1. Introduction
1.1. Basics of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs)
The term “extracellular vesicles” is an umbrella term to include all the particles defined by a lipid bilayer that cannot be self-divided and are secreted by cells into the extracellular space [
1]. The secreted EVs contribute to communication between cells, mainly via the transfer of their content from donor (cells that secrete EVs) to recipient (cells that uptake EVs) cells. The EV content consists of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, RNA, DNA and lipids and their release to the cytosol of recipient cells can trigger phenotypic alterations of the acceptor cells. It has been suggested that the EV content highly reflects the cellular content from where they originate. Nevertheless, an integrative proteo-transcriptomic study using matched EV and cell extracts from the same donor cell line revealed that EVs are enriched in distinct protein and transcriptomic signatures, compared to cellular counterpart [
2].
An important feature of EVs is their heterogeneity, in terms of biogenesis site, size, composition of intraluminal content, as well as expression of membranous protein markers. A specific cell type produces and secretes EVs of different size and different cargo among individual EVs. Regarding their biosynthetic routes, EVs arise either from budding of the plasma membrane towards the extracellular space and they are called microvesicles or within multivesicular bodies (MVBs) in the endosomal system, the latter designated as exosomes. Microvesicles have diameter in the range of 50-1000 nm, whereas exosomes are smaller (50-150 nm) [
3]. At this point, it should be noted that according to the Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018) recommendations the use of the term “exosome” is not adequately describing EV identity and, therefore, its use is not endorsed anymore [
4]. The use of the term “exosome” to describe specific EV subpopulations in some of the following sections, is solely due to the nomenclature used in older studies, before the MISEV2018 suggestions and we did not rephrase it for consistency.
In terms of EV protein marker expression, different EV populations express different protein markers, however some protein markers are shared among EVs of different origin and size. For example, some markers such as flotillin-1, heat-shock 70-kDa proteins (HSP10/HSP72, HSC70/HSP73) and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class proteins, previously considered to be found in small EVs (sEVs), have been identified in larger EVs too. The large EVs (lEVs) are highly enriched in the endoplasmic reticulum protein GP96, which is not present in medium-sized or sEVS. The proteins actinin-4 and mitofilin mark the lEVs and medium-sized EVs but not sEVs. The sEVs can be subcategorized further based on distinct protein patterns (mainly the presence or not of different combinations of tetraspanins) as demonstrated by Kowal et al., using EVs from human primary monocyte-derived dendritic cells [
5]. The subpopulation that is enriched in the simultaneous expression of CD63, CD9 and CD81 transmembrane proteins, as well as endosomal proteins such as syntenin-1 and tumor susceptibility 101 (TSG101) is considered as bona fide exosomes. Although well-defined protein markers are now routinely used to characterize heterogeneous EV populations, we still lack on specific RNA markers that could potentially be used to classify EV subpopulations.
1.2. A plethora of Diverse RNA Biotypes Can Be Packaged into EVs
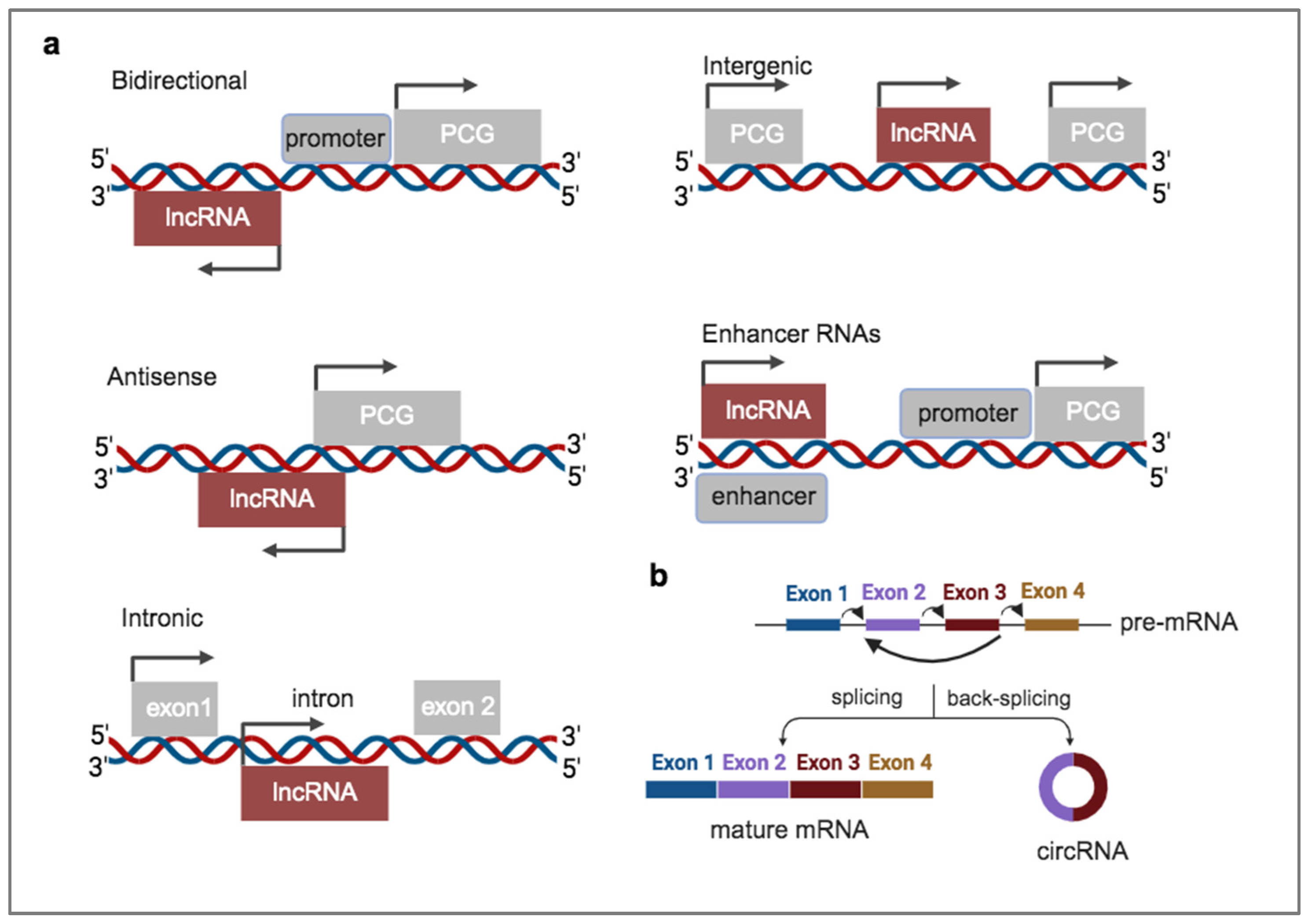
Pervasive transcription of the human genome results in the generation of multiple transcripts, the majority of which are non-protein coding. These non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are categorized to short (< 200 nucleotides) or long (> 200 nucleotides) and functions as important regulatory molecules that modulate gene expression. Among the short ncRNAs different types are classified, such as microRNAs (miRNAs), short interfering RNAs (siRNAs), small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs). The group of long ncRNAs include several subtypes of lncRNAs. A simple classification of the different types of lncRNAs is based on their genomic location with respect to nearby protein coding genes [
6]. Thus, lncRNAs may be bidirectional, antisense, intronic, intergenic or enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) (
Figure 1A). The class of lncRNAs structurally resemble mRNAs, in terms of transcription by polymerase II, addition of methylguanosine cap at the 5′ end and poly-A tail at the 3′ end and splicing. However, several lncRNAs do not follow this rule and are not considered as mRNA-like [
7]. They function as regulatory molecules, cooperating with proteins, other type of RNA or chromatin to modulate gene expression at the epigenetic, co-transcriptional or post-transcriptional levels [
8]. Specific molecular roles as decoys, scaffolds or guides have been assigned to nuclear lncRNAs that assist or prevent transcription factors or chromatin modifiers from targeting regulatory genomic regions. The cytoplasmic lncRNAs exert mostly post-transciptional regulatory roles by modulating mRNA stability and translation or by acting as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) for miRNAs, thereby preventing the latter from interacting to target mRNAs [
9]. Another type of lncRNA is the circular RNAs (circRNAs) which derive from backsplicing of precursor messenger RNA (mRNA), without 5′ or 3′ ends (
Figure 1B).
