1. Introduction
In late 2019, initial cases of pneumonia of unknown origin were reported in Wuhan, China. These cases were later attributed to a novel coronavirus, subsequently named SARS-CoV-2. The disease caused by this virus was named COVID-19, reflecting its relationship to the previously known SARS coronavirus.[
1] This novel virus rapidly spread worldwide, leading the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare it a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on January 30, 2020, and subsequently a pandemic on March 11, 2020. [
2,
3] As COVID-19 proliferated globally, it not only posed significant health challenges but also triggered widespread social and economic disruption, underscoring the need for effective control and prevention measures.
Belonging to the
Sarbecovirus subgroup of the
Betacoronavirus genus, alongside SARS CoV and MERS CoV, SARS-CoV-2 utilizes the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor for cell entry, with the spike (S) protein playing a pivotal role [
4]. Comprising two subunits, S1 and S2, the S1 subunit’s receptor-binding domain (RBD) binds to ACE2, while the S2 subunit facilitates membrane fusion [
5]. This precise understanding of the interaction between the cellular receptor and viral receptor-binding antigen provided the basis for the formulation of numerous disease control and prevention strategies.
Although the approval of various vaccines [
6] marked a significant milestone in combating the disease, the production of effective vaccines is both time-consuming and costly [
7]. Furthermore, the ongoing viral evolution may lead to mutations that compromise vaccine effectiveness [
8]. Immunocompromised patients exhibit lower seroconversion rates [
9], and vaccine hesitancy, coupled with limited access, poses challenges, particularly in less developed regions [
10,
11]. Hence, there remains a constant need for alternative methods to mitigate the spread of COVID-19 in the general population or among individuals with specific needs.
In cases where effective vaccination is impractical or the generated immune response is suboptimal (e.g., in the elderly or immunocompromised patients), passive immunotherapy emerges as a viable alternative for infection prevention. This therapeutic approach has been employed in treating COVID-19 patients, utilizing specific IgG antibodies derived from the plasma of recovered individuals to induce clinical improvement [
12]. However, challenges such as limited IgG availability and potential side effects persist [
13]. A potential avenue for passive immunotherapy involves the neutralization of the virus at the cellular entry point, and specific IgY antibodies may offer a promising solution.
Derived from egg yolk, IgY serves as a homologue to mammalian IgG, demonstrating efficacy in various respiratory and digestive diseases in both humans and animals [
14,
15,
16,
17]. The production of IgY antibodies is more hygienic, comfortable, and cost-effective compared to traditional methods of IgG collection. Importantly, IgY production aligns with the principles of animal welfare (3 R: reduction, refinement, replacement). Notably, immunocomplexes containing IgY do not activate the human complement system and thus are incapable of triggering antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) reactions, as IgY cannot bind to human Fc receptors. Additionally, purified IgY antibodies exhibit remarkable stability, maintaining their titer for years when stored at 4°C [
18].
In our experiments, we developed specific IgY antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 through the immunization of SPF laying hens. We conducted analyses to evaluate the purity and specific virus neutralization titer of these egg yolk antibodies. Our focus was not on determining the minimal effective dose but rather on the robust examination of the potential of IgY, typically absent in mammals, as a viable means to mitigate the consequence of infection. This investigation aimed at assessing IgY’s efficacy as a medication option in mammals, exemplified by the Syrian hamster model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antigen Preparations
Selection of Antigens and Adjuvants: For vaccine development, three distinct antigens – Spike protein (S), Spike protein subunit 1 (S1), and the Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) – were selected. These antigens were utilized in two dosages, 1µg and 10µg. Accompanying adjuvants included TiterMax Gold, Montanide, and a combination of Montanide with CpG oligonucleotide. All antigens, sourced as recombinant proteins with a HIS-tag from HEK 293 cells, were provided by Acrobiosystem (Newark, DE, USA; Cat. Nos. S protein – SPNC52H3; S1 – S1NC52H4; RBD – SPDC52H5).
Adjuvant Formulation: Two water-in-oil type adjuvants were employed: TiterMax (Sigma Aldrich, Cat. No. T2684) and MontanideTM ISA 71R VG (Seppic GmbH, Cologne, Germany). To potentiate the immunogenic response, Montanide was used alone and in combination with CpG oligonucleotide (sequence: 5’CTAGTTCGTCGAAGTCGTTTTGGGGGGT-3’).
Vaccine Preparations and Immunization: In total, 18 different vaccine formulations were prepared, combining the spike antigen variations with different adjuvant types. These formulations were systematically utilized in chicken immunization studies to evaluate their efficacy.
Table 1.
Combinations of Antigens and Adjuvants Used in Vaccine Formulation. The table outlines the structured grouping (G1–G18) based on the type of adjuvant and antigen used, along with the antigen dosage per vaccine dose. Three antigens—Spike protein (S), Spike protein subunit 1 (S1), and the Receptor Binding Domain (RBD)—were tested in two concentrations (1 µg and 10 µg) with TiterMax Gold, Montanide, and a combination of Montanide with CpG oligonucleotide as adjuvants. A total of 18 vaccine formulations were prepared for immunization studies in chickens to assess efficacy. Antigens were procured as recombinant proteins with a HIS-tag from HEK 293 cells with catalog numbers SPNC52H3 for S, S1NC52H4 for S1, and SPDC52H5 for RBD. TiterMax Gold and MontanideTM ISA 71R VG served as the primary adjuvants, with CpG oligonucleotide enhancing the immunogenic response in selected formulations. Solvent Name: Aqua destillata pro injection.
Table 1.
Combinations of Antigens and Adjuvants Used in Vaccine Formulation. The table outlines the structured grouping (G1–G18) based on the type of adjuvant and antigen used, along with the antigen dosage per vaccine dose. Three antigens—Spike protein (S), Spike protein subunit 1 (S1), and the Receptor Binding Domain (RBD)—were tested in two concentrations (1 µg and 10 µg) with TiterMax Gold, Montanide, and a combination of Montanide with CpG oligonucleotide as adjuvants. A total of 18 vaccine formulations were prepared for immunization studies in chickens to assess efficacy. Antigens were procured as recombinant proteins with a HIS-tag from HEK 293 cells with catalog numbers SPNC52H3 for S, S1NC52H4 for S1, and SPDC52H5 for RBD. TiterMax Gold and MontanideTM ISA 71R VG served as the primary adjuvants, with CpG oligonucleotide enhancing the immunogenic response in selected formulations. Solvent Name: Aqua destillata pro injection.
| Group ID |
Adjuvant |
Antigen |
Antigen quantity |
| G1 |
TiterMax Gold |
S |
1 µg |
| G2 |
TiterMax Gold |
S |
10 µg |
| G3 |
TiterMax Gold |
S1 |
1 µg |
| G4 |
TiterMax Gold |
S1 |
10 µg |
| G5 |
TiterMax Gold |
RBD |
1 µg |
| G6 |
TiterMax Gold |
RBD |
10 µg |
| G7 |
Montanide |
S |
1 µg |
| G8 |
Montanide |
S |
10 µg |
| G9 |
Montanide |
S1 |
1 µg |
| G10 |
Montanide |
S1 |
10 µg |
| G11 |
Montanide |
RBD |
1 µg |
| G12 |
Montanide |
RBD |
10 µg |
| G13 |
Montanide +CpG |
S |
1 µg |
| G14 |
Montanide +CpG |
S |
10 µg |
| G15 |
Montanide +CpG |
S1 |
1 µg |
| G16 |
Montanide +CpG |
S1 |
10 µg |
| G17 |
Montanide +CpG |
RBD |
1 µg |
| G18 |
Montanide +CpG |
RBD |
10 µg |
2.2. Immunization of Laying Hens
Hen Housing and Grouping: In preparatory experiments, 180 sixteen-week-old Babcock Specified Pathogen-Free (SPF) laying hens were housed in a Filtered Air Positive Pressure (FAPP) environment. Each bird received individual markings for identification. The hens were then divided into 18 groups, with each group comprising 10 hens housed in separate laying cages. (Ethical Committee Approval: Baranya County Government Office Ref. No. BAI/35/56-92/2017)
Acclimatization and Immunization Schedule: A two-week acclimatization period was observed before initiating the immunization protocol. The hens received their first subcutaneous vaccination under the neck skin on Day 0 (D0). This was followed by additional immunizations on Day 35 (D35), Day 49 (D49), and Day 125 (D125).
Antibody Response Assessment and Egg Collection: The virus-specific antibody response induced by the vaccine formulations was evaluated using a virus neutralization test (VN test). Following the third vaccination, daily egg collection commenced. Collected eggs were sorted and labelled according to their respective groups and stored at a temperature range of 16–20°C for further analysis.
2.3. Isolation of IgY from Egg Yolk
Preparation of Egg Yolks: Eggs from groups selected based on serum VN test results were used for Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) extraction. The eggs concurrent with blood sampling were pooled before processing. After cracking, the egg whites were separated, and the yolks were reserved for extraction.
IgY Extraction Procedure by In-house Method: The yolks were diluted in a 3 mM Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) solution at a 1:10 ratio. The mixture was first centrifuged at 300 rpm (Megafuge 16R; ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) for 30 minutes at room temperature, providing optimal conditions for phase separation. Following this, the pH of the mixture was adjusted to 5.0 (range: 4.9–5.1) using 10% Acetic Acid, a critical step for protein stability. A secondary centrifugation was performed at the same speed for 30 minutes, followed by a high-speed centrifugation at 10,000 g for 15 minutes at 4°C. Then (NH4)2SO4 was added to the supernatant at 35 w/w% and subsequently 65 w/w%, with centrifugation at 10,000 g for 15 minutes at 4°C after each addition. The precipitate containing IgY was separated, resuspended in PBS to the original yolk volume, and stored below -15°C.
IgY Extraction Procedure by Commercial Kit: Egg yolks were processed for IgY extraction using the Pierce Chicken IgY Purification Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, Cat. No. 89835), adhering to the manufacturer’s instructions. The samples were stored at –20°C until use.
2.4. Analysis of Egg Yolk Extracts
The assessment of the total protein content in the IgY extracts was performed utilizing the Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA) assay. Furthermore, the purity of these extracts was verified through polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), ensuring a thorough evaluation of the IgY antibodies in terms of both concentration and integrity.
