Introduction
Pediatric bronchoscopy is a crucial diagnostic and therapeutic procedure widely employed to assess and manage respiratory conditions in children. Despite its utility, bronchoscopy is often associated with postoperative complications, including laryngeal edema, hypoxemia, and respiratory distress, which can significantly affect patient recovery [
1,
2]. If not properly managed, these complications may lead to prolonged hospital stays and increased healthcare costs, making postoperative care critical in pediatric bronchoscopy management [
3]. Nursing interventions, including continuous monitoring of oxygen saturation, airway management, and sedation protocols, play an essential role in mitigating postoperative complications [
4,
5]. Previous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of these interventions in reducing morbidity and improving outcomes in various clinical settings [
6]. However, evidence regarding the efficacy of specific nursing interventions in pediatric bronchoscopy remains both limited and inconsistent [
7].
Given the importance of nursing care in postoperative management and the variability of findings in the existing literature, there is a clear need for a comprehensive synthesis of evidence to guide clinical practice. A meta-analysis can provide robust insights into the overall effectiveness of nursing interventions by pooling data from multiple studies, thereby offering more reliable conclusions [
8]. Moreover, understanding the extent to which nursing interventions reduce postoperative complications can inform the development of standardized care protocols, ultimately improving patient outcomes in pediatric bronchoscopy. This study aims to conduct a meta-analysis to evaluate the impact of nursing interventions on the incidence of postoperative complications following pediatric bronchoscopy. By analyzing the available evidence, we seek to clarify the role of nursing interventions in minimizing adverse outcomes and providing recommendations for integrating these interventions into clinical practice [
9,
10].
1. Literature Search
A systematic literature search was conducted in the PubMed, CNKI, JSTOR, and Arxiv databases to identify studies published between January 2018 and July 2023. The search strategy combined the following terms and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH): "bronchoscopy," "nursing interventions," "postoperative complications," and "pediatric" [
1,
3]. The specific search formulas used were as follows:
Similar keyword combinations were applied in the JSTOR and Arxiv databases. Additionally, manual searches of the reference lists from the included articles were performed to identify any relevant studies that may have been missed in the initial search. No language restrictions were applied. Studies were eligible if they investigated the effect of nursing interventions on postoperative complications following pediatric bronchoscopy.
2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Inclusion criteria:
Study design: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs), retrospective studies, and cohort studies that evaluated the effectiveness of nursing interventions in reducing postoperative complications following pediatric bronchoscopy.
Participants: Pediatric patients (<18 years) who underwent bronchoscopy and received postoperative nursing interventions.
Outcomes: Studies reporting the incidence of postoperative complications, such as laryngeal edema, hypoxemia, and respiratory distress [
4,
5].
3. Data Extraction
Data were extracted independently by two reviewers using a predefined extraction form. Disagreements were resolved through discussion or by consulting a third reviewer. The extracted data included the following:
Study characteristics: Author, publication year, study design, sample size, and interventions used.
Outcomes: Incidence of postoperative complications (e.g., laryngeal edema, hypoxemia, respiratory distress) in both the intervention and control groups.
Statistical information: Effect sizes (Odds Ratios [OR]) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) [
8].
4. Statistical Analysis
A meta-analysis was performed using the random-effects model to account for potential heterogeneity among studies. The primary outcome was the pooled odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI), which assessed the impact of nursing interventions on the incidence of postoperative complications [
9]. Heterogeneity was quantified using the I² statistic, with values of 25%, 50%, and 75% indicating low, moderate, and high heterogeneity, respectively. The significance of heterogeneity was further assessed using the Q test, where a p-value of <0.05 indicated significant heterogeneity [
10].
To evaluate publication bias, funnel plots were generated, and Egger’s regression test was performed. A p-value of <0.05 in Egger’s test was considered indicative of significant publication bias [
7,
9]. Additionally, a trim-and-fill method was applied to adjust for potential biases.
5. Ethics Statement
This study was based solely on previously published data and did not involve direct human participants; therefore, no ethical approval was required [
1,
3].
