1. Introduction
Cholesterol is a fundamental lipidic metabolite in the human body and a crucial component of all cell membranes. It plays a key role in maintaining cell membrane structure, function and dynamics through its general effects on membrane proteins, thus supporting various essential biological processes [
1,
2,
3]. However, excessive accumulation of circulating cholesterol in the blood, where it is bound to lipoproteins, and the dysregulation of its homeostasis are associated with metabolic disorders and inflammatory activation of immune cells, contributing to cardiovascular diseases (CVD), neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory disorders such as Parkinson and Alzheimer’s disease [
4,
5,
6]. Abnormal cholesterol levels outside the normal range of 3.23–5.17 mM (125–200 mg/dL) in humans have been identified as a risk factor for cancer, atherosclerosis and CVD, among other illnesses [
7,
8,
9]. Therefore, the development of sensitive, accurate and time-saving cholesterol biosensors is essential for monitoring cholesterol levels and enabling early disease diagnosis in clinical and medical applications.
Detection of small molecules such as cholesterol is challenging because of the inherent complexity involved in conventional sandwich assays utilizing antibody pairs [
10]. Over the years, advances in biotechnology and nanotechnology have led to the design of a plethora of cholesterol biosensors mainly based on its enzymatic detection by cholesterol oxidase (ChOx) or host-guest complex with β-cyclodextrin resulting in colorimetric, fluorescent or electrochemical devices [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. Optical imaging methods such as plasmonic-based sensing, have currently garnering attention, as they show significant advantages over conventional analytical methods, like enhanced sensitivity and specificity, higher signal-to-noise ratio and the possibility of direct testing, overcoming the necessity of component or sample pretreatments and complicated and time-consuming procedures [
19,
20,
21,
22]. In this regard, optical biosensing is conducted by the transduction of the optical signal generated when the ideal biomolecular interaction bioreceptor-analyte takes place [
23].
Moreover, gold nanoparticles (GNPs) have been recognized as promising scaffolds in plasmon resonance platforms for the highly sensitive and selective detection of small molecules, biological targets and molecular diagnosis [
24,
25,
26,
27]. GNPs exhibit distinctive physicochemical characteristics, including easily tunable surface chemistry due to their high surface-to-volume ratio, biocompatibility, and unique optoelectronic properties [
27,
28,
29,
30,
31]. The potential application of GNPs is based on their ability to function as highly sensitive and selective transducers for the binding events between analytes and recognition elements, leveraging their localized surface plasmon resonance (SPR) properties, making them reliable sensors [
32]. The plasmon resonance phenomenon involves the excitation of surface electrons in a metal when irradiated with incident light at a specific wavelength, resulting in the collective coherent oscillation of the electronic charge. This process generates localized plasmon resonance, electromagnetic waves, and intense light scattering of the absorbed light [
33,
34,
35,
36,
37].
Peptide-based biosensors have recently emerged as promising biorecognition elements due to their exceptional stability, chemical versatility, tunability, structural diversity, and high affinity for proteins [
38]. For instance, specific peptide sequences exhibit higher affinity towards target analytes with enhanced conformational and chemical stability compared to proteins, thereby facilitating the development of sensitive biosensors for the recognition of biological targets or small molecules [
39,
40]. As previously mentioned, cholesterol modulates the activity of several membrane proteins through its interaction with the transmembrane domain of these proteins [
1,
41]. Consequently, in the context of lipid-protein interaction mechanisms, significant attention has been directed towards the cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid consensus (CRAC) motif, as putative peptide sequences containing this motif are predicted to bind cholesterol within cellular membranes [
42,
43,
44].
The integration of the superb properties of small peptides and GNPs within a single system thus provides an opportunity to achieve sensitive single-molecule plasmonic biosensing, addressing the limitations of current optical and colorimetric sensors for the detection of low-molecular-weight molecules [
40,
45,
46,
47].
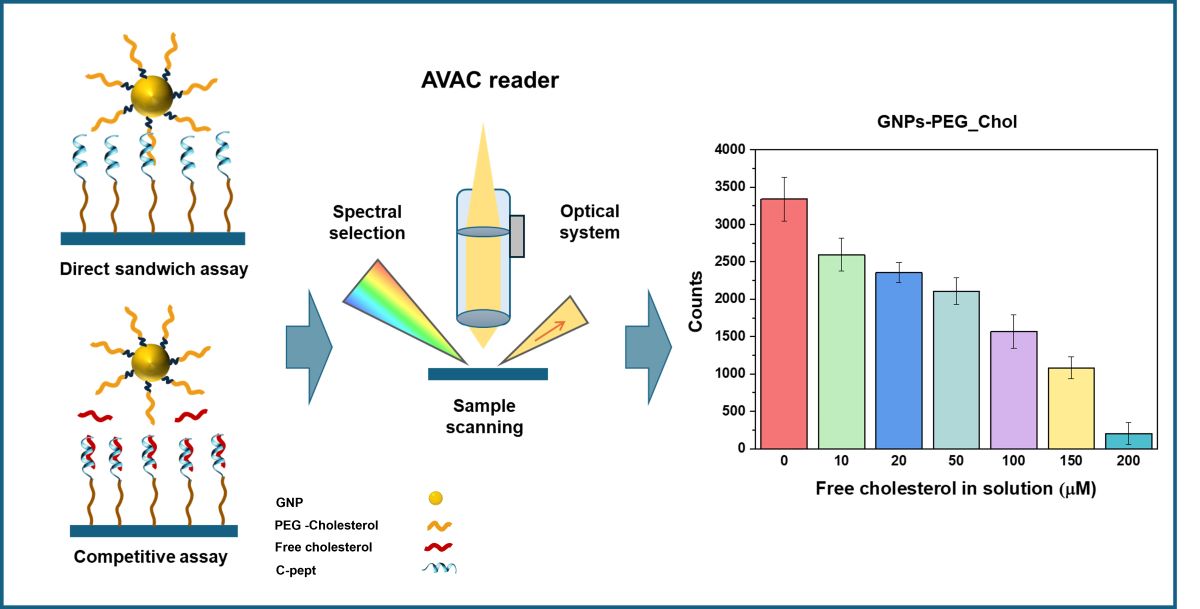
In this study, we have devised an innovative strategy that exploits the scattering properties of GNPs’ SPR in the presence of a dielectric silicon-based substrate. GNPs functionalized with cholesterol molecules were used as optical markers, and the light scattered by GNPs immobilized on the surface was optically detected and monitored using AVAC technology, a dark-field microscopy-based method [
48,
49,
50,
51].
We exploited the affinity and conformational selectivity of a CRAC motif-based peptide sequence, hereafter referred to as C-pept, to develop a novel plasmonic biosensor for the quantitative detection of cholesterol through a competitive assay approach leveraging AVAC technology. This strategy enables rapid, high-throughput screening and presents potential applications in future point-of-care biosensors. One of the main challenges of this study was adapting sandwich immunoassay technology to detect a low-molecular-weight molecule such as cholesterol. The system presented herein is the first to employ a cholesterol-binding peptide as a biorecognition element in a plasmonic biosensor based on a competitive assay for the quantification of free cholesterol.