2.4.1. BCA Assay
Protein concentrations in egg yolk extracts enriched with IgY were quantified using the Bicinchoninic Acid Protein Assay Kit (Sigma-Aldrich, Cat. Nos. BCA1 and B9643), with modifications for specific assay volumes. The BCA Working Reagent was prepared by mixing Reagent A and B at a 1:8 ratio, tailored for 40, 80, and 96 wells. Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) standards, ranging from 31.25 to 2000 µg/ml, established a standard curve. IgY samples were diluted in PBS at ratios of 10 to 500.
Assays were conducted in 96-well plates, incorporating negative (PBS) and positive (BSA standards) controls, where 25 µl of each Sample or BSA standard was mixed with 200 µl of the BCA Working Reagent and incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes in darkness.
Absorbance was measured at 562 nm using an iEMS Reader MF (Thermo Labsystems, Vantaa, Finland), with data analyzed by Ascent Software (Thermo Labsystems, Vantaa, Finland), to calculate sample concentrations and assess extraction efficiency through statistical analyses using Python’s Pandas and NumPy libraries.
2.4.2. SDS-PAGE
SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining were employed to analyze egg yolk extracts. Gels were prepared using the TGX™ FastCast™ Acrylamide Kit 7.5% (Bio-Rad, Cat. No. 1610171) and cast on 1.5 mm glass plates. The sample buffer was composed of 2.5 ml 1M Tris-HCl, 1g SDS, 0.8 ml 0.1% Bromophenol Blue, 4 ml glycerol, 2 ml β-mercaptoethanol, and 0.5 ml water, adjusted to 10 ml. Running buffer (10X) included 30.3 g Tris Base, 144 g Glycine, and 10 g SDS in 1 L of water.
Protein extracts were mixed 1:1 with sample buffer, denatured at 95°C for 5 minutes, and 20 µl of each sample and IgY (1 mg/ml) and Ovalbumin (OVA, 1 mg/ml) as control proteins in each gel, serving as references for band identification and comparison were loaded into the gels alongside 4 µl of Precision Plus Protein™ Standards (Bio-Rad, Cat. No. 161-0374) for molecular weight marking. Electrophoresis was performed at 200 volts and 150 milliamperes for 30 minutes. For staining, a solution containing 0.25 g Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250, 100 ml methanol, and 25 ml acetic acid in 125 ml was used, followed by destaining in a solution of 380 ml water, 80 ml methanol, and 40 ml acetic acid. Gels were documented using the ChemiDoc™ Imaging System (Bio-Rad, Cat. No. 12003153) and analyzed with Image Lab™ Software version 2.4.0.03.
2.5. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assay
VeroE6 cells (ATCC®, CRL-1586™) sourced from African green monkey kidney tissue, were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (Merck Cat. No. D6429) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (Gibco, Cat. No. 16140071) and 1% Penicillin-Streptomycin (Merck Cat. No. 4333) and maintained at 37°C with 5% CO2. Cells were infected with the Wuhan SARS-CoV-2 isolate (hCoV-19/Hungary/SRC_isolate_2/2020, Accession ID: EPI_ISL_483637). Prior to utilization in the assays, its infectious titer was quantified by a TCID50 assay. Experiments with the active virus were performed under BSL-4 conditions.
Hen sera and IgY fractions underwent two-fold serial dilution and subsequent heat inactivation at 56°C for 30 minutes. The treated samples were mixed with DMEM containing 400 TCID50 of SARS-CoV-2 and incubated for 1 hour at 37°C in 96-well plates (TPP Cat. No. 92096). The assay included a positive control with 400 TCID50 of SARS-CoV-2 and a negative control consisting solely of DMEM, devoid of sera, IgY fraction, or virus.
Post-neutralization, 100 μl of the virus-serum mixture was used to infect confluent (100%) VeroE6 cells for 30 minutes. Subsequently, cells were maintained in 200 μl of “post- infection” culture media (DMEM with 2% FBS and 1% Pen/Strep) for three days under the same incubation conditions. The neutralizing capacity of the serum was assessed by determining the highest dilution that prevented viral infection in 50% of the wells.
2.6. Syrian Golden Hamster Model for Assessing and IgY Treatment Efficacy
After careful selection of the IgY extract with most effective neutralization capacity, in vivo experiments were initiated in Syrian golden hamsters. First, animals were acclimatized in a BSL- 4 laboratory environment where they were housed in separate cages so that neither direct nor indirect contact (such as shared airspace, food, drinking-water) was allowed. Animals were divided into three groups for the experiment, which lasted for 7 days after infection. The negative control group received PBS and DMEM. The IgY treatment group was administered IgY extract and subsequently with the active virus (challenge). The positive control group was given PBS and active virus, like the IgY treatment group. Since SARS-CoV-2 is not fatal to hamsters, the experiments concluded with the euthanasia of the animals. The experiments with Syrian hamsters were conducted in accordance with the animal ethics license (License number: BA02/2000-26/2021).
2.6.1. Housing and Preparation of Syrian Golden Hamsters
Specific Pathogen-Free (SPF) male Syrian golden hamsters, 5-6 weeks old, were obtained from Janvier Labs, France. Individual housing in ventilated cages (Allentown, Animal Transfer Unit) was provided, including cellulose bedding, nesting materials, and chewable wood. Animals had continuous access to food and 400 ml of tap water, replenished every two days. Animals were acclimatized out of a BSL-4 laboratory environment where they were housed in separate cages so that neither direct nor indirect contact (such as shared airspace, food, drinking water) was allowed. A 4-day acclimatization period was followed by the start of experiments, in the BSL- 4 laboratory.
2.6.2. BSL-4 Laboratory Environment and Animal Management
The BSL-4 laboratory maintained a constant temperature (23°C) and humidity (20–40%). Isoflurane (Aeranne, Baxter Hungary) anesthesia was administered via SomnoSuite (Kent Scientific) anesthesia machine (induction and maintenance at 5%). An Ohaus Scout scale, throat swabs made with Copan FloqSwab sticks (Cat. No. 520CS01) for sampling and for euthanasia, we used retroorbital venipuncture with glass capillaries. (Harvard Apparatus, Cat. No. 30-0037).
2.6.3. Pre-Infection Treatment and Inoculation
Hamsters were treated with IgY extract or PBS (for control groups) intranasally (10–10 μl/nostril by an automated pipette) one hour before inoculation with 180 PFU of the Wuhan strain of SARS-CoV-2 per animal. The negative control group was treated with DMEM as mock inoculation. Virus dilution was previously prepared in DMEM (Merck, Cat. No. D6429).
2.6.4. Daily Observation and Post-Infection Procedure
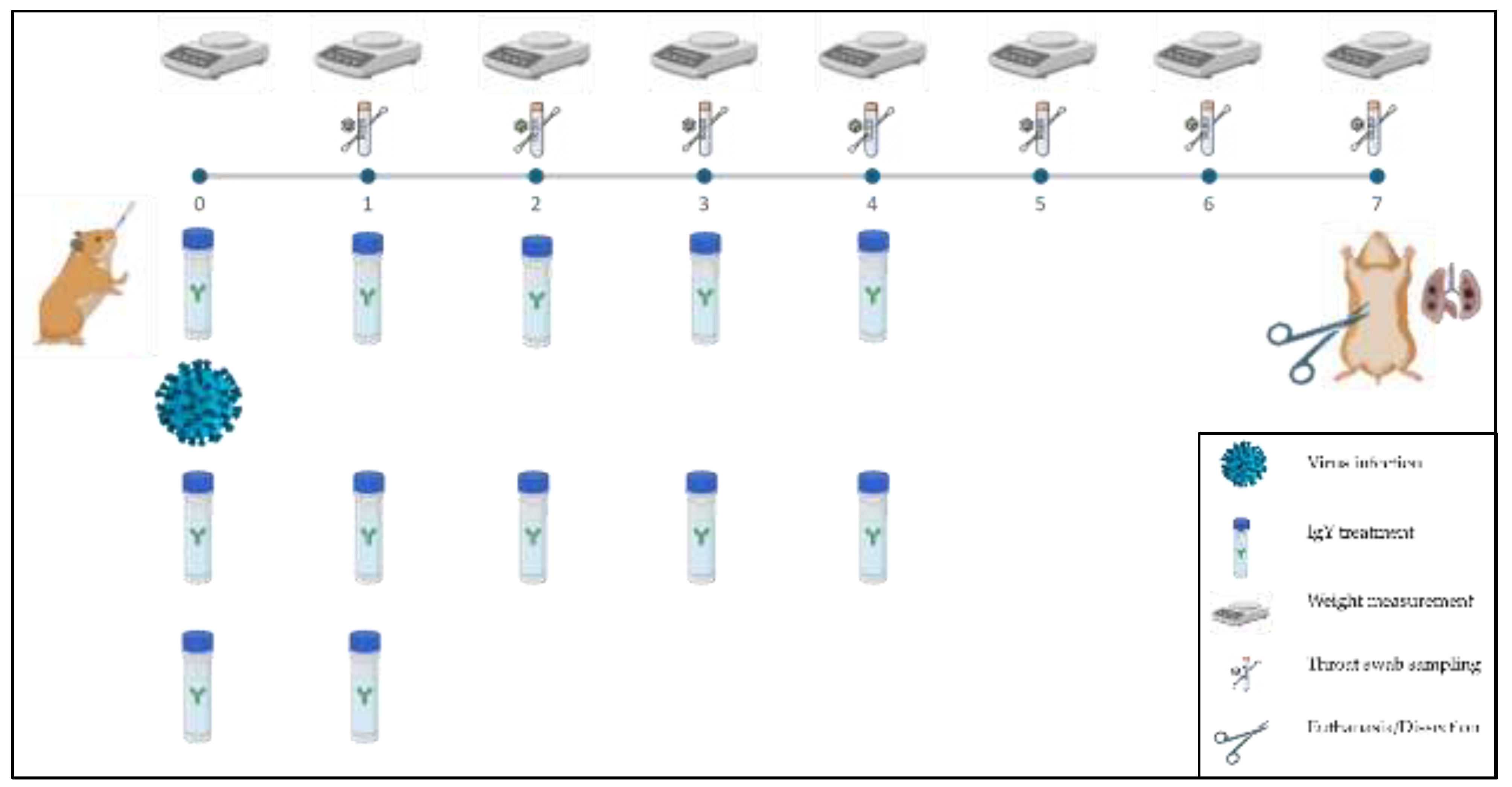
Daily assessments included weight measurement, throat swab sampling, and general health status. IgY or PBS treatment was given every 8 hours for the first three days and then every 12 hours until 4 dpi. Euthanasia was performed on day 7 post-infection via retroorbital bleeding under exsanguination (
Figure 1.).
