Submitted:
09 October 2024
Posted:
10 October 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
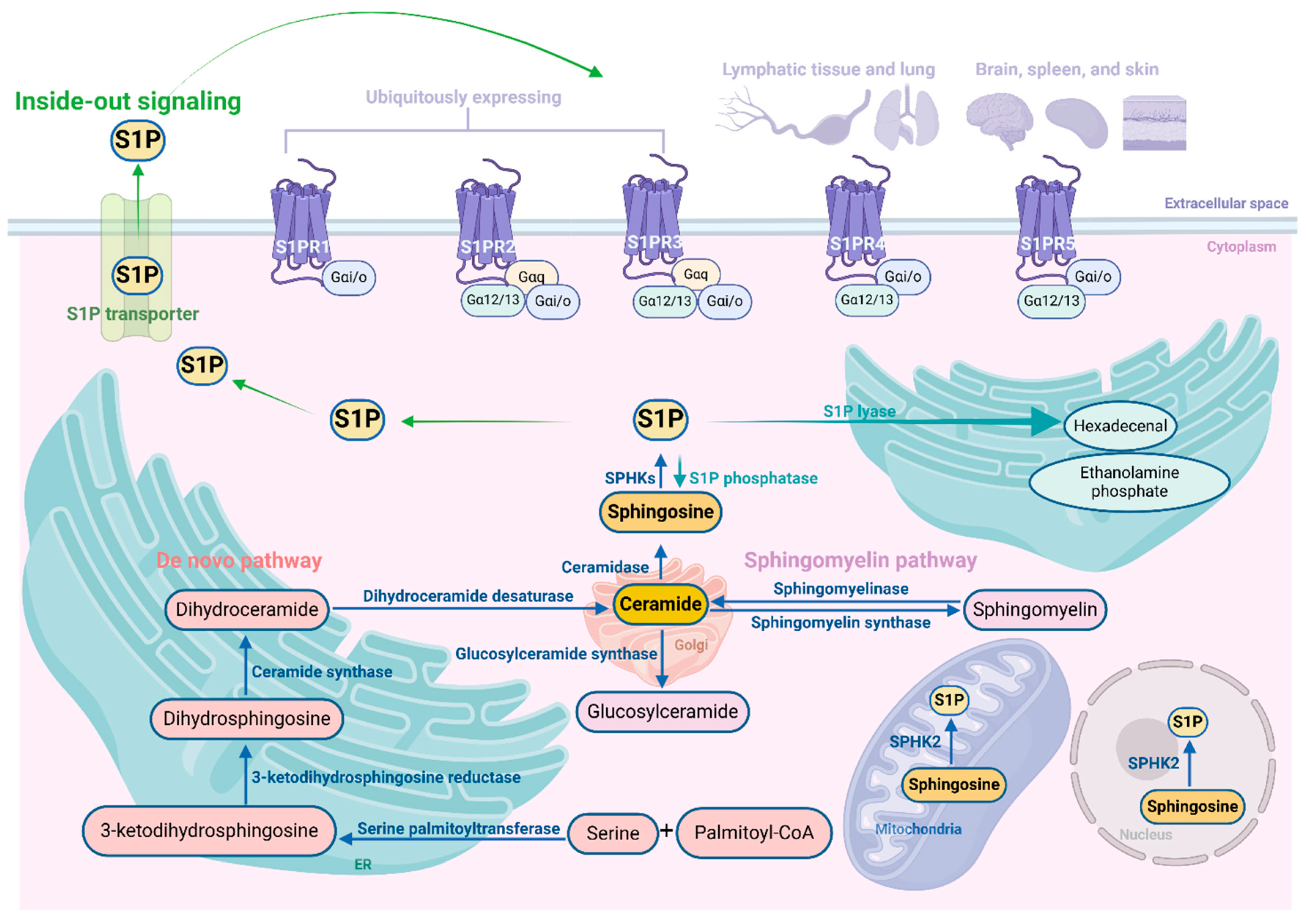
3. Basics of the S1P Signaling Pathway
3.1. Synthesis, Degeneration, and Transport of S1P
3.2. Sphingosine Kinases
3.3. S1P Receptors (S1PRs)
3.4. Current Therapeutic Strategies Targeting S1P Signaling: Regulating SPHKs and S1PRs
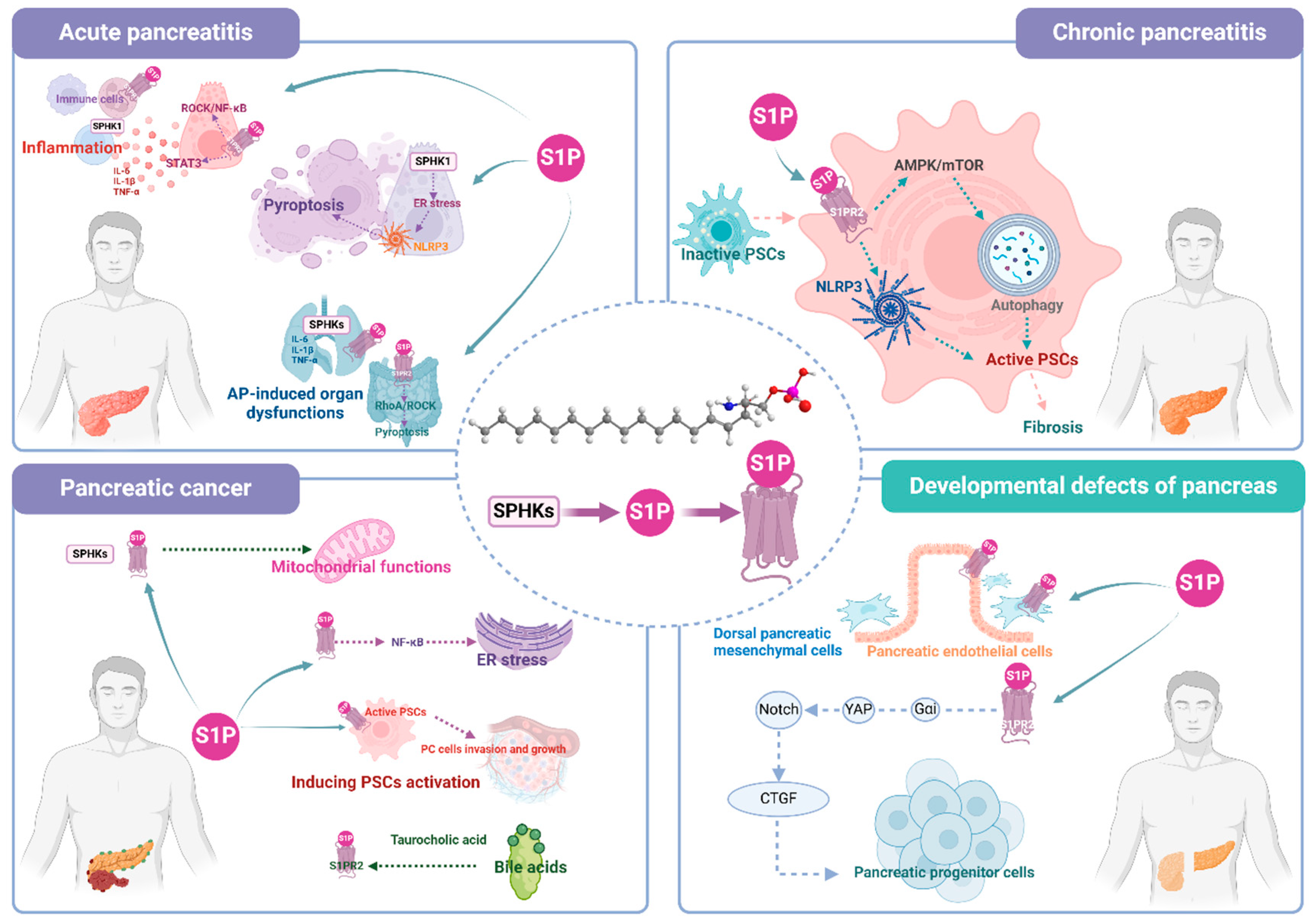
4. Role of S1P Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Diseases
4.1. AP
4.1.1. Functioning as Potential Biomarkers for Severity of AP
4.1.2. Mediating Local and Systematic Inflammation
4.1.3. Inducing Pyroptosis of Pancreatic Acinar Cells (PACs)
4.1.4. Involving in AP-induced Organ Injury
4.2. CP
4.3. PC
4.3.1. Targeting S1P Signaling for PC Therapy
4.3.2. Impacting Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis of PC Cells
4.3.3. Inhibiting S1P Signaling Improves PC by Inducing ER Stress of PC Cells
4.3.4. Mediating PSCs Activation That Transferring to PC
4.3.5. Being Activated by Bile acids (BAs)
5. S1P Signaling Participates in the Developmental Defects of Pancreas (DDP)
6. Conclusions and Future Prospectives
| Compound | Structure | Primarily used as | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| N,N-dimethylsphingosine (DMS) | 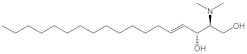 |
Antagonist of SPHK1 and SPHK2 | [74,156] |
| SKI-II | 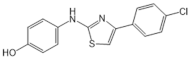 |
Antagonist of SPHK1 and SPHK2 | [75,157] |
| SKI 5c | 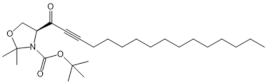 |
Antagonist of SPHK1 | [72] |
| PF-543 | 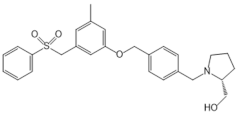 |
Antagonist of SPHK1 | [59,73] |
| Opaganib (ABC294640) | 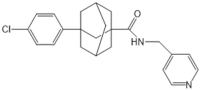 |
Antagonist of SPHK2 | [76] |
| K145 | 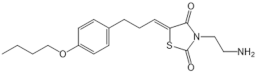 |
Antagonist of SPHK2 | [158] |
| Fingolimod (FTY720) | 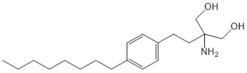 |
Modulator of S1PR1, S1PR3, S1PR4 and S1PR5, antagonist of SPHK1 | [17,53,58] |
| Etrasimod (APD334) | 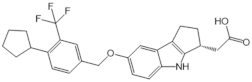 |
Modulator of S1PR1, S1PR4 and S1PR5 | [159] |
| Siponimod (BAF312) | 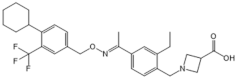 |
Modulator of S1PR1 and S1PR5 | [160] |
| Ozanimod (RPC1063) | 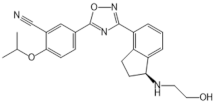 |
Agonist of S1PR1 and S1PR5 | [161] |
| VPC23019 | 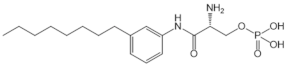 |
Antagonist of S1PR1 and S1PR3 | [77] |
| SEW2871 | 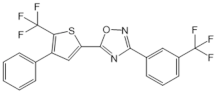 |
Agonist of S1PR1 | [162] |
| Ponesimod (ACT-128800) | 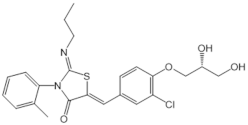 |
Agonist of S1PR1 | [163] |
| NIBR-0213 | 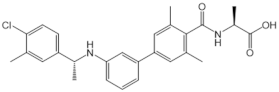 |
Antagonist of S1PR1 | [164] |
| CYM5520 | 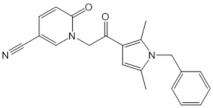 |
Agonist of S1PR2 | [58] |
| JTE-013 | 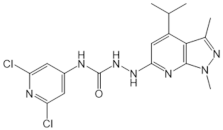 |
Antagonist of S1PR2 | [70] |
| CYM5541 | 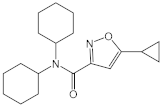 |
Agonist of S1PR3 | [165] |
| TY52156 | 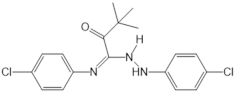 |
Antagonist of S1PR3 | [164] |
| CYM50358 | 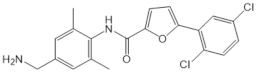 |
Antagonist of S1PR4 | [166] |
| A-971432 |  |
Agonist of S1PR5 | [167] |
| Object | Disease | Subject | Model | Treatment | Effects | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPHK1 | AP | Severe AP patients | / | / | ↑ Peripheral blood leukocytes SPHK1 in the early stage of severe AP patients | [80] | |
| SPHK1 | AP | Mild and severe AP patients | / | / | ↑ Peripheral blood leukocytes SPHK1 in the early stage of mild and severe AP patients. | / | [81] |
| SPHK1/S1PR3 | AP | Severe AP patients | / | / | ↑ SPHK1 and S1PR3 in the early stage of severe AP patients, but recovered to normal level at the restoration stage. SPHK1 expression of peripheral neutrophils, monocytes, and CD4+ T lymphocytes was positively correlated with the APACHE score of severe AP patients | [82] | |
| S1P | AP | Wistar rats | Cerulein | / | ↑Pancreatic S1P | / | [25] |
| S1P | AP | Severe AP patients | / | / | ↓Plasma S1P in severe AP patients | / | [85] |
| SPHK2/S1P | AP | AP patients | / | / | ↓Serum S1P in AP patients | / | [86] |
| Female C57BL/6 mice | Cerulein | / | ↓Serum S1P, pancreatic S1P and SPHK2 | ||||
| AR42J cells | Cerulein | / | ↓S1P, SPHK2 | ||||
| S1P | AP | AP patients | / | / | ↑ Plasma S1P in the early stage (days 1 and 3) of mild AP patients, then returned to normal level at day 7 | / | [87] |
| ↓ Plasma S1P in the early stage (days 1 and 3) of severe AP patients, then returned to normal level at day 7 | |||||||
| S1PR2 | AP | Male ICR mice | Cerulein, injection of TCA into the pancreatic duct | / | ↑Pancreatic S1PR2 | S1PR2 regulated ROCK/NF-κB signaling | [26] |
| Inhibition of S1PR2 by JTE-013, knockdown of S1pr2 | ↓Pancreatic damage, NF-κB | ||||||
| PACs, primary peritoneal macrophages, RAW264.7 cells | TCA | / | ↑S1PR2 | ||||
| Inhibition of S1PR2 by JTE-013, knockdown of S1pr2 | ↓NF-κB, macrophage recruitment and macrophage polarization toward the M1 phenotype | ||||||
| S1PR | AP | Female apolipoprotein CIII transgenic C57BL/6J mice | Cerulein | Modulation of S1PR by FTY720 | ↓Pancreatic pathological injury, MCP-1 | / | [92] |
| S1PR | AP | Wistar rats | Injection of 5% sodium taurocholate into the biliopancreatic duct | Modulation of S1PR by FTY720 | ↓IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α in plasma/serum, necrosis, inflammation and number of CD4+/CD8+ cells in pancreas | / | [66] |
| S1PR1 | AP | Male ICR mice | Cerulein | Activation of S1PR1 by SEW2871 | ↓Pathological injury of pancreas, serum amylase, lipase, IL-6 and TNF-α, pancreatic MPO, number of CD45+CD4+ T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood, infiltration of CD4+ T cells in pancreas, inflammation | S1PR1 regulated the phosphorylation of STAT3 | [93] |