2. Materials and Equipment
2.1. Materials
One-side polished silicon wafers were purchased from Si-Mat (Germany). Peptide sequences, herein called C-pept and Pept-4, were synthesized by ProteoGenix S.A. (France). Cholesterol-PEG-NH2 was purchased from Abbexa (UK). N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), N-Hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt (Sulfo-NHS), Cholesterol powder, 4-Morpholineethanesulfonic acid MES low moisture content ≥ 99%, (3-Aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES), Glutaraldehyde solution 50 wt% in H2O, Poly(ethylene glycol) bis(amine) Mw: 20000 (PEG-diamine 20 kDa), Poly(ethylene glycol)diamine Mn: 3000 (PEG-diamine 3 kDa), Tween20 and 1X Phosphate buffer saline (PBS) tablets were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Spain). All reagents were of analytical grade. All solutions and buffers were prepared using ultrapure milli-Q water. Commercial gold nanoparticles (GNPs) with carboxyl polymer coating were obtained from Nanopartz (GNPs- C11-100-TC-DICH-50-1) with a standard diameter of 100 nm. FlexWell one-side adhesive 16-well incubation chambers made of clear silicone (6.8 x 6.8 x 3.2 mm depth) were purchased from Grace Bio-Labs (Oregon, USA). All aqueous solutions were prepared in ultra-pure milli-Q water with a resistivity of 18.2 MΩ cm (at 25 °C).
2.2. Equipment
Optical detection, analysis and quantification of the plasmonic GNPs were done using an AVAC platform (Mecwins S.A) with the corresponding analysis software, a Stuart rotator SB2 (VWR), ultrasound cleaning bath USC100T (VWR), microcentrifuge PrismR (Labnet), Vortex mixer Reaxtop (VWR) were used for the functionalization of GNPs. The UV/Vis spectrophotometer Nanodrop2000 (Thermoscientific) was used for the optical quantification of GNPs. The KSV CAM 200 optical contact angle meter (KSV Instruments, Finland) was used for the measurements of the water contact angle (WCA) of liquid droplets on the functionalized surfaces, images and analysis were processed with CAM200 software in static mode.
3. Methods and Experimental Part
3.1. Silica Surface Functionalization with Glutaraldehyde Chemistry for Peptide Immobilization
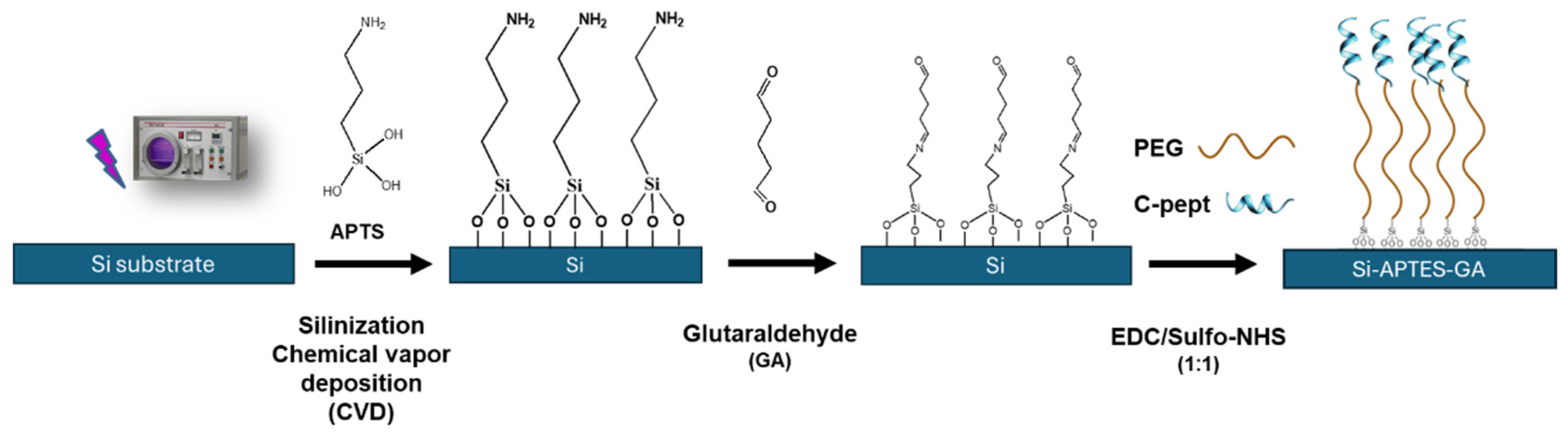
Silanization process of silicon (Si) wafer was conducted via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). The silicon substrate was amine-functionalized by reaction with (3-Aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES), and Si-APTES surfaces were stored under vacuum at 4 ºC until their use. Si-APTES wafers were cut into slides with a dimension of 27 x 77 mm for the 16-well experiments.
Si-APTES slides were treated with a 5% glutaraldehyde solution (GA) in 1X PBS on a rocker for 1 h at room temperature for the purpose of surface functionalization. Slides were rinsed with PBS and milli-Q water twice for 5 minutes each, avoiding the drying of the surface between washes. Then, slides were dried under nitrogen flux and 16-well adhesive chambers were carefully roll-pressed on their functionalized side.
Afterwards, slides were incubated with 150 µL of 10 µg/mL (1%) of PEG linker in PBS for 30 min at 37 ºC. PEG diamine was selected as spacer between the surface and the peptide to reduce the possible false positives and create an oriented position of the peptide.
In the meanwhile, solutions of EDC and Sulfo-NHS were prepared in an aqueous solution in acidic conditions. The stock solution of C-pept in milli-Q water was diluted to 80 µg/mL in MES with pH 5.5.
Finally, the covalent coupling of C-pept on the pegylated substrate was achieved by using the EDC/NHS carbodiimide method. Slides were rinsed with PBS and immediately incubated with 150 µL/well of the vortexed peptide solution pre-mixed with a 1:1 solution of EDC/NHS with 80 µg/mL of C-pept for 1h at 37 ºC on static. Prior to the incubation of the GNPs for the bioassay, the surface was rinsed with PBS to remove unreacted peptide molecules.
3.2. Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles (GNPs)
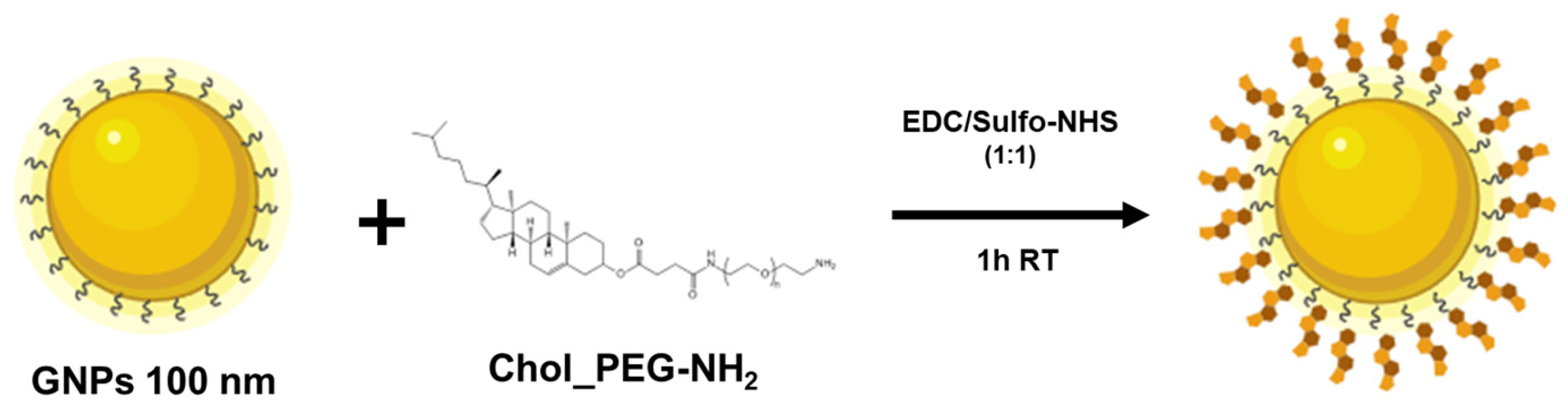
Commercial carboxylate gold nanoparticles (GNPs) obtained from Nanopartz with a standard diameter of 100 nm were selected for the experiments conducted. The concentration of the GNPs stock in milli-Q water was calculated using Nanodrop, measuring its absorbance at 569 nm (SPR peak) to obtain the necessary volume to be added for its functionalization at a final concentration of 192.31 µg/mL.