2.7. ddPCR Analysis for SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load Quantification
Nucleic Acid Extraction: Nucleic acid extraction was performed from both throat swab and lung tissue samples. For the throat swab samples, the medium in which the swab was initially placed was used for extraction. In the case of lung tissue samples, the samples (~50 µg) were homogenized prior to extraction. This critical step was performed to ensure efficient RNA recovery from tissue samples. The throat swab samples were extracted Zybio Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit (Zybio, Catalog No. CoV2-32, Dadukou, Chongqing, China) and for the lung tissues the Monarch® Total RNA Miniprep Kit (New England Biolabs, Ipswitch, MA, USA) were used according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.8. ddPCR Methodology for Viral Load Determination
Preparation of ddPCR Master Mix: The ddPCR master mix was composed of 1X supermix, 20 U/µl reverse transcriptase, 15 mM dithiothreitol, 11.1 µL nuclease-free water, 900 nM each of forward and reverse primers, 250 nM TaqMan probe, and 2 µL of the 100-fold diluted RNA extract. The primers and probe targeted the SARS-CoV-2 Charité/Berlin RdRp gene (Integrated DNA Technologies, , Coralville, IA, USA).
Droplet Generation and PCR Amplification: Droplet generation was conducted using the QX200 Droplet Generator (Bio-Rad, USA) with a specified reaction mix volume (volume details needed). The thermal cycling in a C1000 Touch Thermal Cycler included:
Reverse transcription at 50 ºC for 60 minutes
Enzyme activation at 95 ºC for 10 minutes
40 cycles of denaturation at 95 ºC for 30 seconds and annealing/extension at 58 ºC for 1 minute
Final enzyme deactivation at 98 ºC for 10 minutes
Storage of amplicons at 4 ºC until droplet reading
Droplet Reading and Data Analysis: The amplicons were analyzed using the QX200 Droplet Reader (Bio-Rad, USA). Viral copy numbers per microliter were calculated automatically by Quantasoft™ Analysis Pro version 1.0 (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA).
2.9. Histopathological Analysis of Lung Tissue
Tissue Fixation and Paraffin Embedding: Lung tissues from 36 hamsters were initially fixed in a 6% neutral buffered formaldehyde solution (Molar Chemicals, Cat. No. 42322-006-340) for at least 24 hours at room temperature. The fixed tissue samples were trimmed and dehydrated with a series of ethanol and xylene in an automatic tissue processor. The dehydrated samples were embedded in paraffin blocks, and 4 µm thin sections were cut manually and mounted onto Superfrost+ adhesion slides (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The unstained sections were deparaffinized and rehydrated in xylene and alcohol, respectively. Routine H&E staining was performed in an automatic staining instrument. The slides were scanned with a Pannoramic Midi slide scanner using a 20× objective (3D Histech, Budapest, Hungary) and visualized by SlideViewer software (3Dhistech, Budapest, Hungary). Representative pictures were obtained with the latter software.
2.9.1. Digital Image Analysis
To quantify the consolidated regions of the lungs a simplified approach of the digital workflow of Mulka et al was performed using QuPath digital image analysis software[
19,
20]. For the QuPath analysis the digital images were further converted to WS DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) format by the SlideMaster software (3D Histech) and analyzed with QuPath (version 0.4.4) software (qupath.github.io),[
19].
Tissues were annotated with the wand tool, then the DoG superpixel segmentation command was applied, and intensity features were added. Distinct annotations were created within the tissues in multiple slides to educate the classifier. These annotations were marked as “consolidated”, “normal”, “blood” or “ignore”. The normal tissue indicates the lung parenchyma without any lesions, and the ignore class included artefacts, atelectasis as well as the walls of large blood vessels and airways. The performance of the classifier was evaluated after each analysis. The consolidation ratio was calculated by dividing the number of consolidated superpixels by the total number of lung superpixels in each case.
2.10. Statistical Analysis of Data
Statistical analysis was performed on non-transformed data using jamovi (Version 2.4) and R (Version 4.1) [
21,
22]. The R packages used for the statistical analyses were retrieved from the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN) snapshot on 2023-04-07. To compare the differences (ddPCR results, body weight, histopathological data) between the negative control, IgY treated, and positive control groups during the 7 day long experiment we used the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Dwass-Steel-Critchlow-Fligner pairwise comparisons, with a predetermined alpha level of 0.05 for statistical significance. Non-parametric tests were initially selected, since we did not expect the data to follow normal distribution in the treatment group, which was apparent after data collection.
3. Results
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assay on Immunized Hen’s Sera
The sera of the hens were collected at different time points after immunization. The virus neutralization capacity of hen sera was measured by using the Wuhan isolate of SARS-CoV-2. The
in vitro virus neutralization titers were used as primary endpoints of the experiments, based on which the most effective immunogen constructs were selected for the consecutive experimental steps (
Figure S1).
The majority of the 18 immunogen preparations was excluded after the first round of evaluation. Certain immunogen preparations induced no or very low virus neutralization titers in immunized hens. This was observed particularly in case of the sera collected from hens immunized with a preparation where the protein component was the S1 subunit. Similar results were obtained with all preparations where the RBD domain was used at 1 µg quantity per animal per dose. Some immunogen preparations induced good antibody response, especially when applied at higher (1 µg vs 10 µg) antigen content.
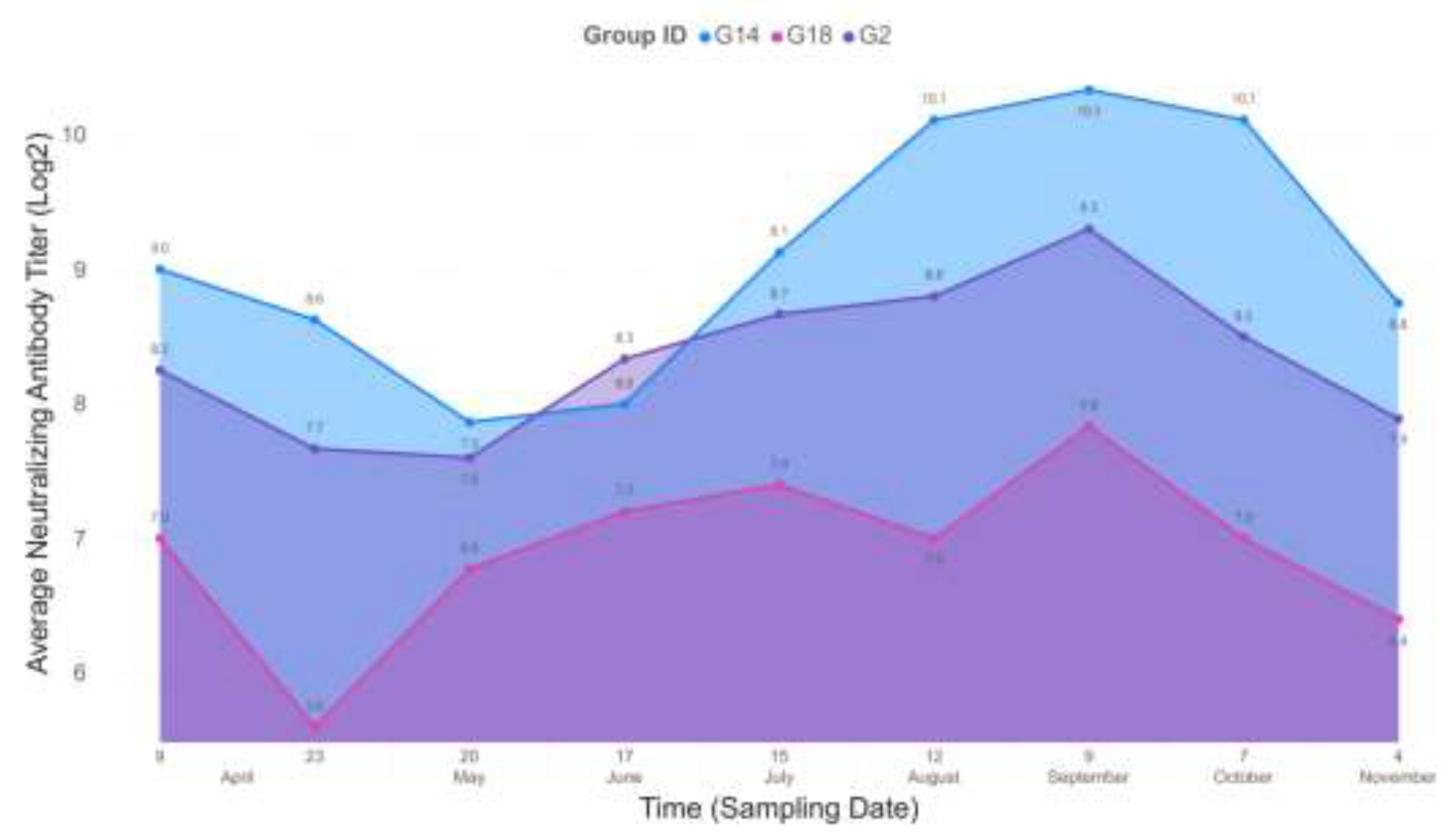
In the end, the eggs of three hens’ groups, receiving antigen-adjuvant combinations that induced the highest virus neutralization titers were selected for egg yolk IgY examination. Hens in the G2 group that were immunized with 10 µg S protein mixed with TiterMax had a mean 8.8 log2 serum virus neutralization titer at week 2 after second immunization and similar value (8.7 log2 titer) at week 19 after receiving the fourth immunizing dose. The groups of hens immunized with 10 µg S protein with Montanide+CpG (G14) had mean serum virus neutralization titers ranging from 9.2 log2 in the first measurement and 9.2 log2 in the last test point. Finally, the group including hens immunized with 10 µg RBD and adjuvated with Montanide+CpG (G18) had a mean 6.4 log2 titer that changed to 6.8 log2 at the end of test period. In all three groups, serum virus neutralization titers plateaued between 3rd and 11th week after the 4th immunization (log2 titers: G2, 10.1; G14, 11.1; G18, 8.7,
Figure 2.).