Several of these different RNA biotypes have been identified in EVs. For example, miRNA is probably the best studied type of RNA within EVs, with multiple miRNAs being detected in EVs. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) or fragments of tRNAs are also found to be highly abundant in EVs. A few snoRNAs and snRNAs have been detected in EVs, although with low abundance. Moreover, some piRNAs have been also observed in EVs, although with no apparent biological function. Multiple lncRNAs have been identified in EVs, with attributed molecular and physiological roles, especially in cancer-derived EVs, a topic which is discussed in more details in next chapters. Recently, another class of lncRNAs designated as circRNAs has attracted a lot of interest as they are highly stable transcripts, due to their resistance to degradation by RNAses and their presence in EVs derived from cell lines but also biofluids, rendering them as excellent circulating RNA biomarkers. Many more RNA biotypes have been observed within EVs, such as Y-RNAs, vault RNAs, fragments of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and retrotransposons [
10]. Last but not least, mRNAs are also detected in EVs, although their intactness is under debate.
Most of the studies focused on EV transcriptome characterization suggest that EV mRNAs (especially those found in sEVs) are shorter or fragmented compared to cellular mRNAs expressed in the EV donor cell line. Interestingly, 3′-untranslated regions (3′-UTRs) of mRNAs have been described to be preferentially augmented in EVs compared to 5′-UTRs or coding sequences (CDS) [
11]. On the contrary, the recent development of robust protocols for long-read sequencing have provided useful evidence towards the theory that full-length transcripts can be found in EVs. Indeed, long-read nanopore sequencing in EV and cellular poly-adenylated RNA of human chronic myelogenous leukemia (K562) revealed the presence of full-length EV transcripts (almost 11% of the total EV transcripts identified). Transcripts enriched or depleted in EVs were identified with lncRNA (42.9%), pseudogenes (35.5%), and mRNA (13.7%) to be the predominant RNA biotypes. Nanopore sequencing offers the advantage to identify the expression of full-length specific isoforms. Notably, the same study revealed that specific isoforms of the same gene were over-represented in EVs, compared to cells of the same origin, hindering preferential transcript variant loading into EVs [
12]. A second recent study utilizing long-read sequencing (PacBio technology), focused on sEVs from postmortem human brain of Alzheimer’s disease patients or healthy individuals and demonstrated that sEVs are enriched in mRNAs that encode ribosomal proteins and transposable elements such as human-specific long interspersed nuclear element 1 (LINE-1) (L1Hs). The authors also observed that 80% of the identified neural sEV transcripts were full-length, a finding that challenges many previous reports and will revolutionize the field if it is reproduced in different biological contexts in the future [
13].
Another report indicates that long and mature mRNA and lncRNA are found in EVs, using an estimation of their coverage, considering the most 5′ and most 3′ mapping reads within the coding regions of mRNAs or full transcript of lncRNAs, but not by performing long read sequencing. The authors observed that EV-associated transcripts are characterized by shorter length, but higher exon density compared to cellular transcripts and in the case of mRNAs lower frequency of AU-rich elements in their 3-UTR, indicating traits of stable transcripts [
14]. Actually, a large cohort of urinary EVs, in comparison to prostate cancer cell lines full transcriptome profiling, using short read sequencing, also reached the same conclusion, as fully mature mRNA and lncRNA transcripts were identified in sEVs, supporting the idea that sEVs contain large fraction of intact genetic material [
15].
1.3. Sorting and Loading of RNAs into EVs: Active or Passive Process?
Several theories for the packaging of RNA into EVs have been developed based on the relative enrichment of a given transcript in EV compared to cellular levels but also on physicochemical and structural properties of RNA molecules. Evidence for both passive and active RNA loading into EVs exist. Passive loading may take place when RNA is abundant at the sites of EV biogenesis and thus can be spontaneously internalized into EVs. RNA stability is an important factor for passive loading as more stable cytoplasmic transcripts have more chances to be found in EV lumen. Active loading includes specific molecular mechanisms for RNA incorporation to EVs. The main determinants for efficient RNA loading are specific RNA motifs and secondary structures, RNA binding proteins (RBPs), modifications in RNA or post-translational modifications of proteins involved in EV RNA packaging and coupling of EV RNA loading to transcription or translation [
16].
A 25-nt RNA sequence, that is called zipcode motif has been described in the highly enriched long transcripts found in EVs of brain and skin cancer cells, although this seems to be tissue-specific. In addition, shorter motifs consisting of 4 to 5 nucleotides have been identified in EV miRNAs, such as the motif UGGA which was found in miRNAs enriched in EVs from MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. In a recent study, it was suggested that a part of the 3′-UTR of mRNA
RAB13 functions as a signal for the loading of this mRNA into small EVs [
17]. A possible mechanism of action for RNA motifs is to establish interactions with lipids within MVBs or plasma membrane at the sites of EV biogenesis, thereby facilitating the loading of the transcripts into newly produced EVs.
The involvement of RBPs in RNA loading into EVs has been better characterized in the case of miRNAs. Several RBPs, such as hnRNPA2B1, hnRNPA1, hnRNPC have been shown to interact to specific EV-enriched miRNAs and this interaction may affect miRNA sorting into EVs [
18]. Another RBP, YBX1-forming cytosolic condensates mediate the sorting of miR-223 into exosomes [
19]. Moreover, the RBP FMR1 is implicated in EV miRNA sorting under inflammatory conditions [
20]. Interestingly, some non-RBP proteins may also facilitate miRNA sorting into EVs. For instance, connexin 43 (Cx43) may interact to a subset of miRNAs with stable secondary structure elements i.e., double-stranded hairpin loops, such as miR-133b and mediate its loading into HEK293 EVs [
21]. The mechanisms of long RNA loading into EVs are not yet extensively studied, as in the case of miRNA, nevertheless a study suggested that hnRNPA2B1 binds to specific motifs in long RNAs (both mRNA and lncRNA) and mediates their sorting into EVs from endothelial cells (HUVECs) [
14]. The identified sequences are enriched in GGAG-, UAG- or GC-contained motifs, which are recognized by classical RBPs, such as RBM5, LIN28A, RBM28 and hnRNPA2B1. Although hnRNPA2B1 has been found in EVs secreted from different cell lines [
22], other studies do not confirm this finding. This discrepancy can be explained due to the different EV isolation techniques, used in different studies. Unpublished data from our team also supports absence of hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPC from MDA-MB-231 secreted sEVs, using size exclusion chromatography (SEC) for EV isolation.
