Submitted:
10 October 2024
Posted:
10 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Sustainable Behavior in Forest Management
2.2. Human Behavior in Forest Management
2.3. Recognition in Forest Conservation Behavior
2.4. Knowledge in Forest Conservation Behavior
2.5. Information in Forest Management Behavior
2.6. Forest Resource Dependency Behavior
2.7. Characteristics of Demographic and Socio-Economic Factors
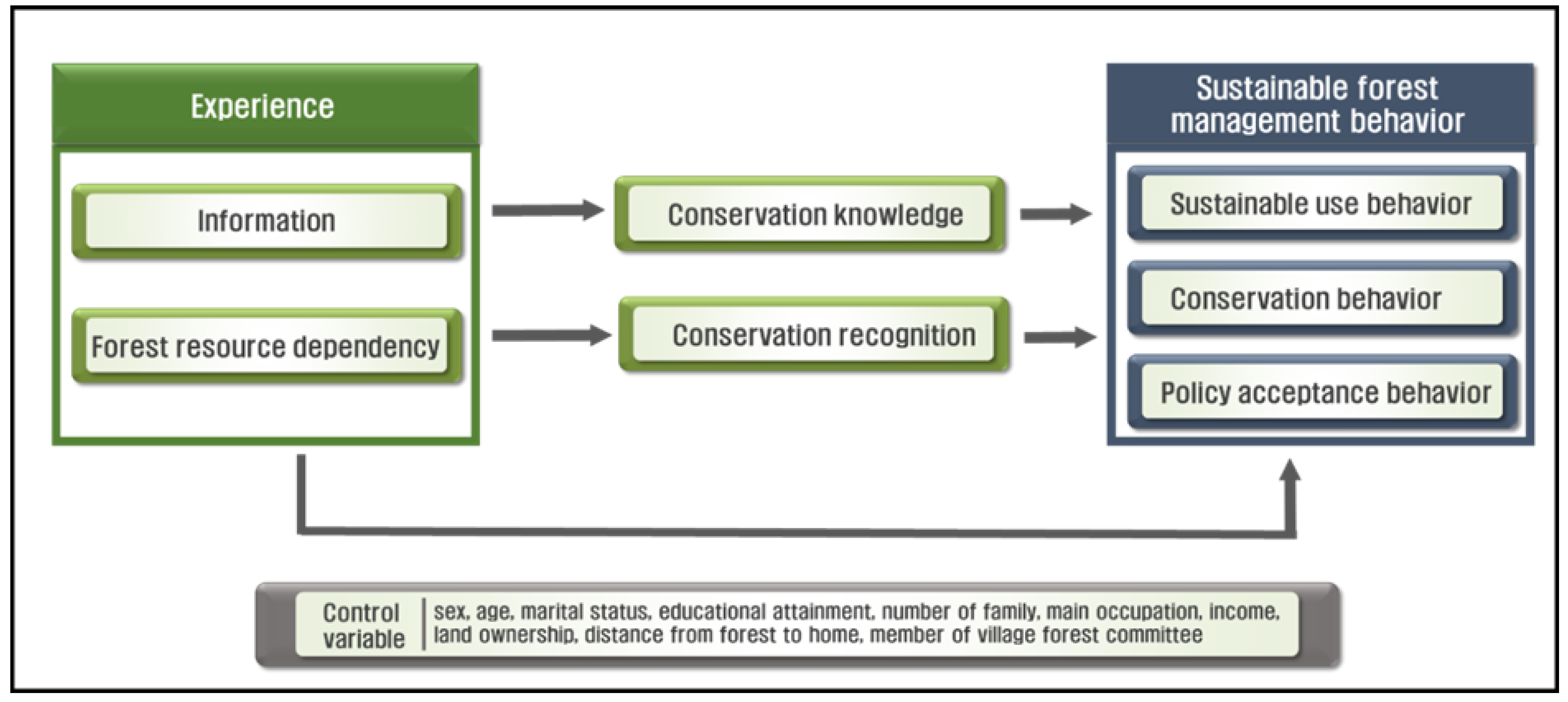
2.8. Conceptual Framework of the research
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
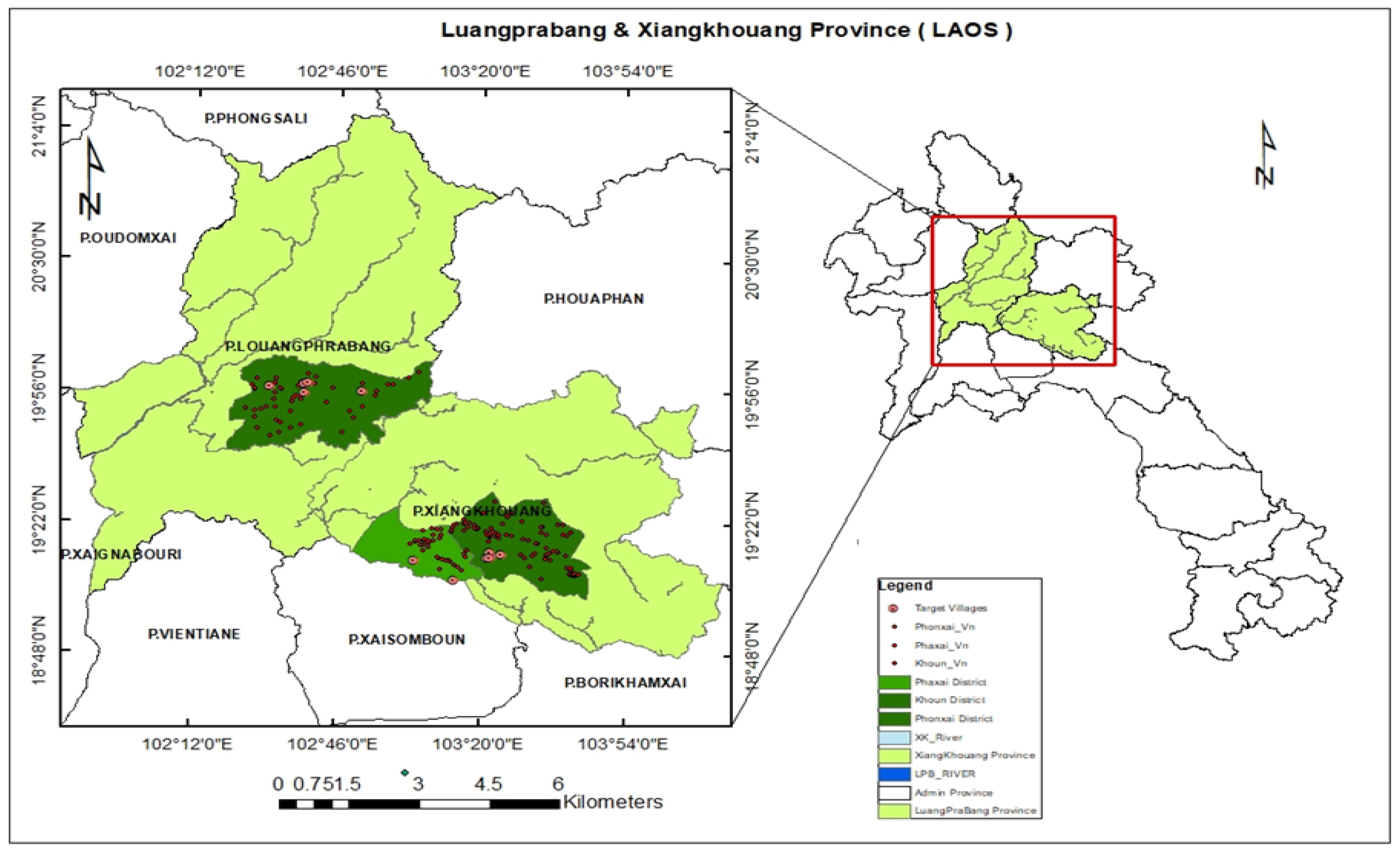
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Data Collection
3.2.2. Description and Variables Measurement
| Variables | Description | Hypothesis | Data source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | The gender of the household head (male or female) | (+) | [38,39] |
| Age | Age is identified based on the age of the household head, whether they are adults or young (in years) | (-) | [41,42] |
| Marital status | Marital status indicates whether an individual is married, single, separated, widowed, or divorced | (+) | [38] |
| Educational attainment | The school grade of the household head | (+/-) | [43,48] |
| Number of family members | The number of household members (persons) | (+/-) | [44,45] |
| Main occupation | The activities typically practiced include farming, working as laborers, holding government positions, or working as businessmen | (+) | [46,48] |
| Total family monthly income (kip) | Sources of family income that are representative of total income obtained from household activities | (+) | [41,47,48] |
| Total land owned (ha) | The size of the farm (in hectares) depends on the landowner | (+) | [48,49] |
| Distance from forest to home (km) | The measurement of distance from one area to another area | (+/-) | [43,44,50,52] |
| Member of village forest committee | Participants of the community forest committee work on forest management units | (+/-) | [44,53] |
| Degree of information | Regarding availability and sources of information | (+) | [48,54] |
| Resource dependence | The majority of the household income comes from forest resources | (+) | [36,37] |
| Knowledge | It measures the level of scores | (+) | [54,55] |
| Recognition/attitude | It measures on a ranking scale of scores | (+) | [56,57] |
3.2.3. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Socio-Demographic Characteristics of Youth
