1. Introduction
The integration of complex networks with evolutionary algorithms (EAs) has improved the performance in solving optimization problems [
1]. The application of network structures such as degree distributions, page rank and clustering coefficient can prevent premature convergence and enhance solution exploration [
2,
3,
4]. These complex network properties allow a deeper understanding of population dynamics, leading to better performance in optimization tasks [
5]. The integration of complex network with EAs has provided significant improvements in adaptability, efficiency, and robustness across a range of applications, including logistics [
6,
7], community detection [
8], and industrial scheduling [
9]. These methods continue to evolve, offering promising directions for future research in optimization.
The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) is one of the most widely studied optimization problems, serving as an ideal test case for applying evolutionary algorithms (EAs). Researchers have explored various network-based approaches to improve the efficiency and convergence of EAs in TSP. In [
10] the authors leveraged the random connectivity patterns of Erdős–Rényi networks, which promote diverse population crossovers, to guide evolutionary algorithms in TSP, leading to significant improvements in convergence rates and execution time. A comprehensive computational study of TSP, offering essential methods for both exact and heuristic algorithms is described in [
11]. Moreover, Laporte reviewed TSP solutions, highlighting exact and approximate algorithms[
12], while Triana et al. [
13] applied complex networks to further enhance TSP-solving capabilities through evolutionary algorithms, improving solution quality and execution time.
Beyond TSP, evolutionary algorithms have also been used in production and scheduling problems. In [
14], genetic algorithms have been proposed for optimizing precedence-constrained production sequencing, demonstrating the effectiveness of genetic approaches in industrial settings. Similarly, [
15] introduced a hybrid optimization algorithm using biological strategies like deer hunting to improve the performance in large-scale TSP instances. Furthermore, complex networks play an essential role in enhancing evolutionary algorithms across various applications [
3,
4,
5].
More recently, the literature has revealed that bio-inspired computation has opened new avenues for optimization research. Del Ser et al. [
16] reviewed bio-inspired algorithms, summarizing trends and future directions in evolutionary computation, while Bucheli et al. [
13,
17] demonstrated how complex networks can guide EAs to solve complex optimization problems like TSP, leading to faster and more reliable solutions. Jamakovic & Van Mieghem explored algebraic connectivity as a means of improving network resilience, a concept that has been applied in evolutionary algorithm-guided networks [
18]. In other optimization contexts, Osaba et al [
5] introduced a discrete water cycle algorithm for solving both symmetric and asymmetric TSP instances, further contributing to the efficiency of EAs in solving large-scale optimization problems [
19]. Similarly, in [
20], the authors improved formulations for minimizing flow costs in Hamiltonian cycles, providing new strategies for tackling optimization challenges.
The literature review reveals a comparative analysis of factors influencing the performance of evolutionary algorithms (EAs) within the context of network structures and their application to problems like the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). TSP application, premature convergence prevention, and network structures stand out as the most critical topics. Other notable elements include bio-inspired computation, heuristic optimization methods, community detection, scale-free networks for EAs, and solution exploration enhancement, all contributing similarly to the literature. Conversely, factors such as algebraic connectivity in networks and random graph theory are lesser considered. These findings highlight the importance of integrating complex network theory with optimization techniques and bio-inspired computation to enhance exploration, mitigate premature convergence, and optimize solutions for computationally intensive tasks such as TSP.
Although previous studies have made substantial efforts and significant advancements in enhancing evolutionary algorithms (EAs) for the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP), several key issues remain unaddressed. This paper analyzes the influence of a network’s degree structure on the performance of evolutionary algorithms in the context of the TSP. The main contribution of this work is the evaluation of different network structures and their effects on the behavior of EAs for the TSP. Notably, the Harary graph with k=2 demonstrated exceptional performance, reducing execution times by up to sevenfold compared to traditional evolutionary approach. While the balanced tree proved nearly five times more efficient than traditional algorithm, probabilistic network-based algorithms, although significantly better than traditional approach, still lag behind the efficiency of Harary graphs.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 presents the proposed method for evaluating the impact of network degree distribution on TSP performance and outlines the experimental setup designed to ensure the robustness of our approach.
Section 3 provides the results of the evaluation, while
Section 4 discusses the implications of these findings. Finally,
Section 5 offers the conclusions and directions for future research.
2. Materials and Methods
The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) is a well-known challenge in optimization, where the objective is to determine the most efficient Hamiltonian cycle—the route with the shortest total distance—that a salesman can take to visit a set of n cities exactly once, returning to the starting city. Since no universal algorithm can solve all instances of the problem efficiently, it is classified as NP-hard [
12,
21]. Attempts to find the shortest tour involve identifying a Hamiltonian cycle, where the initial vertex is repeated at the end to complete the cycle, in a Hamiltonian graph G. If successful, the result is a list, with the first element indicating the vertex count of G [
20].
One approach to tackling the Traveling Salesman Problem is through the use of evolutionary algorithms. These algorithms mimic the process of natural selection by iterative evolving a population of candidate solutions, selecting the fittest, and applying crossover and mutation operations to explore the solution space. Although they do not guarantee an optimal solution, evolutionary algorithms are often effective in finding near-optimal solutions for NP-hard problems, like the TSP, in a reasonable amount of time [
15,
22].