| SPHK1 | AP | Male C57BL/6J mice | Cerulein | / | ↑Pancreatic SPHK1 | SPHK1 regulated PERK/TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling | [83] |
| Knockout of Sphk1 | ↓Pancreatic damage, pyroptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress | ||||||
| 266-6 cells | CCK8 | / | ↑ SPHK1 | ||||
| Knockdown of Sphk1 | ↓LDH, pyroptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress | ||||||
| SPHK1 | AP | SD rats | Injection of 5% sodium taurocholate into the biliopancreatic duct | / | ↑SPHK1 in pancreas and peripheral blood neutrophils | / | [61] |
| Inhibition of SPHK1 by SKI 5c | ↑Survival rate | ||||||
| ↓Serum amylase, lipase, TNF-α and IL-1β; MPO in the lung, protein content of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, pathological injury of the lung | |||||||
| S1P/S1PR | AP | Male Wistar rats | Injection of 5% sodium taurocholate into the biliopancreatic duct | 100 μg/kg S1P, i.p., once, modulation of S1PR by FTY720 | ↓IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, protein concentration, total cell count, PMN percentage in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, NF-κB activity of alveolar macrophages, capillary leakage and MPO in the lung. Pathological injury of pancreas and lung | / | [67] |
| S1P | AP | Wistar rats | Injection of 5% sodium taurocholate into the biliopancreatic duct | 50 μg/kg S1P, i.p., once | ↓Serum amylase and lipase, protein concentration, leucocyte and neutrophil count of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, MPO of the lung tissue, pathological injury of pancreas and lung | / | [100] |
| S1PR2 | AP | Male C57BL/6 mice | Cerulein+ lipopolysaccharide | Inhibition of S1PR2 by JTE-013 | ↓Pathological injury of pancreas, inflammation, intestinal tissue injury and pyroptosis | S1PR2 regulated RhoA/ROCK signaling | [57] |
| THP-1 cells | Lipopolysaccharide +ATP | Knockdown or overexpression of S1pr2 | S1PR2 positively regulated macrophage pyroptosis, and negatively regulated cohesin expression in FHC cells after co-culture of FHC and THP-1 cells | ||||
| S1P/S1PR2 | CP | Male Wistar rats | Dibutyltin dichloride | / | ↑Plasma and pancreatic S1P | S1P binding to S1PR2 promoted PSC activation and pancreatic fibrosis in CP by regulating autophagy and the NLRP3 inflammasome sequentially | [71] |
| 200 μg/kg/day S1P, i.p., 4 weeks | ↑Pancreatic damage, fibrosis, autophagy, S1PR2, NLRP3 | ||||||
| PSCs | / | 5 μM S1P, 24h | ↑PSC activation, autophagy, S1PR2, NLRP3 | ||||
| Inhibition of S1PR2 by JTE-013, knockdown of S1pr2 | ↓PSC activation, autophagy, NLRP3 | ||||||
| SPHK1/S1P/S1PR2 | CP | C57BL/6 mice | Cerulein, pancreatic duct ligation | / | ↑Serum S1P, pancreatic SPHK1, S1PR2 | PACs-derived S1P contributed to fibrosis of CP via inducing autophagy and activation of PSCs through the AMPK/mTOR signaling | [59] |
| Knockout of Sphk1, inhibition of SPHK1 or S1PR2 by PF-543 and JTE-013, respectively | ↓Pathological injury of pancreas, fibrosis, inflammation, atrophy of the pancreas | ||||||
| PACs | CCK, hypoxia | / | ↑SPHK1, S1P in PACs | ||||
| Knockout of Sphk1 in PACs, PSCs treated with S1P, knockdown of S1pr2 or inhibition of S1PR2 in PSCs | SPHK1/S1P/S1PR2 signaling positively regulated activation and autophagy of PSCs | ||||||
| S1PR | CP | Male Wistar rats | Male WBN/Kob rats | Modulation of S1PR by FTY720 | ↑Pancreas weights | S1PR regulated IFN-γ and TGF-β1 expression | [68] |
| ↓Pancreatic MPO activity, hydroxyproline content, pathological injury of pancreas, inflammation, fibrosis, necrosis, infiltration of CD4 and CD8-positive T cells in the pancreas | |||||||
| S1P | PC | C57BL/6 mice | PANC-2 cells, subcutaneous | PhotoImmunoNanoTherapy | ↓Tumor volume | / | [112] |
| Athymic nude mice | Human BxPC-3-GFP cells, orthotopic | PhotoImmunoNanoTherapy | ↑Surem S1P | ||||
| SPHK2 | PC | BxPC-3 cells | / | Inhibition of SPHK2 by ABC294640, sorafenib | ↓Cell viability, ↑Cell apoptosis | / | [78] |
| SCID mice | Human BxPC-3 cells, subcutaneous | Inhibition of SPHK2 by ABC294640, sorafenib | ↓Tumor growth, ↑Tumor cell apoptosis | ||||
| SPHK2 | PC | SCID mice | Human BxPC-3 cells, subcutaneous | Inhibition of SPHK2 by ABC294640 | ↓Tumor growth | / | [63] |
| SPHK1 | PC | BxPC-3 or PANC-1 cells | Gemcitabine | Inhibition of SPHK1 by SKI or knockdown of Sphk1 | ↓Cell viability | / | [114] |
| Overexpression of Sphk1 | ↑Cell viability | ||||||
| SPHKs/S1P | PC | C57BL/6 mice | PDAC cells, metastatic | PAPTP + ABC294640 | ↓Tumor growth | SPHKs regulated the mitochondrial Kv1.3 ion | [124] |
| MIA PaCa-2 cells | Inhibition of Kv1.3 by PAPTP | / | ↑Sphingosine, S1P-phosphatase | ||||
| Inhibition of S1P-phosphatase by XY-14 | ↓Sphingosine, death of pancreas cancer cells | ||||||
| Inhibition of SPHK2 by ABC294640 | ↑Sphingosine, death of pancreas cancer cells | ||||||
| SPHK1/S1P | PC | MIA PaCa-2, PANC-1 or Capan-1 cells | / | Inhibition of SPHK1 by mebendazole | ↓Cell migration, proliferation and viability, ↑Cell mitochondrial apoptosis | SPHK1 regulated the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway, JAK2/STAT3 and FAK/Vimentin signaling pathway | [125] |
| SPHKs | PC | PSN1 cells | / | Inhibition of SPHKs by SKI-II | ↓Cell proliferation | SPHKs regulated the ratio of S1P/C16 Cer | [62] |
| S1PR1 | PC | MIA PaCa-2 or PAN02 cells | / | Inhibition of S1PR1 by FTY720 | ↓Cell migration, proliferation | S1PR1 regulated the mitochondrial membrane potential, S1PR1-STAT3 loop, and epithelial to mesenchymal transition | [69] |
| MIA PaCa-2 or PAN02 cells | Gemcitabine | Inhibition of S1PR1 by FTY720 | ↑Cell death, ↓Cell proliferation | ||||
| NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid/J mice or C57BL/6 mice | luciferase-tagged MIA PaCa-2 cells | Treatment of FTY720 and gemcitabine | ↓Tumor volume, tumor cell metastasis, proliferation, ↑Cell apoptosis or necrosis | ||||