4.2. Utilization of Forest Resources by Youth
4.3. Impact of Socio-Demographic Factors on Forest Conservation Knowledge and Recognition.
4.4. Impact of Socio-Demographic Factors on Sustainable Forest Management Behavior
5. Discussion
5.1. Sustainable Use Behavior
5.2. Conservation Behavior
5.3. Policy Acceptance Behavior
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sophathilath, P. , Assessment of the contribution of forestry to poverty alleviation in Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Making forestry work for the poor: Assessment of the contribution of forestry to poverty alleviation in Asia and the Pacific. 2010, 175-208.
- Phongoudome, C. and K. Sirivong, Forest restoration and rehabilitation in Lao PDR. Keep Asia Green. 2007. 1.
- Chanthirath, K. Towards Sustainable Forest Management in Lao P.D.R. 1999; Available from: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Towards-Sustainable-Forest-Management-in-Lao-Pd/faa348cb37fae92e6dfa2f73ab1c909a39861652#paper-header.
- Lao, P. , Production Forestry Policy. Status and issues for dialogue. 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lao, P. , Forestry Strategy to the Year 2020 of Lao PDR. 2005, Vientiane, Lao PDR.
- Department of Forestry, Report of Forest cover in nationwide of Department of Forestry, Ministry of agriculture and forestry, D.o. Forestry, Editor. 2010.
- Thephavanh, M. , et al., Spatial changes in the use of non timber forest products in four villages of Viengkham district, Luang Prabang province, Lao PDR. Lao Journal of Agriculture and Forestry. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Manivong, K. and P. Sophathilath, Status of community based forest management in Lao PDR. NAFRI and RECOFT. 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, L. Ziegler, and T. Grever, Utilization of forest products and environmental services in Bach Ma National Park, Vietnam. German Development Service, Hanoi Vietnam. 2002.
- Costenbader, John, et al. Drivers affecting forest change in the greater mekong subregion (GMS): an overview. FAO: Rome, Italy. 2015.
- Lamb, D. and D. Gilmour, Rehabilitation and restoration of degraded forests. Issues in forest conservation. 2003, IUCN, Gland (Suiza) WWF, Gland (Suiza).
- Kim, S.B. and O. Alounsavath, Forest policy measures influence on the increase of forest cover in northern Laos. Forest science and technology. 2015, 11, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.A. Lao PDR: Environmental Profile - Rainforests – Mongabay. 1994 [cited 2016 15 December,]; Available from: https://rainforests.mongabay.com/20laos.htm.
- Mori, T. , Sustainable Forest Management in Laos. 2013.