Surface functionalization of GNPs was conducted via carbodiimide coupling by the terminal carboxylic acid groups. Then, in a low-binding Eppendorf tube the appropriate amounts of Chol_PEG- NH2 and GNPs for the preparation of solutions at 100 µg/mL in PBS and 250 µg/mL in milli-Q water, respectively, were mixed with 1 mL of an aqueous solution in acidic conditions. Before any step of the GNPs functionalization, the solution was sonicated to ensure homogenization.
To this mixed solution, 100 µL of each coupling reagent EDC and NHS-Sulfo solutions at a concentration ratio 1:1 in acidic conditions were immediately incorporated. Finally, the mix was incubated for 1 h on a rotator at RT.
Thereafter, unreacted Chol_PEG- NH2 molecules were removed by centrifugation and washing steps in PBST (PBS 0.05 %Tween) for four times at 17000 x g and 4 ºC for 5 min each in a microcentrifuge. Before each centrifugation step, GNPs were sonicated and further vortexed to avoid aggregation. Functionalized GNPs were stored in storage buffer solution at 4 ºC until their use.
Before each experiment, the GNP concentration was determined by measuring the absorbance at around 569 nm with a NanoDrop spectrophotometer.
3.3. Competitive Plasmonic Bioassay for Cholesterol Determination
Before the determination of cholesterol, a cholesterol solution in ethanol with concentration of 10 mM was prepared and stored at 4 ºC until its use. After the washing steps, each well of the fully assembled Si/APTES/GA/PEG/C-pept substrate was incubated with 150 µL of 5 µg/mL GNPs-Chol in PBST for 1 h at 37 ºC. The competitive assays were performed by adding increasing concentrations of free cholesterol in the bioassay buffer media in presence of functionalized GNPs.
To verify the selectivity of the C-pept in the developed cholesterol plasmonic biosensor system and the sensitivity of the method, a modified peptide sequence lacking affinity for cholesterol was investigated under the same conditions, immobilizing the bioreceptor as explained in section 3.1
3.4. AVAC Analyzer
Analysis and quantification of surface-bound GNPs was performed with the AVAC platform, patented by Mecwins S.A. (US11519843B2 and US11519856B2). The AVAC platform represents an innovative approach to biomarker detection and quantification, using digital counting of plasmonic gold nanoparticles imaged with reflective dark-field microscopy to achieve high sensitivity and precise quantification of analytes at ultralow concentrations. The output provided is the number of GNPs counted per well, from which the amount of the analyte in the sample can be calculated [
50,
51].
3.5. Surface Characterization
Contact angle measurements were performed in a KSV CAM 200 optical contact angle meter connected to a computer supported with CAM200 software to process the images and analyze the WCA measurements. The volume used in the study was 1 μL of milli-Q water. After each step of surface modification, the values of the angle (n = 3) were obtained.
4. Results and Discussion
In this study, we aimed to develop an innovative method for detecting free cholesterol (Chol) using C-pept, a 13-amino acid synthetic peptide previously characterized as a cholesterol-binding motif [
52]. synthetic peptide previously characterized as a cholesterol-binding motif [
52]. C-pept was chosen as the biorecognition element for an optical biosensor based on plasmonic gold nanoparticles (GNPs) and localized dark-field spectrophotometry. The effectiveness of plasmonic biosensing for the sensitive and direct monitoring of biomolecular interactions in in vitro assays is well-established in the scientific literature. Plasmonic biosensor prototypes are often designed around the antigen-antibody recognition event, either in label-free (direct) or sandwich (GNP-assisted) formats, which have shown significant promise as medical devices for the specific and sensitive detection of disease biomarkers in point-of-care applications. In this work, we extend the applicability of the conventional plasmonic biosensor by utilizing it as a sensitive biosensor for free cholesterol detection, employing the cholesterol-binding peptide C-pept in a competitive assay format.
4.1. Functionalization of Silicon Surface with C-pept as Recognition Element
In the context of plasmonic biosensors, the use of dielectric materials such as silica provides an ideal platform substrate enhancing the sensitivity, stability and functionalization capabilities [
53,
54]. The surface functionalization protocol for silicon was adapted and optimized considering the hydrophobicity, small size, and alpha-helical structure of C-pept, ensuring appropriate orientation and stability to enable effective interaction with cholesterol molecules
The surface functionalization strategy is illustrated in
Scheme 1. Silicon wafers were silanized using CVD, activating the surfaces and forming a smooth monolayer of APTES [
54]. The resulting amine-functionalized surface was sectioned into slides and incubated in a 5% GA solution for 1 hour at room temperature. GA is widely employed as a crosslinker, enabling spontaneous covalent bonding to amino groups of biomolecules, such as antibodies [
53,
55]. In this study, we further optimized the platform design by introducing PEG diamine moieties as linkers. This strategy provided the necessary spacing for accurate C-pept/Chol biorecognition and ensured the vertical orientation and stability of C-pept, which was conjugated via the widely used EDC/NHS chemistry.
The sequential steps comprised a full wet-chemistry protocol where the crosslinking PEG moieties and further covalent immobilization of C-pept were done directly on each well chamber. Employing this method, we were able not only to assess the reproducibility between different independent replicates, but also the accuracy of the functionalization steps ensuring the correct deposition and homogeneity of the required reagents within the wells.
Additionally, water contact angle measurements were performed to characterize the sequential chemical modifications of silicon surfaces, from initial Si activation to final functionalization. Variations in the contact angle values of water droplets on the modified surface correlated with the introduction of hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups, reflecting the chemical changes induced by the incorporated elements during the functionalization process.
The analysis of the contact angle measurements (
Table 2) confirmed variations in the hydrophilicity properties of the silicon surface and the subsequent incorporation of functional moieties during the biofunctionalization process. Notably, the water contact angle (WCA) exhibited a significant increase from 67 ± 3 º to 78 ± 3 º on the PEGylated substrate upon the incorporation of C-pept. This change is attributed to the hydrophobic nature of the selected peptide and the presence of charged molecules on the surface.
4.2. GNPs Functionalization with Cholesterol
One of the most commonly employed methods for GNP biofunctionalization involves the direct covalent bonding of thiol-containing biomolecules to its surface via strong and stable sulfide bonds. Alternatively, EDC/NHS coupling chemistry is frequently used to conjugate bioreceptors through their amino or carboxyl groups and to incorporate linkers or adapter molecules such as avidin/biotin [
30,
56]. Moreover, to ensure proper orientation of the biomolecule, reduce non-specific interactions, and enhance GNP stability and biocompatibility, bifunctional linkers and/or polymeric ligands are typically used as coating agents.
In this study, we aimed to covalently functionalize GNPs with cholesterol molecules. Cholesterol is known to be highly hydrophobic and insoluble in aqueous media unless organic solvents or detergents such as Triton X-100 or Tween 20 are present, and its only functional moiety is a hydroxyl group [
57]. To address this, we employed a strategy to anchor PEGylated cholesterol molecules onto the GNP surface [
58]. By using PEG as a linker, we mitigated potential steric hindrance, detachment, and incorrect orientation of cholesterol during its interaction with the peptide on the Si substrate, thereby reducing the cost and time required for the conjugation reaction.
GNPs-COOH with an average size of 100 nm in Milli-Q water were functionalized through carbodiimide coupling with Chol_PEG molecules, as illustrated in
Scheme 2. Stock solutions of Chol_PEG-NH
2 and GNPs were diluted to 100 µg/mL and 250 µg/mL, respectively, in 100 µL of PBS and Milli-Q water, and mixed with 100 µL of EDC/NHS (1:1) coupling agents in 1000 µL of an aqueous solution under acidic conditions.