Regarding the precise mechanism by which an RBP facilitates RNA loading into EVs, several hypotheses have been suggested. For example, an RBP may locate transcripts at the sites of EV biogenesis and therefore indirectly affect their incorporation into EVs. Alternatively, RBPs may bind both target RNAs and proteins at the EV membrane e.g., tetraspanins and directly mediate EV RNA loading. In the case of miR-223, which was described above, the miRNA is retained within mitochondria due to its interaction with the mitochondrial protein YBAP1. Upon binding to YBX1 it is translocated in cytosolic condensates that ultimately sort it in endosome-derived exosomes [
23].
1.4. Functionality and Fate of Transferred EV RNA in Recipient Cells
The presence of RNA in EVs is undoubtable as it has been confirmed by several studies, however the potential biological role of the EV RNA on recipient cells has been the center of debate since decades. The skepticism towards the functionality of EV RNA stems from two main arguments. First, the idea that EVs contain content (not only RNA but also proteins) that cells deposit for extracellular disposal. Second, the identification of mainly short RNAs or fragments of long RNAs in EVs, using the current RNA extraction protocols and short-read sequencing technologies, led to the notion that full-length mRNAs or lncRNAs are not dominating in EVs and therefore the functionality of the RNA fragments is questionable. Even in the case of miRNAs, the best described class of ncRNA found in EVs, the identification of high levels of EV-miRNA does not necessarily mean that adequate copies of a specific miRNA are delivered to recipient cells to exert its function towards mRNA degradation or inhibition of mRNA translation.
Another caveat on the capability of transferred EV RNA to exert physiological effects on recipient cells stems from the fact that the delivered EV RNA should escape the degradation pathways in the endocytic compartments of acceptor cells [
24]. Since EV uptake by recipient cells is mediated by diverse pathways, such as endocytosis (clathrin or caveolin-dependent), micropinocytosis, phagocytosis and lipid raft-mediated internalization [
25], a large part of delivered EV transcripts need to exit from the endocytic routes that lead to lysosomes and travel towards the cytosol, where they can be translated into proteins or directly function as ncRNAs. Different mechanisms for endosomal escape have been suggested. First, direct fusion of EVs with plasma membrane of recipient cells, thereby avoiding encountering with endosomes. For those EVs that enter into recipient cells through endocytic routes, it has been proposed that a portion of them escapes endosome entrapment via back-fusion [
26] or pH buffering [
27] and ultimately release their content in the cytosol. Indeed, an elegant study, utilizing luciferase- or fluorescent-protein tagged cytosolic EV cargoes, demonstrated that only approximately 30% of the uptaken EVs are able to release their content to the cytosol and endosomal acidification plays a crucial role for efficient cytosolic release [
28]. Nevertheless, a part of delivered EV RNA will survive from decay and eventually will be released to the cytosol of recipient cells. It remains a question whether the released transcripts have adequate time to exert their functions and shape the responses of recipient cells. A few studies convincingly provide evidence for a functional role of EV transferred mRNAs which can be translated into recipient cells. Engineered cells ectopically expressing a bioluminescent reporter encoding the Gaussia luciferase B (GlucB) gene produced EVs enriched in GlucB mRNA. Purified GlucB EVs were uptaken by recipient cells and nascent mRNA translation was observed in recipient cells by luciferase assays and verified by inhibiting protein synthesis using cycloeximide [
29]. Moreover, functional EV mRNA delivery was shown between mouse brain cells in vivo, using brain-derived EVs enriched in Cre mRNA and monitoring the functional release of Cre mRNA with a fluorescent reporter gene expressing tdTomato only upon translation of transferred Cre mRNA in recipient cells [
30].
Although, the above reports prove efficient delivery of a functional mRNA via EVs, they are based on over-expression systems, whereby a gene is constantly expressed in donor cells and therefore the transcribed mRNA is passively loaded into EVs. However, caution should be shown using these approaches as an over-expressed protein may be also secreted in the cell conditioned medium when found in high copies, with the possibility to also be packages in EVs together with its mRNA. This may lead to false positive results as shown in a study [
31]. To overcome this obstacle the authors developed an assay whereby they specifically block the production of nanoluciferase protein in donor cells, but leaving intact the produced nanoluciferase mRNA, which could be enriched in EVs. By using guide RNAs an RNA editing tools, they, subsequently, correct the RNA sequence in the recipient cells, so that the delivered nanoluciferase mRNA can give rise to nascent nanoluciferase protein, using the translation machinery of recipient cells [
31].
1.5. EVs Possess Multiple Functional Roles during Cancer Progression
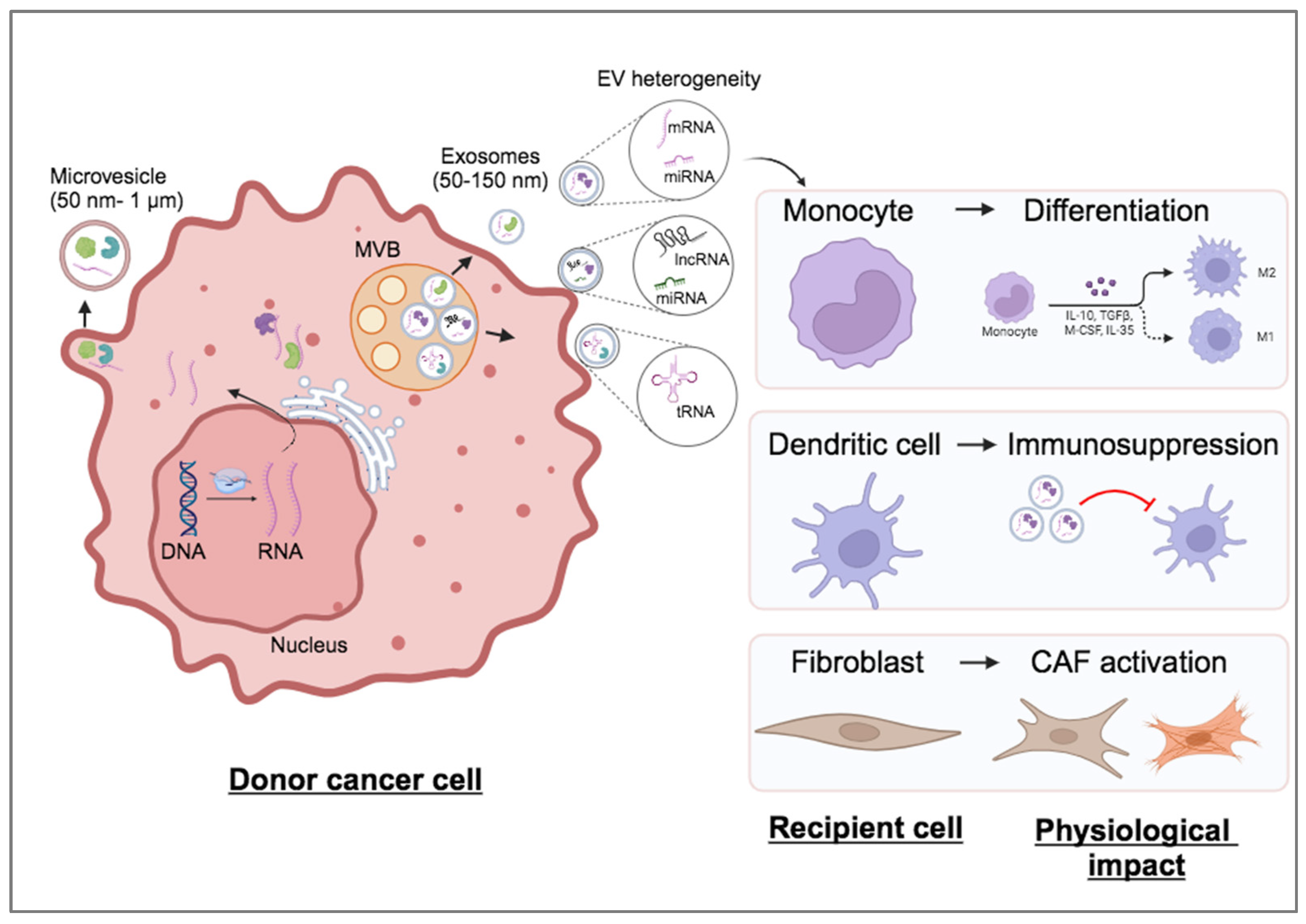
The roles of EVs in cancer progression have been extensively studied and reviewed over the years. For efficient growth, tumors develop a complex microenvironment in their vicinity that fuels them with sufficient nutrients and growth factors, but also enables them to escape immune surveillance. The tumor microenvironment (TME) consists of non-cancerous cells of different origin which constantly exchange information with cancer cells, through signaling networks. To this point, EVs are considered as one of the most important carriers of messages between the different cell types within the TME [
32]. Cancer-secreted EVs can be uptaken by immune cells, such as monocytes or dendritic cells or by fibroblasts and modulate their physiological responses to favor tumor progression. For example, in monocytes, EVs from cancer cells can trigger differentiation towards different populations of macrophages, such as M1 or M2 macrophages. Cancer EVs can also elicit immune suppression via repressing dendritic cells, which are important for antigen presentation and activation of immune responses against cancer antigens. Cancer EVs can also promote activation of quiescent fibroblasts to cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) via transfer of growth factors, such as the transforming growth factor β (TGFβ), miRNAs or mutant p53. CAFs support tumor growth by secreting components of extracellular matrix (ECM) and cytokines (
