water economy with smart water system in the City of Carouge,” 2022 IEEE International Conference on Omni-Layer Intelligent Systems, COINS 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Attard, Y. Everingham, B. Philippa, and W. Xiang, “Smarter irrigation management in the sugarcane farming system using internet of things,” 2018. Available online: https://www.assct.com.au/component/assct/search-result?search_cat=title&filter_search=Smarter%20irrigation%20management%20in%20the%20sugarcane%20far&publisher=any&Itemid=0 (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Y. Lin, Y. B. Y. Lin, Y. B. Lin, W. L. Chen, F. L. Ng, J. H. Yeh, and Y. W. Lin, “IoT-Based Bacillus Number Prediction in Smart Turmeric Farms Using Small Data Sets,” IEEE Internet Things J, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 5146–5157, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Tan and, Q. Le-Trung, “A Novel 5G PMN-Driven Approach for AI-powered Irrigation and Crop Health Monitoring,” IEEE Access, pp. 1–1, 2024. [CrossRef]
- D. Islam et al., “Rapid Rice Yield Estimation Using Integrated Remote Sensing and Meteorological Data and Machine Learning,” Remote Sensing 2023, Vol. 15, Page 2374, vol. 15, no. 9, p. 2374, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- N. Kundu et al., “Disease detection, severity prediction, and crop loss estimation in MaizeCrop using deep learning,” Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture, vol. 6, pp. 276–291, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Dilmurat, V. Sagan, and S. Moose, “AI-DRIVEN MAIZE YIELD FORECASTING USING UNMANNED AERIAL VEHICLE-BASED HYPERSPECTRAL AND LIDAR DATA FUSION,” ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, vol. V-3–2022, no. 3, pp. 193–199, 22. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, M. X. Wang, M. Kang, H. Sun, P. De Reffye, and F. Y. Wang, “DeCASA in AgriVerse: Parallel Agriculture for Smart Villages in Metaverses,” IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, vol. 9, no. 12, pp. 2055–2062, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- “Decentralised Material Recovery for a Sustainable Future.”. Available online: https://ercim-news.ercim.eu/en138/special/decentralised-material-recovery-for-a-sustainable-future (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- J. Han et al., “IETA: A Robust and Scalable Incremental Learning Framework for Time-of-Arrival Estimation,” Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, vol. 23, pp. 4100–4111, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- X. Chen, J. X. Chen, J. Wang, and K. Xie, “TrafficStream: A Streaming Traffic Flow Forecasting Framework Based on Graph Neural Networks and Continual Learning,” IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 3620–3626, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A.Maipradit et al., “PAVEMENT: Passing Vehicle Detection System with Autonomous Incremental Learning using Camera and Vibration Data,” IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, vol. 2022-September, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Nan, S. Y. Nan, S. Jiang, and M. Li, “Large-scale Video Analytics with Cloud–Edge Collaborative Continuous Learning,” ACM Trans Sens Netw, vol. 20, no. 1, p. 14, Oct. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z. Chen, J. Wang, D. Dai, and H. Zhao, “Lifelong Vehicle Trajectory Prediction Framework Based on Generative Replay,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 24, no. 12, pp. 13729–13741, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Habibi MIT, N. Jaipuria, and J. P. How MIT, “SILA: An Incremental Learning Approach for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction,” 2020.