Despite the contributions of the aforementioned studies, several open research questions remain. One critical area that has yet to be fully explored is the specific principles of complex networks that influence the performance of evolutionary algorithms. This paper seeks to address the following research question: How does the degree distribution of a network influence the performance of the evolutionary algorithms? Understanding the relationship between network structure and algorithmic performance could provide valuable insights for optimizing evolutionary algorithms in solving complex problems like the Traveling Salesman Problem.
According to [
11], the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) can be mathematically described as follows: Let
be a complete undirected graph, where
V is the set of cities and E is the set of edges representing the connections between the cities. Each edge
has a non-negative weight or cost
associated with it, representing the distance or travel cost between cities
u and
v. We aim to find a Hamiltonian cycle
C in G that visits each vertex in V exactly once and returns to the starting vertex. A Hamiltonian cycle is a closed path that passes through every vertex in a graph exactly once, except for the starting and ending vertices which coincide.
The objective function of the TSP (F) is to minimize the total cost or length of the Hamiltonian cycle C. This can be represented as the sum of the weights of the edges in C:
for all e ∈ C
Subject to:
Each vertex v∈ V must be visited exactly once.
The cycle C must be closed, i.e., it starts and ends at the same vertex.
The cycle C must not contain any subcycles, i.e., it must be simple.
2.1. The Networks Approach
Regular networks, such as rings, lattices, or trees, display a uniform structure where each node adheres to the same interconnection pattern, resulting in homogeneous connectivity. In contrast, both random networks, exemplified by the Erdős–Rényi model, and scale-free networks, like those produced by the Barabási–Albert model, lead to heterogeneous connectivity, although through different mechanisms. Erdős–Rényi networks form random connections between nodes, while Barabási–Albert networks follow a preferential attachment process[
11]. In this work, the networks used can be classified into two main categories: probabilistic and regular networks. Erdős-Rényi random networks exemplify probabilistic networks, where connections between pairs of nodes are established with a fixed probability. This results in a degree distribution that approximates a Poisson distribution. Consequently, most nodes have a similar number of connections, leading to a relatively homogeneous degree distribution [
23]. In the random network model, the interaction partners of a node are selected at random. However, in most real-world networks, new nodes tend to connect to nodes with higher connectivity, a phenomenon known as preferential attachment. Barabási-Albert networks serve as a model where the preferential attachment is a probabilistic process where a new node can connect to any node in the network, regardless of whether it is a hub or has just one link [
24]. However, the probability of connecting to a node increases with its degree, meaning a node with more connections is more likely to attract new links than one with fewer. The principle of preferential attachment leads to a scale-free degree distribution. This distribution features a few highly connected nodes (hubs) alongside a majority of nodes with relatively few connections.
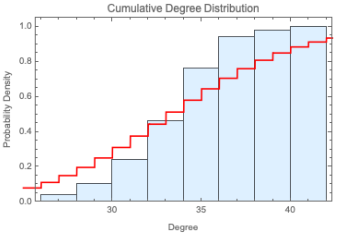
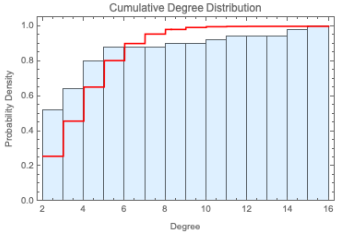
Table 1. shows the networks and corresponding degree distributions.
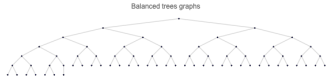
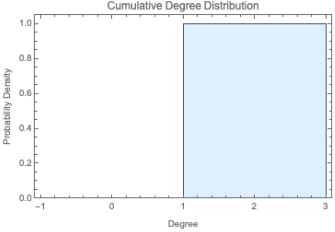
Balanced tree graphs, often referred to as complete
r-ary trees, are a type of regular network characterized by a predictable degree distribution governed by their hierarchical structure. In these trees, each node has a maximum degree defined by the branching factor
r, which specifies the number of children each internal node can have. As connected, acyclic graphs, balanced trees do not contain cycles, adhering to the fundamental property that the number of edges in a tree with
n nodes is always
[
25]. The nodes within these trees represent hierarchical relationships, ranging from simple family trees to more complex structures utilized in computer science, such as data organization and search algorithms. The balanced nature of these trees ensures that all leaf nodes are equidistant from the root, maintaining an efficient structure for various applications. Overall, while balanced trees are among the simplest forms of graphs, their rich structural properties enable a wide array of practical uses.
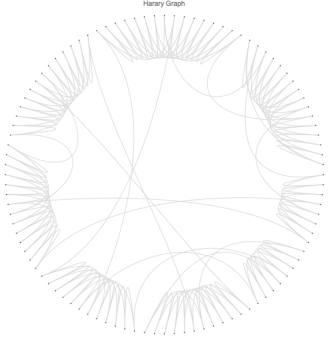
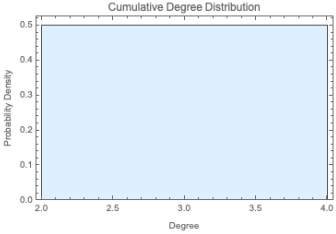
Lastly, Harary graphs, denoted as
, represent a class of
k-connected graphs that minimize the number of edges for a given node connectivity
k and a specified number of nodes
n. These graphs can also be viewed as regular graphs that exhibit a homogeneous degree distribution, which can be finely tuned using the parameter
r in the
r-p model of Harary. This model enables the exploration of various connectivity configurations while ensuring high efficiency in information transmission. The Harary graph achieves the smallest possible number of edges, mathematically expressed as
, where
denotes the ceiling function. Furthermore, when either
n or
k is even, the resulting graph
forms a circulant graph, while
corresponds to the complete graph
.