| SPHK2 | PC | MIA PaCa-2 or PANC-1 cells | Oxaliplatin | Inhibition of SPHK2 by ABC294640 or knockdown of Sphk2 | ↓Cell viability, ↑ER stress | SPHK2 modulated ER stress, thereby regulating PERK/eIF2α phosphorylation and ICD | [130] |
| Male C57BL/6 mice | KPC cells, orthotopic | Oxaliplatin +ABC294640 | ↓Tumor weight, ↑ICD | ||||
| S1P/S1PR2 | PC | PANC-1 or L3.6 cells | Conditioned media collected from S1P-treated PSCs | / | ↑Cell proliferation, migration | S1P regulated tumor microenvironment and the interactions of PSCs with cancer cells | [28] |
| PANC-1 cells | Conditioned media collected from S1P-treated PSCs | Inhibition of S1PR2 by JTE-013, Knockdown of S1pr2 | ↓Cell migration, invasion | ||||
| Male nude mice | L3.6 cells + PSCs or ASPC-1 cells + PSCs, orthotopic | / | ↑Tumor volume, weight, metastasis | ||||
| Knockdown of S1pr2 | ↓Tumor volume, weight, metastasis | ||||||
| S1PR2 | PC | PANC-1 or CFPAC-1 cells | Gemcitabine | Inhibition of S1PR2 by JTE-013 | ↑Gemcitabine -induced apoptosis, ↓Cell migration, invasion | TCA contributes to gemcitabine ineffectiveness by activating S1PR2/ERK signaling | [142] |
| S1P/S1PR2 | PC | Male C57BL/6 mice | PANC-2-luc cells + bile duct ligation, orthotopic,metastatic | Activation of S1PR2 by CYM5520 | ↑Tumor growth | / | [58] |
| Treated with anti-S1P-antibody, sphingomab | ↓Survival, ↑tumor burden | ||||||
| PANC-2-luc or ASPC-1 cells | TCA, CYM5520 | / | ↑Cell growth | ||||
| Inhibition of S1PR2 by JTE-013 | ↓Cell growth, migration, viability | ||||||
| Inhibition of all S1PRs except S1PR2 by FTY720 | ↑Cell viability | ||||||
| SPHKs | PC | PAN02 cells | / | Knockdown of Sphk1 | ↑Cell proliferation, migration | / | [27] |
| PAN02 cells | / | Knockdown of Sphk2 | ↓Cell proliferation, migration | ||||
| Male C57BL/6 mice | Sphk1 KO PAN02 cells | / | ↑Survival | ||||
| Male C57BL/6 mice | Sphk2 KO PAN02 cells | / | ↓Survival | ||||
| Sphingosine | PC | Male nude mice | PANC-1 or PANC-1 TRCs, orthotopic | / | Sphingosine significantly decreased in TRCs | / | [143] |
| SPHK2 | PC | Male C57BL/6 mice | PAN02 cells | Inhibition of SPHK2 by ABC294640 | ↓Tumor growth | / | [144] |
| S1P | PC | Capan-1 or PANC-1 cells | / | S1P, 0.5 and 1 μΜ; Inhibition Src by PP2 | ↓Cell proliferation, migration | / | [145] |
| SPHK1 | PC | BxPC-3 cells | / | Overexpression of Sphk1 | ↑Cell proliferation, migration | / | [146] |
| SPHK1 | PC | SWl990 cells | / | Inhibition of SPHK1 by DMS | ↓Cell proliferation, ↑Cell apoptosis | / | [147] |
| Activation of SPHK1 by phorbol 12-myristate13-acetate | ↑Cell proliferation, ↓Cell apoptosis | ||||||
| S1P/S1PRs | PC | PANC-1 cells | / | S1P, 20-200 nΜ; Inhibition of S1PRs by VPC23019 | ↓Cell migration, invasion | / | [79] |
| S1P | PC | Female athymic nude mice | PANC-2-SAL, TPAN1-IFA, metastatic | Inhibition of S1P Lyase by LX2931 | ↓Tumor volume, Hypoxia marker | S1P regulated tumor hypoxia and therapy efficacy in solid tumors | [149] |
| S1PR2 | PC | Nude mice | HPAF II tumor cells expressing S1PR2-GFP | / | ↓Tumor size and metastatic frequency | / | [150] |
| S1P | PC | PANC-1 or MIA PaCa-2 cells | / | S1P, 0-10 μΜ | ↓DNA synthesis | / | [151] |
| SPHK1 | PC | C57BL/6 mice | PANC-2-luc cells | Knockout of Sphk1 | ↓Tumor burden, cell proliferation | / | [148] |
| S1P | DDP | In vitro culture of pancreatic explants of mice embryos | Cdh2–/– (N-cadherin knockout) | S1P, 0.1 µM | ↑ Early morphogenesis of the dorsal pancreas, formation of the dorsal pancreatic bud, dorsal pancreatic mesenchymal cell proliferation, development of dorsal pancreatic endoderm, mesenchyme and endothelium | S1P stimulated mesenchymal cell proliferation | [29] |
| S1PR | DDP | C57BL6 mice embryos | / | Knockout of S1pr | ↓ Volume of the dorsal and ventral pancreata, proliferation of Pdx1+ progenitors | S1PR regulated proliferation rate of Pdx1+ progenitors, hypervascularization | [30] |
| ↑ Aberrant development of the pancreatic endoderm, vascular density of dorsal pancreas | |||||||
| S1PR2 | DDP | C57BL/6J mice embryos | / | Knockout of S1pr2 | ↓ Development of pancreas, survival and commitment of pancreas progenitors, endocrine and acinar differentiation | S1PR2 regulated Gαi-mediated YAP stabilization and Notch attenuation, then partially activated CTGF | [56] |
| ↑ Lpar1, S1PR3 in the epithelium |
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kimita, W.; Petrov, M.S. Iron metabolism and the exocrine pancreas. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2020, 511, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Melton, D.A. Pancreas regeneration. Nature 2018, 557, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struyvenberg, M.R.; Martin, C.R.; Freedman, S.D. Practical guide to exocrine pancreatic insufficiency - Breaking the myths. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.K.; Yadav, D.; Garg, P.K. Diagnosis and management of chronic pancreatitis: A review. JAMA 2019, 322, 2422–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.J.; Gao, C.F.; Wei, D.; Wang, C.; Ding, S.Q. Acute pancreatitis: etiology and common pathogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Peng, X.; Du, J.X.; Boohaker, R.; Estevao, I.L.; Grajeda, B.I.; Cox, M.B.; Almeida, I.C.; Lu, W. Oncogenic KRASG12D reprograms lipid metabolism by upregulating SLC25A1 to drive pancreatic tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 3739–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerle, J.; Sendler, M.; Hegyi, E.; Beyer, G.; Lerch, M.M.; Sahin-Tóth, M. Genetics, cell biology, and pathophysiology of pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1951–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.C.; Leung, P.S. Acute pancreatitis: Animal models and recent advances in basic research. Pancreas 2007, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtezion, A.; Gukovskaya, A.S.; Pandol, S.J. Acute pancreatitis: A multifaceted set of organelle and cellular interactions. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, A.Y.; Ditillo, M.; Castanon, L. Pancreatitis. Surg. Clin. North Am. 2018, 98, 895–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Jones, E.K.; Manohar, M.; Li, L.; Yadav, D.; Conwell, D.L.; Hart, P.A.; Vege, S.S.; Fogel, E.L.; Serrano, J. Distinct serum immune profiles define the spectrum of acute and chronic pancreatitis from the multicenter prospective evaluation of chronic pancreatitis for epidemiologic and translational studies (PROCEED) study. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Xue, J.; Jaffee, E.M.; Habtezion, A. Role of immune cells and immune-based therapies in pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1230–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnedl, W.J.; Piswanger-Soelkner, C.; Wallner, S.J.; Reittner, P.; Krause, R.; Lipp, R.W.; Hohmeier, H.E. Agenesis of the dorsal pancreas and associated diseases. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 481–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.D.; Maceyka, M.; Cowart, L.A.; Spiegel, S. Sphingolipids in metabolic disease: The good, the bad, and the unknown. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, G.; Cedeño, R.R.; Casadevall, M.P.; Ramió-Torrentà, L. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P) and S1P signaling pathway modulators, from current insights to future perspectives. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, E.; Farina, C. Lessons from S1P receptor targeting in multiple sclerosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 230, 107971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstockt, B.; Vetrano, S.; Salas, A.; Nayeri, S.; Duijvestein, M.; Vande Casteele, N. Sphingosine 1-phosphate modulation and immune cell trafficking in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeyens, A.; Bracero, S.; Chaluvadi, V.S.; Khodadadi-Jamayran, A.; Cammer, M.; Schwab, S.R. Monocyte-derived S1P in the lymph node regulates immune responses. Nature 2021, 592, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, G. S1P signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1223, 129–153. [Google Scholar]
- Stepanovska, B.; Huwiler, A. Targeting the S1P receptor signaling pathways as a promising approach for treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 154, 104170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartier, A.; Hla, T. Sphingosine 1-phosphate: Lipid signaling in pathology and therapy. Science 2019, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelson, K.; Evans, T.; Hla, T. Sphingosine 1-phosphate signalling. Development. 2014, 141, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konończuk, T.; Łukaszuk, B.; Mikłosz, A.; Chabowski, A.; Żendzian-Piotrowska, M.; Kurek, K. Cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis affects sphingomyelin signaling pathway in rats. Pancreas 2018, 47, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tang, X.; Li, B.; Shi, J. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2 mediated early stages of pancreatic and systemic inflammatory responses via NF-kappa B activation in acute pancreatitis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuza, K.; Nakajima, M.; Nagahashi, M.; Tsuchida, J.; Hirose, Y.; Miura, K.; Tajima, Y.; Abe, M.; Sakimura, K.; Takabe, K. Different roles of sphingosine kinase 1 and 2 in pancreatic cancer progression. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 232, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Ji, B.; Kang, N.; Yang, L.; Simonetto, D.A.; Kwon, J.H.; Kamath, M.; Cao, S.; Shah, V. Sphingosine-1-phosphate mediates a reciprocal signaling pathway between stellate cells and cancer cells that promotes pancreatic cancer growth. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 2791–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edsbagge, J.; Johansson, J.K.; Esni, F.; Luo, Y.; Radice, G.L.; Semb, H. Vascular function and sphingosine-1-phosphate regulate development of the dorsal pancreatic mesenchyme. Development. 2005, 132, 1085–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, F.W.; Hörnblad, A.; Johansson, J.K.; Lorén, C.; Edsbagge, J.; Ståhlberg, A.; Magenheim, J.; Ilovich, O.; Mishani, E.; Dor, Y. Growth-limiting role of endothelial cells in endoderm development. Dev. Biol. 2011, 352, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyrst, H.; Saba, J.D. An update on sphingosine-1-phosphate and other sphingolipid mediators. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, P.J.; Dunn, T.M.; Campopiano, D.J. Sphingolipid biosynthesis in man and microbes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 921–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jozefczuk, E.; Guzik, T.J.; Siedlinski, M. Significance of sphingosine-1-phosphate in cardiovascular physiology and pathology. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 156, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.H.; Yi, G.H. Regulation of metabolism and transport of sphingosine-1-phosphate in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2012, 363, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandhuvula, P.; Saba, J.D. Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase in immunity and cancer: Silencing the siren. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandala, S.M. Sphingosine-1-phosphate phosphatases. Prostaglandins. Other. Lipid. Mediat. 2001, 64, 143–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Książek, M.; Chacińska, M.; Chabowski, A.; Baranowski, M. Sources, metabolism, and regulation of circulating sphingosine-1-phosphate. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, A.; Nishi, T.; Hisano, Y.; Fukui, H.; Yamaguchi, A.; Mochizuki, N. The sphingolipid transporter spns2 functions in migration of zebrafish myocardial precursors. Science 2009, 323, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, S.; Maczis, M.A.; Maceyka, M.; Milstien, S. New insights into functions of the sphingosine-1-phosphate transporter SPNS2. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aye, I.L.; Singh, A.T.; Keelan, J.A. Transport of lipids by ABC proteins: interactions and implications for cellular toxicity, viability and function. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 180, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, T.M.; Pitson, S.M. Cellular signalling by sphingosine kinase and sphingosine 1-phosphate. IUBMB. Life 2006, 58, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitson, S.M.; Moretti, P.A.; Zebol, J.R.; Lynn, H.E.; Xia, P.; Vadas, M.A.; Wattenberg, B.W. Activation of sphingosine kinase 1 by ERK1/2-mediated phosphorylation. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5491–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitson, S.M.; Xia, P.; Leclercq, T.M.; Moretti, P.A.; Zebol, J.R.; Lynn, H.E.; Wattenberg, B.W.; Vadas, M.A. Phosphorylation-dependent translocation of sphingosine kinase to the plasma membrane drives its oncogenic signalling. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, N.; Okada, T.; Hayashi, S.; Fujita, T.; Jahangeer, S.; Nakamura, S. Sphingosine kinase 2 is a nuclear protein and inhibits DNA synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46832–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.; Maceyka, M.; Strub, G.M.; Harikumar, K.B.; Singh, S.K.; Luo, C.; Marmorstein, R.; Kordula, T.; Milstien, S. Regulation of histone acetylation in the nucleus by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Science 2009, 325, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceyka, M.; Sankala, H.; Hait, N.C.; Le Stunff, H.; Liu, H.; Toman, R.; Collier, C.; Zhang, M.; Satin, L.S.; Merrill, A.H., Jr. SphK1 and SphK2, sphingosine kinase isoenzymes with opposing functions in sphingolipid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37118–37129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strub, G.M.; Maceyka, M.; Hait, N.C.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Extracellular and intracellular actions of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 688, 141–155. [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. The outs and the ins of sphingosine-1-phosphate in immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, K.; Hla, T. Vascular and immunobiology of the circulatory sphingosine 1-phosphate gradient. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Y. Progress in regulation of vascular function by sphingosine-1-phosphate in atherosclerosis. Chinese Journal of Pathophysiology 2023, 39, 2288–2295. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, H.C.; Han, M.H. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) and S1P signaling pathway: Therapeutic targets in autoimmunity and inflammation. Drugs 2016, 76, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarthi, J.J.; Darendeliler, M.A.; Pushparaj, P.N. Dissecting the role of the S1P/S1PR axis in health and disease. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Liu, H.; Geng, M. Targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling for cancer therapy. Sci. China Life Sci. 2017, 60, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinley, M.P.; Cohen, J.A. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulators in multiple sclerosis and other conditions. Lancet 2021, 398, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, N.; Salmon, J.E.; Hla, T. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-targeted therapeutics in rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafimidis, I.; Rodriguez-Aznar, E.; Lesche, M.; Yoshioka, K.; Takuwa, Y.; Dahl, A.; Pan, D.; Gavalas, A. Pancreas lineage allocation and specification are regulated by sphingosine-1-phosphate signalling. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2000949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Peng, M.; Zhu, Q.; Pan, X. S1PR2 participates in intestinal injury in severe acute pancreatitis by regulating macrophage pyroptosis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1405622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, J.; Aoki, H.; Wu, R.; Aoki, M.; Hylemon, P.; Zhou, H.; Takabe, K. Conjugated bile acids accelerate progression of pancreatic cancer metastasis via S1PR2 signaling in cholestasis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 1630–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Han, S.; Lv, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhuo, W.; Zeng, Z.; Tang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, J. Pancreatic acinar cells-derived sphingosine-1-phosphate contributes to fibrosis of chronic pancreatitis via inducing autophagy and activation of pancreatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 1488–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukocheva, O.A.; Furuya, H.; Ng, M.L.; Friedemann, M.; Menschikowski, M.; Tarasov, V.V.; Chubarev, V.N.; Klochkov, S.G.; Neganova, M.E.; Mangoni, A.A. Sphingosine kinase and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling pathway in inflammatory gastrointestinal disease and cancers: A novel therapeutic target. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 207, 107464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C. The role of sphingosine kinase 1 in acute lung injury with severe acute pancreatitis. 2015, Southwest Medical University.