Figure 2). The intercellular communication between cancer and TME cells is not unilateral. Secreted EVs from TME cells can also affect the physiology of cancer cells to further sustain tumor progression. Cancer EVs may play important roles also in the process of metastasis. In locally invading tumors, EVs are secreted with high rates at invadopodia, protrusions of the plasma membrane at the migratory front that allows cancer cells to degrade ECM and therefore promote invasiveness. In addition, at the metastatic sites, EVs can promote metastatic colonization [
33].
2. EV-ncRNAs with Functional Relevance in Cancer
2.1. EV-ncRNAs in Breast Cancer
Several examples of lncRNAs transferred through EVs and with functional consequences in breast cancer progression have been described. For instance, in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) positive breast cancers, the
Linc00969 lncRNA has been found to promote resistance to trastuzumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets HER2 expressed in cancer cells. Exosomes isolated from plasma of patients that developed resistance to trastuzumab were found to have elevated
Linc00969 levels, compared to sensitive patients. In addition, in vitro studies confirmed that
Linc00960 enriched in exosomes can induce trastuzumab resistance by stabilizing HER2 mRNA levels, via binding to the RNA binding protein HuR and by enhancing autophagy [
34]. In another study, the
small nucleolar RNA host gene 12 (SNHG12) was identified to be highly expressed in triple negative breast cancer cells (TNBCs) and also in their secreted exosomes. Exosomes isolated from the MDA-MB-231 TNBC cell line boosted proliferation, migration and tube formation capacity of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Using gain and loss of function experiments, the authors demonstrated that
SNHG12 lncRNA packaged in exosomes can be transferred to HUVECs and induce their angiogenesis. To exert its functions in recipient cells,
SNHG12 forms ribonucleoprotein complexes with PBRM1 protein to induce MMP10 up-regulation, thereby eliciting angiogenesis [
35].
Breast cancer progression is often shaped by the crosstalk between cancer cells and non-cancerous cells of the tumor microenvironment (TME), such as macrophages and fibroblasts. An extensive signaling network between cells of the TME and cancer cells is established to facilitate a favorable environment for efficient tumor growth. Signals originate from fibroblasts or immune cells and transferred to cancer cells (and vice versa) partially via EVs, but also through other pathways. Indeed, tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs) secrete EVs-containing lncRNA
HIF-1α-stabilizing long noncoding RNA (
HISLA), and potentiate aerobic glycolysis and resistance to apoptosis in recipient breast cancer cells, by blocking the interaction of PHD2 and HIF-1α, thereby stabilizing HIF-1α [
36]. In another study, EVs secreted by hypoxia-induced tumor-associated fibroblasts contain lncRNA
H19, which can be delivered to recipient breast cancer cells and cause a reduction of miR-497 levels, in a DNMT1-dependent manner. This molecular function of EV-contained
H19 has also physiological consequences on the recipient breast cancer cells as it promotes their growth and resistance to paclitaxel [
37].
2.2. EV-ncRNAs in Prostate Cancer
The role of EV-lncRNAs in prostate cancer is also well documented. In a study in which a transcriptomic analysis was performed using EV RNA and matched cellular RNA from 4 prostate cancer cell lines (VCaP, LNCaP, DU145 and PC3), lncRNAs with specific miRNA seed regions in their sequences were enriched in exosomes. Interestingly, the corresponding miRNAs that match with the seed regions of the exosomal lncRNAs were also found highly abundant in the same exosomes. The top identified EV miRNAs belonged to the let-7 and miR-17 families [
38]. In a different study, the expression of
lncRNA AY927529 is elevated in prostate cancer cell lines and their produced exosomes, compared to human benign prostatic hyperplasia cells [
39]. Moreover, the lncRNA
NORAD is highly expressed in prostate cancer cells and tissues and potentiates the secretion and uptake of prostate cancer EVs in recipient cells, via regulating the miR-541-3p-pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) axis [
40]. RNA sequencing using EVs in serum from castration resistant prostate cancer patients before or after acquiring resistance to second generation androgen receptor (AR) axis-targeted therapy (ARAT) revealed up-regulation of AR signaling-related lncRNAs, such as
PCAT1,
H19,
HOXA-11AS,
ZEB1-AS1,
ARLNC1,
PART1,
CTBP1-AS and
PCA3. Among them,
H19 expressed in EVs may negatively correlate with AR-signaling and could serve as a marker for diagnosis of ARAT-resistance [
41].
EV RNA content has also been utilized for diagnostic purposes in prostate cancer. For instance, the transcriptome of EVs isolated from urine samples from 20 prostate cancer patients were compared to urinary EV RNA transcriptome from 9 healthy individuals and it was observed that 5 miRNAs (miR-196a-5p, miR-34a-5p, miR-143-3p, miR-501-3p and miR-92a-1-5p) were downregulated in prostate cancer exosomes. Using an independent cohort the authors further confirmed the decrease of miR-196a-5p and miR-501-3p in prostate cancer exosomes [
42]. The first study to compare the transcriptomic profiling of human prostate cancer tissue to urinary EVs transcriptome from the same patients revealed that urinary EVs are enriched in shorter and intronless cytoplasmic transcripts, compared to the tissue of origin. Notably, circRNA and lncRNA dominate the RNA population in these prostate cancer EVs. Validation of the transcriptomic data from patients using in vitro prostate cancer cell lines identified a few circRNAs with biological function in prostate cancer cells and lncRNAs that may encode peptides with potential tumorigenic function [
15].