1. Study Selection and Characteristics
A total of eight studies, comprising 661 pediatric patients, were included in this meta-analysis [
1,
2]. The studies, published between 2018 and 2023, had sample sizes ranging from 20 to 120 patients. All studies evaluated the impact of nursing interventions on postoperative complications following pediatric bronchoscopy, with primary outcomes including laryngeal edema, hypoxemia, and respiratory distress [
3,
4]. Study characteristics are summarized in
Table 1.
2. Meta-Analysis of Postoperative Complications
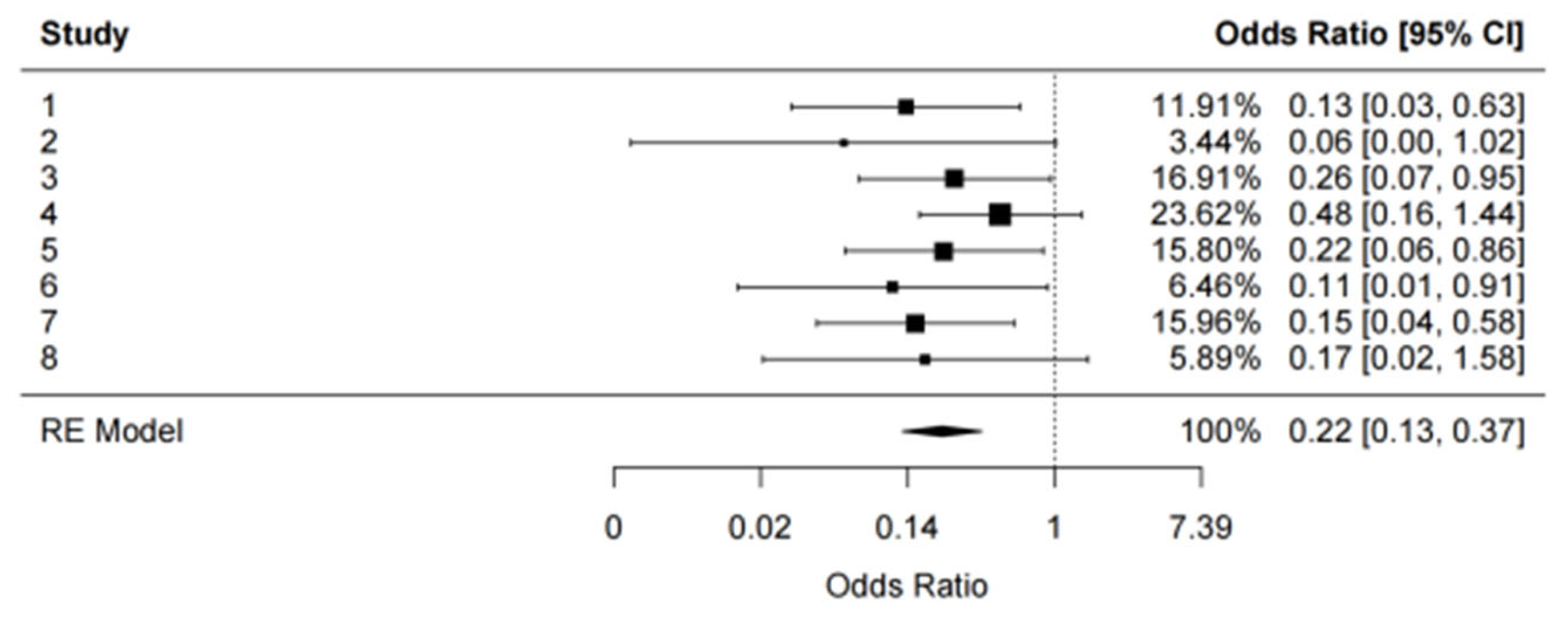
The pooled analysis revealed a significant reduction in the incidence of postoperative complications in the nursing intervention group compared to the control group. The random-effects model yielded a pooled odds ratio (OR) of 0.22 (95% CI: 0.13, 0.37; p < 0.0001), indicating that nursing interventions were associated with a 78% reduction in the risk of postoperative complications [
1,
4,
6]. The analysis demonstrated strong statistical significance (z = -5.58, p < 0.0001), underscoring the robustness of the effect (
Figure 1).