To confirm the correct conjugation, concentration and agglomeration state of the GNPs, shifts on the SPR peak and signal intensity were studied by measuring the absorbance at 569 nm before and after the functionalization process using a UV-visible Nanodrop spectrophotometer. The functionalized GNPs (GNPs-Chol) were stored in PBST (0.05%) at 4ºC and remained stable without presenting significative aggregation for 3 days.
4.3. Peptide-Based Plasmonic Competitive Assay for Cholesterol Quantification
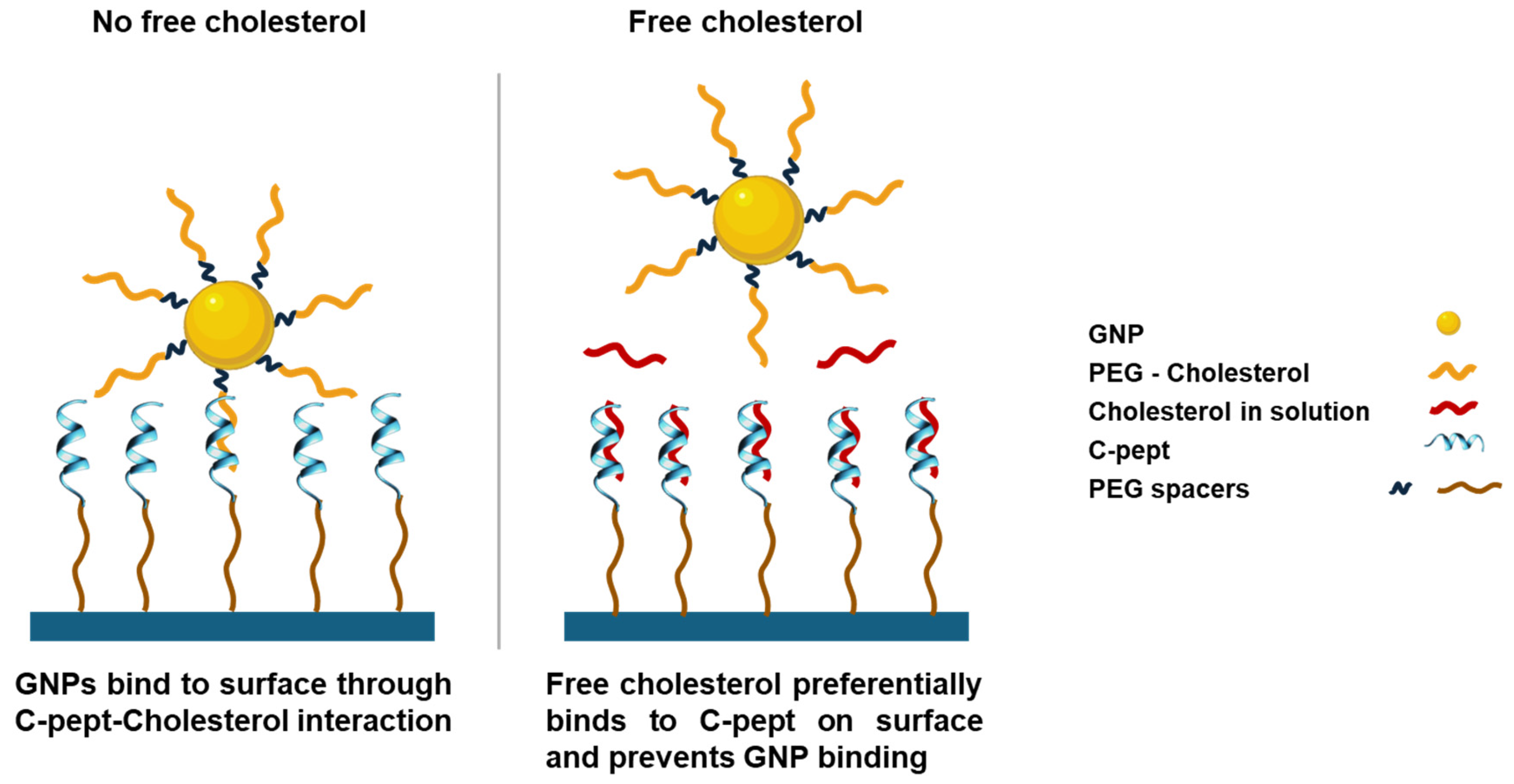
In this work, the main challenge and limitation for the detection of free cholesterol molecules via sandwich assays derives from their small size and amphiphilic character. In addition, the precise orientation and conformation on an alpha-helix secondary structure of the peptide is crucial for the particular interaction with cholesterol molecules through it apolar-aromatic-basic branching sequence. Hence, to overcome this obstacle, and achieve the detection and quantification of cholesterol by C-pept, a competitive assay strategy was followed as depicted in
Scheme 3.
In the proposed competitive assay for cholesterol detection, cholesterol molecules were immobilized onto beads, hereafter referred to as GNP-Chol, which served as the immobilized component. A peptide with high affinity for recognizing and binding cholesterol (C-pept) was immobilized onto the dielectric Si substrate. In this assay, the peptide can bind either to the cholesterol immobilized on the beads or to the free cholesterol present in the sample. Thus, free cholesterol in the sample competes with GNP-Chol for binding to the peptide. GNP-Chol was incubated in a 16-well chamber placed on the Si-C-pept surface. After the incubation period, unbound components were removed, and the number of GNPs bound to the peptide-functionalized surface was quantified. The results showed that the amount of GNPs bound was inversely proportional to the concentration of cholesterol in the sample, indicating that higher cholesterol levels result in fewer GNPs binding, thereby enabling the quantitative detection of cholesterol. Images of GNPs were captured under various conditions using an AVAC reader to quantify the GNPs immobilized by their interaction with C-pept. The plasmonic biosensor was thus designed to evaluate the competition between GNP-Chol and free cholesterol in solution as detected by C-pept.