2.3. EV-ncRNAs in Liver Cancer
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer, associated with high mortality, due to its asymptomatic nature at early stages of the disease. The roles of EV lncRNAs in HCC progression, drug resistance and metastasis have been elucidated over the last years. Among the numerous lncRNAs described to be enriched in HCC EVs, the antisense RNA of SLC16A1 (
SLC16A1-AS1) is transferred via HCC-secreted EVs to macrophages present in the TME, whereby it promotes M2 macrophage polarization. M2 macrophage secreted cytokine IL6 which, in turn, boosted proliferation, invasion and glycolysis of HCC cells, suggesting that EV enriched
SLC16A1-AS1 is a functional mediator of the communication between cancer and TME cells. Moreover, the lncRNA
focally amplified lncRNA on chromosome 1 (
FAL1) is highly enriched in EVs isolated from serum of HCC patients and treatment of macrophages with
FAL1-enriched EVs leads to their polarization towards M2 macrophages, with pro-tumorigenic properties. Co-culturing EV-induced M2 macrophages with HepG2 HCC cells boosted proliferation, stem cell properties and chemoresistance of the latter, through activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway [
43]. In addition, the long intergenic non-coding RNA (lincRNA) ROR (
linc-ROR) is enriched in HCC EVs in response to stimulation with the cytokine TGFβ. Moreover, treatment with sorafenib, a chemotherapeutic drug commonly used in HCC also increased the cellular and EV expression of linc-ROR. Uptake of HCC EVs with high
linc-ROR expression by recipient cells led to enhanced chemoresistance of HepG2 cells to sorafenib treatment [
44].
2.4. EV-ncRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer
In pancreatic cancer, an aggressive type of cancer characterized by poor prognosis, EV lncRNAs with major roles in the progression of this disease have been also identified. In the TME of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), CAFs secrete EVs enriched in the lncRNA
RP11-161H23.5 that contribute to immune evasion, by limiting the expression of HLA-A in PDAC cells. Mechanistically,
RP11-161H23.5 interacts with the CNOT4 subunit of the CCR4-NOT complex and promotes the destabilization of HLA-A mRNA, by deadenylating its poly-A tail [
45]. The lncRNA
NNT-AS1 is found to be highly expressed in exosomes from CAFs and to be delivered to PDAC cells, where it acts as a ceRNA for mir-889-3p to stabilize expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1), thereby enhancing anaerobic glycolysis and PDAC progression [
46]. The lncRNA XIST (
lncXIST), which has well-established functions towards X chromosome inactivation, has been identified in EVs from pancreatic cancer cells and it is delivered in recipient neural cells, thereby facilitating perineural invasion. Concerning its molecular mechanism of action,
lncXIST is a ceRNA for miR-211-5p, the latter targeting glial-cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), which positively regulates perineural invasion [
47]. Another EV-enriched lncRNA with implications in PDAC progression is
LINC01133.
LINC01133 was found to be highly expressed in exosomes secreted by PDAC cells and positively correlated with poor overall survival of PDAC patients [
48].
3. EV ncRNA in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapeutics
3.1. EV ncRNA as Biomarkers in Cancer
An emerging area in the field of cancer diagnosis is the early detection of cancer with non-invasive methods, especially for solid tumors that are more challenging to perform tissue biopsies. The idea of identifying cancer-specific biomarkers in biofluids of patients, such as blood (plasma or serum) and urine is appealing, as it can provide a rapid assessment of the expression of specific to each type of cancer transcripts or proteins. However, this is not a trivial task, as molecules that may serve as biomarkers for cancer have to be identified and validated and the most appropriate type of human biofluid for detection should be determined. Speaking of this, circulating EVs secreted from tumor tissues have the potential to serve as excellent carriers of RNA or protein biomarkers, as their cargo is protected from degradation by the EV lipid membrane. Nevertheless, the challenge of identifying circulating EV RNA biomarkers specific to tumor remains, as blood contains EVs secreted from different tissues of origin and, thus, a direct comparison of the expression levels of a biomarker to the bulk tumor tissue is mandatory. Therefore, for particular cancer types, such as prostate cancer, urine collection after prostate massage may represent a better source of EVs that bear cancer-specific biomarkers, which are not diluted in the pool of EVs from different origins within blood.
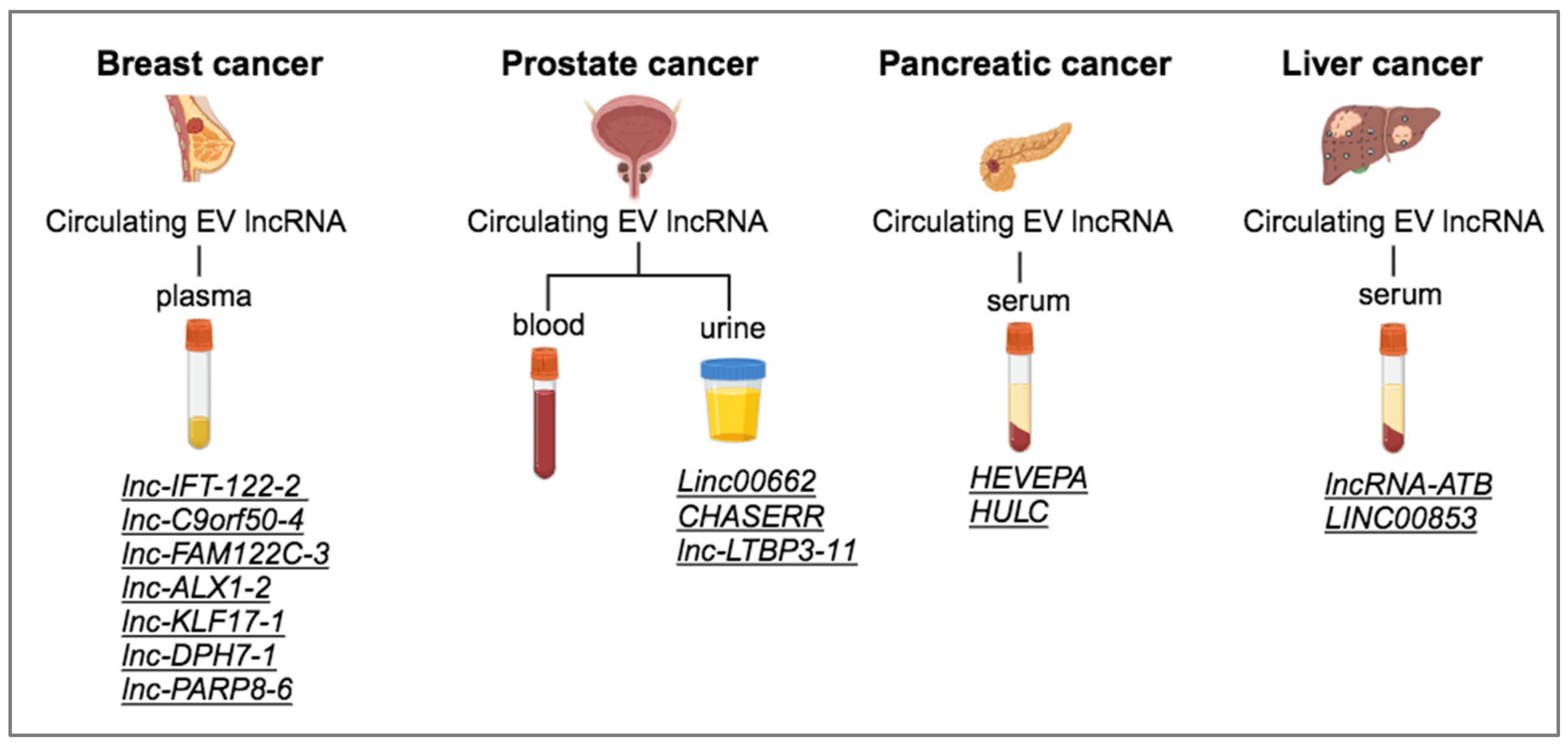
The use of liquid biopsies for identifying EV RNA biomarkers in breast cancer is still at its infancy. However, in a study that aimed to elucidate potential RNA biomarkers comparing plasma EVs from 32 patients with locally advanced breast cancer when diagnosed or 7 days post-surgery and also with 30 healthy individuals, the authors constructed a signature of eight RNAs (SNORD3H, SNORD1C, SNORA74D, miR-224-5p, piR-32949, lnc-IFT-122-2, lnc-C9orf50-4, and lnc-FAM122C-3) capable of discerning breast cancer from healthy EVs [
49]. In a different study, the same group investigated the potential use of circulating EV RNA for predicting breast cancer patients’ response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC). RNA sequencing revealed that 6 miRNAs, 4 lncRNAs (lnc-ALX1-2, lnc-KLF17-1, lnc-DPH7-1, and lnc-PARP8-6) and 1 snoRNA were expressed at higher levels in EVs from non-responders than responders at the time of diagnosis and throughout the period of NAC, and significantly lower levels in healthy individuals, thereby representing promising biomarker candidates for the prediction of response to NAC [
50].