- T. Bandaragoda, D. T. Bandaragoda, D. De Silva, D. Kleyko, E. Osipov, U. Wiklund, and D. Alahakoon, “Trajectory clustering of road traffic in urban environments using incremental machine learning in combination with hyperdimensional computing,” 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference, ITSC 2019, pp. 1664–1670, Oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- “D3 – An AI-based Solution to Road Defect Detection.”. Available online: https://ercim-news.ercim.eu/en138/r-i/d3---an-ai-based-solution-to-road-defect-detection (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- S. S. Nuvvula et al., “Optimizing Electric Vehicle Fleet Operations with Predictive Analytics: A Renewable Energy-Centric Approach,” pp. 309–311, Jul. 2024. [CrossRef]
- P. Bellini, S. P. Bellini, S. Bilotta, E. Collini, M. Fanfani, and P. Nesi, “Mobility and Transport Data for City Digital Twin Modeling and Exploitation,” Proceedings of 2023 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference, ISC2 2023, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Nkechinyere Njoku, C. Ifeanyi Nwakanma, and D.-S. Kim, “Evaluation of Spectrograms for Keyword Spotting in Control of Autonomous Vehicles for The Metaverse”. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/361558505 (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- B. Li et al., “Sharing Traffic Priorities via Cyber-Physical-Social Intelligence: A Lane-Free Autonomous Intersection Management Method in Metaverse,” IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 2025–2036, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Tan et al., “Speech Emotion Recognition Enhanced Traffic Efficiency Solution for Autonomous Vehicles in a 5G-Enabled Space-Air-Ground Integrated Intelligent Transportation System,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 2830–2842, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Fan, D. Cao, C. Zeng, B. Li, Y. Li, and F. Y. Wang, “Cognitive-Based Crack Detection for Road Maintenance: An Integrated System in Cyber-Physical-Social Systems,” IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, vol. 53, no. 6, pp. 3485–3500, Jun. 2023. [CrossRef]
- T. Hu, W. T. Hu, W. Wu, Q. Guo, H. Sun, L. Shi, and X. Shen, “Very short-term spatial and temporal wind power forecasting: A deep learning approach,” CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 434–443, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Hong and H. S. Lee, “Robust Energy Management System With Safe Reinforcement Learning Using Short-Horizon Forecasts,” IEEE Trans Smart Grid, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 2485–2488, 23. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos Donatos, Tzimotoudis Panagiotis, and Korakis Thanasis, “Enhancing Residential Energy Efficiency and Management Through IoT and Smart Grid Integration.”. Available online: https://ercim-news.ercim.eu/en138/special/enhancing-residential-energy-efficiency-and-management-through-iot-and-smart-grid-integration (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Y. M. Abid et al., “Analysis of the Energy Efficiency of Smart City Buildings Based on Deep Learning Algorithms Using AI,” 2024 International Conference on Smart Systems for Electrical, Electronics, Communication and Computer Engineering (ICSSEECC), pp. 672–677, Jun. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Khan, S. U. Khan, F. U. M. Ullah, M. Y. Lee, and S. W. Baik, “AI-Assisted Hybrid Approach for Energy Management in IoT-Based Smart Microgrid,” IEEE Internet Things J, vol. 10, no. 21, pp. 18861–18875, Nov. 2023. [CrossRef]
- X. He et al., “Situation Awareness of Energy Internet of Things in Smart City Based on Digital Twin: From Digitization to Informatization,” IEEE Internet Things J, vol. 10, no. 9, pp. 7439–7458, 23. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- F. Qayyum et al., “Energy Trading Framework Based on IoT and Digital Twin for Nanogrid Environment,” Proceedings - 2023 IEEE International Conference on Metaverse Computing, Networking and Applications, MetaCom 2023, pp. 749–755, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ma, M. Liu, G. Hong, S. Yang, and R. Deng, “Grid-Metaverse: The Path From Digital Twins and Prototype Tests on DC Microgrids,” Proceedings - 2023 IEEE International Conference on Metaverse Computing, Networking and Applications, MetaCom 2023, pp. 290–296, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Farooq and M. A. Bazaz, “A novel adaptive deep learning model of Covid-19 with focus on mortality reduction strategies,” Chaos Solitons Fractals, vol. 138, p. 110148, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- E. Camargo, J. E. Camargo, J. Aguilar, Y. Quintero, F. Rivas, and D. Ardila, “An incremental learning approach to prediction models of SEIRD variables in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic,” Health Technol (Berl), vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 867–877, Jul. 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Wang, D. M. Wang, D. Yu, W. He, P. Yue, and Z. Liang, “Domain-incremental learning for fire detection in space-air-ground integrated observation network,” International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, vol. 118, p. 103279, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Kim, S. J. Kim, S. Hong, M. Song, and K. Kim, “Visual Attention and Pulmonary VR Training System for Children With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder,” IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 53739–53751, 2024. [CrossRef]