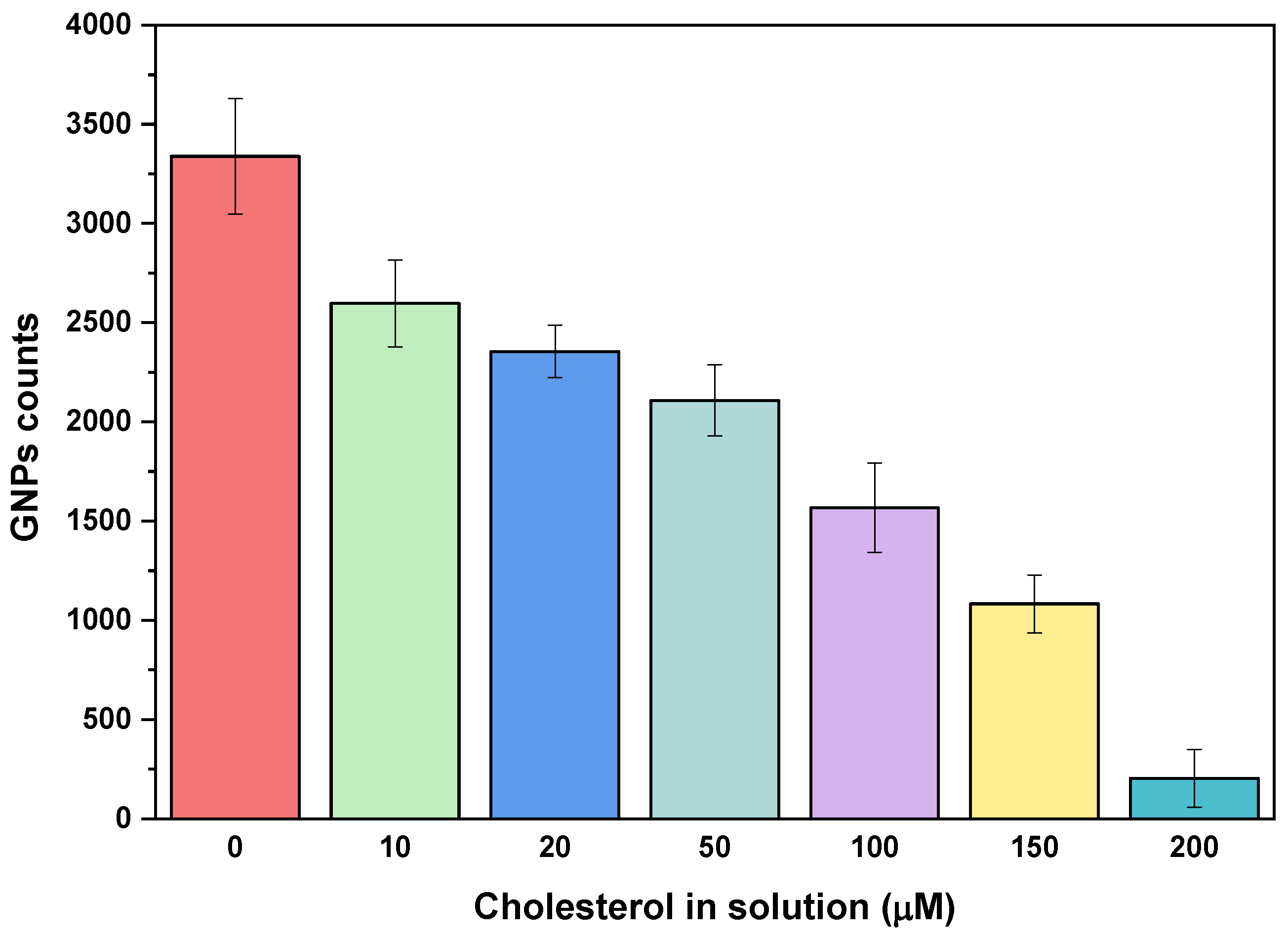
The sensitivity of the biosensing assay was assessed by exposing a fixed concentration of GNP-Chol to various concentrations of free cholesterol, ranging from 10 to 200 µM in buffer media. It was observed that increasing concentrations of free cholesterol resulted in a reduction in the number of GNPs immobilized on the surface, as shown in
Figure 1. The interaction of C-pept with GNP-Chol led to GNP immobilization on the surface; however, the presence of free cholesterol in the sample inhibited or displaced this interaction, likely due to steric and more accessible interactions between the small molecules. Thus, a competitive assay for free cholesterol quantification in solution was performed. The quantitative analysis revealed a linear response (R² = 0.983) over the cholesterol concentration range of 10–200 µM, with a limit of detection (LOD) of 21.95 µM. The LOD was calculated using the equation LOD = 3σ/b, where σ is the standard deviation of the counts, and b is the slope (counts per concentration). Furthermore, strong competition was observed when the system was exposed to 200 µM of free cholesterol, which may indicate the upper detection limit and saturation of the proposed system.
These results demonstrate the capability of C-pept to bind cholesterol molecules in aqueous media, suggesting its potential application as a sensitive biosensor for cholesterol quantification in small sample volumes.
The coefficient of variation (CV), calculated as the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean, for three independent experiments at each cholesterol concentration, ranging from 10 µM to 200 µM, was between 5.6% and 14.4%, confirming the sensitivity and reproducibility of the proposed method.
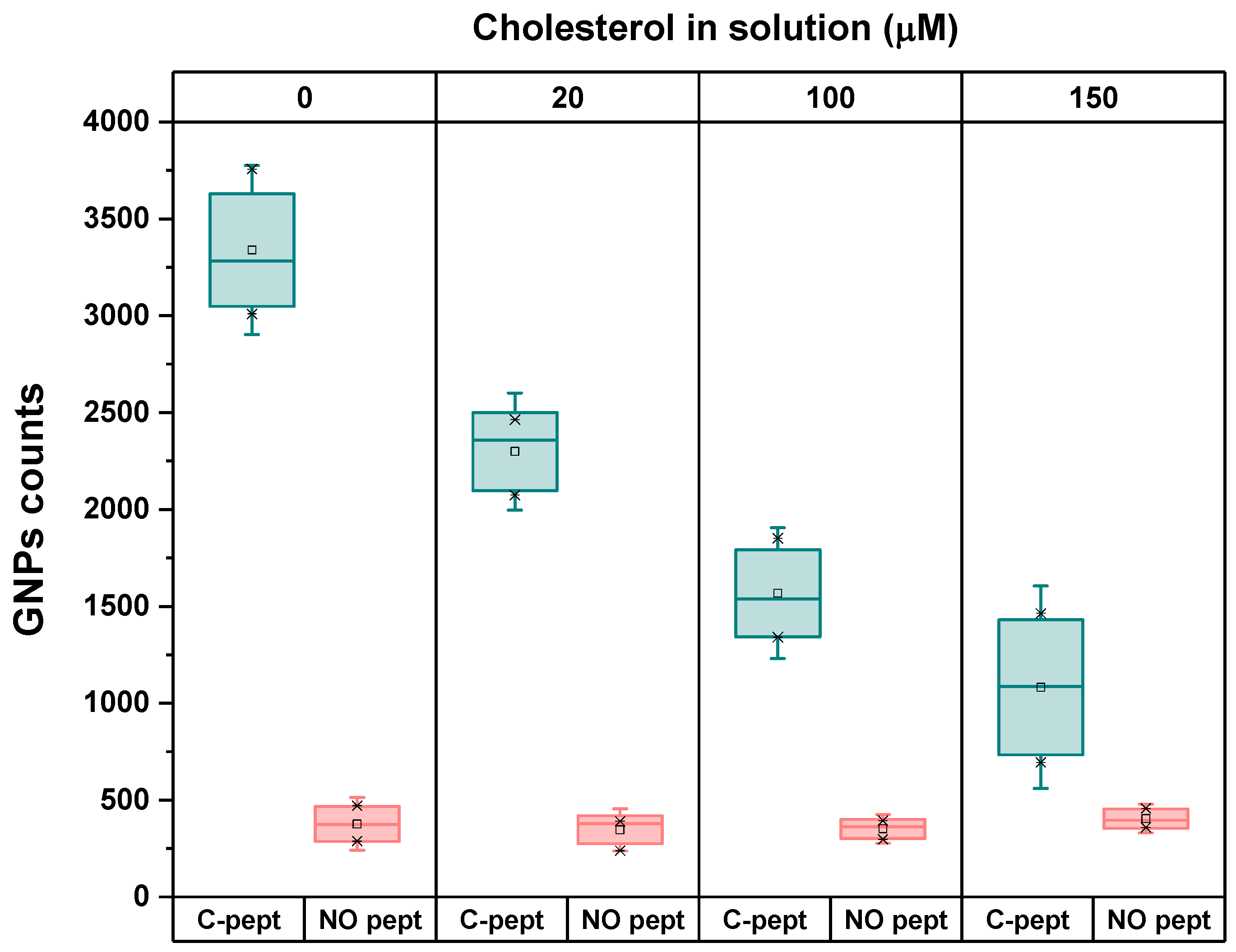
Subsequently, to validate the capability of the Si-APTES-GA-PEG-C-pept system to detect cholesterol, experiments were performed under the same conditions without peptide immobilization on the substrate, serving as a negative control.
The results presented in
Figure 2 demonstrate the recognition capability and high sensitivity of C-pept in the system for detecting cholesterol. The absence of a biorecognition element suggests that PEG moieties on the Si substrate are exposed, which may lead to non-specific binding of GNPs through direct adsorption, crosslinking of functional groups, or aggregation. It is noteworthy that the signal of GNPs attached to the surface in the absence of cholesterol (control condition) was found to be 8-fold higher in the presence of the peptide. Furthermore, no significant changes in the GNP signal were observed on the control surface in the presence of free cholesterol at varying concentrations, remaining constant throughout the titration assay. Conversely, the presence of C-pept facilitated the correct interaction with cholesterol, as previously demonstrated. These findings validate the detection method using the proposed plasmonic system, confirming that GNP attachment resulted from the successful interaction and binding of the cholesterol-C-pept pair rather than from non-specific binding.