3.2. Quantification of IgY from Egg Yolk
The eggs of the hens in the selected groups were collected, marked, and stored for further processing. The extraction of the IgY content from the eggs was performed as described above.
The virus neutralizing activity of egg yolk origin IgY of the three selected laying hen groups with the highest serum virus neutralization titers was tested in a similar way as described above for testing of serum virus neutralization titers. The first egg yolk sampling was performed at week 2 after the 3rd immunization of hens and repeated as many times as sampling for serum antibody neutralization test was performed. The virus neutralization titer peaked at week 10 after the 3rd dose and kept constant values after the 4th dose was administered. At week 19 after the 4th dose, the titers decreased for G14 and G18 (log2 titers, 7) and remained constant with the G2 immunogen (log2 titer, 10). However, the highest virus neutralization titers were achieved with egg yolk IgY extracts of G14, therefore further experiments were carried out with this product.
3.3. Analysis of Egg Yolk Extracts
IgY Extraction and Purity: The study evaluated the efficacy of two IgY extraction methods from egg yolk, focusing on their yield, purity, and concentration. In group G14, the egg yolk extract exhibited a total protein content of 16.5 mg/ml, with an IgY concentration of 6.6 mg/ml and a purity rate of 40%. Despite the relevance of purity for certain applications, the intended local treatment use of these extracts deemed this factor less critical.
Comparative Analysis of Extraction Methods: The proprietary extraction method yielded Egg Yolk extracts with approximately 40% purity, as opposed to the higher purity levels achieved using the commercial Pierce™ Chicken IgY Purification Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, Cat. No: 44918). However, the in-house method consistently produced higher IgY concentrations, albeit with an increase in other protein levels. This suggests a trade-off between purity and IgY yield, with the in-house method favoring the latter (
Table S1 and
Figure S2).
Variability in Extraction Efficiency: A comparative study of the Pierce Kit and the in-house method revealed distinct differences in performance. The Pierce Kit maintained high purity levels (average: 87.64%, SD: 4.42%), showcasing its reliability and efficiency. Conversely, the in-house method exhibited lower purity (average: 41.88%) with greater variability (SD: 5.33%), indicating a less consistent performance.
IgY Yield Analysis: The analysis of IgY yield, in relation to the total protein extracted, highlighted the efficiency of the methods used. Yields ranged from 82% to 96%, illustrating the high capability of the employed methods, especially the Pierce Kit, to selectively purify IgY antibodies from egg yolks.
3.4. Syrian Golden Hamster Model for Assessing IgY Treatment Efficacy
Hamsters were acclimatized during 4-6 days outside the BSL-4 facility followed by 1-4 days inside the facility. Monitoring of specific physiological parameters began on Day 0 of the experiments. Animal activity was only assessed for humane handling purposes, and the potential termination of animals in severe distress was determined according to the animal ethics permit. Due to the subjective nature of activity assessment, it cannot be numerically described and does not contribute to a robust experimental setup.
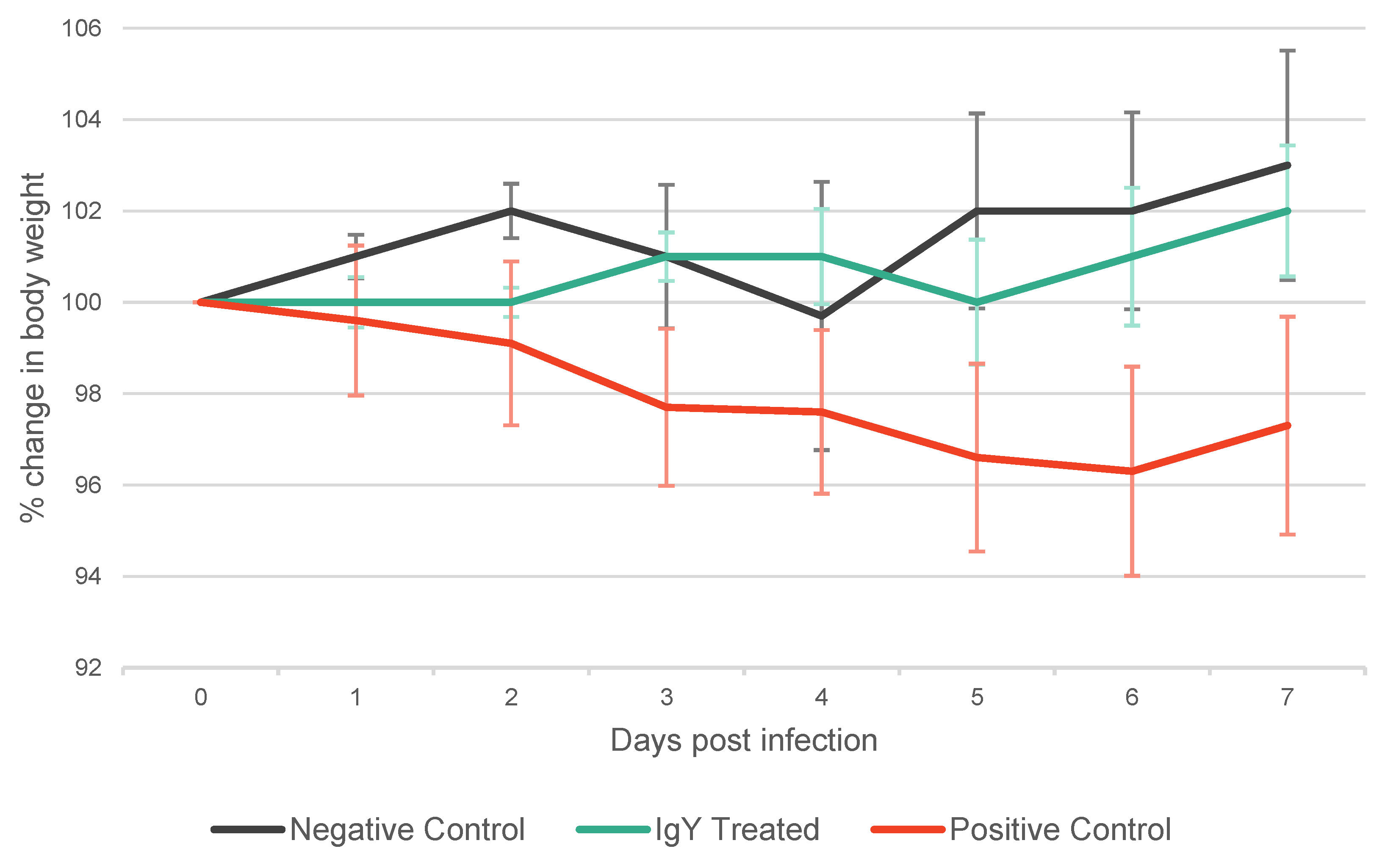
In contrast, the weight of the animals is a widely accepted parameter for infection evaluation. Generally, negative control animals are expected to gain weight, while infected animals typically experience weight loss. According to the literature, expected weight changes fall within a +/– 10% range of the original weights. In our study, the overall average weight by the end of the experiment (Day 7) was 86.46 g ± 7.05 g.
The IgY Treated group exhibited a tendency to gain weight (Day 7 Mean: 101.93% of mean weight at Day 0), similarly to the Negative Control group (Day 7 Mean: 103.16% of mean weight at Day 0). Conversely, the positive control group predominantly exhibited weight loss (Day 7 Mean: 97.28% of mean weight at Day 0) (
Table S2,
Figure 3.). Discernible trend in weight changes were exhibited by the groups, although notably pronounced weight trend differences are only anticipated with higher levels of infectious doses. For the purposes of this experimental framework and considering the extent and methods through which we assess the impact of SARS-CoV-2 in the animal model (specifically through ddPCR and subsequent histopathological evaluation) the administration of a higher SARS-CoV-2 dose would yield no scientific advantage. Therefore, for ethical considerations, we opted for a lower but still viable PFU for the experiment.