- Kennedy, J.J., J. W. Thomas, and P. Glueck, Evolving forestry and rural development beliefs at midpoint and close of the 20th century. Forest Policy and Economics. 2001, 3, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, W.A. and T. Knoke, Sustainable development and sustainable forestry: analogies, differences, and the role of flexibility. European Journal of Forest Research. 2010, 129, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A., T. Noguchi, and R. Pothitan, Community forest management in Thailand: current situation and dynamics in the context of sustainable development. New Forests. 2006, 31, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.R., G. C. Muangirwa, and N.K. Tiwary, A review of the role of institutions in participatory forest management in Tanzania. International Journal of Society Systems Science. 2019, 11, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boedhidartono, A.K. , Can community forests be compatible with biodiversity conservation in Indonesia? Land 2017, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steg, L. and C. Vlek, Encouraging pro-environmental behaviour: An integrative review and research agenda. Journal of environmental psychology. 2009, 29, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmi, N. and S. Arnon, The role of future orientation in environmental behavior: Analyzing the relationship on the individual and cultural levels. Society & Natural Resources. 2014, 27, 1304–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Mustalahti, I. and J.F. Lund, Where and how can participatory forest management succeed? Learning from Tanzania, Mozambique, and Laos. Society & Natural Resources. 2009, 23, 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, P. , et al., The recognition of forest rights in Latin America: Progress and shortcomings of forest tenure reforms. Society & Natural Resources. 2012, 25, 556–571. [Google Scholar]
- Frisk, E. and K.L. Larson, Educating for sustainability: Competencies & practices for transformative action. Journal of Sustainability Education. 2011, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gotschi, E. , et al., The role of knowledge, social norms, and attitudes toward organic products and shopping behavior: Survey results from high school students in Vienna. The Journal of Environmental Education. 2009, 41, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjade, M. Schanz, and C. Leeuwis, Discourses of information in community forest user groups in Nepal. International Forestry Review. 2006; 8, 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, M.L.S. , et al., Facilitating access to biodiversity information: A survey of users’ needs and practices. Environmental management. 2014, 53, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.D. , Human information behavior. Informing science. 2000, 3, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, N.J. , et al., Cases, scripts, and information-seeking strategies: On the design of interactive information retrieval systems. Expert systems with applications. 1995, 9, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, N.V. and S. Noriko, Forest allocation policy and level of forest dependency of economic household groups: a case study in Northern Central Vietnam. Small-scale Forestry. 2008, 7, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 31.
- Jain, P. and H. Sajjad, Household dependency on forest resources in the Sariska Tiger Reserve (STR), India: Implications for management. Journal of Sustainable Forestry. 2016, 35, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N., X. Hu, and J. Hussain, The dependency of rural livelihood on forest resources in Northern Pakistan's Chaprote Valley. Global Ecology and Conservation. 2020, e01001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, M. , et al., Dependence on forest resources and tropical deforestation in Ghana. Environment, Development and Sustainability. 2009, 11, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yali, W., T. T. Htun, and A.C.K. Ko, Assessment of forest resources dependency for local livelihood around protected area: a case study in Popa Mountain Park, Central Myanmar. International Journal of Sciences. 2017, 6, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, M., S. Nagata, and M. Adhikari, Rural household and forest: an evaluation of household’s dependency on community forest in Nepal. Journal of Forest Research. 2004, 9, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatiso, T.T. , Households’ dependence on community forest and their contribution to participatory forest management: evidence from rural Ethiopia. Environment, Development and Sustainability. 2019, 21, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly-Lingani, P. , et al., Factors influencing people's participation in the forest management program in Burkina Faso, West Africa. Forest Policy and Economics. 2011, 13, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthiga, P.M. , Understanding local communities’ perceptions of existing forest management regimes of a Kenyan rainforest. International Journal of Social Forestry. 2008, 1, 145–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, B., P. Mukherjee, and R.N. Bhattacharya, Attitudes and cooperation: does gender matter in community-based forest management? Environment and Development Economics. 2017, 22, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolisca, F. , et al., Factors influencing farmers’ participation in forestry management programs: A case study from Haiti. Forest ecology and management. 2006, 236, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A. and B. Behera, Household participation and effects of community forest management on income and poverty levels: Empirical evidence from Bhutan. Forest Policy and Economics. 2015, 61, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, B., S. Di Falco, and J.C. Lovett, Household characteristics and forest dependency: evidence from common property forest management in Nepal. Ecological economics. 2004, 48, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, B.B.K. , et al., Community forestry in the hills of Nepal: Determinants of user participation in forest management. Forest Policy and Economics. 2013, 30, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, S., M. Woldetsadik, and F. Senbeta, Forest users’ level of participation in a participatory forest management program in southwestern Ethiopia. Forest science and technology. 2017, 13, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannat, M., M. K. Hossain, and M. Uddin, Socioeconomic factors of forest dependency in developing countries: lessons learned from the Bandarban hill district of Bangladesh. Am. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Gunatilake, H. , Factors influencing peripheral villager dependency on forest resources use in the Knuckles forest range. Sri Lankan Journal of Agricultural Economics. 1994, 2, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lestari, S., K. Kotani, and M. Kakinaka, Enhancing voluntary participation in community collaborative forest management: A case of Central Java, Indonesia. Journal of environmental management. 2015, 150, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwembe, U.L. , Impact of conservation and development interventions on livelihoods and forest resources management in Pangani River Basin: a case of Muheza District, Tanzania. 2008, Sokoine University of Agriculture.