- M. Zanitti et al., “MetaLung: Towards a Secure Architecture for Lung Cancer Patient Care on the Metaverse,” Proceedings - 2023 IEEE International Conference on Metaverse Computing, Networking and Applications, MetaCom 2023, pp. 201–208, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Qiao et al., “SPReCHD: Four-Chamber Semantic Parsing Network for Recognizing Fetal Congenital Heart Disease in Medical Metaverse,” IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, vol. 28, no. 6, pp. 3672–3682, Jun. 2024. [CrossRef]
- D. K. Murala, S. K. D. K. Murala, S. K. Panda, and S. P. Dash, “MedMetaverse: Medical Care of Chronic Disease Patients and Managing Data Using Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain, and Wearable Devices State-of-the-Art Methodology,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 138954–138985, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y. Lu, J. Yu, J. Fan, P. Tang, and L. Zhang, “A Privacy-Preserving Framework for Mental Health Chatbots Based on Confidential Computing,” Proceedings - 2022 IEEE SmartWorld, Ubiquitous Intelligence and Computing, Autonomous and Trusted Vehicles, Scalable Computing and Communications, Digital Twin, Privacy Computing, Metaverse, SmartWorld/UIC/ATC/ScalCom/DigitalTwin/PriComp/Metaverse 2022, pp. 1119–1124, 2022. [CrossRef]
- P. Zikas et al., “MAGES 4.0: Accelerating the World’s Transition to VR Training and Democratizing the Authoring of the Medical Metaverse,” IEEE Comput Graph Appl, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 43–56, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. Zikas et al., “Covid-19 - VR Strikes Back: Innovative medical VR training,” ACM SIGGRAPH 2021 Immersive Pavilion, SIGGRAPH 2021, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Nandi, and S. K. Nandi, “An Implementation and Analysis of Zero Knowledge Based E-Voting Solution With Proof of Vote on Public Ethereum Blockchain,” Proceedings - 2023 IEEE International Conference on Metaverse Computing, Networking and Applications, MetaCom 2023, pp. 423–427, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Mahmoud, M. M. Mahmoud, M. Perez-Ortiz, S. A. Asad Bokhari, and S. Myeong, “Use of Artificial Intelligence in Smart Cities for Smart Decision-Making: A Social Innovation Perspective,” Sustainability 2022, Vol. 14, Page 620, vol. 14, no. 2, p. 620, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- “Decision Support System for Inclusive Smart City Design: Baby Boomers as a Use Case.”. Available online: https://ercim-news.ercim.eu/en138/special/decision-support-system-for-inclusive-smart-city-design-baby-boomers-as-a-use-case (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- N. Khansari, B. G. N. Khansari, B. G. Silverman, Q. Du, J. B. Waldt, W. W. Braham, and J. M. Lee, “An agent-based decision tool to explore urban climate & smart city possibilities,” 11th Annual IEEE International Systems Conference, SysCon 2017 - Proceedings, 17. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- Ding, J. Li, R. Qin, R. Kozma, and F. Y. Wang, “A New Architecture and Mechanism for Decentralized Science MetaMarkets,” IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, vol. 53, no. 9, pp. 5321–5330, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Abraham, H. M. Abraham, H. Aithal, and K. Mohan, “Blockchain and Collaborative Intelligence based next generation Smart Toll Application,” 2020 2nd Conference on Blockchain Research and Applications for Innovative Networks and Services, BRAINS 2020, pp. 206–207, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- T. Zhang et al., “IHPPPVis: Interactive Visual Analytics Approach for Production Performance Monitoring of Heavy-Plate Production Process,” IEEE Trans Cybern, vol. 54, no. 7, pp. 3864–3877, 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. Hou et al., “Hybrid Residual Multiexpert Reinforcement Learning for Spatial Scheduling of High-Density Parking Lots,” IEEE Trans Cybern, vol. 54, no. 5, pp. 2771–2783, 24. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- F. Sun et al., “Digital-Twin-Assisted Skill Learning for 3C Assembly Tasks,” IEEE Trans Cybern, vol. 54, no. 7, pp. 3852–3863, 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. H. Kim, M. J. H. Kim, M. Kim, M. Park, and J. Yoo, “Immersive interactive technologies and virtual shopping experiences: Differences in consumer perceptions between augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR),” Telematics and Informatics, vol. 77, p. 101936, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- B. P. Ashwini, R. M. B. P. Ashwini, R. M. Savithramma, and R. Sumathi, “Artificial Intelligence in Smart City Applications: An overview,” Proceedings - 2022 6th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems, ICICCS 2022, pp. 986–993, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. N. Njoku, C. I. J. N. Njoku, C. I. Nwakanma, G. C. Amaizu, and D. S. Kim, “Prospects and challenges of Metaverse application in data-driven intelligent transportation systems,” IET Intelligent Transport Systems, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 1–21, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- A.C. Serban and M. D. Lytras, “Artificial intelligence for smart renewable energy sector in europe - Smart energy infrastructures for next generation smart cities,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 77364–77377, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, F. Alshehri, F. Karray, A. El Saddik, M. Alsulaiman, and T. H. Falk, “A comprehensive survey on multimodal medical signals fusion for smart healthcare systems,” Information Fusion, vol. 76, pp. 355–375, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Batista, P. E. Batista, P. Lopez-Aguilar, and A. Solanas, “Smart Health in the 6G Era: Bringing Security to Future Smart Health Services,” IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 62, no. 6, pp. 74–80, Jun. 2024. [CrossRef]
- N. Said et al., “Natural disasters detection in social media and satellite imagery: a survey,” Multimed Tools Appl, vol. 78, no. 22, pp. 31267–31302, Nov. 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Musamih, A. A. Musamih, A. Dirir, I. Yaqoob, K. Salah, R. Jayaraman, and D. Puthal, “NFTs in Smart Cities: Vision, Applications, and Challenges,” IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 9–23, Mar. 2024. [CrossRef]
- “Deep Learning Computer Vision Algorithms, Customer Engagement Tools, and Virtual Marketplace Dynamics Data in the Metaverse Economy,” Journal of Self-Governance and Management Economics, vol. 10, no. 2, p. 37, 2022. [CrossRef]
- G. Mohamed et al., “Enhancing Immersive Virtual Shopping Experiences in the Retail Metaverse Through Visual Analytics, Cognitive Artificial Intelligence Techniques, Blockchain-Based Digital Assets, and Immersive Simulations: A Systematic Literature Review,” pp. 305–318, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Chatzopoulou, P. Tsoutsa, and P. Fitsilis, “How Metaverse is Affecting Smart Cities Economy,” ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, pp. 254–259, Nov. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Liu, N. Meyendorf, and N. Mrad, “The role of data fusion in predictive maintenance using digital twin,” AIP Conf Proc, vol. 1949, no. 1, p. 20023, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- A.R. Javed, W. A.R. Javed, W. Ahmed, S. Pandya, P. K. R. Maddikunta, M. Alazab, and T. R. Gadekallu, “A Survey of Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Smart Cities,” Electronics 2023, Vol. 12, Page 1020, vol. 12, no. 4, p. 1020, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, J. M. Corchado, R. Mehmood, R. Y. M. Li, K. Mossberger, and K. Desouza, “Responsible Urban Innovation with Local Government Artificial Intelligence (AI): A Conceptual Framework and Research Agenda,” Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 2021, Vol. 7, Page 71, vol. 7, no. 1, p. 71, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Kuppa and N., A. Le-Khac, “Black Box Attacks on Explainable Artificial Intelligence(XAI) methods in Cyber Security,” Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K. Li, N. Mhaisen, W. Ni, E. Tovar, and M. Guizani, “Exploring Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Assisted Federated Learning for Online Resource Allocation in Privacy-Preserving EdgeIoT,” IEEE Internet Things J, vol. 9, no. 21, pp. 21099–21110, Nov. 2022. [CrossRef]

| Paper | Short Description | Key Technologies covered | Applications Covered |
|---|---|---|---|
| [46] 2023 |
Integration of IoT-enabled technologies and AI for smart city development | IoT, AI | Mobility, governance, education, economy, healthcare, environment, living |
| [22] 2023 |
Multi-agent-driven smart city applications | Multi-agent systems, distributed AI | Home, governance, environment, mobility |
| [28] 2023 |
Artificial intelligence for the Metaverse | AI, NLP, blockchain, machine vision, networking, neural interface | Healthcare, manufacturing, smart cities, gaming |
| [30] 2024 |
Metaverse for intelligent transportation systems | XR, blockchain, AI, digital twin, IoT, 5G/6G, distributed computing | Transportation systems |
| [38] 2024 |
AGI in the Metaverse for smart cities and societies | AGI, parallel intelligence | Smart cities, societal management, urban infrastructure |
| [39] 2023 |
The Metaverse as a virtual model of platform urbanism | AIoT, XR, neurotechnology, nanobiotechnology | Urbanism, platform urbanism, smart cities |
| [40] 2023 |
The potential of the Metaverse and artificial intelligence for the Internet of City Things | AIoT, XR, IoT, 5G, digital twins, cloud computing | Smart city infrastructure, urban mobility, energy, healthcare, education |