4.4. Selection of the System Configuration
Conventional methods for immobilizing proteins or other bioreceptors on silicon surfaces typically employ APTES and GA as crosslinking agents. However, the APTES-GA method has limitations due to the use of GA, which contains two functional groups capable of binding nonspecifically to proteins, leading to irregular binding when the surface is not blocked. Additional spacers can be incorporated to mitigate this issue.
In this context, the correct orientation of C-pept is critical for its interaction and binding with cholesterol molecules, as defined by its putative cholesterol-binding motif. Furthermore, not only the orientation but also the conformational folding of C-pept can be affected by environmental and buffer media conditions.
Therefore, C-pept was immobilized on the surface via covalent linkage through its carboxyl-terminal group to the amino groups of the PEG spacer. The effectiveness of its interaction with GNPs-PEG_Chol was evaluated using PEGs of different molecular weights (Mw). The results indicated that a higher Mw for the chosen spacer reduced steric hindrance, increased detection sensitivity, and minimized nonspecific signals in the proposed system [
59].
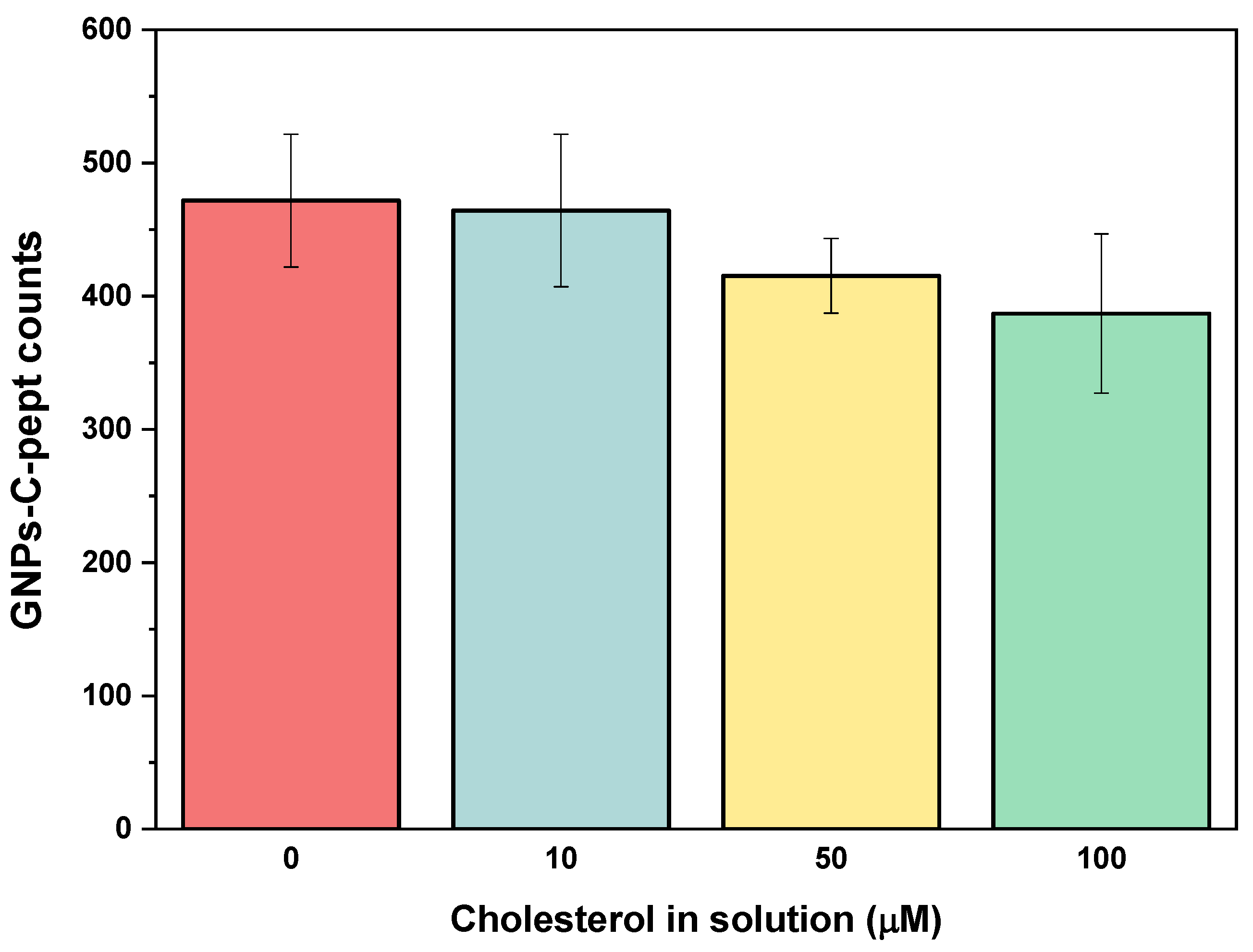
To further investigate the optimal configuration and functionality of the system, additional experiments were conducted using the inverted configuration, where PEG-Chol molecules were immobilized on the Si-APTES-GA substrate and GNPs functionalized with C-pept were utilized. Under these conditions, the competitive bioassay for free cholesterol in solution exhibited a decreasing trend, as expected from previous findings (
Figure 3). Nevertheless, while the results confirmed the biorecognition and binding of C-pept to cholesterol, the interaction and specificity were lower when using this reversed configuration compared to the originally proposed biosensor strategy. The reduced number of GNPs interacting could be attributed to the denaturation of C-pept, affecting its proper alpha-helical conformation during the GNP functionalization process.
4.5. Specificity of the Biorecognition Peptide Element
We further evaluated the specificity of the plasmonic platform by selecting a non-binding cholesterol peptide. The peptide sequence chosen, designated as Pept-4, was modified by altering one of the putative amino acids responsible for cholesterol binding within the CRAC motif.
The protocol for surface functionalization and bioreceptor immobilization was carried out under the same conditions described in section 3.2 for C-pept.
As shown in
Figure 4, the new sequence Pept-4, used as a negative control, exhibited a negligible interaction response with cholesterol. In contrast to the C-pept response, minimal plasmonic signals from GNPs were observed on the surface, both in the presence and absence of cholesterol as an interference. The resulting GNP binding was significantly lower than when no biorecognition element was present. This effect is directly attributed to minimal nonspecific binding of GNPs-Chol to the free terminal groups of PEG or GA, as no blocking agent was used. These findings confirm the successful surface modification and verify that the observed results were indeed due to the specific molecular recognition between cholesterol and C-pept.
5. Conclusion
A novel plasmonic-optical biosensor based on a competitive assay for the detection of cholesterol has been successfully developed using C-pept, a cholesterol-binding peptide, as the biorecognition element. The biosensor employs a one-step competitive cholesterol bioassay system, involving the selective interaction of C-pept with cholesterol molecules immobilized on GNPs which serve as optical markers. The AVAC platform facilitates the quantification of GNPs functionalized with PEG-Chol motifs bound to C-pept, competing with free cholesterol in aqueous media, resulting in a calibration curve. This bioassay exhibits a highly sensitive detection limit of 21.95 µM, establishing it as an advanced, high-throughput tool for the quantification of free cholesterol presumably useful for clinical diagnostics. In conclusion, this peptide-based plasmonic approach provides novel insights for detecting lipidic, low-molecular-weight targets and metabolites, advancing the field of biosensing technology.