- Speirs, M.M.P.; Swensen, A.C.; Chan, T.Y.; Jones, P.M.; Holman, J.C.; Harris, M.B.; Maschek, J.A.; Cox, J.E.; Carson, R.H.; Hill, J.T. Imbalanced sphingolipid signaling is maintained as a core proponent of a cancerous phenotype in spite of metabolic pressure and epigenetic drift. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 449–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beljanski, V.; Lewis, C.S.; Smith, C.D. Antitumor activity of sphingosine kinase 2 inhibitor ABC294640 and sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseh, M.; Vatanparast, J.; Rafati, A.; Bayat, M.; Haghani, M. The emerging role of FTY720 as a sphingosine 1-phosphate analog for the treatment of ischemic stroke: The cellular and molecular mechanisms. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e02179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaho, V.A.; Hla, T. Regulation of mammalian physiology, development, and disease by the sphingosine 1-phosphate and lysophosphatidic acid receptors. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6299–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.A.; Belyaev, O.; Burr, W.; Munding, J.; McArthur, N.; Bergmann, U.; Werner, J.; Tannapfel, A.; Uhl, W. Effects of FTY720 and rapamycin on inflammation in taurocholate-induced acute pancreatitis in the rat. Pancreas 2012, 41, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Cui, N.Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.H.; Xue, X.P. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and its analogue FTY720 diminish acute pulmonary injury in rats with acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Pancreas 2008, 36, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Yamada, T.; Kuno, A.; Ogawa, K.; Tang, M.; Sano, H.; Ohara, H.; Nakao, H.; Kataoka, H.; Shirai, T. FTY720, an immunosuppressant, attenuates chronic pancreatitis in rats by suppressing T-cell infiltration. Pancreas. 2005, 30, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankadasari, M.B.; Aparna, J.S.; Mohammed, S.; James, S.; Aoki, K.; Binu, V.S.; Nair, S.; Harikumar, K.B. Targeting S1PR1/STAT3 loop abrogates desmoplasia and chemosensitizes pancreatic cancer to gemcitabine. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3824–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, H.W.; Tian, J.Y.; Wang, Z.K.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, T.T.; Ma, C.Y.; Feng, M.; Cao, S.F.; Zhao, Y. Myeloid-derived growth factor suppresses VSMC dedifferentiation and attenuates postinjury neointimal formation in rats by activating S1PR2 and its downstream signaling. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Yao, G.; Zhuo, Y.; Cui, N.; Zhang, S. S1P/S1PR2 promote pancreatic stellate cell activation and pancreatic fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis by regulating autophagy and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 380, 110541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wang, S. Sphingosine kinases are involved in the regulation of all-trans retinoic acid sensitivity of K562 chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Tang, X.; Li, T.; Chen, L.; He, H.; Wu, X.; Xiang, C.; Cao, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Therapeutic potential of the sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitor, PF-543. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzunova, V.; Tzoneva, R.; Stoyanova, T.; Pankov, R.; Skrobanska, R.; Georgiev, G.; Maslenkova, L.; Tsonchev, Z.; Momchilova, A. Dimethylsphingosine and miltefosine induce apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells in a synergistic manner. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 310, 108731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grbčić, P.; Tomljanović, I.; Klobučar, M.; Kraljević Pavelić, S.; Lučin, K.; Sedić, M. Dual sphingosine kinase inhibitor SKI-II enhances sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppression of osteopontin and FAK/IGF-1R signalling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Bai, A.; Smith, C.D.; Rodriguez, P.C.; Yu, F.; Qin, Z. ABC294640, A novel sphingosine kinase 2 inhibitor, induces oncogenic virus-infected cell autophagic death and represses tumor growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2724–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Remaley, A.T. HDL and sphingosine-1-phosphate activate stat3 in prostate cancer DU145 cells via ERK1/2 and S1P receptors, and promote cell migration and invasion. Prostate 2011, 71, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beljanski, V.; Knaak, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Smith, C.D. Combined anticancer effects of sphingosine kinase inhibitors and sorafenib. Invest. New Drugs 2011, 29, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Sui, S.; Meng, Q.; Liu, P.; Lin, H.; Xin, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, L. The influence of sphlngosine 1-phosphate on migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer PANC1 cells. Chin. J. Pancreatol. 2016, 16, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, R.; Tang, L.; Li, D.; Li, K. Sphingosine kinase 1 change in early stage for severe acute pancreatitis. Journal of Frontiers of Medicine. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhong, M.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yan, H.; Tang, L.; Li, D. Value of sphingosine kinase 1 and C-reactive protein in prediction of severity degree of acute pancreatitis. Medical Journal of Chinese People's Liberation Army. 2014, 26, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, C.; Li, N.; Li, J. The role of sphingosine kinase 1 in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Ann. Surg. 2012, 255, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J. Mechanism of sphingosine kinase 1 mediating acinar cell pyroptosis through PERK/TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling axis in acute pancreatitis. 2022, Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
- Yang, J.X.; Wang, M.J.C.; Qiu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Pu, Q.L.; Jiang, N.; Wang, R.; Wen, L.; Zhang, X.Y. Time-course lipidomics of ornithine-induced severe acute pancreatitis model reveals the free fatty acids centered lipids dysregulation characteristics. Metabolites 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollny, T.; Wątek, M.; Wnorowska, U.; Piktel, E.; Góźdź, S.; Kurek, K.; Wolak, P.; Król, G.; Żendzian-Piotrowska, M.; Bucki, R. Hypogelsolinemia and decrease in blood plasma sphingosine-1-phosphate in patients diagnosed with severe acute pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Lin, H.; Liu, B.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jin, J. Decreased S1P and SPHK2 are involved in pancreatic acinar cell injury. Biomark. Med. 2019, 13, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konończuk, T.; Łukaszuk, B.; Żendzian-Piotrowska, M.; Dąbrowski, A.; Krzyżak, M.; Ostrowska, L.; Kurek, K. Plasma sphingolipids in acute pancreatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtezion, A. Inflammation in acute and chronic pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 31, 395–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Wang, B.; Wu, X.; Cheng, J.; Ye, J.; Wang, C.; Zhu, H.; Liu, X. How do sphingosine-1-phosphate affect immune cells to resolve inflammation? Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1362459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, B.; Luz, S.; Sotuyo, N.; Pearson-Leary, J.; Moorthy, G.S.; Zuppa, A.F.; Bhatnagar, S. FTY720 (Fingolimod), a modulator of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors, increases baseline hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal axis activity and alters behaviors relevant to affect and anxiety. Physiol. Behav. 2021, 240, 113556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, D.A.; Riddy, D.M.; Stamp, C.; Bradley, M.E.; McGuiness, N.; Sattikar, A.; Guerini, D.; Rodrigues, I.; Glaenzel, A.; Dowling, M.R. Investigating the molecular mechanisms through which FTY720-P causes persistent S1P1 receptor internalization. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 4797–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, P.; Zhang, L.; Kayoumu, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Gao, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G. FTY720 attenuates acute pancreatitis in hypertriglyceridemic apolipoprotein CIII transgenic mice. Shock 2015, 44, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Ke, L.; Wu, C.; Tong, Z.; Li, W.; Li, N.; Li, J. SEW2871 Alleviates the severity of caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, P.S.; Ip, S.P. Pancreatic acinar cell: its role in acute pancreatitis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Chen, Z.; Chi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, B. Endogenous tRNA-derived small RNA (tRF3-Thr-AGT) inhibits ZBP1/NLRP3 pathway-mediated cell pyroptosis to attenuate acute pancreatitis (AP). J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 10441–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Song, J.; Pan, X.; Wan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lv, S.; Mi, L.; Wang, Y.; Tian, F. Downregulating gasdermin D reduces severe acute pancreatitis associated with pyroptosis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e927968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Dong, X.; Gong, W.; Huang, W.; Xue, J.; Zhu, Q.; Ma, N.; Chen, W.; Fu, X.; Gao, X. Acinar cell NLRP3 inflammasome and gasdermin D (GSDMD) activation mediates pyroptosis and systemic inflammation in acute pancreatitis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 3533–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.; Luo, Y.; Okoye, C.S.