3. Heterogeneity Assessment
Heterogeneity among the included studies was low, with an I² value of 0%, suggesting that the results were consistent across the included studies [
7]. The Q test yielded a non-significant p-value (Q = 3.98, p = 0.7825), further supporting the low heterogeneity across the studies. The low I² and Q test results indicate that the variability in effect sizes was due to chance rather than systematic differences across the studies [
8].
4. Publication Bias
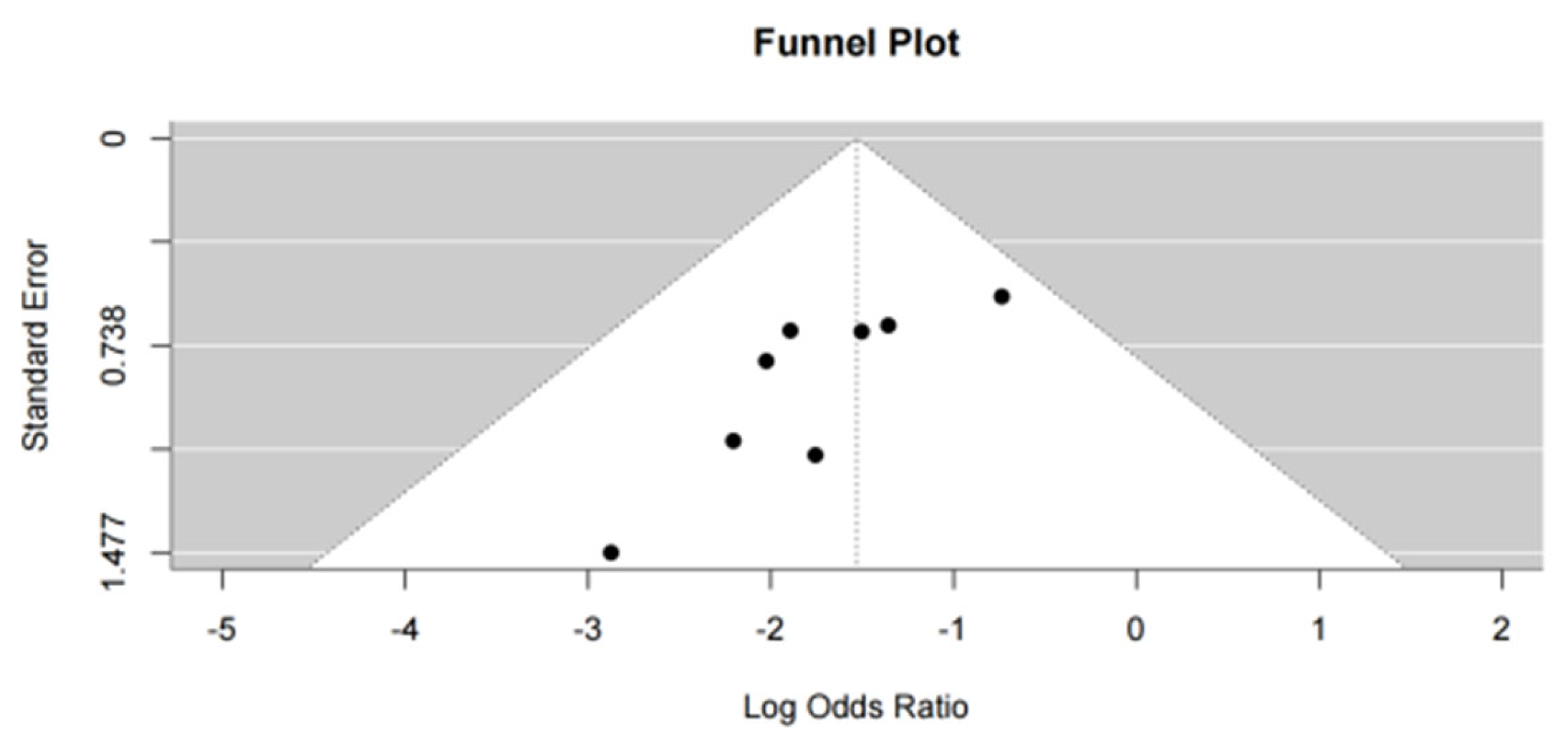
A funnel plot was generated to assess publication bias, and slight asymmetry was observed, raising potential concerns about publication bias (
Figure 2). However, Egger’s test showed no significant evidence of publication bias (p = 0.1213), suggesting that the observed effect was unlikely to be influenced by unpublished studies with null or negative results [
7,
9]. Additionally, a trim-and-fill analysis was performed, which did not alter the overall pooled estimate, confirming the robustness of the findings despite the slight asymmetry in the funnel plot [
9].
5. Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analyses were conducted by excluding one study at a time to assess the impact of individual studies on the overall pooled results. The pooled OR remained stable across all sensitivity analyses, with no single study exerting a disproportionate influence on the effect size. These results further confirm the reliability and robustness of the overall findings [
9,
10].
1. Clinical Implications
Nursing interventions, including close monitoring of oxygen saturation, appropriate airway management, and postoperative sedation protocols, play a critical role in preventing complications such as laryngeal edema, hypoxemia, and respiratory distress following pediatric bronchoscopy [
1,
2]. The significant reduction in postoperative complications observed in this analysis highlights the importance of tailored nursing care in the postoperative management of pediatric patients. Given that the majority of included studies focused on fundamental nursing care, the results suggest that even basic interventions can provide substantial benefits, reinforcing the need for these measures to be integrated into standard clinical practice [
3].
2. Comparison with Existing Literature
The results of this meta-analysis align with previous findings in adult populations, where nursing interventions have been demonstrated to reduce postoperative morbidity [
5]. However, there is limited evidence specifically addressing pediatric patients, particularly in bronchoscopy-related settings. This study fills that gap by providing comprehensive evidence of the efficacy of nursing interventions in the pediatric population. In contrast to earlier studies that reported conflicting results regarding the effectiveness of nursing interventions [
2,
3], the consistent findings across the included studies in this meta-analysis highlight the robustness of the intervention effects in pediatric care.
3. Heterogeneity and Study Consistency
One of the strengths of this meta-analysis is the low level of heterogeneity (I² = 0%), which indicates that the effect of nursing interventions on postoperative complications was consistent across the included studies. This consistency may be attributed to the similarity in patient populations, intervention types, and outcome measures used in the included studies. The lack of substantial variation across studies reinforces the reliability of the pooled estimate, suggesting that nursing interventions can be effectively applied in different clinical settings without considerable variation in outcomes [
6].
4. Publication Bias and Sensitivity Analysis
Although the funnel plot displayed slight asymmetry, indicating potential publication bias, Egger’s test (p = 0.1213) did not reveal significant evidence of bias [
7]. This suggests that the observed effect is unlikely to be influenced by unpublished studies with negative or null results. Furthermore, the results of the trim-and-fill analysis showed no change in the pooled OR, confirming the robustness of the findings despite the potential for slight bias [
8]. Sensitivity analyses also demonstrated that excluding individual studies did not significantly alter the overall effect size, further confirming the stability of the results [
9].
5. Limitations
Despite the strengths of this meta-analysis, several limitations need to be considered. First, the included studies were predominantly observational in nature, with only a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Although the quality of the included studies was assessed, potential residual bias cannot be entirely excluded [
10]. Second, the sample sizes of some studies were relatively small, potentially limiting the generalizability of the findings [
4]. Finally, despite the low heterogeneity, the types of nursing interventions varied slightly across studies, potentially affecting the uniformity of the intervention effects [
7].
6. Future Directions
Future research should prioritize conducting larger, high-quality RCTs to further validate the impact of specific nursing interventions on postoperative complications following pediatric bronchoscopy [
6]. Additionally, exploring the cost-effectiveness of these interventions across various healthcare settings could provide valuable insights into their broader implementation [
9]. Tailoring nursing care to specific risk factors, such as patient comorbidities and procedural complexity, may also enhance postoperative outcomes [
10].