- Htun, N.Z., N. Mizoue, and S. Yoshida, Changes in determinants of deforestation and forest degradation in Popa Mountain Park, Central Myanmar. Environmental management. 2013, 51, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon, M.S. , et al., Factors affecting deforestation and forest degradation in selectively logged production forest: A case study in Myanmar. Forest Ecology and Management. 2012, 267, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giliba, R.A. , et al., The influence of socio-economic factors on deforestation: a case study of the Bereku Forest Reserve in Tanzania. Journal of Biodiversity. 2012, 2, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togolai, P. , Factors influencing effectiveness of Joint Forest Management Approach in Conservation and Management of Forest Reserves: A Case of Kimboza Forest Reserve in Morogoro, Tanzania. 2015, The University of Dodoma.
- Apipoonyanon, C. , et al., Factors influencing household participation in community forest management: evidence from Udon Thani Province, Thailand. Journal of Sustainable Forestry. 2020, 39, 184–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macura, B. , et al., Local community attitudes toward forests outside protected areas in India. Impact of legal awareness, trust, and participation. Ecology and society. 2011, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratsimbazafy, C.L., K. Harada, and M. Yamamura, Forest resources use, attitude, and perception of local residents towards community based forest management: Case of the Makira Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) Project, Madagascar. Journal of Ecology and the Natural Environment. 2012, 4, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, M.V. , et al., Evolutionarily enlightened management. Biological Conservation. 2003, 111, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eneji, C. , et al., Factors Influencing Gender Participation in the Exploitation and Management of Forest Resources in the Protected Areas of Cross River National Park Enclave Communities, Nigeria. Journal of Resources Development and Management. 2015, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Atmiş, E. , et al., Factors affecting women's participation in forestry in Turkey. Ecological Economics. 2007, 60, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmiş, E. , et al., Factors affecting forest cooperative's participation in forestry in Turkey. Forest Policy and Economics. 2009, 11, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lise, W. , Factors influencing people’s participation in forest management in India. Ecological economics. 2000, 34, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sam, H., K. Nanthavong, and P.J. Kessler, Trees of Laos and Vietnam: A field guide to 100 economically or ecologically important species. Blumea-Biodiversity, Evolution and Biogeography of Plants. 2004, 49, 201–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketphanh, J.F.a.S. The Importance of Non-Timber ForestProducts in the Lao Uplands. 2005. Available online: http://lad.nafri.org.la/fulltext/LAD010320071064.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Phounvisouk, L., Z. Ting, and N.C. Kiat, Non-timber forest products marketing: Trading Network of trader and market chain in Luang Namtha Province, Lao PDR. IOSR. Journal of Humanities and Social Science. 2013, 18, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiyegunhi, L., B. Oppong, and M. Senyolo, Socio-economic factors influencing mopane worm (Imbrasia belina) harvesting in Limpopo Province, South Africa. Journal of forestry research. 2016, 27, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunatilake, H. , The role of rural development in protecting tropical rainforests: evidence from Sri Lanka. Journal of Environmental management. 