Table 2. shows the network and corresponding degree distributions. This classification highlights the intrinsic link between the structural properties of networks and their connection formation processes, along with the resultant degree distributions, thereby providing valuable insights into the design of evolutionary algorithms.
2.2. The Evolutionary Algorithm and Evolutionary Algorithm-N
In [
5], Osaba and his colleagues highlight that heuristic algorithms are frequently used to solve the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). Prior studies have introduced various complex network characteristics of the TSP, such as community detection [
3] and pageRank distance [
4]. Moreover, researchers have examined the features of small-world networks, including the clustering coefficient and average path length [
13].
A traditional evolutionary algorithm operates in several stages: it begins with the creation of a population of candidate solutions, followed by processes such as selection, crossover, recombination, mutation, replacement, and termination [
26]. The first stage, initialization, generates a random population of individuals to serve as the initial set of solutions. Each individual’s quality or performance is then assessed through a fitness function. During the selection phase, individuals with higher fitness scores are chosen to become parents for the next generation, typically through probabilistic methods such as roulette wheel or tournament selection. These selected parents undergo recombination, or crossover, to produce offspring. Recombination, analogous to genetic crossover in biology, is a key operator in evolutionary algorithms. Offspring are then subjected to mutations, introducing random variations to promote diversity. Finally, the offspring replace some individuals in the population, maintaining a consistent population size. The process continues until a predefined stopping criterion is met, such as reaching a set number of generations or achieving a satisfactory solution.
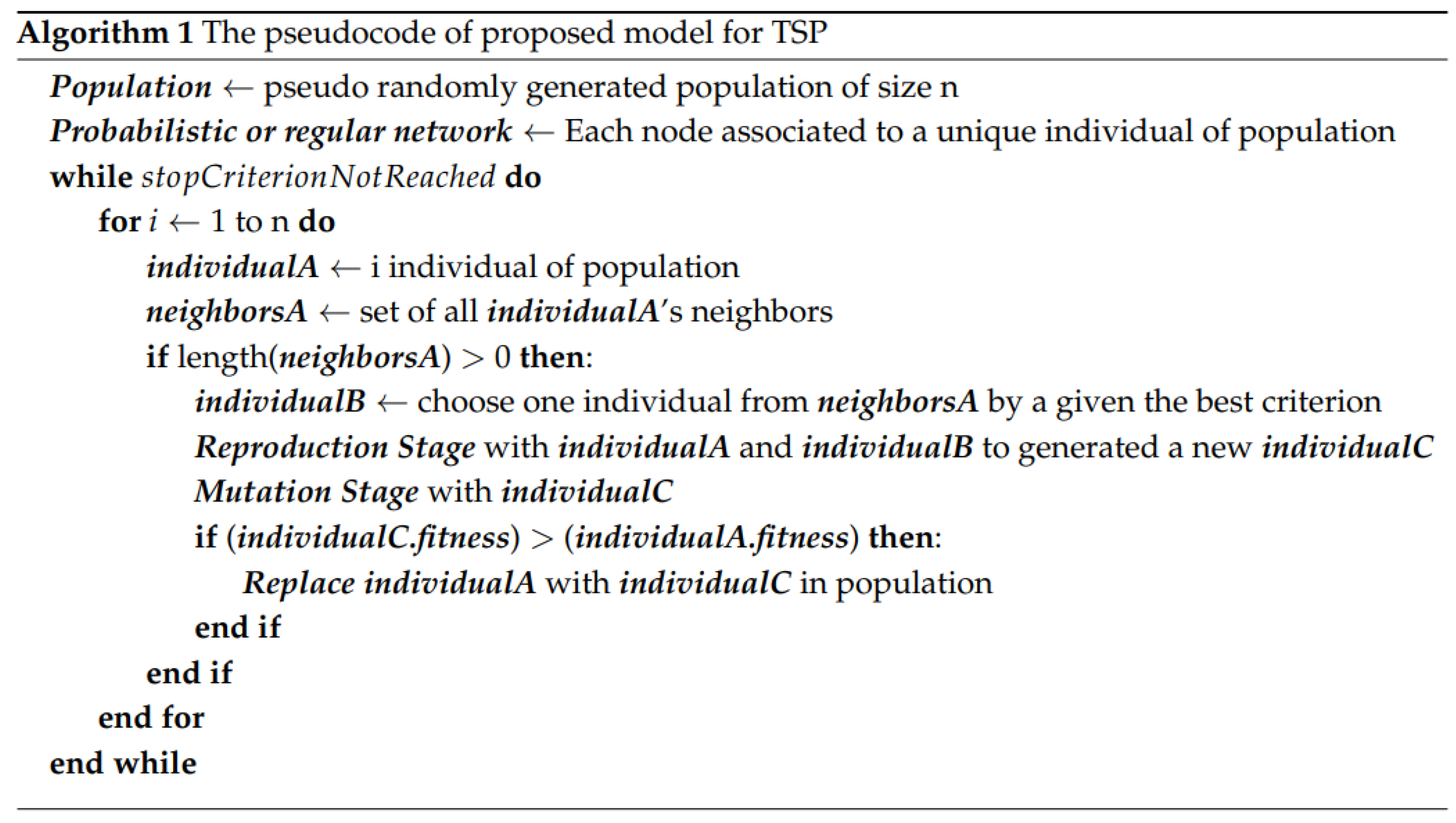
The evolutionary algorithm-N enhances traditional evolutionary processes by incorporating the structure of networks, specifically Erdős–Rényi, Barabási-Albert, Balanced tree, and Harary graphs. It is incorporated into the initialization, selection, and recombination stages. In contrast to conventional approaches that rely solely on random processes, the evolutionary algorithm-N leverages the properties of networks to guide these operations. Thus, in the initialization phase, the population of solutions is randomly assigned to nodes in a network, where each node represents a potential solution, and the connections between nodes dictate how selection and recombination occur. The selection process is driven by the degree distribution of the network, meaning that individuals (solutions) connected to more highly connected nodes are more likely to be chosen for reproduction. This network-guided selection aims to increase the exploration of the solution space by exploiting the topological properties of the network.