3.5. ddPCR Analysis for SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load Quantification
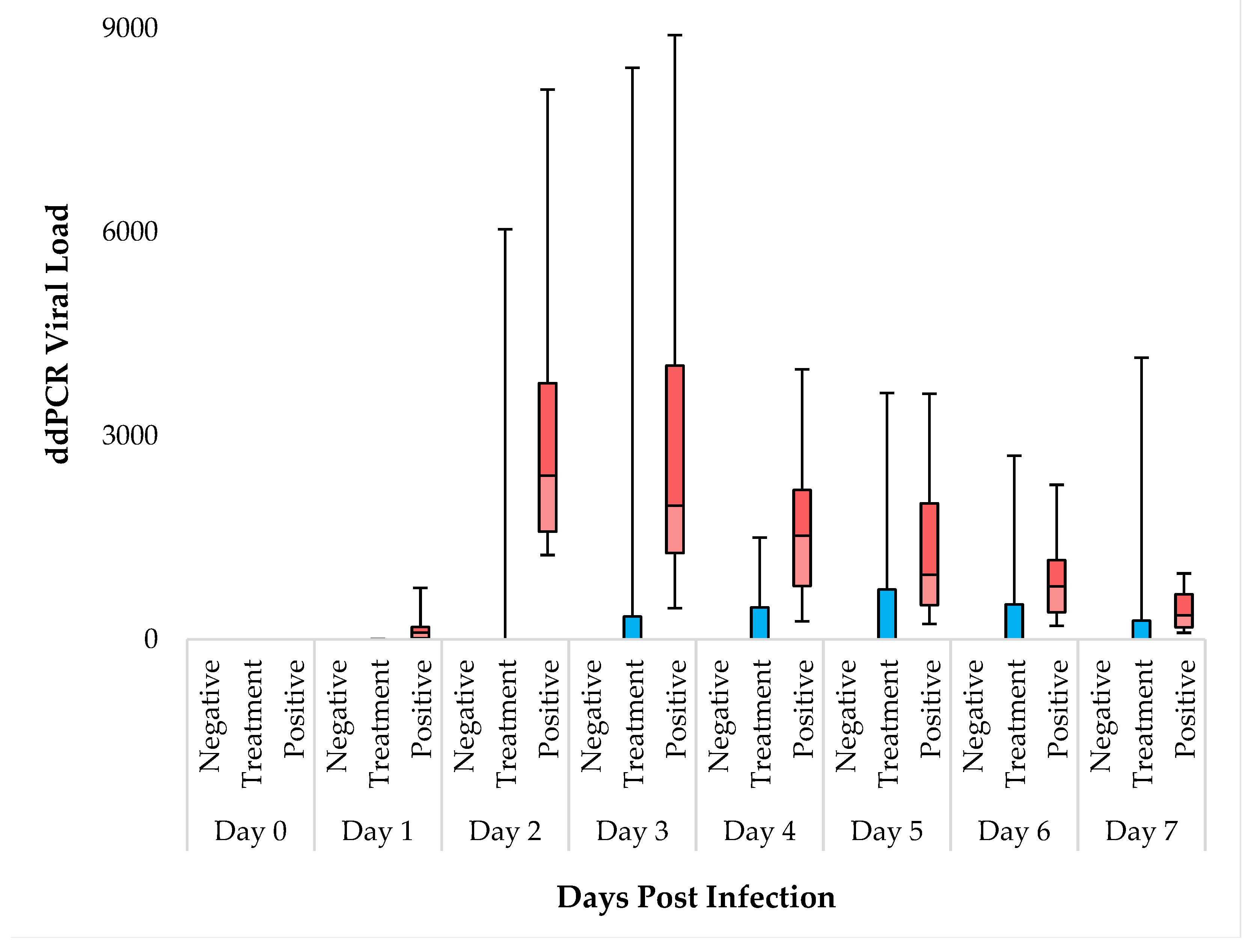
The results obtained from ddPCR measurements show significant differences among the groups from Day 1. On all days of the experiment, the negative control group (N=12) consistently tested negative. In the IgY treated group (N=12), 66% (8 animals) remained negative throughout, while 4 animals displayed signs of SARS-CoV-2 in their samples (
Table S3). Conversely, in the positive control group (N=12), all animals tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 from Day 1 onwards. Our data indicate that virus infection and SARS-CoV-2 levels peaked on Days 2 and 3. The IgY treated group notably exhibited an overall lower average copy number compared to the positive control (
Table S4.). Employing Kruskal-wallis test significant differences were observed between the groups from Day 1 to Day 7 (
Table S5.). DSCF pairwise comparison post-hoc analysis showed no significant differences between the negative control and IgY treated groups (α=0.05). However, the ddPCR copy numbers in the positive control group were consistently significantly higher compared to both the Negative Control, and the IgY Treated group throughout the experiment. Notably, from Day 1 to Day 5, the difference in copy number between the positive control group and IgY treated groups was significant, while on Days 6 and 7, it was not (
Table S6. and
Figure 4.). The positive control group thus exhibited a mean value with a standard deviation (SD) that differed from that of the IgY treated group. However, as detailed before within the IgY treated group (N=12), 8 animals displayed essentially zero copy numbers during the 7 days, while 4 had comparable copy numbers to that of the positive control group. This data distribution within the IgY treated group introduces a certain level of statistical bias. Nonetheless, while acknowledging this limitation we deemed conducting a subgroup analysis within the IgY treated group unreasonable, since there is a very low number of animals in this subgroup.
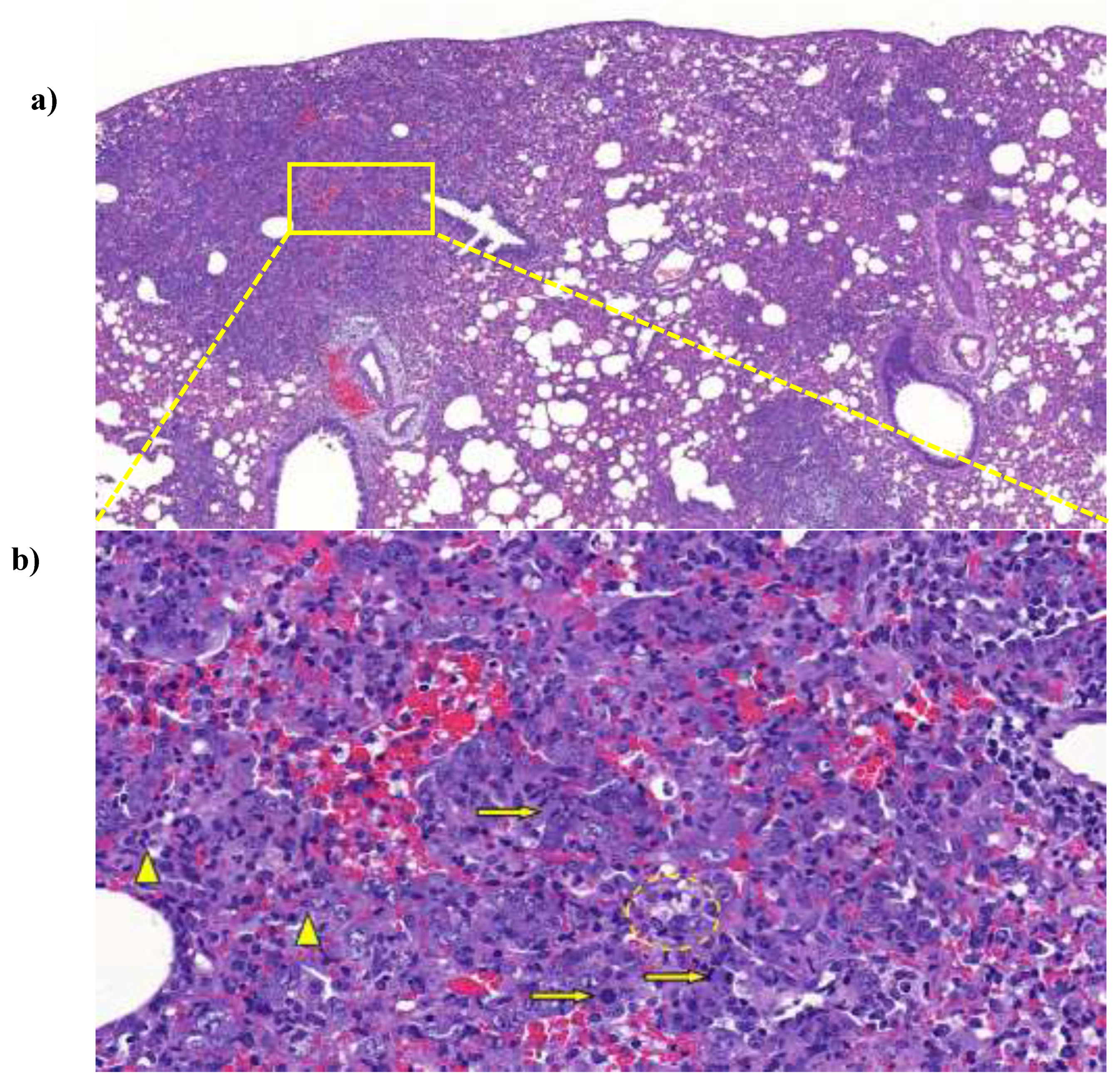
3.6. Lung Tissue Histopathological Analysis
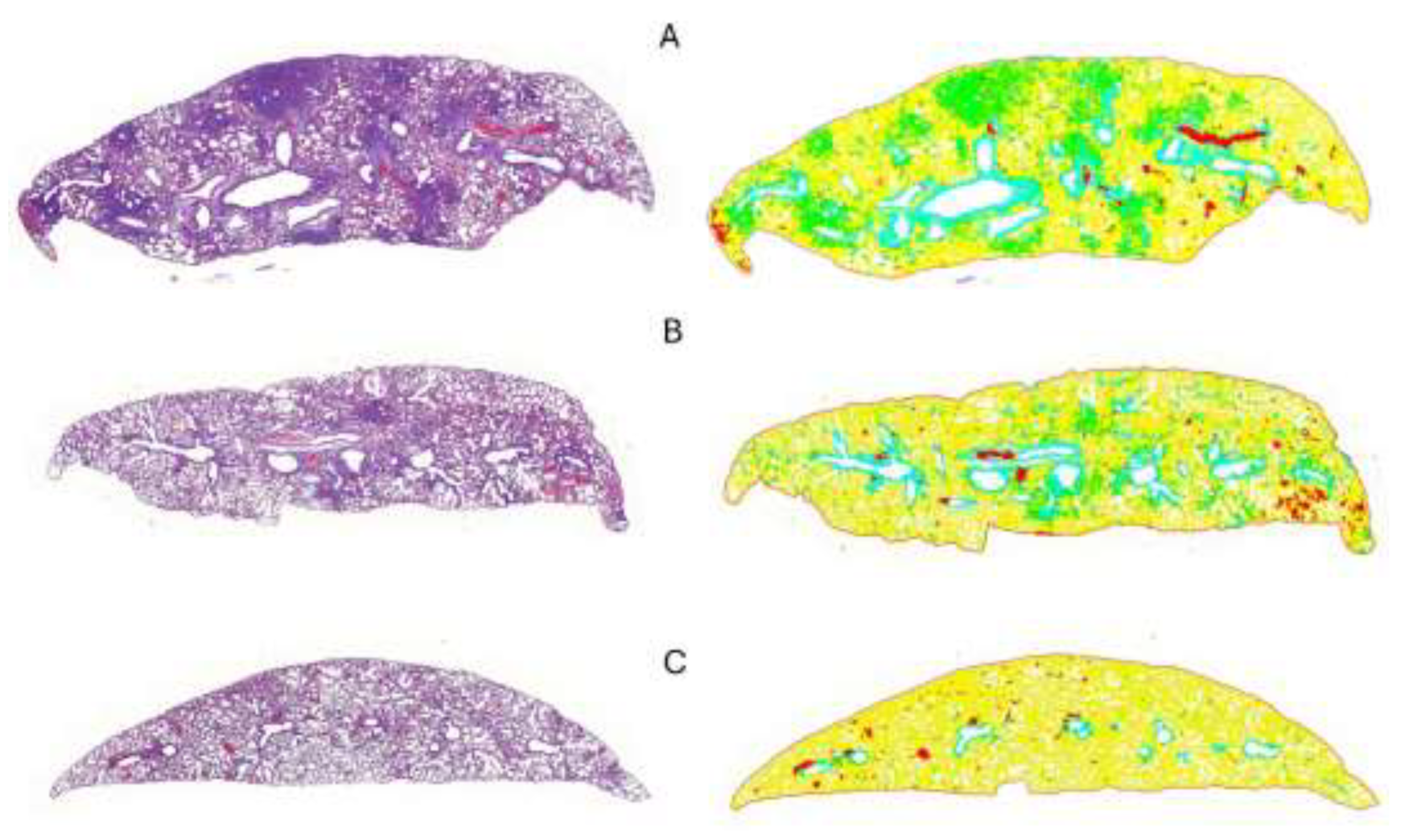
Animals in the positive control group showed various degree of lung consolidation consisting of type II pneumocyte hyperplasia with the presence of numerous mitotic figures, interstitial and intraalveolar accumulation of macrophages, lymphocytes and a few neutrophil granulocytes indicating interstitial pneumonia. Lymphocytic perivasculitis with perivascular edema was also observed. The IgY-treated animals showed similar, but substantially less severe lesions compared to the non-treated group. Animals in the negative control group showed only background or procedure-related changes, such as congestion and alveolar emphysema (
Figure 5.).