1998, 53, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, M. and B. Behera, Determinants of household collection of non-timber forest products (NTFPs) and alternative livelihood activities in Similipal Tiger Reserve, India. Forest Policy and Economics. 2016, 73, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiyegunhi, L. and G. Fraser, Vulnerability and poverty dynamics in rural areas of Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Ghana Journal of Development Studies. 2011, 8, 84–100. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, H.W. , et al., Assessing the potential for forest management practitioner participation in climate change adaptation. Forest Ecology and Management. 2016, 360, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, S.A. and D. Teketay, Perceptions and attitudes of local people towards participatory forest management in Tarmaber District of North Shewa Administrative Zone, Ethiopia: the case of Wof-Washa forests. Ecological Processes. 2017, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poung-ngamchuen, J. , et al., Development of indicators affecting sustainability of community forest management in upper northern Thailand. International Journal of Social Science and Humanity. 2017, 7, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly-Lingani, P. , et al., Determinants of access to forest products in southern Burkina Faso. Forest Policy and Economics 2009, 11, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashu, K. and O. Aminu, Participatory forest management and smallholder farmers’ livelihoods improvement nexus in Northwest Ethiopia. Journal of Sustainable Forestry. 2019, 38, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eneji, C. , et al., Factors Influencing Gender Participation in Forest Resources Management in the Cross River National Park Enclave Communities, Nigeria. Journal of Environment Protection and Sustainable Development. 2015, 1, 234–244. [Google Scholar]
| Socio-demographiccharacteristics | Phonsay (n=110) | Khoun (n=110) | Phaxay (n=110) | Total (n=330) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | % | Frequency | % | Frequency | % | Frequency | % | |
| Age | ||||||||
| < 20 | 5 | 1.52 | 3 | 0.91 | 12 | 3.63 | 20 | 6.06 |
| 20–29 | 41 | 12.42 | 65 | 19.70 | 61 | 18.48 | 167 | 50.61 |
| > 30 | 64 | 19.39 | 42 | 12.73 | 37 | 11.21 | 143 | 43.33 |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Male | 71 | 21.51 | 62 | 18.79 | 87 | 26.36 | 220 | 66.67 |
| Female | 39 | 11.81 | 48 | 14.54 | 23 | 6.97 | 110 | 33.33 |
| Educational attainment | ||||||||
| Uneducated | 21 | 6.36 | 45 | 13.64 | 24 | 7.27 | 90 | 27.27 |
| Primary school | 56 | 16.97 | 26 | 7.88 | 32 | 9.70 | 114 | 34.55 |
| Secondary school | 26 | 7.88 | 29 | 8.79 | 37 | 11.21 | 92 | 27.88 |
| Upper secondary and higher, diploma or equivalent and more than | 7 | 2.12 | 10 | 3.03 | 17 | 5.15 | 34 | 10.30 |
| Marital status | ||||||||
| Married, Widow | 103 | 31.21 | 103 | 31.21 | 93 | 28.18 | 299 | 90.61 |
| Single | 7 | 2.12 | 7 | 2.12 | 17 | 5.15 | 31 | 9.39 |
| Family members | ||||||||
| < 5 | 38 | 11.51 | 18 | 5.45 | 27 | 8.18 | 83 | 25.15 |
| 5–10 | 66 | 20.00 | 74 | 22.42 | 72 | 21.81 | 212 | 64.24 |
| >10 | 6 | 1.82 | 18 | 5.45 | 11 | 3.33 | 35 | 10.61 |
| Economic | ||||||||
| N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Yes | 110 | 33.33 | 110 | 33.33 | 110 | 33.33 | 330 | 100 |
| Monthly income (KIP) | ||||||||
| >1600001 | 14 | 4.24 | 40 | 12.12 | 8 | 2.42 | 62 | 18.78 |
| 1100001–1600000 | 21 | 6.36 | 13 | 3.94 | 7 | 2.12 | 41 | 12.42 |
| 700001–1100000 | 34 | 10.30 | 28 | 8.48 | 15 | 4.55 | 77 | 23.33 |