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Xu, C.; Chen, H. Intestinal barrier damage, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, and acute lung injury: A troublesome trio for acute pancreatitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Fan, Z. Signal pathways and markers involved in acute lung injury induced by acute pancreatitis. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 9947047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X; Liu, H; Cui, N; Li, D; Li, J; Wang, Q. The protective effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate on lung injury in acute necrotizing pancreatitis in rats. The Chinese Journal of General Surgery. 2008, 17, 7–232. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, V.; Dudek, S.M.; Jacobson, J.R.; Moreno-Vinasco, L.; Huang, L.S.; Abassi, T.; Mathew, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Bittman, R. Sphingosine-1-phosphate, FTY720, and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors in the pathobiology of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Luo, Y.; Ge, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, H.; Yang, Q.; Ma, S.; Chen, H. The gut-lung axis in severe acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury: The protection by the gut microbiota through short-chain fatty acids. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichler, A.; Jang, S. Chronic pancreatitis: Epidemiology, diagnosis, and management updates. Drugs 2020, 80, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, M.; Pirola, R.; Wilson, J. The fibrosis of chronic pancreatitis: new insights into the role of pancreatic stellate cells. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 2711–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobel, K.; Menyhart, K.; Killer, N.; Renault, B.; Bauer, Y.; Studer, R.; Steiner, B.; Bolli, M.H.; Nayler, O.; Gatfield, J. Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor agonists mediate pro-fibrotic responses in normal human lung fibroblasts via S1P2 and S1P3 receptors and Smad-independent signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 14839–14851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yue, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L. Sphingosine kinase/sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P)/S1P receptor axis is involved in liver fibrosis-associated angiogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ritter, J.K.; Li, N. Sphingosine-1-phosphate pathway in renal fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2018, 315, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; He, X.; Zeng, M. The role of S1P and the related signaling pathway in the development of tissue fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1504. [Google Scholar]
- Furuya, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Kawamori, T. Sphingolipids in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011, 30, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fan, F.; Yang, W. Sphingosine kinase 1 and sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. Functions of the multifaceted family of sphingosine kinases and some close relatives. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 2125–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, B.M.; Shanmugavelandy, S.S.; Kaiser, J.M.; McGovern, C.; Altınoğlu, E.; Haakenson, J.K.; Hengst, J.A.; Gilius, E.L.; Knupp, S.A.; Fox, T.E. PhotoImmunoNanoTherapy reveals an anticancer role for sphingosine kinase 2 and dihydrosphingosine-1-phosphate. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2132–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Adnane, L.; Newell, P.; Villanueva, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Lynch, M. Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 3129–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillermet-Guibert, J.; Davenne, L.; Pchejetski, D.; Saint-Laurent, N.; Brizuela, L.; Guilbeau-Frugier, C.; Delisle, M.B.; Cuvillier, O.; Susini, C.; Bousquet, C. Targeting the sphingolipid metabolism to defeat pancreatic cancer cell resistance to the chemotherapeutic gemcitabine drug. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Ricciardiello, F.; Yang, G.; Qiu, J.; Huang, H.; Xiao, J.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Luo, W. The role of mitochondria in the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer cells. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhard, M.C.; Schmid, R.M.; Häcker, G. Analysis of the cytochrome c-dependent apoptosis apparatus in cells from human pancreatic carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cao, Z.; Yan, H.; Wood, W.C. Coexistence of high levels of apoptotic signaling and inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in human tumor cells: implication for cancer specific therapy. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6815–6824. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, S.; Bankier, A.T.; Barrell, B.G.; de Bruijn, M.H.; Coulson, A.R.; Drouin, J.; Eperon, I.C.; Nierlich, D.P.; Roe, B.A.; Sanger, F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 1981, 290, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Meng, Q.; Lu, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Hao, J. Mitofusin2 induces cell autophagy of pancreatic cancer through inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2798070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Cowart, L.A. Sphingolipids in mitochondria-from function to disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1302472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Gao, P.; Chen, S.X.; Novák, P.; Yin, K.; Zhu, X. Sphingosine-1-phosphate in mitochondrial function and metabolic diseases. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leanza, L.; Henry, B.; Sassi, N.; Zoratti, M.; Chandy, K.G.; Gulbins, E.; Szabò, I. Inhibitors of mitochondrial Kv1.3 channels induce Bax/Bak-independent death of cancer cells. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leanza, L.; Romio, M.; Becker, K.A.; Azzolini, M.; Trentin, L.; Managò, A.; Venturini, E.; Zaccagnino, A.; Mattarei, A.; Carraretto, L. Direct pharmacological targeting of a mitochondrial ion channel selectively kills tumor cells in vivo. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 516–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.H.; Wilson, G.C.; Wu, Y.; Keitsch, S.; Wilker, B.; Mattarei, A.; Ahmad, S.A.; Szabo, I.; Gulbins, E. Sphingosine is involved in PAPTP-induced death of pancreas cancer cells by interfering with mitochondrial functions. J. Mol. Med. (Berl). 2024, 102, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbu, K.R.; Chhetri, R.B.; Oh, Y.S.; Baek, D.J.; Park, E.Y. Mebendazole impedes the proliferation and migration of pancreatic cancer cells through SK1 inhibition dependent pathway. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lépine, S.; Allegood, J.C.; Park, M.; Dent, P.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate phosphohydrolase-1 regulates ER stress-induced autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 350–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Ikushiro, H.; Seo, H.S.; Shin, K.O.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, Y.M.; Yano, T.; Holleran, W.M.; Elias, P. ER stress stimulates production of the key antimicrobial peptide, cathelicidin, by forming a previously unidentified intracellular S1P signaling complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2016, 113, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, T.; Bergelin, N.; Meinander, A.; Löf, C.; Slotte, J.P.; Eriksson, J.E.; Törnquist, K. An autocrine sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling loop enhances NF-kappaB-activation and survival. BMC Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hong, I.K.; Kim, B.R.; Shim, S.M.; Sung Lee, J.; Lee, H.Y.; Soo Choi, C.; Kim, B.K.; Park, T.S. Activation of sphingosine kinase 2 by endoplasmic reticulum stress ameliorates hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in mice. Hepatology 2015, 62, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Janakiraman, H.; Xiao, Y.; Kang, S.W.; Dong, J.; Choi, J.; Ogretmen, B.; Lee, H.S.; Camp, E.R. Sphingosine-1-phosphate inhibition increases endoplasmic reticulum stress to enhance oxaliplatin sensitivity in pancreatic cancer. World J. Oncol. 2024, 15, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, S.; Zhou, W. Pancreatic stellate cells: Key players in pancreatic health and diseases (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2024, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, M.V.; Wilson, J.S.; Lugea, A.; Pandol, S.J. A starring role for stellate cells in the pancreatic cancer microenvironment. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Masamune, A.; Hamada, S.; Kikuta, K.; Takikawa, T.; Motoi, F.; Unno, M.; Shimosegawa, T. Kindlin-2 in pancreatic stellate cells promotes the progression of pancreatic cancer. Cancer. Lett. 2017, 390, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothula, S.P.; Pirola, R.C.; Wilson, J.S.; Apte, M.V. Pancreatic stellate cells: Aiding and abetting pancreatic cancer progression. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Xue, S.; Shentu, D.; Mao, T.; Li, S.; Yue, M.; Cui, J. The role of bile acids in pancreatic cancer. Curr. Cancer. Drug. Targets. 2024, 24, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gál, E.; Veréb, Z.; Kemény, L.; Rakk, D.; Szekeres, A.; Becskeházi, E.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Takács, T.; Czakó, L.; Hegyi, P. Bile accelerates carcinogenic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells through the overexpression of MUC4. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Režen, T.; Rozman, D.; Kovács, T.; Kovács, P.; Sipos, A.; Bai, P.; Mikó, E. The role of bile acids in carcinogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Role of bile acids in carcinogenesis of pancreatic cancer: An old topic with new perspective. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7463–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagathihalli, N.S.; Beesetty, Y.; Lee, W.; Washington, M.K.; Chen, X.; Lockhart, A.C.; Merchant, N.B. Novel mechanistic insights into ectodomain shedding of EGFR Ligands Amphiregulin and TGF-α: Impact on gastrointestinal cancers driven by secondary bile acids. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2062–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, X.; Liang, X.; Campbell, D.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Shi, R.; Wang, G.; Pandak, W.M. Conjugated bile acids promote cholangiocarcinoma cell invasive growth through activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2. Hepatology 2014, 60, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahashi, M.; Takabe, K.; Liu, R.; Peng, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Hait, N.C.; Wang, X.; Allegood, J.C.; Yamada, A. Conjugated bile acid-activated S1P receptor 2 is a key regulator of sphingosine kinase 2 and hepatic gene expression. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yuan, H.; Gu, J.; Xu, D.; Wang, M.; Qiao, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yao, M.; Gu, J. ABCA8-mediated efflux of taurocholic acid contributes to gemcitabine insensitivity in human pancreatic cancer via the S1PR2-ERK pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, L.; Du, X.; Qi, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Cao, X.; Xia, J. Transcriptome and lipidomic analysis suggests lipid metabolism reprogramming and upregulating SPHK1 promotes stemness in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma stem-like cells. Metabolites 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maines, L.W.; Schrecengost, R.S.; Zhuang, Y.; Keller, S.N.; Smith, R.A.; Green, C.L.; Smith, C.D. Opaganib protects against radiation toxicity: Implications for homeland security and antitumor radiotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.X.; Ma, Y.J.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Han, J.A.; Zhu, Y. Role of sphingosine 1-phosphate in human pancreatic cancer cells proliferation and migration. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 20349–20354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Clinical significanceof SPHK1 genein pancreatic adenocarcinoma and its effect on proliferation and migration of pancreatic cancer cells. Acta Medicinae Universitatis Scientiae et Technologiae Huazhong. 2021, 50, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, D.; Su, Y.; Tang, J. Department effect of sphingosine kinase 1 on the proliferation and apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cell line SW1990. Hainan Medical Journal. 2017, 28, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, H.; Aoki, M.; Katsuta, E.; Ramanathan, R.; Idowu, M.O.; Spiegel, S.; Takabe, K. Host sphingosine kinase 1 worsens pancreatic cancer peritoneal carcinomatosis. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 205, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, M.; Ives, A.; Auclair, C. Is Sphingosine-1-phosphate a regulator of tumor vascular functionality? Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Shea, J.; Slattum, G.; Firpo, M.A.; Alexander, M.; Mulvihill, S.J.; Golubovskaya, V.M.; Rosenblatt, J. Defective apical extrusion signaling contributes to aggressive tumor hallmarks. eLife 2015, 4, e04069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Okajima, F.; Ohwada, S.; Kondo, Y. Growth inhibition of human pancreatic cancer cells by sphingosylphosphorylcholine and influence of culture conditions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1997, 53, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Kanematsu, T. Annular pancreas causing localized recurrent pancreatitis in a child: Report of a case. Surg. Today 2008, 38, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutta, A.; Fogel, E.; Sherman, S. Identification and management of pancreas divisum. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019, 13, 1089–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakal, B.; Pant, S.; Choudhary, S.; Basnet, B.; Neupane, S. Dorsal pancreatic agenesis: A case report. Ann. Med. Surg. (Lond). 2023, 85, 2949–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfmann, R. Control of early development of the pancreas in rodents and humans: implications of signals from the mesenchyme. Diabetologia 2000, 43, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.W.; Inagaki, Y.; Hwang, Y.A.; Mitsutake, S.; Ryu, Y.W.; Lee, W.K.; Ha, H.J.; Park, C.S.; Igarashi, Y. Synthesis and evaluation of sphingoid analogs as inhibitors of sphingosine kinases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 3475–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoon, J.W.; White, M.D.; Burow, M.E.; Beckman, B.S. Dual inhibition of sphingosine kinase isoforms ablates TNF-induced drug resistance. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1779–86. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Qiao, J.; Mu, B.; Zuo, B.; Yuan, J. 3-(2-amino-ethyl)-5-[3-(4-butoxyl-phenyl)-propylidene]-thiazolidine-2,4-dione (K145) ameliorated dexamethasone induced hepatic gluconeogenesis through activation of Akt/FoxO1 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Vermeire, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Dubinsky, M.C.; Panes, J.; Yarur, A.; Ritter, T.; Baert, F.; Schreiber, S.; Sloan, S. Etrasimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis (ELEVATE): two randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies. Lancet 2023, 401, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, A.; Takeuchi, H.; Komiya, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Kubota, S.; Hashiguchi, S.; Takahashi, K.; Kunii, M.; Tanaka, K. Anti-inflammatory effects of siponimod on astrocytes. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 184, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Feagan, B.G.; Wolf, D.C.; D'Haens, G.; Vermeire, S.; Hanauer, S.B.; Ghosh, S.; Smith, H.; Cravets, M.; Frohna, P.A. Ozanimod induction and maintenance treatment for ulcerative colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mork, B.E.; Lamerand, S.R.; Zhou, S.; Taylor, B.K.; Sheets, P.L. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 agonist SEW2871 alters membrane properties of late-firing somatostatin expressing neurons in the central lateral amygdala. Neuropharmacology 2022, 203, 108885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Ponesimod: First approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafizi, R.; Imeri, F.; Stepanovska Tanturovska, B.; Manaila, R.; Schwalm, S.; Trautmann, S.; Wenger, R.H.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Huwiler, A. Sphk1 and Sphk2 differentially regulate erythropoietin synthesis in mouse renal interstitial fibroblast-like cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradiso, E.; Lazzaretti, C.; Sperduti, S.; Antoniani, F.; Fornari, G.; Brigante, G.; Di Rocco, G.; Tagliavini, S.; Trenti, T.; Morini, D. Sphingosine-1 phosphate induces cAMP/PKA-independent phosphorylation of the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) in granulosa cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 520, 111082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cencetti, F.; Bernacchioni, C.; Tonelli, F.; Roberts, E.; Donati, C.; Bruni, P. TGFβ1 evokes myoblast apoptotic response via a novel signaling pathway involving S1P4 transactivation upstream of Rho-kinase-2 activation. Faseb. J. 2013, 27, 4532–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pardo, A.; Castaldo, S.; Amico, E.; Pepe, G.; Marracino, F.; Capocci, L.; Giovannelli, A.; Madonna, M.; van Bergeijk, J.; Buttari, F. Stimulation of S1PR5 with A-971432, a selective agonist, preserves blood-brain barrier integrity and exerts therapeutic effect in an animal model of Huntington's disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 2490–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