This work investigates four types of networks to guide evolutionary processes (Erdős Rény, Barabási-Albert, Balanced tree, and Harary networks). Each network type is constructed using distinct mechanisms, which ensure that highly fit solutions are more likely to propagate across generations. The Erdős–Rényi and Barabási-Albert models are explored in previous works [
10,
27]. Balanced tree graphs, with their hierarchical structure, offer a predictable degree distribution, making them ideal for tasks requiring a stable balance between exploration and exploitation. Harary graphs, characterized by their minimal edge configuration while maintaining connectivity, enable efficient information flow between solutions, optimizing recombination and enhancing the exchange of genetic material. The integration of a network in the evolutionary algorithm-N not only moves beyond purely random processes but also adapts to different problem landscapes, thereby enhancing the overall performance of the evolutionary search process.
According to [
10], the algorithm begins by generating a pseudo-random population, where each individual is associated with a node in the network, then the following stages are regulated by network structure. The algorithm iterates until a stop criterion is met. In each iteration, for every individual in the population, it identifies the set of neighbors from the network. If the individual has neighbors, one is selected based on a fitness criterion. A reproduction stage follows, where the selected individual and the current one generate a new offspring. This offspring undergoes mutation, and if its fitness exceeds that of the original individual, it replaces the original individual in the population. The process continues across the population and repeats until the stop criterion is satisfied, ensuring an evolutionary optimization approach guided by network structure, see
Figure 1.
2.3. Experimental Settings
According to [
10,
13], and consistent with prior research on evolutionary computation for addressing the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP), the parameter selections in this study are based on comprehensive investigations into their impacts on the efficiency of evolutionary algorithms applied to TSP, as discussed in [
10,
27,
28]. In this study, we employed identical parameter settings and instance configurations, focusing on instances with 25 cities. The parameters included a population size of 100, a mutation rate of
, a maximum of 100 and 200 iterations, 100 runs, and a stopping criterion of 100. To account for the stochastic nature of evolutionary algorithms, the experiments were performed over 100 independent runs using various random seeds. This setup enabled a comprehensive evaluation of key performance metrics, such as average fitness values (across 100 independent runs) and convergence speed, ensuring that the results reflect consistent performance across different instances of the TSP with 25 cities.
Additionally, a statistical hypothesis test was conducted to evaluate the performance of the evolutionary algorithm-Ns (Erdős–Rényi, Barabási-Albert, balanced tree, or Harary networks). A one-way ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) was used to compare performance across different methods, to determine if there are statistically significant differences in their effectiveness at solving the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). Following the one-way ANOVA, a Tukey post-hoc test was performed to further analyze these differences. The experiments were executed on a dedicated computer system with specific hardware and software configurations. The hardware setup included a 2-core Xeon 2.2 GHz processor, 13 GB of memory, and a 33 GB hard disk. For software, we used Python 3.7 to implement the TSP algorithm and employed Spyder 3.3.3 and the Networkx 2.4 library to model complex networks. The full implementation and testing process, including source code, is available in our GitHub repository:
http://github.com/jodatm/complex_networks_in_EA.
3. Results
The results of the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) using evolutionary algorithms, including both regular and complex networks, are presented below. This section highlights trends, differences between the methods, and their effectiveness.