A comparison of the RNA content of plasma and urinary EVs from 10 prostate cancer patients before or after prostatectomy led to the identification of novel RNA biomarkers whose expression is elevated in tumor tissues and in EVs before operation, but also lost in EVs after patients’ surgery. Interestingly, 63 mRNAs, 3 lncRNAs (
Linc00662,
CHASERR and
lnc-LTBP3-11), 2 miRNAs (miR375-3p and miR92a-1-5p) and one piRNA (piR-28004) were found to be highly expressed in prostate cancer tissues and diminished in urinary EVs post-prostatectomy. This study also confirmed that the use of urinary EVs is superior to the use of plasma EVs for the identification of prostate cancer RNA biomarkers, as plasma contains a mixture of EV populations secreted by different tissues, while urine is enriched in prostate cancer derived EVs [
51].
In HCC, circulating exosomes isolated from serum of 79 patients contained
lncRNA-ATB and miRNA-21. High expression of exosomal
lncRNA-ATB and miRNA-21 correlated with worse outcome for these patients, as well as larger tumor size and increased C-reactive protein levels, suggesting that these two ncRNAs have prognostic value in HCC [
52]. In another study, lncRNA
LINC00853 is over-represented in sEVs derived from HCC patients’ sera, showing potent discriminatory capacity for early HCC diagnosis with high sensitivity and specificity [
53].
In pancreatic cancer, liquid biopsy was performed to isolate EVs from serum samples derived from 20 patients with PDAC, 22 patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms, and 21 healthy individuals and subjected to lncRNA profiling. A highly expressed EV lncRNA designated as
HEVEPA was identified among PDAC patients’ serums, but not in the other two control groups [
54]. In an independent study, EV-enriched lncRNA
HULC was shown to function as a circulating biomarker for PDAC, as it was overexpressed in serum samples from 20 PDAC patients, in comparison to 22 intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) patients and 21 healthy individuals [
55].
Overall, several EV-enriched lncRNAs isolated mainly from patient blood or urine samples have been suggested as candidate circulating biomarkers in certain types of cancer (
Figure 3), but it would require further confirmation using robust large-scale validation cohort of patients from multicenter studies.
3.2. EVs as Delivery Tools for Therapeutic Purposes
Drug delivery systems using synthetic nanocarriers are gaining interest in the field of targeted therapy including cancer. Synthetic lipid nanoparticles can be loaded with small molecules and can be engineered to target specifically cancer cells, thereby minimizing non-desirable side effects. Nonetheless, there are still important challenges to face while using synthetic drug delivery systems, such as increased cytotoxicity, reduced biocompatibility and triggered immunogenicity [
56]. The unique properties of EVs related to protective lipid bilayer that safeguards their cargo, enhanced biocompatibility with minor host immune reactions and tissue penetrating capacity make them attractive alternative candidates for drug or oligonucleotide delivery-based therapeutic approaches [
57]. Indeed, engineered EVs, genetically or chemically modified to express certain biomolecules in their membrane or lumen, have been used in cancer therapy either to specifically target cancer cells or to educate the host immune system against tumor-specific antigens. Synthetic miRNA mimics loaded into EVs are able to prevent migration and self-renewal of glioma cells, upon their delivery. Notably, dendritic cell-derived EVs, bearing membrane proteins important for antigen presentation, have been utilized in phase I clinical trials in certain cancers such as melanoma and colorectal cancer [
58].
Apart from cancer, EVs have been used in therapeutics of other diseases. For example, liver fibrosis is characterized by ECM accumulation in the liver tissue, in response to chronic damage and can potentially lead to HCC development. To combat the progression of fibrosis, exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells loaded with exogenous siRNA or antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) against the transcription factor STAT3, a positive regulator of this disease, have been used in a mouse model of liver fibrosis. These engineered EVs efficiently repressed STAT3 and ameliorated liver health [
59]. Although the advances in EV therapeutics open up exciting directions for precision medicine in the future, a continuous improvement is needed in multiple aspects of this field, mainly in relation to selecting the most appropriate EV donors, enhancing the efficiency of exogenous cargo loading, as well as improving the specificity of target destinations.
4. Future Perspectives
The field of EV transcriptomics has been boosted over the last years, mainly due to the improvements in old and development of new EV isolation protocols and also in technological advances in RNA sequencing methods. Nevertheless, a lot of open questions exist and the future research directions in the field include the areas of decoding EV heterogeneity by developing single EV RNA sequencing [
60], investigating EV RNA integrity using long-read sequencing and unraveling the roles of EVs in TME by establishing cancer cell 3D cultures and organoids to better recapitulate the cancer-TME crosstalk. Most of the in vitro studies on cancer cell EVs make use of 2D cultures, a model that does not mimic the structural complexity of tumors in vivo. On the contrary, the development of 3D cultures or spheroids derived from cancer cell lines shortens the distance between conventional cancer cell culture conditions and cancer tissue. Recent reports suggest that the cargo composition of EVs derived from 3D cultures is different from the 2D culture of the same cell line. In addition, 3D cultures seem to enhance EV secretion compared to 2D cultures [
61].
Another important task in the field is to better understand whether the EV-mediated effects on recipient cells are the collective outcome of the full cargo transfer or attributed to a few individual biomolecules that are biologically functional. In order to elucidate this possibility, a deconvolution of EV cargo biomolecules is necessary, with the development of EV RNA tracing approaches to monitor the routes and fate of EV RNA from EV biogenesis in donor cells till their delivery into the cytoplasm of recipient cells. From the cancer biomarker perspective, blood, serum and urine biofluids are gold-standard sources of EV RNA biomarker identification, however EVs are secreted in 20 different human biofluids, a finding that open up possibilities for unravelling novel biomarkers for different disorders or elucidating the functions of EVs in various human physiological processes in the future [
62].