3.7. Statistical Analysis of Histopathological Data
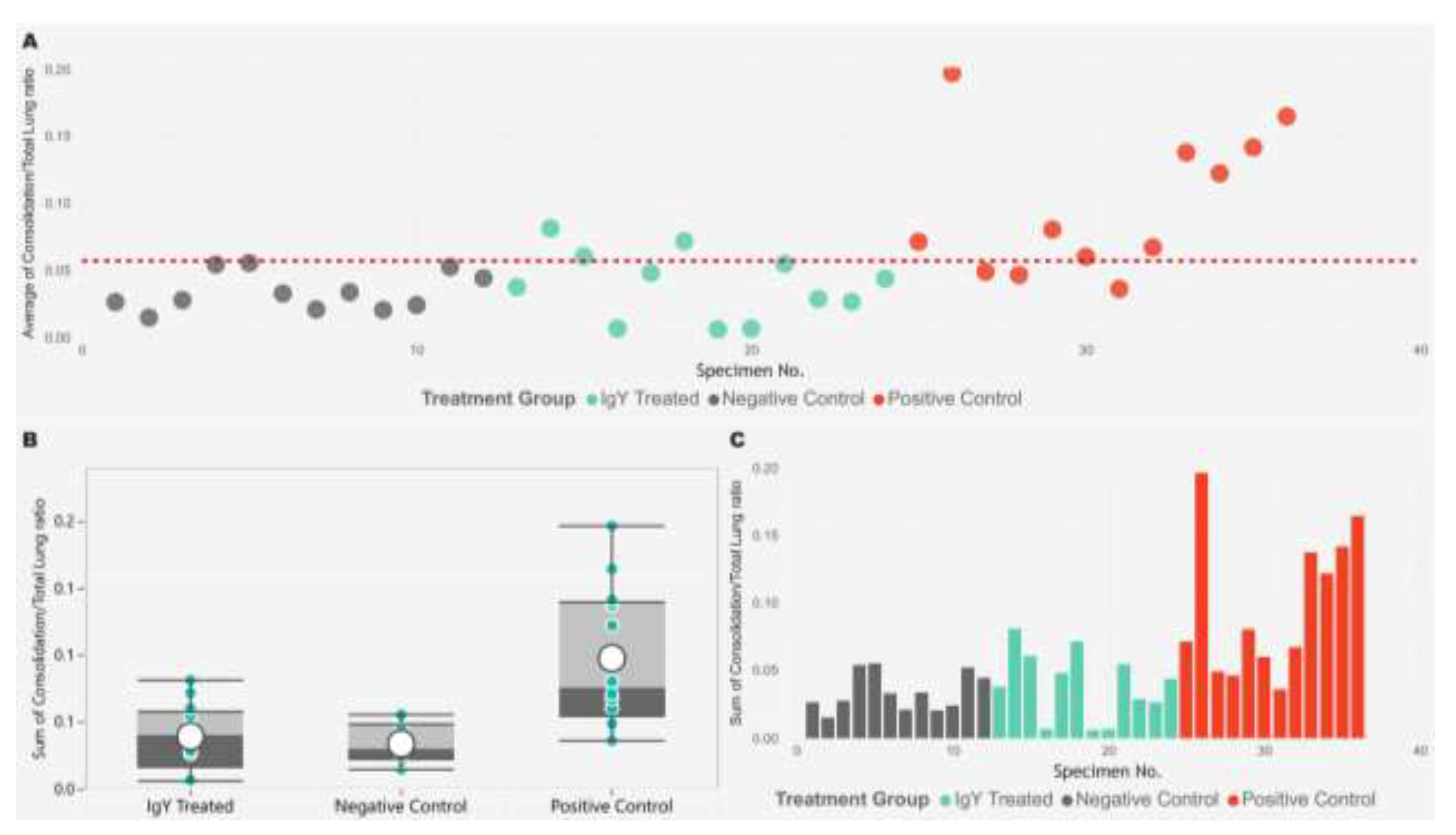
We used digital image analysis to objectively quantify the percentage of lung are as affected by consolidation consisting of interstitial pneumonia and type II pneumocyte hyperplasia in the infected animals (
Figure 6). The Kruskal- Wallis test was used to identify differences in the percentage of consolidation to total lung area pixel density data across all groups. The test indicated that at least one group differed significantly from the others (p < 0.001, ε² = 0.4032). Following this, we conducted Dwass-Steel-Critchlow-Fligner pairwise comparisons to pinpoint the specific group differences. This analysis revealed that the data from the IgY treated group did not significantly differ from the negative control group (p = 0.801). However, both the IgY treated group and the negative control group were significantly different from the positive control group (p = 0.001 and p = 0.0015, respectively) (
Figure 7.).
Note: Effect sizes were categorized as small (ε² < 0.01), medium (0.01 ≤ ε² < 0.06), and large (ε² ≥ 0.06), which corresponded to minimal, moderate, and substantial practical significance, respectively. Detailed individual scores and pairwise comparison results are available in the supplementary tables (
Table S7.).
Figure 6.
Representative images of lung tissues from Syrian hamsters in different treatment groups. The left column shows Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE)-stained lung sections at low magnification (2.8×), while the right column displays QuPath-generated color-coded areas. In the color-coded images, green areas indicate lung tissue consolidation, and yellow indicates normal lung parenchyma. (A) Positive control group shows severe, multifocal, coalescing areas of consolidation; (B) IgY-treated group displays mild, multifocal areas of consolidation; (C) Negative control group exhibits no significant consolidation, reflecting normal lung tissue.
Figure 6.
Representative images of lung tissues from Syrian hamsters in different treatment groups. The left column shows Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE)-stained lung sections at low magnification (2.8×), while the right column displays QuPath-generated color-coded areas. In the color-coded images, green areas indicate lung tissue consolidation, and yellow indicates normal lung parenchyma. (A) Positive control group shows severe, multifocal, coalescing areas of consolidation; (B) IgY-treated group displays mild, multifocal areas of consolidation; (C) Negative control group exhibits no significant consolidation, reflecting normal lung tissue.
Figure 7.
The image displays three plots analyzing the consolidation to total lung area ratio across different treatment groups. (A) The scatter plot shows the consolidation/total lung ratio for individual specimens, with each point color-coded by treatment group (IgY Treated in cyan, Negative Control in gray, and Positive Control in red). A horizontal dashed red line represents the reference value for the average consolidation/total lung ratio. The x-axis denotes the specimen number, while the y-axis indicates the consolidation ratio. (B) The box plot provides a summary of the consolidation/total lung ratios for each treatment group, with overlaid individual data points. The box illustrates the median, interquartile range, and potential outliers. (C) The bar plot shows the sum of the consolidation/total lung ratios for each specimen, grouped by treatment group. The data indicates that the Positive Control group has higher consolidation/total lung ratios compared to the other groups.
Figure 7.
The image displays three plots analyzing the consolidation to total lung area ratio across different treatment groups. (A) The scatter plot shows the consolidation/total lung ratio for individual specimens, with each point color-coded by treatment group (IgY Treated in cyan, Negative Control in gray, and Positive Control in red). A horizontal dashed red line represents the reference value for the average consolidation/total lung ratio. The x-axis denotes the specimen number, while the y-axis indicates the consolidation ratio. (B) The box plot provides a summary of the consolidation/total lung ratios for each treatment group, with overlaid individual data points. The box illustrates the median, interquartile range, and potential outliers. (C) The bar plot shows the sum of the consolidation/total lung ratios for each specimen, grouped by treatment group. The data indicates that the Positive Control group has higher consolidation/total lung ratios compared to the other groups.
4. Discussion
The initially incontrollable spread and massive disease burden of COVID-19 led to concerted research and development efforts worldwide. This unprecedented global health emergency demanded innovative approaches in drug and vaccine development strategies [
23,
24]. The realization that eliciting an immune response by vaccination is unlikely to be always effective for or available to everyone sparked interest in the development of products, which provide safe and effective passive immunity. The attention of researchers was partly focused on IgY based therapy [
16,
25]. IgY antibodies, derived from egg yolks, offer several advantages over traditional IgG-based therapies; these include the cost-effective production, the enhanced stability, and the reduced risk of adverse immune responses, making them a promising alternative for combating viral infections. Furthermore, IgY is far more suitable for industrial-scale production than most other therapeutic antibodies [
18,
26,
27].