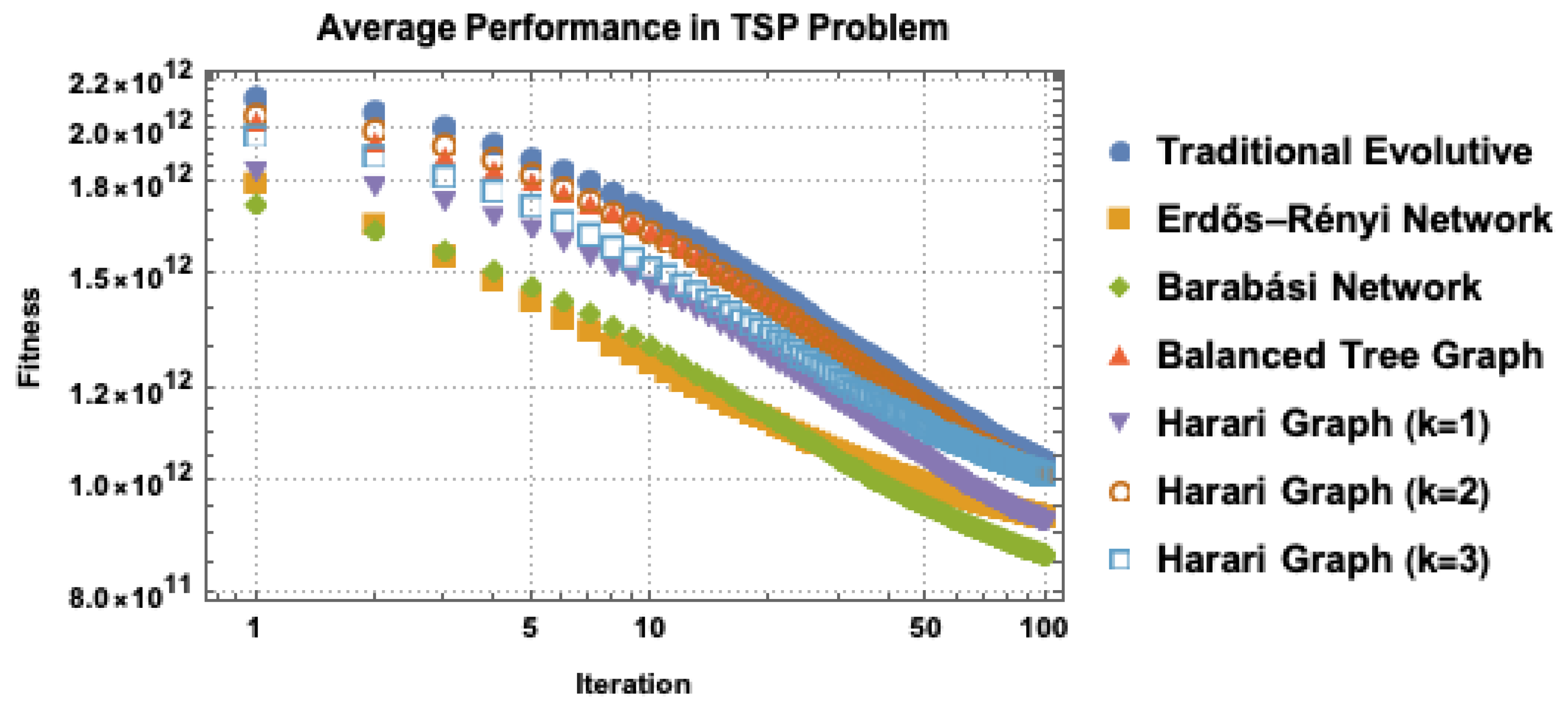
Figure 2 illustrates the evolution of fitness across iterations for each evaluated algorithm.
The trend analysis shows that the traditional evolutionary algorithm consistently yields the highest values in each iteration, indicating that this evolutionary algorithms, generates less efficient solutions compared to the other algorithms. In contrast, algorithms-N with Erdős-Rényi and Barabási-Albert networks tend to produce better solutions (lower in terms of fitness obtained in each TSP iteration) when compared to the traditional evolutionary algorithm. This is reasonable given that they are network models capable of representing more efficient connectivity patterns, which impacts the solutions and convergence, as observed in previous studies [
10,
27].
Furthermore, the balanced tree and networks (degrees ) achieve better results than the traditional evolutionary algorithm. In the case of , degrees and are more efficient. This suggests that regular networks contribute to improving TSP solutions, like Erdős-Rényi or Barabási-Albert networks.
The comparison between methods shows that Erdős-Rényi and Barabási-Albert consistently stand out by providing the best solutions. This may be due to their ability to capture key properties of random graphs and scale-free networks, facilitating the crossover and creation of superior solutions or communities of solutions. The network tends to outperform the traditional evolutionary algorithm in most iterations, but its performance varies depending on the degree (1, 2, and 3). Balanced trees offer intermediate efficiency between ErdősRényi and Barabási-Albert and Harary graphs. This is expected, as balanced trees are usually structured around a central node, which can limit the length of the paths.
Convergence shows that the results of the algorithms tend to improve as iterations progress. For all methods, values generally decrease as iterations advance. This is a positive sign, suggesting that the algorithms are converging towards optimal solutions. The algorithms-N that incorporate complex networks or regular networks exhibit similar convergence rates, indicating that they may be effectively capturing the underlying structure of the problem and offering shorter and more efficient paths. Thus,
Figure 2. shows that the traditional evolutionary algorithm is the least efficient. Erdős-Rényi and Barabási-Albert are the best algorithms, making them excellent candidates for optimizing the TSP in this context. Finally, Harary is sensitive to the increase in degree
k, as higher degrees lead to poorer results.
Table 3. describes the results of fitting a logarithmic function, to the average performance curve in a TSP problem, for each algorithm evaluated. The analysis of the logarithmic coefficients provides notable insights into the performance of each algorithm. The intercepts and coefficients for the algorithms-N, particularly for the Harari Graph (
), indicate a strong fit, as evidenced by the highest adjusted R-squared (
) value of
. Similarly, the other algorithms also achieve high adjusted R-squared values.
Furthermore, the consistency in the absolute values of the coefficients across the different algorithms signifies a relatively uniform level of influence on the optimization outcomes. Although all algorithms demonstrate substantial effectiveness, the marginal differences in the coefficients suggest that varying parameters and structures may yield different efficiencies in solving the TSP.