| 400000–700000 | 28 | 8.48 | 18 | 5.45 | 24 | 7.27 | 70 | 21.2 |
| < 400000 | 13 | 3.94 | 11 | 3.33 | 56 | 16.97 | 80 | 24.24 |
| Occupation | ||||||||
| Government officers, small businesses, and workers | 10 | 3.03 | 28 | 8.48 | 6 | 1.82 | 44 | 13.34 |
| Shifting cultivator | 59 | 17.88 | 40 | 12.12 | 47 | 14.24 | 146 | 44.24 |
| Distance | ||||||||
| < 0.025 | 20 | 6.06 | 8 | 2.42 | 28 | 8.48 | 56 | 16.97 |
| 0.025–0.5 | 48 | 14.54 | 67 | 20.30 | 81 | 24.54 | 196 | 59.39 |
| 0.51–1.0 | 1 | 0.30 | 30 | 9.09 | 1 | 0.30 | 32 | 9.70 |
| >1.0 | 41 | 12.42 | 5 | 1.52 | 0 | 0 | 46 | 13.94 |
| Member of village forest committee | ||||||||
| No | 90 | 27.27 | 95 | 28.79 | 103 | 31.21 | 288 | 87.27 |
| Yes | 20 | 6.06 | 15 | 4.55 | 3 | 0.91 | 38 | 11.52 |
| Total own land | ||||||||
| < 0.02 | 65 | 19.70 | 11 | 3.33 | 17 | 5.15 | 93 | 28.18 |
| 0.02–0.05 | 19 | 5.76 | 22 | 6.67 | 37 | 11.21 | 78 | 23.64 |
| 0.05-0.2 | 8 | 2.42 | 30 | 9.09 | 53 | 16.06 | 91 | 27.57 |
| > 0.2 | 15 | 4.55 | 47 | 14.24 | 3 | 0.91 | 65 | 19.7 |
| Species of NTFPs | Utilization (n=330) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sell | Consumption | Medicine | Instruments/ Material | |||||
| Frequency | % | Frequency | % | Frequency | % | Frequency | % | |
| Plants | ||||||||
| Vegetables | 25 | 7.58 | 228 | 69.09 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mushroom | 19 | 5.76 | 256 | 77.58 | 4 | 1.21 | 0 | 0 |
| Rattan | 43 | 13.03 | 148 | 44.85 | 1 | 0.30 | 27 | 8.18 |
| Broussonetia papyrifera Vent | 78 | 23.64 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32 | 9.70 |
| Persea kurzii Kosterm | 75 | 22.73 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 2.73 |
| Dioscorea filiformis | 3 | 0.91 | 15 | 4.55 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.30 |
| Dioscorea hispida | 3 | 0.91 | 25 | 7.58 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Arenga westerhoutii Griff. | 47 | 14.24 | 43 | 13.03 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.61 |
| Brooms grass (Roxb) | 98 | 29.70 | 18 | 5.45 | 2 | 0.61 | 0 | 0 |
| Other (tubers; bamboo hoot) | 107 | 32.42 | 34 | 10.30 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 2.42 |
| Herbs | ||||||||
| Cardamom (Amomum sp.) | 30 | 9.09 | 12 | 3.64 | 18 | 5.45 | 2 | 0.61 |
| Medicine vine | 13 | 3.94 | 1 | 0.30 | 1 | 0.30 | 2 | 0.61 |
| Curcuma longa L. | 1 | 0.30 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1.52 | 0 | 0 |
| Molineria latifolia | 2 | 0.61 | 1 | 0.30 | 5 | 1.52 | 2 | 0.61 |
| Others | 12 | 3.64 | 3 | 0.91 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1.52 |
| Wild animals | ||||||||
| Tiger | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.61 | 1 | 0.30 | 1 | 0.30 |
| Muntja deer | 3 | 0.91 | 129 | 39.09 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.61 |
| Wild boar | 15 | 4.55 | 180 | 54.55 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.61 |
| Deer | 2 | 0.61 | 8 | 2.42 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.61 |
| Monkey | 2 | 0.61 | 24 | 7.27 | 1 | 0.30 | 0 | 0 |
| Pangolin | 1 | 0.30 | 4 | 1.21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Common palm civet | 12 | 3.64 | 152 | 46.06 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.61 |
| King cobra | 1 | 0.30 | 23 | 6.97 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Turtle | 6 | 1.82 | 44 | 13.33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Squirrel | 2 | 0.61 | 74 | 22.42 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.91 |
| Wood | ||||||||
| Rosewood | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.30 |
| Dalbergia cultrata Benth. | 3 | 0.91 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 10.00 |
| Afzeliaxylocarpa(Kurz) Craib | 1 | 0.30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 6.36 |