Authors Contribution
Conceptualization, A.L.B., A.P., V.C., O.A., S.O. and E.D.; Methodology, A.L.B.; Validation, A.L.B. and A.P.; Formal analysis, A.L.B. and A.P.; Investigation, A.L.B.; Resources, V.C., O.A., S.O. and E.D.; Data curation, A.L.B; Writing original draft, A.L.B.; Writing review & editing, A.L.B., A.P., V.C., O.A., S.O. and E.D.; Visualization, A.L.B.; Supervision, V.C., O.A., S.O. and E.D.; Project administration, V.C., O.A., S.O. and E.D.; Funding acquisition, O.A, S.O, E.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement BioInspireSensing No 955643.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available under request
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement BioInspireSensing No 955643 for this work. Anne Parra acknowledges funding of her PhD training to the Agencia Estatal de Investigaciónfrom Project DIN2020-011175/AEI/10.13039/501100011033.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Oddi, S.; Dainese, E.; Fezza, F.; Lanuti, M.; Barcaroli, D.; De Laurenzi, V.; Centonze, D.; MacCarrone, M. Functional Characterization of Putative Cholesterol Binding Sequence (CRAC) in Human Type-1 Cannabinoid Receptor. J Neurochem 2011, 116, 858–865. [CrossRef]
- Morales-Lázaro, S.L.; Rosenbaum, T. Cholesterol as a Key Molecule That Regulates TRPV1 Channel Function. Adv Exp Med Biol 2019, 1135, 105–117. [CrossRef]
- Dainese, E.; De Fabritiis, G.; Sabatucci, A.; Oddi, S.; Angelucci, C.B.; Di Pancrazio, C.; Giorgino, T.; Stanley, N.; Del Carlo, M.; Cravatt, B.F.; et al. Membrane Lipids Are Key Modulators of the Endocannabinoid-Hydrolase FAAH. Biochemical Journal 2014, 457, 463–472. [CrossRef]
- Dainese, E.; Oddi, S.; Bari, M.; Maccarrone, M. Modulation of the Endocannabinoid System by Lipid Rafts. Curr Med Chem 2007, 14, 2702–2715. [CrossRef]
- Maccarrone, M.; Bernardi, G.; Agrò, A.F.; Centonze, D. Cannabinoid Receptor Signalling in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Potential Role for Membrane Fluidity Disturbance. Br J Pharmacol 2011, 163, 1379–1390. [CrossRef]
- Oddi, S.; Caporali, P.; Dragotto, J.; Totaro, A.; Maiolati, M.; Scipioni, L.; Angelucci, C.B.; Orsini, C.; Canterini, S.; Rapino, C.; et al. The Endocannabinoid System Is Affected by Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis: Insights from a Murine Model of Niemann Pick Type C Disease. Neurobiol Dis 2019, 130. [CrossRef]
- Sniderman, A.; McQueen, M.; Contois, J.; Williams, K.; Furberg, C.D. Why Is Non−high-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol a Better Marker of the Risk of Vascular Disease than Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol? J Clin Lipidol 2010, 4, 152–155. [CrossRef]
- Golier, J.A.; Marzuk, P.M.; Leon, A.C.; Weiner, C.; Tardiff, K. Low Serum Cholesterol Level and Attempted Suicide. 2006, 152, 419–423. [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.; Li, B.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, B.; Robinson, J.G.; Bao, W. Association of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels with More than 20-Year Risk of Cardiovascular and All-Cause Mortality in the General Population. J Am Heart Assoc 2022, 11, 23690. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cohen, L.; Wang, J.; Walt, D.R. Competitive Immunoassays for the Detection of Small Molecules Using Single Molecule Arrays. J Am Chem Soc 2018, 140, 18132–18139. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Shang, K.; Gao, X.; Wang, X. Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Cholesterol Using a Portable Paper Sensor Based on the Synergistic Effect of Cholesterol Oxidase and Nanoporous Gold. Int J Biol Macromol 2021, 189, 356–362. [CrossRef]
- Salazar, P.; Martín, M.; González-Mora, J.L. In Situ Electrodeposition of Cholesterol Oxidase-Modified Polydopamine Thin Film on Nanostructured Screen Printed Electrodes for Free Cholesterol Determination. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 2019, 837, 191–199. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Solanki, P.R.; Pandey, M.K.; Malhotra, B.D. Cholesterol Biosensor Based on Cholesterol Esterase, Cholesterol Oxidase and Peroxidase Immobilized onto Conducting Polyaniline Films. Sensors and Actuators B 2006, 115, 534–541. [CrossRef]
- Mukai, M.; Krause, M.R.; Regen, S.L. Peptide Recognition of Cholesterol in Fluid Phospholipid Bilayers. J Am Chem Soc 2015, 137, 12518–12520. [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Basiruddin, S.K.; Chakraborty, A.; Jana, N.R. β-Cyclodextrin Functionalized Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Colloid for Cholesterol Separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2015, 7, 1340–1347. [CrossRef]
- Ballesta-Claver, J.; Salinas Velázquez, P.; Valencia-Mirón, M.C.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F. SPE Biosensor for Cholesterol in Serum Samples Based on Electrochemiluminescent Luminol Copolymer. Talanta 2011, 86, 178–185. [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.R.; Yang, C.R.; Huang, Y.F.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Chang, H.T. Ratiometric Fluorescence Probe of Vesicle-like Carbon Dots and Gold Clusters for Quantitation of Cholesterol. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 160. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.C.; Li, H. Sensitive Cholesterol Determination by β-Cyclodextrin Recognition Based on Fluorescence Enhancement of Gold Nanoclusters. Microchemical Journal 2022, 175, 107125. [CrossRef]
- Calvo, R.; Rodriguez Mariblanca, I.; Pini, V.; Dias, M.; Cebrian, V.; Thon, A.; Saad, A.; Salvador-Matar, A.; Ahumada, Ó.; Manso Silván, M.; et al. Novel Characterization Techniques for Multifunctional Plasmonic–Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2929. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Leustean, L.; Inci, F.; Zheng, M.; Demirci, U.; Wang, S. Plasmonic-Based Platforms for Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases at the Point-of-Care. Biotechnol Adv 2019, 37, 107440. [CrossRef]
- Mauriz, E.; Lechuga, L.M. Plasmonic Biosensors for Single-Molecule Biomedical Analysis. Biosensors (Basel) 2021, 11, 123. [CrossRef]
- Nyembe, S.; Mkhohlakali, A.; May, B.; Mhlanga, N.; Nyembe, S.; Mkhohlakali, A.; May, B.; Mhlanga, N. Application of Plasmonic Nanostructures in Molecular Diagnostics and Biosensor Technology: Challenges and Current Developments. Plasmonic Nanostructures—Basic Concepts, Optimization and Applications 2022. [CrossRef]
- Rosman, C.; Prasad, J.; Neiser, A.; Henkel, A.; Edgar, J.; Sönnichsen, C. Multiplexed Plasmon Sensor for Rapid Label-Free Analyte Detection. Nano Lett 2013, 13, 3243–3247. [CrossRef]
- Kumalasari, M.R.; Alfanaar, R.; Andreani, A.S. Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs): A Versatile Material for Biosensor Application. Talanta Open 2024, 9, 100327. [CrossRef]
- Pellas, V.; Hu, D.; Mazouzi, Y.; Mimoun, Y.; Blanchard, J.; Guibert, C.; Salmain, M.; Boujday, S. Gold Nanorods for LSPR Biosensing: Synthesis, Coating by Silica, and Bioanalytical Applications. Biosensors (Basel) 2020, 10, 146. [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, E. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Plasmonic Biosensors. Biosensors (Basel) 2023, 13, 411. [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.; Agasti, S.S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.; Rotello, V.M. Gold Nanoparticles in Chemical and Biological Sensing. Chem Rev 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.C.; Creran, B.; Rotello, V.M. Gold Nanoparticles: Preparation, Properties, and Applications in Bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1871–1880. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Yong, K.T.; Roy, I.; Dinh, X.Q.; Yu, X.; Luan, F. A Review on Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Biosensing Applications. Plasmonics 2011 6:3 2011, 6, 491–506. [CrossRef]