The analysis of the Barabási and Erdős–Rényi networks in the context of optimization methods for the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) highlights their distinct structural properties and their implications for algorithm performance. The Barabási network, characterized by its scale-free nature, tends to exhibit hubs that can significantly influence traversal efficiency, resulting in a logarithmic coefficient of approximately and an adjusted R-squared value of . In contrast, the Erdős–Rényi network, with its random connection pattern, demonstrated a slightly lower logarithmic coefficient of and an adjusted R-squared value of , indicating a less optimal fit for the TSP compared to the Barabási network. These findings suggest that the inherent properties of the network topology play a critical role in the efficacy of optimization algorithms, with scale-free networks offering advantages in solving combinatorial problems like the TSP.
The analysis of the Balanced tree and Harari graph optimization algorithms-N reveals distinct characteristics that influence their effectiveness in solving the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). The tree structure, known for its hierarchical organization and straightforward connectivity, provides a fundamental framework for exploring potential solutions; however, it may lack the complexity needed to navigate intricate networks efficiently. In contrast, the Harari graph exhibits a more intricate connectivity pattern, characterized by its tunable parameter k, which allows for greater flexibility and adaptability in capturing various network properties. This adaptability enhances the Harari Graph’s capacity to provide optimized solutions in diverse scenarios, making it a more robust choice for complex TSP instances. Thus, while both methods have their merits, the Harari Graph’s sophisticated structure generally offers superior performance in the context of optimization tasks involving intricate relationships among nodes.
To demonstrate that the Harary graphs with show the best performance among all algorithms presented, we can apply a statistical hypothesis test. Given the multiple groups (Traditional evolutive, Erdős-Rényi, Barabási-Albert, Balanced Trees, Harary graphs ), a one-way ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) is appropriate to compare the performance across these algorithms. The objective is to determine if there are statistically significant differences in their performance of addressing the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP).
The null hypothesis posits that there are no significant performance differences among the algorithms, while the alternative hypothesis suggests that at least one algorithm performs significantly better. After running the one-way ANOVA, the was calculated as , with a p-value of , which is significantly lower than the threshold. This result indicates that we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that at least one method outperforms the others.
Following the ANOVA, a Tukey post-hoc test was conducted to identify which specific algorithm differ significantly in performance. The Tukey test revealed that the Harary graphs with perform significantly better than several other methods, including the evolutionary traditional approach and balanced trees. However, when compared to the Barabási-Albert networks and Harary graphs, no significant performance differences were found. This implies that while Harary graphs () are competitive, they are not conclusively the top performer across all comparisons.
In sum, based on the statistical analysis, the Harary graphs with demonstrate strong performance, but they are not definitively the best across all the algorithms tested. The results show that Barabási-Albert networks also exhibit strong performance, and there is no significant difference between Harary graphs with and Harary graphs with . Further testing with additional iterations or other problem instances could provide more insights into the relative strengths of these methods.
Table 4. shows a comparison of CPU times for addressing the TSP problem. The analysis of execution times for different algorithms applied to the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) with 25 cities and 200 iterations reveals a clear distinction in efficiency between the algorithms. Algorithms-N using networks based on Harari graphs (particularly with
and
are the most efficient, with CPU times around 8 minutes and 30 seconds, significantly lower compared to traditional and evolutionary algorithm, which show CPU times close to 57 minutes. Notably, the method based on Barabási networks, with a CPU time of 17 minutes, performs considerably better than the traditional algorithms but is still less efficient than Harari graphs, see
Table 4. The differences in execution time become even more pronounced when the number of iterations is reduced to 100, where again Harari graphs dominate in efficiency, with times close to 7 minutes, while the traditional approach requires nearly half an hour. This analysis suggests that the underlying network structure plays a fundamental role in optimizing the TSP, with Harari graphs and the balanced tree showing a clear advantage over Erdős-Rényi and Barabási networks, as well as traditional algorithm. This difference arises due to the topological organization of the networks, which directly impacts the speed at which solutions are explored. Comparing the most efficient algorithm with the least efficient ones, we can observe that Harari graphs with
and
, which have CPU times around 8 minutes, are approximately 7 times faster than the traditional evolutionary algorithm, whose CPU time is 57 minutes. Even the balanced tree, with a CPU time of 11 minutes, is nearly 5 times more efficient than the traditional algorithm. This remarkable difference in performance highlights how the topological structure of networks can significantly reduce computation time in addressing the TSP.
4. Discussion
The Traveling Salesperson Problem (TSP) is a classic example of an NP-hard problem, meaning there’s no known algorithm that can efficiently solve all instances of the problem in polynomial time. As the number of cities increases, the number of possible routes grows exponentially, making an exhaustive search for the optimal solution computationally impractical for large instances. In this context, evolutionary algorithms and complex networks emerge as powerful tools to tackle the TSP. The article demonstrates how integrating complex network structures into evolutionary algorithms can significantly improve the efficiency in finding near-optimal solutions for the TSP. The experimental results reveal that methods based on Harari graphs, in particular, achieve a remarkable reduction in execution times, being up to 7 times faster than the traditional evolutionary algorithm. This acceleration in finding solutions highlights the potential of networks to address NP-hard problems, offering a promising avenue for optimizing complex problems in various fields.