7. Conclusions
In conclusion, this meta-analysis provides robust evidence indicating that nursing interventions significantly reduce the incidence of postoperative complications following pediatric bronchoscopy. The results suggest that integrating these interventions into routine clinical practice can substantially improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden of postoperative morbidity. Given the consistency of the findings, healthcare providers should consider adopting these strategies as part of standardized postoperative care protocols for pediatric patients undergoing bronchoscopy [
1,
3,
5].
This meta-analysis demonstrates that nursing interventions significantly reduce the incidence of postoperative complications in pediatric patients following bronchoscopy. The pooled analysis revealed that nursing interventions were associated with a 78% reduction in the risk of postoperative complications, with a pooled odds ratio (OR) of 0.22 (95% CI: 0.13, 0.37; p < 0.0001). Furthermore, the consistency of results across studies, indicated by low heterogeneity (I² = 0%), reinforces the robustness of these effects across various clinical settings [
1,
2,
6].
The findings emphasize the critical role of tailored nursing care, particularly in mitigating common complications such as laryngeal edema and hypoxemia, which are prevalent in pediatric patients undergoing bronchoscopy [
4,
5]. The minimal heterogeneity across studies suggests that these interventions can be effectively implemented in diverse clinical environments, yielding consistent positive outcomes [
6,
7]. Although publication bias was minimal based on Egger’s test (p = 0.1213), further research is warranted to validate these findings through larger, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) [
9]. Additionally, future studies should focus on exploring the cost-effectiveness and long-term impacts of specific nursing interventions in pediatric bronchoscopy [
9,
10].
In conclusion, integrating structured nursing interventions into postoperative care protocols for pediatric bronchoscopy is strongly recommended. These interventions not only reduce the risk of postoperative complications but also improve overall patient outcomes, reinforcing the need for their widespread adoption in clinical practice [
3,
5,
7].
References
- Huang QR, Wang ZT, Lin XL, Jian JL. Application value of time-sensitive care nursing model in pediatric bronchoscopy. *Jilin Med J*. 2023;44(5):1411-1415.
- Ning WY. Evaluation of risk factors and nursing interventions for adverse events in pediatric bronchoscopy. *Med Theory Pract*. 2021;34(6):1045-1047.
- Liu WJ, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Gu AJ, Yu DW. Risk factors and nursing strategies for adverse events in pediatric bronchoscopy. *Guide Health Care*. 2018;(46):190.
- Wang H, Fei Y, Li J. Application of body language communication combined with interest-induced nursing intervention in the removal of airway foreign bodies in children under painless bronchoscopy. *J Qilu Nurs*. 2023;29(6):92-95.
- Liu DM, Zhou YJ. Nursing intervention for children with refractory Mycoplasma pneumonia treated with fiberoptic bronchoscopy. *Health Must-Read Mag*. 2020;(30):130.
- Chang Q, Wang YQ, Pu Q. Application of enhanced nursing interventions during the perioperative period of pediatric bronchoscopic foreign body removal. *Psychologist*. 2018;24(19):241-243.
- Li QM, Luo L, Zhou YP, Tang Y, Zhang K. Application effect of clinical nursing pathway in the perioperative period of pediatric patients undergoing fiberoptic bronchoscopy. *Anhui Med J*. 2020;41(5):591-593.
- Luo L. Nursing methods and effects of bronchoalveolar lavage with fiberoptic bronchoscopy in children with refractory lung infections. *Fam Med*. 2018;(2):207.
- Fan WJ. Application of standardized nursing intervention in the diagnosis and treatment of tracheobronchial foreign bodies in children using fiberoptic bronchoscopy. *Med Theory Pract*. 2020;33(13):2215-2216.
- Song J, Zhou YQ. Research progress in preventive measures for postoperative complications in children with severe pneumonia undergoing fiberoptic bronchoscopy. *Contemp Nurse*. 2021;28(4):31-34.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).