5. Conclusions
Although both lncRNA and EVs were considered as “junk genomic regions” and “carriers of unneeded cellular components destined for disposal”, respectively, when they were first discovered, the scientific community now appreciates their unique biological functions towards cancer progression and their utility in cancer diagnosis as biomarkers and in therapeutics as natural nanocarriers. This fact highlights the need of a meticulous delineation of the functions of newly identified molecules or biological entities, before undermining their biological significance, as they may hold promising potential for biological systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.P. and A.M.; writing—original draft preparation, P.P.; writing—review and editing, P.P. and A.M.; funding acquisition, A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Institut National du Cancer (INCA), grant numbers PLBIO21-100 and PLBIO22-222.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge all members of the “ncRNA, Epigenetics and Genome Fluidity” (UMR3244) and “Extracellular vesicles, immune responses and cancer” (U932) teams at Institut Curie for useful discussions. We apologize to the authors whose work was not cited due to space limitations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV2023): From Basic to Advanced Approaches. J of Extracellular Vesicle 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Gonzalez-Kozlova, E.; Soleymani, T.; La Salvia, S.; Kyprianou, N.; Sahoo, S.; Tewari, A.K.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Stolovitzky, G.; Dogra, N. Extracellular Vesicles Carry Distinct Proteo-Transcriptomic Signatures That Are Different from Their Cancer Cell of Origin. iScience 2022, 25, 104414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding Light on the Cell Biology of Extracellular Vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J of Extracellular Vesicle 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Proteomic Comparison Defines Novel Markers to Characterize Heterogeneous Populations of Extracellular Vesicle Subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, H.; Wang, B.; Yuan, F. Research Progress on the Roles of lncRNAs in Plant Development and Stress Responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1138901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Definitions, Functions, Challenges and Recommendations. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.-J.; Chen, L.-L.; Huarte, M. Gene Regulation by Long Non-Coding RNAs and Its Biological Functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoutsoglou, P.; Moustakas, A. Long Non-coding RNAs and TGF-β Signaling in Cancer. Cancer Science 2020, 111, 2672–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, A.; Story, M.D. The Long and Short of It: The Emerging Roles of Non-Coding RNA in Small Extracellular Vesicles. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batagov, A.O.; Kurochkin, I.V. Exosomes Secreted by Human Cells Transport Largely mRNA Fragments That Are Enriched in the 3′-Untranslated Regions. Biol Direct 2013, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, J.-C.A.; Barutcu, S.; Malet, L.; Deschamps-Francoeur, G.; Calderon, V.; Kwon, E.; Lécuyer, E. Profiling the Polyadenylated Transcriptome of Extracellular Vesicles with Long-Read Nanopore Sequencing. BMC Genomics 2023, 24, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransom, L.S.; Liu, C.S.; Dunsmore, E.; Palmer, C.R.; Nicodemus, J.; Ziomek, D.; Williams, N.; Chun, J. Human Brain Small Extracellular Vesicles Contain Selectively Packaged, Full-Length mRNA. Cell Rep 2024, 43, 114061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Grady, T.; Njock, M.-S.; Lion, M.; Bruyr, J.; Mariavelle, E.; Galvan, B.; Boeckx, A.; Struman, I.; Dequiedt, F. Sorting and Packaging of RNA into Extracellular Vesicles Shape Intracellular Transcript Levels. BMC Biol 2022, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.; Gabriel, M.; Firlej, V.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lejars, M.; Cipolla, R.; Petit, F.; Vogt, N.; San-Roman, M.; Dingli, F.; et al. Urinary Extracellular Vesicles Contain Mature Transcriptome Enriched in Circular and Long Noncoding RNAs with Functional Significance in Prostate Cancer. J of Extracellular Vesicle 2022, 11, e12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellar, E.R.; Hill, C.; Melling, G.E.; Carter, D.R.F.; Baena-Lopez, L.A. Unpacking Extracellular Vesicles: RNA Cargo Loading and Function. J Extracell Biol 2022, 1, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Kawasaki, Y. A Novel Sorting Signal for RNA Packaging into Small Extracellular Vesicles. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 17436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, C.; Barreca, M.M.; Zichittella, C.; Alessandro, R.; Conigliaro, A. Molecular Mediators of RNA Loading into Extracellular Vesicles. Cells 2021, 10, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-M.; Ma, L.; Schekman, R. Selective Sorting of microRNAs into Exosomes by Phase-Separated YBX1 Condensates. Elife 2021, 10, e71982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, A.L.; Adams, A.; King, K.E.; Dunn, W.; Christenson, L.K.; Hung, W.-T.; Weinman, S.A. The RNA Binding Protein FMR1 Controls Selective Exosomal miRNA Cargo Loading during Inflammation. J Cell Biol 2020, 219, e201912074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Marques, T.; Costa, M.C.; Catarino, S.; Simoes, I.; Aasen, T.; Enguita, F.J.; Girao, H. Cx43-Mediated Sorting of miRNAs into Extracellular Vesicles. EMBO Rep 2022, 23, e54312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbiano, F.; Corsi, J.; Gurrieri, E.; Trevisan, C.; Notarangelo, M.; D’Agostino, V.G. RNA Packaging into Extracellular Vesicles: An Orchestra of RNA-binding Proteins? J of Extracellular Vesicle 2020, 10, e12043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Singh, J.; Schekman, R. Two RNA-Binding Proteins Mediate the Sorting of miR223 from Mitochondria into Exosomes. Elife 2023, 12, e85878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, K.; Breyne, K.; Ughetto, S.; Laurent, L.C.; Breakefield, X.O. RNA Delivery by Extracellular Vesicles in Mammalian Cells and Its Applications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2020, 21, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, L.A.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R.F. Routes and Mechanisms of Extracellular Vesicle Uptake. J Extracell Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebelman, M.P.; Bun, P.; Huveneers, S.; van Niel, G.; Pegtel, D.M.; Verweij, F.J. Real-Time Imaging of Multivesicular Body-Plasma Membrane Fusion to Quantify Exosome Release from Single Cells. Nat Protoc 2020, 15, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Park, D.J.; Eliceiri, B.P. Defining Tropism and Activity of Natural and Engineered Extracellular Vesicles. Front Immunol 2024, 15, 1363185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsergent, E.; Grisard, E.; Buchrieser, J.; Schwartz, O.; Théry, C.; Lavieu, G. Quantitative Characterization of Extracellular Vesicle Uptake and Content Delivery within Mammalian Cells. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.P.; Kim, E.Y.; Badr, C.E.; Weissleder, R.; Mempel, T.R.; Tannous, B.A.; Breakefield, X.O. Visualization and Tracking of Tumour Extracellular Vesicle Delivery and RNA Translation Using Multiplexed Reporters. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufino-Ramos, D.; Leandro, K.; Perdigão, P.R.L.; O’Brien, K.; Pinto, M.M.; Santana, M.M.; van Solinge, T.S.; Mahjoum, S.; Breakefield, X.O.; Breyne, K.; et al. Extracellular Communication between Brain Cells through Functional Transfer of Cre mRNA Mediated by Extracellular Vesicles. Mol Ther 2023, 31, 2220–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somiya, M.; Kuroda, S. Verification of Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Functional mRNA Delivery via RNA Editing 2022.