Both [
10,
27] previous studies observe a significant improvement in the performance of evolutionary algorithms by incorporating complex networks into their structure. The inclusion of networks, whether of the Erdős–Rényi type [
10] or Barabási–Albert [
27], allows for more effective guidance of the crossover and selection processes within the algorithm, resulting in faster convergence towards optimal solutions and a reduction in execution times. These findings confirm that the structure and dynamics of complex networks can provide valuable information to improve the efficiency of evolutionary algorithms in solving complex optimization problems, such as the Traveling Salesperson Problem (TSP). In both studies, algorithm incorporating complex networks outperform traditional evolutionary algorithm, supporting the idea that the integration of complex networks is a promising strategy to enhance the problem-solving capabilities of evolutionary algorithms. This paper expands the analysis to include not only Erdos-Renyi and Barabasi-Albert networks but also regular networks like balanced trees and Harary graphs. This inclusion of regular networks provides a broader perspective on how different network topological structures impact the performance of evolutionary algorithms in solving the TSP.
Although [
13] applied complex networks to enhance TSP-solving capabilities through evolutionary algorithms, this paper goes further by conducting a comprehensive statistical analysis, including a one-way ANOVA hypothesis test and a Tukey post-hoc test, to assess the significance of the observed performance differences among the evaluated algorithms. In contrast to the study presented in [
15], which introduced a hybrid optimization algorithm using biological strategies to improve performance in large-scale TSP instances, this paper focuses on the specific impact of different network structures on the efficiency of evolutionary algorithms.
Whereas [
16] provided a review of bio-inspired algorithms, and unlike reference [
22], which investigated the use of genetic algorithms to improve the robustness of complex networks, this paper not only utilizes such algorithms but also integrates them with complex network structures and performs a quantitative and qualitative analysis of the results. The inclusion of an analysis of CPU execution times, along with traditional performance metrics, allows for a comprehensive evaluation of the computational efficiency of the proposed algorithms.
The degree distribution in complex networks significantly influences the convergence of evolutionary algorithms, as it determines the balance between exploration of the solution space and exploitation of already discovered solutions. This structure also impacts critical evolutionary operations such as selection and crossover. In highly connected networks, selection pressure increases, allowing fitter solutions to propagate more quickly. Conversely, in more uniformly connected networks, selection pressure is distributed more evenly, encouraging exploration of less-promising solutions, which can help avoid early stagnation in suboptimal areas.
In networks with heterogeneous degree distributions, such as Barabási-Albert networks, hubs facilitate rapid information dissemination, speeding up convergence toward high-quality solutions. However, this can increase the risk of premature convergence to local optima if diversity is not properly maintained. On the other hand, in networks with homogeneous degree distributions, like Harary graphs, information spreads more uniformly, slowing convergence but enhancing exploration of the solution space, reducing the likelihood of getting trapped in suboptimal solutions. This highlights the role of degree distribution as a key regulator in evolutionary algorithm performance. The right choice of network structure can optimize the balance between convergence speed and solution quality. For applications requiring both computational efficiency and precision, selecting a network with a heterogeneous distribution for faster convergence or a homogeneous one for improved quality becomes crucial.
In essence, the connectivity and degree structure of a network directly influence how efficiently an evolutionary algorithm explores the solution space and how quickly it converges to optimal solutions, affecting both convergence time and the quality of the results.
5. Conclusions
This paper demonstrates that integrating complex networks into evolutionary algorithms significantly improves performance in solving the Traveling Salesperson Problem (TSP), an NP-hard problem. Networks like Harary and Barabási-Albert enhance the efficiency of solution exploration, reducing execution times by up to 7 times compared to traditional methods. These results confirm that network structure directly influences convergence, the quality of the solutions obtained, and the time execution.
The statistical hypothesis testing confirms the validity of the performance differences between the algorithms used to solve the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). The one-way ANOVA yielded a highly significant result, indicating that there are distinct differences in performance across the evaluated algorithms. Specifically, the Harary graphs with showed competitive results, and the Tukey post-hoc analysis revealed that this method performed significantly better than some others, particularly the traditional evolutionary approach. However, when compared to Barabási-Albert networks and other Harary graphs, no statistically significant difference was found. This suggests that while Harary graphs are efficient, they are not conclusively superior to other complex networks in all cases. The robustness of these results is supported by a high value in the logarithmic fit and a strong overall statistical foundation, demonstrating the statistical validity of the conclusions. Nonetheless, further testing with additional problem instances and iterations is proposed as future work to provide deeper insights into these differences, along with a study of the computational complexity of the algorithms.
Future research directions based on the findings of this article could focus on several key areas to further enhance the performance of evolutionary algorithms when solving NP-hard problems like the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). One potential avenue is the exploration of hybrid network models, combining characteristics of different network topologies to balance exploration and exploitation more effectively. Additionally, further investigation into the dynamic adaptation of network properties during the optimization process could yield improvements, allowing the algorithm to adjust the network structure in response to evolving problem landscapes. Another promising direction is the integration of machine learning techniques with network-guided evolutionary algorithms to predict optimal parameter settings and network configurations for various problem instances. Lastly, scaling these methods to larger, more complex instances of the TSP or other combinatorial optimization problems, while maintaining computational efficiency, represents a significant challenge that future work could address. Exploring these areas could provide deeper insights into how network structures can be leveraged for even greater performance in evolutionary algorithms.
Additionally, network characteristics beyond connectivity, such as the clustering coefficient and community structure, play a crucial role in improving algorithm performance. Future research could explore hybrid network models and the integration of machine learning techniques to dynamically adjust network properties during the optimization process, enabling more efficient solutions for larger-scale problems.