- Jazayeri, M.H.; Amani, H.; Pourfatollah, A.A.; Pazoki-Toroudi, H.; Sedighimoghaddam, B. Various Methods of Gold Nanoparticles (GNPs) Conjugation to Antibodies. Sens Biosensing Res 2016, 9, 17–22. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xianyu, Y.; Jiang, X. Surface Modification of Gold Nanoparticles with Small Molecules for Biochemical Analysis. Acc Chem Res 2017, 50, 310–319. [CrossRef]
- Pellas, V.; Sallem, F.; Blanchard, J.; Miche, A.; Concheso, S.M.; Méthivier, C.; Salmain, M.; Boujday, S. Silica-Coated Gold Nanorods Biofunctionalization for Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR) Biosensing. Talanta 2023, 255, 124245. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Pal, T. Interparticle Coupling Effect on the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Gold Nanoparticles: From Theory to Applications. Chem Rev 2007, 107, 4797–4862. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.B.; Zijlstra, P. Single-Molecule Plasmon Sensing: Current Status and Future Prospects. ACS Sens 2017, 2, 1103–1122. [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wei, Q. Plasmonic Molecular Assays: Recent Advances and Applications for Mobile Health. Nano Res 2018, 11, 5439. [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.T. Plasmonic Biosensors. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 2015, 7, 152. [CrossRef]
- D’Agata, R.; Bellassai, N.; Spoto, G. Exploiting the Design of Surface Plasmon Resonance Interfaces for Better Diagnostics: A Perspective Review. Talanta 2024, 266, 125033. [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, A.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; Guardia, M. de la Peptide Based Biosensors. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2018, 107, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Boyd, B.J. Peptide-Based Biosensors. Talanta 2015, 136, 114–127. [CrossRef]
- Saadati, A.; Hassanpour, S.; Guardia, M. de la; Mosafer, J.; Hashemzaei, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Baradaran, B. Recent Advances on Application of Peptide Nucleic Acids as a Bioreceptor in Biosensors Development. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2019, 114, 56–68. [CrossRef]
- Koyiloth, M.; Gummadi, S.N. Interaction of Human Phospholipid Scramblase 1 with Cholesterol via CRAC Motif Is Essential for Functional Regulation and Subcellular Localization. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 209, 850–857. [CrossRef]
- Volynsky, P.E.; Galimzyanov, T.R.; Akimov, S.A. Interaction of Peptides Containing CRAC Motifs with Lipids in Membranes of Various Composition. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 2021, 15, 98–108. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, Z.X.; Degenhardt, B.; Teper, G.; Papadopoulos, V. Cholesterol Binding at the Cholesterol Recognition/Interaction Amino Acid Consensus (CRAC) of the Peripheral-Type Benzodiazepine Receptor and Inhibition of Steroidogenesis by an HIV TAT-CRAC Peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98, 1267–1272. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Papadopoulos, V. Peripheral-Type Benzodiazepine Receptor Function in Cholesterol Transport. Identification of a Putative Cholesterol Recognition/Interaction Amino Acid Sequence and Consensus Pattern. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 4991–4997. [CrossRef]
- Giarola, J.F.; Santos, J.; Estevez, M.C.; Ventura, S.; Pallarès, I.; Lechuga, L.M. An α-Helical Peptide-Based Plasmonic Biosensor for Highly Specific Detection of α-Synuclein Toxic Oligomers. Anal Chim Acta 2024, 1304, 342559. [CrossRef]
- Heo, N.S.; Oh, Y.; Ryu, M.Y.; Hoon Baek, S.; Park, J.; Choi, C.; Huh, Y.S.; Park, J.P. Affinity Peptide-Guided Plasmonic Biosensor for Detection of Noroviral Protein and Human Norovirus. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering 2019, 24, 318–325. [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Dolci, M.; Zijlstra, P. Single-Molecule Optical Biosensing: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. ACS Physical Chemistry Au 2023, 3, 143–156. [CrossRef]
- Calvo, R.; Thon, A.; Saad, A.; Salvador-Matar, A.; Manso-Silván, M.; Ahumada, Ó.; Pini, V. Size Characterization of Plasmonic Nanoparticles with Dark-Field Single Particle Spectrophotometry. Scientific Reports | 123AD, 12, 17231. [CrossRef]
- Sriram, M.; Markhali, B.P.; Nicovich, P.R.; Bennett, D.T.; Reece, P.J.; Brynn Hibbert, D.; Tilley, R.D.; Gaus, K.; Vivekchand, S.R.C.; Gooding, J.J. A Rapid Readout for Many Single Plasmonic Nanoparticles Using Dark-Field Microscopy and Digital Color Analysis. Biosens Bioelectron 2018, 117, 530–536. [CrossRef]
- Pini, V.; Thon, A.; Salvador -Matar Renteria, A.; Cebrián Hernando, V.; García Aguado, C.; Ahumada Heredero, J.Ó. Biosensor Platform and Method for the Simultaneous, Multiplexed, Ultra-Sensitive and High Throughput Optical Detection of Biomarkers. U.S. Patent and Trademark Office 2020, US11519843B2.
- Thon, A.; Pini, V.; Salvador-Matar Renteria, A.; Cebrián Hernardo, V.; García Aguado, C.; Ahumada Heredero, J.Ó. Method for Optically Detecting Biomarkers. U.S. Patent and Trademark Office 2022, US11519856B2.
- Bernardo, A.L.; Mohammed-Sadhakathullah, A.H.M.; Angelucci, C.B.; Estrany, F.; Berghella, A.; Torras, J.; Armelin, E.; Oddi, S.; Dainese, E. Non-Enzymatic Cholesterol Biosensor: Electrochemical Sensing Based on Peptide-PLA Thin Film. Int J Biol Macromol 2024. [CrossRef]
- Bañuls, M.J.; Puchades, R.; Maquieira, Á. Chemical Surface Modifications for the Development of Silicon-Based Label-Free Integrated Optical (IO) Biosensors: A Review. Anal Chim Acta 2013, 777, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, M.; Tsounidi, D.; Petrou, P.S.; Beltsios, K.G.; Kakabakos, S.E. Functionalization of Silicon Dioxide and Silicon Nitride Surfaces with Aminosilanes for Optical Biosensing Applications. Med Devices Sens 2020, 3. [CrossRef]
- Soler, M.; Lechuga, L.M. Biochemistry Strategies for Label-Free Optical Sensor Biofunctionalization: Advances towards Real Applicability. Anal Bioanal Chem 2022, 414, 5071. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.P.; Prado, A.R.; Keijok, W.J.; Antunes, P.W.P.; Yapuchura, E.R.; Guimarães, M.C.C. Impact of Conjugation Strategies for Targeting of Antibodies in Gold Nanoparticles for Ultrasensitive Detection of 17β-Estradiol. Sci Rep 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, A.I.; Lee, K.-P.; Ragupathy, D. Development of a Stable Cholesterol Biosensor Based on Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes-Gold Nanoparticles Composite Covered with a Layer of Chitosan-Room-Temperature Ionic Liquid Network. Biosens Bioelectron 2009, 24, 2211–2217. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-De-Souza, J.L.; Nag, O.K.; Oh, E.; Huston, A.L.; Vurgaftman, I.; Pepperberg, D.R.; Bezanilla, F.; Delehanty, J.B. Cholesterol Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles Enhances Photoactivation of Neural Activity. ACS Chem Neurosci 2019, 10, 1478–1487. [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Loh, K.C. Immobilization of Hydrophobic Peptidic Ligands to Hydrophilic Chromatographic Matrix: A Preconcentration Approach. Anal Biochem 2012, 423, 202–209. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).