Recent years have seen several research papers reporting the potential efficacy of IgY against SARS-CoV-2 infection [
28,
29,
30,
31]. For example, published data indicated that egg-yolk derived IgY recognizes and cross-neutralizes diverse SARS-CoV-2 variants and nasal administration of IgY products may have an overall positive effect on the outcome of acute infection [
28,
29,
32,
33]. The present study reinforces earlier observations concerning the effectiveness of IgY antibodies in the reduction of viral load and improvement of respiratory pathology by using a Syrian hamster model. These results suggest the potential of egg-yolk derived IgY as a pre- and post-exposure therapeutic tool against COVID-19, especially for individuals who are immunocompromised or cannot access vaccines.
As we noticed in literature, previous SARS-CoV-2-based IgY therapy studies wrote succinctly about the optimization of the antigen-adjuvant formulations used in hen immunization [
29,
34,
35]. As there is increasing interest in the utilization of egg(-derived) products in biomedicine, the authors felt it important to conduct experiments to maximize the IgY response and improve product quality for future formulation design. The results of virus neutralization assay showed that hens immunized with higher doses of spike protein or receptor-binding domain (RBD) antigens, particularly when combined with potent adjuvants like Montanide and CpG oligonucleotide, produced strong neutralizing antibody responses. Notably, the G14 group, which received 10 µg of full-length spike protein with Montanide + CpG adjuvant, exhibited the highest virus neutralization titers. Nonetheless, experimental data concerning the superiority of full-length S protein as antigen over other S protein domains (eg RBD or S2 protein) were not evident in other studies [
32,
36]. Therefore, further investigation on the optimal combination of antigen type, antigen dose and adjuvant formulation are still worth investigating in order to achieve more robust immune response in hens.
The industry-scale production of therapeutic IgY products requires the use of cost-effective procedures that avoid the use of toxic substances. Morgan et al (2021) [
37] overviewed the most widely used IgY extraction techniques, including commercial solutions. Some of the readily scalable methods (eg, water dilution, PEG precipitation) are commonly used in relevant SARS-CoV-2 studies. In our study, we did not aim to compare all available methods, mainly because each of them would have required separate laboratory optimization. Instead, we used and compared a commercial IgY extraction method and an in-house IgY precipitation method. The comparison of these two IgY extraction methods showed that the in-house technique produced higher amounts of IgY but lower purity than the commercial purification kit. However, since the antibodies are intended for topical or mucosal use, the level of purity was less critical. We believe that our modified extraction technique (patent application identifier, P 22 00361), which allows for the efficient production of SARS-CoV-2-specific IgY antibodies with potent neutralizing activity, represents a significant advancement in future immunotherapy and viral infection management.
Rodent models used in IgY therapy projects against SARS-CoV-2 showed variable in vivo efficacy along different parameters [
29,
36,
38,
39]. In this study, we used Syrian hamster in in vivo experiments. In this animal model, ddPCR analysis for virus detection confirmed that IgY treatment significantly reduced SARS-CoV-2 viral loads compared to the positive control group (where animals received no IgY treatment). The IgY-treated animals showed a markedly lower virus load, with 66% of the animals in the treatment group remaining virus-free throughout the experiment. This finding led us to conclude that IgY could effectively neutralize the virus at the cellular entry point, thereby preventing severe infection, a finding that Wei and coworkers already hypothesized in their study [
40]. In addition, the lung histopathological analysis showed that IgY-treated animals experienced substantially less tissue consolidation and inflammation than untreated animals, further supporting the protective role of IgY in mitigating the impact of SARS-CoV-2, which was previously described by Zhao et al [
27]. The digital image analysis of lung tissues provided a quantifiable measure of the treatment efficacy, showing significant differences between the IgY-treated and positive control groups in terms of lung consolidation ratios. The reduced lung damage in the IgY-treated group demonstrates the therapeutic potential of IgY in protecting against COVID-19-associated pneumonia, one of the most severe complications of the disease.
5. Conclusions
The investigation into IgY-mediated prophylaxis against SARS-CoV-2 reveals the potential and feasibility of a safe, scalable, and ethically sourced prophylactic strategy that can serve as a complement to, or an alternative for, traditional therapeutic approaches. This study demonstrates that IgY antibodies, specifically targeting the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, can effectively inhibit viral replication and alleviate disease pathology in a relevant animal model. Further optimization of the specific dosage, frequency, and duration of IgY application could help address the therapeutic needs of individuals for whom vaccination is not feasible or effective. These promising results establish a strong foundation for future research exploring the role of IgY antibodies in combating not only COVID-19 but also a broader spectrum of respiratory viral infections.
6. Patents
The work reported in this manuscript has led to the filing of a patent application, which is disclosed in the „Szabadalmi Közlöny és Védjegyértesítő”, the official journal of the National Office of Intellectual Property of Hungary, volume 128, issue 18, dated September 28, 2023. The patent application, identified by the number P 22 00361, filed on September 9, 2022, by PROPHYL Animal Health, Diagnostics, Research, and Service Limited Liability Company, is centered around an IgY antibody with potent in vitro neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 antigens, rendering it suitable for application in combating viral infections.
The inventors listed for this patent are Dr. Szabóné Dr. Benyeda Zsófia, Dr. Palya Vilmos, Dr. Nemes Csaba Miklós, Dr. Bajnóczi Pál, and Faragó-Sipos Orsolya, who have contributed to the development of this IgY antibody. Their invention encompasses the use of this antibody in the treatment of viral infections, highlighting its potential application in managing and preventing diseases caused by SARS-CoV-2.
This patent application represents a significant advancement in the field of immunotherapy and infectious disease control, providing a novel approach to addressing the ongoing challenges posed by COVID-19 and potentially other viral pathogens. The development and application of this IgY antibody could offer a new line of defense against viral infections, complementing existing vaccines and therapeutic strategies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: Evaluation of Virus Neutralization in a 96-Well Plate Format. Figure S2: Comparative SDS-PAGE Analysis of IgY Purification and Protein Complexes. Table S1: Comparative Analysis of Egg Yolk Extracts Using Different Extraction Methods. Table S2: Body Weight Changes in Syrian Golden Hamsters Over a 7-Day Period Post-Experiment. Table S3: The Virus Copy Numbers by ddPCR Related to Hamster Individuals Table S4: Descriptive Statistics of ddPCR Viral Copy Numbers Over Time by Treatment Group. Table S5: Daily Viral Load Evaluation by ddPCR in Three Experimental Hamster Groups. Table S6: Daily Pairwise Comparison of Viral Load in Hamster Groups Using Dwass-Steel-Critchlow-Fligner Method. Table S7: The table presents the results of a Kruskal-Wallis test and subsequent pairwise comparisons for the consolidation to total lung area ratio data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Csaba Nemes, Vilmos Palya, and Pál Bajnóczi; Data curation, Roland Hetényi, Dániel Hanna, Mónika Madai, and Dávid Géza Horváth; Formal analysis, Mónika Madai, Pál Bajnóczi, Csaba Nemes, Gyula Balka, and Dániel Hanna; Funding acquisition, Pál Bajnóczi and Csaba Nemes; Investigation, Mónika Madai, Orsolya Faragó-Sipos, Fanni Földes, Zsófia Lanszki, Brigitta Zana, Balázs Somogyi, Anett Kuczmog, Gyula Balka, and Xinkai Jia; Methodology, Vilmos Palya, Gyula Balka, Mónika Madai, Orsolya Faragó-Sipos, Pál Bajnóczi, and Csaba Nemes; Supervision, Mónika Madai and Gábor Kemenesi; Validation, Mónika Madai and Péter Balogh; Visualization, Roland Hetényi and Dániel Hanna; Writing—original draft preparation, Roland Hetényi, Dániel Hanna, Mónika Madai, Pál Bajnóczi, and Csaba Nemes; Writing—review and editing, Roland Hetényi, Krisztián Bányai, and Dániel Hanna. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by Prophyl Kft. as part of a service agreement, with the support of the Health Sector Support Program (ETP) of the Hungarian Government, Ministry of Finance. The University of Pécs (PTE) was not directly involved as a partner but engaged as a service provider. The project No. TKP-2021-EGA-13 was implemented with support from the National Research, Development, and Innovation Fund of Hungary, financed under the TKP2021-EGA funding scheme. Project no. TKP2020-NKA-01 has been implemented with the support provided by the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary, financed under the Tématerületi Kiválósági Program 2020 (2020-4.1.1-TKP2020) funding scheme.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Baranya County Government Office (protocol code BAI/35/56-92/2017). All experiments were conducted in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations for the care and use of animals in research.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this study are available on request from the corresponding authors. Due to privacy and ethical restrictions related to the handling of animal models, the data cannot be made publicly accessible. Further inquiries regarding the datasets can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Ferenc Jakab for his intellectual contributions to the preparation of this article. He passed away on the 16th of February 2024. The authors would like to express their gratitude to Róbert Glávits for his valuable contribution in the field of histopathological analysis of hamster lung samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lu, H., C.W. Stratton, and Y.W. Tang, Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: The mystery and the miracle. J Med Virol, 2020. 92(4): p. 401-402. [CrossRef]
- Organization, W.H. COVID-19 Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) Global research and innovation forum. 12 February 2020 [cited 2024 2024-02-02]; Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-public-health-emergency-of-international-concern-(pheic)-global-research-and-innovation-forum.
- Organization, W.H. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. [cited 2024 2024-02-02]; Available from: https://www.who.int/europe/emergencies/situations/covid-19.
- Viruses, I.C.o.T.o. Current ICTV Taxonomy Release, Virus Taxonomy: 2022 Release. 2023 [cited 2024 2024-02-02]; Available from: https://ictv.global/taxonomy.
- Lamers, M.M. and B.L. Haagmans, SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2022. 20(5): p. 270-284. [CrossRef]
- Team, V.G.C.V.T. 12 Vaccines Granted Emergency Use Listing (EUL) by WHO. 2024; Available from: https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/agency/who/.