- Tao, S.-C.; Guo, S.-C. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Tumour Microenvironment. Cell Commun Signal 2020, 18, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; McAndrews, K.M. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer. Cell 2023, 186, 1610–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Lu, C.; Yixi, L.; Hong, J.; Dong, F.; Ruan, S.; Hu, T.; Zhao, X. Exosomal Linc00969 Induces Trastuzumab Resistance in Breast Cancer by Increasing HER-2 Protein Expression and mRNA Stability by Binding to HUR. Breast Cancer Res 2023, 25, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, W. Exosomal lncRNA SNHG12 Promotes Angiogenesis and Breast Cancer Progression. Breast Cancer 2024, 31, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, Q.; Yin, D.; Lin, D.; Wong, P.-P.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Packaged HIF-1α-Stabilizing lncRNA from Tumour-Associated Macrophages Regulates Aerobic Glycolysis of Breast Cancer Cells. Nat Cell Biol 2019, 21, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Shi, B.; Ren, Q.; Zhuang, Y.; Qian, X. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Hypoxia-Induced Tumor-Associated Fibroblasts Impart Chemoresistance to Breast Cancer Cells via Long Noncoding RNA H19 Delivery. FASEB J 2024, 38, e23165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahadi, A.; Brennan, S.; Kennedy, P.J.; Hutvagner, G.; Tran, N. Long Non-Coding RNAs Harboring miRNA Seed Regions Are Enriched in Prostate Cancer Exosomes. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 24922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hu, J.; Shi, Y.; Xiao, M.; Bi, T.; Wang, C.; Yan, L.; Li, X. Exosomal lncAY927529 Enhances Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion through Regulating Bone Microenvironment. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 2531–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-Y.; Chen, J.; Qin, X.-H.; You, P.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.-D. Long Non-Coding RNA NORAD Promotes the Prostate Cancer Cell Extracellular Vesicle Release via microRNA-541-3p-Regulated PKM2 to Induce Bone Metastasis of Prostate Cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2021, 40, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Kawakami, K.; Mizutani, K.; Ando, T.; Sakai, Y.; Sakurai, K.; Toyota, S.; Ehara, H.; Ito, H.; Ito, M. H19 in Serum Extracellular Vesicles Reflects Resistance to AR Axis-Targeted Therapy Among CRPC Patients. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2023, 20, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Bajo-Santos, C.; Hessvik, N.P.; Lorenz, S.; Fromm, B.; Berge, V.; Sandvig, K.; Linē, A.; Llorente, A. Identification of Non-Invasive miRNAs Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer by Deep Sequencing Analysis of Urinary Exosomes. Mol Cancer 2017, 16, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Wang, J.; Li, L. Extracellular Vesicular lncRNA FAL1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Inducing Macrophage M2 Polarization. J Physiol Biochem 2023, 79, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yan, I.K.; Kogure, T.; Haga, H.; Patel, T. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of Long Non-Coding RNA ROR Modulates Chemosensitivity in Human Hepatocellular Cancer. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Huang, C.; Zou, J.; Liang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhong, Z.; Zhou, S.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Packaged lncRNA from Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promotes Immune Evasion by Downregulating HLA-A in Pancreatic Cancer. J Extracell Vesicles 2024, 13, e12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Q.; Lu, W.; Zhang, F.; Wu, D.; Sun, J. NNT-AS1 in CAFs-Derived Exosomes Promotes Progression and Glucose Metabolism through miR-889-3p/HIF-1α in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Pan, J.; Liu, Q.; Ji, Y.; Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Sun, J.; Gong, M.; et al. Exosomal lncRNA XIST Promotes Perineural Invasion of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via miR-211-5p/GDNF. Oncogene 2024, 43, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, T.; Yang, X.; Qin, P.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Bai, M.; Wu, R.; Li, F. Tumor-Derived Exosomal Long Noncoding RNA LINC01133, Regulated by Periostin, Contributes to Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway by Silencing AXIN2. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3164–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayakin, P.; Sadovska, L.; Eglītis, K.; Romanchikova, N.; Radoviča-Spalviņa, I.; Endzeliņš, E.; Liepniece-Karele, I.; Eglītis, J.; Linē, A. Extracellular Vesicles-A Source of RNA Biomarkers for the Detection of Breast Cancer in Liquid Biopsies. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15, 4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadovska, L.; Zayakin, P.; Eglītis, K.; Endzeliņš, E.; Radoviča-Spalviņa, I.; Avotiņa, E.; Auders, J.; Keiša, L.; Liepniece-Karele, I.; Leja, M.; et al. Comprehensive Characterization of RNA Cargo of Extracellular Vesicles in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 1005812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajo-Santos, C.; Brokāne, A.; Zayakin, P.; Endzeliņš, E.; Soboļevska, K.; Belovs, A.; Jansons, J.; Sperga, M.; Llorente, A.; Radoviča-Spalviņa, I.; et al. Plasma and Urinary Extracellular Vesicles as a Source of RNA Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer in Liquid Biopsies. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 980433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.R.; Kim, G.; Tak, W.Y.; Jang, S.Y.; Kweon, Y.O.; Park, J.G.; Lee, H.W.; Han, Y.S.; Chun, J.M.; Park, S.Y.; et al. Circulating Exosomal Noncoding RNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2019, 144, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Baek, G.O.; Ahn, H.R.; Sung, S.; Seo, C.W.; Cho, H.J.; Nam, S.W.; Cheong, J.Y.; Eun, J.W. Serum Small Extracellular Vesicle-Derived LINC00853 as a Novel Diagnostic Marker for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol Oncol 2020, 14, 2646–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Inuzuka, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Sawamoto, K.; Taniue, K.; Ono, Y.; Asai, F.; Koyama, K.; Sato, H.; Kawabata, H.; et al. Liquid Biopsy for Pancreatic Cancer by Serum Extracellular Vesicle-Encapsulated Long Noncoding RNA HEVEPA. Pancreas 2024, 53, e395–e404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Ota, Y.; Kogure, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Yamakita, K.; Kitano, Y.; Fujii, S.; Haneda, M.; Patel, T.; et al. Circulating Extracellular Vesicle-Encapsulated HULC Is a Potential Biomarker for Human Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Sci 2020, 111, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yin, B.; Lian, J.; Wang, X. Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery System for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payandeh, Z.; Tangruksa, B.; Synnergren, J.; Heydarkhan-Hagvall, S.; Nordin, J.Z.; Andaloussi, S.E.; Borén, J.; Wiseman, J.; Bohlooly, -Y. M.; Lindfors, L.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Transport RNA between Cells: Unraveling Their Dual Role in Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Molecular Aspects of Medicine 2024, 99, 101302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.A.; Baba, S.K.; Sadida, H.Q.; Marzooqi, S.A.; Jerobin, J.; Altemani, F.H.; Algehainy, N.; Alanazi, M.A.; Abou-Samra, A.-B.; Kumar, R.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles as Tools and Targets in Therapy for Diseases. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2024, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Sugimoto, H.; Yang, S.; Yang, C.; LeBleu, V.S.; McAndrews, K.M.; Kalluri, R. Therapeutic Targeting of STAT3 with Small Interference RNAs and Antisense Oligonucleotides Embedded Exosomes in Liver Fibrosis. FASEB J 2021, 35, e21557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Luo, L.; Sun, N.; Pei, R. Current Advances in Technologies for Single Extracellular Vesicle Analysis and Its Clinical Applications in Cancer Diagnosis. Biosensors 2023, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousafzai, N.A.; El Khalki, L.; Wang, W.; Szpendyk, J.; Sossey-Alaoui, K. Advances in 3D Culture Models to Study Exosomes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulstaert, E.; Morlion, A.; Avila Cobos, F.; Verniers, K.; Nuytens, J.; Vanden Eynde, E.; Yigit, N.; Anckaert, J.; Geerts, A.; Hindryckx, P.; et al. Charting Extracellular Transcriptomes in The Human Biofluid RNA Atlas. Cell Reports 2020, 33, 108552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).