Author Contributions
Victor Buchelli conceptualized and designed the research methodology, performed the experiments, performed the computation work, and analyzed the results. Mauricio Gaona validated the data obtained from experiments and performed the initial manuscript draft. Oswaldo Solarte validated data from experiments, prepared figures and tables, authored or reviewed manuscript drafts, and approved the final draft.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zelinka, I.; Davendra, D.; Snášel, V.; Jašek, R.; Šenkeřik, R.; Oplatková, Z. Preliminary investigation on relations between complex networks and evolutionary algorithms dynamics. 2010 International Conference on Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management Applications (CISIM). IEEE, 2010, pp. 148–153.
- Zelinka, I.; Davendra, D.; Lampinen, J.; Senkerik, R.; Pluhacek, M. Evolutionary algorithms dynamics and its hidden complex network structures. 2014 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). IEEE, 2014, pp. 3246–3251.
- Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z. A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on similarity for community detection from signed social networks. IEEE transactions on cybernetics 2014, 44, 2274–2287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, S. Traveling salesman problems with PageRank Distance on complex networks reveal community structure. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2016, 463, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaba, E.; Del Ser, J.; Sadollah, A.; Bilbao, M.N.; Camacho, D. A discrete water cycle algorithm for solving the symmetric and asymmetric traveling salesman problem. Applied Soft Computing 2018, 71, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhan, P.; Zhou, M. Optimization of a logistics transportation network based on a genetic algorithm. Mobile Information Systems 2022, 2022, 1271488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meepetchdee, Y.; Shah, N. Logistical network design with robustness and complexity considerations. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management 2007, 37, 201–222. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzuti, C. Evolutionary computation for community detection in networks: A review. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 2017, 22, 464–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramteke, M.; Srinivasan, R. Large-scale refinery crude oil scheduling by integrating graph representation and genetic algorithm. Industrial & engineering chemistry research 2012, 51, 5256–5272. [Google Scholar]
- Bucheli, V.A.; Pabón, O.S.; Ordoñez, H. Evolutionary algorithms guided by Erdos–Rényi complex networks. PeerJ Computer Science 2024, 10, e1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, W.J.; Applegate, D.L.; Bixby, R.E.; Chvatal, V. The traveling salesman problem: a computational study; Princeton university press, 2011.
- Laporte, G. The traveling salesman problem: An overview of exact and approximate algorithms. European Journal of Operational Research 1992, 59, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triana, J.; Bucheli, V.; Garcia, A. Traveling salesman problem solving using evolutionary algorithms guided by complex networks. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence 2020, 18, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, S.D.; Marian, R.M. Genetic algorithms for integrated optimisation of precedence-constrained production sequencing and scheduling; Springer, 2013.
- Kanna, S.R.; Sivakumar, K.; Lingaraj, N. Development of Deer Hunting linked Earthworm Optimization Algorithm for solving large scale Traveling Salesman Problem. Knowledge-Based Systems 2021, 227, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Ser, J.; Osaba, E.; Molina, D.; Yang, X.S.; Salcedo-Sanz, S.; Camacho, D.; Das, S.; Suganthan, P.N.; Coello, C.A.C.; Herrera, F. Bio-inspired computation: Where we stand and what’s next. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation 2019, 48, 220–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanos-Mosquera, J.M.; Muriel-López, G.L.; Triana-Madrid, J.D.; Bucheli-Guerrero, V.A. Algoritmos evolutivos guiados por redes complejas libres de escala. Revista científica 2022, pp. 228–241.
- Jamakovic, A.; Van Mieghem, P. On the robustness of complex networks by using the algebraic connectivity. International conference on research in networking. Springer, 2008, pp. 183–194.
- Paul, P.V.; Moganarangan, N.; Kumar, S.S.; Raju, R.; Vengattaraman, T.; Dhavachelvan, P. Performance analyses over population seeding techniques of the permutation-coded genetic algorithm: An empirical study based on traveling salesman problems. Applied soft computing 2015, 32, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Astorquiza, C.; Contreras, I.; Laporte, G. The Minimum Flow Cost Hamiltonian Cycle Problem: A comparison of formulations. Discrete Applied Mathematics 2015, 187, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applegate, D.L. The traveling salesman problem: a computational study; Vol. 17, Princeton University Press, 2006.
- Pizzuti, C.; Socievole, A. A genetic algorithm for enhancing the robustness of complex networks through link protection. Complex Networks and Their Applications VII: Volume 1 Proceedings The 7th International Conference on Complex Networks and Their Applications COMPLEX NETWORKS 2018 7. Springer, 2019, pp. 807–819.
- Erdos, P.; Rényi, A.; others. On the evolution of random graphs. Publ. math. inst. hung. acad. sci 1960, 5, 17–60.
- Arney, C. Linked: how everything is connected to everything else and what it means for business, science, and everyday life. Mathematics and Computer Education 2009, 43, 271. [Google Scholar]
- Valiente, G. Algorithms on trees and graphs; Vol. 112, Springer, 2002.
- Yu, X.; Gen, M. Introduction to evolutionary algorithms; Springer Science & Business Media, 2010.
- Andres Bucheli, V.; Solarte Pabón, O.; Diaz Molano, L.L.; Armando Ordoñez, H. Algoritmos Evolutivos Guiados por Redes Barabási-Albert: El Problema del Agente Viajero. Investigación e Innovación en Ingenierías 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Deng, Y. A cluster-growing dimension of complex networks: From the view of node closeness centrality. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2019, 522, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).