| [41] 2022 |
The Metaverse as a virtual form of smart cities | AI, IoT, digital twins, XR, big data | Urban planning, smart cities |
| [42] 2024 |
Applications, benefits, and challenges of Metaverse in smart city | AI, IoT, digital twins, XR, blockchain | Urban planning, citizen services, transportation systems |
| [43] 2021 |
Amalgamation of advanced technologies for smart city environment | IoT, AI, blockchain, big data, cloud computing, wireless sensor networks (WSN) | Smart cities, healthcare, transportation, energy management |
| [45] 2023 |
Metaverse applications in smart cities | IoT, AI, blockchain, XR, digital twins, cloud computing | Healthcare, energy management, transportation, smart homes, supply chain, and logistics |
| [27] 2024 |
Metaverse for smart cities | IoT, AI, cyber-physical systems (CPS), digital twins, blockchain | Urban monitoring, governance, emergency management, simulation |
| Our study | Integration of AI-enabled technologies and Metaverse for sustainable smart city | AI, big data, NLP, computer vision, digital twin, IoT, blockchain, 5G/6G, edge/cloud Computing | Environment, mobility, energy, health, governance, economy |
| Search Criteria | Content and Evaluation |
|---|---|
| Period | Past six years |
| Databases | IEEE Xplore (115), ACM Digital Library (16), MDPI (24), Springer (15), Science Direct (35), and other sources (48); Total (253) |
| Article Type | Early-access, Peer-reviewed conference and journal papers. |
| Screening Process | Each paper’s relevance to the research topic is determined by the Title, Abstract, Introduction and Conclusion |
| Search String | " AI for Metaverse", "digital twins", "blockchain for Metaverse", "explainable AI", "IoT enabled Metaverse", "6G powered for the Metaverse", "edge and cloud computing for the Metaverse"," smart city", "sustainable smart city" |
| Search strategy | Boolean (AND, OR, and NOT) combination |
| Technology | Example of AI Techniques Used | Challenges Addressed | Some Applications in Metaverse for Smart Cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Big Data | Spatiotemporal autoregressive models, time-series clustering, GNNs, GATs | Manages heterogeneous data from various sources, realism in virtual environments, simulation | Real-time traffic flow prediction, environmental simulations, urban planning and infrastructure visualization, optimizing resource allocation and customized services |
| Natural Language Processing | RNNs, CNNs, LSTM, attention mechanisms, hybrid models, knowledge graphs | Enhances user interaction, accessibility and personalization, machine translation, enriches immersion through avatars | Speech-to-text and text-to-speech tasks, Virtual assistants for navigation and support, chatbots, avatars mimicking facial expressions and body language |
| Computer Vision | CNNs, GANs, Diffusion Models | Rendering of avatars and scenes, object recognition/detection, enables VR/AR/MR | Creation of realistic avatars and 3D spaces, enables MR experiences through holographic devices |
| Digital Twin | Multimodal models, knowledge graphs, ML algorithms | Synchronizes physical and virtual worlds, predictive maintenance, improves immersion, simulation and visualisation | Real-time monitoring and predictive analysis, remote operation of systems, optimizing space utilization and maintenance, urban planning and multisystem simulations |
| Blockchain | ML techniques integrated with blockchain methods | Protects data within decentralised systems, secure data storage, sharing and management, Strengthens data integrity in digital twins and IoT, digital economies | Managing digital assets and transactions, security in smart city infrastructures, virtual economies, secure mapping processes in IoT, data reliability for digital twins |
| Internet of Things | Semantic communication, ML-driven semantic technologies | Real-Time Data Mapping, context awareness, interoperability, data exchange challenges, creation of digital twins of physical elements | Real-time control of physical and virtual objects, context-aware AR/VR applications, optimises decision making, standardizing and fusing diverse urban data |
| Edge AI | DL, soft computing, ML | Enhances performance for immersive VR/AR, efficiency at the network edge, ultra-reliable low-latency communication, energy consumption | Real-time synchronization between physical and virtual worlds, spectrum management and utilization efficiency, supporting mission-critical applications |
| 5G/6G Communication | DRL, federated learning integrated with blockchain, AI for network intelligence | High-speed data communication, ultra-low latency connectivity, edge computation and storage, IoT communication | Immersive and interconnected Metaverse experiences, optimizing network performance and resource management, enhancing connectivity for autonomous vehicles, pervasive intelligence with minimal latency and high bandwidth |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