- Shahcheraghi, S.H., et al., An overview of vaccine development for COVID-19. Ther Deliv, 2021. 12(3): p. 235-244. [CrossRef]
- Flores-Vega, V.R., et al., SARS-CoV-2: Evolution and Emergence of New Viral Variants. Viruses, 2022. 14(4). [CrossRef]
- Lee, A., et al., Efficacy of covid-19 vaccines in immunocompromised patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Bmj, 2022. 376: p. e068632. [CrossRef]
- Sallam, M., COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy Worldwide: A Concise Systematic Review of Vaccine Acceptance Rates. Vaccines (Basel), 2021. 9(2). [CrossRef]
- Ekström, A.M., et al., The battle for COVID-19 vaccines highlights the need for a new global governance mechanism. Nature Medicine, 2021. 27(5): p. 739-740. [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J., Passive antibody therapy in COVID-19. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2020. 20(7): p. 401-403. [CrossRef]
- Montelongo-Jauregui, D., et al., Convalescent serum therapy for COVID-19: A 19th century remedy for a 21st century disease. PLoS Pathog, 2020. 16(8): p. e1008735. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.T., et al., IgY antibodies for the immunoprophylaxis and therapy of respiratory infections. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2019. 15(1): p. 264-275. [CrossRef]
- Diraviyam, T., et al., Effect of chicken egg yolk antibodies (IgY) against diarrhea in domesticated animals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2014. 9(5): p. e97716. [CrossRef]
- Constantin, C., et al., IgY - turning the page toward passive immunization in COVID-19 infection (Review). Exp Ther Med, 2020. 20(1): p. 151-158. [CrossRef]
- Leiva, C.L., et al., IgY-technology (egg yolk antibodies) in human medicine: A review of patents and clinical trials. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020. 81: p. 106269. [CrossRef]
- Schade, R., et al., Chicken egg yolk antibodies (IgY-technology): a review of progress in production and use in research and human and veterinary medicine. Altern Lab Anim, 2005. 33(2): p. 129-54. [CrossRef]
- Bankhead, P., et al., QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Scientific Reports, 2017. 7(1): p. 16878. [CrossRef]
- Mulka, K.R., et al., Progression and Resolution of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection in Golden Syrian Hamsters. Am J Pathol, 2022. 192(2): p. 195-207. [CrossRef]
- jamovi, The jamovi project. 2023.
- Team, R.C., R: A Language and environment for statistical computing. 2022.
- Chan, J.F., et al., COVID-19 drug discovery and treatment options. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2024. 22(7): p. 391-407. [CrossRef]
- Thanh Le, T., et al., The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2020. 19(5): p. 305-306. [CrossRef]
- Pérez de la Lastra, J.M., et al., Can Immunization of Hens Provide Oral-Based Therapeutics against COVID-19? Vaccines (Basel), 2020. 8(3). [CrossRef]
- Kovacs-Nolan, J. and Y. Mine, Egg yolk antibodies for passive immunity. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol, 2012. 3: p. 163-82. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B., et al., Rapid development and mass production of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing chicken egg yolk antibodies with protective efficacy in hamsters. Biol Res, 2024. 57(1): p. 24. [CrossRef]
- Artman, C., et al., Avian antibodies (IgY) targeting spike glycoprotein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) inhibit receptor binding and viral replication. PLoS One, 2021. 16(5): p. e0252399. [CrossRef]
- Frumkin, L.R., et al., Egg-Derived Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) With Broad Variant Activity as Intranasal Prophylaxis Against COVID-19. Front Immunol, 2022. 13: p. 899617. [CrossRef]
- Shen, H., et al., Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgY Isolated from Egg Yolks of Hens Immunized with Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 for Immunoprophylaxis of COVID-19. Virol Sin, 2021. 36(5): p. 1080-1082. [CrossRef]
- Wongso, H., et al., Preclinical Evaluation of Chicken Egg Yolk Antibody (IgY) Anti-RBD Spike SARS-CoV-2-A Candidate for Passive Immunization against COVID-19. Vaccines (Basel), 2022. 10(1). [CrossRef]
- Schön, J., et al., Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2-Specific IgY Antibodies: Production, Reactivity, and Neutralizing Capability against Virus Variants. Int J Mol Sci, 2024. 25(14).
- Wei, S., et al., Chicken Egg Yolk Antibodies (IgYs) block the binding of multiple SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants to human ACE2. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021. 90: p. 107172. [CrossRef]
- Bao, L., et al., Egg yolk immunoglobulin (IgY) targeting SARS-CoV-2 S1 as potential virus entry blocker. J Appl Microbiol, 2022. 132(3): p. 2421-2430. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., et al., Novel neutralizing chicken IgY antibodies targeting 17 potent conserved peptides identified by SARS-CoV-2 proteome microarray, and future prospects. Front Immunol, 2022. 13: p. 1074077. [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.T., et al., Immunoglobulin Y Specific for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Subunits Effectively Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity and Ameliorates Disease Manifestations In Vivo. Biomedicines, 2022. 10(11).
- Zhang, X., et al., Editorial: IgY technology: theory, technical aspects, applications, and innovations. Front Immunol, 2023. 14: p. 1267926. [CrossRef]
- El-Kafrawy, S.A., et al., SARS-CoV-2-specific immunoglobulin Y antibodies are protective in infected mice. PLoS Pathog, 2022. 18(9): p. e1010782. [CrossRef]
- Ravlo, E., et al., Antiviral Immunoglobulins of Chicken Egg Yolk for Potential Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Viruses, 2022. 14(10). [CrossRef]
- Wei, J., et al., A chicken IgY can efficiently inhibit the entry and replication of SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the ACE2 binding domain in vitro. bioRxiv, 2021: p. 2021.02.16.430255.
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the animal experimental arrangement. Syrian hamsters were treated with IgY or PBS and challenged with SARS-CoV-2. The experimental timeline is shown, where animals were weighed daily, and throat swabs were collected on days 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 post-infection. Animals were treated with IgY or PBS every 8 hours for the first 3 days and every 12 hours until day 4 post-infection. On day 7, animals were euthanized, and lung tissue samples were collected for further histopathological analysis. Each row depicts the timeline and the corresponding actions performed, including sample collection, treatment, and final tissue dissection.
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the animal experimental arrangement. Syrian hamsters were treated with IgY or PBS and challenged with SARS-CoV-2. The experimental timeline is shown, where animals were weighed daily, and throat swabs were collected on days 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 post-infection. Animals were treated with IgY or PBS every 8 hours for the first 3 days and every 12 hours until day 4 post-infection. On day 7, animals were euthanized, and lung tissue samples were collected for further histopathological analysis. Each row depicts the timeline and the corresponding actions performed, including sample collection, treatment, and final tissue dissection.
Figure 2.
Temporal progression of average neutralizing antibody titers (Log2)
across three groups: G14, G18, and G2. The y-axis represents the average
neutralizing antibody titer in Log2 scale, while the x-axis displays the
sampling dates over time, from April to November. Group G14 (blue) consistently
exhibited the highest neutralizing titers, peaking at 10.3 Log2 in early
September. Group G2 (purple) followed a similar trend with a slightly lower
peak of 9.3 Log2. Group G18 (pink) maintained the lowest titers throughout the
study, peaking at 7.8 Log2 in September. The data highlight the temporal
changes in neutralizing titers among the three groups, with G14 showing the
strongest and most sustained response.
Figure 2.
Temporal progression of average neutralizing antibody titers (Log2)
across three groups: G14, G18, and G2. The y-axis represents the average
neutralizing antibody titer in Log2 scale, while the x-axis displays the
sampling dates over time, from April to November. Group G14 (blue) consistently
exhibited the highest neutralizing titers, peaking at 10.3 Log2 in early
September. Group G2 (purple) followed a similar trend with a slightly lower
peak of 9.3 Log2. Group G18 (pink) maintained the lowest titers throughout the
study, peaking at 7.8 Log2 in September. The data highlight the temporal
changes in neutralizing titers among the three groups, with G14 showing the
strongest and most sustained response.
Figure 3.
Trajectory of Mean Body Weight Changes as a Percentage of Day 0 Across Seven Days in Syrian Golden Hamsters. This graph illustrates the daily percentage changes in mean body weight for three groups: Negative Control (black line), IgY Treated (green line), and Positive Control (red line). Error bars indicate standard deviation, underscoring the fluctuation in weight within each group. Values over 100% indicate an overall increase in weight relative to Day 0, while values under 100% reflect a decrease, suggesting weight gain or loss trends among the experimental cohorts throughout the study period.
Figure 3.
Trajectory of Mean Body Weight Changes as a Percentage of Day 0 Across Seven Days in Syrian Golden Hamsters. This graph illustrates the daily percentage changes in mean body weight for three groups: Negative Control (black line), IgY Treated (green line), and Positive Control (red line). Error bars indicate standard deviation, underscoring the fluctuation in weight within each group. Values over 100% indicate an overall increase in weight relative to Day 0, while values under 100% reflect a decrease, suggesting weight gain or loss trends among the experimental cohorts throughout the study period.
Figure 4.
Daily ddPCR Viral Load Analysis in Syrian Golden Hamsters. The boxplots represent the distribution of viral loads in three experimental groups: Negative, Treatment, and Positive. Minimum and maximum values are indicated by the whiskers, the interquartile range (IQR) by the boxes, and the median by the horizontal line within each box.
Figure 4.
Daily ddPCR Viral Load Analysis in Syrian Golden Hamsters. The boxplots represent the distribution of viral loads in three experimental groups: Negative, Treatment, and Positive. Minimum and maximum values are indicated by the whiskers, the interquartile range (IQR) by the boxes, and the median by the horizontal line within each box.
Figure 5.
Representative low (a) and high power (b) pictures from a positive control animal showing multifocal, coalescing areas of severe interstitial pneumonia causing visible consolidation. Numerous mitotic figures were observed among the hyperplastic type II pneumocytes (arrows), whereas degenerating neutrophil granulocytes (arrowheads) and foamy macrophages (dashed circle) were seen in the alveoli. Original magnification, a: 10×; b: 70×.
Figure 5.
Representative low (a) and high power (b) pictures from a positive control animal showing multifocal, coalescing areas of severe interstitial pneumonia causing visible consolidation. Numerous mitotic figures were observed among the hyperplastic type II pneumocytes (arrows), whereas degenerating neutrophil granulocytes (arrowheads) and foamy macrophages (dashed circle) were seen in the alveoli. Original magnification, a: 10×; b: 70×.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).