| Alstoniascholaris (L.) R.Br. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 8.48 |
| Maidaeng (local name) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 38 | 11.52 |
| Mailongleng (local name) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.30 | 12 | 3.64 |
| Maimanpa (local name) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 1.82 |
| Dalbergiacultrata Grahamex Benth. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1.21 |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 230 | 69.70 |
| Variables | Conservation knowledge | Conservation recognition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Beta | p | B | Beta | p | |
| Sex | 0.103 | 0.059 | 0.334 | 0.222 | 0.127 | 0.026 |
| Age | -0.008 | -0.047 | 0.437 | -0.006 | -0.038 | 0.501 |
| Marital status | -0.023 | -0.008 | 0.895 | -0.130 | -0.046 | 0.420 |
| Educational attainment | 0.109 | 0.139 | 0.026 | 0.126 | 0.162 | 0.005 |
| Number of families | 0.009 | 0.026 | 0.650 | -0.005 | -0.014 | 0.790 |
| Main occupation | -0.041 | -0.025 | 0.657 | 0.119 | 0.072 | 0.168 |
| Total family monthly income (kip) | 0.000 | 0.009 | 0.886 | 0.000 | -0.123 | 0.033 |
| Total land owned (ha) | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.953 | -0.042 | -0.123 | 0.027 |
| Distance from forest to home (km) | 0.049 | 0.052 | 0.365 | 0.098 | 0.103 | 0.052 |
| Member of village forest committee | 0.101 | 0.039 | 0.500 | 0.047 | 0.018 | 0.736 |
| Degree of information | 0.070 | 0.112 | 0.064 | 0.158 | 0.253 | 0.000 |
| Resource dependence | 0.013 | 0.028 | 0.614 | -0.038 | -0.083 | 0.113 |
| Constant | 3.174 | 0.000 | 3.346 | 0.000 | ||
| R square | 0.059 | 0.191 | ||||
| Adjusted R square | 0.023 | 0.161 | ||||
| F | 1.646 | 6.243 | ||||
| Sig | 0.078 | 0.000 | ||||
| Variables | Sustainable use behavior | Conservation behavior | Policy acceptance behavior | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Beta | p | B | Beta | p | B | Beta | p | |
| Knowledge | -0.010 | -0.015 | 0.775 | 0.132 | 0.121 | 0.026 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.829 |
| Recognition | -0.040 | -0.061 | 0.296 | 0.209 | 0.191 | 0.001 | 0.384 | 0.409 | 0.000 |
| Degree of information | 0.015 | 0.036 | 0.534 | 0.098 | 0.143 | 0.015 | 0.081 | 0.139 | 0.010 |
| Resource dependence | 0.113 | 0.376 | 0.000 | 0.023 | 0.047 | 0.381 | -0.001 | -0.003 | 0.953 |
| Distance from forest to home (km) | 0.010 | 0.016 | 0.772 | 0.060 | 0.058 | 0.287 | 0.020 | 0.023 | 0.645 |
| Member of village forest committee | -0.010 | -0.006 | 0.916 | 0.019 | 0.007 | 0.902 | 0.212 | 0.088 | 0.082 |
| Sex | -0.031 | -0.027 | 0.643 | -0.058 | -0.031 | 0.598 | 0.181 | 0.110 | 0.039 |
| Age | -0.002 | -0.021 | 0.713 | -0.011 | -0.064 | 0.261 | 0.005 | 0.032 | 0.537 |
| Marital status | -0.066 | -0.035 | 0.540 | -0.031 | -0.010 | 0.864 | -0.312 | -0.118 | 0.028 |
| Educational attainment | 0.084 | 0.165 | 0.006 | 0.102 | 0.120 | 0.045 | 0.034 | 0.046 | 0.399 |
| Number of family members | 0.007 | 0.033 | 0.537 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.784 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.866 |
| Main occupation | 0.072 | 0.066 | 0.208 | -0.282 | -0.155 | 0.004 | -0.064 | -0.041 | 0.400 |
| Total family monthly income (kip) | 0.000 | -0.023 | 0.692 | 0.000 | -0.051 | 0.383 | 0.000 | -0.009 | 0.870 |
| Total land owned (ha) | 0.009 | 0.040 | 0.475 | 0.035 | 0.095 | 0.093 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.853 |
| Constant | 1.874 | 0.000 | 1.236 | 0.005 | 1.433 | 0.000 | |||
| R square | 0.181 | 0.176 | 0.301 | ||||||
| Adjusted R square | 0.145 | 0.139 | 0.270 | ||||||
| F | 4.985 | 4.809 | 9.698 | ||||||
| Sig | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





